Long term time series analysis and prediction of waves at Hainan offshore zone based on Prophet algorithm
-
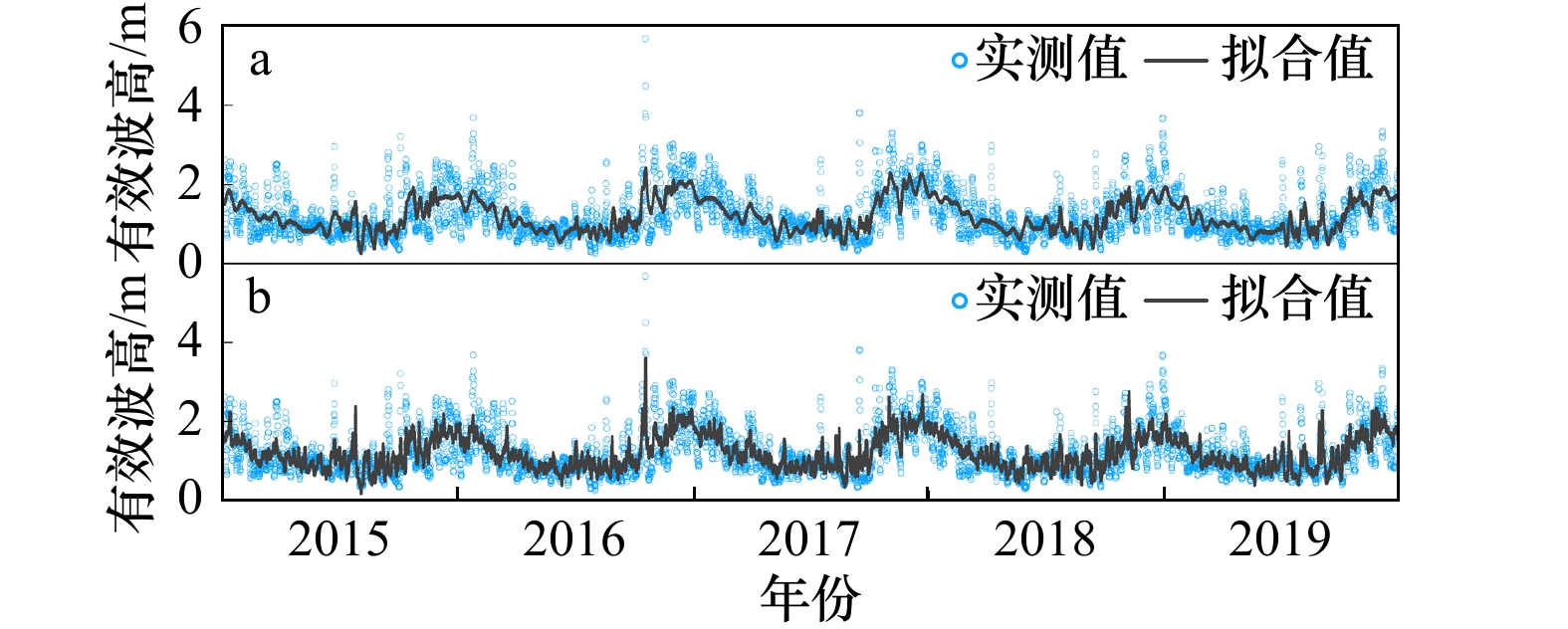
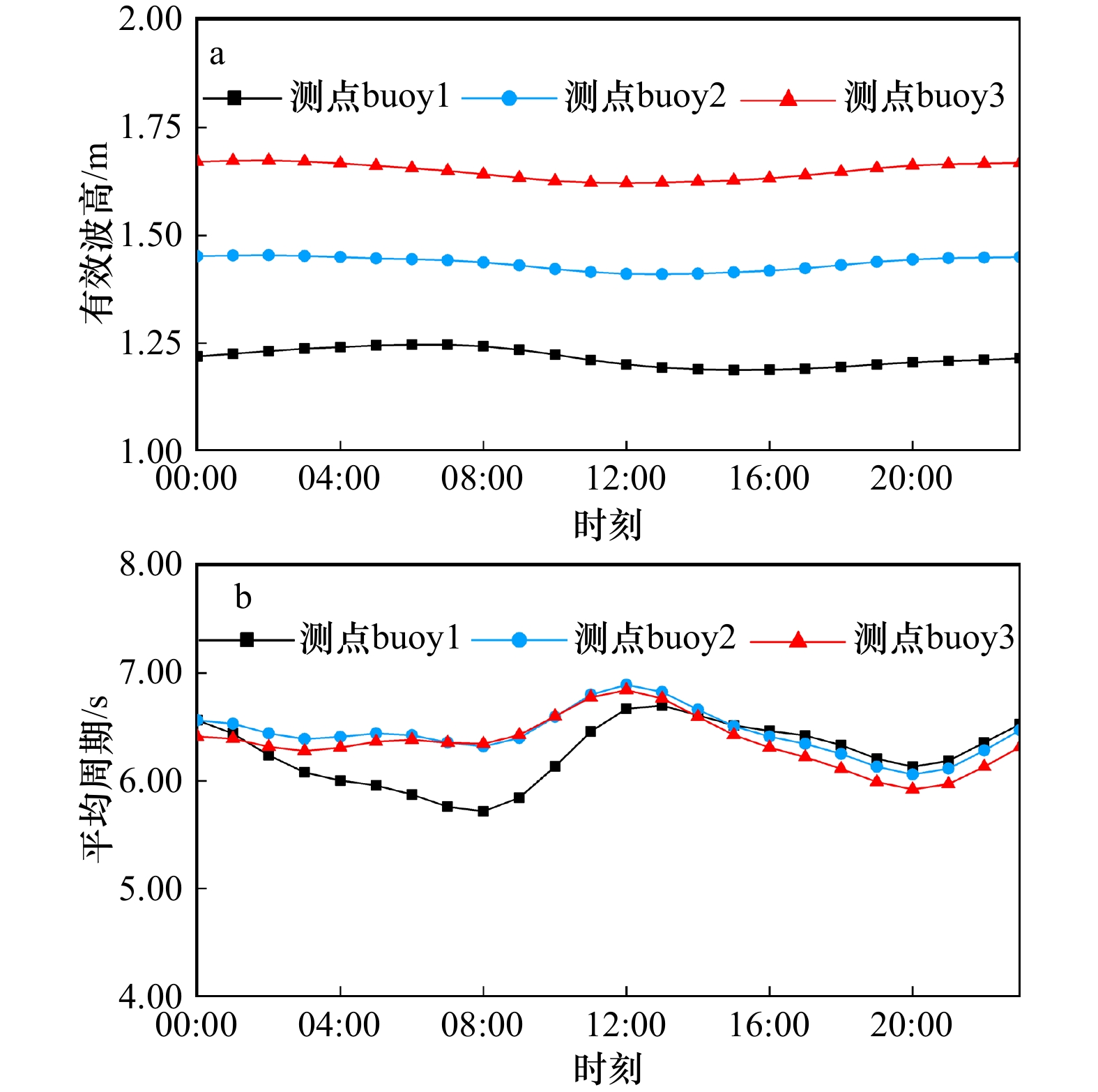
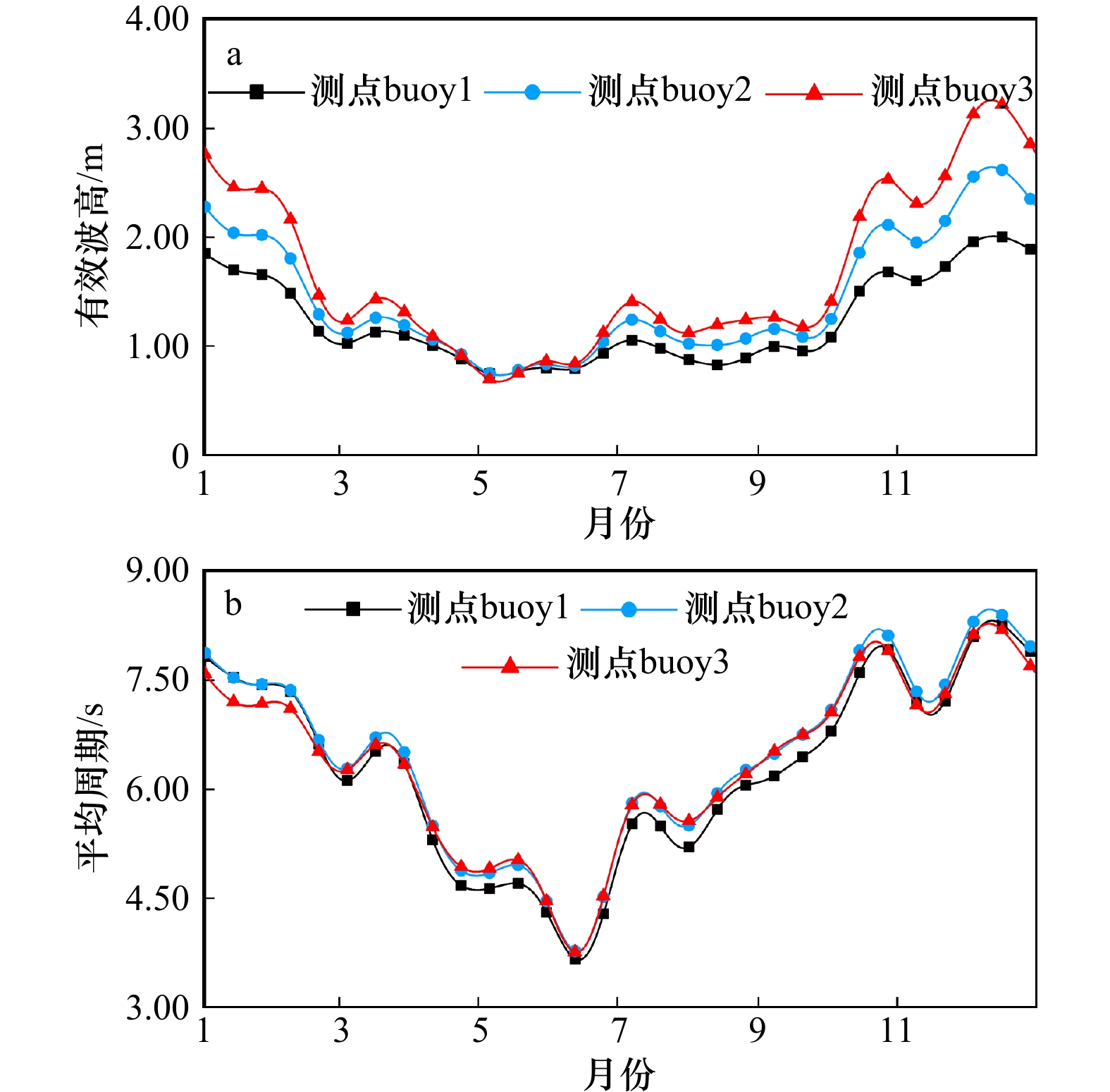
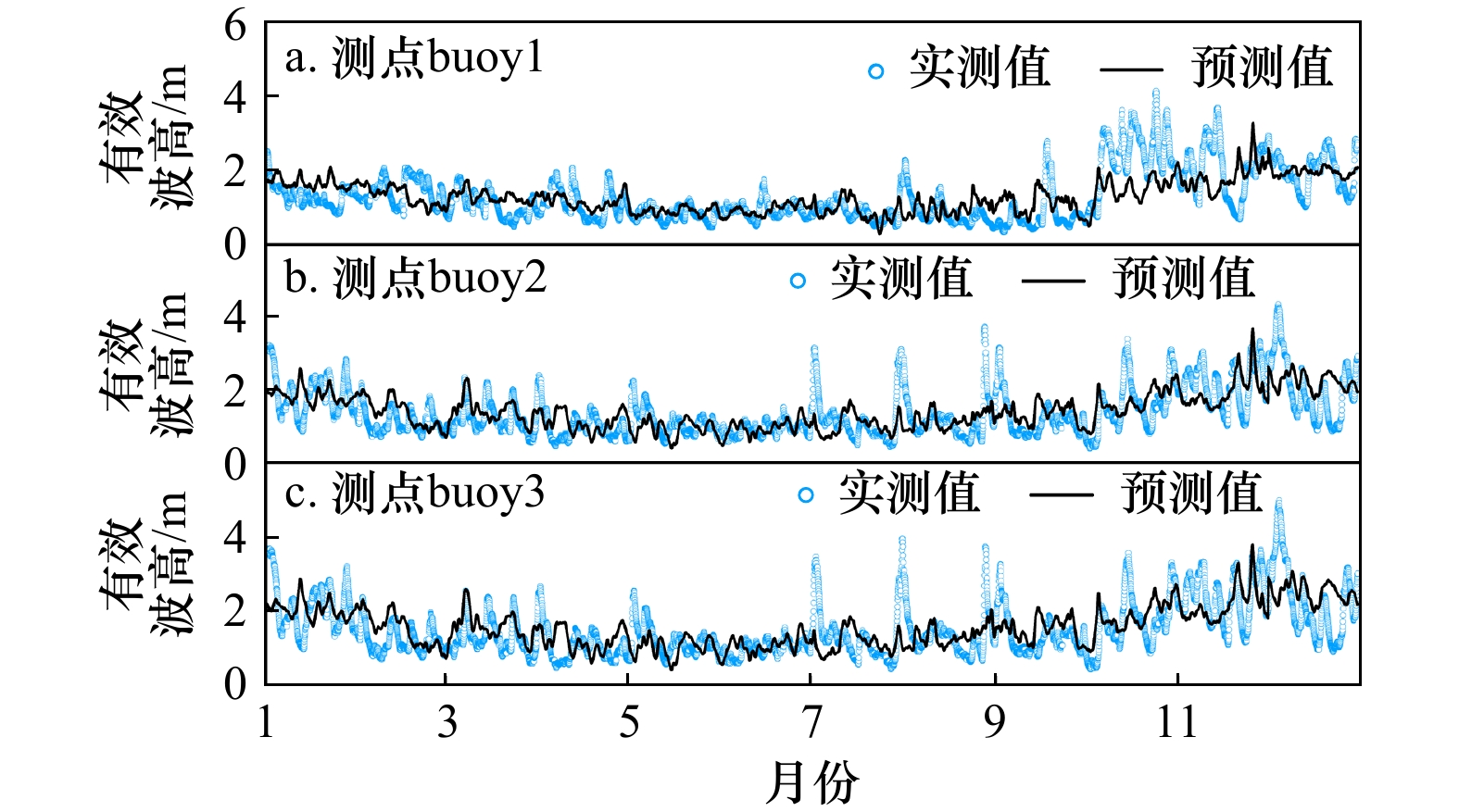
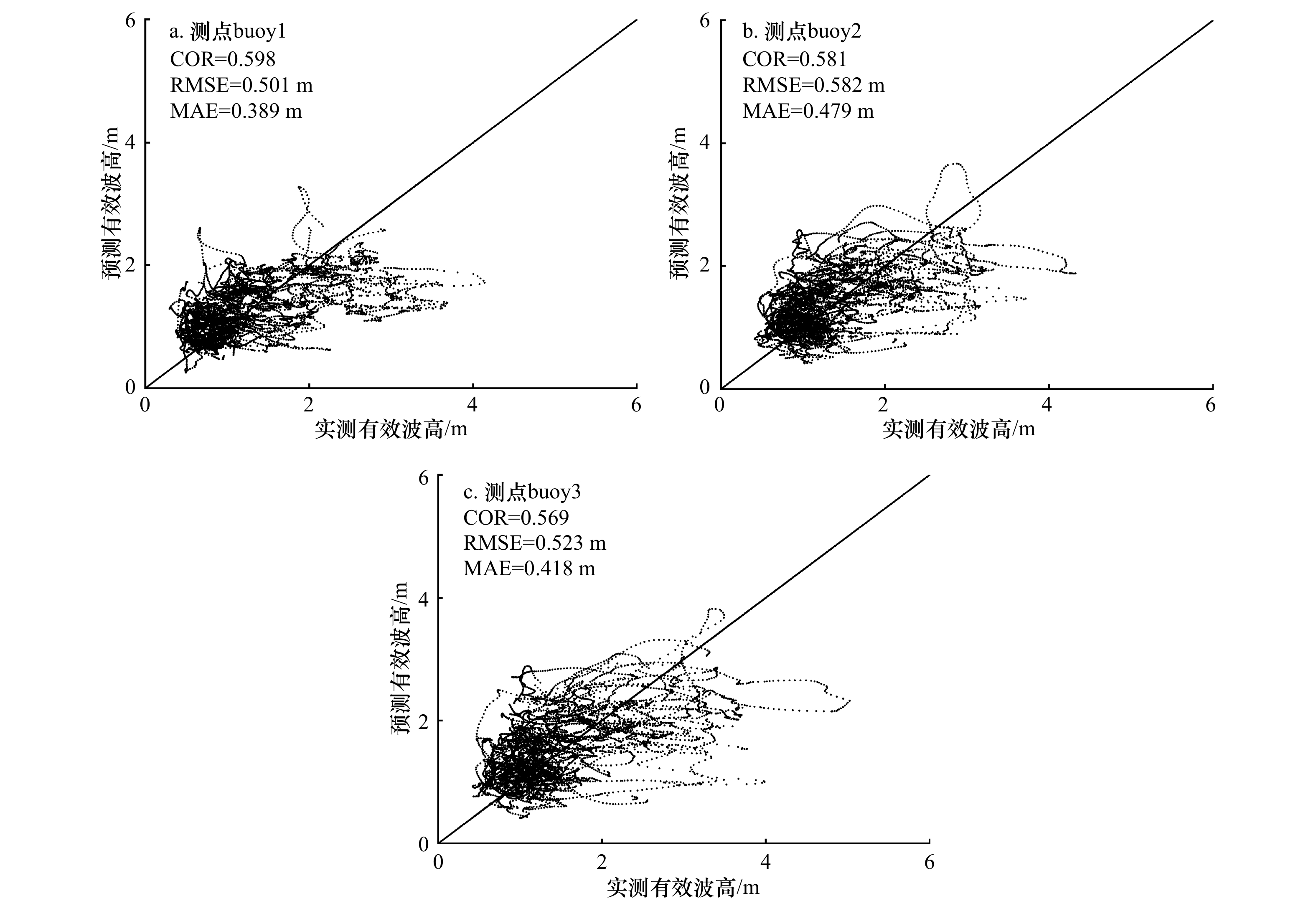
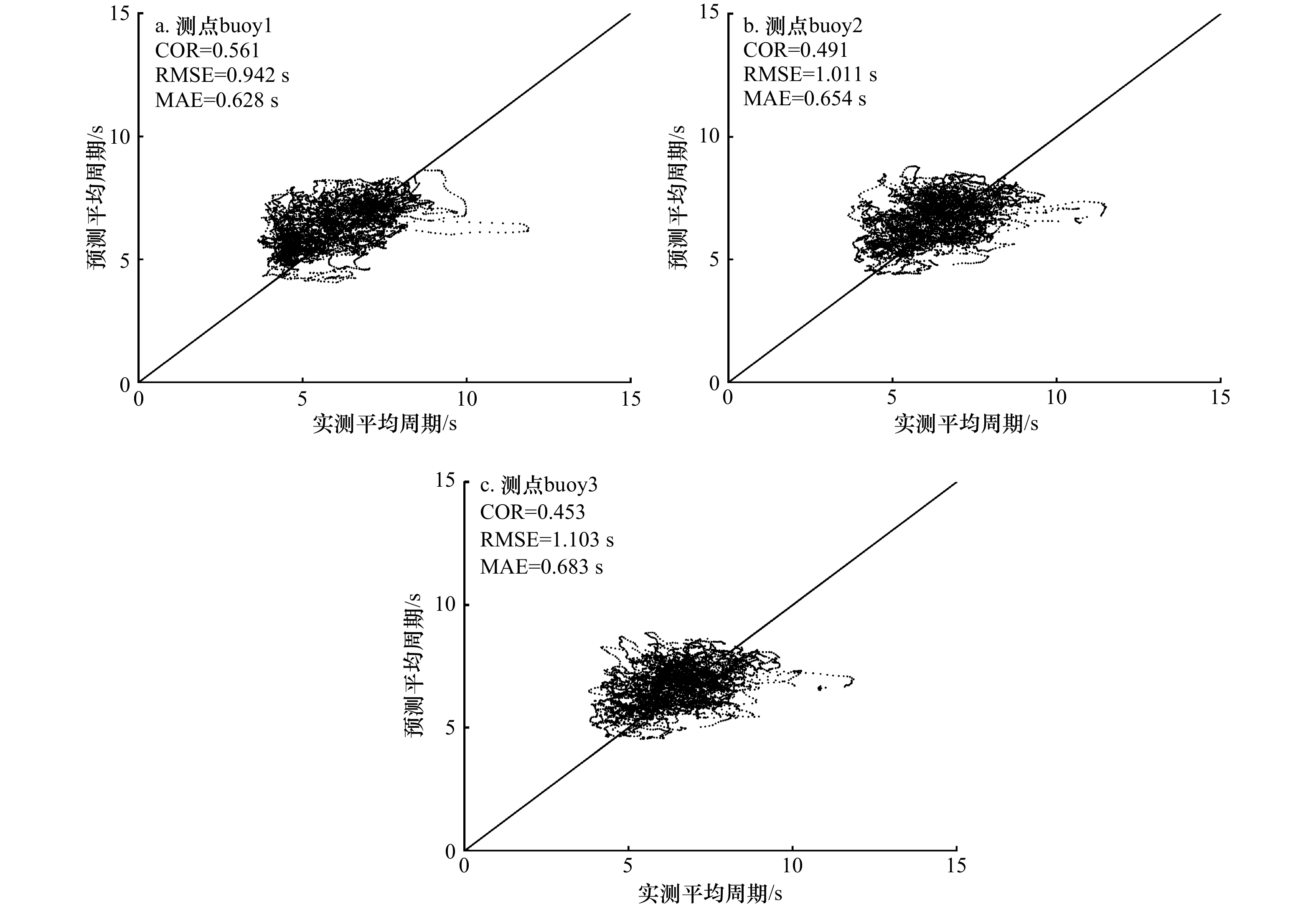
摘要: 近年来,以大数据为基础的人工智能算法逐步兴起并被用于海洋波浪短期预测。本文采用2015−2019年海南近海逐时波浪实测时序数据,基于Prophet算法建立了海南近海波浪长时段时序预测模型,分析了2015−2019年海南近海波浪日、月、年变化特性,并对海南近海2020年波浪变化过程进行了预测。结果显示,Prophet算法模型对波浪波高和周期的预测值和实测值整体吻合良好,可有效用于长时段波浪的特性分析和时序预测。Abstract: In recent years, various artificial intelligence algorithms based on big data have gradually emerged and have been applied in short-term time series wave forecasting. Based on the measured time series data of hourly waves in Hainan offshore from 2015 to 2019, a prediction model for long-term time series waves of Hainan offshore based on Prophet algorithm is established in this paper. The daily, monthly and annual variation characteristics of waves in Hainan offshore from 2015 to 2019 are analyzed, and the waves in Hainan offshore in 2020 are predicted. The results show that the predicted values of wave height and period by prophet algorithm model are in good agreement with the measured values. Prophet algorithm model can be effectively used for long-term wave characteristic analysis and time series prediction.
-
Key words:
- coast and offshore /
- water wave /
- Prophet algorithm /
- big data /
- artificial intelligence
-
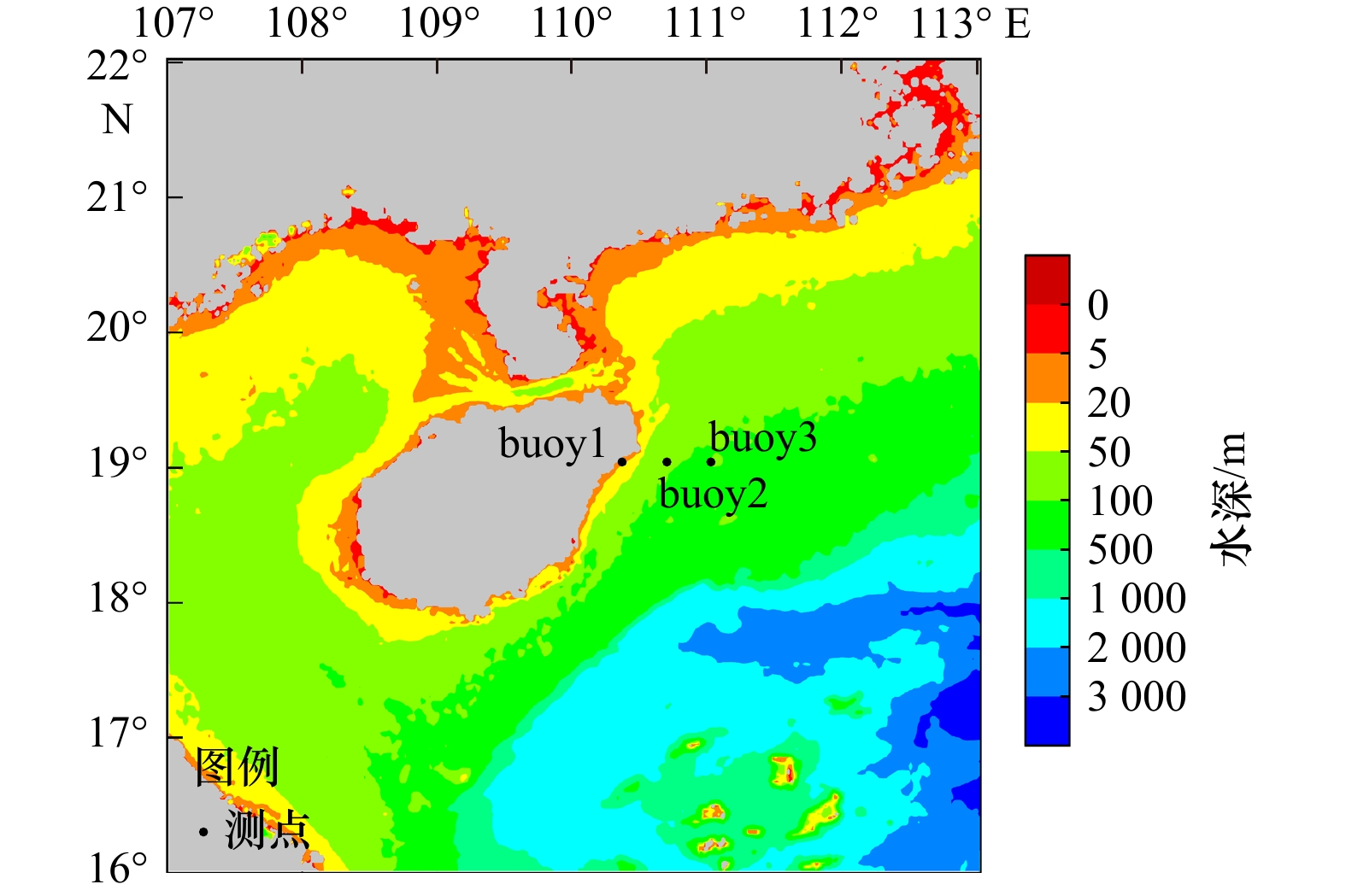
表 1 测点坐标及水深
Tab. 1 Location and water depth of survey points
测点 纬度 经度 水深/m buoy1 19.05°N 110.35°E 15.5 buoy2 19.05°N 110.70°E 101.4 buoy3 19.05°N 111.05°E 186.7 -
[1] 李博, 李骏旻, 李毅能, 等. 人工神经网络在岛屿近岸海浪模拟中的应用[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 59(3): 420−427.Li Bo, Li Junmin, Li Yineng, et al. Application of artificial neural network to numerical wave simulation in the coastal region of island[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2020, 59(3): 420−427. [2] 莫忠璇, 时闽生, 吕迎雪, 等. 基于SWAN-MIKE21嵌套模型在大连湾某工程区的波浪后报模拟应用[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2021, 41(2): 20−23. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs202102005Mo Zhongxuan, Shi Minsheng, Lü Yingxue, et al. Wave hindcast simulation based on SWAN-MIKE21 nested model in an engineering area in Dalian Bay[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2021, 41(2): 20−23. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs202102005 [3] 滕陈轲敏, 岳显昌, 吴雄斌, 等. 风场对SWAN模式在台湾海峡后报结果的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(5): 59−69.Teng Chenkemin, Yue Xianchang, Wu Xiongbin, et al. Impacts of wind data on the hindcast of wave height simulated by SWAN model on the Taiwan Strait[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(5): 59−69. [4] Choi Y K, Seo S N, Choi J Y, et al. Wave prediction in a port using a fully nonlinear Boussinesq wave model[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 38(7): 36−47. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1456-2 [5] Viitak M, Avilez-Valente P, Bio A, et al. Evaluating wind datasets for wave hindcasting in the NW Iberian Peninsula coast[J]. Journal of Operational Oceanography, 2021, 14(2): 152−165. doi: 10.1080/1755876X.2020.1738121 [6] 李巧生, 唐军, 吕义港. 适于模拟不规则水域波浪的缓坡方程两种数值模型比较[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(1): 31−39.Li Qiaosheng, Tang Jun, Lü Yigang. Comparisons of the two numerical models of elliptic mild-slope equation for wave propagation in irregular coastal zones[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(1): 31−39. [7] 林毅辉, 郑艺妃, 潘伟然, 等. 西沙湾工程波浪推算及波浪场数值模拟[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(1): 80−86.Lin Yihui, Zheng Yifei, Pan Weiran, et al. Engineering wave calculation and wave field numerical simulation in Xisha Bay[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2020, 39(1): 80−86. [8] 聂梓超. 广东典型红树林海湾波浪特性数值模拟研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019.Nie Zichao. Numerical study of wave characteristics in typical mangroves bays of Guangdong Province[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. [9] 郭云霞, 侯一筠, 齐鹏. Monte-Carlo模拟与经验路径模型预测台风极值风速的对比[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(7): 64−77.Guo Yunxia, Hou Yijun, Qi Peng. Comparison of extreme wind speeds predicted by Monte-Carlo simulation and empirical track model[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(7): 64−77. [10] Kim T Y, Oh K J, Kim C, et al. Artificial neural networks for non-stationary time series[J]. Neurocomputing, 2004, 61: 439−447. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2004.04.002 [11] Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Deep, narrow sigmoid belief networks are universal approximators[J]. Neural Computation, 2008, 20(11): 2629−2636. doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.12-07-661 [12] 高丽斌, 郭民权, 张少涵, 等. 基于长短期记忆网络的波高预报[J]. 福建电脑, 2018, 34(8): 105−107.Gao Libin, Guo Minquan, Zhang Shaohan, et al. Wave height prediction based on long short-term memory network[J]. Fujian Computer, 2018, 34(8): 105−107. [13] 赵凯欣. 基于SVR和LSTM算法反演散射计下有效波高研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2021, 43(1): 27−32.Zhao Kaixin. Research on retrieval of significant wave height from scatterometer based on SVR and LSTM algorithms[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2021, 43(1): 27−32. [14] 阚世宜, 于婷, 刘莉. 基于EMD分解的海浪有效波高短期预测研究[J]. 海洋科学前沿, 2019, 6(2): 51−63. doi: 10.12677/AMS.2019.62007Kan Shiyi, Yu Ting, Liu Li. Short-term prediction of significant wave height based on EMD decomposition[J]. Advances in Marine Sciences, 2019, 6(2): 51−63. doi: 10.12677/AMS.2019.62007 [15] Roh M, Kim H S, Chang P H, et al. Numerical simulation of wind wave using ensemble forecast wave model: a case study of Typhoon Lingling[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 475. doi: 10.3390/jmse9050475 [16] 杨飞虎, 许国平, 刘贤松, 等. 基于Prophet时序算法的无线网络突变小区识别方法研究[J]. 邮电设计技术, 2021(2): 25−30.Yang Feihu, Xu Guoping, Liu Xiansong, et al. Research on recognition method of abrupt cells in wireless network based on Prophet sequence algorithm[J]. Designing Techniques of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021(2): 25−30. [17] 王晓, 揣锦华, 张立恒. 基于Prophet算法的铁路客流量预测研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2020, 30(6): 130−134,150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2020.06.025Wang Xiao, Chuai Jinhua, Zhang Liheng. Research on railway passenger flow forecast based on Prophet time series algorithm[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2020, 30(6): 130−134,150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2020.06.025 [18] 张海燕. 南海区台风风暴潮时空分布特征[J]. 海洋预报, 2019, 36(6): 1−8. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2019.06.001Zhang Haiyan. Spatio-temporal distribution of typhoon storm surge along the South China Sea coast[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2019, 36(6): 1−8. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2019.06.001 -





 下载:
下载: