Evaluation and optimization of pretreatment technology for biological monitoring of marine microplastic pollution based on mussel indicator
-
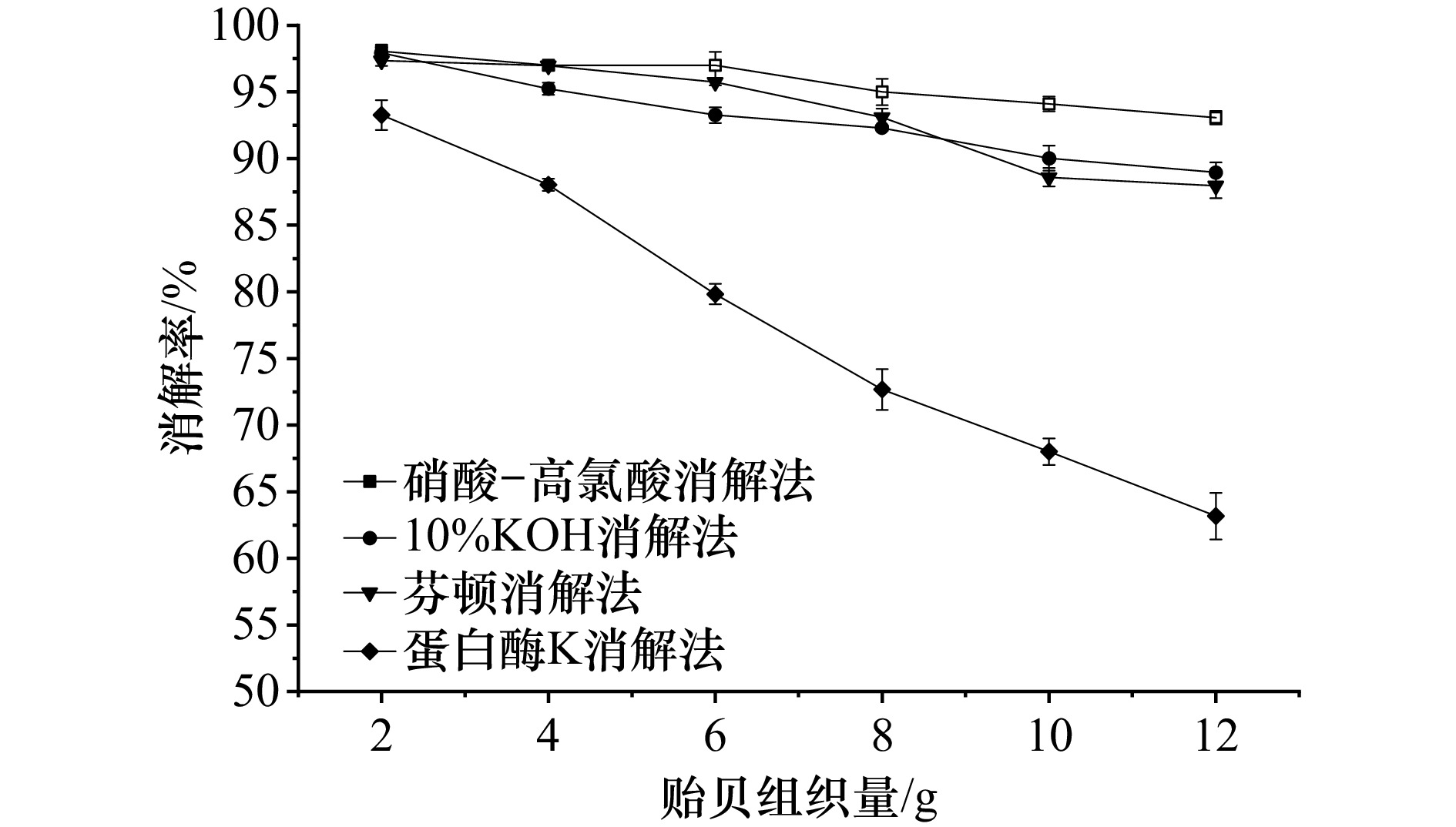
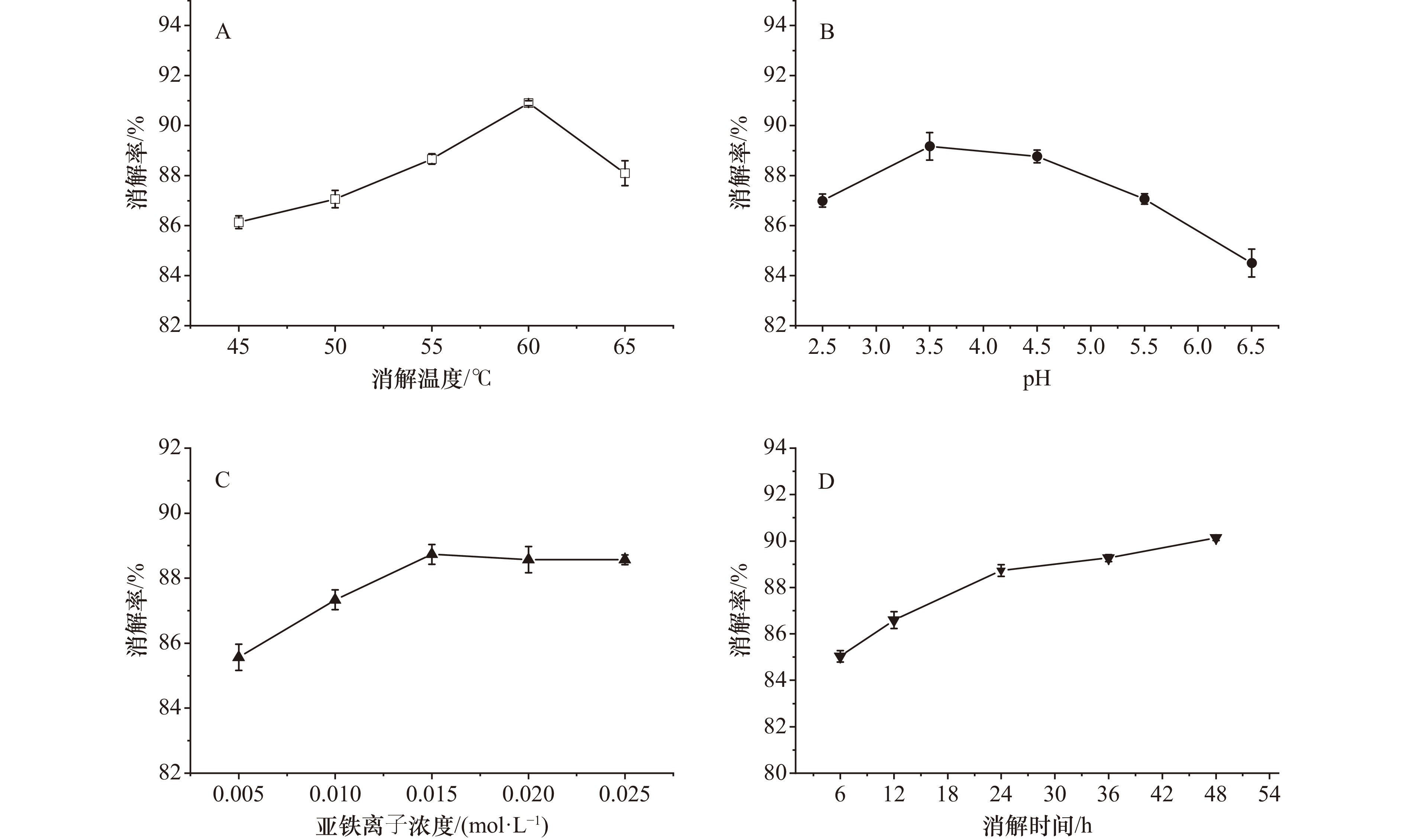
摘要: 基于贻贝指示的海洋微塑料污染生物监测是一种具有广阔应用前景的监测方法,然而目前该法前处理技术包含贻贝组织消解和微塑料密度分离操作多样,且各操作方案的科学性有待验证,导致利用该法得到的海洋微塑料污染监测结果准确性难以保证且数据不易对比。为全面评估多种贻贝组织消解和微塑料密度分离操作的准确性,并获得一种高效经济和可靠的前处理技术方案,本研究开展4种常见消解法(混合酸消解法、氢氧化钾消解法、芬顿消解法和蛋白酶K消解法)对比试验和3种浮选液(氯化钠饱和溶液、碘化钠饱和溶液和甲酸钾饱和溶液)微塑料密度分离试验,评估不同消解法对贻贝组织消解效率和对海洋中常见微塑料的形貌、光谱特征和回收率的影响及不同浮选液的微塑料分离效果,并通过单因素和响应面试验对消解条件进行优化。结果表明,芬顿消解法兼具对贻贝组织的高消解性和对微塑料的低破坏性,可作为优选消解方法,且经优化后,该法在H2O2(30%)体积40 mL,Fe2+浓度0.020 mol/L,温度59℃,pH 3.7和消解时间24 h条件下,对10 g贻贝组织的消解率达96.7%。同时本研究证实甲酸钾饱和溶液可替代氯化钠和碘化钠饱和溶液,用于高效分离提取消解液中的微塑料。以上研究的开展为基于贻贝指示的海洋微塑料污染生物监测前处理技术完善和标准化提供参考。Abstract: Biological monitoring of marine microplastic pollution based on mussel indicator is a monitoring method with broad application prospects. However, the current pretreatment process includes a variety of mussel tissue digestion and microplastic density separation technologies, and the scientific nature of pretreatment technology has yet to be verified, which makes it difficult to guarantee the accuracy of marine microplastic pollution monitoring results obtained by this method and the data are difficult to compare. In order to comprehensively evaluate the accuracy of multiple mussel tissue digestion and microplastic density separation operations and to obtain a cost-effective and reliable pretreatment technology, comparison tests of 4 common digestion methods (mixed acid digestion, potassium hydroxide digestion, Fenton digestion and protease K digestion) and density separation tests of 3 microplastic flotation fluids (sodium chloride saturated solution, sodium iodide saturated solution and potassium formate saturated solution) were carried out. The effects of different digestion methods on the digestion efficiency of mussel tissue and on the morphology, spectral characteristics and recovery rate of common microplastic in the ocean, as well as the separation effect of microplastic in different flotation fluids were evaluated, and the digestion conditions were optimized by single factor and response surface tests. The results showed that the Fenton digestion method had both efficient digestion of mussel tissue and low destructive effect on microplastic, and could be used as the optimal method for digestion of mussel tissue. After optimization, under the conditions of H2O2 (30%) volume 40 mL, Fe2+ concentration 0.020 mol/L, temperature 59℃, pH 3.7 and digestion time 24 h, the digestion rate of 10 g mussel tissue reached 96.7%. At the same time, this study confirmed that potassium formate saturated solution could replace sodium chloride and sodium iodide saturated solution as the flotation fluid with high efficiency. The development of the above research provides a reference for the improvement and standardization of the pretreatment technology for biological monitoring of marine microplastic pollution based on mussel indicator.
-
图 3 PC,PET和PS 颗粒消解前后扫描电镜图
注:1-3分别为PC,PET和PS;A-E分别为消解前,硝酸-高氯酸消解,10%KOH消解,芬顿消解和蛋白酶K消解
Fig. 3 Scanning electron microscope of PC, PET and PS particles before and after digestion
Note: 1-3 are respectively PC, PET and PS; A-E refer to pre digestion, nitric acid-perchloric acid digestion, 10%KOH digestion, Fenton digestion and protease K digestion, respectively
表 1 单因素试验因子水平
Tab. 1 Different factor levels in single factor experiments
水平 因素 温度/℃ pH Fe2+浓度/mol·L−1 时间/h 1 45 2.5 0.005 6 2 50 3.5 0.010 12 3 55 4.5 0.015 24 4 60 5.5 0.020 36 5 65 6.5 0.025 48 表 2 响应面优化试验因素与水平设计
Tab. 2 Experimental factors and level design of response surface optimization
水平 因素 A 温度/℃ B pH C Fe2+浓度/mol·L−1 −1 55 2.5 0.010 0 60 3.5 0.015 1 65 4.5 0.020 表 3 不同消解法对6种微塑料回收率(%)的影响
Tab. 3 Effect of different digestion treatments on recovery rates (%) of 6 kinds of microplastic
消解方法 PC PE PET PP PS PVC 硝酸-高氯酸 91.7±3.1 93.2±1.8 83.8±3.0 94.2±1.3 94.3±2.5 92.5±1.3 10%KOH 63.0±5.3 89.3±1.6 77.7±3.5 91.7±1.5 93.7±2.1 92.6±3.6 芬顿 92.0±1.7 93.7±2.5 92.3±2.3 92.0±1.7 93.0±2.0 91.3±3.2 蛋白酶K 93.3±2.1 94.3±2.1 94.1±0.1 92.7±1.5 94.7±2.3 93.7±3.1 -
[1] Andrady A L. Microplastics in the marine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1596−1605. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030 [2] Mathalon A, Hill P. Microplastic fibers in the intertidal ecosystem surrounding Halifax Harbor, Nova Scotia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 81(1): 69−79. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.02.018 [3] Zhao Shiye, Zhu Lixin, Wang Teng, et al. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: first observations on occurrence, distribution[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 86(1/2): 562−568. [4] Peng Xiaotong, Chen M, Chen Shun, et al. Microplastics contaminate the deepest part of the world’s ocean[J]. Geochemical Perspectives Letters, 2018, 9: 1−5. [5] Lusher A L, Tirelli V, O’Connor I, et al. Microplastics in Arctic polar waters: the first reported values of particles in surface and sub-surface samples[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 14947. doi: 10.1038/srep14947 [6] Goswami P, Vinithkumar N V, Dharani G. First evidence of microplastics bioaccumulation by marine organisms in the Port Blair Bay, Andaman Islands[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 155: 111163. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111163 [7] Li Jiana, Green C, Reynolds A, et al. Microplastics in mussels sampled from coastal waters and supermarkets in the United Kingdom[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 241: 35−44. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.038 [8] Baalkhuyur F M, Bin Dohaish E J A, Elhalwagy M E A, et al. Microplastic in the gastrointestinal tract of fishes along the Saudi Arabian Red Sea coast[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 131: 407−415. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.04.040 [9] Digka N, Tsangaris C, Torre M, et al. Microplastics in mussels and fish from the Northern Ionian Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 135: 30−40. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.063 [10] de Sá L C, Oliveira M, Ribeiro F, et al. Studies of the effects of microplastics on aquatic organisms: what do we know and where should we focus our efforts in the future?[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 645: 1029−1039. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.207 [11] Reichert J, Arnold A L, Hammer N, et al. Reef‐building corals act as long‐term sink for microplastic[J]. Global Change Biology, 2022, 28(1): 33−45. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15920 [12] Barboza L G A, Vethaak A D, Lavorante B R B O, et al. Marine microplastic debris: an emerging issue for food security, food safety and human health[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 133: 336−348. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.047 [13] Bouwmeester H, Hollman P C H, Peters R J B. Potential health impact of environmentally released micro-and nanoplastics in the human food production chain: experiences from nanotoxicology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(15): 8932−8947. [14] Li Jiana, Yang Dongqi, Li Lan, et al. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 207: 190−195. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.09.018 [15] De Witte B, Devriese L, Bekaert K, et al. Quality assessment of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis): comparison between commercial and wild types[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 85(1): 146−155. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.006 [16] Nan Bingxu, Su Lei, Kellar C, et al. Identification of microplastics in surface water and Australian freshwater shrimp Paratya australiensis in Victoria, Australia[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 259: 113865. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113865 [17] Prata J C, da Costa J P, Girão A V, et al. Identifying a quick and efficient method of removing organic matter without damaging microplastic samples[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 686: 131−139. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.456 [18] Cole M, Webb H, Lindeque P K, et al. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4(1): 4528. doi: 10.1038/srep04528 [19] 李楠楠, 石戈, 杨宵旭, 等. 厚壳贻贝Mytilus coruscus足丝盘及足丝的多巴分析(英文)[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2011, 27(2): 148−153.Li Nannan, Shi Ge, Yang Xiaoxu, et al. Detection of dihydroxyphenylalanine in native foot proteins from Mytilus coruscus byssus[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2011, 27(2): 148−153. [20] Hurley R R, Lusher A L, Olsen M, et al. Validation of a method for extracting microplastics from complex, organic-rich, environmental matrices[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(13): 7409−7417. [21] Wagner J, Wang Zhongmin, Ghosal S, et al. Novel method for the extraction and identification of microplastics in ocean trawl and fish gut matrices[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(9): 1479−1490. doi: 10.1039/C6AY02396G [22] Dehaut A, Cassone A L, Frère L, et al. Microplastics in seafood: benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 215: 223−233. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.018 [23] 刘中兴, 谢传欣, 石宁, 等. 过氧化氢溶液分解特性研究[J]. 齐鲁石油化工, 2009, 37(2): 99−102,105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9859.2009.02.006Liu Zhongxing, Xie Chuanxin, Shi Ning, et al. Study on decomposition behavior of hydrogen peroxide solution[J]. Qilu Petrochemical Technology, 2009, 37(2): 99−102,105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9859.2009.02.006 [24] Tang Heqing, Xiang Qingqing, Lei Min, et al. Efficient degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid by UV-Fenton process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 184: 156−162. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.020 [25] Masomboon N, Ratanatamskul C, Lu Mingchun. Chemical oxidation of 2, 6-dimethylaniline in the Fenton process[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(22): 8629−8634. [26] Plastics Europe. Plastics-the facts 2017: an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data[R]. Plastics Europe, 2017. (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的出版地信息, 请确认) [27] 李昇昇, 李良忠, 李敏, 等. 环境样品中微塑料及其结合污染物鉴别分析研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 960−974. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019102304Li Shengsheng, Li Liangzhong, Li Min, et al. Study on identification of microplastics and the combined pollutants in environmental samples[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 960−974. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019102304 -




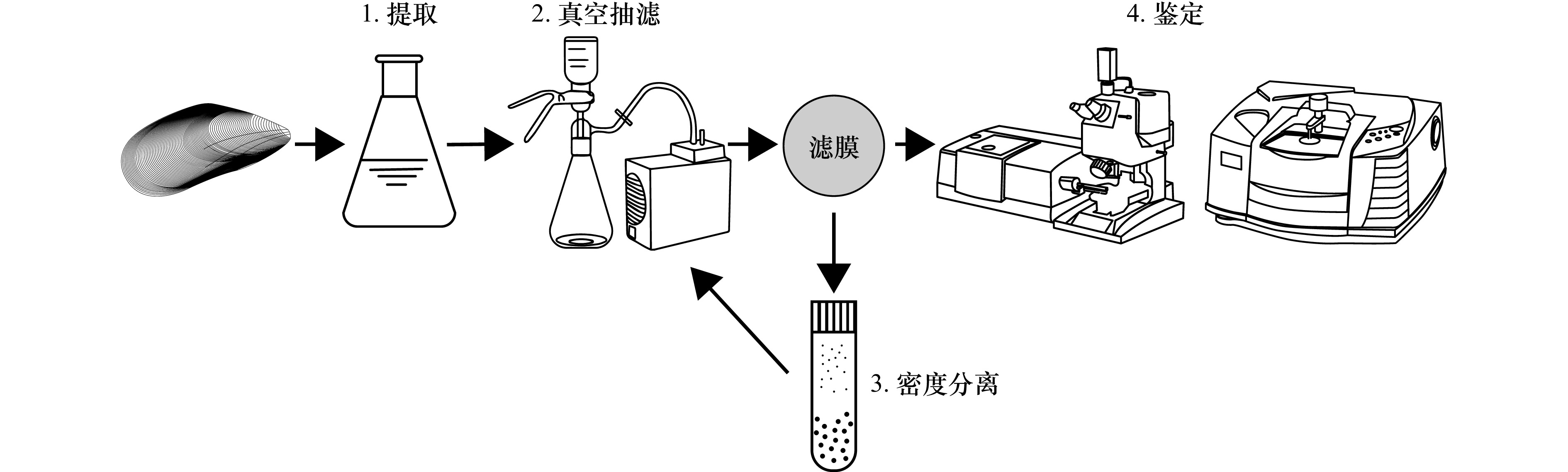
 下载:
下载: