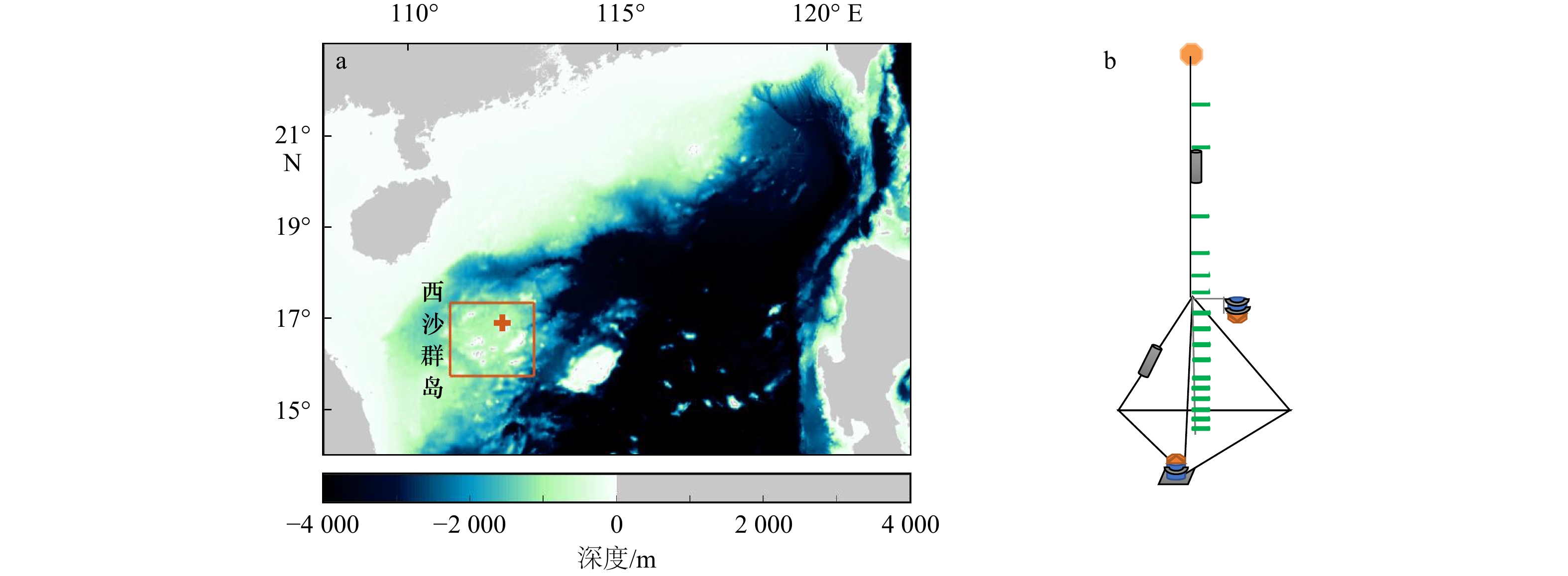
Study on tidal characteristics of coral reef lagoon of Xisha Islands in the South China Sea based on mooring observation
-
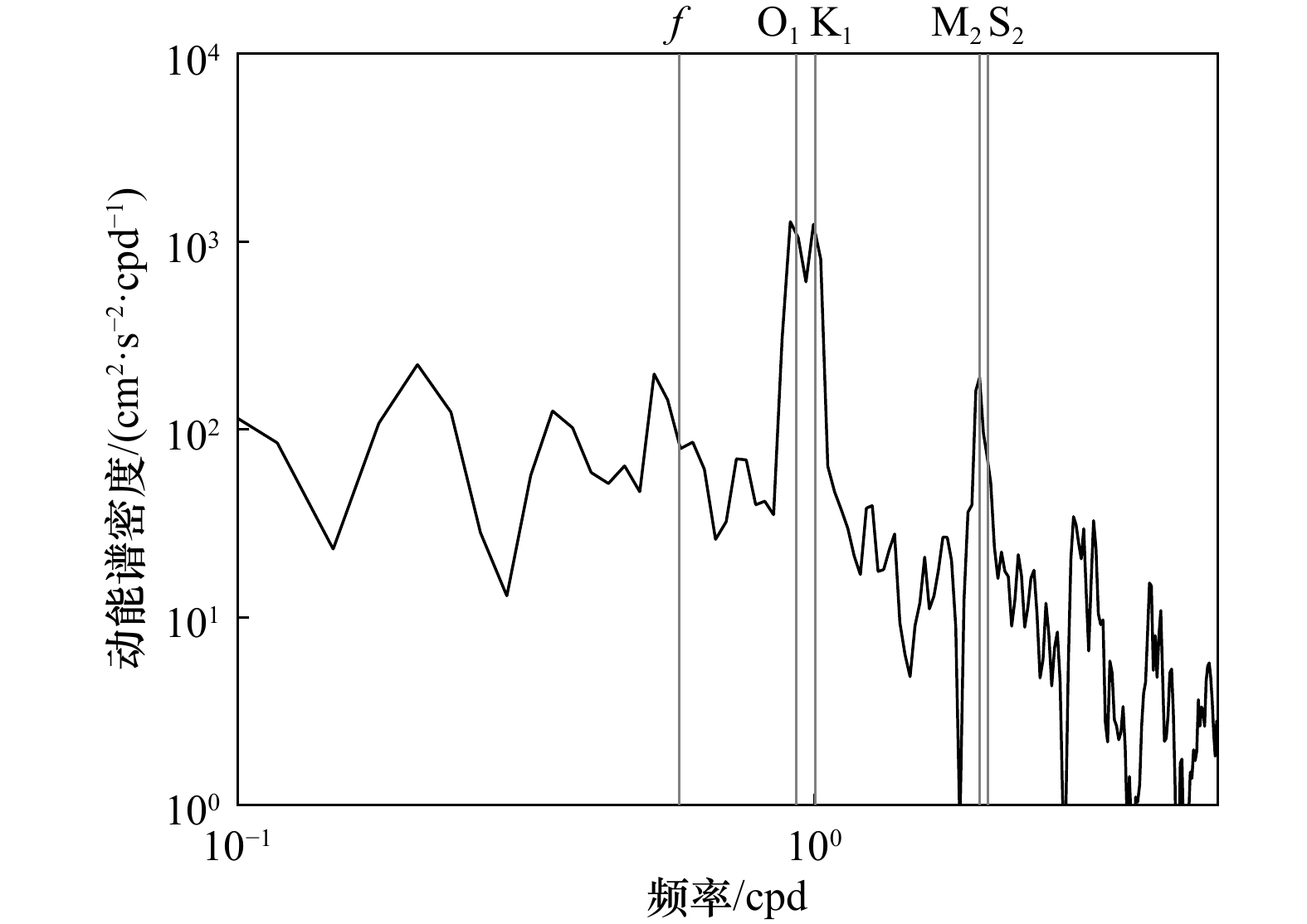
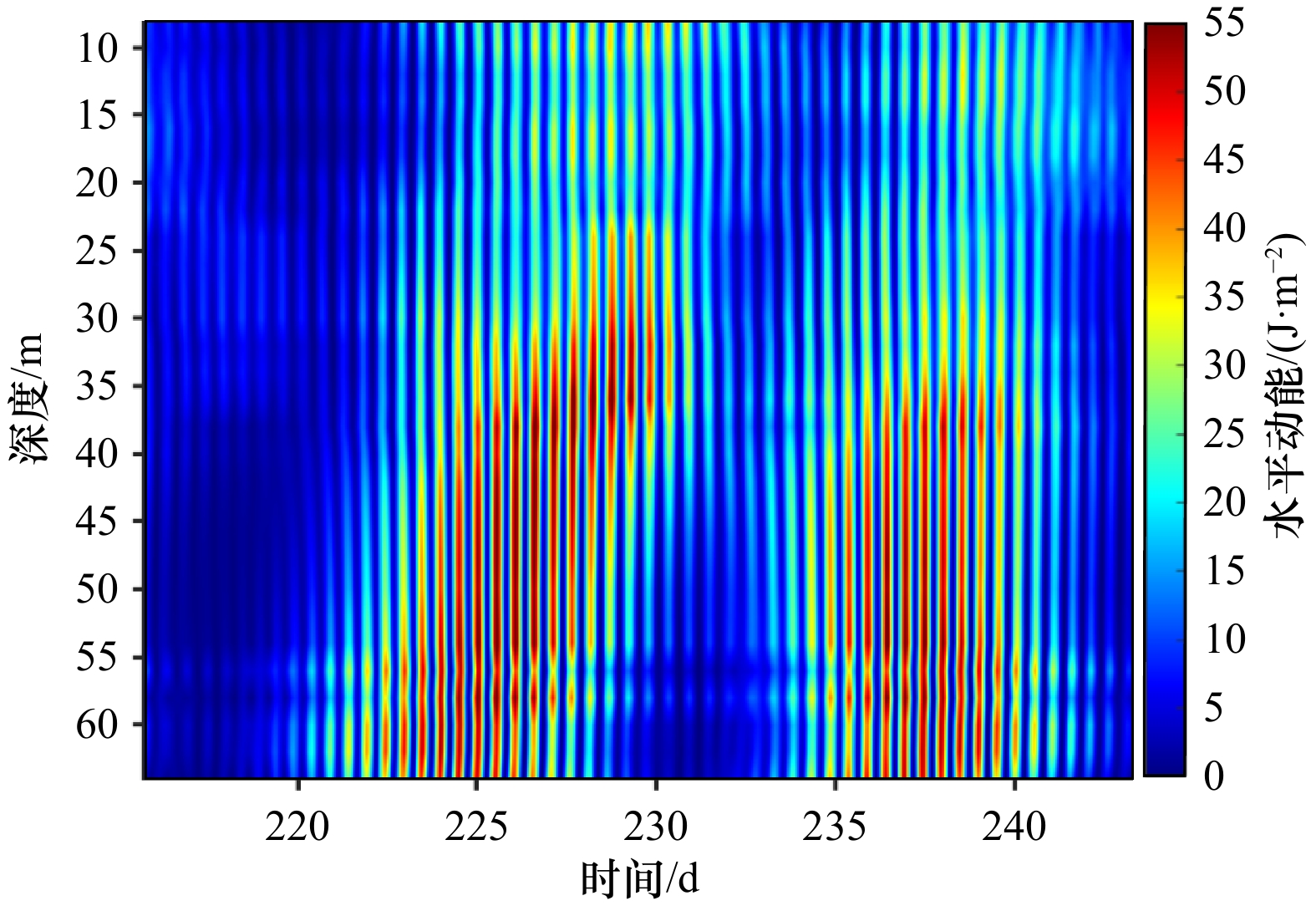
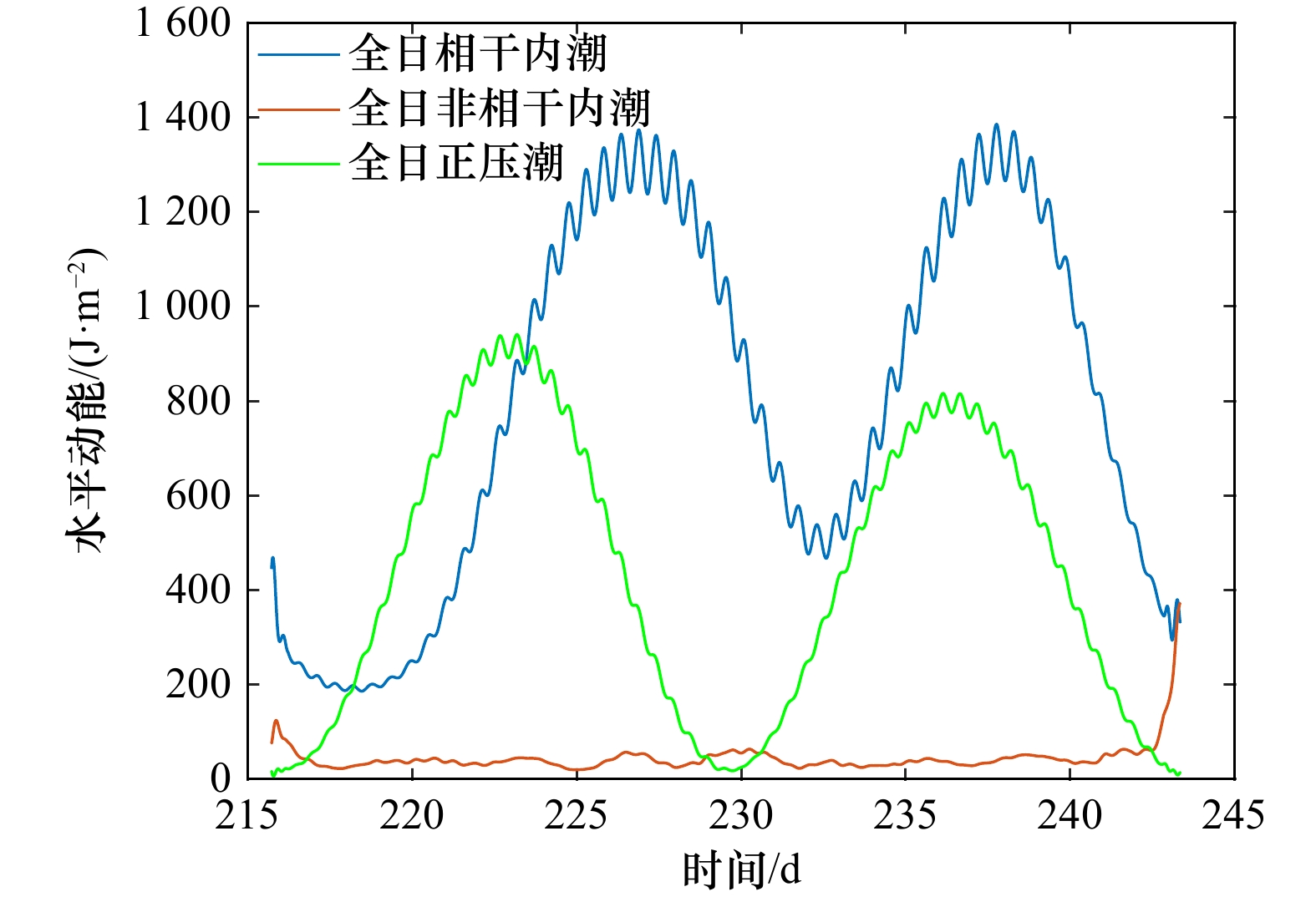
摘要: 本文利用南海西沙群岛潟湖区29 d的全水深浮标观测资料研究了潟湖区内正压潮和内潮的基本特征,采用深度平均方法分析海流的适用性,并讨论潟湖区内潮的主要来源。深度平均流的动能谱显示全日潮流占主导,其动能占整体海流动能的41%。对比分析深度平均流和Tpxo7.2模式预测的全日、半日潮流的调和常数,两者均表明全日正压潮流受地形调制,主轴方向为西北−东南向,而半日正压潮流主轴方向为东−西向。两种方法得到的全日正压潮流大−小潮存在半个相位(6~7 d)的差异,进一步分析发现全日正压潮和全日内潮潮龄不同,存在部分相互抵消,且全日内潮大潮发生时间在深度上存在差异,推测由于缺少海表和海底的测量数据,导致深度平均方法得到的全日正压潮仍然包含全日内潮信号。调和分析结果表明,全日内潮的动能中相干部分占比高达91%,说明潟湖区的全日内潮是正压潮与局地岛礁地形相互作用产生,而从远场传播而来的可能性很小。Abstract: Based on the 29-day full-depth mooring data of coral reef lagoon of Xisha Islands in South China Sea, we investigated the characteristics of the internal tides (ITs), the applicability of depth-averaging method for current analysis, and the source of ITs. The depth-averaged currents indicated that the diurnal tides were dominant, their HKE (horizontal kinetic energy) accounted for 41% of the total currents. The harmonic analyses of depth-averaged current and Tpxo7.2 model current indicated that the barotropic diurnal currents were modulated by topography, its main axis orientation was northwest-southeast. The spring-neap periods of barotropic diurnal currents with two methods have the half-phase shift (6−7 days). It is proposed that the depth-averaged barotropic diurnal currents contain the baroclinic diurnal components (diurnal internal tides) due to the lacking of measurements near the surface and bottom ocean. Further analysis showed that the barotropic and baroclinic diurnal currents had different amplitudes with the variable phase shift. The coherent diurnal ITs contributed 91% HKE to the total diurnal ITs, which implied that ITs was most generated in Xisha Islands.
-
Key words:
- coral reef lagoon /
- internal tide /
- coherent internal tide /
- barotropic tide
-
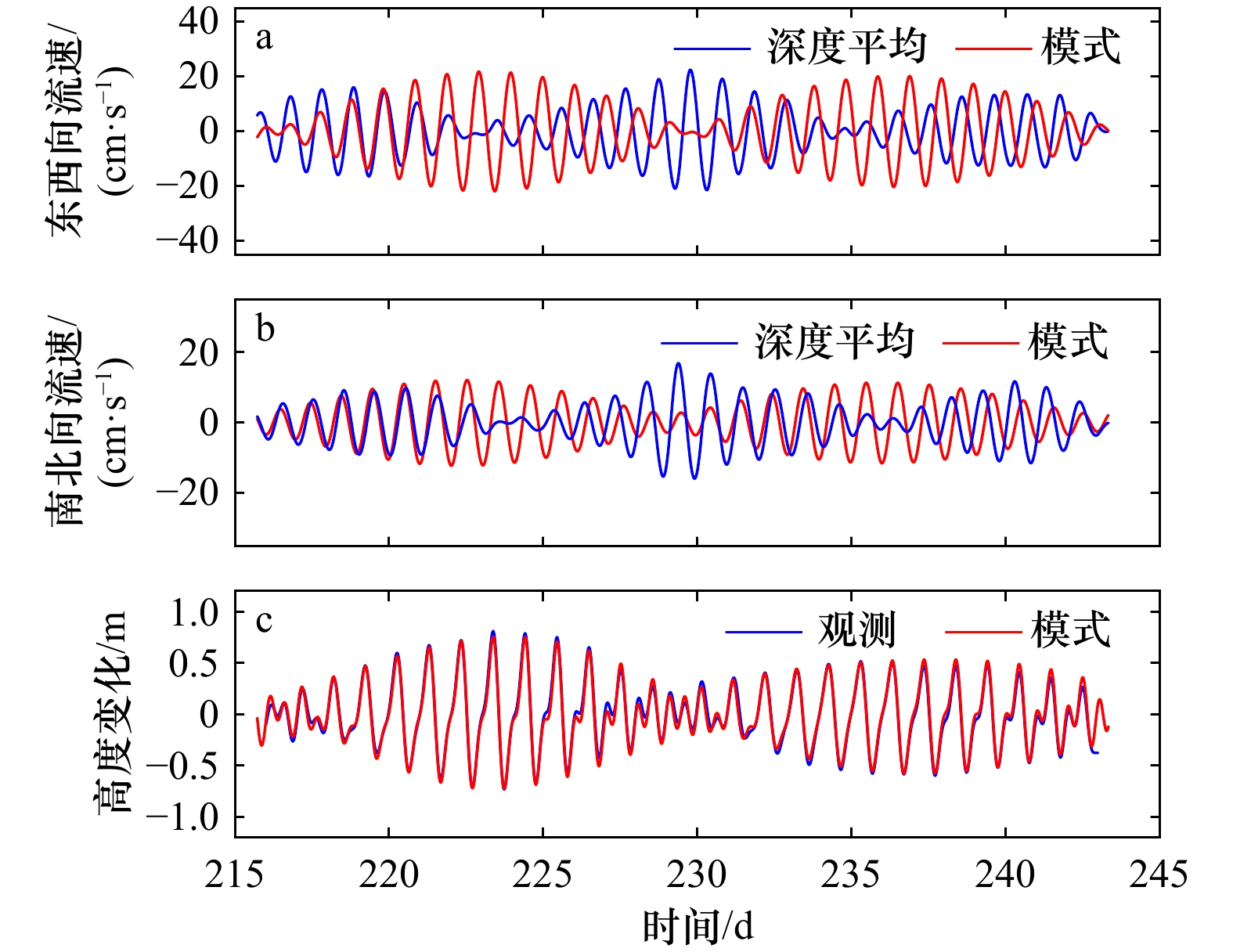
图 4 正压潮的时间序列
蓝线:观测的全日潮;红线:模式预测的全日潮。a. 东西方向的速度;b. 南北方向的速度;c. CTD观测的海底压强变化和模式预测的海平面高度变化的时间序列
Fig. 4 Time series of barotropic current
Blue lines: observed diurnal tides; red lines: diurnal tides predicted by model. a. East-west velocity; b. north-south velocity; c. time series of sea bottom pressure measured by CTD and sea level height predicted by model
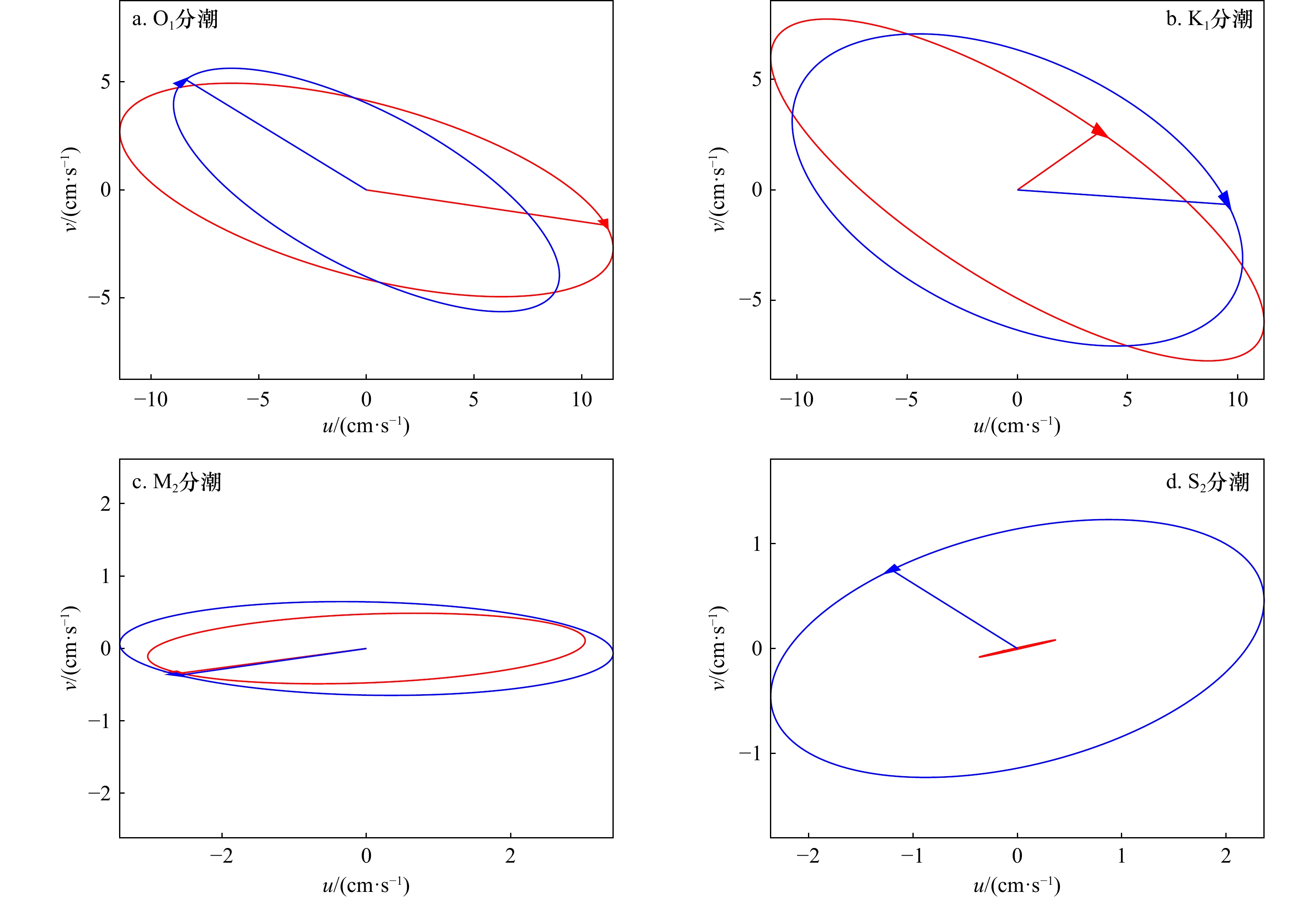
表 1 深度平均流的主要分潮的椭圆要素
Tab. 1 Elliptical elements of four major constituents of depth-averaged currents
分潮 长轴/(cm·s−1) 短轴/(cm·s−1) 倾角/(°) 迟角/(°) O1 9.95 –3.62 152.24 350.27 K1 10.91 –5.94 155.35 214.78 M2 3.42 0.64 178.86 319.17 S2 2.42 1.12 13.99 245.89 表 2 模式预测的主要分潮的椭圆要素
Tab. 2 Elliptical elements of four major constituents of model
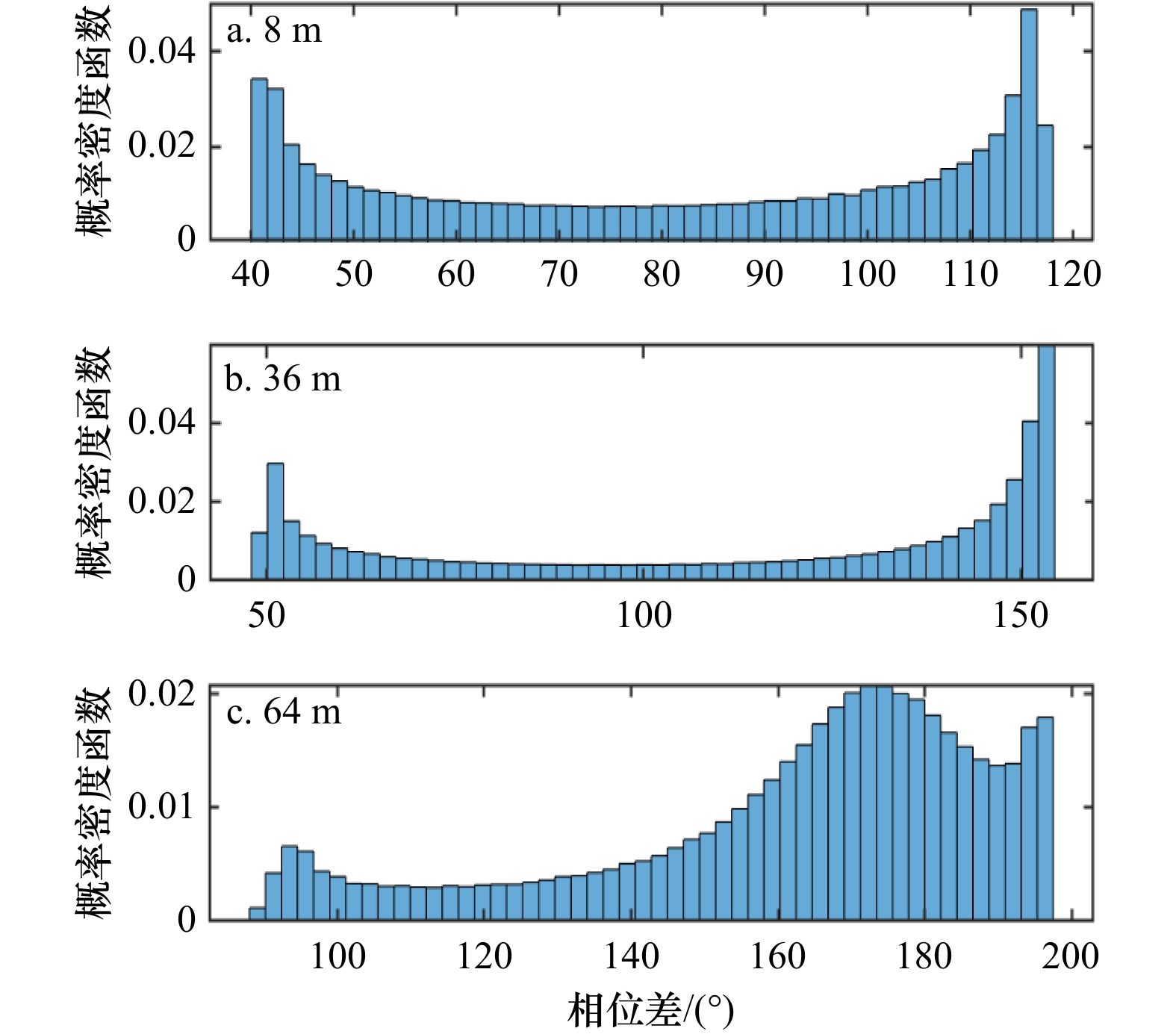
分潮 长轴/(cm·s−1) 短轴/(cm·s−1) 倾角/(°) 迟角/(°) O1 11.81 –4.01 164.95 199.07 K1 12.92 –4.25 148.06 262.06 M2 3.03 0.47 2.10 148.73 S2 0.37 0.01 12.62 248.55 表 3 O1分潮概率密度函数峰值对应的相位差
Tab. 3 Phase difference corresponding probability density function peak of O1 constituent
深度/m 相位差/(°) 8 207 36 191 64 167 表 4 K1分潮概率密度函数峰值对应的相位差
Tab. 4 Phase difference corresponding probability density function peak of K1 constituent
深度/m 相位差/(°) 8 116 36 154 64 175 -
[1] Briscoe M G. Internal waves in the ocean[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1975, 13(3): 591−598. doi: 10.1029/RG013i003p00591 [2] Munk W, Wunsch C. Abyssal recipes II: energetics of tidal and wind mixing[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1998, 45(12): 1977−2010. doi: 10.1016/s0967-0637(98)00070-3 [3] Wang Yuhuai, Dai Changfeng, Chen Y Y. Physical and ecological processes of internal waves on an isolated reef ecosystem in the South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(18): L18609. doi: 10.1029/2007GL030658 [4] Osborne A R, Burch T L. Internal solitons in the Andaman Sea[J]. Science, 1980, 208(4443): 451−460. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4443.451 [5] Duda T F, Lynch J F, Irish J D, et al. Internal tide and nonlinear internal wave behavior at the continental slope in the northern South China Sea[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2004, 29(4): 1105−1130. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.836998 [6] Simmons H, Chang M H, Chang Yating, et al. Modeling and prediction of internal waves in the South China Sea[J]. Oceanography, 2011, 24(4): 88−99. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2011.97 [7] Beardsley R C, Duda T F, Lynch J F, et al. Barotropic tide in the Northeast South China Sea[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2004, 29(4): 1075−1086. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.833226 [8] Alford M H, Peacock T, MacKinnon J A, et al. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7550): 65−69. doi: 10.1038/nature14399 [9] Zhao Ruixiang, Zhu Xiaohua, Park J H, et al. Internal tides in the northwestern South China Sea observed by pressure-recording inverted echo sounders[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2018, 168: 112−122. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2018.09.019 [10] van Haren H. Incoherent internal tidal currents in the deep ocean[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2004, 54(1): 66−76. doi: 10.1007/s10236-003-0083-2 [11] Kelly S M, Nash J D. Internal-tide generation and destruction by shoaling internal tides[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(23): L23611. doi: 10.1029/2010GL045598 [12] 王越, 黄晓冬, 杨运超, 等. 南海东北部全日非相干内潮的特征及其成因[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2021, 51(5): 1−9. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20200175Wang Yue, Huang Xiaodong, Yang Yunchao, et al. Characteristics and cause analysis of diurnal incoherent internal tides in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(5): 1−9. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20200175 [13] 翟荣伟, 陈桂英, 尚晓东. 南海北部相干内潮和非相干内潮演变特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(11): 24−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2017.11.003Zhai Rongwei, Chen Guiying, Shang Xiaodong. Evolution characteristics of coherent and incoherent internal tides in the northern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(11): 24−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2017.11.003 [14] 梁辉, 郑洁, 田纪伟. 南海西北陆坡区内潮与近惯性内波观测研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(11): 32−42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.11.003Liang Hui, Zheng Jie, Tian Jiwei. Observation of internal tides and near-inertial internal waves on the continental slope in the northwestern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(11): 32−42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.11.003 [15] Storlazzi C D, Cheriton O M, van Hooidonk R, et al. Internal tides can provide thermal refugia that will buffer some coral reefs from future global warming[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 13435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70372-9 [16] Lee I H, Wang Yuhuai, Yang Y, et al. Temporal variability of internal tides in the Northeast South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C2): C02013. doi: 10.1029/2011JC007518 [17] Wu Ziku, Lu Xiangqing, Tian Jiwei. Simulation of barotropic and baroclinic tides in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 24(2): 1−8. [18] 邓晓东, 刘军亮, 蔡树群. 南海西沙群岛陆架区的潮流特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(4): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.002Deng Xiaodong, Liu Junliang, Cai Shuqun. Analyses of the tidal current characteristics on the continental shelf of the Xisha Islands in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(4): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.002 [19] Egbert G D, Erofeeva S Y. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2002, 19(2): 183−204. doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2002)019<0183:EIMOBO>2.0.CO;2 [20] Holloway P E, Chatwin P G, Craig P. Internal tide observations from the Australian north west shelf in summer 1995[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2001, 31(5): 1182−1199. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2001)031<1182:Itofta>2.0.Co;2 [21] Kurapov A L, Egbert G D, Allen J S, et al. The M2 internal tide off Oregon: inferences from data assimilation[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2003, 33(8): 1733−1757. doi: 10.1175/2397.1 [22] Martini K I, Alford M H, Kunze E, et al. Observations of internal tides on the Oregon continental slope[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2011, 41(9): 1772−1794. doi: 10.1175/2011JPO4581.1 [23] Xu Zhenhua, Yin Baoshu, Hou Yijun, et al. Variability of internal tides and near-inertial waves on the continental slope of the northwestern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(1): 197−211. doi: 10.1029/2012JC008212 [24] Codiga D L. Unified tidal analysis and prediction using the UTide Matlab functions[R]. Narragansett: University of Rhode Island, 2011. [25] van Haren H. Bottom-pressure observations of deep-sea internal hydrostatic and non-hydrostatic motions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 714: 591−611. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2012.507 [26] Holloway P E, Merrifield M A. On the spring-neap variability and age of the internal tide at the Hawaiian ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2003, 108(C4): 3126. doi: 10.1029/2002jc001486 [27] Davis K A, Arthur R S, Reid E C, et al. Fate of internal waves on a shallow shelf[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2020, 125(5): e2019JC015377. doi: 10.1029/2019jc015377 [28] Lowe R J, Falter J L. Oceanic forcing of coral reefs[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2015, 7: 43−66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015834 -




 下载:
下载: