Characteristics of heavy metals and their influential factors between sediments and water of the Zhujiang River Estuary in summer
-
摘要: 珠江口受复杂径−潮动力耦合作用的影响,河口重金属迁移转化机制复杂多变。本文基于2018年夏季珠江口及其邻近海域海水和沉积物的调查资料,研究了珠江口多动力因子驱动下7种重金属元素汞、砷、锌、镉、铅、铜和铬的沉积、迁移和积累机制。结果表明:相比于溶解态重金属(水体中)的赋存状况,吸附态重金属(沉积物中)更稳定,污染也更严重;采用皮尔逊相关分析和主成分分析计算出重金属元素与环境因子之间的响应关系,溶解态重金属主要以稀释混合过程为主,吸附态重金属受有机碳和氧化还原作用的影响较大;沉积物−水界面重金属的分配系数显示出铅和铬易被吸附在颗粒物上,而镉和汞易溶解在水体中,揭示了河口复杂动力影响下元素在不同介质的形态转换特征;除了镉−铬、镉−铜和铬−砷这3组元素间不显著相关,其他元素间的显著相关性表明了重金属元素具有相似的来源,并采用主成分分析探讨了重金属元素的潜在来源,主要来源为工业废水,农业和大气沉降次之。研究结果可为有效控制重金属的排放和河口污染治理提供重要支撑。Abstract: Characteristics of heavy metals in the Zhujiang River Estuary are mainly influenced by the interacting river-tide dynamics. Water and sediment samples were collected in the Zhujiang River Estuary and its adjacent zones in the summer of 2018. The present study aimed to investigate the estuarine behaviors (i.e., sedimentary, transportation, accumulation) of seven metals Hg, As, Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, and Cr, which were co-influenced by the physicochemical properties in the estuary. The levels of heavy metals in sediments were higher than those dissolved in water. The heavy metals in sediments were more stable and the pollution was thus more serious. The results of Pearson correlation and principal component analysis showed that dissolved metals were more easily diluted and mixed, and the sediment metals were significantly influenced by the total organic carbon and redox. The metal partitioning between sediments and water was discussed as well in this study under the influence of estuarine dynamics, which indicated the phase exchange between multimedia in the estuary; Pb and Cr were more easily absorbed in the particulate particles, while Cd and Hg were intended to dissolve in water. The significant correlations between metals (e.g., Hg, Pb, and Zn) indicated the similar sources, and the principal component analysis was used to probe into the source contributions of heavy metals in sediments of the Zhujiang River Estuary, contributed mainly by industrial pollution, followed by agricultural pollution and atmospheric deposition. These findings will provide important information for the effective controls of heavy metal inputs and estuary management.
-
表 1 不同重金属风险熵水平中站位比例
Tab. 1 The ratio of stations in different heavy metal risk quotient levels
风险熵 汞 砷 锌 镉 铅 铜 铬 表层水体风险熵 RQ<0.1 100% 100% 62% 100% 100% 0.1≤RQ <1 38% 100% 100% RQ≥1.0 底层水体风险熵 RQ<0.1 100% 100% 88% 100% 100% 0.1≤RQ<1 13% 100% 94% RQ≥1.0 6% 注:RQ<0.1为低生态风险;0.1≤RQ<1.0为中度生态风险;RQ≥1.0为高生态风险。 表 2 重金属分配系数与环境因子的皮尔逊相关系数
Tab. 2 Pearson correlation coefficient of heavy metal distribution coefficient and environmental factors
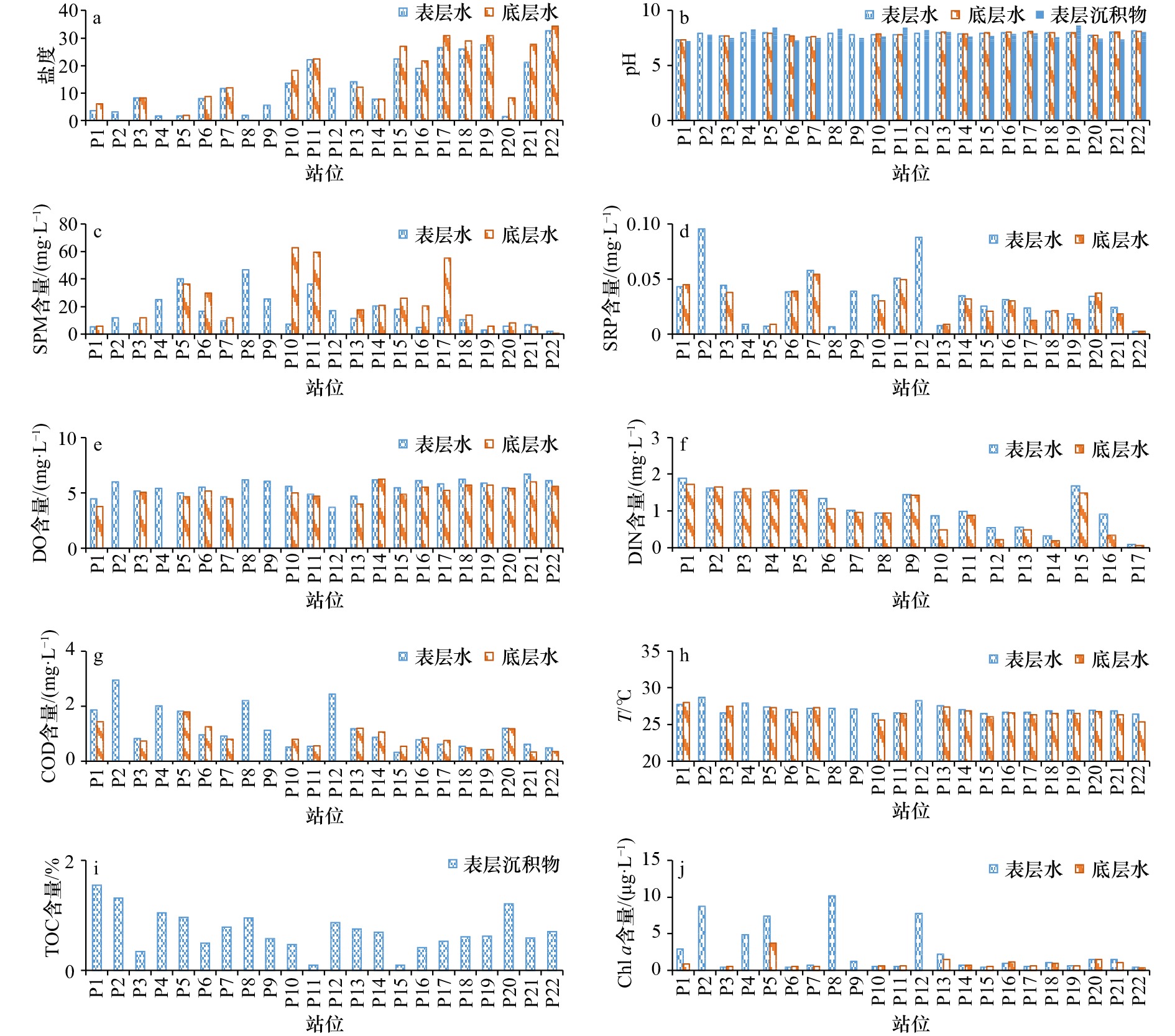
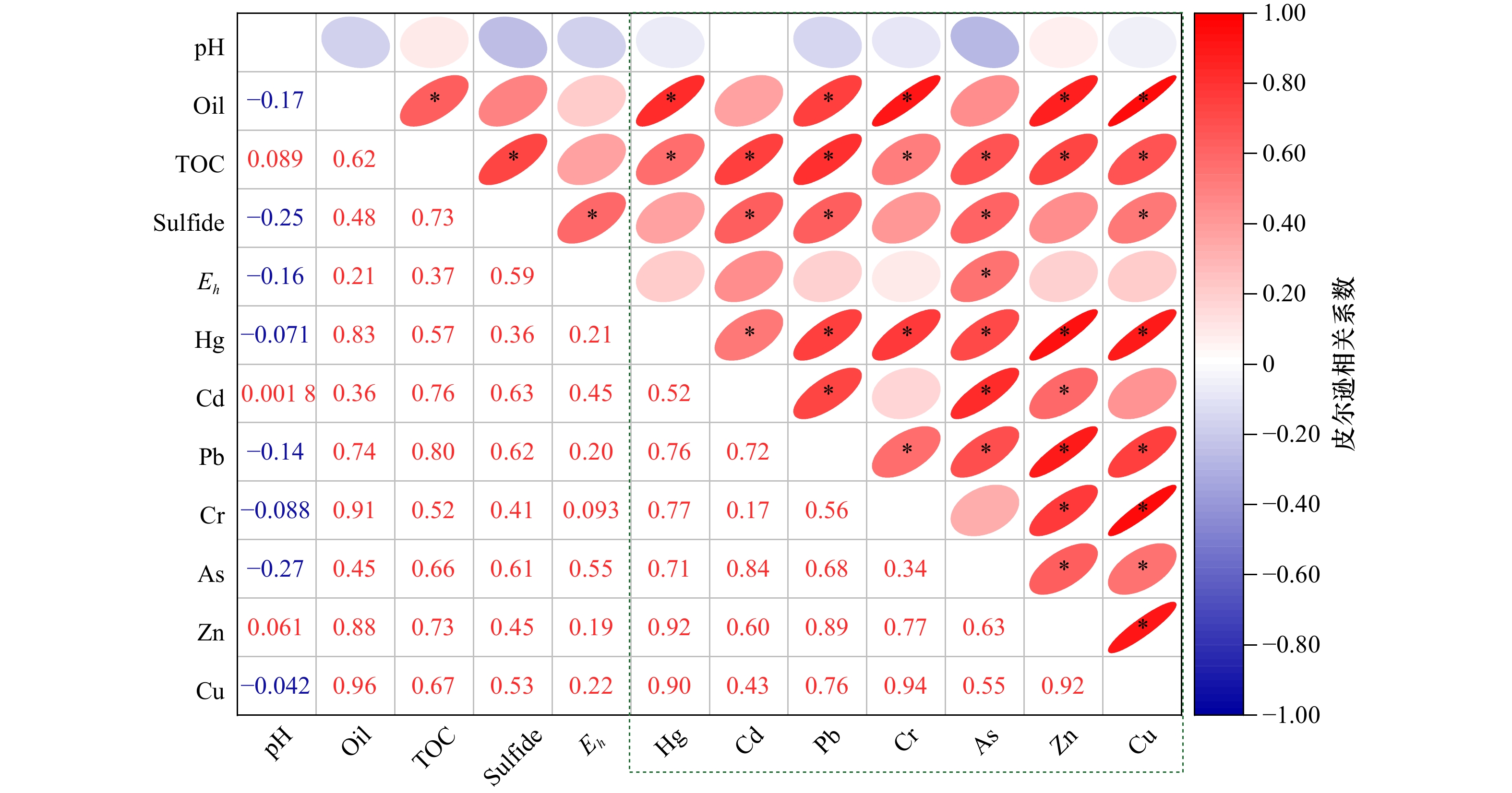
分配系数 S T DO含量 COD Chl a含量 SPM含量 DIN含量 SRP含量 Sulfide含量 Eh TOC含量 Hg −0.51* 0.54* −0.24 0.52* 0.16 −0.21 0.38 0.10 0.40 0.59* 0.69* Cd −0.33 0.54* −0.51* 0.43 0.01 −0.29 0.34 0.25 0.67* 0.51* 0.71* Pb −0.29 0.18 −0.23 0.27 0.01 0.14 0.42 0.54* 0.53 0.16 0.33 Cr −0.28 0.38 −0.09 0.34 −0.14 −0.20 0.32 0.23 0.44 0.28 0.55* As −0.54* 0.65* −0.41 0.66* 0.36 −0.30 0.44 0.05 0.55 0.57* 0.85* Zn −0.52* 0.52* −0.29 0.49* 0.07 −0.35 0.43 0.21 0.57 0.44 0.70* Cu −0.51* 0.32 0.02 0.65* 0.68* −0.08 0.22 −0.33 −0.03 0.32 0.65* 注:*代表相关性在0.05水平上显著。 -
[1] 廖宝淦, 刘秋辛, 贾珍珍, 等. 珠江口磨刀门水体中重金属分布、分配特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(1): 8−15. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190250Liao Baogan, Liu Qiuxin, Jia Zhenzhen, et al. Heavy metal distribution patterns and their influence factors in Modaomen Estuary of the Pearl River[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(1): 8−15. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190250 [2] Jia Zhenzhen, Li Shiyu, Liu Qiuxin, et al. Distribution and partitioning of heavy metals in water and sediments of a typical estuary (Modaomen, South China): the effect of water density stratification associated with salinity[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 287: 117277. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117277 [3] 李嘉怡, 董汉英, 牛丽霞, 等. 珠江虎门河口夏季悬浮物中重金属分布特征及其风险评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(2): 184−189, 199. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200021Li Jiayi, Dong Hanying, Niu Lixia, et al. The characteristics and risk assessments of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter during summer in the Humen outlet of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(2): 184−189, 199. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200021 [4] 鲁晶晶. 河口环境综合管理的美国经验及借鉴—以美国“国家河口计划”为中心[J]. 太原理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2020, 38(2): 70−76.Lu Jingjing. US experiences and references on integrated management of estuary environment—Focus on the U. S. “National Estuary Program”[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2020, 38(2): 70−76. [5] Zhuang Wen, Zhou Fengxia. Distribution, source and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent East China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 164: 112002. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112002 [6] Niu Lixia, Li Jiayi, Luo Xiangxin, et al. Identification of heavy metal pollution in estuarine sediments under long-term reclamation: ecological toxicity, sources and implications for estuary management[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 290: 118126. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118126 [7] 旷泽行, 汪慧娟, 谷阳光, 等. 海南岛昌化江河口海域生物体重金属富集特征与概率健康风险评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(5): 699−706. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200208Kuang Zexing, Wang Huijuan, Gu Yangguang, et al. The characteristics of heavy metal enrichment and probabilistic health risk assessment of organisms from Changhua River Estuary in Hainan Island[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(5): 699−706. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200208 [8] Liu Qiuxin, Jia Zhenzhen, Li Siyu, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and quantitative source apportionment in surface sediments along a partially mixed estuary (Modaomen, China)[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 225: 829−838. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.063 [9] 李平, 郭晓娟, 杨清书, 等. 珠江磨刀门河口表层沉积物中重金属的分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2017, 36(5): 746−753.Li Ping, Guo Xiaojuan, Yang Qingshu, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in Modaomen distributary mouth of Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(5): 746−753. [10] Niu Lixia, Luo Xiangxin, Cai Huayang, et al. Seasonal dynamics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons between water and sediment in a tide-dominated estuary and ecological risks for estuary management[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 162: 111831. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111831 [11] 陈斌, 吕向立, 王中瑗, 等. 珠江口表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险及生物富集评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(7): 73−82.Chen Bin, Lü Xiangli, Wang Zhongyuan, et al. Assessment of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments and biological accumulation in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(7): 73−82. [12] Niu Lixia, Cai Huayang, Jia Liangwen, et al. Metal pollution in the Pearl River Estuary and implications for estuary management: the influence of hydrological connectivity associated with estuarine mixing[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 225: 112747. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112747 [13] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 17378.3−2007, 海洋监测规范 第3部分: 样品采集、贮存与运输[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB 17378.3−2007, The specification for marine monitoring. Part 3: Sample collection storage and transportation[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [14] 赵华林. 城市半封闭河道水体重金属污染分配特征研究[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(6): 120−124.Zhao Hualin. Study on distribution characteristics of heavy metal pollution in semi-closed rivers in cities[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2019, 38(6): 120−124. [15] Ollenweider R A, Giocanardi F, Montanari G, et al. Characterization of the trophic conditions of marine coastal waters with special reference t o the NW Adriatic Sea: proposal for a trophic scale, turbidity and generalized water quality index[J]. Environmetrics, 1998, 9(3): 329−357. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-095X(199805/06)9:3<329::AID-ENV308>3.0.CO;2-9 [16] 左平, 汪亚平, 程珺, 等. 深圳湾海域表层和柱样沉积物中的重金属分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2008, 30(4): 71−79.Zuo Ping, Wang Yaping, Cheng Jun, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments and core sediments of the Shenzhen Bay in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2008, 30(4): 71−79. [17] Zhao Shou, Feng Chenghong, Wang Dongxin, et al. Salinity increases the mobility of Cd, Cu, Mn, and Pb in the sediments of Yangtze Estuary: relative role of sediments' properties and metal speciation[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(7): 977−984. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.001 [18] 杜佳, 王永红, 黄清辉, 等. 珠江河口悬浮物中重金属时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2): 625−632.Du Jia, Wang Yonghong, Huang Qinghui, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in Pearl River Estuary and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(2): 625−632. [19] 徐程, 杨斌, 朱雪菁, 等. 大风江口海域沉积物酸可挥发性硫化物、重金属分布及风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(6): 1530−1538.Xu Cheng, Yang Bin, Zhu Xuejing, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of acid volatile sulfide and heavy metals in sediments of Dafengjiang River Estuary[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(6): 1530−1538. [20] 刘士涛, 吕小鸿, 姚然, 等. 菌藻共生高效产氢体系研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2021, 41(S1): 48−53.Liu Shitao, Lü Xiaohong, Yao Ran, et al. Research progress on bacteria-algal symbiosis system for efficient production of hydrogen[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(S1): 48−53. [21] 张日旭, 蒋旭光, 池涌, 等. 酸洗污泥与煤共燃烧过程中重金属的迁移分布研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(7): 790−797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.07.003Zhang Rixu, Jiang Xuguang, Chi Yong, et al. Migration and distribution of heavy metals during co-combustion of pickling sludge and coal[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2015, 43(7): 790−797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.07.003 [22] Zhao Guangming, Ye Siguan, Yuan Hongming, et al. Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24: 2966−2979. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8003-4 [23] Gu Yangguang, Li Qusheng, Fang Jianhong, et al. Identification of heavy metal sources in the reclaimed farmland soils of the Pearl River Estuary in China using a multivariate geostatistical approach[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 105: 7−12. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.003 [24] Lu Qiongqiong, Bai Junhong, Zhang Guangliang, et al. Effects of coastal reclamation history on heavy metals in different types of wetland soils in the Pearl River Delta: levels, sources and ecological risks[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 272: 122668. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122668 [25] Zhang Hanxiao, Huo Shouliang, Yeager K M, et al. Accumulation of arsenic, mercury and heavy metals in lacustrine sediment in relation to eutrophication: impacts of sources and climate change[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 93: 771−780. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.059 -





 下载:
下载: