Comparative Research of Water Environmental Carrying Capacity in Xiangshan Bay
-
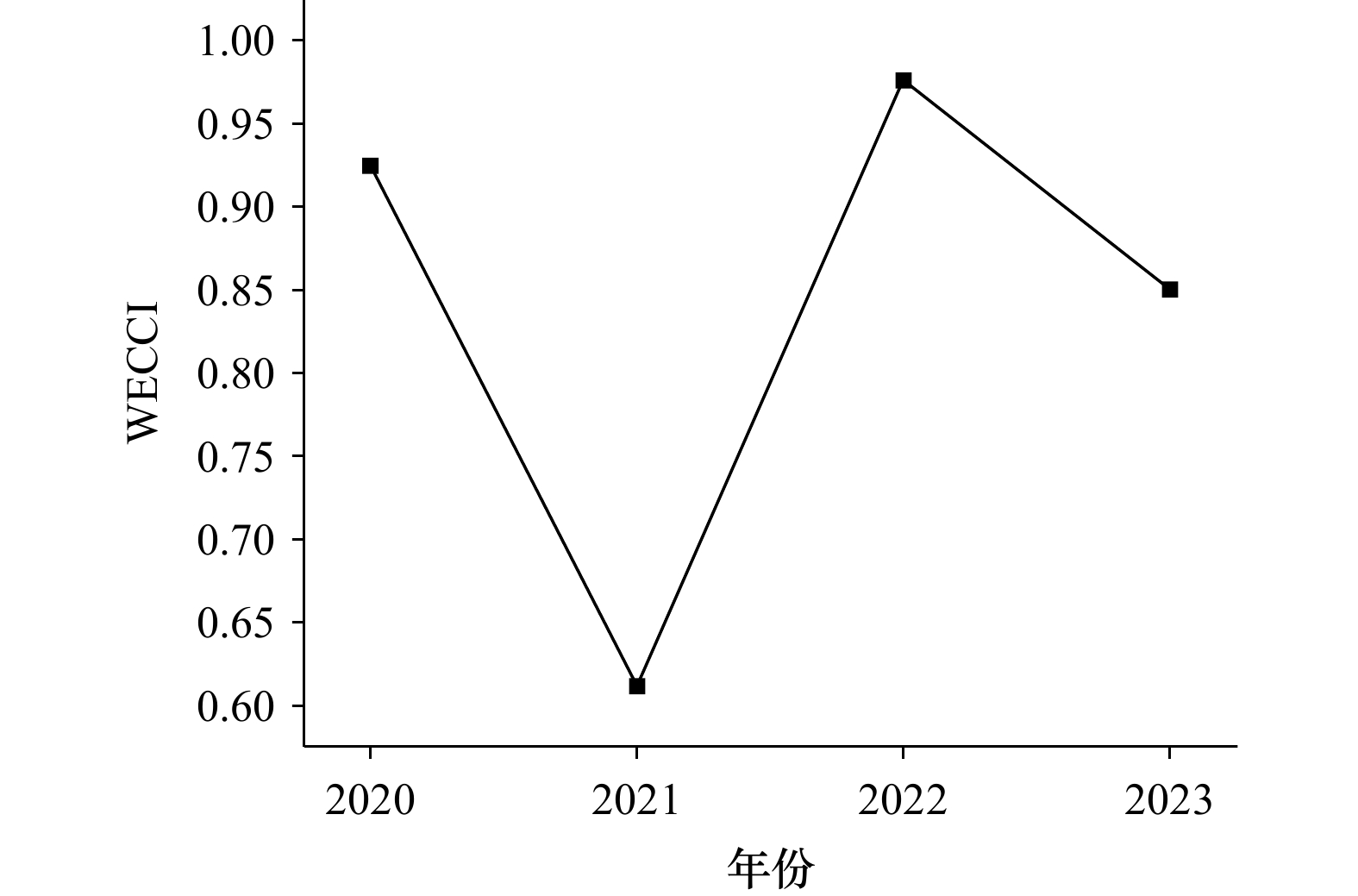
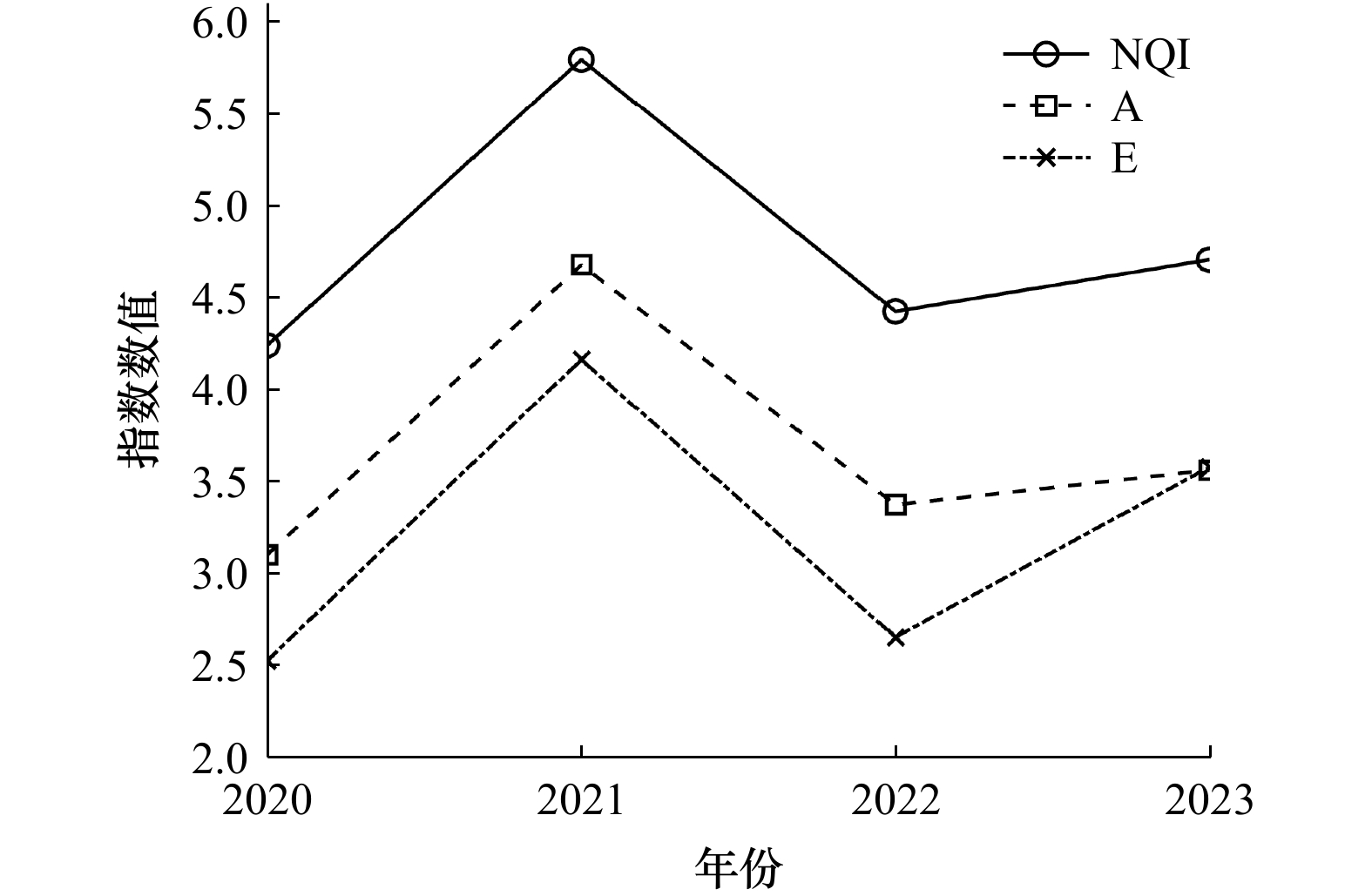
摘要: 近年来,海洋经济的快速发展导致了沿海区域环境污染问题加剧,特别是象山港作为重要的水产养殖基地,其水环境状况直接影响当地的经济发展和生态环境。本文以DO、COD、DIN、DIP四项水质监测指标构建BP神经网络模型,研究了象山港2020至2023年水环境承载力的空间分布和时间变化特征。结果显示,象山港的水环境承载力指数(WECCI)呈现出显著的年际波动,并在2022年达到峰值。象山港内湾由于水体交换能力较弱,污染物滞留时间较长,其水环境承载力显著低于外湾。本文还结合NQI、A、E三个水环境评价指数对象山港的水环境状况进行研究,结果同样发现2022年象山港的水环境质量有所改善。分析2022年干旱背景下的水环境变化,发现河流径流量的减少和盐水入侵导致象山港内营养盐浓度降低,从而提高了当年的水环境承载力值。相比水环境指数评价法,BP神经网络模型在综合评估水环境承载力及其空间差异方面表现出显著优势。Abstract: In recent years, the rapid development of the marine economy has led to intensified environmental pollution in coastal areas. As an important aquaculture base, the water environment status of Xiangshan Bay directly affects local economic development and the ecological environment. This study established a BP neural network model based on four water quality monitoring indicators DO, COD, DIN and DIP to analyze the spatial distribution and variation characteristics of the water environmental carrying capacity in Xiangshan Bay from 2020 to 2023. Results show that the Water Environmental Carrying Capacity Index (WECCI) exhibited significant interannual fluctuations, reaching its peak in 2022. Spatially, the inner bay exhibited significantly lower water environmental carrying capacity than the outer bay, attributable to diminished hydrodynamic exchange capacity and prolonged pollutant retention duration. Additional analysis incorporating three water quality evaluation indices NQI, A, and E also indicated improved water environmental quality in 2022. Analysis of the 2022 drought conditions revealed that reduced river runoff and saltwater intrusion led to decreased nutrient concentrations, consequently enhancing the water environmental carrying capacity. Compared to traditional water quality index evaluation methods, the BP neural network model demonstrated superior performance in comprehensively assessing water environmental carrying capacity and its spatial heterogeneity.
-
图 6 2020−2023年象山港WECCI空间分布(a−d为2020−2023年各年份WECCI空间分布,e为2020−2023年4年平均WECCI空间分布)
Fig. 6 The spatial distribution of WECCI in Xiangshan Bay from 2020 to 2023 (a−d show the spatial distribution of WECCI in each year from 2020 to 2023, and e shows the average spatial distribution of WECCI in the four years from 2020 to 2023)
图 8 2020−2023年象山港NQI指数空间分布(a−d为2020−2023年各年份NQI空间分布,e为2020−2023年4年平均NQI空间分布)
Fig. 8 The spatial distribution of NQI index in Xiangshan Bay from 2020 to 2023 (a−d show the spatial distribution of NQI in each year from 2020 to 2023, and e shows the average spatial distribution of NQI in the four years from 2020 to 2023)
图 9 2020−2023年象山港A指数空间分布(a−d为2020−2023年各年份A空间分布,e为2020−2023年4年平均A空间分布)
Fig. 9 The spatial distribution of A index in Xiangshan Bay from 2020 to 2023 (a−d show the spatial distribution of A in each year from 2020 to 2023, and e shows the average spatial distribution of A in the four years from 2020 to 2023)
图 10 2020−2023年象山港E指数空间分布(a−d为2020−2023年各年份E空间分布,e为2020−2023年4年平均E空间分布)
Fig. 10 The spatial distribution of E index in Xiangshan Bay from 2020 to 2023 (a−d show the spatial distribution of E in each year from 2020 to 2023, and e shows the average spatial distribution of E in the four years from 2020 to 2023)
表 1 象山港2010年至2019年DO、COD、DIN、DIP数据正态分布拟合均值μ和方差σ
Tab. 1 Normal distribution fitting mean (μ) and variance (σ) of DO, COD, DIN, DIP data in Xiangshan Bay from 2010 to 2019
数据 指标数据 DO/mg/L COD/mg/L DIN/mg/L DIP/mg/L 均值μ 6.7209 0.9503 0.6797 0.0494 方差σ 0.9551 0.3617 0.1509 0.0190 表 2 BP神经网络模型样本数据输入输出取值
Tab. 2 BP neural network model sample data input and output values
数据 样本数据输入 样本数据输出(WECCI) DO COD 1/COD DIN 1/DIN DIP 1/DIP (mg/L) (mg/L) (L/mg) (mg/L) (L/mg) (mg/L) (L/mg) 最优值 8.6312 0.2269 4.4070 0.3779 2.6463 0.0114 87.4583 0.977 较优值 7.6760 0.5886 1.6990 0.5288 1.8911 0.0304 32.8588 0.841 中间值 6.7209 0.9503 1.0523 0.6797 1.4713 0.0494 20.2296 0.500 较差值 5.7658 1.3119 0.7622 0.8306 1.2040 0.0684 14.6131 0.159 最差值 4.8106 1.6736 0.5975 0.9815 1.0188 0.0874 11.4376 0.023 表 3 2020-2023年模型输出WECCI
Tab. 3 Model output WECCI from 2020 to 2023
站位 年份 站位平均 2020 2021 2022 2023 S1 0.8026 0.4054 0.9759 0.5783 0.5889 S2 0.9490 0.4727 0.9768 0.5854 0.7849 S3 0.5949 0.6412 0.9757 0.5005 0.6069 S4 0.9762 0.4839 0.9765 0.7717 0.9700 S5 0.8448 0.5798 0.9768 0.6970 0.9002 S6 0.9148 0.8941 0.9768 0.9762 0.9738 S7 0.5180 0.9755 0.9658 0.0258 0.9746 S8 0.5842 0.9764 0.9726 0.6953 0.9729 年平均 0.9249 0.6120 0.9765 0.8507 0.8978 表 4 年平均NQI、A、E环境指数分析
Tab. 4 Analysis of annual average NQI, A, E environmental index
年份 数据 DO/mg/L COD/mg/L DIN/mg/L DIP/mg/L NQI A E 2020 6.8450 1.2063 0.0211 0.4468 4.2452 3.1044 2.5298 2021 6.7050 0.8700 0.0388 0.5563 5.7996 4.6821 4.1672 2022 6.3238 1.0763 0.0335 0.3316 4.4296 3.3756 2.6570 2023 6.8775 1.3538 0.0255 0.4666 4.7100 3.5638 3.5796 平均 6.6878 1.1266 0.0297 0.4503 4.7961 3.6815 3.3503 -
[1] 洪刚. 总体性海洋发展观: 中国海洋新发展理念的特征与意义[J]. 山东大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2024(3): 131−139.Hong Gang. The holistic ocean development concept: characteristics and significance of China's new theory of ocean development[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2024(3): 131−139. [2] 白怀宇, 李秋芬, 张艳, 等. 象山港中部养殖海区营养盐的季节变化及富营养化[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(6): 24−30.Bai Huaiyu, Li Qiufen, Zhang Yan, et al. Seasonal variation in nutrients and evaluation of eutrophication in the aquaculture areas in the middle water areas of Xiangshan Harbor[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(6): 24−30. [3] 欧阳玉蓉, 王翠, 李青生, 等. 厦门湾海域营养盐时空分布与富营养化状况分析[J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(1): 88−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.01.018Ouyang Yuron, Wang Cui, Li Qingsheng, et al. Analysis of the space-time distribution of nutrients and the degree of eutrophication in Xiamen Bay[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(1): 88−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.01.018 [4] 黄秀清, 齐平, 秦渭华, 等. 象山港海洋生态环境评价方法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(8): 63−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.08.006Huang Xiuqing, Qi Ping, Qin Weihua, et al. Research on the evaluation method of marine ecological environment in Xiangshan Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(8): 63−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.08.006 [5] 郑云龙, 朱红文, 罗益华. 象山港海域水质状况评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2000, 19(1): 56−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2000.01.013Zheng Yunlong, Zhu Hongwen, Luo Yihua. Assessment on the situation of water quality at Xiangshan Port[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2000, 19(1): 56−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2000.01.013 [6] 唐剑武, 叶文虎. 环境承载力的本质及其定量化初步研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 1998, 18(3): 227−230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.1998.03.009Tang Jianwu, Ye Wenhu. Study on environmental bearing capacity and its quantification[J]. China Environmental Science, 1998, 18(3): 227−230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.1998.03.009 [7] 龙腾锐, 姜文超. 水资源(环境)承载力的研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 2003, 14(2): 249−253. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2003.02.024Long Tengrui, Jiang Wenchao. Advances in water resources and water environmental carrying capacity[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2003, 14(2): 249−253. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2003.02.024 [8] Wang Liting, Zeng Weihua, Cao Ruoxin, et al. Overloading risk assessment of water environment-water resources carrying capacity based on a novel Bayesian methodology[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 622: 129697. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129697 [9] Yin Mingchao, Cao Haijin, Zhao Wenlu, et al. Tide-driven microplastics transport in an elongated semi-closed bay: a case study in Xiangshan Bay, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 846: 157374. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157374 [10] 叶林安, 费岳军, 王琼, 等. 象山港周边主要入海污染物特征研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2022, 41(2): 215−223. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2022.02.011Ye Lin'an, Fei Yuejun, Wang Qiong, et al. Research on characteristics of main pollutants entering the sea around Xiangshan Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2022, 41(2): 215−223. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2022.02.011 [11] 郑军勇, 毛新燕, 生小萱, 等. 象山港溶解无机氮环境容量研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(4): 13−20. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190507002Zheng Junyong, Mao Xinyan, Sheng Xiaoxuan, et al. Environmental capacity assessment of dissolved inorganic nitrogen in the Xiangshan Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(4): 13−20. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190507002 [12] 楼文高. BP神经网络模型在水环境质量综合评价应用中的一些问题[J]. 水产学报, 2002, 26(1): 90−96.Lou Wengao. Some aspects on application of BP neural network to comprehensive assessment of water environmental quality[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2002, 26(1): 90−96. [13] 李星, 丁文祥, 李雪丁, 等. 基于人工神经网络构建的赤潮短期预报模型及应用[J]. 海洋预报, 2023, 40(2): 67−76. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2023.02.007Li Xing, Ding Wenxiang, Li Xueding, et al. Short-term forecasting model of red tide based on artificial neural network and its application[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2023, 40(2): 67−76. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2023.02.007 [14] Meng Yinghui, Chen Yuewen, Zhu Ffubao, et al. The integration of marine biodiversity information resources based on big data technology[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2020, 103(SI): 806−811. [15] 丁鹏, 邹晓荣, 许回, 等. 基于BP神经网络的长鳍金枪鱼渔获量与气候因子关系研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2024, 46(9): 88−95. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2024100Ding Peng, Zou Xiaorong, Xu Hui, et al. Study on the relationship between catch of Thunnus alalunga and climatic factors based on BP neural network[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2024, 46(9): 88−95. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2024100 [16] 张克鑫, 陆开宏, 金春华, 等. 基于BP神经网络的湖南镇水库叶绿素a浓度预测模型的研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2011(2): 91−99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2011.02.013Zhang Kexin, Lu Kaihong, Jin Chunhua, et al. Predicting model of the concentration of chlorophyll-a based on BP neural network in Hunanzhen Reservoir[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2011(2): 91−99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2011.02.013 [17] 李萍, 曾令可, 税安泽, 等. 基于MATLAB的BP神经网络预测系统的设计[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2008, 25(4): 149−150,184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2008.04.056Li Ping, Zeng Lingke, Shui Anze, et al. Design of forecast system of back propagation neural network based on matlab[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2008, 25(4): 149−150,184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2008.04.056 [18] 黄奇华, 吴雄斌, 岳显昌, 等. 基于BP神经网络的高频地波雷达海流空间插值[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(5): 138−145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.05.013Huang Qihua, Wu Xiongbin, Yue Xianchang, et al. Spatial interpolation of current mapped by HF surface wave radar using BP neural network[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(5): 138−145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.05.013 [19] 范高锋, 王伟胜, 刘纯. 基于人工神经网络的风电功率短期预测系统[J]. 电网技术, 2008, 32(22): 72−76.Fan Gaofeng, Wang Weisheng, Liu Chun. Artificial neural network based wind power short term prediction system[J]. Power System Technology, 2008, 32(22): 72−76. [20] 冯玉芳, 卢厚清, 殷宏, 等. 基于BP神经网络的故障诊断模型研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(6): 24−30. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1811-0008Feng Yufang, Lu Houqing, Yin Hong, et al. Study on Fault diagnosis model based on BP neural network[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(6): 24−30. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1811-0008 [21] 刘浩民, 杨洪才, 刘战, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的电弧增材制造焊道尺寸反向传播神经网络预测模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2024, 48(2): 97−102. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202402015Liu Haomin, Yang Hongcai, Liu Zhan, et al. Backpropagation neural network prediction model of arc additive manufacturing weld size base on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 48(2): 97−102. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202402015 [22] . 杨格, 沈晗瑞, 王贞, 等. 基于参数识别和神经网络代理模型的实时混合试验方法[J/OL]. 工程力学, 2024. https://www.engineeringmechanics.cn/cn/article/doi/10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2024.02.0116.Yang Ge, Shen Hanrui, Wang Zhen, et al. Real-time hybrid simulation method based on parameter identification and neural network surrogate model[J/OL]. Engineering Mechanics, 2024. https://www.engineeringmechanics.cn/cn/article/doi/10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2024.02.0116. (查阅网上资料,未找到文献引用日期,请确认) [23] 杨文举, 赵映东, 闫宏华. 基于优化BP神经网络的泾河输沙量预测研究[J]. 水文, 2024, 44(5): 40−46.Yang Wenju, Zhao Yingdong, Yan Honghua. Prediction of sediment discharge in jinghe river based on optimized BP neural network[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2024, 44(5): 40−46. [24] . 史素霞, 常婉秋, 宋志英. 基于UCI数据集的OCR光学字符识别[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2022, 12(35): 50−53.Shi Suxia, Chang Wanqiu, Song Zhiying. OCR optical character recognition based on UCI dataset[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2022, 12(35): 50−53. (查阅网上资料, 未找到文献翻译, 请确认) [25] . 陈于望. 厦门港海域营养状况的分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1987, 6(3): 14−19.Chen Yuwang. Analysis of nutrient status in Xiamen Harbor[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1987, 6(3): 14−19. (查阅网上资料, 未找到文献翻译, 请确认) [26] 周艳荣, 唐伟, 赵蓓, 等. 山东威海双岛湾海域营养状态及有机污染状况分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2008, 27(3): 115−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.03.018Zhou Yanrong, Tang Wei, Zhao Bei, et al. Analysis of nutrients and organic pollution in the Shuangdao Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2008, 27(3): 115−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.03.018 [27] . 邹景忠, 董丽萍, 秦保平. 渤海湾富营养化和赤潮问题的初步探讨[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1983, 2(2): 41−54.Zou Jingzhong, Dong Liping, Qin Baoping. Preliminary study on eutrophication and red tide in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1983, 2(2): 41−54. (查阅网上资料, 未找到文献翻译, 请确认) [28] 王雅萌, 汪金涛, 陈新军, 等. 基于BP神经网络的西北太平洋柔鱼资源丰度时空变化研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(6): 81−89.Wang Yameng, Wang Jintao, Chen Xinjun, et al. Spatio-temporal dynamic of abundance index of Neon flying squid in relation to environmental variables in the Northwest Pacific Ocean using BP neural network[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(6): 81−89. [29] 张鹏, 吴通, 李中, 等. BP神经网络法预测顺北超深碳酸盐岩储层应力敏感程度[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2020, 42(5): 622−626.Zhang Peng, Wu Tong, Li Zhong, et al. Application of BP neural network method to predict the stress sensitivity of ultra deep carbonate reservoir in Shunbei Oilfield[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5): 622−626. [30] 何华锋, 何耀民, 徐永壮. 基于改进型BP神经网络的导引头测高性能评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(7): 1544−1550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.07.15He Huafeng, He Yaomin, Xu Yongzhuang. High performance evaluation of seeker measurement based on improved BP neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(7): 1544−1550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.07.15 [31] 夏军, 陈进, 佘敦先. 2022年长江流域极端干旱事件及其影响与对策[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53(10): 1143−1153.Xia Jun, Chen Jin, She Dunxian. Impacts and countermeasures of extreme drought in the Yangtze River Basin in 2022[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(10): 1143−1153. [32] 孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 764−770. doi: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0764Sun Zhaoxuan, Zhang Qiang, Sun Rui, et al. Characteristics of the extreme high temperature and drought and their main impacts in southwestern China of 2022[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 764−770. doi: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0764 [33] Liang Miaoling, Yuan Xing, Zhou Shiyu, et al. Spatiotemporal evolution and nowcasting of the 2022 Yangtze River mega-flash drought[J]. Water, 2023, 15(15): 2744. doi: 10.3390/w15152744 [34] Lyu Zhuzhu, Gao Hui, Gao Rong, et al. Extreme characteristics and causes of the drought event in the whole Yangtze River basin in the midsummer of 2022[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2023, 14(5): 642−650. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2023.09.007 [35] 王玉琦, 李铖, 刘安琪, 等. 2022年长江口夏季咸潮入侵及影响机制研究[J]. 人民长江, 2023, 54(4): 7−14Wang Yuqi, Li Cheng, Liu Anqi, et al. Dynamic mechanism of saltwater intrusion at Yangtze River estuary in summer, 2022[J]. Yangtze River, 2023, 54(4): 7−14. [36] 乔红杰, 王金华, 张志林, 等. 2022年后汛期长江口严重咸潮空间分布特征分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2024, 42(7): 68−72.Qiao Hongjie, Wang Jinhua, Zhang Zhilin, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of serious saltwater intrusion of Yangtze River estuary in post-flood season of 2022[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2024, 42(7): 68−72. [37] . 宁波市水利局. 2022年宁波市水资源公报[R]. 宁波: 宁波市水利局, 2023.Ningbo Water Resources Bureau. 2022 Ningbo water resources bulletin[R]. Ningbo: Ningbo Water Resources Bureau, 2023. (查阅网上资料, 未找到文献翻译, 请确认) [38] 吴燕妮, 李冬玲, 叶林安, 等. 象山港海域水质与沉积物主要污染因子及污染源分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2017, 36(3): 328−335.Wu Yanni, Li Dongling, Ye Lin'an, et al. Analysis of major pollution factors in sea water and surface sediments and contribution of pollution sources in Xiangshan bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(3): 328−335. [39] 王登超, 李发东, 李曹乐, 等. 降雨对河流水质影响及污染源解析: 以鉴江茂名段为例[J]. 环境科学, 2025, 46(4): 2165−2178.Wang Dengchao, Li Fadong, Li Caole, et al. Impact of rainfall on river water quality and source identification: an example in the maoming section of the Jianjiang River[J]. Environmental Science, 2025, 46(4): 2165−2178. [40] Luo Jian, Straffelini E, Bozzolan M, et al. Saltwater intrusion in the Po River Delta (Italy) during drought conditions: analyzing its Spatio-temporal evolution and potential impact on agriculture[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 2024, 12(3): 714−725. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2023.09.009 -





 下载:
下载: