Metabolomic analysis of Trachinotus ovatus under flow velocity stress
-
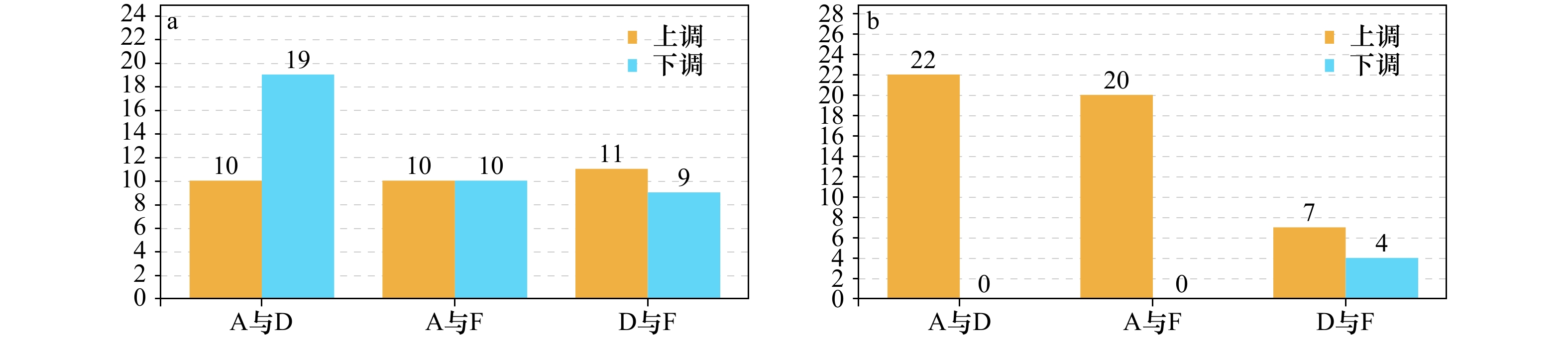
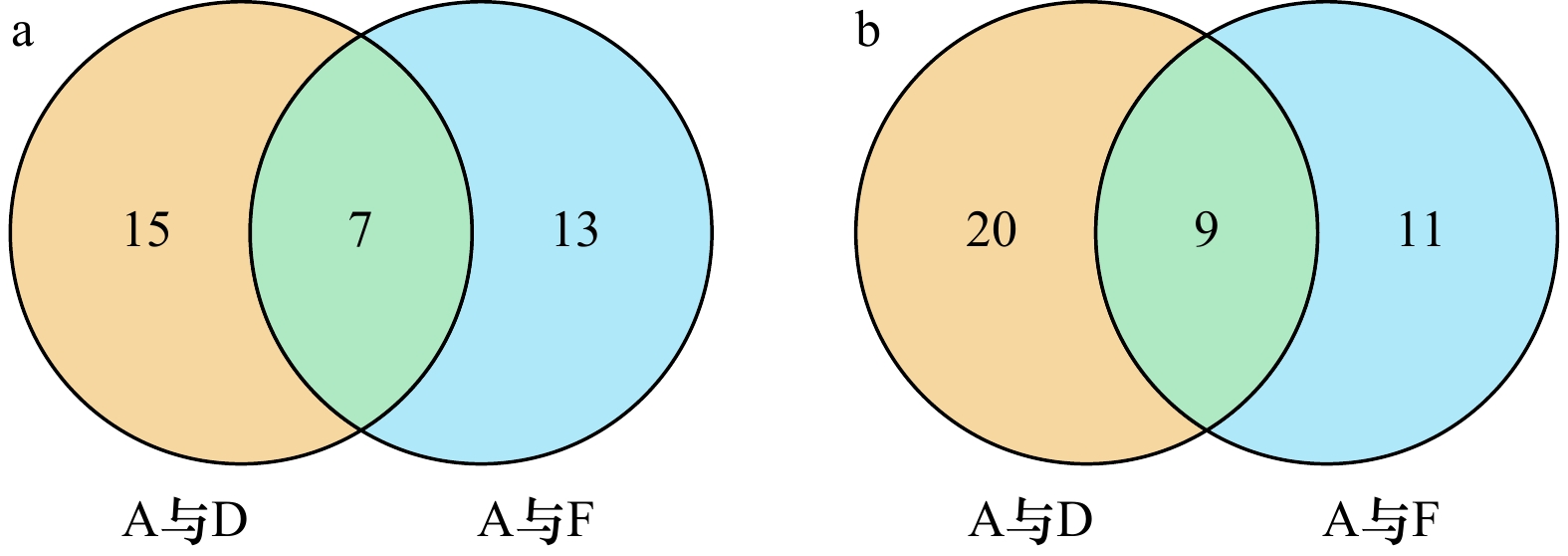
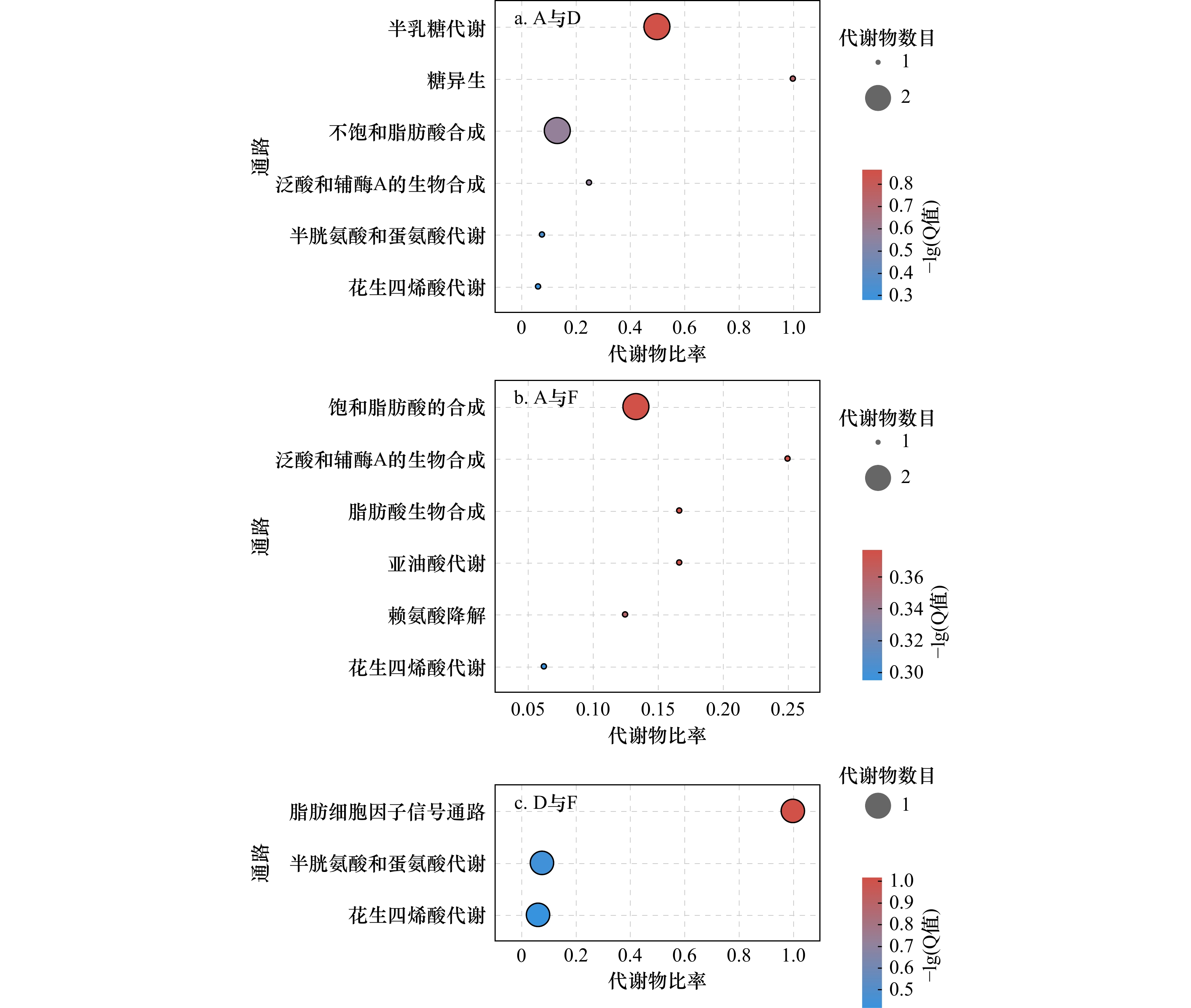
摘要: 流速是深远海养殖的关键环境因子之一。为了深入解析卵形鲳鲹在流速胁迫下的分子调控机制,分别以静水环境、中等流速(54 cm/s)和高流速(90 cm/s)水流对卵形鲳鲹进行胁迫,利用LC/MS的代谢组学技术探究肝脏内源性代谢物的变化,寻找差异代谢物以及相关的代谢通路。结果表明,与静水组相比,中流速组有51种代谢产物的含量发生显著变化,富集在40条通路中,主要包括半乳糖代谢(galactose metabolism)、糖异生(gluconeogenesis)、不饱和脂肪酸的合成(biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids)、花生四烯酸代谢(arachidonic acid metabolism)等;高流速组有40种代谢产物的含量发生显著变化,富集在22条通路中,主要包括饱和脂肪酸的合成(biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids)、泛酸和辅酶A的生物合成(pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis)、赖氨酸降解(lysine degradation)、花生四烯酸代谢(arachidonic acid metabolism)、亚油酸代谢(linoleic acid metabolism)等。与中流速组相比,高流速组有31种代谢产物含量发生显著变化,富集在12条通路中,主要包括花生四烯酸代谢(arachidonic acid metabolism)、脂肪细胞因子信号通路(adipocytokine signaling pathway)、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢(cysteine and methionine metabolism)等。通路分析表明中、高流速胁迫均促进了不饱和脂肪酸代谢、花生四烯酸代谢和泛酸的合成,鱼体通过加强代谢来提高游泳能力,中流速组主要显著影响了半乳糖代谢、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸的代谢,卵形鲳鲹此时产生了更多能量用于运动;高流速组则显著影响了L-赖氨酸、维甲酸的代谢,揭示了在面对高流速胁迫时,鱼体的游泳能力在下降,部分免疫机能触发。Abstract: Flow velocity is one of the key environmental factors for deep sea aquaculture. In order to further understand the molecular regulation mechanism of golden pompano (T. ovatus) under flow velocity stress, the fishes were stressed under the static water, medium flow velocity (54 cm/s) and high flow velocity (90 cm/s), and the LC/MS metabolomics technology was used to explore the changes of endogenous metabolites in the liver to look for differential metabolites and related metabolic pathways. The results show that 51 metabolites in the medium flow velocity group have significant difference with which in the static water and are enriched in 40 pathways, mainly including galactose metabolism, gluconeogenesis, biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, arachidonic acid metabolism, etc. Forty metabolites in the high flow velocity group have significant difference with which in the static water and are enriched in 22 pathways, mainly including biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, lysine degradation, arachidonic acid metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, etc. Compared with the medium flow velocity group, 31 metabolites in the high flow velocity group have significant difference and are enriched in 12 pathways, mainly including arachidonic acid metabolism, adipocytokine signaling pathway, cysteine and methionine metabolism, etc. Pathway analysis shows that both medium and high flow velocity stress promoted unsaturated fatty acid metabolism, arachidonic acid metabolism and pantothenic acid synthesis. The ability of swimming is improved to against the stress of flow velocity by strengthening metabolism. The medium flow velocity group mainly significantly affected the metabolism of galactose, cysteine and methionine. At this time, more and more energy produced by fish is used for exercise. The high flow velocity group mainly significantly affect the metabolism of L-lysine and retinoic acid, which reveals that the swimming ability of fish may be decreased and some immune functions may be triggered under the high flow velocity stress.
-
Key words:
- Trachinotus ovatus /
- velocity stress /
- metabolome analysis
-
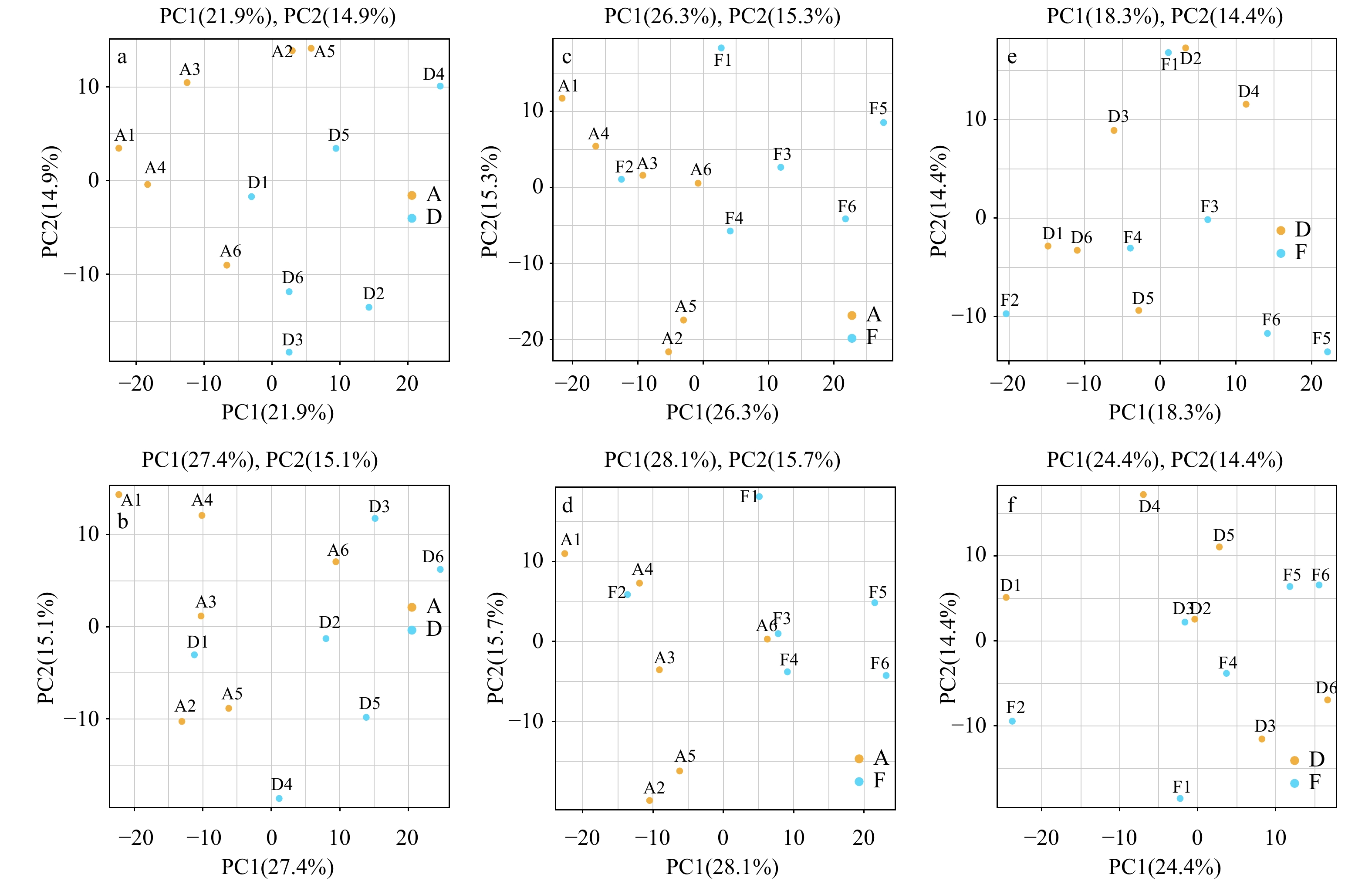
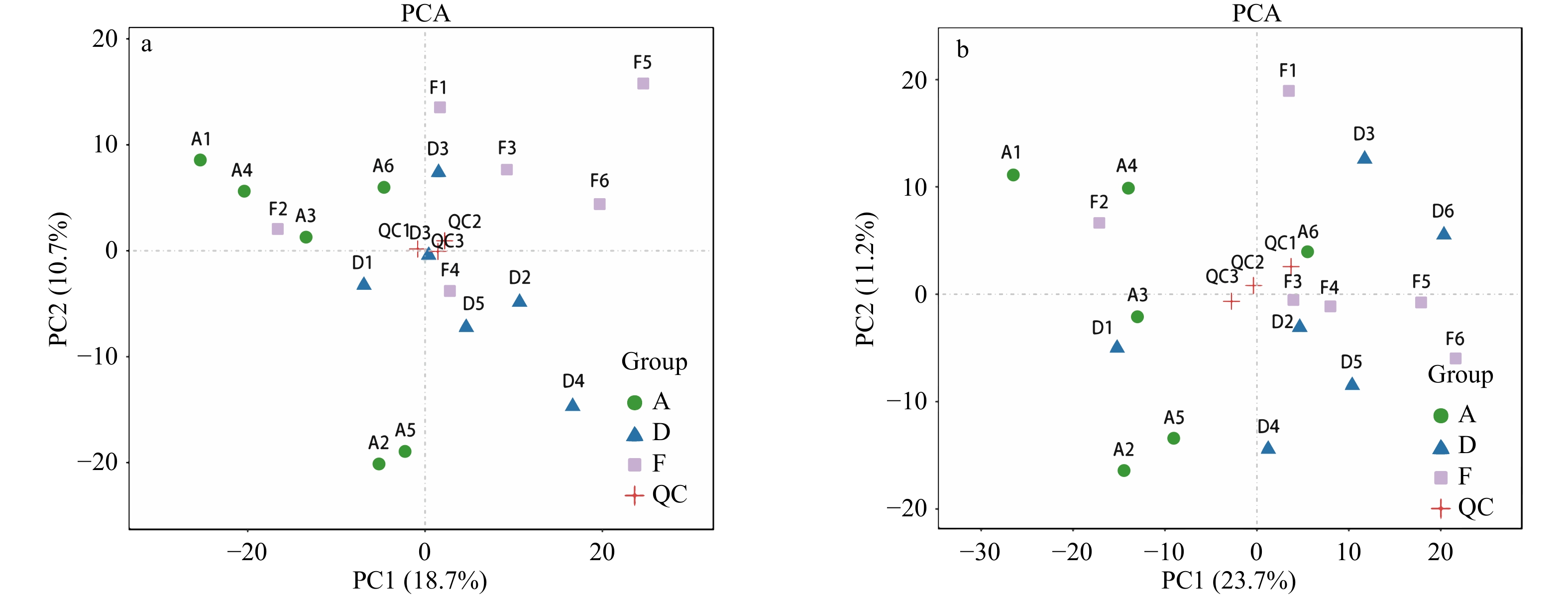
图 2 QC样本PCA分析
a. 正离子模式下A与D;b. 负离子模式A与D;c. 正离子模式下A与F;d 负离子模式A与F;e. 正离子模式下D与F;f. 负离子模式D与F
Fig. 2 Sample QC PCA analysis
a. A and D in positive ion mode; b. A and D in negative ion mode; c. A and F in positive ion mode; d. A and F in negative ion mode; .e. D and F in positive ion mode; f. D and F in negative ion mode
图 3 OPLS-DA得分图
a. 正离子模式下A与D;b. 负离子模式A与D;c. 正离子模式下A与F;d. 负离子模式A与F;e. 正离子模式下D与F;f. 负离子模式D与F
Fig. 3 OPLS-DA model
a. A and D in positive ion mode; b A and D in negative ion mode; c. A and F in positive ion mode; d. A and F in negative ion mode; e. D and F in positive ion mode; f. D and F in negative ion mode
表 1 代谢物鉴定结果
Tab. 1 Metabolite identification results
类型 共得到的峰的数目 二级图谱匹配到
物质名称一级图谱匹配到的
物质名称利用一级图谱和二级图谱
鉴定到的物质总数目无法鉴定的
物质数目POS正离子模式 837 736 101 837 0 NEG负离子模式 736 637 99 736 0 表 2 部分关键代谢物
Tab. 2 Some key metabolites
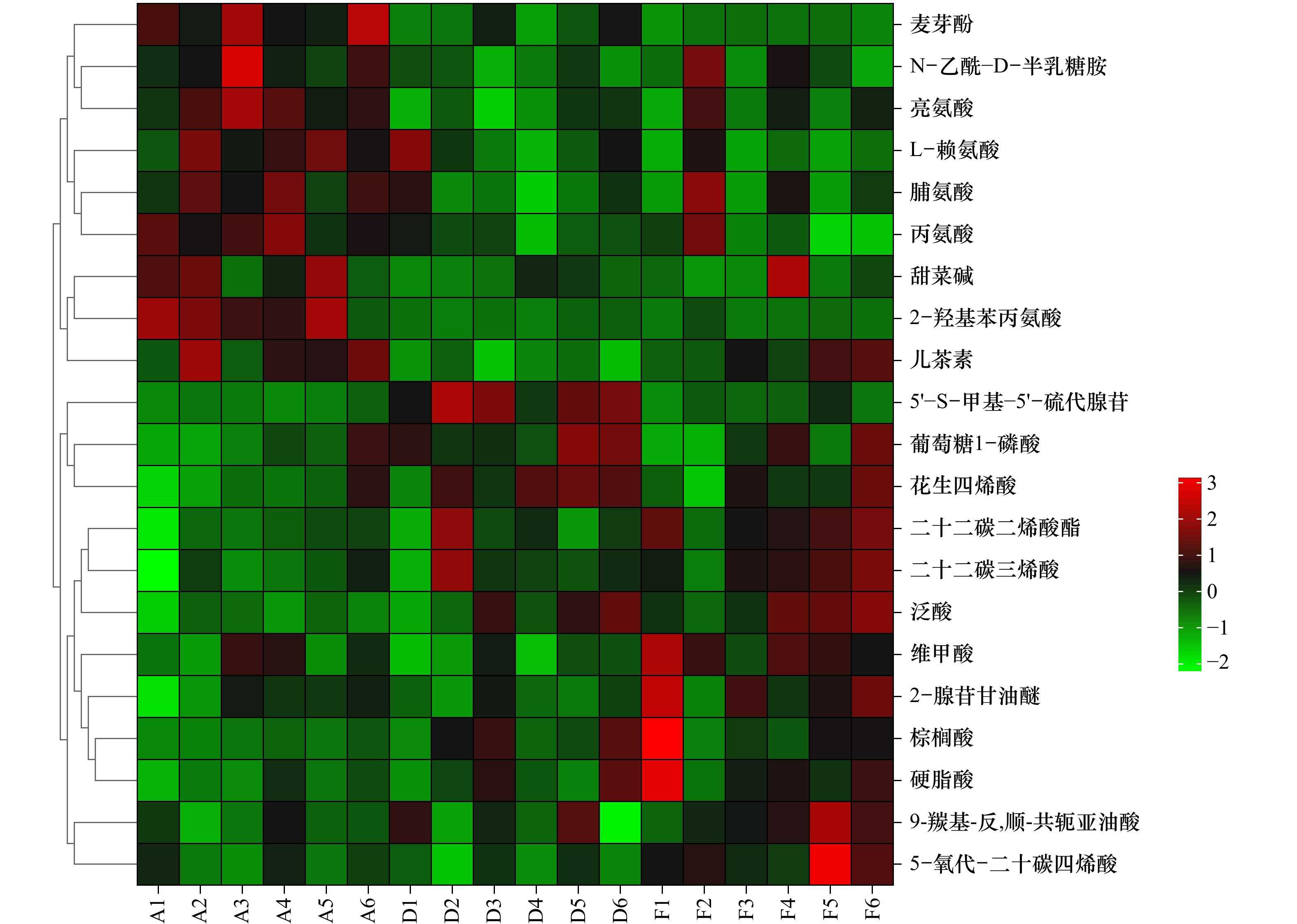
组别 代谢物名称 变化趋势 VIP p值 D与A 花生四烯酸(Arachidonic acid) ↑ 10.26 0.024 9 棕榈酸(Palmitic acid) ↑ 3.16 0.045 8 泛酸(Pantothenic acid) ↑ 2.28 0.049 9 葡萄糖1-磷酸(Glucose 1-phosphate) ↑ 1.55 0.035 1 5'-S-甲基-5'-硫代腺苷(5'-S-Methyl-5'-thioadenosine) ↑ 2.93 0.000 2 麦芽酚(Maltol) ↓ 2.13 0.008 5 N-乙酰-D-半乳糖胺(N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine) ↓ 1.08 0.017 3 F与A 5-氧代-二十碳四烯酸(5-OxoETE) ↑ 3.31 0.033 9 麦芽酚(Maltol) ↓ 2.41 0.000 7 L-赖氨酸(L-Lysine) ↓ 1.04 0.005 7 硬脂酸(Stearic acid) ↑ 2.17 0.033 6 泛酸(Pantothenic acid) ↑ 2.12 0.004 6 二十二碳二烯酸酯(13Z,16Z-Docosadienoic Acid) ↑ 2.10 0.008 0 F与D 5-氧代-二十碳四烯酸(5-OxoETE) ↑ 3.72 0.016 9 5'-S-甲基-5'-硫代腺苷(5'-S-Methyl-5'-thioadenosine) ↓ 2.66 0.001 1 维甲酸(Tretinoin) ↑ 2.08 0.006 0 -
[1] 农业农村部, 生态环境部, 自然资源部, 等. 关于加快推进水产养殖业绿色发展的若干意见[Z/OL]. (2019–01–11) [2022–08–07]. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/YYJ/201902/t20190215_6171447.htm.Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China, Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China, et al. Some opinions on accelerating the green development of aquaculture[Z/OL].(2019–01–11) [2022–08–07]. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/YYJ/201902/t20190215_6171447.htm. [2] 许晓娟, 李加儿, 区又君. 盐度对卵形鲳鲹胚胎发育和早期仔鱼的影响[J]. 南方水产, 2009, 5(6): 31−35.Xu Xiaojuan, Li Jiaer, Ou Youjun. Effects of salinity on embryonic development and early larvae in ovate pompano Trachinotus ovatus[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2009, 5(6): 31−35. [3] 孙莘溢, 黄小林, 黄忠, 等. 卵形鲳鲹摄食、耗氧节律和胃肠排空时间的研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2019, 15(5): 77−83. doi: 10.12131/20190072Sun Xinyi, Huang Xiaolin, Huang Zhong, et al. Diet feeding, oxygen consumption rhythm and gastrointestinal evacuation time of Trachinotus ovatus[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2019, 15(5): 77−83. doi: 10.12131/20190072 [4] 黄倩倩, 林黑着, 周传朋, 等. 卵形鲳鲹幼鱼对维生素B2的需要量[J]. 南方水产科学, 2019, 15(1): 69−76.Huang Qianqian, Lin Heizhao, Zhou Chuanpeng, et al. Vitamin B2 requirement of juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus)[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2019, 15(1): 69−76. [5] 刘锡强, 马学坤, 刘康, 等. 华南地区金鲳鱼养殖报告[J]. 当代水产, 2014, 39(2): 26−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9049.2014.02.002Liu Xiqiang, Ma Xuekun, Liu Kang, et al. Report on the culture of golden pompano in south China[J]. Current Fisheries, 2014, 39(2): 26−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9049.2014.02.002 [6] 李丹, 林小涛, 李想, 等. 水流对杂交鲟幼鱼游泳行为的影响[J]. 淡水渔业, 2008, 38(6): 46−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2008.06.010Li Dan, Lin Xiaotao, Li Xiang, et al. Effects of water current on swimming performance of juvenile hybird sturgeon (Huso duricus Georgi ♂ × Acipenser schrencki Brandt ♀)[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2008, 38(6): 46−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2008.06.010 [7] 殷名称. 鱼类生态学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1995.Yin Mingcheng. Fish Ecology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1995. [8] Merino G E, Piedrahita R H, Conklin D E. The effect of fish stocking density on the growth of California halibut (Paralichthys californicus) juveniles[J]. Aquaculture, 2007, 265(1/4): 176−186. [9] 黄宁宇, 程起群, 高露娇, 等. 流速、温度对西伯利亚鲟幼鱼生长的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2007, 31(1): 31−37.Huang Ningyu, Cheng Qiqun, Gao Lujiao, et al. Effect of water current and temperature on growth of juvenile Acipenser baeri[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2007, 31(1): 31−37. [10] 宋波澜, 林小涛, 王伟军, 等. 不同流速下红鳍银鲫趋流行为与耗氧率的变化[J]. 动物学报, 2008, 54(4): 686−694.Song Bolan, Lin Xiaotao, Wang Weijun, et al. Effects of water velocities on rheotaxis behaviour and oxygen consumption rate of tinfoil barbs Barbodes schwanenfeldi[J]. Current Zoology, 2008, 54(4): 686−694. [11] Ogata H Y, Oku H. Effects of water velocity on growth performance of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2000, 31(2): 225−231. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-7345.2000.tb00357.x [12] 胡佳, 李艳华, 王鲁, 等. 不同流速下西杂鲟稚鱼生长对比研究[J]. 水产科学, 2022, 41(6): 1023−1028. doi: 10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.21028Hu Jia, Li Yanhua, Wang Lu, et al. Comparative growth of juvenile sturgeon hybrid Acipenser baerii ♀×A. schrenckii ♂ under different water velocity[J]. Fisheries Science, 2022, 41(6): 1023−1028. doi: 10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.21028 [13] 朱晏苹, 曹振东, 付世建. 不同游泳速度条件下瓦氏黄颡幼鱼的有氧和无氧代谢反应[J]. 水生生物学报, 2010, 34(5): 905−912.Zhu Yanping, Cao Zhendong, Fu Shijian, et al. Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism in response to different swimming speed of juvenile darkbarbel catfish(Pelteobagrus Vachelli richardson)[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2010, 34(5): 905−912. [14] Pelley J W. Fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism[M]//Pelley J W. Elsevier’s Integrated Review Biochemistry. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012: 81–88. [15] 徐冬青, 陈家琦, 李静先. 力竭运动对大鼠骨骼肌自由基代谢及肌细胞膜通透性的影响[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 1999, 14(3): 27−29, 33. doi: 10.13297/j.cnki.issn1005-0000.1999.03.009Xu Dongqing, Chen Jiaqi, Li Jingxian, et al. Effects of exhaustive exercise on free radical metabolism and cell membrane permeability in rat skeletal muscle[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Sport, 1999, 14(3): 27−29, 33. doi: 10.13297/j.cnki.issn1005-0000.1999.03.009 [16] Litalien C, Beaulieu P. Molecular mechanisms of drug actions: from receptors to effectors[M]//Fuhrman B P, Zimmerman J J. Pediatric Critical Care. 4th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2011: 1553–1568. [17] 袁成凌, 姚建铭, 余增亮. 花生四烯酸及其代谢物的生物学作用[J]. 中国药物化学杂志, 2000, 10(1): 78−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0108.2000.01.023Yuan Chengling, Yao Jianming, Yu Zengliang. Synthesis of cetirizine hydrochloride[J]. Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2000, 10(1): 78−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0108.2000.01.023 [18] O’Flaherty J T, Rogers L C, Paumi C M, et al. 5-Oxo-ETE analogs and the proliferation of cancer cells[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) —Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2005, 1736(3): 228−236. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2005.08.009 [19] Aggarwal B B, Sethi G, Nair A, et al. Nuclear factor-κb: a holy grail in cancer prevention and therapy[J]. Current Signal Transduction Therapy, 2006, 1(1): 25−52. doi: 10.2174/157436206775269235 [20] 杨春, 李恒, 李海, 等. 5-烷基间苯二酚诱导人结直肠癌细胞凋亡的机制探讨[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2017, 25(29): 2621−2630. doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v25.i29.2621Yang Chun, Li Heng, Li Hai, et al. Mechanism study of 5-alkylresorcinols-induced colon cancer cell apoptosis in vitro[J]. World Chinese Journal of Digestology, 2017, 25(29): 2621−2630. doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v25.i29.2621 [21] Fujinaka H, Nakamura J, Kobayashi H, et al. Glucose 1-phosphate increases active transport of calcium in intestine[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2007, 460(2): 152−160. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.09.006 [22] Aiello D P, Fu L W, Miseta A, et al. Intracellular Glucose 1-Phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate levels modulate Ca2+ homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(48): 45751−45758. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208748200 [23] 张金良, 任懂平. D-半乳糖胺/脂多糖诱导急性肝衰竭机制的研究进展[J]. 武警医学院学报, 2011, 20(9): 761−763, 767.Zhang Jinliang, Ren Dongping. The recent research and development of mechanisms of D-galactosamine combined with Lipopolysaccharide induced acute liver failure[J]. Acta Academiae Medicinae CPAF, 2011, 20(9): 761−763, 767. [24] Zappia V, Cartenì-Farina M, Cacciapuoti G, et al. Recent studies on the metabolism of 5’-methylthioadenosine[M]//Cavallini D, Gaull G E, Zappia V. Natural Sulfur Compounds: Novel Biochemical and Structural Aspects. New York: Springer, 1980: 133–148. [25] 张可, 王小玉, 黄淑莹, 等. 斑马鱼腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶基因短片段缺失突变体的构建与鉴定[J]. 成都医学院学报, 2022, 17(4): 416−420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2257.2022.04.002Zhang Ke, Wang Xiaoyu, Huang Shuying, et al. Constructionand and identification of zebrafish adenosyImethionine decarboxylase 1 short segment deletion mutant[J]. Journal of Chengdu Medical College, 2022, 17(4): 416−420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2257.2022.04.002 [26] 方婷婷, 刘光芒, 贾刚, 等. 多胺对动物肠道稳态的调控作用及可能机制[J]. 动物营养学报, 2016, 28(11): 3400−3407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2016.11.005Fang Ting, Liu Guangmang, Jia Gang, et al. Polyamines: regulation on intestinal homeostasis and possible mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2016, 28(11): 3400−3407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2016.11.005 [27] 田颖, 时明慧. 赖氨酸生理功能的研究进展[J]. 美食研究, 2014, 31(3): 60−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4717.2014.03.014Tian Ying, Shi Minghui. The research progress of the physiologic functions of lysine[J]. Journal of Researches on Dietetic Science and Culture, 2014, 31(3): 60−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4717.2014.03.014 [28] 罗敏蓉, 熊正英. 赖氨酸与运动能力的关系[J]. 四川体育科学, 2006(3): 43−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6891.2006.03.013Luo Minrong, Xiong Zhengying. The relationship between lysine and exercise capacity[J]. Sichuan Sports Science, 2006(3): 43−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6891.2006.03.013 [29] 陆志范, 周全保. 赖氨酸的药用功能[J]. 药学实践杂志, 1996(4): 255−256.Lu Zhifan, Zhou Quanbao. Medicinal function of lysine[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice, 1996(4): 255−256. [30] Combs Jr Gerald F, Mcclung J P. Chapter 15—Pantothenic acid[M]//Combs Jr Gerald F, Mcclung J P. The Vitamins. 6th ed. London, England: Academic Press, 2022: 435-452. [31] 杨延辉, 肖春玲. 泛酸的功能和生物合成[J]. 生命的化学, 2008, 28(4): 448−452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1336.2008.04.020Yang Yanhui, Xiao Chunling. The functions and biosynthesis of pantothenate[J]. Chemistry of Life, 2008, 28(4): 448−452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1336.2008.04.020 [32] 于长青, 李丽娜. 花生四烯酸研究进展[J]. 农产品加工·学刊, 2007(4): 10−12.Yu Changqing, Li Lina. Research advancement on arachidonic acid[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing, 2007(4): 10−12. [33] 方年富, 李弼民, 冷芳. 维甲酸的免疫调节与炎症性肠病[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2011, 19(27): 2857−2862.Fang Nianfu, Li Bimin, Leng Fang. Role of retinoic acid in immune regulation: implications in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. World Chinese Journal of Digestology, 2011, 19(27): 2857−2862. [34] Evans T R J, Kaye S B. Retinoids: present role and future potential[J]. British Journal of Cancer, 1999, 80(1/2): 1−8. [35] Wauben-Penris P, Den Brok J, Cemeus D. Immunomodulatory effects of tretinoin: promotion of Th2 responses[J]. Immunology Letters, 1997, 56: 170−171. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2478(97)87520-7 -




 下载:
下载: