Research on Ship based Digital Image Processing and Sea Ice Concentration Recognition Based on Deep Learning
-
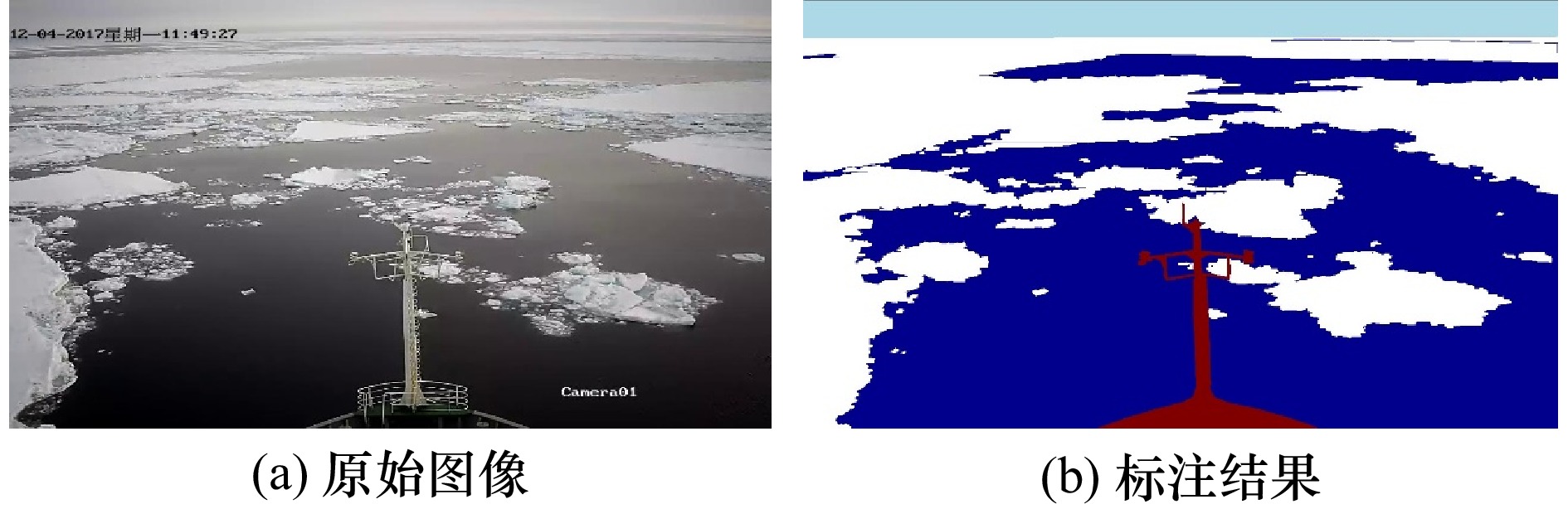
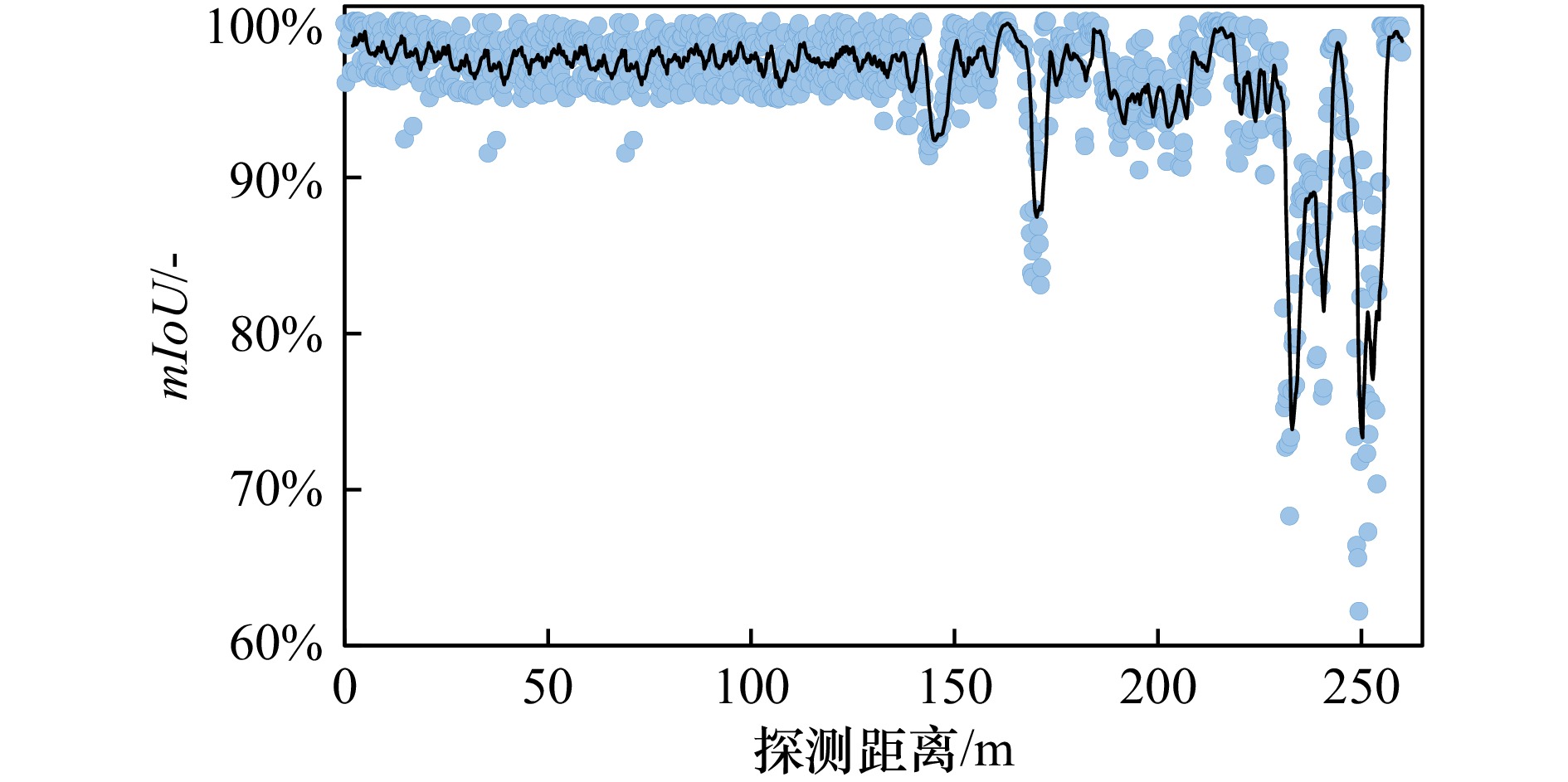
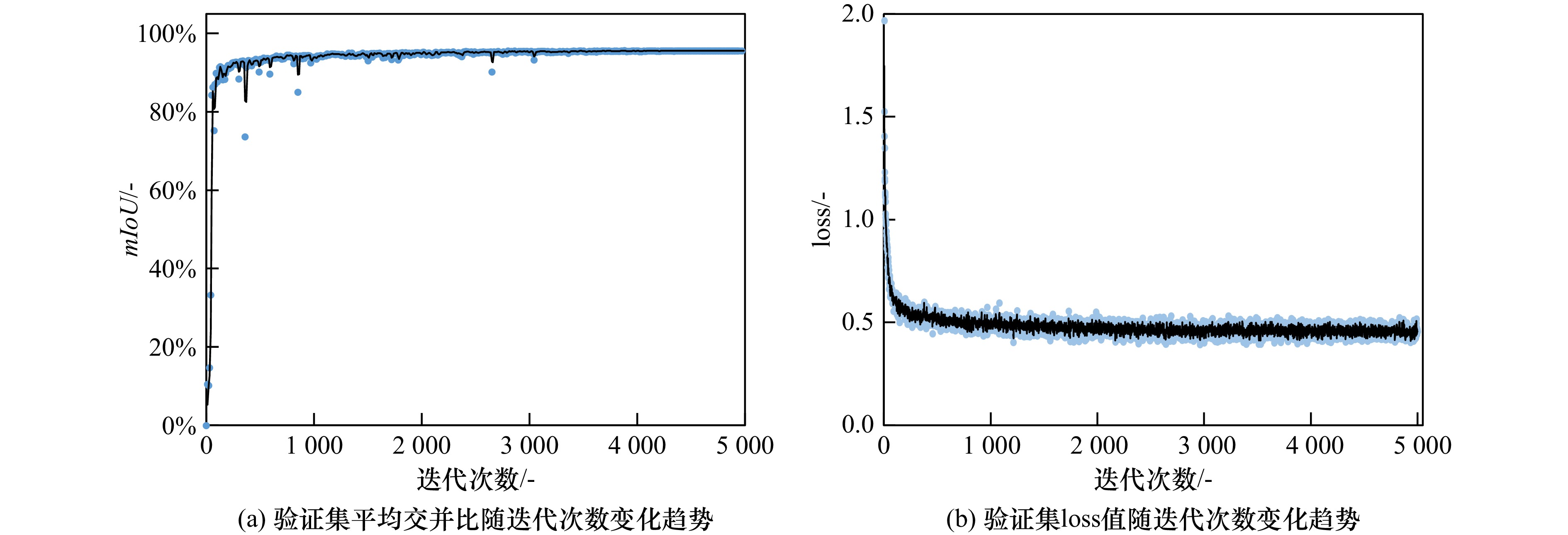
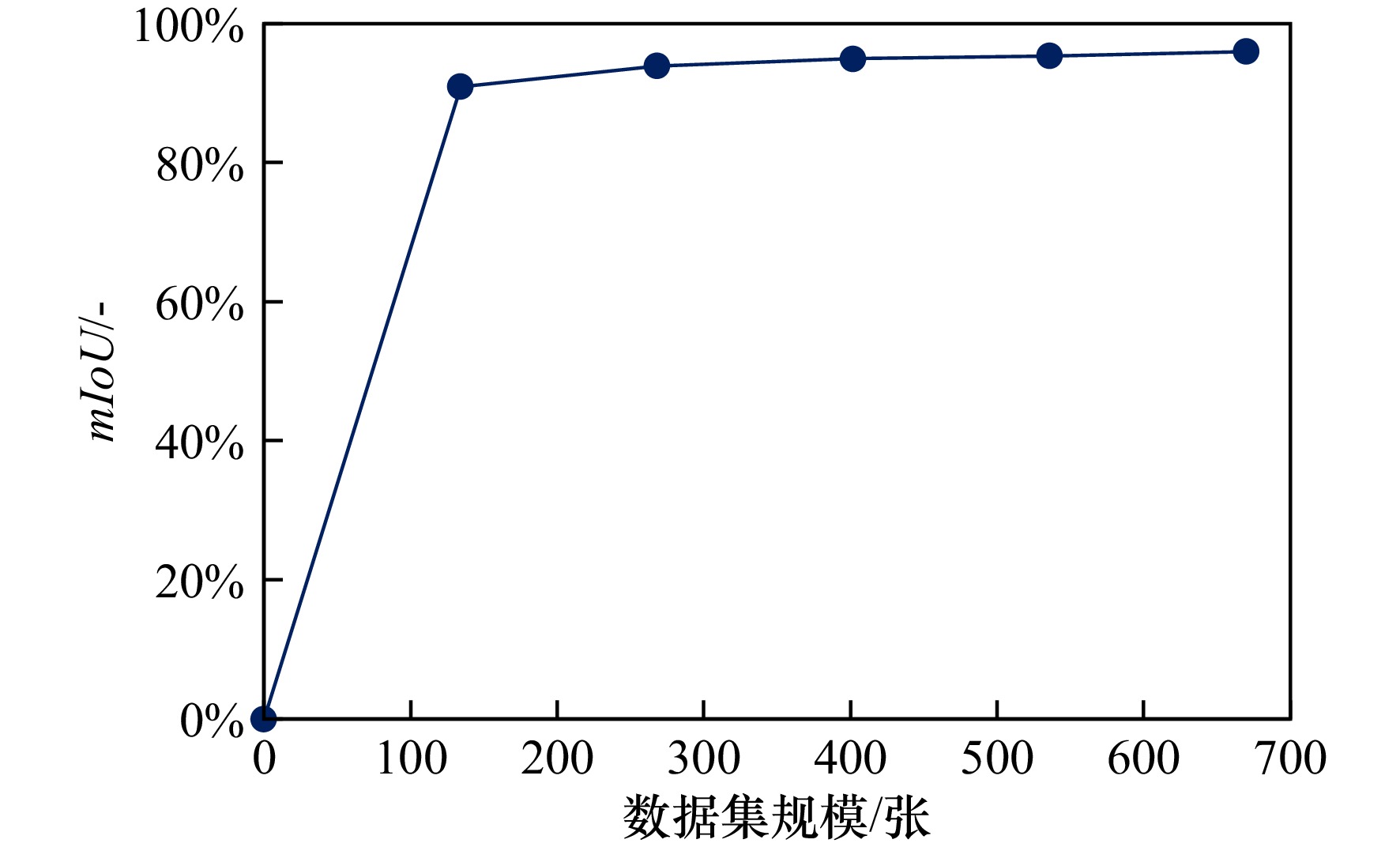
摘要: 海冰是极地海域的典型环境特征,对船载视频图像进行像素级分类可获取高分辨率的海冰信息。由于极地场景中的光照条件与海冰形态较为复杂,传统计算机图形学方法的泛化性难以满足海冰要素的智能识别需求。因此,本文采用基于DeeplabV3+语义分割网络结构的深度学习方法对极地场景中海冰要素进行识别。将“雪龙”号科考船在冰区航行中的实测海冰图像制作为数据集,并对深度学习模型进行训练与验证。根据海冰要素的识别需求与走航观测视频图像特点,将像素信息划分为海冰、天空、海水与船体四种语义类别。根据训练集中的图像信息与语义信息间关联构建深度学习模型,并通过所训练模型对验证集或其他图像中像素点的语义信息进行预测,从而实现海冰信息的自动识别。为了研究该方法的鲁棒性进一步分析了海冰密集度、光照条件以及海冰类型对识别结果的影响。此外,研究了数据集规模与迭代次数对识别精度的影响。图像识别结果显示,四类语义信息识别结果的平均交并比高于95%。这表明深度学习方法能够在极地复杂的环境中较为准确的获取各类要素分类信息。
-
关键词:
- 海冰 /
- DeeplabV3+ /
- 语义分割 /
- 图像识别 /
- 深度学习
Abstract: Sea ice is a typical environmental feature of polar sea areas, and pixel-level classification of ship-borne video images can provide high-resolution sea ice information. Due to the complex light conditions and sea ice morphology in polar scenes, traditional computer graphics methods lack the generalization needed for intelligent identification of sea ice elements. Therefore, this paper deploys a deep learning approach based on the DeeplabV3+ semantic segmentation network structure to identify sea ice elements in polar scenes. The dataset consists of sea ice images captured by the icebreaker ‘Xuelong’ during its navigation in ice-covered regions, and also is used to train and validate the deep learning model. To meet the requirements of sea ice element identification and the characteristics of the underway observation video images, the pixel information is divided into four semantic categories: sea ice, sky, seawater, and ship. The deep learning model is built based on the correlation between image information and semantic information in the training set. The model trained is used to predict the semantic information of pixels in the validation set or other images, thereby achieving automatic identification of sea ice information. To study the robustness of this method, the influences of sea ice concentration, lighting conditions, and sea ice types on the identification results was further analyzed. Additionally, the effects of dataset size and the number of iterations on identification accuracy were examined. The recognition results for images show that the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) for the four types of semantic information exceeds 95%, indicating that the deep learning method can accurately classify various elements in the polar environment.-
Key words:
- sea ice /
- DeeplabV3+ /
- semantic segmentation /
- image recognition /
- deep learning
-
表 1 海冰图像识别的软硬件配置
Tab. 1 Configurations of hardwares and softwares for identification of sea ice images
硬件参数 CPU Intel i7 RAM 16 GB Graphics card Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060 LaptopGPU Memory 6 GB 软件参数 Operating system Windows 11 Python Python 3.8 Framework Tensorflow-gpu 2.6 CUDA 11.2 表 2 针对不同场景识别结果的单项交并比与平均交并比
Tab. 2 IoU and mIoU of different samples
IoU-Sea(%) IoU-Ice (%) IoU-Sky(%) IoU-Ship(%) mIoU(%) 场景1 99.9 97.6 − 97.4 98.3 场景2 99.8 93.5 87.9 87.7 90.8 场景3 99.9 92.1 97.1 95.7 96.2 场景4 96.9 95.3 98.8 93.3 96.9 场景5 95.9 96.2 98.8 93.9 97.2 验证集(67张) 96.9 97.4 96.5 95.8 96.0 -
[1] 苏洁, 郝光华, 叶鑫欣, 等. 极区海冰密集度AMSR-E数据反演算法的试验与验证[J]. 遥感学报, 2013, 17(3): 495−513. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20132043Su Jie, Hao Guanghua, Ye Xinxin, et al. The experiment and validation of sea ice concentration AMSR-E retrieval algorithm in polar region[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 17(3): 495−513. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20132043 [2] 魏彬航, 李宝辉, 刘煜, 等. 辽东湾海冰分布面积历史数据重构及其影响因素分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2023, 45(11): 20−33.Wei Binhang, Li Baohui, Liu Yu, et al. Reconstruction of sea ice extent in the Liaodong Bay and analysis of its impact factors[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2023, 45(11): 20−33. [3] 崔洪宇, 胡大士, 孔帅, 等. 基于正则化方法的雪龙号破冰船冰载荷反演的研究[J]. 中国造船, 2020, 61(1): 109−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2020.01.011Cui Hongyu, Hu Dashi, Kong Shuai, et al. Study on inversion of ice load for Xue Long icebreaker based on regularization method[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2020, 61(1): 109−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2020.01.011 [4] 邓娟, 柯长青, 雷瑞波, 等. 2009年春夏季北极海冰运动及其变化监测[J]. 极地研究, 2013, 25(1): 96−104. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1084.2013.00096Deng Juan, Ke Changqing, Lei Ruibo, et al. Monitoring the motion of arctic sea-ice and its changes in summer and winter 2009[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2013, 25(1): 96−104. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1084.2013.00096 [5] 张培宣, 陈晓东, 孔帅, 等. 基于Hough变换原理的海冰厚度识别方法[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(7): 161−169. doi: 10.12284/j.issn.0253-4193.2022.7.hyxb202207015Zhang Peixuan, Chen Xiaodong, Kong Shuai, et al. Research on sea ice thickness identification method based on Hough transform principle[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(7): 161−169. doi: 10.12284/j.issn.0253-4193.2022.7.hyxb202207015 [6] Laxon S W, Giles K A, Ridout A L, et al. CryoSat-2 estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(4): 732−737. doi: 10.1002/grl.50193 [7] Aldenhoff W, Berg A, Eriksson L E B. Sea ice concentration estimation from Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar images over the Fram Strait[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2016: 7675−7677. [8] Liu Yinghui, Key J, Mahoney R. Sea and freshwater ice concentration from VIIRS on suomi NPP and the future JPSS satellites[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(6): 523. doi: 10.3390/rs8060523 [9] 郑付强, 匡定波, 胡勇, 等. 基于U-ASPP-Net的北极独立海冰精细识别方法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2021, 40(6): 798−808. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2021.06.014Zheng Fuqiang, Kuang Dingbo, Hu Yong, et al. Refined segmentation method based on U-ASPP-Net for Arctic independent sea ice[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2021, 40(6): 798−808. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2021.06.014 [10] 周嘉儒, 卢鹏, 王庆凯, 等. 基于视频图像获取冰面特征的自动检测算法研究[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程, 2021, 4(5): 60−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-5419.2021.05.014Zhou Jiaru, Lu Peng, Wang Qingkai, et al. Research on automatic detection algorithm based on video image acquisition for ice surface feature[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering, 2021, 4(5): 60−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-5419.2021.05.014 [11] Toyota T, Haas C, Tamura T. Size distribution and shape properties of relatively small sea-ice floes in the Antarctic marginal ice zone in late winter[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2011, 58(9/10): 1182−1193. [12] 季顺迎, 王安良, 王宇新, 等. 渤海海冰现场监测的数字图像技术及其应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(4): 79−87.Ji Shunying, Wang Anliang, Wang Yuxin, et al. A digital image technology and its application for the sea ice field observation in the Bohai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2011, 33(4): 79−87. [13] Blunt J D, Garas V Y, Matskevitch D G, et al. Image analysis techniques for high arctic, deepwater operation support[C]//Proceedings of the OTC Arctic Technology Conference. Houston: OTC, 2012. [14] Ijitona T B, Ren Jinchang, Hwang P B. SAR sea ice image segmentation using watershed with intensity-based region merging[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology. Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2014: 168−172. [15] Zhang Qin, Skjetne R, Metrikin I, et al. Image processing for ice floe analyses in broken-ice model testing[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2015, 111: 27−38. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2014.12.004 [16] Kalke H, Loewen M. Support vector machine learning applied to digital images of river ice conditions[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 155: 225−236. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.08.014 [17] 田萱, 王亮, 丁琪. 基于深度学习的图像语义分割方法综述[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(2): 440−468.Tian Xuan, Wang Liang, Ding Qi. Review of image semantic segmentation based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(2): 440−468. [18] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015: 3431−3440. [19] Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481−2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [20] Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834−848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [21] Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams C K I, et al. The Pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303−338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [22] Garcia-Garcia A, Orts-Escolano S, Oprea S, et al. A survey on deep learning techniques for image and video semantic segmentation[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 70: 41−65. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.05.018 [23] Zhu Xiaoxiang, Tuia D, Mou Lichao, et al. Deep learning in remote sensing: a comprehensive review and list of resources[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2017, 5(4): 8−36. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2017.2762307 [24] Hesamian M H, Jia Wenjing, He Xiangjian, et al. Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: achievements and challenges[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2019, 32(4): 582−596. doi: 10.1007/s10278-019-00227-x [25] Cooke C L V, Scott K A. Estimating sea ice concentration from SAR: training convolutional neural networks with passive microwave data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(7): 4735−4747. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2892723 [26] Wang Lei, Scott K A, Xu Linlin, et al. Sea ice concentration estimation during melt from dual-pol SAR scenes using deep convolutional neural networks: a case study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4524−4533. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2543660 [27] Wang Yiran, Li Xiaoming. Arctic sea ice cover data from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar by deep learning[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2021, 13(6): 2723−2742. doi: 10.5194/essd-13-2723-2021 [28] 宋巍, 祝敏, 石少华, 等. 基于改进DeepLabV3+的轻量化SAR图像冰间水道分割[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024(4). (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的卷期页码信息, 请确认) Song Wei, Zhu Min, Shi Shaohua, et al. Lightweight SAR image lead segmentation based on improved DeepLabV3+[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024(4). [29] 孙士昌, 王志勇, 李振今, 等. 基于改进DeepLabV3+模型的海冰提取方法——以北极格陵兰海为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2024, 46(8): 131−142.Sun Shichang, Wang Zhiyong, Li Zhenjin, et al. An extraction method for sea ice based on improved DeepLabV3+ model: taking the arctic Greenland sea as an example[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2024, 46(8): 131−142. [30] Zhang Chengqian, Chen Xiaodong, Ji Shunying. Semantic image segmentation for sea ice parameters recognition using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2022, 112: 102885, doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2022.102885 [31] Chen L C, Zhu Yukun, Papandreou G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49. -





 下载:
下载: