Sedimentary geochemical records and their indications for environmental variations in Bohai Bay
-
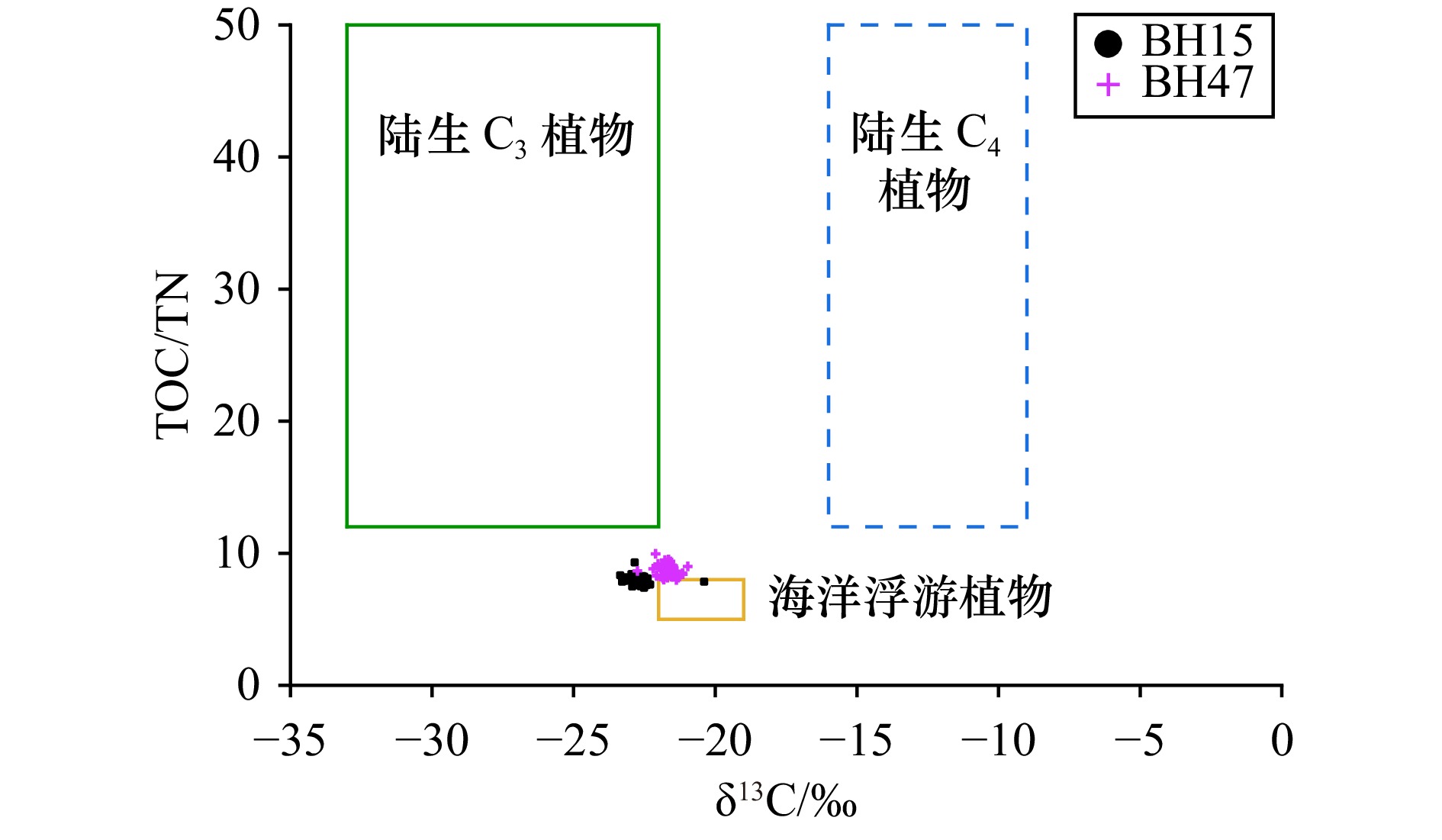
摘要: 为了解渤海湾营养环境的长周期变化特征及关键影响因素,于2018年4月和6月在渤海湾湾口外侧海域(BH47)及渤海湾湾口(BH15)采集沉积物柱状样,对沉积物柱状样中总有机碳(TOC)、总氮(TN)、磷(P)、生物硅(BSi)的含量以及碳、氮稳定同位素组成(δ13C、δ15N)进行了分析,并结合气候和周围人类活动变化讨论以上参数的变化诱因。研究结果显示,两柱状样中TN含量自1980s起随时间呈现增加的变化趋势,与水体溶解无机氮(DIN)的长周期变化一致。污水排放、化肥施用和海水养殖是渤海湾氮的主要来源,其中农业化肥氮输入自2007年起有所下降,海水养殖和生活污水入海排放呈现持续上升的趋势。无机磷(IP)是沉积物中磷的主要存在形式,湾内的BH15柱中IP含量自1990s中期起呈现下降的趋势,湾口的BH47柱中IP含量呈现1970s后先减少,1990s起缓慢增加的变化趋势,两者均体现出明显的陆源输入特征。TOC/TN比值、δ13C值以及δ13C二端元混合模型对有机质来源的指示结果表明,渤海湾口及临近海域沉积物有机质受陆源输入和海洋自生共同影响,总体以海源有机质为主,自1990s起海源有机质贡献有所下降。与湾口的BH47柱相比,BH15柱更靠近近岸地区,受陆源输入的影响更显著,TN含量和陆源有机质贡献相对更高。本研究表明,为实现渤海湾水环境的有效治理,在对农业化肥的使用进行管制的同时,今后还需重点加强对海水养殖和生活污水入海排放的管控。Abstract: In order to understand the long−term variations in the nutritional environment and the key influencing factors of Bohai Bay, sediment cores from the mouth of the bay (BH15) and the outer area of the bay (BH47) were collected in April and June 2018 separately. The contents of total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), phosphorus (P), biogenic silica (BSi), and stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen (δ13C, δ15N) were analyzed, and the causes of the changes of the above parameters were discussed in combination with the changes of climate and surrounding human activities. The results showed that the TN content in both sediment cores exhibited an increasing trend since the 1980s, which is consistent with the long-term variations in dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) in the sea water. Sewage discharge, fertilizer application and mariculture are the main sources of nitrogen in the Bohai Bay, among which the input of agricultural fertilizer has decreased since 2007, while the discharge of mariculture and domestic sewage into the sea has shown a continuous upward trend. Inorganic Phosphorus (IP) was the main form of phosphorus in sediments. The IP in BH15 in the bay has shown a decreasing trend since the mid-1990s, while the IP in BH47 from the mouth of the bay has shown a decreasing trend after 1970s and a slow increasing trend since 1990s. All of them show obvious terrigenous input characteristics. The results of TOC/TN ratio、δ13C value and δ13C two-endmember mixing model indicated that the sediment organic matter in the mouth of Bohai Bay and adjacent sea area was influenced by both terrestrial input and marine autochthonous sources, with marine organic matter being the dominant source, the contribution of marine organic matter has decreased Since the 1990s. Compared with the BH47 core from the mouth of the bay, the BH15 core is closer to the coastal area, more significantly affected by terrestrial input, with higher TN content and contribution of terrestrial organic matter. This study shows that in order to effectively manage the water environment of Bohai Bay, it is necessary to strengthen the control of mariculture and domestic sewage discharge into the sea while controlling the use of agricultural fertilizers in the future.
-
表 1 不同区域柱状沉积物中有机质的比较
Tab. 1 Comparison of organic matter in sediment cores from different study areas
研究区域 TOC/% TN/ % BSi/ % δ13C/‰ TOC/TN 参考文献 渤海湾 0.40~0.64 0.06~0.08 0.52~1.11 −23.3~−20.4 7.4~9.3 本研究 0.40~0.61 0.06~0.08 0.39~1.46 −22.8~−21.0 8.0~10.0 四十里湾 0.38~0.58 0.04~0.06 − −22.8~−21.3 9.1–11.0 [92] 胶州湾 0.14~ 0.41 0.02~0.05 − −22.2~−20.4 8.2~ 11.5 [93] 大亚湾 0.79~1.11 0.10~0.14 − −20.8 ~−22.5 5.2~8.3 [94] 黄河口邻近海域 0.21~0.32 0.02~0.04 − −23.4~−22.5 8.5~12.0 [95] 长江口邻近海域 0.37~ 0.62 0.03~ 0.08 0.75~0.80 − 7.7~ 8.6 [96] 珠江口邻近海域 0.80~1.90 0.13~0.20 0.98~2.35 − 5.5~12.7 [97] 注:“−”表示无数据。 -
[1] Howarth R W, Anderson D B, Cloern J E, et al. Nutrient pollution of coastal rivers, bays, and seas[J]. Issues in Ecology, 2000(7): 1−16. [2] Diaz R J, Rosenberg R. Marine benthic hypoxia: a review of its ecological effects and the behavioural response of benthic macrofauna[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology, 1995, 33: 245−303. [3] Capriulo G M, Smith G, Troy R, et al. The planktonic food web structure of a temperate zone estuary, and its alteration due to eutrophication[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2002, 475−476(1): 263−333. [4] Imai I, Yamaguchi M, Hori Y. Eutrophication and occurrences of harmful algal blooms in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan[J]. Plankton and Benthos Research, 2006, 1(2): 71−84. doi: 10.3800/pbr.1.71 [5] 孟伟, 刘征涛, 范薇. 渤海主要河口污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2004, 17(6): 66−69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2004.06.017Meng Wei, Liu Zhengtao, Fan Wei. Study on pollutant characters of main estuary of Bohai Bay[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2004, 17(6): 66−69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2004.06.017 [6] 陈燕珊, 万萌萌, 林锟, 等. 渤海湾渔业碳汇分析与预测初探[J]. 海洋科学, 2022, 46(9): 77−84. doi: 10.11759/hykx20220224001Chen Yanshan, Wan Mengmeng, Lin Kun, et al. Analysis and prediction of the fishery carbon sink in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2022, 46(9): 77−84. doi: 10.11759/hykx20220224001 [7] 王勇智, 吴頔, 石洪华, 等. 近十年来渤海湾围填海工程对渤海湾水交换的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(3): 471−480. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140700194Wang Yongzhi, Wu Di, Shi Honghua, et al. Impact of reclamation on water exchange in Bohai Bay in recent decade[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(3): 471−480. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140700194 [8] 孙百顺, 左书华, 谢华亮, 等. 近40年来渤海湾岸线变化及影响分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017(4): 139−148.Sun Baishun, Zuo Shuhua, Xie Hualiang, et al. Analysis of impact effects and changes of the coastline in the Bohai Bay during the past 40 years[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2017(4): 139−148. [9] 杨世民, 董树刚, 窦明武, 等. 渤海湾海域生态环境的研究 Ⅱ. 水体富营养化的评价与分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2007, 26(6): 541−545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2007.06.011Yang Shimin, Dong Shugang, Dou Mingwu, et al. Study on ecological environment in the Bohai Bay Ⅱ. Assessment of coastal eutrophication[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2007, 26(6): 541−545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2007.06.011 [10] 王彬, 崔健, 李玲, 等. 渤海湾赤潮特征研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(2): 200−206. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190242Wang Bin, Cui Jian, Li Ling, et al. Characteristics of red tide in the Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(2): 200−206. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190242 [11] Zou Jingzhong, Dong Liping, Qin Baoping. Preliminary studies on eutrophication and red tide problems in Bohai Bay[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1985, 127(1): 27−30. doi: 10.1007/BF00004660 [12] Xie Linping, Xu Hanyue, Xin Ming, et al. Regime shifts in trophic status and regional nutrient criteria for the Bohai Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 170: 112674. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112674 [13] 秦延文, 孟伟, 郑丙辉, 等. 渤海湾水环境氮、磷营养盐分布特点[J]. 海洋学报, 2005, 27(2): 172−176. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2005.02.023Qin Yanwen, Meng Wei, Zheng Binghui, et al. Distribution features of nitrogen and phosphorus in aquatic environments of the Bohai Gulf[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2005, 27(2): 172−176. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2005.02.023 [14] Clarke A L, Weckström K, Conley D J, et al. Long-term trends in eutrophication and nutrients in the coastal zone[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2006, 51: 385−397 [15] Ellegaard M, Clarke A L, Reuss N, et al. Multi-proxy evidence of long-term changes in ecosystem structure in a Danish marine estuary, linked to increased nutrient loading[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2006, 68(3/4): 567−578. [16] 刘东艳, 申旭红, 王玉珏, 等. 烟台四十里湾表层沉积物有机质来源及环境意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(5): 205−212.Liu Dongyan, Shen Xuhong, Wang Yujue, et al. Tracking the sources of organic matter in the surface sediments of Sishili Bay, northern Yellow Sea and the environmental implication[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(5): 205−212. [17] Bratton J F, Colman S M, Seal R R. Eutrophication and carbon sources in Chesapeake Bay over the last 2700 yr: human impacts in context[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(18): 3385−3402. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00131-5 [18] Liu Dongyan, Shen Xuhong, Di Baoping, et al. Palaeoecological analysis of phytoplankton regime shifts in response to coastal eutrophication[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2013, 475: 1−14. [19] 赵广明, 叶思源, 李广雪, 等. 渤海湾沉积地球化学记录及其对环境变迁的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5): 51−57.Zhao Guangming, Ye Siyuan, Li Guangxue, et al. Sedimentary geochemical records: indications of environmental changes in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 51−57. [20] 王润梅, 唐建辉, 黄国培, 等. 环渤海地区河流河口及海洋表层沉积物有机质特征和来源[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(3): 497−507. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140800225Wang Runmei, Tang Jianhui, Huang Guopei, et al. Provenance of organic matter in estuarine and marine surface sediments around the Bohai Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(3): 497−507. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140800225 [21] 冯秀丽, 魏飞, 刘杰, 等. 渤海湾西部表层沉积物粒度及黏土矿物特征分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(8): 70−77. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130411001Feng Xiuli, Wei Fei, Liu Jie, et al. The sediment grain size characteristics and analysis of sources in the western Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(8): 70−77. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130411001 [22] Zhang Yan, Lu Xueqiang, Liu Honglei, et al. Identifying the sources of organic matter in marine and riverine sediments of Bohai Bay and its catchment using carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 33(1): 204−209. doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4068-z [23] 陈彬, 胡利民, 邓声贵, 等. 渤海湾表层沉积物中有机碳的分布与物源贡献估算[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 37−42.Chen Bin, Hu Limin, Deng Shenggui, et al. Organic carbon in surface sediments of the Bohai Bay, China and its contribution to sedimentation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 37−42. [24] 江辉煌. 渤海沉积物中生源要素的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Jiang Huihuang. Study on biogenic elements in sediments of the Bohai Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [25] Wang Liping, Liu Lusan, Zheng Binghui, et al. Analysis of the bacterial community in the two typical intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China by pyrosequencing[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 72(1): 181−187. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.04.005 [26] Duan Liqin, Song Jinming, Xu Yayan, et al. The distribution, enrichment and source of potential harmful elements in surface sediments of Bohai Bay, North China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 183(1/3): 155−164. [27] 赵保仁, 庄国文, 曹德明, 等. 渤海的环流、潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(5): 466−473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003Zhao Baoren, Zhuang Guowen, Cao Deming, et al. Circulation, tidal residual currents and their effects on the sedimentations in the Bohai Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1995, 26(5): 466−473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003 [28] 董娇娇, 孙健, 陈燕珍, 等. 渤海岸线及水深变化对水动力影响的数值模拟[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2020, 38(4): 676−687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.04.011Dong Jiaojiao, Sun Jian, Chen Yanzhen, et al. Numerical simulation of the hydrodynamics affected by coastline and bathymetry changes in the Bohai Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2020, 38(4): 676−687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.04.011 [29] 张龙军, 夏斌, 桂祖胜, 等. 2005年夏季环渤海16条主要入海河流的污染状况[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(11): 2409−2415. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.11.001Zhang Longjun, Xia Bin, Gui Zusheng, et al. Contaminative conditions evaluation of sixteen main rivers flowing into sea around Bohai Sea, in Summer of 2005[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(11): 2409−2415. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.11.001 [30] Huang Jinliang, Li Qingsheng, Huang Ling, et al. Watershed-scale evaluation for land-based nonpoint source nutrients management in the Bohai Sea Bay, China[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2013, 71: 314−325. [31] 王友华, 秦华伟, 王秋莲, 等. 2006—2020年渤海湾水质变化趋势分析和富营养化状况评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2023, 42(5): 693−703.Wang Youhua, Qin Huawei, Wang Qiulian, et al. Evaluation of spatial and temporal distribution of water quality and eutrophication in Bohai Bay during 2006−2020[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2023, 42(5): 693−703. [32] Shou Weiwei, Zong Haibo, Ding Pingxing, et al. A modelling approach to assess the effects of atmospheric nitrogen deposition on the marine ecosystem in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 208: 36−48. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.04.025 [33] Liu Sumei, Li Lingwei, Zhang Zhinan. Inventory of nutrients in the Bohai[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2011, 31(16): 1790−1797. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.08.004 [34] 汪迁迁. 镭氡同位素评估渤海湾海底地下水排泄及其陆源物质输送通量[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.Wang Qianqian. Estimating submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and its associated terrestrial material fluxes into Bohai Bay using Radium and Radon isotopes[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020. [35] Sanchez−Cabeza J A, Masqué P, Ani−Ragolta I. 210Pb and 210Po analysis in sediments and soils by microwave acid digestion[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 1998, 227(1): 19−22. [36] Masqué P, Isla E, Sanchez−Cabeza J A, et al. Sediment accumulation rates and carbon fluxes to bottom sediments at the Western Bransfield Strait (Antarctica)[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2002, 49(4/5): 921−933. [37] 周连成, 李军, 高建华, 等. 长江口与舟山海域柱状沉积物粒度特征对比及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5): 21−27.Zhou Liancheng, Li Jun, Gao Jianhua, et al. Comparison of core sediment grain−size characteristics between Yangtze River estuary and Zhoushan Islands and its significance to sediment source analysis[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 21−27. [38] Shepard F P. Nomenclature based on sand−silt−clay ratios[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1954, 24(3): 151−158. [39] Aspila K I, Agemian H, Chau A S Y. A semi−automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments[J]. Analyst, 1976, 101(1200): 187−197. doi: 10.1039/an9760100187 [40] Demaster D J. The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(10): 1715−1732. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90006-5 [41] Shultz D J, Calder J A. Organic carbon 13C/12C variations in estuarine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1976, 40(4): 381−385. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(76)90002-8 [42] Yi Wan, Hu Jianying, An Lihui, et al. Determination of trophic relationships within a Bohai Bay food web using stable δ15N and δ13C analysis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(10): 1021−1025. doi: 10.1360/04wd0283 [43] Guo Zhigang, Li Juyuan, Feng Jialiang, et al. Compound−specific carbon isotope compositions of individual long−chain n−alkanes in severe Asian dust episodes in the North China coast in 2002[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(17): 2133−2140. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-2071-7 [44] Liu Xihan, Liu Dongyan, Wang Yujue, et al. Temporal and spatial variations and impact factors of nutrients in Bohai Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 140: 549−562. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.02.011 [45] 王福, 王宏, 李建芬, 等. 渤海地区210Pb、137Cs同位素测年的研究现状[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(2): 244−250. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.02.015Wang Fu, Wang Hong, Li Jianfen, et al. Current study of 210Pb and 137Cs geochronology in the circum−Bohai Sea region[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(2): 244−250. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.02.015 [46] 李凤业, 高抒, 贾建军, 等. 黄、渤海泥质沉积区现代沉积速率[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(4): 364−369. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004Li Fengye, Gao Shu, Jia Jianjun, et al. Contemporary deposition rates of fine−grained sediment in the Bohai and Yellow Seas[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(4): 364−369. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004 [47] 国家防汛抗旱总指挥部办公室, 水利部南京水文水资源研究所. 中国水旱灾害[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 1997.Office of State Flood Control and Drought Relief Headquarters, Nanjing Institute of Hydrology and Water Resources. China Flood and Drought Disaster[M]. Beijing: China Water&Power Press, 1997. [48] Liu Dongyan, Li Xin, Emeis K C, et al. Distribution and sources of organic matter in surface sediments of Bohai Sea near the Yellow River Estuary, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 165: 128−136. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.09.007 [49] 刘建国, 李安春, 陈木宏, 等. 全新世渤海泥质沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(6): 559−568. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2007.06.004Liu Jianguo, Li Anchun, Chen Muhong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediments in the Bohai Sea mud area during Holocene[J]. Geochimica, 2007, 36(6): 559−568. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2007.06.004 [50] 田立柱, 耿岩, 裴艳东, 等. 渤海湾西部表层沉积物粒度特征与沉积混合[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(5): 668−674. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.005Tian Lizhu, Geng Yan, Pei Yandong, et al. The grain−size characteristics and sediment mixing pattern of surface sediment from the western Bohai Bay, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(5): 668−674. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.005 [51] 杨作升, 李国刚, 王厚杰, 等. 55年来黄河下游逐日水沙过程变化及其对干流建库的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(6): 9−18.Yang Zuosheng, Li Guogang, Wang Houjie, et al. Variation of daily water and sediment discharge in the yellow river lower reaches in the past 55 years and its response to the dam operation on its main stream[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(6): 9−18. [52] 段晓勇, 李艳霞, 印萍. 渤海表层沉积物中铜的分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(6): 135−141.Duan Xiaoyong, Li Yanxia, Yin Ping. Distribution of Cu in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea and its influence factors[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(6): 135−141. [53] 刘静玲, 李毅, 史璇, 等. 海河流域典型河流沉积物粒度特征及分布规律[J]. 水资源保护, 2017, 33(6): 9−19. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2017.06.02Liu Jingling, Li Yi, Shi Xuan, et al. Grain size characteristics and distribution regularities of typical river sediments in Haihe River Basin[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2017, 33(6): 9−19. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2017.06.02 [54] 刘素美. 黄、渤海沉积物−水界面营养盐的交换及其质量平衡[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2001.Liu Sumei. Nutrient exchange and mass balance at water interface at the sediment−water interface in the sediments of Bohai and Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2001. [55] 范俊甫, 马廷, 周成虎, 等. 1992−2010年基于DMSP−OLS图像的环渤海城市群空间格局变化分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2013, 15(2): 280−288. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2013.001280Fan Junfu, Ma Ting, Zhou Chenghu, et al. Changes in spatial patterns of urban landscape in Bohai Rim from 1992 to 2010 using DMSP−OLS data[J]. Journal of Geo−Information Science, 2013, 15(2): 280−288. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2013.001280 [56] Krom M D, Neori A. A total nutrient budget for an experimental intensive fishpond with circularly moving seawater[J]. Aquaculture, 1989, 83(3/4): 345−358. [57] Xin Ming, Wang Baodong, Xie Linping, et al. Long−term changes in nutrient regimes and their ecological effects in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 146: 562−573. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.011 [58] 阚文静, 张秋丰, 石海明, 等. 近年来渤海湾营养盐变化趋势研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2010, 29(2): 238−241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.02.017Kan Wenjing, Zhang Qiufeng, Shi Haiming, et al. Study on variation trend of nutrient salts in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2010, 29(2): 238−241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.02.017 [59] 郑丙辉, 秦延文, 孟伟, 等. 1985~2003年渤海湾水质氮磷生源要素的历史演变趋势分析[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(3): 494−499. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.03.009Zheng Binghui, Qin Yanwen, Meng Wei, et al. Historical evolvement trends of nutrients in waters of Bohai Bay from 1985 to 2003[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(3): 494−499. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.03.009 [60] Wei Qi, Sun Conghui, Wu Guanghong, et al. Haihe River discharge to Bohai Bay, North China: trends, climate, and human activities[J]. Hydrology Research, 2017, 48(4): 1058−1070. doi: 10.2166/nh.2016.142 [61] Liu Sumei, Li Lingwei, Zhang Guiling, et al. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) estuary[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 430−431: 103−110. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.005 [62] 江辉煌, 刘素美. 渤海沉积物中磷的分布与埋藏通量[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(1): 125−132.Jiang Huihuang, Liu Sumei. Distribution and burial flux of phosphorus in sediments of the Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(1): 125−132. [63] Duan Liqin, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang, et al. Distribution of selenium and its relationship to the eco−environment in Bohai Bay seawater[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2010, 121(1/4): 87−99. [64] 夏斌, 张龙军, 桂祖胜, 等. 海河流域的富营养化状况及污染物入海通量[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(S2): 33−38.Xia Bin, Zhang Longjun, Gui Zusheng, et al. The eutrophication condition and the pollutant fluxes entering the sea via the rivers in the Haihe River Basin[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(S2): 33−38. [65] 李慧垠, 王广, 季宏兵, 等. 北京水源地水体中颗粒有机质的碳氮同位素研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(12): 2663−2671.Li Huiyin, Wang Guang, Ji Hongbing, et al. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope composition of particulate organic matter in water source of Beijing[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(12): 2663−2671. [66] 康萍萍. 滨海地下水氮的同位素溯源及其源贡献率研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016.Kang Pingping. Identifying nitrogen sources and quantitfying the contributions of nitrate sources in coastal zone[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2016. [67] Ruiz−Fernández A C, Hillaire−Marcel C, Ghaleb B, et al. Recent sedimentary history of anthropogenic impacts on the Culiacan River Estuary, northwestern Mexico: geochemical evidence from organic matter and nutrients[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2002, 118(3): 365−377. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00287-1 [68] 肖化云, 刘丛强. 氮同位素示踪贵州红枫湖河流季节性氮污染[J]. 地球与环境, 2004, 32(1): 71−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2004.01.012Xiao Huayun, Liu Congqiang. Nitrogen isotope studies on seasonal nitrogen pollution of inflowing rivers of Hongfeng Lake, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology−geochemistry, 2004, 32(1): 71−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2004.01.012 [69] Liu K K, Kaplan I R. The eastern tropical Pacific as a source of 15N−enriched nitrate in seawater off southern California[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1989, 34(5): 820−830. doi: 10.4319/lo.1989.34.5.0820 [70] Waser N A D, Harrison P J, Nielsen B, et al. Nitrogen isotope fractionation during the uptake and assimilation of nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, and urea by a marine diatom[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1998, 43(2): 215−224. doi: 10.4319/lo.1998.43.2.0215 [71] 吴莹, 张经, 张再峰, 等. 长江悬浮颗粒物中稳定碳、氮同位素的季节分布[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(5): 546−552. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.012Wu Ying, Zhang Jing, Zhang Zaifeng, et al. Seasonal variability of stable carbon and nitrogen isotope of suspended particulate matter in the Changjiang River[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(5): 546−552. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.012 [72] Sigman D M, Altabet M A, Francois R, et al. The isotopic composition of diatom−bound nitrogen in southern Ocean sediments[J]. Paleoceanography, 1999, 14(2): 118−134. doi: 10.1029/1998PA900018 [73] 钟文聪, 王朝晖, 江涛. 渤海中部海域表层沉积物生源要素分布特征及其环境评价分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020, 39(1): 39−45,52. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20200106Zhong Wencong, Wang Zhaohui, Jiang Tao. Distribution characteristics and environmental assessment of biogenic elements in surface sediments from the central Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020, 39(1): 39−45,52. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20200106 [74] Charles C D, Froelich P N, Zibello M A, et al. Biogenic opal in Southern Ocean sediments over the last 450, 000 years: implications for surface water chemistry and circulation[J]. Paleoceanography, 1991, 6(6): 697−728. doi: 10.1029/91PA02477 [75] 孙军, 刘东艳, 杨世民, 等. 渤海中部和渤海海峡及邻近海域浮游植物群落结构的初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(5): 461−471. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.002Sun Jun, Liu Dongyan, Yang Shimin, et al. The preliminary study on phytoplankton community structure in the central Bohai Sea and the Bohai Strait and its adjacent area[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(5): 461−471. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.002 [76] 杨阳, 孙军, 关翔宇, 等. 渤海网采浮游植物群集的季节变化[J]. 海洋通报, 2016, 35(2): 121−131. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.02.001Yang Yang, Sun Jun, Guan Xiangyu, et al. Seasonal variation of netz−phytoplankton community in Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2016, 35(2): 121−131. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.02.001 [77] 栾青杉, 康元德, 王俊. 渤海浮游植物群落的长期变化(1959~2015)[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(4): 9−18.Luan Qingshan, Kang Yuande, Wang Jun. Long−term changes in the phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea (1959−2015)[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(4): 9−18. [78] 尹翠玲, 张秋丰, 阚文静, 等. 天津近岸海域营养盐变化特征及富营养化概况分析[J]. 天津科技大学学报, 2015, 30(1): 56−61.Yin Cuiling, Zhang Qiufeng, Kan Wenjing, et al. Nutrient variation and eutrophication assessment of Bohai Bay in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2015, 30(1): 56−61. [79] 刘西汉. 渤海湾营养盐与浮游植物群落结构的变化特征及关系分析[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所), 2019.Liu Xihan. The variations of nutrients and phytoplankton assemblages in the Bohai Bay and their correlation analysis[D]. Yantai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. [80] Li Lei, Wang Yujue, Liu Dongyan. Phytoplankton shifts in the Central Bohai Sea over the last 250 years reflect eutrophication and input from the Yellow River[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 126: 107676. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107676 [81] 王亮. 东海典型泥质区高分辨沉积记录及其对气候环境变化的响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Wang Liang. High−resolution sedimentary record in the typical mud areas of East China Sea and its response to climate and environmental changes[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [82] Pancost R D, Boot C S. The palaeoclimatic utility of terrestrial biomarkers in marine sediments[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 92(1/4): 239−261. [83] O’Leary M H. Carbon isotopes in photosynthesis[J]. BioScience, 1988, 38(5): 328−336. doi: 10.2307/1310735 [84] Meyers P A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 114(3/4): 289−302. [85] Andrews J E, Greenaway A M, Dennis P F. Combined carbon isotope and C/N ratios as indicators of source and fate of organic matter in a poorly flushed, tropical estuary: Hunts bay, Kingston Harbour, Jamaica[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 46(5): 743−756. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0305 [86] Gao Xuelu, Yang Yuwei, Wang Chuanyuan. Geochemistry of organic carbon and nitrogen in surface sediments of coastal Bohai Bay inferred from their ratios and stable isotopic signatures[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(6): 1148−1155. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.03.028 [87] Hopmans E C, Weijers J W H, Schefuß E, et al. A novel proxy for terrestrial organic matter in sediments based on branched and isoprenoid tetraether lipids[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 224(1/2): 107−116. [88] Goñi M A, Ruttenberg K C, Eglinton T I. A reassessment of the sources and importance of land−derived organic matter in surface sediments from the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(18): 3055−3075. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00217-8 [89] Hu Limin, Guo Zhigang, Shi Xuefa, et al. Temporal trends of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the Bohai Sea, China: evidence from the sedimentary record[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(10): 1181−1193. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.08.009 [90] 张凌, 陈繁荣, 殷克东, 等. 珠江口及近海表层沉积有机质的特征和来源[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(1): 98−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.01.015Zhang Ling, Chen Fanrong, Yin Kedong, et al. The characteristics and sources of surface sediments in the Pearl River Estuary and its adjacent shelves[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(1): 98−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.01.015 [91] Wang Yujue, Liu Dongyan, Xiao Wupeng, et al. Coastal eutrophication in China: trend, sources, and ecological effects[J]. Harmful Algae, 2021, 107: 102058. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102058 [92] Wang Yujue, Liu Dongyan, Richard P, et al. A geochemical record of environmental changes in sediments from Sishili Bay, northern Yellow Sea, China: anthropogenic influence on organic matter sources and composition over the last 100 years[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 77(1/2): 227−236. [93] Kang Xuming, Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao, et al. The sources and composition of organic matter in sediments of the Jiaozhou Bay: implications for environmental changes on a centennial time scale[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(11): 68−78. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1076-1 [94] 曲宝晓, 宋金明, 袁华茂. 近百年来大亚湾沉积物有机质的沉积记录及对人为活动的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(10): 119−130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.10.012Qu Baoxiao, Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao. Sediment records and responses for anthropogenic activities of organic matter in the Daya Bay during recent one hundred years[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(10): 119−130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.10.012 [95] Wu Weichao, Zhao Liang, Pei Yandong, et al. Variability of tetraether lipids in Yellow River−dominated continental margin during the past eight decades: implications for organic matter sources and river channel shifts[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2013, 60: 33−39. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.04.014 [96] Cheng F, Song X, Yu Z, et al. Historical records of eutrophication in Changjiang (Yangtze) River estuary and its adjacent East China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences Discussions, 2012, 9: 6261−6291. [97] 贾国东, 彭平安, 傅家谟. 珠江口近百年来富营养化加剧的沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2002, 22(2): 158−165. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2002.02.009Jia Guodong, Peng Pingan, Fu Jiamo. Sedimentary records of accelerated eutrophication for the last 100 years at the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2002, 22(2): 158−165. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2002.02.009 -





 下载:
下载: