Effect of viscosity difference in static stratified fluids on the convective flux of double-diffusion
-
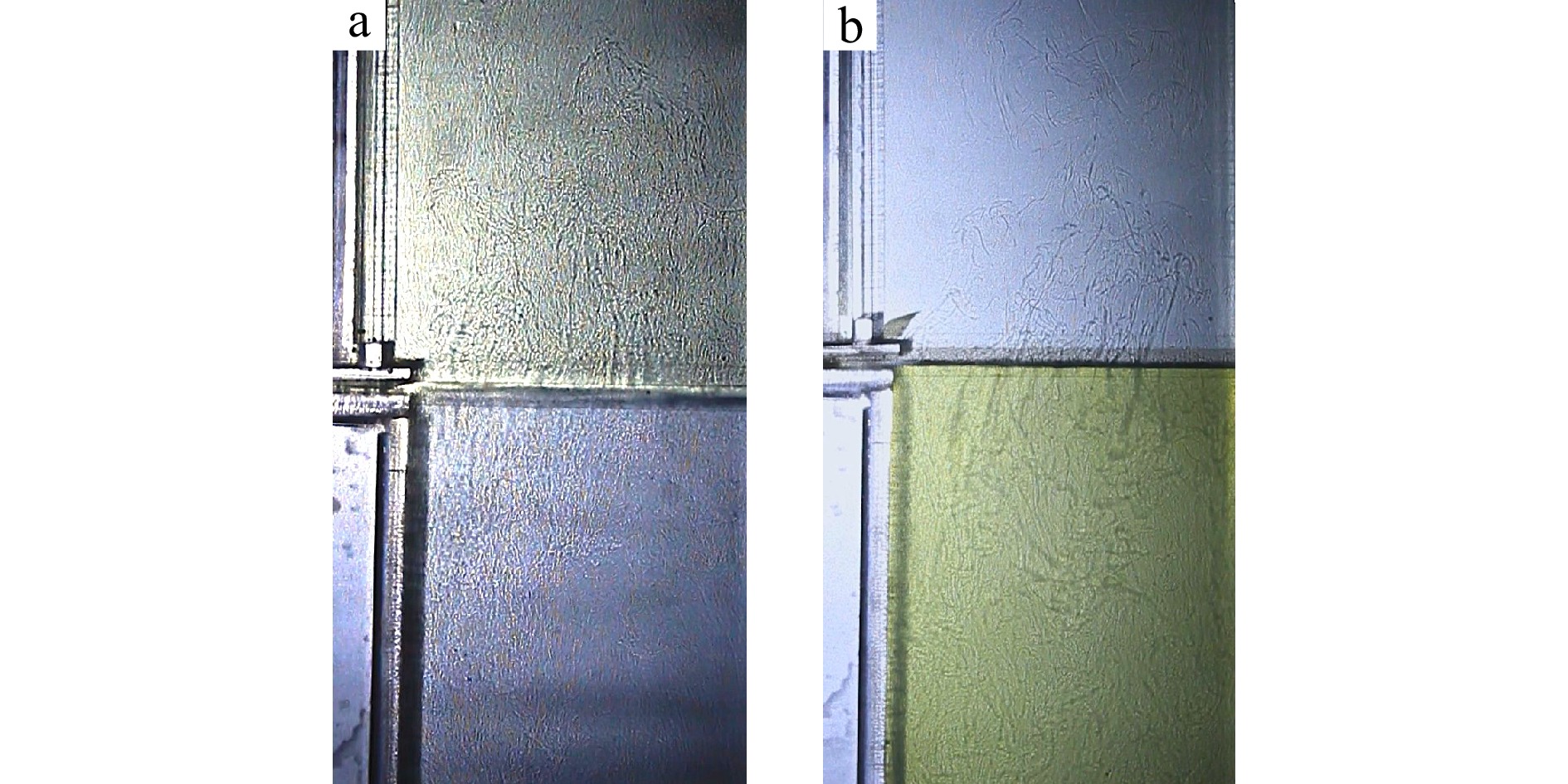
摘要: 为研究双扩散对流过程中流体黏性对通量的影响,设计梯度浓度的双扩散试验,黏度随着浓度的增大而增大。在设计有中间挡板的试验水箱中注入根据糖盐组分质量分数精确配制的溶液,以控制盐指密度稳定比在1.073;扩散型密度稳定比在0.93。移开挡板后,水箱会内形成静止状态的糖盐双层系统。为了更精确地评估双扩散现象并最小化误差,试验设置了三种时间段的双扩散试验,分别为300 s、600 s和
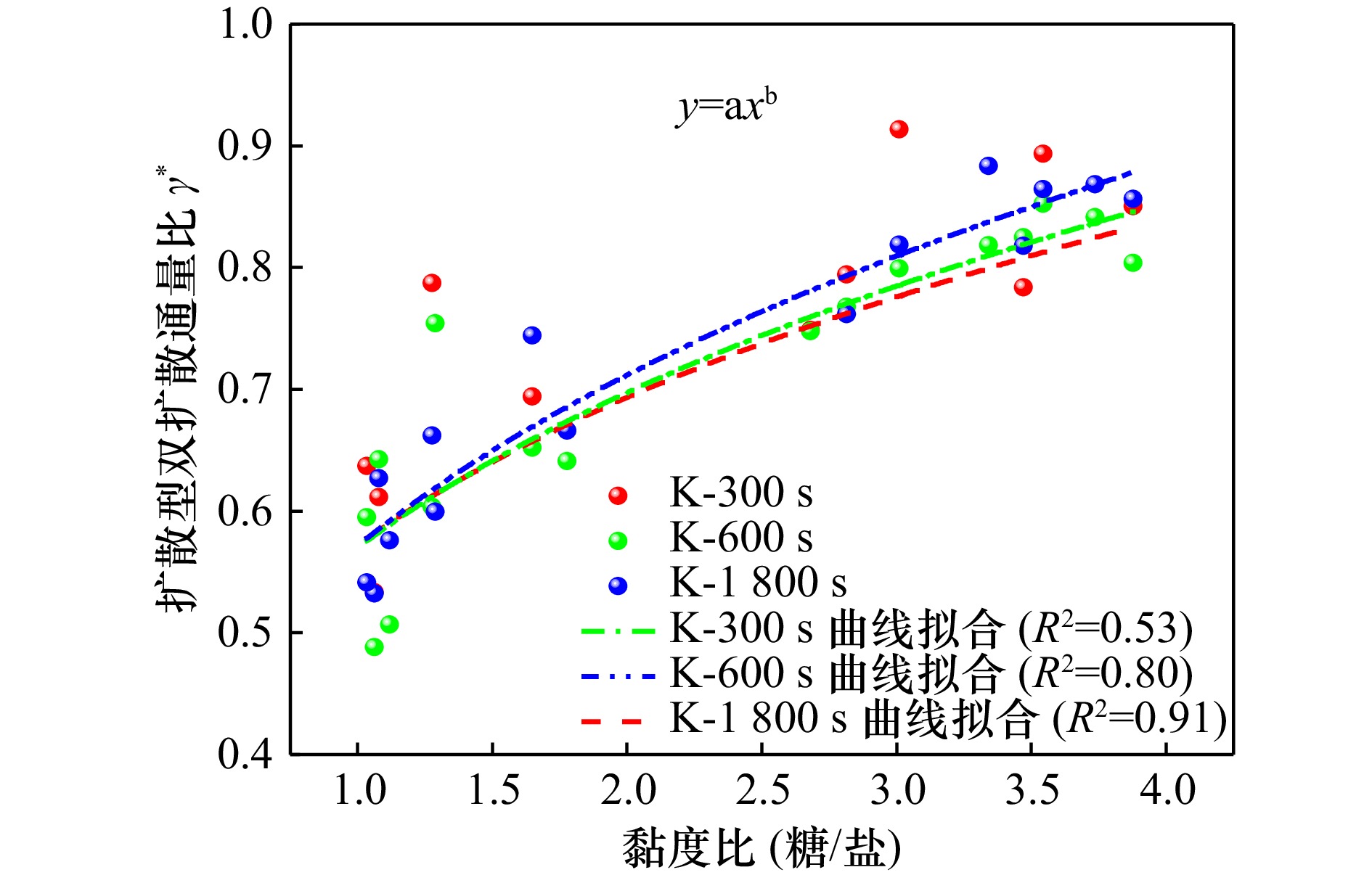
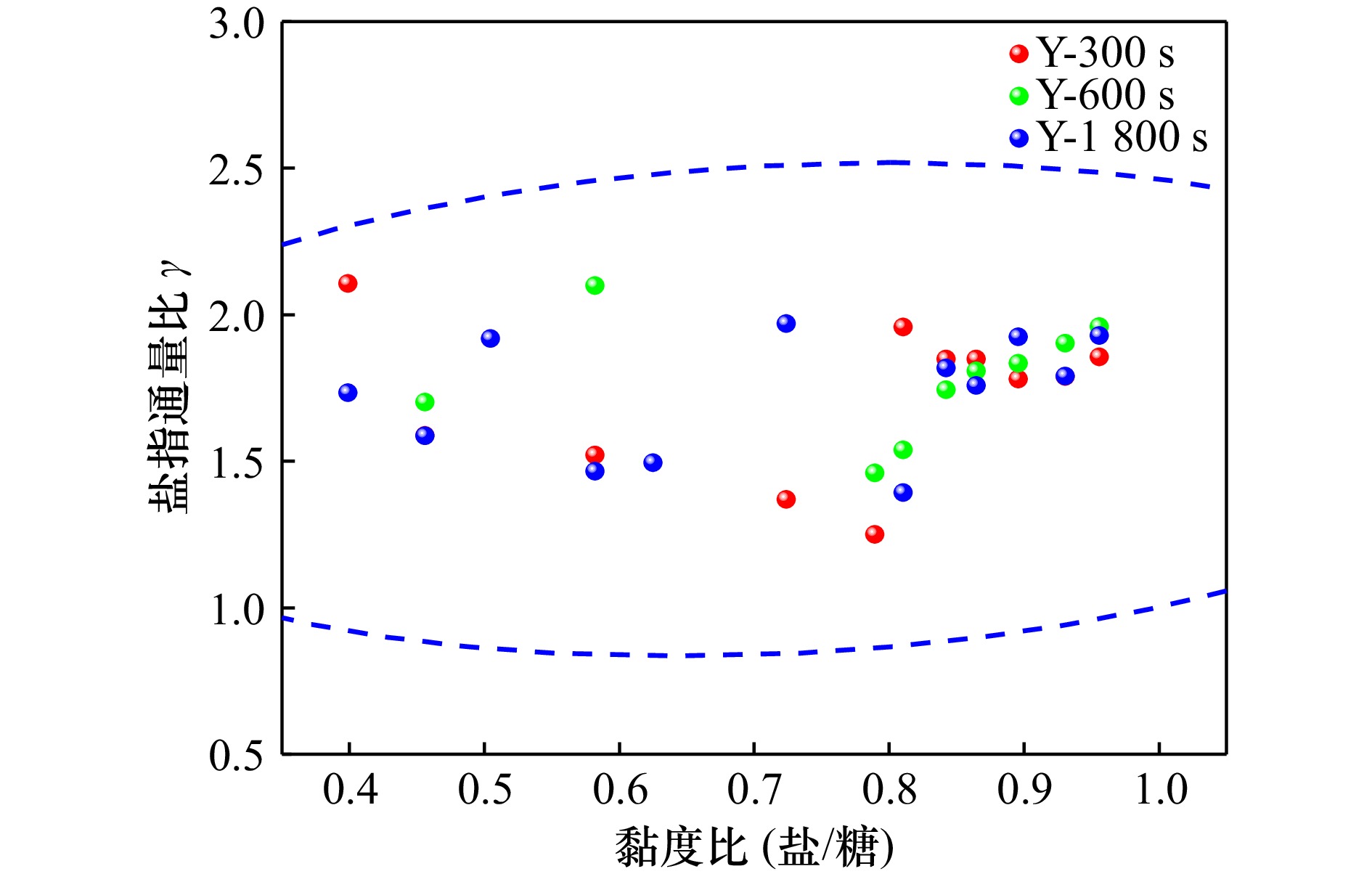
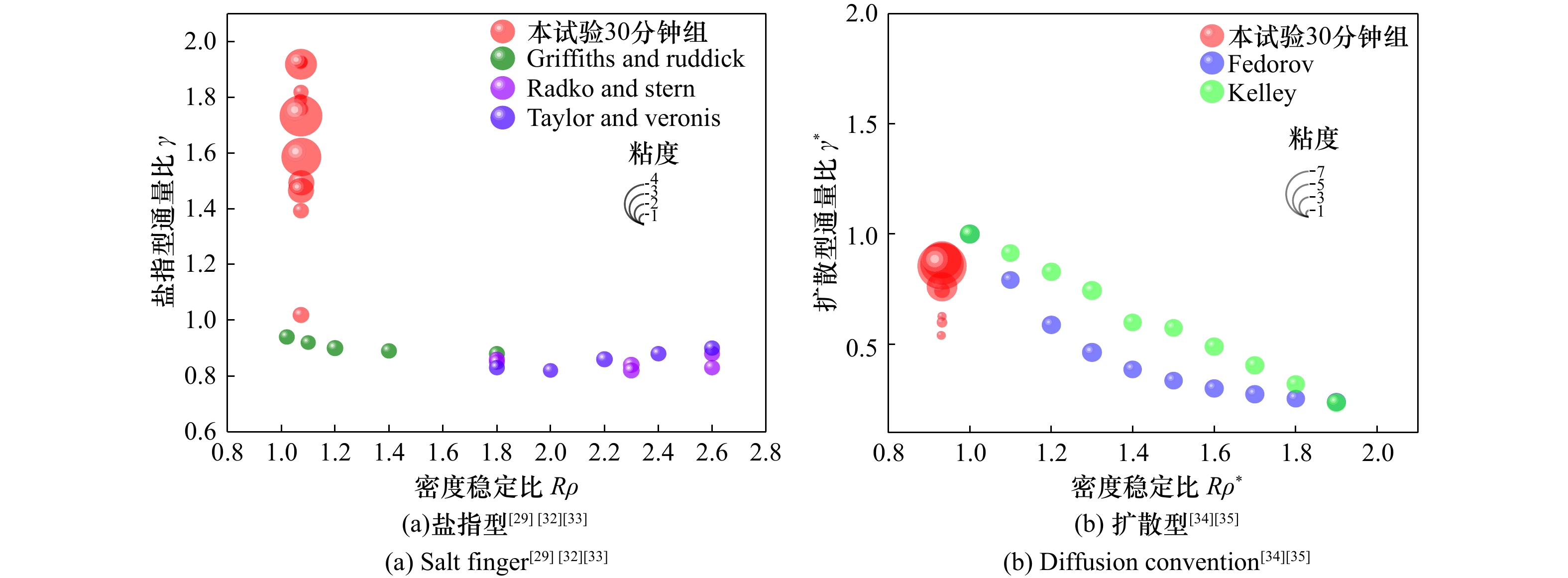
1800 s。试验发现:短时间内通量会受黏度影响而显著减小,但随着时间的增长,这些影响被继发的扩散通量所掩盖。盐指型和扩散型双扩散的糖通量与黏度之间均存在非线性关系,在扩散型双扩散中通量比γ*与黏度比之间拟合得出两者呈幂律关系;而盐指型通量比 γ 与黏度比之间的变化则相对复杂,需要更精细化研究。Abstract: To investigate the impact of fluid viscosity on flux during double-diffusive convection, a gradient-concentration double-diffusion experiment was designed, where viscosity increases with concentration. Precisely formulated sugar-salt solutions based on mass fraction were injected into a test tank equipped with an intermediate baffle, controlling the salt-fingering density stability ratio at 1.073 and the diffusion-dominated density stability ratio at 0.93. After removing the baffle, a stationary sugar-salt two-layer system formed within the tank. To accurately evaluate double-diffusive phenomena and minimize experimental errors, three time intervals were established for the double-diffusion tests: 300 s, 600 s, and1800 s. The experimental results revealed that short-term flux is significantly reduced under the influence of viscosity. However, this effect becomes masked by subsequent diffusive fluxes as time progresses. Both salt-fingering and diffusion-dominated double-diffusion exhibit nonlinear relationships between sugar flux and viscosity. In diffusion-dominated double-diffusion, a power-law correlation was established between the flux ratio γ* and viscosity ratio. Nonetheless, the discrepancy between γ and the viscosity ratios of salt finger fluxes is relatively intricate and necessitates a more exhaustive analysis.-
Key words:
- double diffusion convection /
- density stability ratio /
- flux ratio /
- viscosity
-
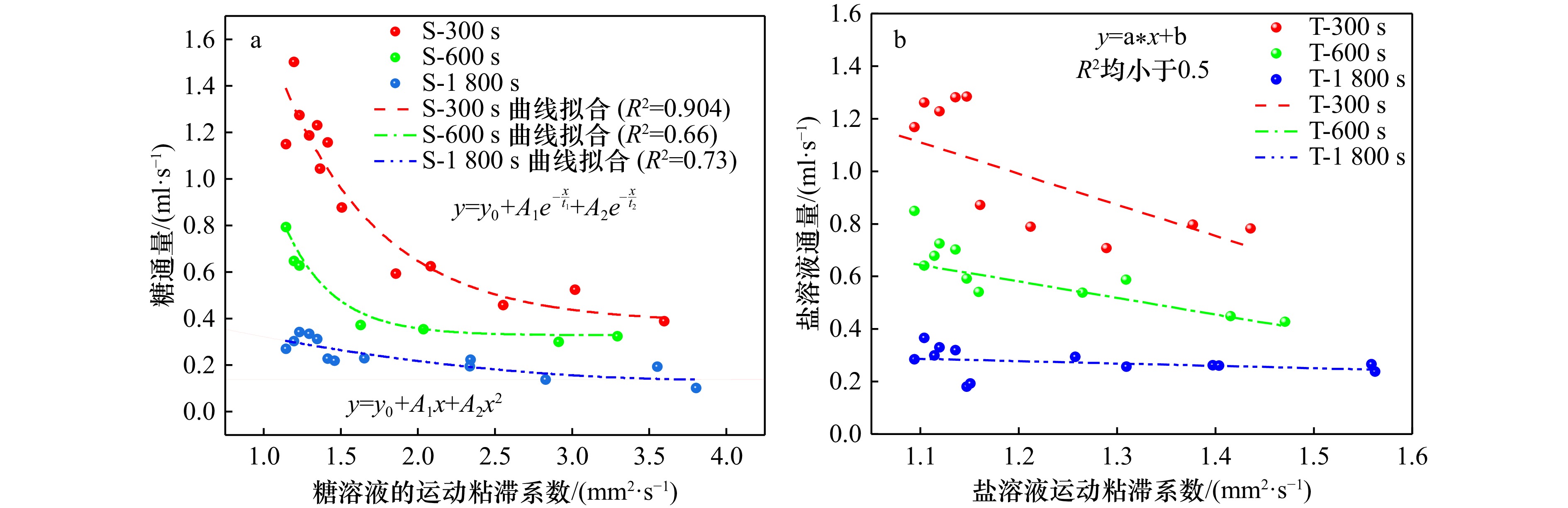
表 1 盐指(a)中的拟合结果
Tab. 1 Fitting results in salt finger (chart a)
组数 A1 A2 t1 t2 R² y0 300 s 2.42 3.5 0.64 0.64 0.9 0.381 600 s 6 12 0.311 0.311 0.658 0.328 1800 s−0.168 0.021 / / 0.729 0.468 表 2 扩散型双扩散的拟合结果
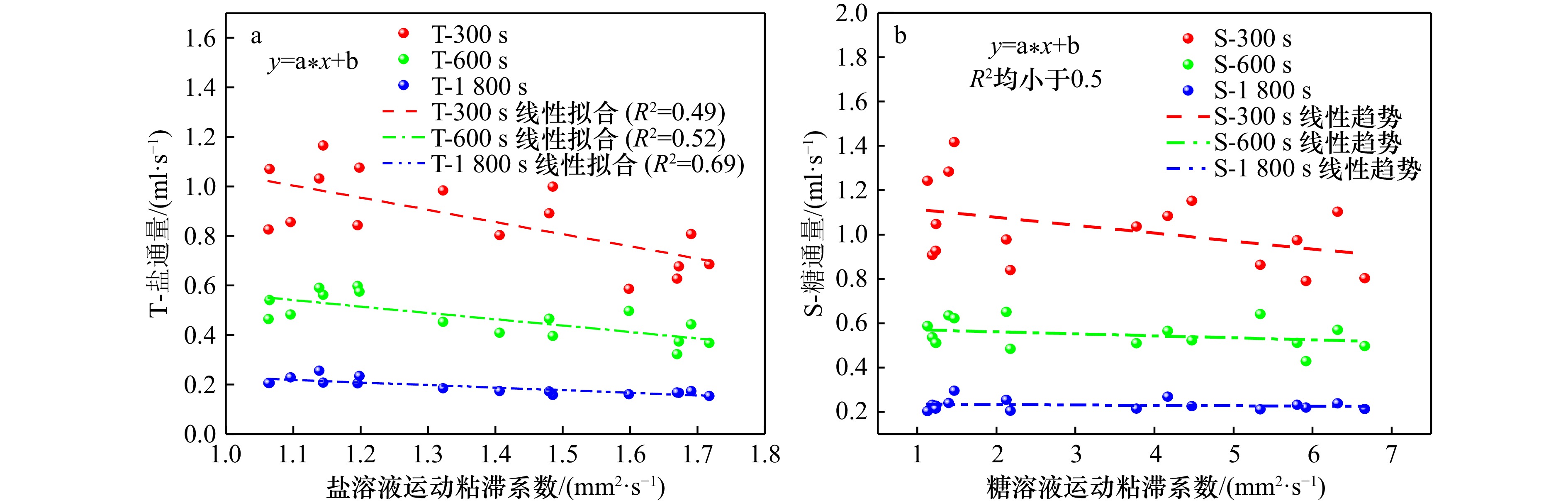
Tab. 2 Fitting results in diffusion convention
时长 a b R² 300 s 0.57 0.28 0.53 600 s 0.57 0.29 0.78 1800 s0.57 0.32 0.91 -
[1] Hu Dunxin, Wang Fan, Sprintall J, et al. Review on observational studies of western tropical Pacific Ocean circulation and climate[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020, 38(4): 906−929. doi: 10.1007/s00343-020-0240-1 [2] Schmitt R W. The salt finger experiments of Jevons (1857) and Rayleigh (1880)[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1995, 25(1): 8−17. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1995)025<0008:TSFEOJ>2.0.CO;2 [3] Radko T, Stern M E. Salt fingers in three dimensions[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1999, 57(3): 471−502. doi: 10.1357/002224099764805165 [4] Omrani N E, Ogawa F, Nakamura H, et al. Key Role of the ocean western boundary currents in shaping the Northern Hemisphere climate[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 3014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39392-y [5] Nagai T, Inoue R, Tandon A, et al. Evidence of enhanced double-diffusive convection below the main stream of the Kuroshio Extension[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(12): 8402−8421. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011288 [6] 宋雪珑, 周生启, Fer I. 北冰洋上层双扩散阶梯热通量的分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(1): 65−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.01.008Song Xuelong, Zhou Shengqi, Fer I. Analysis of the double-diffusive heat flux in the upper Arctic Ocean[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(1): 65−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.01.008 [7] 张贤良, 程灵巧, 高郭平. 双扩散在南极文森湾海域热盐结构演变中的作用[J]. 极地研究, 2018, 30(1): 32−41.Zhang Xianliang, Cheng Lingqiao, Gao Guoping. Effect of double diffusive convection during the evolution of seawater thermohaline structure in Vincennes Bay, Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2018, 30(1): 32−41. [8] 曹勇, 赵进平. 2011-2014年中国北极物理海洋学的研究进展[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(11): 1−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.11.001Cao Yong, Zhao Jinping. Progress in Arctic physical oceanography in China during 2011-2014[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(11): 1−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.11.001 [9] 屈玲, 宋雪珑, 周生启. 加拿大海盆东南部锚定观测双扩散阶梯的时间演化研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(1): 21−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.01.003Qu Ling, Song Xuelong, Zhou Shengqi. Temporal evolution of mooring-based observations of double diffusive staircases in the southeast Canada Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(1): 21−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.01.003 [10] 徐松年. 评玄武岩柱状节理形成机理的一种新假说——双扩散对流作用说[J]. 杭州大学学报, 1983, 10(3): 385−394.Xu Songnian. Comment on double-diffusive convective processes-a recent hypothesis of the genetic mechanism of columnar joints in basalt suggested by Kantha L. H.[J]. Journal of Hangzhou University, 1983, 10(3): 385−394. [11] 马文驹, 郑云. 双扩散对流与晶体生长[J]. 力学进展, 1991, 21(2): 219−225. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-1991-2-J1991-026Ma Wenju, Zheng Yun. Double-diffusive convection and crystal growth[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 1991, 21(2): 219−225. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-1991-2-J1991-026 [12] 徐兆, 张涤明. 温盐双扩散系统非线性周期对流稳定性分析[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1989, 28(2): 1−4.Xu Zhao, Zhang Diming. On stability analysis of nonlinear periodic convection in the thermohaline double-diffusive systems[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1989, 28(2): 1−4. [13] 张涤明, 李琳, 黄海. 温盐双扩散系统对流扩散周期解的线性与非线性稳定性分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 1996, 17(9): 821−828.Zhang Diming, Li Lin, Huang Hai. Stability analysis of linear and nonlinear periodic convection in thermohaline double-diffusive systems[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1996, 17(9): 821−828. [14] 詹杰民, 李毓湘, 郑珺婷. 求解温盐双扩散系统的一种高精度方法[J]. 计算力学学报, 2002, 19(3): 353−358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2002.03.020Zhan Jieming, Li Yuling, Zhen Junting. A high order method for thermohaline driven flow system[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2002, 19(3): 353−358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2002.03.020 [15] 詹杰民, 李毓湘. 温盐双扩散均衡场中的振荡现象[J]. 物理学报, 2002, 51(4): 828−834. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2002.04.023Zhen Jiemin, Li Yushu. Oscillation phenomena in a thermohaline double-diffusive convection system[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2002, 51(4): 828−834. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2002.04.023 [16] 万伟, 屈玲, 周生启. 双扩散对流中台阶结构的实验研究[J]. 力学学报, 2014, 46(2): 217−223. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-13-230Wan Wei, Qu Ling, Zhou Shengqi. Laboratory studies on the staircase structure of double-diffusive convection[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2014, 46(2): 217−223. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-13-230 [17] Stern M E, Turner J S. Salt fingers and convecting layers[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1969, 16(5): 497−500. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(69)90038-2 [18] Linden P F. On the structure of salt fingers[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1973, 20(4): 325−332. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(73)90057-0 [19] Turner J S. The coupled turbulent transports of salt and and heat across a sharp density interface[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1965, 8(5): 759−760. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(65)90022-0 [20] Griffiths R W, J S Turner. The response of salt fingers to a spatially periodic shear[J]. Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 7027−7037. (查阅网上资料, 未找到文献信息, 请确认) [21] Sommer T, Carpenter J R, Schmid M, et al. Interface structure and flux laws in a natural double-diffusive layering[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(11): 6092−6106. doi: 10.1002/2013JC009166 [22] Sreenivas K R, Singh O P, Srinivasan J. On the relationship between finger width, velocity, and fluxes in thermohaline convection[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2009, 21(2): 026601. doi: 10.1063/1.3070527 [23] Turner J S. Salt fingers across a density interface[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1967, 14(5): 599−608. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(67)90066-6 [24] Turner J S. Salt fingers across a density interface[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1967, 14(5): 599−608. (查阅网上资料, 本条文献与第23条文献重复, 请确认) [25] McDougall T J, Taylor J R. Flux measurements across a finger interface at low values of the stability ratio[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1984, 42(1): 1−14. doi: 10.1357/002224084788506095 [26] Schmitt R W. Form of the temperature-salinity relationship in the Central Water: evidence for double-diffusive mixing[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1981, 11(7): 1015−1026. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1981)011<1015:FOTTSR>2.0.CO;2 [27] Merryfield W J. Origin of thermohaline staircases[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2000, 30(5): 1046−1068. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2000)030<1046:OOTS>2.0.CO;2 [28] Taylor J R, Veronis G. Experiments on double-diffusive sugar-salt fingers at high stability ratio[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1996, 321: 315−333. doi: 10.1017/S0022112096007744 [29] Griffithss R W, Ruddick B R. Accurate fluxes across a salt-sugar finger interface deduced from direct density measurements[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1980, 99(1): 85−95. doi: 10.1017/S0022112080000511 [30] 陈铂, 徐孝勤, 黄筱云, 等. 流体黏性对盐指型双扩散对流扩散通量影响的试验研究[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2024, 44(1): 16−22. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2024.01.003Chen Bo, Xu Xiaoqin, Huang Xiaoyun, et al. Experimental study on effect of fluid viscosity on salt-finger double diffusion convection flux[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2024, 44(1): 16−22. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2024.01.003 [31] Buckingham E. On physically similar systems; illustrations of the use of dimensional equations[J]. Physical Review, 1914, 4(4): 345−376. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.4.345 [32] Taylor J R, Veronis G. Experiments on double-diffusive sugar–salt fingers at high stability ratio[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1996, 321: 315−333. (查阅网上资料, 本条文献与第28条文献重复, 请确认) [33] Radko T, Stern M E. Salt fingers in three dimensions[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1999, 57(3): 471−502. (查阅网上资料, 本条文献与第3条文献重复, 请确认) [34] Fedorov K N. Layer thicknesses and effective diffusivities in "Diffusive" thermohaline convection in the ocean[J]. Elsevier Oceanography Series, 1988, 46: 471−479. [35] Kelley D E. Fluxes through diffusive staircases: a new formulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1990, 95(C3): 3365−3371. doi: 10.1029/JC095iC03p03365 -




 下载:
下载: