Response of tidal dynamics to geomorphic evolution and depositional effects in the Huanghe River Delta
-
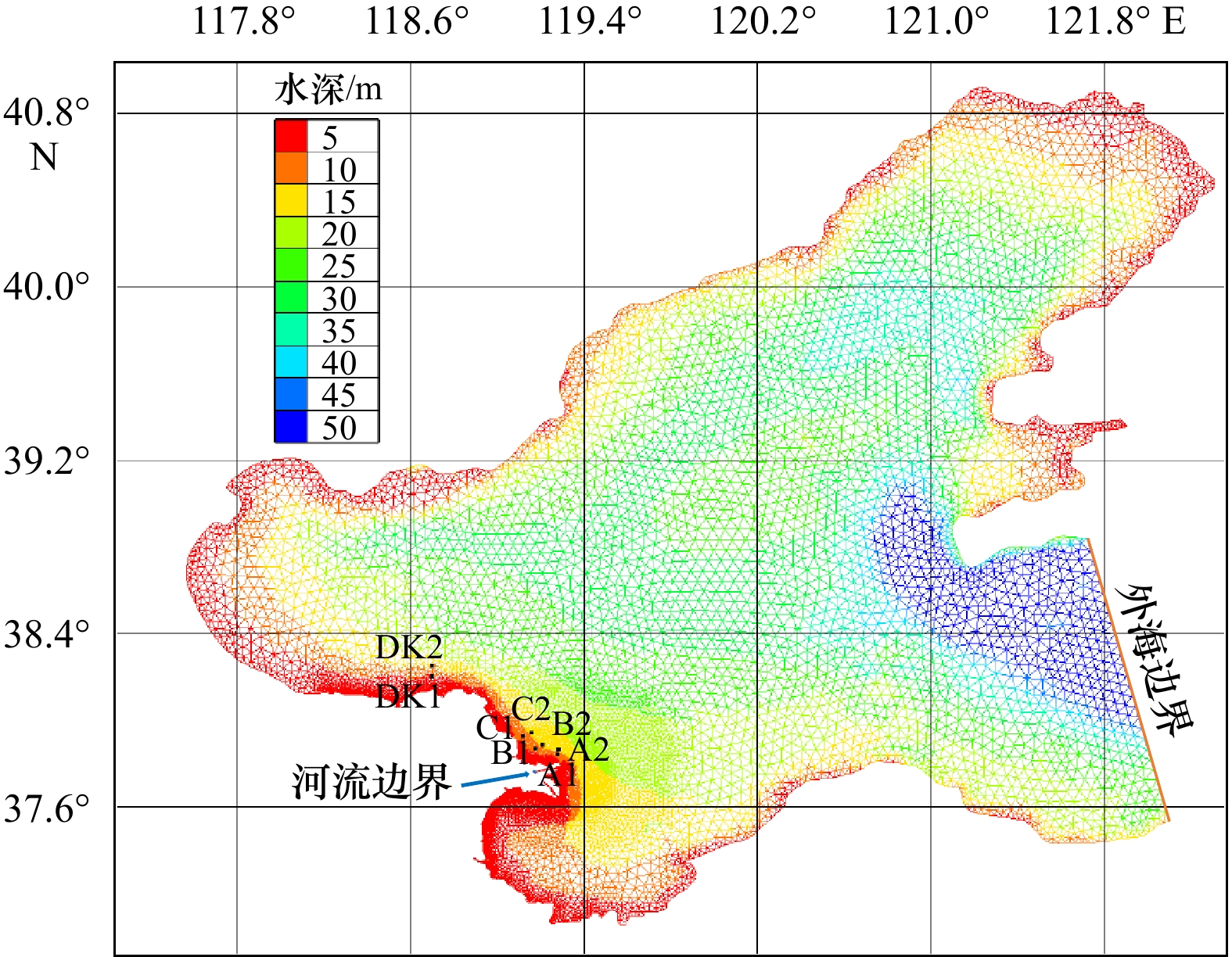
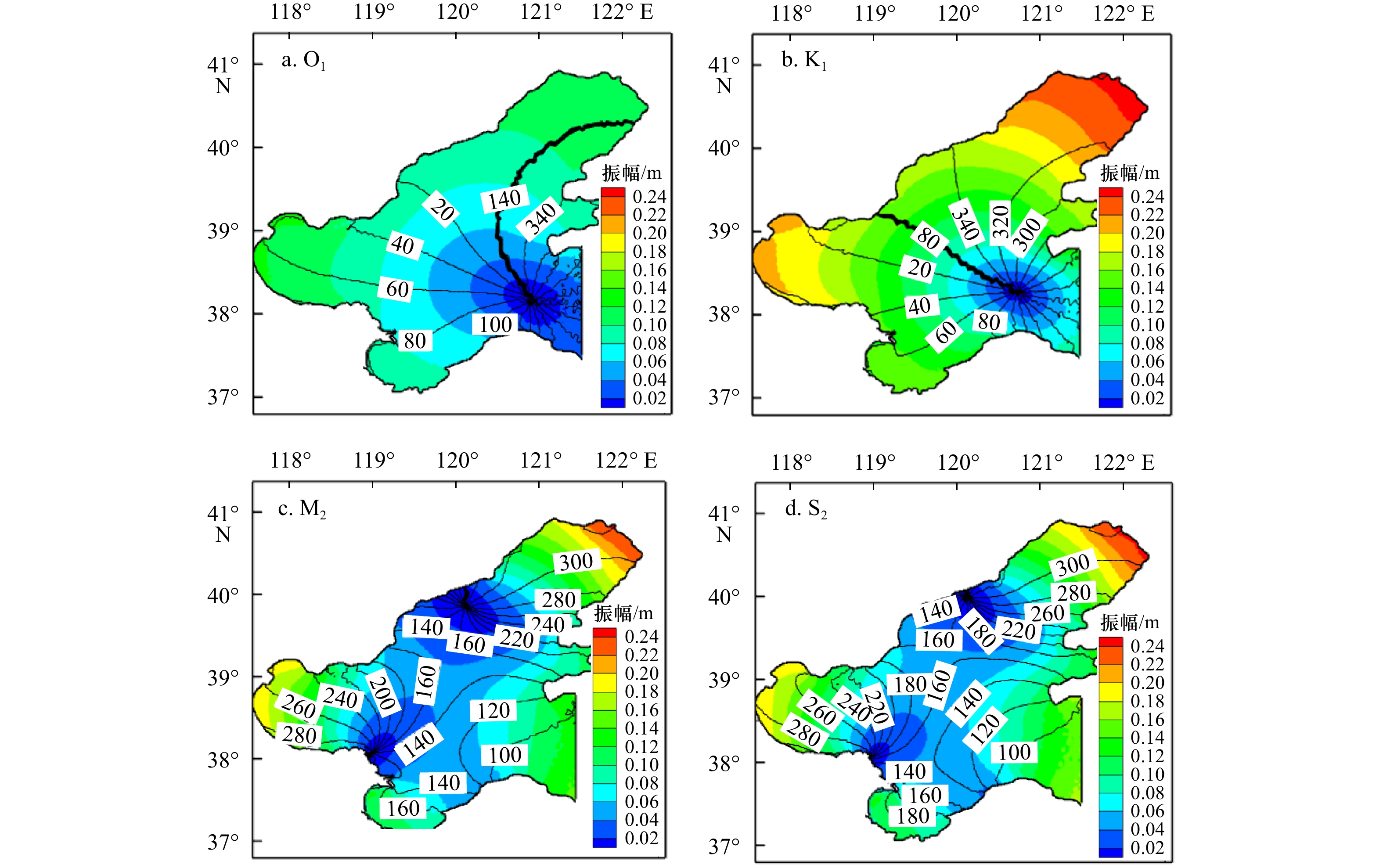
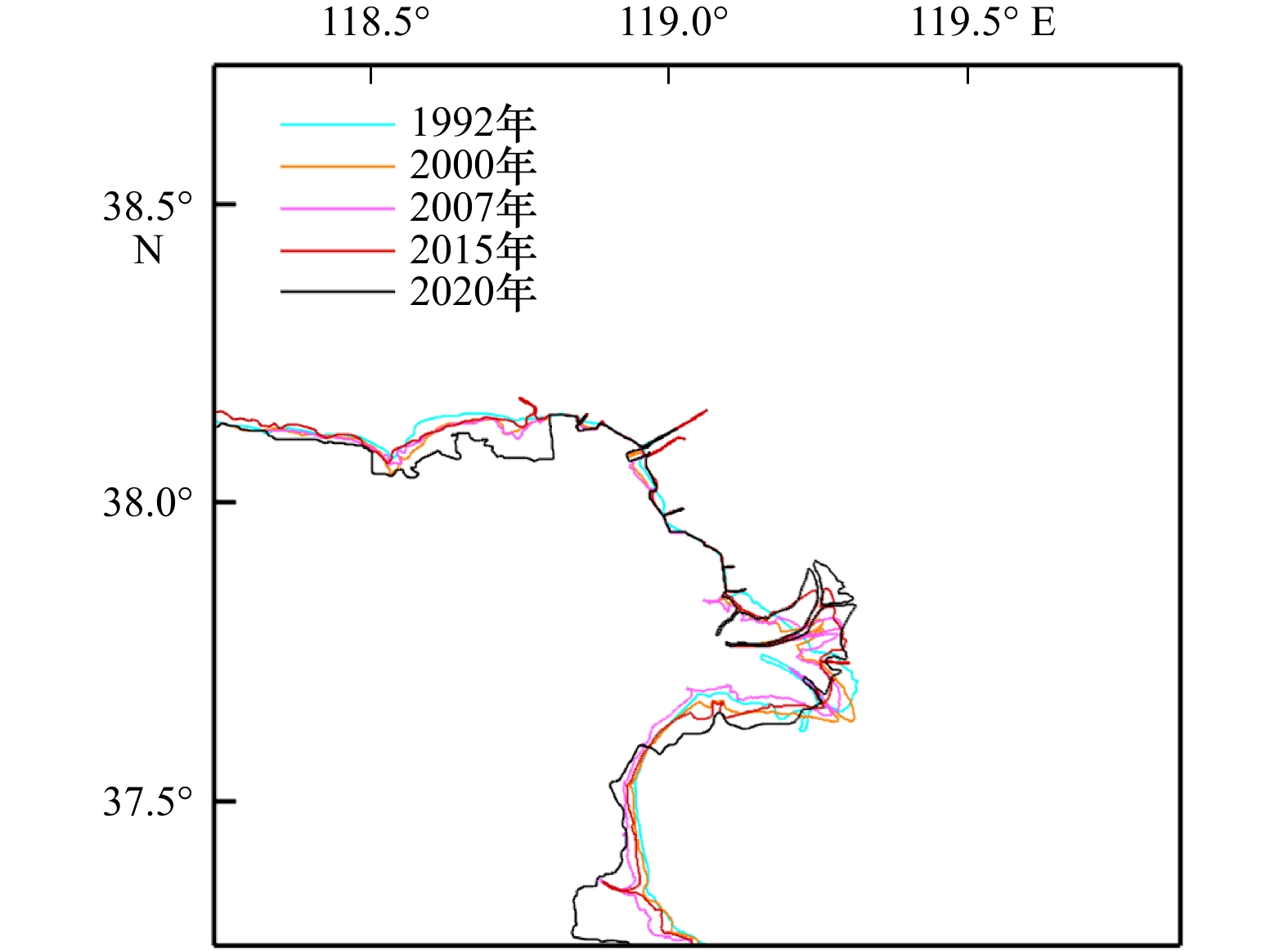
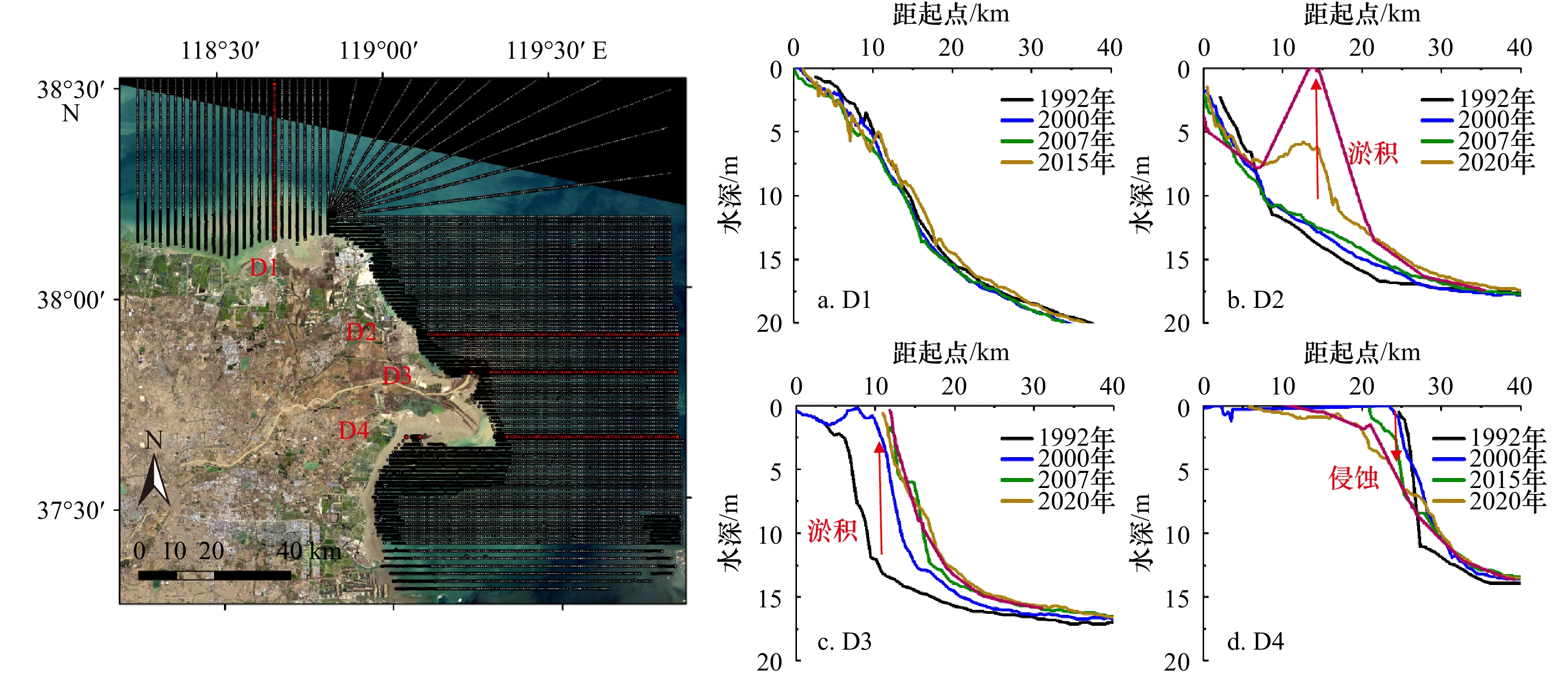
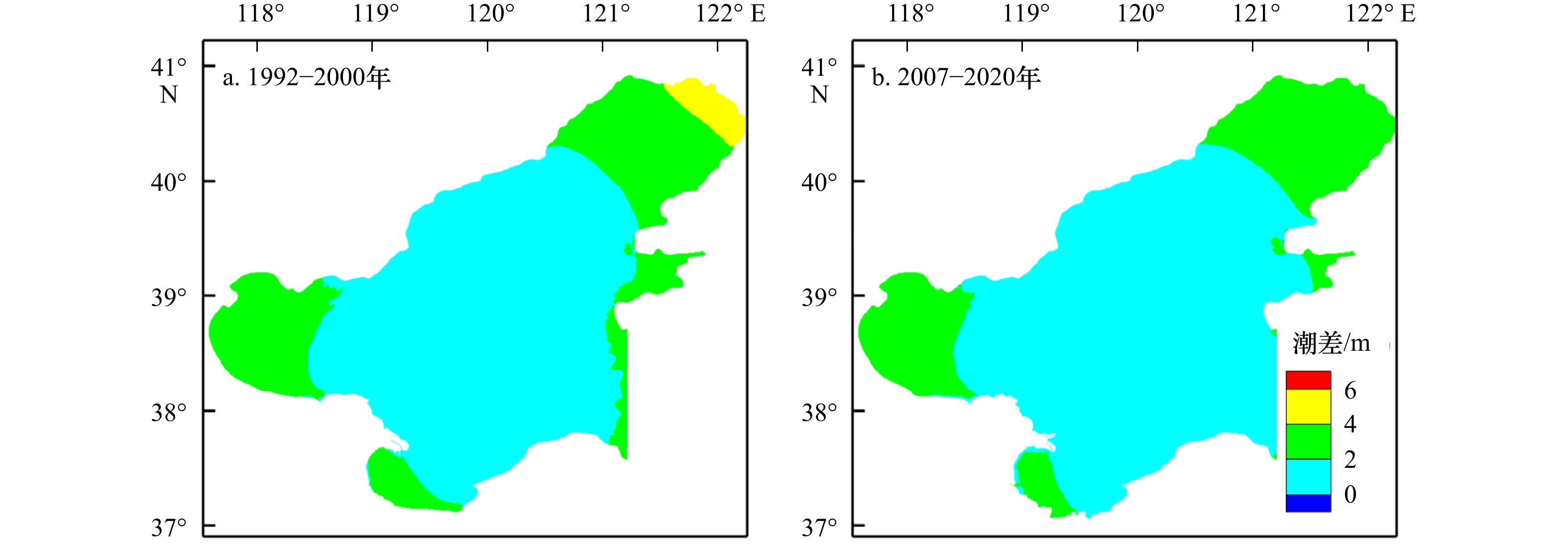
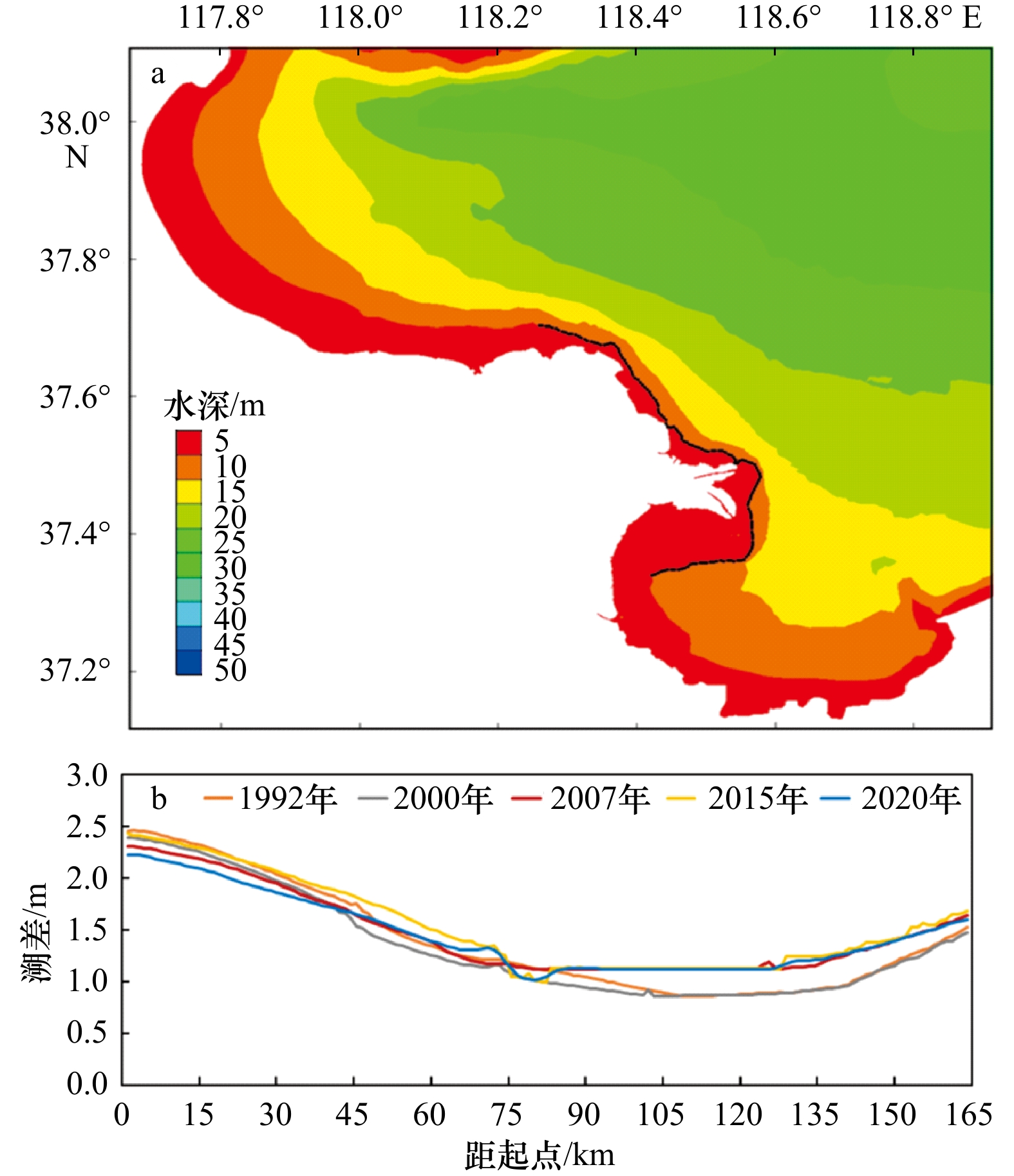
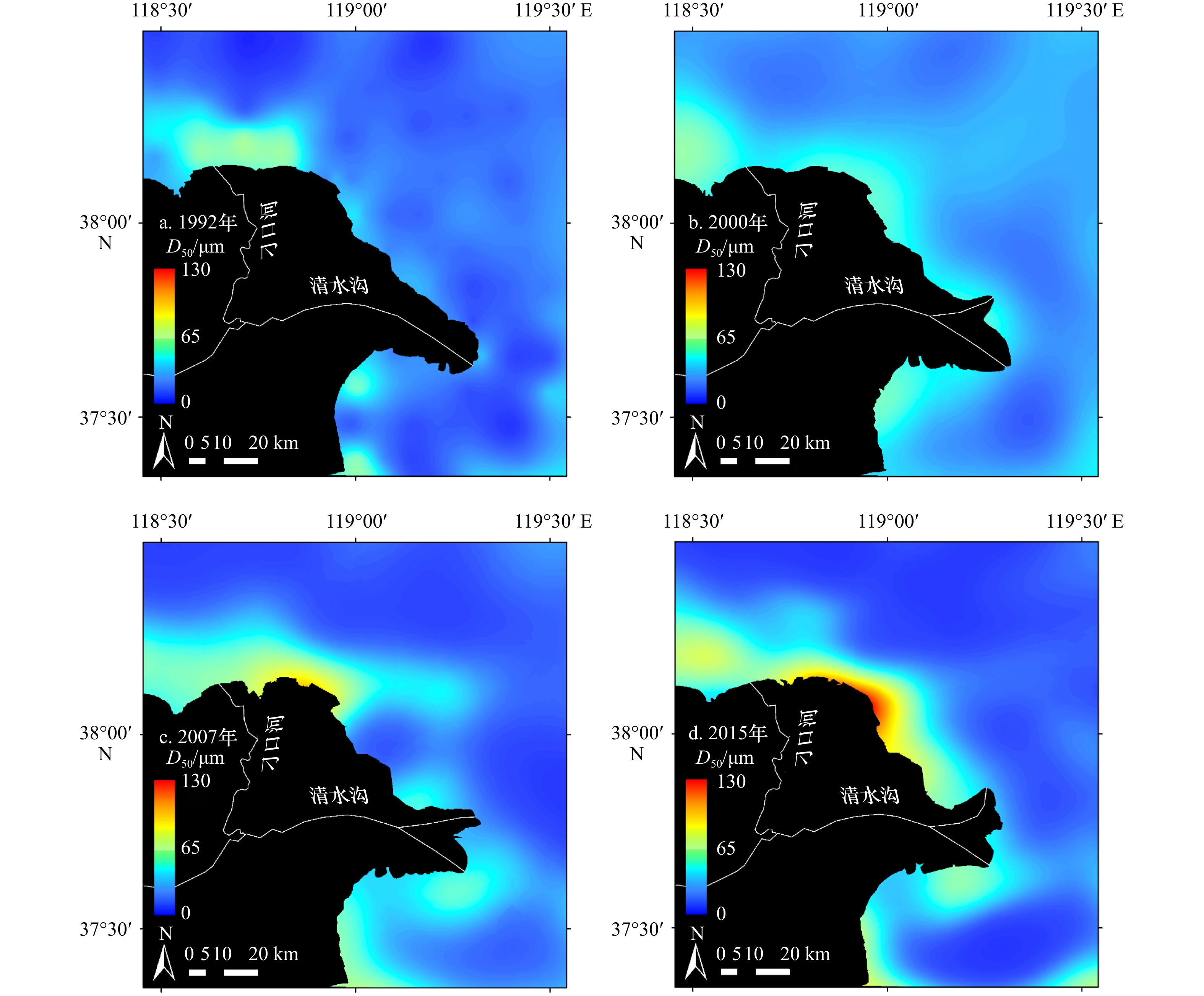
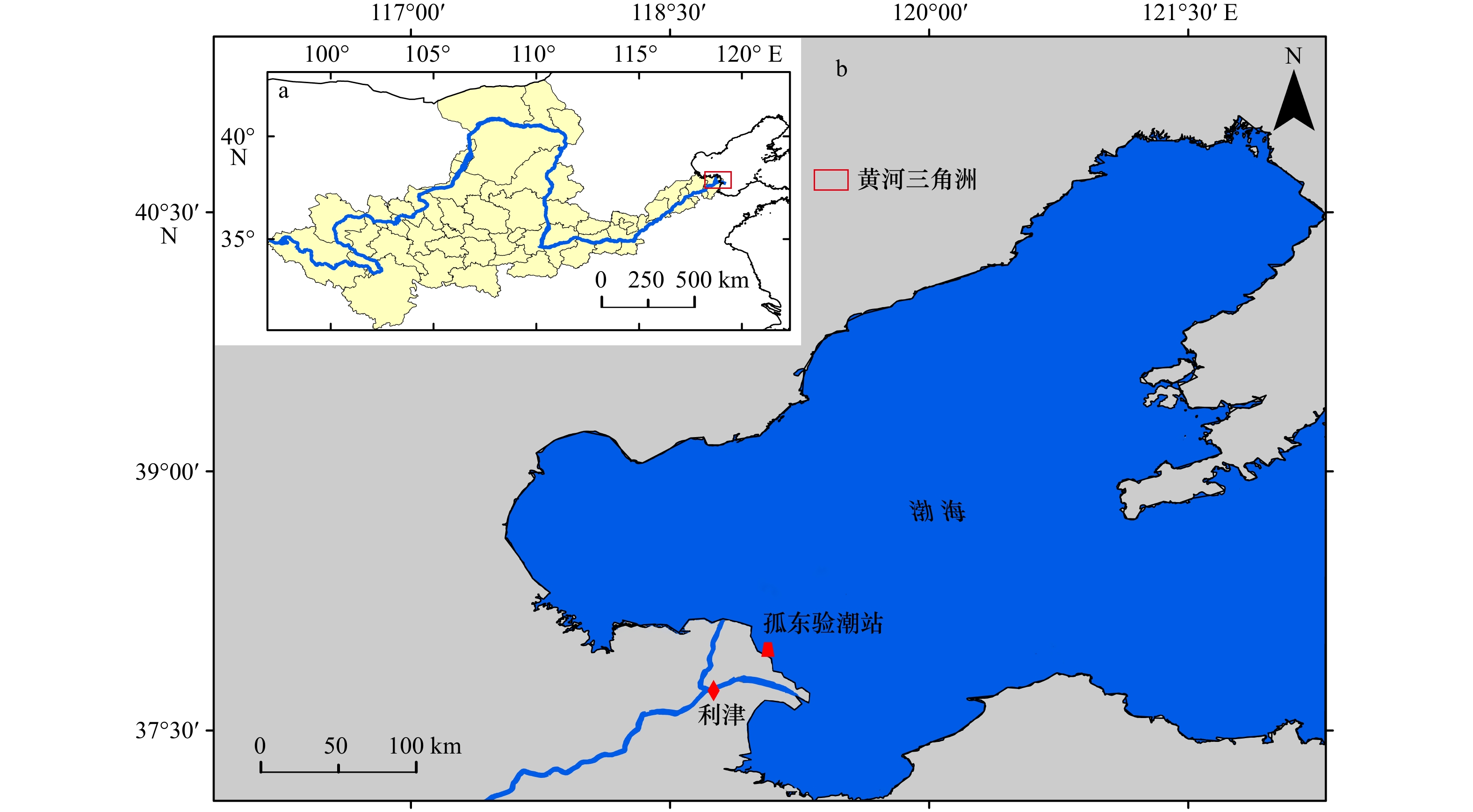
摘要: 近年来自然过程和人类活动显著改变了黄河入海流路以及近岸地貌格局,而剧烈的地貌演变对近岸水动力环境的影响尚未得到充分研究。为厘清近30年来黄河三角洲近岸水文动力格局对地貌演变的响应过程,本文基于Landsat系列遥感影像和多期测深数据,分析了1992–2020年黄河三角洲岸线和地形变化,并采用TELEMAC-2D建立了多套覆盖整个渤海的数值模型,研究了地貌演变对黄河三角洲邻近海域潮汐动力的影响及其沉积效应。结果表明,黄河三角洲近岸冲淤格局呈现显著的时空异质性,分布多个淤积和侵蚀中心,且2000–2020年南侧老清水沟外侵蚀中心向南移动9.6 km,1992–2015年北侧刁口河口外侵蚀中心东移6.4 km。中长时间尺度黄河三角洲岸线和地形变化主导了潮汐动态,三角洲北部刁口河口近岸潮差减小,清水沟河口外潮差增大,5 m水深处的潮差变化增大幅度达0.27 m;黄河口近岸K1分潮振幅显著增加,M2分潮振幅明显减小,东营港附近无潮点向东迁移3.8 km。刁口河口和老河口外高流速区持续减弱,现行河口外逐渐发育形成另一高流速区,持续稳定的高流速区造成了水下三角洲的冲刷,南北侧高流速区沉积物粗化。Abstract: In recent years, natural processes and human activities have significantly altered the Huanghe River channel and the coastal geomorphic pattern, while the impact of the dramatic geomorphic evolution on the coastal hydrodynamics has not been fully studied. Based on series images captured by the Landsat satellites and bathymetric measurements, this paper analyzed the shorelines and topography changes of the Huanghe River Delta from 1992 to 2020. Several sets of numerical models covering the entire Bohai Sea were established by TELEMAC-2D to investigate the response of tidal dynamics to geomorphic evolution and its depositional effects in the Huanghe River Delta. The results show that the erosion and deposition had significant spatial and temporal heterogeneity, and there were multiple siltation and erosion centers. The erosion center outside the old Qingshuigou Estuary moved 9.6 km to the south during 2000–2020, and the one outside the Diaokou Estuary moved 6.4 km to the east during 1992–2015. The tidal dynamics were dominated by the coastline and terrain changes on the medium and long time scales. The tidal range of the Diaokou estuary decreased, while the old and the new estuary increased. And the tidal range at 5 m depth had a maximum variation of 0.27 m. The K1 tidal amplitude increased significantly, while the M2 tidal amplitude was considerably reduced, and the amphidromic point near Dongying port eastward migration of 3.8 km. The high velocity outside the Diaokou Estuary and the old estuary continued to weaken, and another high velocity area gradually developed outside the current estuary. The continuous and stable high velocity area caused the erosion of the subaqueous delta and the coarsening of sediment.
-
表 1 卫星遥感影像和潮高
Tab. 1 List of different satellite date and tidal heights
编号 成像时间 卫星传感器 潮高/cm 编号 成像时间 传感器 潮高/cm 1 1992年8月24日 TM 95.30 11 2007年5月14日 TM 120.80 2 1992年9月25日 TM 112.95 12 2007年5月30日 TM 118.8 3 1992年11月12日 TM 62.30 13 2015年3月1日 OLI_TIRS 82.73 4 1992年12月14日 TM 38.55 14 2015年5月4日 OLI_TIRS 96.15 5 2000年2月4日 TM 85.75 15 2015年10月11日 OLI_TIRS 112.32 6 2000年2月20日 TM 74.00 16 2015年10月27日 OLI_TIRS 96.83 7 2000年3月7日 TM 67.00 17 2020年5月1日 OLI_TIRS 144.37 8 2000年4月8日 TM 93.20 18 2020年5月17日 OLI_TIRS 133.27 9 2007年2月7日 TM 52.00 19 2020年7月20日 OLI_TIRS 138.22 10 2007年3月11日 TM 70.00 20 2020年10月24日 OLI_TIRS 42.80 表 2 精度验证结果
Tab. 2 Results of accuracy verification
类型 非水体 水体 小计 用户精度 总体精度 Kappa系数 非水体 118 13 131 0.901 水体 4 109 113 0.965 小计 122 122 244 0.930 0.861 生产者精度 0.967 0.893 表 3 黄河水下三角洲冲淤体积和速率
Tab. 3 Erosion/accretion volumes and rates at the Huanghe River Subaqueous Delta
时间 淤积/% 侵蚀/% 淤积量/(108 m3) 侵蚀量/(108 m3) 净变化/(108 m3) 净变化率/(108m3·a−1) 1992−2000年 73 27 80.54 30.11 50.43 6.30 2000−2007年 15 85 16.61 94.26 −77.66 −11.09 2007−2015年 77 23 86.33 25.19 61.14 7.64 2015−2020年 31 69 10.50 23.80 −13.29 −2.66 -
[1] Arkema K K, Guannel G, Verutes G, et al. Coastal habitats shield people and property from sea-level rise and storms[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2013, 3(10): 913−918. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1944 [2] Konlechner T M, Kennedy D M, O’Grady J J, et al. Mapping spatial variability in shoreline change hotspots from satellite data; a case study in Southeast Australia[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 246: 107018. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107018 [3] Temmerman S, Meire P, Bouma T J, et al. Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7478): 79−83. doi: 10.1038/nature12859 [4] Pardo-Pascual J E, Almonacid-Caballer J, Ruiz L A, et al. Automatic extraction of shorelines from Landsat TM and ETM+ multi-temporal images with subpixel precision[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 123: 1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.02.024 [5] Jabaloy-Sánchez A, Lobo F J, Azor A, et al. Human-driven coastline changes in the Adra River deltaic system, Southeast Spain[J]. Geomorphology, 2010, 119(1/2): 9−22. [6] Dai Zhijun, Liu J T, Wei Wen, et al. Detection of the three gorges dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4(1): 6600. doi: 10.1038/srep06600 [7] Jiang Chao, Chen Shenliang, Pan Shuqi, et al. Geomorphic evolution of the Yellow River Delta: quantification of basin-scale natural and anthropogenic impacts[J]. CATENA, 2018, 163: 361−377. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.12.041 [8] Byun D S, Wang X H, Holloway P E. Tidal characteristic adjustment due to dyke and seawall construction in the Mokpo coastal zone, Korea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 59(2): 185−196. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2003.08.007 [9] Takekawa J Y, Woo I, Spautz H, et al. Environmental threats to tidal-marsh vertebrates of the San Francisco Bay Estuary[J]. Avian Biology, 2006, 32: 176−197. [10] Blum M D, Roberts H H. Drowning of the Mississippi Delta due to insufficient sediment supply and global sea-level rise[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(7): 488−491. doi: 10.1038/ngeo553 [11] Maloney J M, Bentley S J, Xu Kehui, et al. Mississippi River subaqueous delta is entering a stage of retrogradation[J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 400: 12−23. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.03.001 [12] 杨世伦, 朱骏, 李鹏. 长江口前沿潮滩对来沙锐减和海面上升的响应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2005, 23(2): 152−158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.02.005Yang Shilun, Zhu Jun, Li Peng. Response of tidal bank on the Changjiang River mouth forel and to drastic decline in riverine sediment supply and sea level rise[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2005, 23(2): 152−158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.02.005 [13] 郭磊城, 朱春燕, 何青, 等. 长江河口潮波时空特征再分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(6): 652−661.Guo Leicheng, Zhu Chunyan, He Qing, et al. Examination of tidal wave properties in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(6): 652−661. [14] 陈道信, 陈木永, 张弛. 围垦工程对温州近海及河口水动力的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37(4): 457−462.Chen Daoxin, Chen Muyong, Zhang Chi. Influence of reclamation projects on hydrodynamic force in offshore and estuary of Wenzhou[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 37(4): 457−462. [15] 陈沈良, 谷硕, 姬泓宇, 等. 新入海水沙情势下黄河口的地貌演变[J]. 泥沙研究, 2019, 44(5): 60−66.Chen Shenliang, Gu Shuo, Ji Hongyu, et al. Processes of the Yellow River Mouth on new water and sediment condition[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2019, 44(5): 60−66. [16] 杨洋, 陈沈良, 徐丛亮. 黄河口滨海区冲淤演变与潮流不对称[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(6): 13−25.Yang Yang, Chen Shenliang, Xu Congliang. Morphodynamics and tidal flow asymmetry of the Huanghe River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(6): 13−25. [17] Lu Jingfang, Zhang Yibo, Lü Xianqing, et al. The temporal evolution of coastlines in the Bohai Sea and its impact on hydrodynamics[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(21): 5549. doi: 10.3390/rs14215549 [18] 梁慧迪, 匡翠萍. 岸线变化及海平面上升对渤海潮波运动影响研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2021, 36(3): 462−470.Liang Huidi, Kuang Cuiping. Impacts of coastline changes and sea level rise on tides in the Bohai Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2021, 36(3): 462−470. [19] Zhang Lili, Shi Hongyuan, Xing Hao, et al. Analysis of the evolution of the Yellow River Delta coastline and the response of the tidal current field[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2023, 10: 1232060. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1232060 [20] 徐丛亮, 陈沈良, 陈俊卿. 新情势下黄河口出汊流路三角洲体系的演化模式[J]. 海岸工程, 2018, 37(4): 35−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2018.04.005Xu Congliang, Chen Shenliang, Chen Junqing. Evolution mode of channel bifurcation delta system at the Yellow River Estuary under the new situation[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2018, 37(4): 35−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2018.04.005 [21] 陈沈良, 张国安, 谷国传. 黄河三角洲海岸强侵蚀机理及治理对策[J]. 水利学报, 2004, 35(7): 1−6, 13.Chen Shenliang, Zhang Guoan, Gu Guochuan. Mechanism of heavy coastal erosion on Yellow River Delta and its countermeasures[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2004, 35(7): 1−6, 13. [22] 刘锋, 陈沈良, 周永东, 等. 黄河2009年调水调沙期间河口水动力及悬沙输移变化特征[J]. 泥沙研究, 2010, 35(6): 1−8.Liu Feng, Chen Shenliang, Zhou Yongdong, et al. Effect of water-sediment regulation in Yellow River on hydrodynamics and suspended sediment transport in its estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2010, 35(6): 1−8. [23] 李鹏, 陈沈良, 刘清兰, 等. 黄河尾闾沙洲及河口形态对水沙变化的响应[J]. 泥沙研究, 2022, 47(2): 57−64.Li Peng, Chen Shenliang, Liu Qinglan, et al. Responses of the processes in the Yellow River lowermost channel sandbars and estuary to the variation of water and sediment[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2022, 47(2): 57−64. [24] 苏国宾, 陈沈良, 徐丛亮, 等. 基于GF-1影像的黄河口潮滩高程定量反演[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(11): 1−9.Su Guobing, Chen Shenliang, Xu Congliang, et al. Quantitative retrival of tidal flat elevation with GF-1 images in the Yellow River Mouth[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(11): 1−9. [25] Jia Mingming, Wang Zongming, Mao Dehua, et al. Rapid, robust, and automated mapping of tidal flats in China using time series Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 255: 112285. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112285 [26] Ran Baichuan, Chen Shenliang, Pan Shunqi, et al. Impacts of sea-access roads on wetland landscape dynamics in the Yellow River Delta front[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2023, 244: 106834. [27] Ji Hongyu, Pan Shunqi, Chen Shenliang. Impact of river discharge on hydrodynamics and sedimentary processes at Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 425: 106210. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106210 [28] McLaren P, Bowles D. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1985, 55(4): 457−470. -




 下载:
下载: