The effect of sediment incipient motion characteristics on phosphorus concentration in water under the influence of xanthan
-
摘要: 泥沙所运载磷的是水域环境中重要的营养因子和生态因子,受沿海潮滩复杂水动力及泥沙表面所附着各类有机物的多重影响,潮滩泥沙具有复杂的运动过程,故探究有机质对泥沙运动和对磷的吸附过程的影响,可为沿海潮滩及近岸水域中磷的预测提供理论支撑。为研究有机质和泥沙起动特性对水体磷浓度的影响,选取黄原胶,通过泥沙起动-再悬浮-吸附实验和恒温振荡实验,探究了变化水流条件下,黄原胶对泥沙运动过程和泥沙吸附磷过程的影响。研究结果表明:1)黄原胶对床沙的起动过程具有明显的抑制作用,使床沙对起动切应力的抵抗能力提升约两倍;2)泥沙起动特性是影响床沙对水体中磷吸附作用的直接因素之一,当床沙开始大量起动后,水体中的磷浓度才开始出现明显变化;3)黄原胶本身对磷吸附作用几乎无影响,但可通过抑制床沙的起动过程进而抑制床沙对水体中磷的吸附作用。Abstract: The transport of phosphorus by suspended sediment plays a pivotal role as a nutrient and ecological factor in aquatic environments, particularly in the complex hydrodynamic and sedimentary settings of Jiangsu's coastal tidal flats, where diverse organic coatings on sediment surfaces further complicate sediment dynamics. Investigating the impact of organic matter on both sediment transport and phosphorus adsorption processes, therefore, is crucial for predicting phosphorus dynamics in coastal tidal flats and nearshore waters. To elucidate the influence of organic matter content and sediment initiation characteristics on aqueous phosphorus concentrations, this study employs xanthan as a model organic substance. Through sediment initiation-resuspension-adsorption experiments and constant-temperature oscillation tests, the study systematically examines how xanthan alters sediment mobility and phosphorus adsorption under varying flow conditions. The research findings are as follows: 1) Xanthan significantly impedes the initiation of sediment motion from the bed, enhancing the bed's resistance to erosive shear stress by approximately twofold. 2) Sediment initiation characteristics act as a direct determinant in the adsorption of phosphorus by the bed sediment, a marked increase in aqueous phosphorus concentration is observed only after substantial sediment initiation commences. 3) While xanthan itself has negligible direct impact on phosphorus adsorption, it indirectly suppresses phosphorus adsorption by the bed sediment through inhibiting sediment initiation.
-
Key words:
- fine sediment /
- hydrodynamic conditions /
- Xanthan /
- initiation /
- phosphorus
-
表 1 泥沙组分表
Tab. 1 Components of experimental sediment
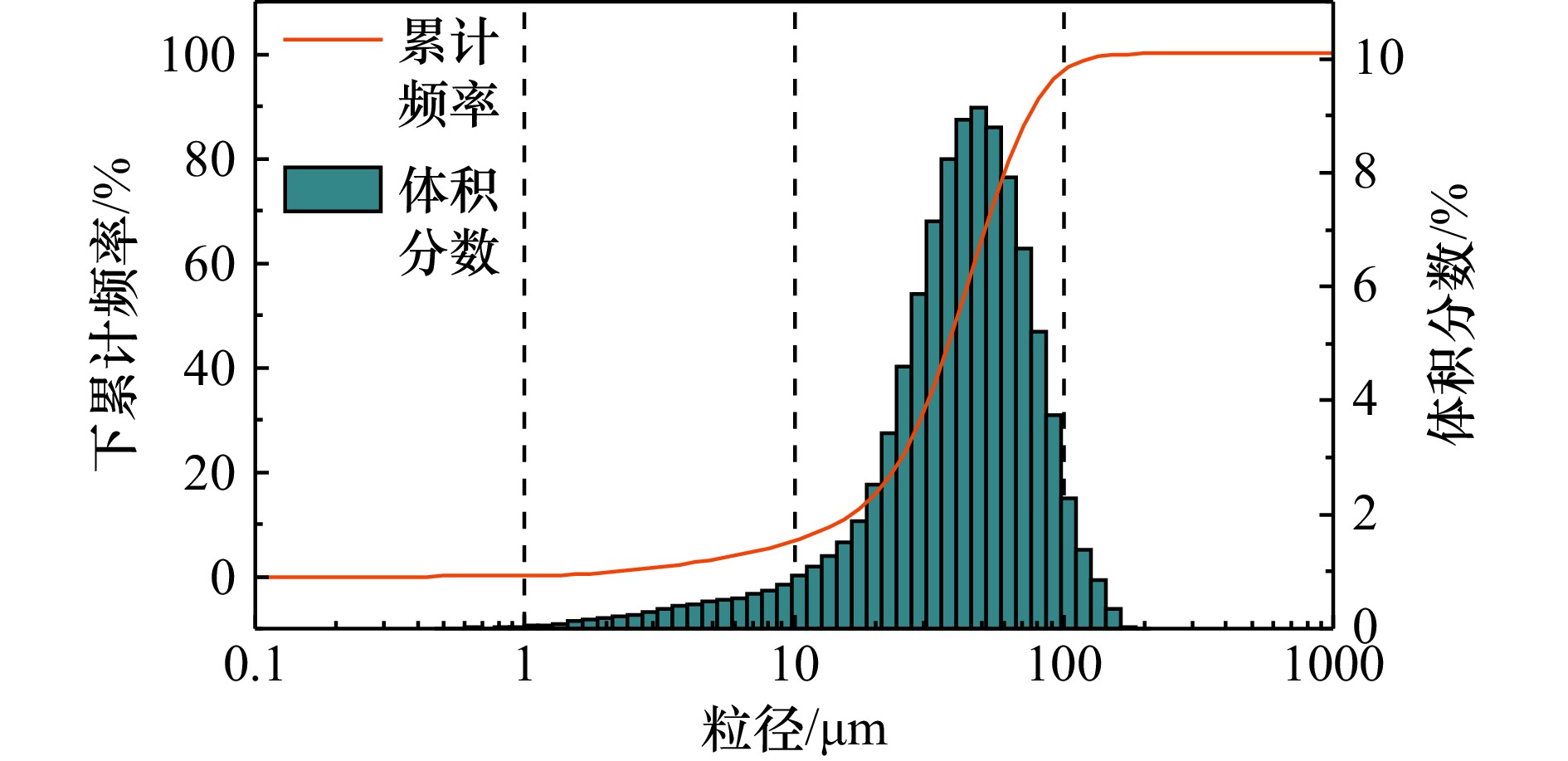
D10/μm D50/μm D90/μm 黏土/% 粉砂/% 砂粒/% 磷解吸量/mg/g 14.79 39.74 73.84 2.30 79.21 18.49 0.000 表 2 水动力测量参数设置表
Tab. 2 Parameters setup for hydrodynamic measurement
水动力等级 转速/rpm 周期/s 垂向剖面距边壁位置/cm 水平剖面距床底位置/cm 拍摄帧率/fps 1 42 0.714 5、10、15、20、25、30、35、
40、45、50、51、5710 1000 2 78 0.384 3 104 0.288 4 128 0.234 5 156 0.192 6 178 0.169 7 196 0.153 表 3 水动力测量参数设置表
Tab. 3 Parameters setup for hydrodynamic measurement
编号 磷浓度
mg/L泥沙浓度
g·L−1黄原胶含量
μg/g编号 磷浓度
mg/L泥沙浓度
g·L−1黄原胶含量
μg/gS1-0 0.5、1、2、3、
4、5、61 0 S10-0 2 10 0 S1-200 200 S10-200 2 10 200 S1-1000 2 1 1000 S10- 1000 2 10 1000 S1-2000 2 1 2000 S10-2000 2 10 2000 表 4 实验结果数据表
Tab. 4 Experimental results
时间
min水动力
等级切应力
Pa不含黄原胶组次 含黄原胶组次 总吸附量变化速率
平均值mg/20 min悬沙浓度变化速率
平均值g/(20 min·L)总吸附量变化速率
平均值mg/20 min悬沙浓度变化速率
平均值g/(20 min·L)0~120 min 一级 0.0023 0.030 0.000 0.016 −0.062 120~240 min 二级 0.0050 0.008 −0.075 0.027 0.040 240~3600 min 三级 0.0205 0.096 0.577 −0.003 0.125 360~480 min 四级 0.0356 0.355 2.602 0.074 0.060 480~600 min 五级 0.0759 0.950 7.667 0.014 0.775 600~720 min 六级 0.1685 0.336 1.665 1.019 6.657 720~840 min 七级 0.3119 0.161 0.298 0.582 3.422 -
[1] 关文海, 骆国辉, 王攀菲, 等. 嘉陵江总磷通量变化及空间来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2024, 44(3): 1448−1456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2024.03.027Guan Wenhai, Luo Guohui, Wang Panfei, et al. Variation of TP flux in Jialing River and spatial source apportionment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2024, 44(3): 1448−1456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2024.03.027 [2] 褚晓琳, 张皓玥. 基于生态系统的海岸带综合管理研究——以广东省湛江市为例[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2023, 45(6): 171−179.Chu Xiaolin, Zhang Haoyue. Ecosystem-based integrated coastal zone management: a case study of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2023, 45(6): 171−179. [3] Barbier E B, Hacker S D, Kennedy C, et al. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services[J]. Ecological Monographs, 2011, 81(2): 169−193. doi: 10.1890/10-1510.1 [4] 陈杰. 中国潮间带滩涂沉积物碳氮磷的埋藏特征[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2021.Chen Jie. The characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus burial in Chinese intertidal wetlands[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2021. [5] Yan Hong, Dai Zhijun, Li Jiufa, et al. Distributions of sediments of the tidal flats in response to dynamic actions, Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2011, 21(4): 719−732. doi: 10.1007/s11442-011-0875-0 [6] 尧印鹏, 许春阳, 陈永平, 等. 泥沙级配与成分对磷吸附作用影响试验研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2023, 48(6): 1−8.Yao Yinpeng, Xu Chunyang, Chen Yongping, et al. Experimental study on the effect of sediment gradation and component on phosphorus adsorption[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2023, 48(6): 1−8. [7] Cheng Xiaolong, Huang Yanan, Li Ran, et al. Impacts of water temperature on phosphorus release of sediments under flowing overlying water[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2020, 235: 103717. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103717 [8] Zhu Xian, Chen Yongping, Xu Chunyang, et al. The influence of turbulence on sediment phosphorus sorption[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2023, 258: 114955. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114955 [9] Nayak S, Takemi T. Statistical analysis of the characteristics of typhoons approaching Japan from 2006 to 2019[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2023, 14(1): 2208722. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2023.2208722 [10] 王一心, 潘毅, 周凤妍, 等. 江苏海域台风浪波高时空分布特性研究[J]. 海洋预报, 2023, 40(5): 23−34.Wang Yixin, Pan Yi, Zhou Fengyan, et al. Study on the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of typhoon wave height in Jiangsu coastal sea[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2023, 40(5): 23−34. [11] Xu Guohui, Sun Zhenhong, Fang Wenyan, et al. Release of phosphorus from sediments under wave-induced liquefaction[J]. Water Research, 2018, 144: 503−511. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.038 [12] 孙小静, 秦伯强, 朱广伟, 等. 持续水动力作用下湖泊底泥胶体态氮、磷的释放[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(6): 1223−1229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.06.010Sun Xiaojing, Qin Boqiang, Zhu Guangwei, et al. Release of colloidal N and P from sediment of lake caused by continuing hydrodynamic disturbance[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(6): 1223−1229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.06.010 [13] Wang Changhui, Wei Zhao, Shen Xinyi, et al. Particle size-related vertical redistribution of phosphorus (P)-inactivating materials induced by resuspension shaped P immobilization in lake sediment profile[J]. Water Research, 2022, 213: 118150. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118150 [14] Xiao Yang, Cheng Haoke, Yu Weiwei, et al. Effects of water flow on the uptake of phosphorus by sediments: an experimental investigation[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2016, 28(2): 329−332. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60636-4 [15] 龚政, 文天翼, 靳闯, 等. 江苏中部潮滩湿地土壤有机碳分布特征及影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(11): 2978−2984.Gong Zheng, Wen Tianyi, Jin Chuang, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in tidal flat wetland of central Jiangsu, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(11): 2978−2984. [16] Donlan R M. Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2002, 8(9): 881−890. doi: 10.3201/eid0809.020063 [17] 陈益山. 细颗粒泥沙生物膜生长及对吸附与解吸影响的实验研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2017.Chen yishan. Experiment on biofilm growth of cohesive sediment and effect on adsorption or desorption[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017. [18] 龚政, 陈欣迪, 周曾, 等. 生物作用对海岸带泥沙运动的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(1): 53−62. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0291Gong Zheng, Chen Xindi, Zhou Zeng, et al. The roles of biological factors in coastal sediment transport: a review[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(1): 53−62. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0291 [19] Costerton J W, Cheng K J, Geesey G G, et al. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 1987, 41: 435−464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251 [20] Flemming H C, Wingender J. The biofilm matrix[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8(9): 623−633. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2415 [21] Turner A, Hyde T L, Rawling M C. Transport and retention of hydrophobic organic micropollutants in estuaries: implications of the particle concentration effect[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1999, 49(5): 733−746. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1999.0519 [22] Pan G, Liss P S, Krom M D. Particle concentration effect and adsorption reversibility[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1999, 151(1/2): 127−133. [23] Judge P K, Sundberg E, DeGroot D J, et al. Effects of biopolymers on the liquid limit and undrained shear strength of soft clays[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81(8): 342. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02830-9 [24] Kwon Y M, Moon J H, Cho G C, et al. Xanthan gum biopolymer-based soil treatment as a construction material to mitigate internal erosion of earthen embankment: a field-scale[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 389: 131716. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131716 [25] Wang Qingren, Li Yuncong. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption behavior on sediments of different origins[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2010, 10(6): 1159−1173. doi: 10.1007/s11368-010-0211-9 [26] 国家环境保护总局. GB 11893-1989, 水质 总磷的测定 钼酸铵分光光度法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1991.GB 11893-1989, Water quality-Determination of total phosphorus-Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometric method[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1991. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献作者翻译和年份, 请确认) [27] 中华人民共和国水利部. SL 42-2010, 河流泥沙颗粒分析规程[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2010.Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. SL 42-2010, Technical standard for determination of sediment particle size in open channels[S]. Beijing: China Water&Power Press, 2010. [28] Chen X D, Zhang C K, Paterson D M, et al. Hindered erosion: the biological mediation of noncohesive sediment behavior[J]. Water Resources Research, 2017, 53(6): 4787−4801. doi: 10.1002/2016WR020105 [29] Soulsby R L. The bottom boundary layer of shelf seas[M]//Elsevier Oceanography Series. New York: Elsevier, 1983: 189-266. [30] Bordi F, Cametti C, Paradossi G. Counterion condensation in xanthan aqueous solutions in the semidilute and concentrated regime[J]. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie, 1996, 100(6): 881−884. [31] Wang Shiyu, Vogt R D, Carstensen J, et al. Riverine flux of dissolved phosphorus to the coastal sea may be overestimated, especially in estuaries of gated rivers: implications of phosphorus adsorption/desorption on suspended sediments[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 132206. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132206 [32] Pan Gang, Liss P S. Metastable-equilibrium adsorption theory: I. theoretical[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1998, 201(1): 71−76. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1998.5396 -




 下载:
下载:








