Transcriptome analysis of liver of juvenile cobia under low temperature stress
-
摘要: 为研究低温胁迫对军曹鱼幼鱼的影响,将军曹鱼幼鱼饲养于常温(30.5±1.0℃)和低温(20.0±0.5℃)7 d后对军曹鱼肝脏进行有参转录组测序,每组3个生物学重复。结果显示,6个测序样品共检测到约243 694 134个raw reads,所有样品Q30%均超过94%,GC%在47.65%-48.16%范围内。共筛选出4 362个差异表达基因,其中2 793个基因上调,1 569个基因下调。KEGG通路富集分析结果显示,在脂质代谢中,大量差异基因富集在脂代谢过程、脂质生物合成过程、甘油磷脂代谢过程、磷脂代谢过程和甘油脂代谢过程等生物过程中, PPAR信号通路中PPARα、PPARβ、SCD-1、CPT-1和CPT-2等多个脂代谢相关基因对军曹鱼幼鱼应对低温胁迫具有关键作用;在糖代谢中,大量基因富集于糖酵解/糖异生、半乳糖代谢、淀粉和蔗糖代谢、戊糖和葡萄糖醛酸酯的相互转化等生物过程,其中G6PC、ENO等基因在军曹鱼幼鱼应对低温胁迫时发挥重要调节作用。Abstract: In order to systematically study the effect of low temperature stress on the lipid metabolism of cobia juvenile, cobia juveniles were raised at normal temperature (30.5±1.0℃) and low temperature (20.0±0.5℃) for 7 days, and then the cobia livers were sequenced with genome-based transcriptome, and there were 3 biological replicates in each group. The research results show that a total of 243,694,134 row reads were found in 6 sequencing samples. The Q30% of all samples exceeded 94%, and the GC% was in the range of 47.65%-48.16%. A total of 4,362 differentially expressed genes were screened, of which 2,793 genes were up-regulated, and 1,569 genes were down-regulated. In terms of lipid metabolism, A large number of differential genes are enriched in biological processes such as lipid metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, glycerophospholipid metabolism, phospholipid metabolism and glycerideid metabolism, and also found that multiple lipid metabolism-related genes in the PPAR signaling pathway, such as PPARα, PPARβ, SCD-1, CPT-1, and CPT-2 play a key role in cobia juvenile under low temperature stress. In terms of glucose metabolism, a great many of genes are enriched in biological processes such as glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, galactose metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, and pentose and glucuronate interconversions. Notably, genes such as G6PC and ENO play crucial regulatory roles in the response of cobia juvenile to low temperature stress.
-
Key words:
- low temperature stress /
- Rachycentron canadum /
- transcriptome /
- lipid metabolism /
- glucose metabolism
-
图 2 富集前20的GO terms
注:第一圈:富集前20的GOterm,圈外为基因数目的坐标尺,不同的颜色代表不同的Ontology;第二圈:背景基因中该GOterm的数目以及Q值,基因越多条形越长,Q值越小颜色越红;第三圈:上下调基因比例条形图,深紫色代表上调基因比例,浅紫色代表下调基因比例,下方显示具体的数值;第四圈:各GOterm的RichFactor值(该GOterm中差异基因数量除以所有数量),背景网格线每一格代表0.1。
Fig. 2 The first 20 enriched GO terms
Note: The first circle: the first 20 enriched GO terms, outside the circle is the coordinate ruler of gene number, and different colors represent different Ontology; The second circle: the number and Q value of the GOterm in the background gene, the more genes, the longer the bars, and the smaller the Q value, the redder the color; The third circle: bar chart of the proportion of up and down genes, dark purple represents the proportion of up genes, light purple represents the proportion of down genes, and specific values are displayed below; The fourth circle: RichFactor value of each GOterm (the number of differential genes in the GOterm divided by all the numbers), and each grid line of the background represents 0.1.
图 4 PPAR信号通路图
注:红色框线表示:该框中的基因对比对照组,表达上调;绿色框线表示:该框中的基因对比对照组,表达下调;红-绿框线表示:该框中的基因对比对照组,部分表达上调,部分下调。
Fig. 4 PPAR signaling pathway
Note:The red box indicates that the genes in this box are up-regulated compared with the control group; the green box indicates that the genes in this box are down-regulated compared with the control group; the red-green box indicates that some genes in this box are up-regulated and some are down-regulated compared with the control group.
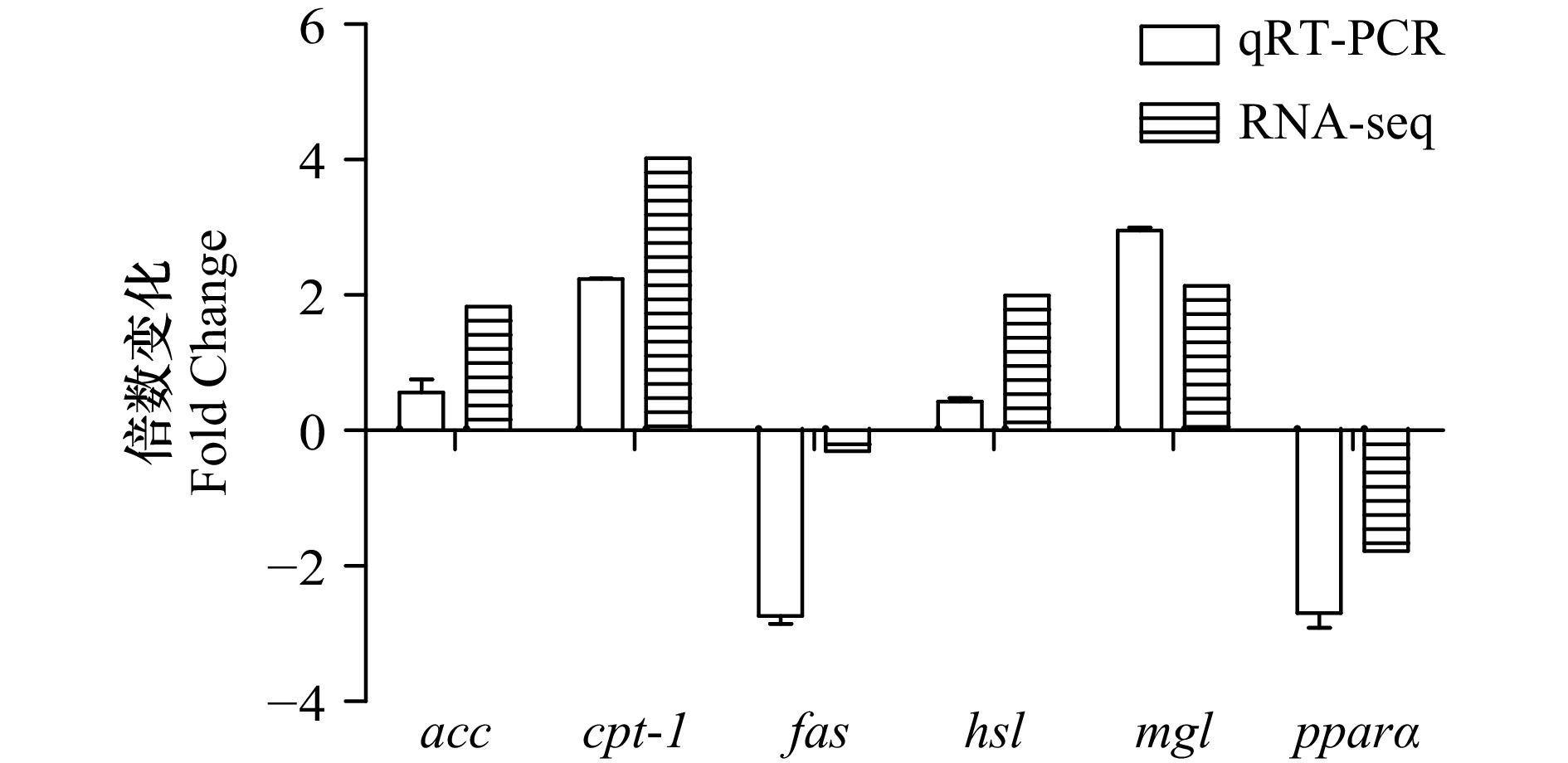
表 1 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
Tab. 1 Primer sequences of genes used for RT-qPCR
基因名称
Gene name基因编号
Gene ID上游引物(5′-3′)
Forward primer(5′-3′)下游引物(5′-3′)
Reverse primer(5′-3′)ACC Rca011875 TCGCCAGTCTCCCAACTCCTAT ACCTGTCCACCTCCTCCTTCAT FAS Rca019519 AGCATCCTGTATCGCCCGTTTGA GTCGGTCCTGTGGGTCTCCTTGT HSL Rca015361 AGCAGTCTGGTTTGGGTTTGGC AGGTTCTGGGTAATGCGTTCA CPT-1 Rca009591 TACCGCTTGGCTATGACTGGAC TTGCTGGAGATGTGGAAGTTGATG MGL Rca013017 CACTGCGACCTTTGACCTCTTTG AACCATCCTTCTGGGCGTAATC PPARα Rca010067 GAGTTCTCATCTTCCTCCTCATCGC GGCACTTGTTGCGGTTCTTCTTT β-actin GU584189 AGGGAAATTGTGCGTGAC AGGCAGCTCGTAGCTCTT 缩写:ACC,acetyl-CoA carboxylase,乙酰辅酶A羧化酶;FAS,fatty acid synthase,脂肪酸合成酶;HSL,hormone-sensitive triglyceride lipase,激素敏感性脂肪酶;CPT-1,carnitine palmityl transferase Ⅰ,肉碱脂酰转移酶Ⅰ;MGL,monoacylglycerol lipase,单酰甘油脂肪酶;PPARα,peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor,过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α。 表 2 样品过滤后测序质量评估统计表
Tab. 2 Statistical table of sequencing quality evaluation after sample filtering
处理 样品 RawDatas CleanData(%) CleanData(bp) GC(%) Q20(%) Q30(%) 对照 GC-1 41052194 40443694 (98.52%)6033805581 47.91% 98.36% 94.96% GC-2 39405242 38872552 (98.65%)5802795648 47.66% 98.24% 94.66% GC-3 38277454 37694004 (98.48%)5623819502 48.03% 98.30% 94.85% 低温 LG-1 41764832 41190146 (98.62%)6148615460 47.65% 98.23% 94.74% LG-2 42025156 41532498 (98.83%)6206078195 47.94% 98.19% 94.63% LG-3 41169256 40660388 (98.76%)6075783071 48.16% 98.33% 94.90% 表 3 测序结果比对基因组情况统计表
Tab. 3 Statistics table of sequencing results compared to the genome
处理 样品 Unmapped(%) Unique_Mapped(%) Multiple_Mapped(%) Total_Mapped(%) 对照 GC-1 2505363 (6.20%)35435211 (87.67%)2477732 (6.13%)37912943 (93.80%)GC-2 2677482 (6.89%)34013307 (87.56%)2154317 (5.55%)36167624 (93.11%)GC-3 2784477 (7.39%)32773501 (87.02%)2103880 (5.59%)34877381 (92.61%)低温 LG-1 2918520 (7.10%)36014174 (87.60%)2177240 (5.30%)38191414 (92.90%)LG-2 2690715 (6.49%)36329768 (87.62%)2440121 (5.89%)38769889 (93.51%)LG-3 2159254 (5.32%)35571430 (87.60%)2875492 (7.08%)38446922 (94.68%)表 4 脂代谢相关生物过程及通路的差异基因富集分析
Tab. 4 Differential gene enrichment analysis of lipid metabolism-related biological processes and pathways
数据库 database 功能/通路
Function/Access基因数
genes number编号
IDGO 脂质代谢过程 lipid metabolic process 294 GO:0006629 细胞脂质代谢过程 cellular lipid metabolic process 218 GO:0044255 脂质生物合成过程 lipid biosynthetic process 82 GO:0008610 细胞脂质分解代谢过程 cellular lipid catabolic process 26 GO:0044242 脂质分解代谢过程 lipid catabolic process 30 GO:0016042 中性脂质代谢过程 neutral lipid metabolic process 38 GO:0006638 脂质稳态 lipid homeostasis 23 GO:0055088 脂质定位 lipid localization 60 GO:0010876 蛋白-脂质复合物亚基组织 protein-lipid complex subunit organization 11 GO:0071825 脂质贮藏的积极调节 positive regulation of lipid storage 7 GO:0010884 脂质储存的调节 regulation of lipid storage 14 GO:0010883 脂质储存 lipid storage 15 GO:0019915 脂质代谢过程的正向调节 positive regulation of lipid metabolic process 13 GO:0045834 脂代谢过程调节 regulation of lipid metabolic process 55 GO:0019216 甘油脂代谢过程 glycerolipid metabolic process 79 GO:0046486 磷脂代谢过程 phospholipid metabolic process 82 GO:0006644 脂质转运 lipid transport 48 GO:0006869 脂质过氧化氢反应 response to lipid hydroperoxide 2 GO:0006982 KEGG 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis 16 ko00100 脂肪酸降解 Fatty acid degradation 25 ko00071 类固醇激素的合成 Steroid hormone biosynthesis 24 ko00140 初级胆汁酸生物合成 Primary bile acid biosynthesis 11 ko00120 脂肪酸生物合成 Fatty acid biosynthesis 10 ko00061 花生四烯酸代谢 Arachidonic acid metabolism 19 ko00590 表 5 糖代谢相关生物过程及通路的差异基因富集分析
Tab. 5 Differential gene enrichment analysis of glucose metabolism-related biological processes and pathways
数据库
database功能/通路
Function/Access基因数
genes number编号
IDGO 单糖代谢过程 monosaccharide metabolic process 78 GO:0005996 己糖代谢过程 hexose metabolic process 71 GO:0019318 KEGG 糖酵解/糖异生 Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis 30 ko00010 半乳糖代谢 Galactose metabolism 15 ko00052 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism 16 ko00500 戊糖和葡萄糖醛酸酯的相互转化 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions 17 ko00040 -
[1] 张宇航, 高扬, 李文红, 等. 低温停食和复温后投喂频率对奥尼罗非鱼幼鱼生长的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(9): 2125−2131.Zhang Yuhang, Gao Yang, Li Wenhong, et al. Effects of feeding frequency after food deprivation with low temperature and rewarming on growth of hybrid tilapia juvenile (Oreochromis niloticus×O. aureus)[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(9): 2125−2131. [2] Li A J, Leung P T Y, Bao V W W, et al. Temperature-dependent physiological and biochemical responses of the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma with consideration of both low and high thermal extremes[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2015, 54: 98−105. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2014.09.011 [3] He Jie, Qiang Jun, Yang Hong, et al. Changes in the fatty acid composition and regulation of antioxidant enzymes and physiology of juvenile genetically improved farmed tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L. ), subjected to short-term low temperature stress[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2015, 53: 90−97. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2015.08.010 [4] Sun Zhenzhu, Tan Xiaohong, Liu Qingying, et al. Physiological, immune responses and liver lipid metabolism of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) under cold stress[J]. Aquaculture, 2019, 498: 545−555. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.08.051 [5] Mininni A N, Milan M, Ferraresso S, et al. Liver transcriptome analysis in gilthead sea bream upon exposure to low temperature[J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 765. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-765 [6] Gracey A Y, Fraser E J, Li Weizhong, et al. Coping with cold: an integrative, multitissue analysis of the transcriptome of a poikilothermic vertebrate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(48): 16970−16975. [7] Zhou Tao, Gui Lang, Liu Mingli, et al. Transcriptomic responses to low temperature stress in the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2019, 84: 1145−1156. [8] 文鑫. 暗纹东方鲀(Takifugu fasciatus)应对低温胁迫的生理响应和分子机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2019.Wen Xin. Physiological responses and molecular mechanisms of the pufferfish (Takifugu fasciatus) to low-temperature stress[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2019. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献英文信息, 请确认) [9] 王维政, 曾泽乾, 黄建盛, 等. 低氧胁迫对军曹鱼幼鱼抗氧化、免疫能力及能量代谢的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2020, 40(5): 12−18.Wang Weizheng, Zeng Zeqian, Huang Jiansheng, et al. Effects of hypoxia stress on antioxidation, immunity and energy metabolism of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2020, 40(5): 12−18. [10] 刘生茂. 微量样本的高通量RNASeq方法研究和应用[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017.Liu Shengmao. Research and application of high throughput RNASeq method for micro sample[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017. [11] Tocher D R. Metabolism and functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish[J]. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 2003, 11(2): 107−184. doi: 10.1080/713610925 [12] 林超, 柳军, 孙宏斌. 脂质生物合成的转录调控、相关靶标确证及新药发现[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2015, 45(9): 923−936. doi: 10.1360/N032015-00114Lin Chao, Liu Jun, Sun Hongbin. Transcriptional regulation of lipid biosynthesis, related target validation and drug discovery[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Chimica, 2015, 45(9): 923−936. doi: 10.1360/N032015-00114 [13] 高正松, 王保成, 徐松泉, 等. 磷脂的合成研究进展[J]. 广州化工, 2020, 48(19): 1−6.Gao Zhengsong, Wang Baocheng, Xu Songquan, et al. Research progress on the synthesis of phospholipids[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2020, 48(19): 1−6. [14] Leather S R, Walters K F A, Bale J S. The Ecology of Insect Overwintering[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1993. [15] Qian Baoying, Xue Liangyi. Liver transcriptome sequencing and de novo annotation of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthy crocea) under heat and cold stress[J]. Marine Genomics, 2016, 25: 95−102. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2015.12.001 [16] Streck G. Chemical and biological analysis of estrogenic, progestagenic and androgenic steroids in the environment[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 28(6): 635−652. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2009.03.006 [17] 李鑫, 杨蕊, 臧强, 等. 糖皮质激素的药理作用机制研究进展[J]. 国际药学研究杂志, 2009, 36(1): 27−30.Li Xin, Yang Rui, Zang Qiang, et al. Pharmacological actions of glucocorticoids: progress in mechanisms[J]. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research, 2009, 36(1): 27−30. [18] Bernier N J, Van Der Kraak G, Farrell A P, et al. Fish Physiology[M]//Bernier N J, Van Der Kraak G, Farrell A P, et al. Fish Neuroendocrinology. Salt Lake City: Academic Press, 2009: 235−311. [19] Bernier N J, Peter R E. The hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal axis and the control of food intake in teleost fish[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2001, 129(2/3): 639−644. [20] 马瑶, 程海东. PPAR基因多态性的研究进展[J]. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2007, 15(9): 6−9.Ma Yao, Cheng Haidong. Research advances in PPAR genetic polymorphisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Birth Health & Heredity, 2007, 15(9): 6−9. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献英文信息, 请确认) [21] 钱伦, 钱云霞, 童丽娟. 大黄鱼PPAR β全长cDNA的克隆和组织表达[J]. 生物学杂志, 2010, 27(6): 1−4.Qian Lun, Qian Yunxia, Tong Lijuan. Cloning of full-length cDNA and RT-PCR expression analysis of PPAR β in Larimichthys crocea[J]. Journal of Biology, 2010, 27(6): 1−4. [22] 徐世文, 樱桃, 李术. PPAR-γ功能的研究进展[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2011, 42(9): 1−6.Xu Shiwen, Ying Tao, Li Shu. Advance on PPAR-γ function[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2011, 42(9): 1−6. [23] Tsai M L, Chen H Y, Tseng M C, et al. Cloning of peroxisome proliferators activated receptors in the cobia (Rachycentron canadum) and their expression at different life-cycle stages under cage aquaculture[J]. Gene, 2008, 425(1-2): 69−78. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.08.004 [24] 蔡润佳, 张静, 黄建盛, 等. 低温胁迫对军曹鱼幼鱼脂代谢相关生理生化的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 123−130.Cai Runjia, Zhang Jing, Huang Jiansheng, et al. Effects of low temperature stress on physiology and biochemistry of lipid metabolism of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2021, 41(3): 123−130. [25] 方玲玲. 卵形鲳鲹PPARα及CPT1基因的克隆及不同条件对其表达影响的分析[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2016.Fang Lingling. Molecular cloning and expression under the different conditions of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors-α and carnitine palmitoyl transferase in Trachinotus ovatus[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2016. [26] Zhang Haibo, Zhang Xiangfei, Wang Zhisheng, et al. Effects of dietary energy level on lipid metabolism-related gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue of Yellow breed × Simmental cattle[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2015, 86(4): 392−400. doi: 10.1111/asj.12316 [27] Hsieh S L, Kuo C M. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase expression and fatty acid composition in milkfish (Chanos chanos) and grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) during cold acclimation[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2005, 141(1): 95−101. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2005.02.001 [28] Zerai D B, Fitzsimmons K M, Collier R J. Transcriptional response of delta-9-desaturase gene to acute and chronic cold Stress in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2010, 41(5): 800−806. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-7345.2010.00422.x [29] Xu Hao, Zhang Dongling, Yu Dahui, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of scd1 gene from large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea under cold stress[J]. Gene, 2015, 568(1): 100−108. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.05.027 [30] 萧培珍. 日粮中添加水飞蓟素对草鱼脂质代谢的影响及其机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2017.Xiao Peizhen. Effect of dietary silymarin on lipid metabolism of grass carp (Ctenopharygodon idellus)[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2017. [31] Melis R, Sanna R, Braca A, et al. Molecular details on gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) sensitivity to low water temperatures from 1H NMR metabolomics[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2017, 204: 129−136. [32] 李志艳, 张小燕, 唐海林, 等. M2型丙酮酸激酶调控肿瘤细胞能量代谢的研究进展[J]. 广东医学, 2016, 37(18): 2829−2831.Li Zhiyan, Zhang Xiaoyan, Tang Hailin, et al. Progress in the regulation of energy metabolism in tumor cells by M2-type pyruvate kinase[J]. Guangdong Medical Journal, 2016, 37(18): 2829−2831. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献英文信息, 请确认) [33] Yang Erjun, Amenyogbe E, Zhang Jiandong, et al. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of the intestine of cobia (Rachycentron canadum) under hypoxia stress[J]. Aquaculture Reports, 2022, 25: 101261. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101261 -





 下载:
下载: