Research of sea surface gust calculation method based on dual-frequency precipitation radar data
-
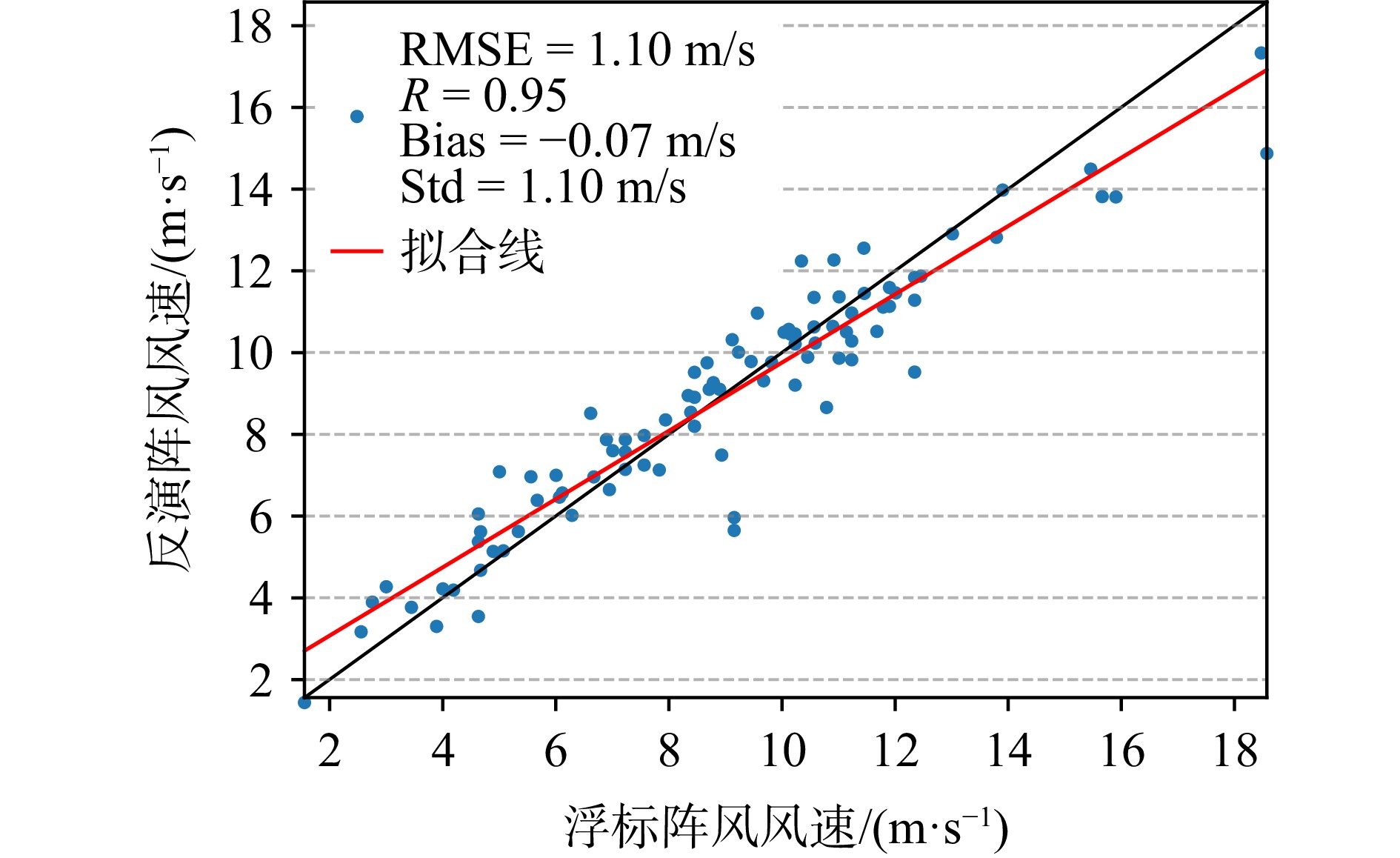
摘要: 海面阵风对海洋资源利用、海洋研究以及海上运输与工程安全具有重要意义。但目前观测手段有限,海面阵风数据缺失严重。林静等基于HY-2B雷达高度计C、Ku波段后向散射系数的差值对海面风速进行修正,计算得到星下点的阵风风速,但观测范围较小。本文在此基础上,选用观测原理与雷达高度计相似的全球降雨观测计划(GPM)搭载的双频降雨雷达(DPR),利用其Ku、Ka波段后向散射系数的差值,并以ERA5海面风速作为观测值,对海面风速进行修正计算,得到阵风风速,以扩展观测范围并提高观测效率。结果表明:计算得到的阵风风速与ERA5阵风风速对比,相关系数(R)为0.96,均方根误差(RMSE)为1.79 m/s,平均偏差(Bias)为0.73 m/s,标准差(Std)为1.64 m/s;与同时期的NDBC浮标数据对比,R为0.91,RMSE为1.50 m/s,Bias为−0.15 m/s,Std为1.50 m/s,说明降雨雷达反演的阵风可靠性较好。进一步使用NDBC浮标海面风速代替ERA5海面风速后,R提高至0.95,RMSE降低至1.10 m/s,Bias为−0.07 m/s,Std为1.50 m/s,反演结果得到提高,说明精确的海面风速对阵风计算结果有较好的影响。Abstract: Sea surface gusts play a critical role in the utilization of ocean resources, marine research, and the safety of maritime transportation and offshore construction. However, current observation methods are limited, resulting in significant data gaps in surface gust measurements. Lin Jing et al. corrected sea surface wind speeds based on the difference in backscattering coefficients between the C and Ku bands observed by the HY-2B radar altimeter, thereby deriving gust wind speeds at nadir points, although the spatial coverage remained relatively limited. Building upon this approach, the present study employs the Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) aboard the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission, whose observational principles are similar to those of radar altimeters. By utilizing the difference in Ku- and Ka-band backscattering coefficients and using ERA5 sea surface wind speed as a reference, surface wind speeds are corrected to retrieve gust speeds, aiming to expand observation coverage and improve observational efficiency. Validation against ERA5 gust data yields a correlation coefficient (r) of 0.96, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 1.79 m/s, a mean bias (Bias) of 0.73 m/s, and a standard deviation (Std) of 1.64 m/s. Comparison with simultaneous NDBC buoy observations shows an r of 0.91, an RMSE of 1.50 m/s, a Bias of −0.15 m/s, and a Std of 1.50 m/s, indicating that gust wind speeds retrieved from DPR data demonstrate good reliability. Furthermore, by replacing ERA5 sea surface wind speeds with NDBC buoy measurements, the r increases to 0.95, the RMSE decreases to 1.10 m/s, the Bias is −0.07 m/s, and the Std remains at 1.50 m/s, further improving the retrieval results. These findings highlight that accurate sea surface wind speeds have a significant positive impact on the accuracy of gust wind retrievals.
-
表 1 ERA5与NDBC浮标匹配分析结果和浮标位置信息
Tab. 1 Matching analysis results of ERA5 and NDBC buoy and specific information of buoys
NDBC
浮标站点纬度 经度 距离/
km匹配对
数量ERA5与浮标
海面风速ERA5与浮标
阵风风速R RMSE/
(m·s−1)R RMSE/
(m·s−1)41002 31.76°N 74.94°W 6.15 2155 0.81 1.94 0.81 2.19 41040 14.54°N 53.14°W 12.92 2197 0.82 1.34 0.81 1.51 41044 21.58°N 58.63°W 15.39 2146 0.73 1.74 0.76 1.82 41048 31.83°N 69.57°W 11.33 2134 0.90 1.07 0.87 1.46 42001 25.93°N 89.66°W 12.04 2052 0.91 1.30 0.90 1.59 44011 41.09°N 66.56°W 11.57 1200 0.69 2.28 0.73 2.49 46005 46.14°N 131.09°W 13.77 2150 0.75 2.15 0.78 2.26 46066 52.77°N 155.01°W 1.78 2060 0.82 1.96 0.85 2.16 46080 57.91°N 150.13°W 12.32 1979 0.85 1.84 0.86 2.10 51001 24.48°N 162.03°W 5.05 2153 0.74 1.66 0.78 1.68 表 2 2020年6−8月阵风风速反演结果表
Tab. 2 Gust wind speed retrieval results from June to August 2020
时间 匹配对数量 R RMSE/
(m·s−1)Bias/
(m·s−1)Std/
(m·s−1)2020年6月 1933334 0.96 1.79 0.73 1.64 2020年7月 2071620 0.96 1.77 0.70 1.63 2020年8月 1529099 0.96 1.81 0.76 1.64 2020年6月至2020年8月 5534053 0.96 1.79 0.73 1.64 -
[1] 徐霈霈. 不同分辨率风场强迫对海洋水动力模拟的影响分析[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2015.Xu Peipei. Analysis of different resolutions of wind forcing on sea hydrodynamic simulation[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2015. [2] 全国科学技术名词审定委员会. 大气科学名词[J]. 中国科技术语, 2009, 11(2): 16−18.China National Committee for Terminology in Science and Technology. Chinese scientific terms of atmospheric science[J]. China Terminology, 2009, 11(2): 16−18. [3] Wang Ke, Lü Xinyu, Huang Jing, et al. Influence of topography and the underlying surface of the Bohai Sea on wind and gust forecasts[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2023, 10(1): e2022EA002705. doi: 10.1029/2022EA002705 [4] 吕艺影, 牛海林, 郝囝, 等. 基于ERA5再分析资料的余姚地区阵风预报模型探究[J]. 气象科学, 2021, 41(4): 551−560. doi: 10.12306/2020jms.0063Lü Yiying, Niu Hailin, Hao Jian, et al. Analysis of wind gust forecast model in Yuyao based on the reanalysis data ERA5[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2021, 41(4): 551−560 doi: 10.12306/2020jms.0063 [5] 胡海川, 代刊. 我国近海阵风预报研究[J]. 气象, 2024, 50(6): 711−722.Hu Haichuan, Dai Kan. Research on gust forecasting in China’s offshore[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2024, 50(6): 711−722. [6] 胡波, 俞燎霓, 滕代高. 高斯过程回归方法在浙江沿海海岛冬春季阵风预报中的应用试验[J]. 热带气象学报, 2019, 35(6): 767−779.Hu Bo, Yu Liaoni, Teng Daigao. Application of Gaussian process regression method to gust forecasting in winter and spring in Zhejiang Coastal Islands[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 2019, 35(6): 767−779. [7] Brasseur O. Development and application of a physical approach to estimating wind gusts[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2001, 129(1): 5−25. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129<0005:DAAOAP>2.0.CO;2 [8] 张有广, 蒋城飞, 贾永君, 等. HY-2B卫星载荷联合观测海面阵风的一种反演方法[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(11): 133−143.Zhang Youguang, Jiang Chengfei, Jia Yongjun, et al. An inversion method for joint observation of wind gusts by HY-2B satellite remote sensors[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(11): 133−143. [9] 林静, 张有广. 基于双频段雷达高度计数据的海面阵风反演研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2024, 46(4): 133−142.Lin Jing, Zhang Youguang. Research of sea surface gust inversion by dual band radar altimeter data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2024, 46(4): 133−142. [10] Skofronick-Jackson G, Petersen W A, Berg W, et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission for science and society[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2017, 98(8): 1679−1695. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00306.1 [11] 余占猷. 利用DPR和GMI探测结果对东亚降水云的个例分析研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2016.Yu Zhanyou. Case Study of precipitation clouds over the east Asia based on DPR and GMI measurements[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2016. [12] 尹红刚, 吴琼, 谷松岩, 等. 风云三号(03)批降水测量卫星探测能力及应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2016, 6(3): 55−61.Yin Honggang, Wu Qiong, Gu Songyan, et al. Analysis of rainfall measurement power in the FY-3(03) rain measurement satellite[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology, 2016, 6(3): 55−61. [13] Panfilova M, Karaev V. Wind speed retrieval algorithm using Ku-band radar onboard GPM satellite[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(22): 4565. doi: 10.3390/rs13224565 [14] Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P, et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2020, 146(730): 1999−2049. doi: 10.1002/qj.3803 [15] 张淑静, 吕聪俐, 马敏. 国内外海上多功能浮标发展探讨[J]. 中国海事, 2019(9): 47−51.Zhang Shujing, Lü Congli, Ma Min. Discussion on the development of domestic and overseas marine multifunction buoy[J]. China Maritime Safety, 2019(9): 47−51. [16] Hsu S A, Meindl E A, Gilhousen D B. Determining the power-law wind-profile exponent under near-neutral stability conditions at sea[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 1994, 33(6): 757−765. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1994)033<0757:DTPLWP>2.0.CO;2 [17] Hwang C, Kao E C, Parsons B. Global derivation of marine gravity anomalies from Seasat, Geosat, ERS-1 and TOPEX/POSEIDON altimeter data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1998, 134(2): 449−459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1998.tb07139.x [18] Gower J F R. Intercalibration of wave and wind data from TOPEX/POSEIDON and moored buoys off the west coast of Canada[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1996, 101(C2): 3817−3829. doi: 10.1029/95JC03281 [19] 刘花, 王静, 齐义泉, 等. 南海北部近岸海域Jason-1卫星高度计与浮标观测结果的对比分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(5): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.05.003Liu Hua, Wang Jing, Qi Yiquan, et al. Comparison of Jason-1 satellite altimeter and buoy measurements in the coastal water of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.05.003 [20] 黎鹏. 星载波谱仪海面风场反演研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.Li Peng. The study on spaceborne spectrometer for sea surface wind field retrieval[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2019. [21] 陈戈. 卫星高度计反演海面风速—模式函数与应用实例[J]. 遥感学报, 1999, 3(4): 305−311, 325Chen Ge. On retrieving sea surface wind speed from satellite altimeters: model functions and an application case[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 1999, 3(4): 305−311, 325 -





 下载:
下载: