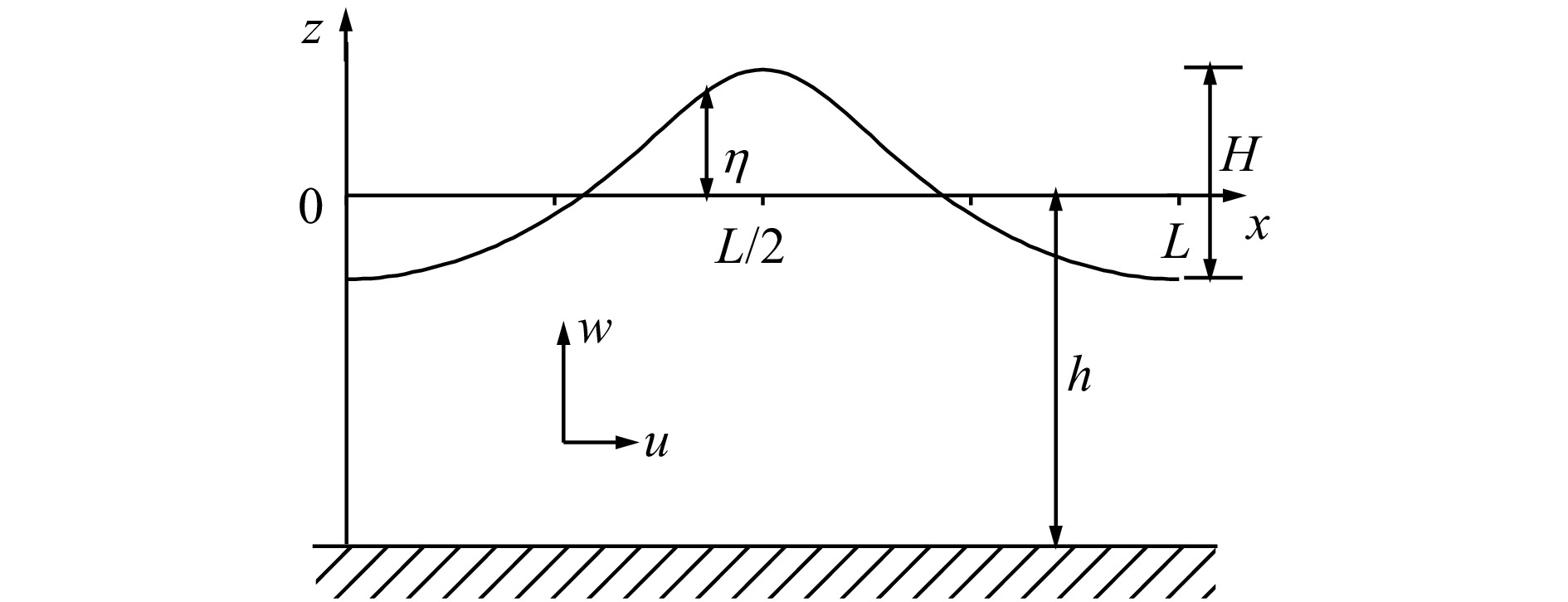
A new method for fast calculation of steady periodic water waves
-
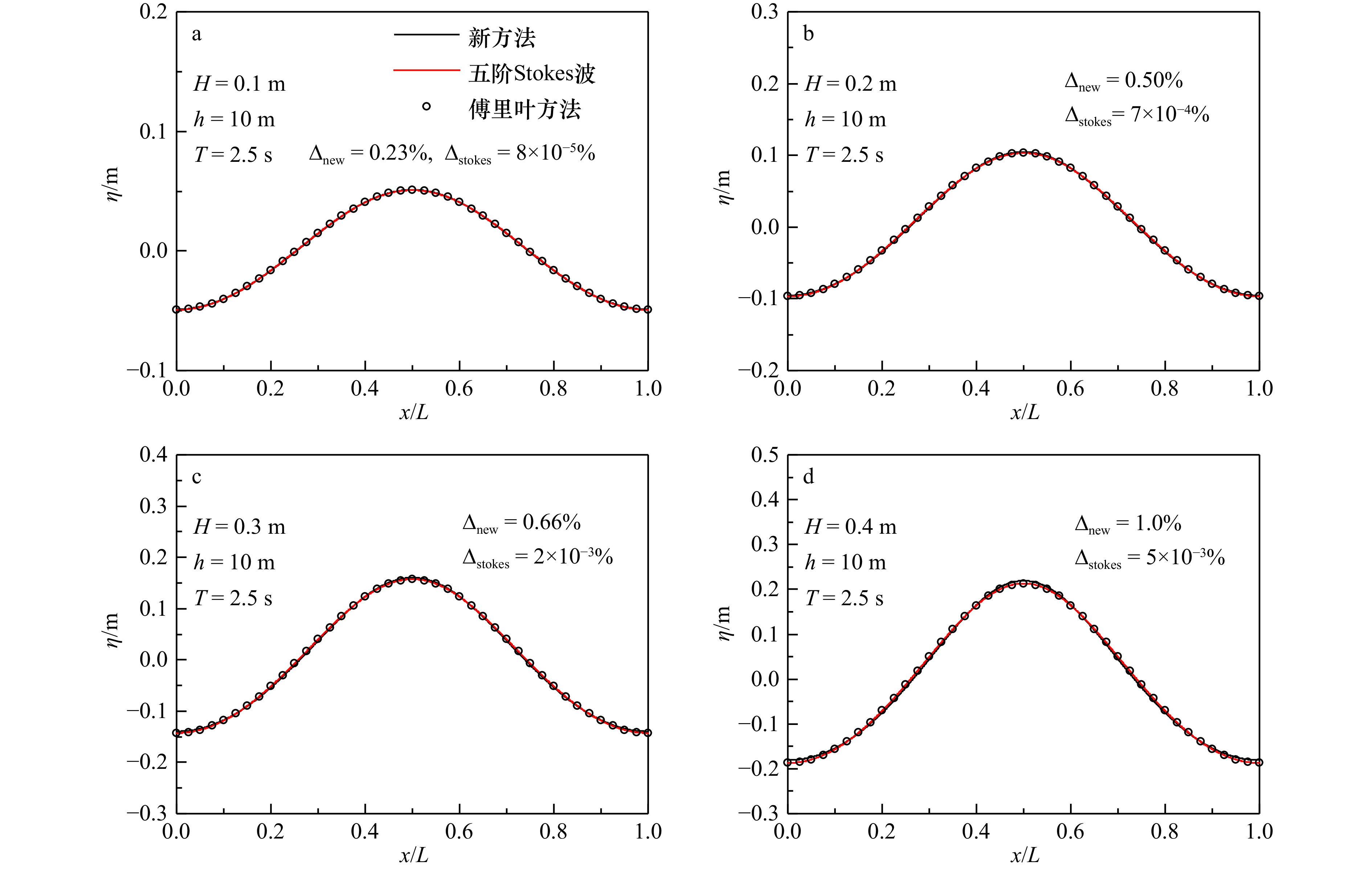
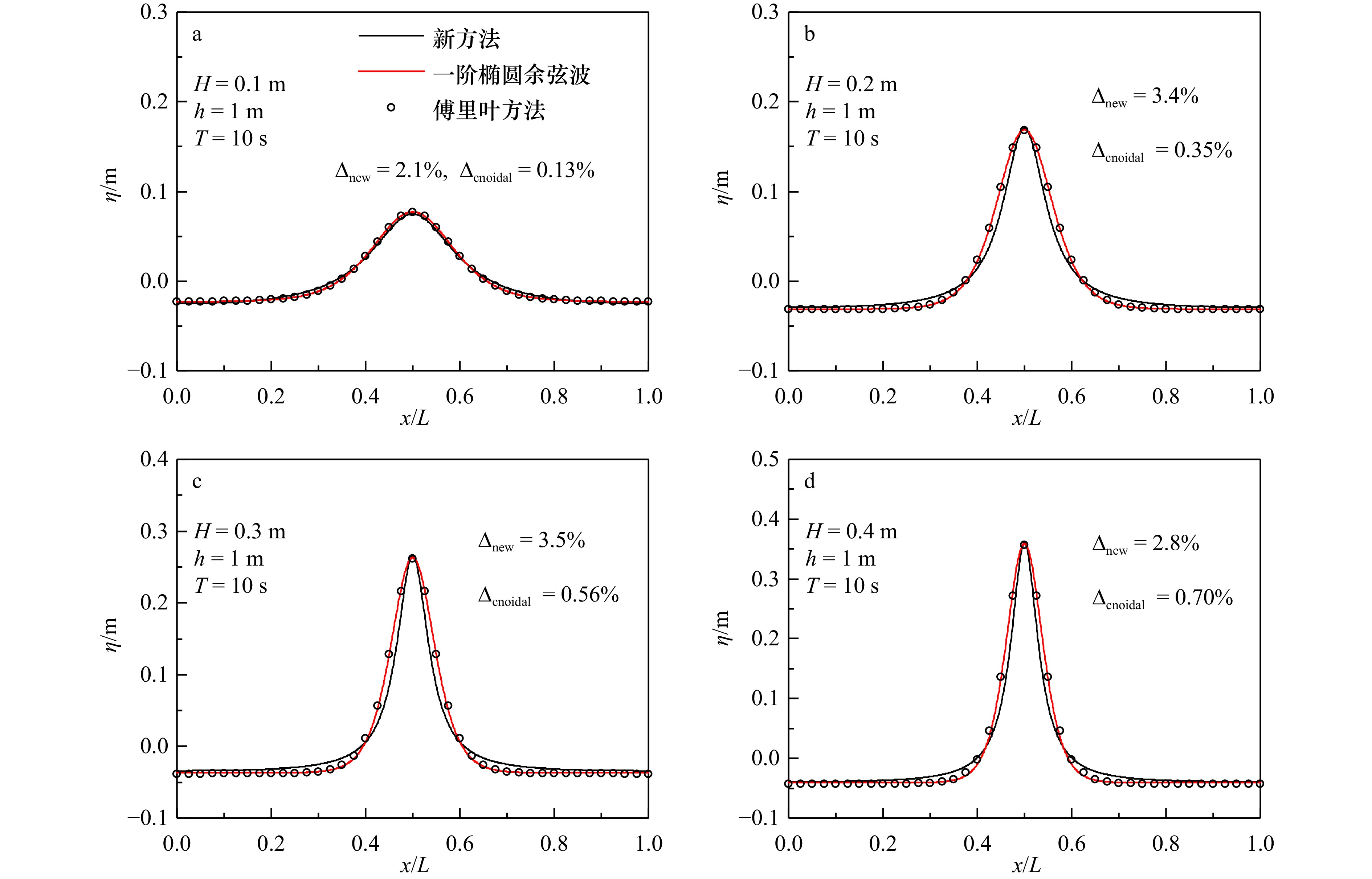
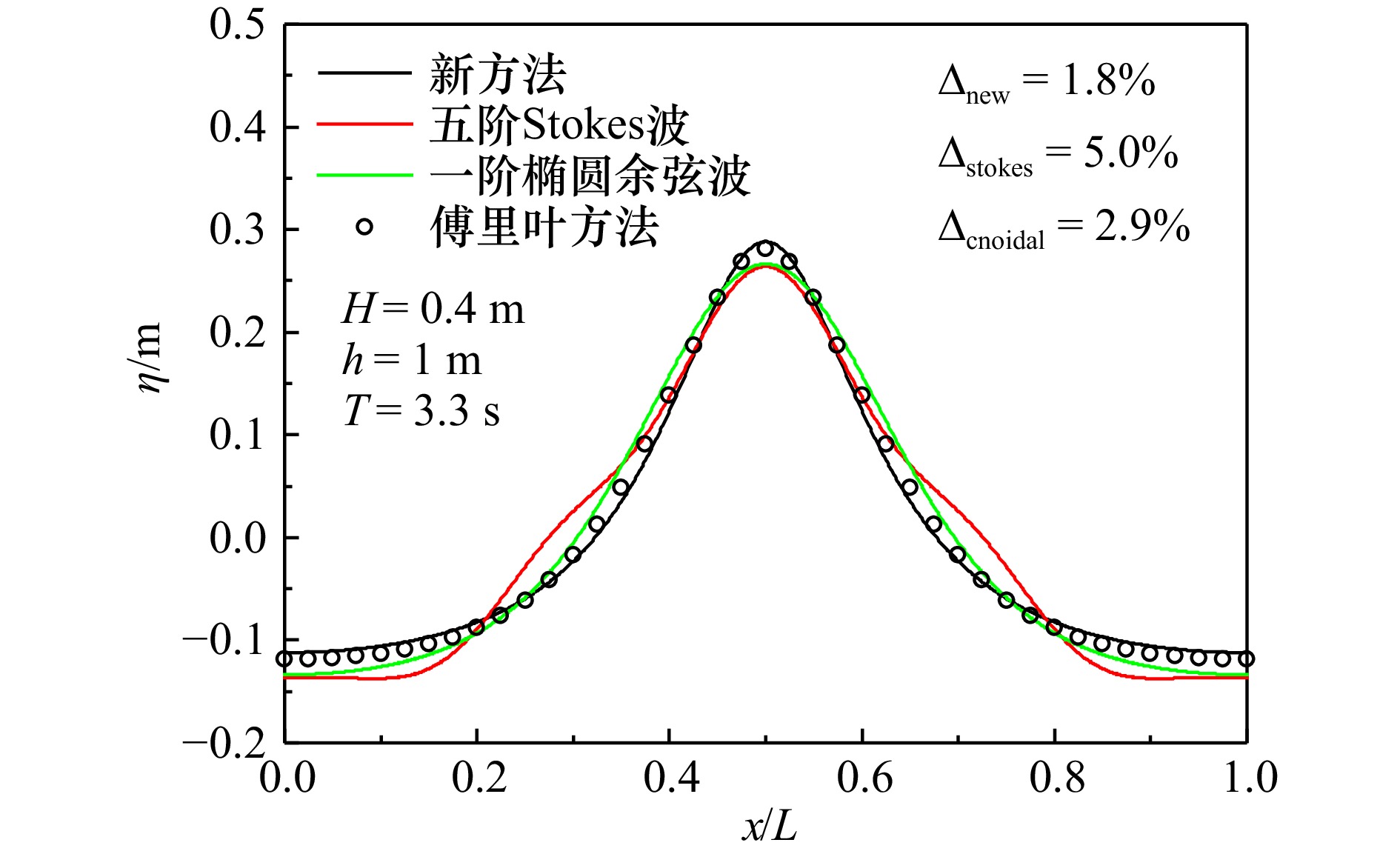
摘要: 本文给出一个利用参数化公式快速计算稳态周期水波波面升高的方法。利用ABR三角级数近似表达稳态周期水波的波面升高,并通过自由表面边界条件数值计算得到ABR级数中的非线性参数数值。采用ABR级数的优点在于其形式简单、仅包含一个待定参数,便于研究该参数与波浪要素之间的参数化关系式,进而快速计算波面升高。针对不同波浪理论(Stokes波理论和椭圆余弦波理论)适用范围情况,将数值计算结果与Stokes波理论解析解、椭圆余弦波理论解析解以及傅里叶方法给出的数值精确解进行对比,讨论了新数值方法计算结果的适用性。此外,给出了利用波陡(深水情况)或厄塞尔数(非深水情况)计算ABR级数中非线性参数的拟合表达式,以便于通过当地波浪要素快速预报波面升高。最后,给出利用波面升高计算时均波浪非线性相关输沙率的方法,以便于实际工程应用。Abstract: A method for the fast calculation of steadily progressing periodic waves by using parameterized expressions is presented. The free surface elevation of steady periodic water waves is approximated by ABR triangular series, and the nonlinear parameter in ABR series is obtained by a numerical calculation of the free surface boundary conditions. The advantage of using ABR series is that it is simple in form and contains only one parameter, so it is convenient to study the relationship between this parameter and wave parameters, and then to estimate the wave free surface elevation. For conditions of different wave theories applying (Stokes wave theory and cnoidal wave theory), the results calculated by the new method are compared with the analytical solutions of Stokes wave theory, cnoidal wave theory, and the numerical solutions given by the Fourier method, and the applicability of the results calculated by the new numerical method is discussed. In addition, the expressions of the nonlinear parameter in the ABR series determined by the wave steepness (in deep water) or the Ursell number (in non-deep water) are given in order to efficiently predict free surface elevations by means of local wave parameters. Finally, the method of calculating time averaged sand transport rates related to wave nonlinearity by using free surface elevation is given for practical engineering applications.
-
Key words:
- steady periodic water wave /
- fast calculation /
- Ursell number
-
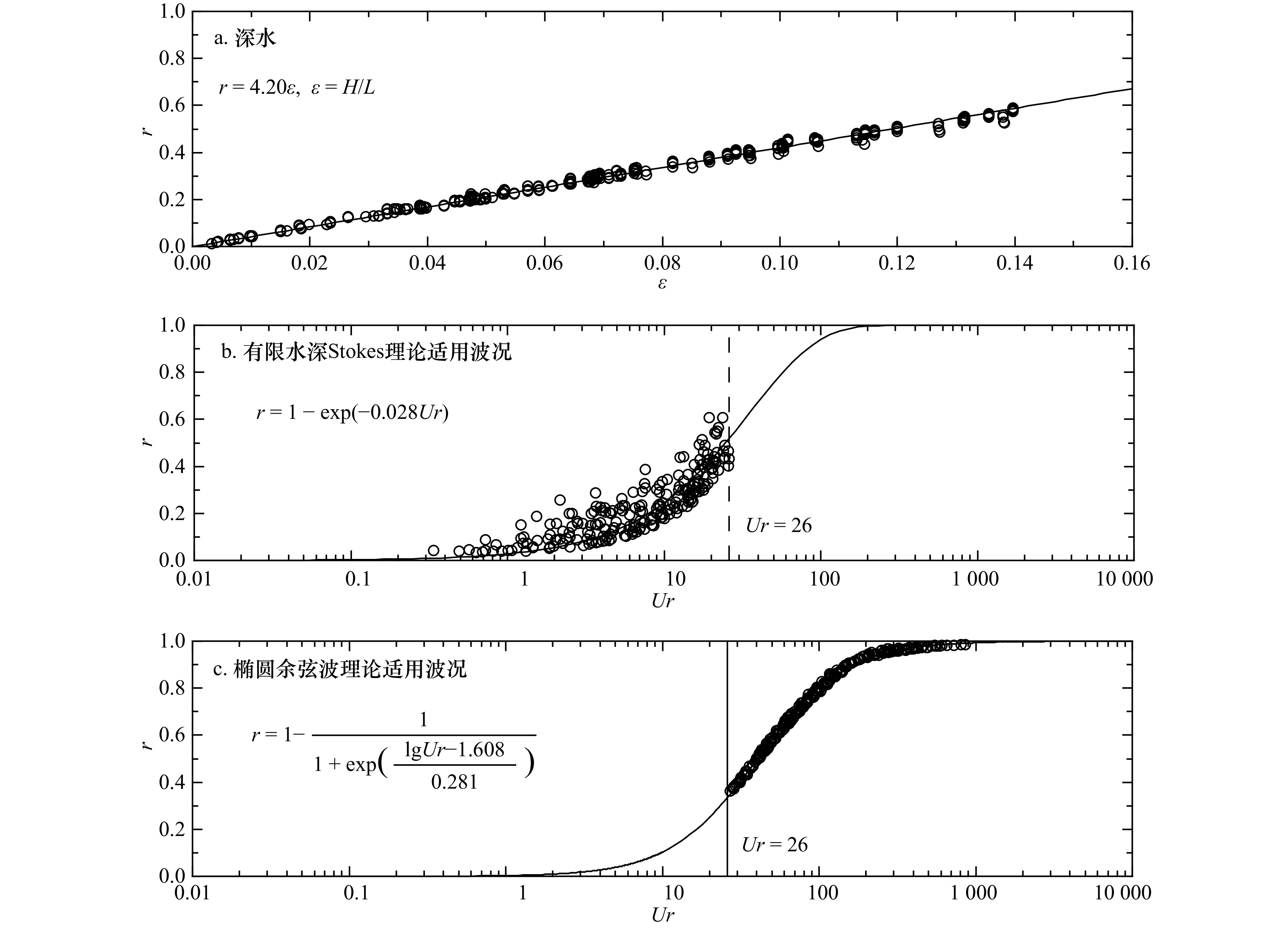
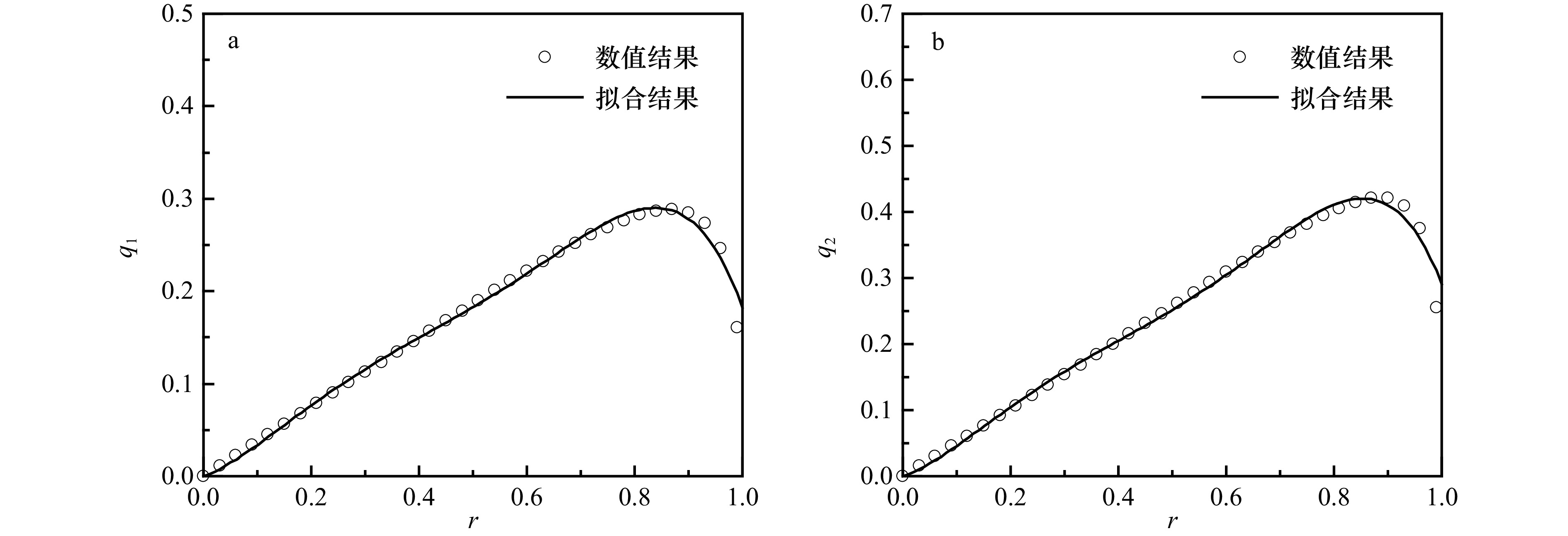
表 1 各波况对应r数值计算结果
Tab. 1 Numerical results of r for different wave cases
水深h/m 周期T/s 波高H/m r 1 2.5 0.1 0.130 1 2.5 0.2 0.265 1 2.5 0.3 0.407 1 2.5 0.4 0.547 1 10 0.1 0.798 1 10 0.2 0.943 1 10 0.3 0.968 1 10 0.4 0.977 10 2.5 0.1 4.65×10−2 10 2.5 0.2 9.56×10−2 10 2.5 0.3 0.138 10 2.5 0.4 0.191 表 2 q1与q2拟合表达式中系数取值
Tab. 2 Values of parameters for the fitting expressions of q1 and q2
系数 数值 系数 数值 $ {a_1} $ 0.214 $ {a_6} $ 0.274 $ {a_2} $ 1.804 $ {a_7} $ 2.628 $ {a_3} $ −6.444 $ {a_8} $ −9.331 $ {a_4} $ 9.158 $ {a_9} $ 13.243 $ {a_5} $ −4.550 $ {a_{10}} $ −6.523 -
[1] Gerstner F. Theorie der wellen: Abhandlungen der Koniglichen Bohmischen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften, Prague[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1809, 32(8): 412−445. [2] Stokes G G. On the theory of oscillatory waves[J]. Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 1847, 8: 441−455. [3] Fenton J D. A fifth-order stokes theory for steady waves[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1985, 111(2): 216−234. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1985)111:2(216) [4] Horikawa K. Nearshore Dynamics and Coastal Processes: Theory, Measurement, and Predictive Models[M]. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, 1988. [5] Zhao Hongjun, Song Zhiyao, Li Ling, et al. On the fifth-order stokes solution for steady water waves[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2016, 30(5): 794−810. doi: 10.1007/s13344-016-0051-5 [6] Zhao Kuifeng, Liu P L F. On stokes wave solutions[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2022, 478(2258): 20210732. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2021.0732 [7] Fang Haiqi, Liu P L F, Tang Lian, et al. The theory of fifth-order Stokes waves in a linear shear current[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2023, 479(2280): 20230565. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2023.0565 [8] Korteweg D J, De Vries G. XLI.On the change of form of long waves advancing in a rectangular canal, and on a new type of long stationary waves[J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1895, 39(240): 422−443. doi: 10.1080/14786449508620739 [9] Fenton J D. A high-order cnoidal wave theory[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1979, 94(1): 129−161. doi: 10.1017/S0022112079000975 [10] Chappelear J E. Direct numerical calculation of wave properties[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1961, 66(2): 501−508. doi: 10.1029/JZ066i002p00501 [11] Dean R G. Stream function representation of nonlinear ocean waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1965, 70(18): 4561−4572. doi: 10.1029/JZ070i018p04561 [12] Rienecker M M, Fenton J D. A Fourier approximation method for steady water waves[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1981, 104: 119−137. doi: 10.1017/S0022112081002851 [13] Zhao Hongjun, Song Zhiyao, Li Ling, et al. On the Fourier approximation method for steady water waves[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(5): 37−47. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0470-1 [14] Abreu T, Silva P A, Sancho F, et al. Analytical approximate wave form for asymmetric waves[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2010, 57(7): 656−667. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.02.005 [15] Ruessink B G, Ramaekers G, Van Rijn L C. On the parameterization of the free-stream non-linear wave orbital motion in nearshore morphodynamic models[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2012, 65: 56−63. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2012.03.006 [16] Svendsen I A. Mass flux and undertow in a surf zone[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1984, 8(4): 347−365. doi: 10.1016/0378-3839(84)90030-9 [17] Lé Méhauté B. An introduction to hydrodynamics and water waves[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1976. [18] Zhao Kuifeng, Wang Yufei, Liu P L F. A guide for selecting periodic water wave theories-Le Méhauté (1976)’s graph revisited[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2024, 188: 104432. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2023.104432 [19] 邹志利. 水波理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.Zou Zhili. Water Wave Theories and Their Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. [20] Bailard J A, Inman D L. An energetics bedload model for a plane sloping beach: local transport[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1981, 86(C3): 2035−2043. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02035 -




 下载:
下载: