Research on Sentinel-1 SAR sea ice detection method in Liaodong Bay based on AUNet++
-
摘要: 冬季海冰会极大影响辽东湾地区近岸工程建筑、石油平台、船舶航行等安全生产活动。星载合成孔径雷达不受天气影响且分辨率高,可用于辽东湾海冰灾害监测。本文在深度学习模型UNet++的基础上引入卷积注意力模块(CBAM),并使用交叉损失函数来优化模型,建立辽东湾Sentinel-1 SAR图像高精度海冰检测模型(AUNet++),并与PSPNet、Deeplabv3+、DAU-Net等多种深度学习方法进行对比。实验结果表明AUNet++海冰检测方法在OA、AA、MIoU、Kappa系数4种指标上分别达到了97.56%、97.53%、95.19%、95.07%,结果优于其他深度学习方法。该方法可以在高风速的干扰下对海冰边缘、光滑冰面完成精确海冰信息提取,能够为辽东湾地区的大范围、高精度海冰检测工作提供技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 海冰检测 /
- Sentinel-1 /
- 合成孔径雷达 /
- 深度学习
Abstract: The sea ice in Bohai Sea in winter affects the safety production activities of oil platform and ship navigation, as well as the safety of offshore engineering and construction. Spaceborne SAR is not affected by weather and has high resolution, which can be used for sea ice disaster monitoring in Bohai Sea. Based on deep learning model UNet++, this paper introduces Convolutional attention module (CBAM) and uses cross loss function to optimize the model, and establishes a high-precision sea ice detection model for Sentinel-1 SAR data in the Liaodong Bay (AUNet++). And it is compared with PSPNet, Deeplabv3+, DAU-Net and other deep learning methods. The experimental results show that AUNet++ sea ice detection method achieves 97.56%, 97.53%, 95.19% and 95.07% in OA, AA, MIoU and Kappa coefficients, respectively, which is superior to other deep learning methods. This method can extract accurate sea ice information from sea ice edge and smooth ice surface under the interference of high wind speed, and can provide technical support for large-scale and high-precision sea ice detection in Liaodong Bay area.-
Key words:
- sea ice detection /
- Sentinel-1 /
- synthetic aperture radar /
- deep learning
-
表 1 研究数据具体参数信息
Tab. 1 Specific parameter information of research data
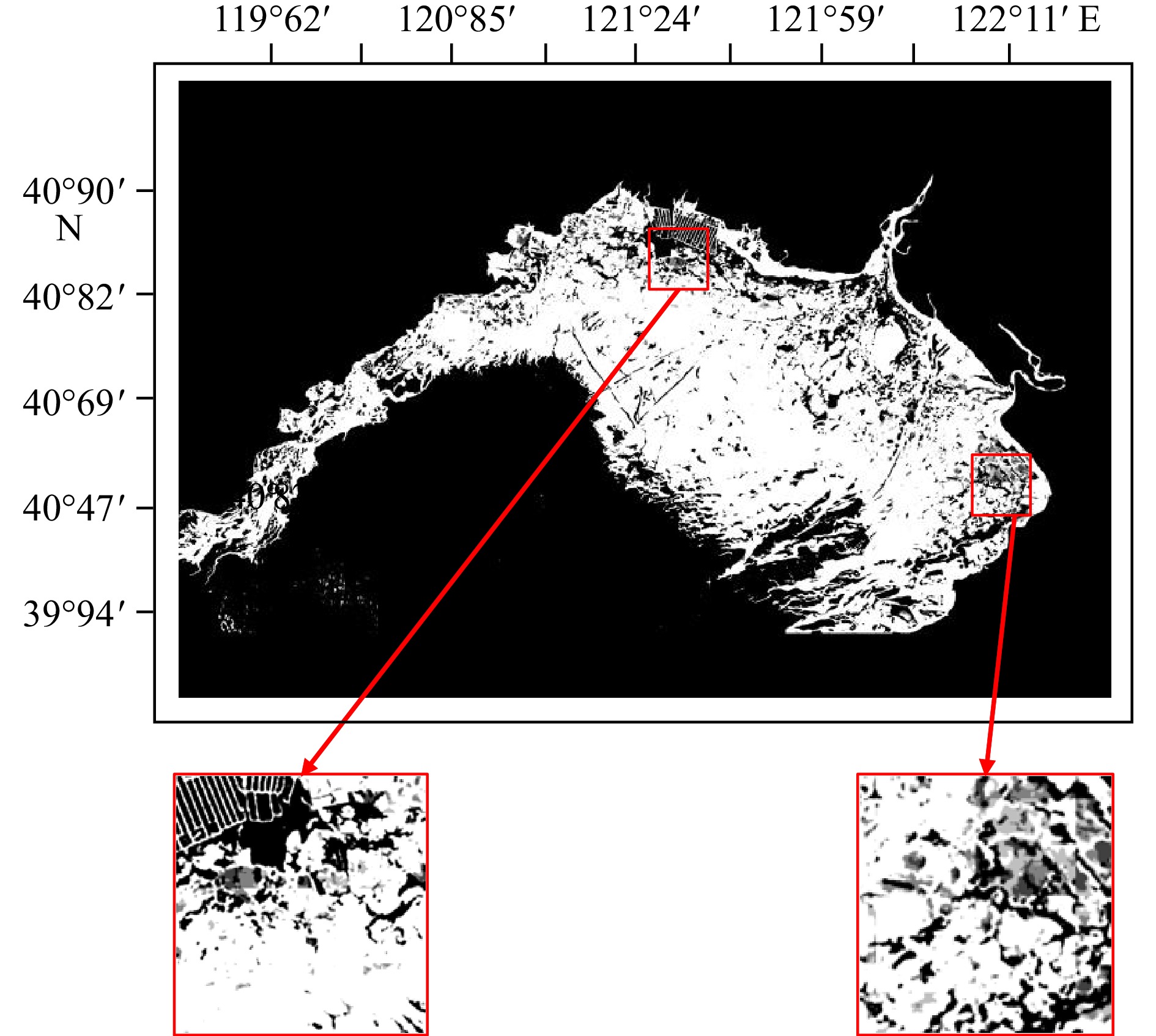
序号 成像时间 数据模式 极化方式 分辨率 卫星 1 2019年12月9日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 2 2020年1月2日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 3 2020年1月8日09:48 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m B星 4 2020年1月14日09:48 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 5 2020年1月20日09:48 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m B星 6 2020年1月26日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 7 2020年2月1日09:48 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m B星 8 2020年2月7日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 9 2020年2月13日09:48 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m B星 10 2020年2月19日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 11 2023年2月3日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 12 2024年1月5日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 13 2024年1月17日09:49 IW VV+VH 5 × 20 m A星 表 2 不同方法对比结果
Tab. 2 Comparison results of different methods
方法 总体精度/% 平均精度/% 均交并比/% Kappa系数/% SegNet 96.65 96.68 93.47 93.24 PSPNet 93.57 93.59 87.84 84.05 DeepLabv3+ 94.48 94.50 92.94 92.67 UNet 96.48 96.49 93.15 92.90 DAU-UNet 96.37 96.35 92.94 92.67 AUNet++ 97.56 97.53 95.19 95.07 表 3 消融实验结果分析
Tab. 3 Analysis of ablation results
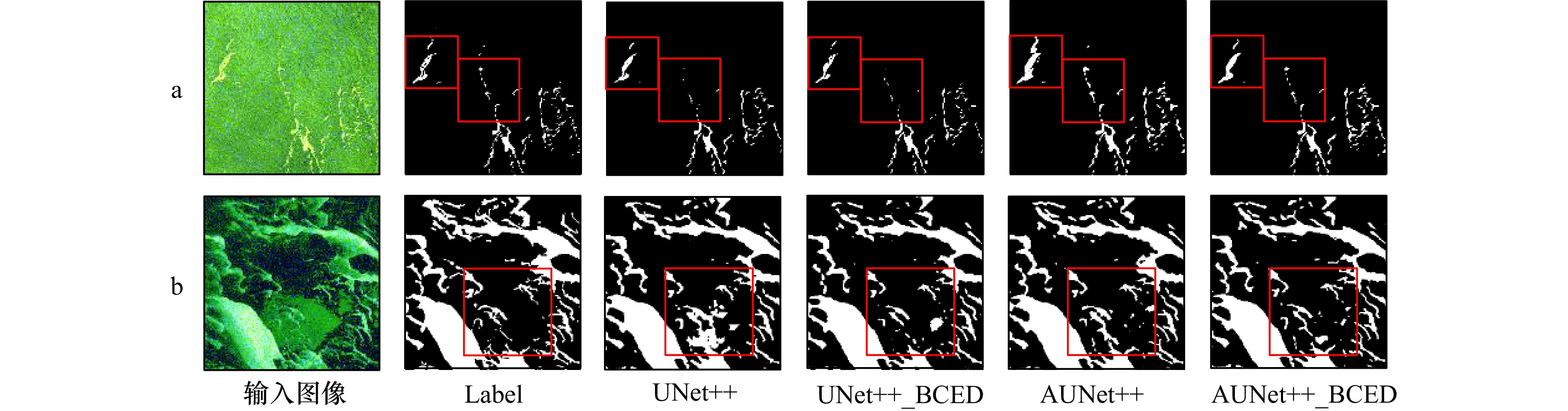
方法 总体精度/% 平均精度/% 均交并比/% Kappa系数 UNet++ 97.17 97.17 94.46 94.30 UNet++_BCED 97.23 97.24 94.57 94.41 AUNet++ 97.37 97.35 94.83 94.69 AUNet++_BCED 97.56 97.53 95.19 95.07 -
[1] Sun Xiaoyu, Zhang Xi, Huang Weimin, et al. Sea ice classification using mutually guided contexts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4204019. [2] 臧金霞, 刘建强, 殷晓斌, 等. 基于最优特征集的HY-1C卫星海岸带成像仪影像海冰分类方法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(5): 35−46.Zang Jinxia, Liu Jianqiang, Yin Xiaobin, et al. Study on sea ice classification of HY-1C satellite coastal zone imager images based on the optimal feature set[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(5): 35−46. [3] 孙劭, 苏洁, 史培军. 2010年渤海海冰灾害特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2011, 20(6): 87−93.Sun Shao, Su Jie, Shi Peijun. Features of sea ice disaster in the Bohai Sea in 2010[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2011, 20(6): 87−93. [4] Liu Huiying, Guo Huadong, Zhang Lu. SVM-based sea ice classification using textural features and concentration from RADARSAT-2 dual-pol ScanSAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(4): 1601−1613. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2365215 [5] 郑敏薇, 李晓明, 任永政. 高分3号星载合成孔径雷达极地海冰自动检测方法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(9): 113−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.010Zheng Minwei, Li Xiaoming, Ren Yongzheng. The method study on automatic sea ice detection with Gao Fen-3 synthetic aperture radar data in polar regions[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(9): 113−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.010 [6] Tan Weikai, Li J, Xu Linlin, et al. Semiautomated segmentation of Sentinel-1 SAR imagery for mapping sea ice in Labrador coast[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(5): 1419−1432. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2806640 [7] Park J W, Korosov A A, Babiker M, et al. Classification of sea ice types in Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar images[J]. The Cryosphere, 2020, 14(8): 2629−2645. doi: 10.5194/tc-14-2629-2020 [8] 冯琦, 李广雪. 基于Sentinel-1的辽东湾海冰冰情监测[J]. 海岸工程, 2024, 43(1): 66−78. doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1002-3682.20230716001Feng Qi, Li Guangxue. Monitoring of sea ice situation in the Liaodong Bay based on Sentinel-1 data[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2024, 43(1): 66−78. doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1002-3682.20230716001 [9] Lu Yiru, Zhang Biao, Perrie W. Arctic sea ice and open water classification from spaceborne fully polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4203713. [10] Li Jinxin, Wang Chao, Wang Shigang, et al. Gaofen-3 sea ice detection based on deep learning[C]//Proceedings of 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall. Singapore: IEEE, 2017: 933−939. [11] Zhang Tianyu, Yang Ying, Shokr M, et al. Deep learning based sea ice classification with Gaofen-3 fully polarimetric SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(8): 1452. doi: 10.3390/rs13081452 [12] 徐欢, 任沂斌. 基于混合损失U-Net的SAR图像渤海海冰检测研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(6): 157−170.Xu Huan, Ren Yibin. Detecting sea ice of Bohai Sea using SAR images based on a hybrid loss U-Net model[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(6): 157−170. [13] Wang Yiran, Li Xiaoming. Arctic sea ice cover data from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar by deep learning[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2021, 13(6): 2723−2742. doi: 10.5194/essd-13-2723-2021 [14] Ren Yibin, Li Xiaofeng, Yang Xiaofeng, et al. Development of a dual-attention U-Net model for sea ice and open water classification on SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4010205. [15] Liang Zeyu, Pang Xiaoping, Ji Qing, et al. An entropy-weighted network for polar sea ice open lead detection from Sentinel-1 SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4304714. [16] Wan Hongyang, Luo Xiaowen, Wu Ziyin, et al. Multi-featured sea ice classification with SAR image based on convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(16): 4014. doi: 10.3390/rs15164014 [17] 庞海洋, 孔祥生, 孙志伟, 等. 基于遥感和气象数据对辽东湾海冰变化预测研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(4): 725−733.Pang Haiyang, Kong Xiangsheng, Sun Zhiwei, et al. The forecast model of sea ice changes in Liaodong Bay using remote sensing and meteorological data[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(4): 725−733. [18] 刘眉洁. 基于高分辨率极化SAR的海冰分类和厚度探测方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016.Liu Meijie. Research on the sea ice classification and thickness detection with high-resolution and polarimetric SAR data[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2016. [19] 自然资源部海洋预警监测司. 2019中国海洋灾害公报[R]. 北京: 自然资源部, 2020.Marine Early Warning and Monitoring Department of the Ministry of Natural Resources. 2019 Bulletin of China marine disaster[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Natural Resources, 2020. [20] 孙湘平. 中国近海区域海洋[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2006.Sun Xiangping. China’s Offshore Regional Oceans[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2006. [21] Murashkin D, Spreen G, Huntemann M, et al. Method for detection of leads from Sentinel-1 SAR images[J]. Annals of Glaciology, 2018, 59(76pt2): 124−136. doi: 10.1017/aog.2018.6 [22] Lopes A, Touzi R, Nezry E. Adaptive speckle filters and scene heterogeneity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1990, 28(6): 992−1000. doi: 10.1109/36.62623 [23] Zhou Zongwei, Rahman Siddiquee M, Tajbakhsh N, et al. UNet++: a nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018. Granada, Spain: Springer, 2018: 3−11. [24] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 3−19. [25] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 18th International Conference. Munich: Springer, 2015: 234−241. [26] Huang Gao, Liu Zhuang, Van Der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 4700−4708. [27] Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S A. V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). Stanford: IEEE, 2016: 565−571. [28] Robbins H, Monro S. A stochastic approximation method[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1951, 22(3): 400−407. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729586 [29] Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481−2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [30] Zhao Hengshuang, Shi Jianping, Qi Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 2881−2890. [31] Chen L C, Zhu Yukun, Papandreou G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 801−818. -





 下载:
下载: