Correlation analysis of zooplankton community structure and environmental factors in the Oujiang River Estuary
-
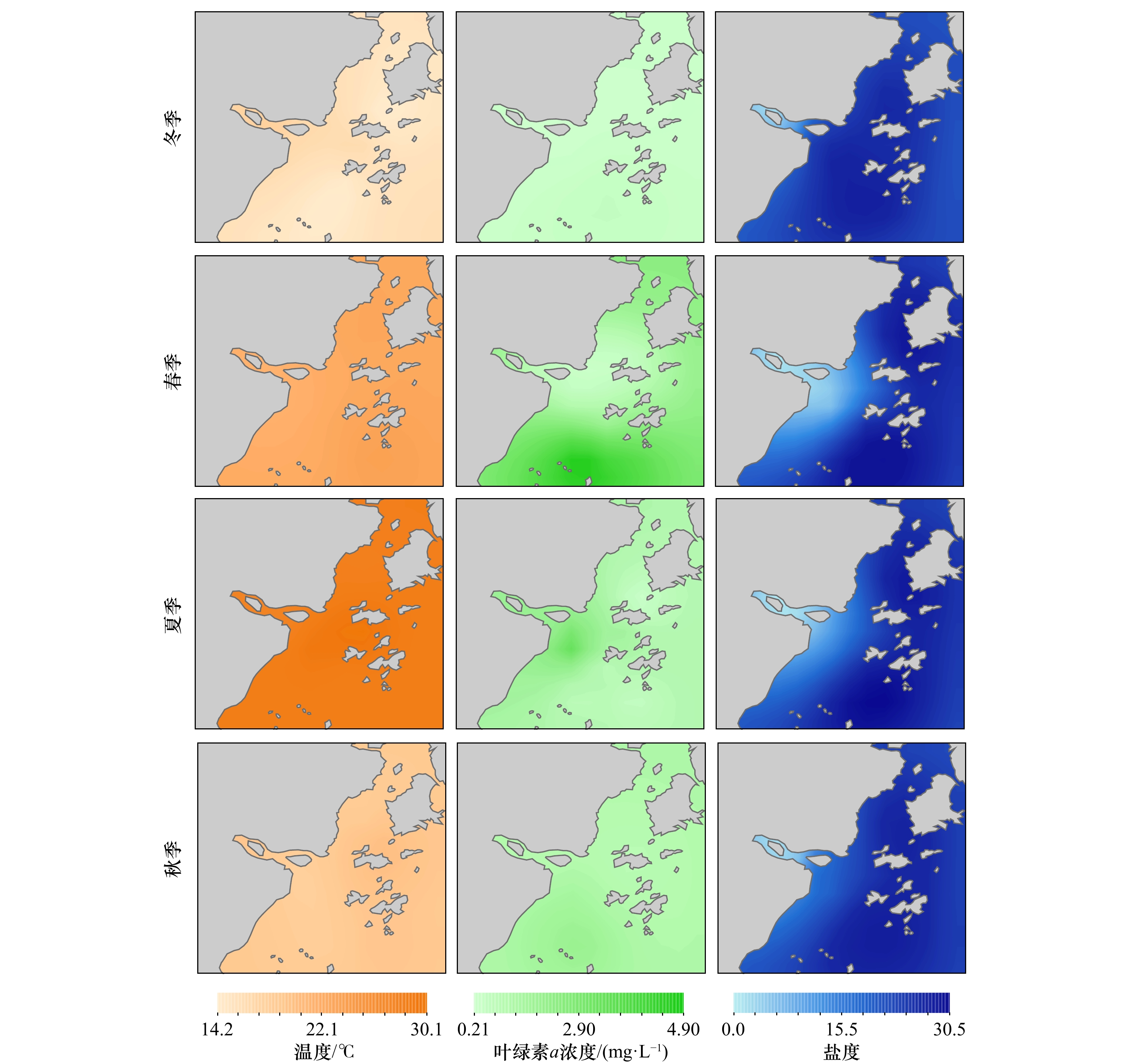
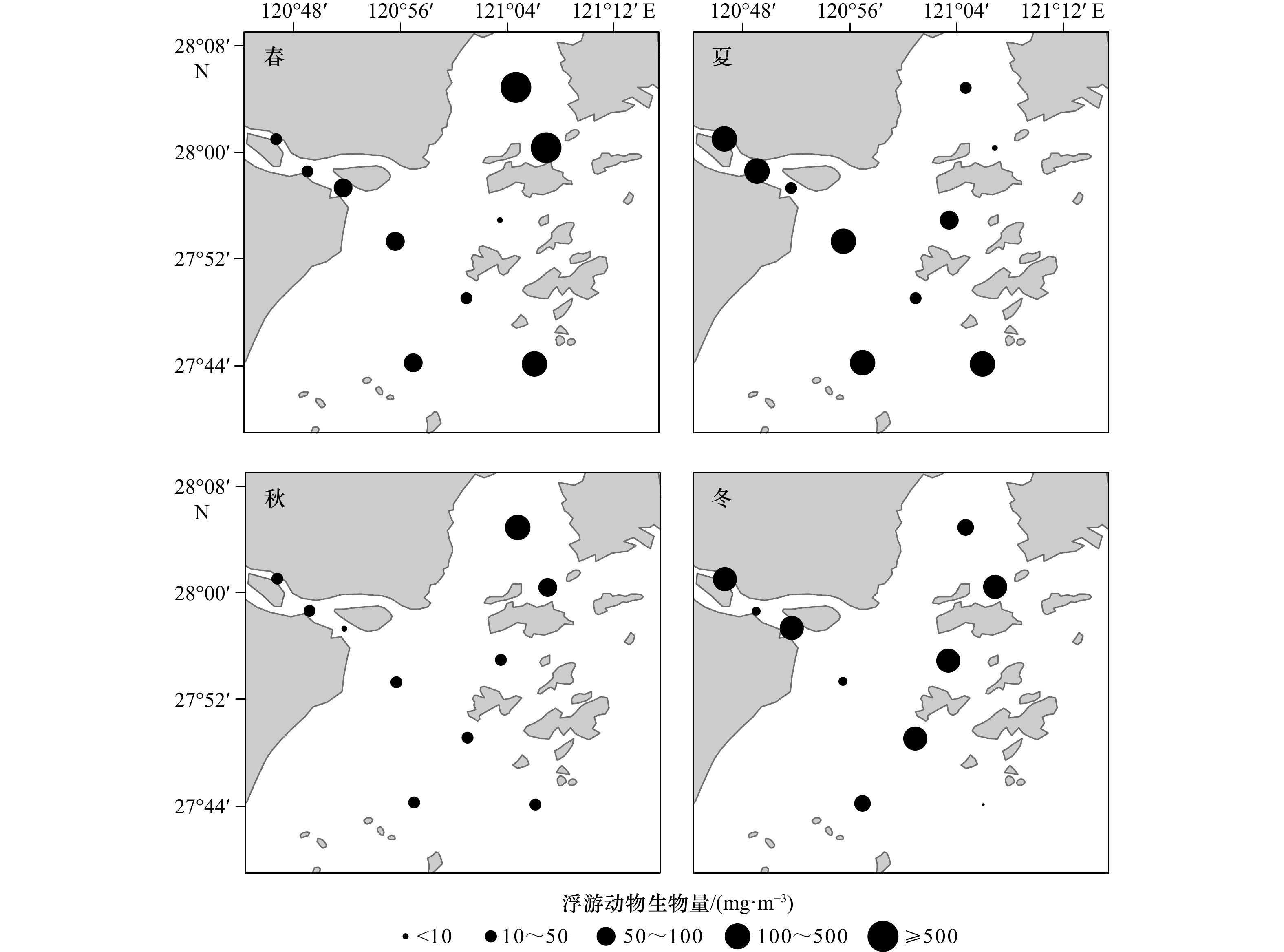
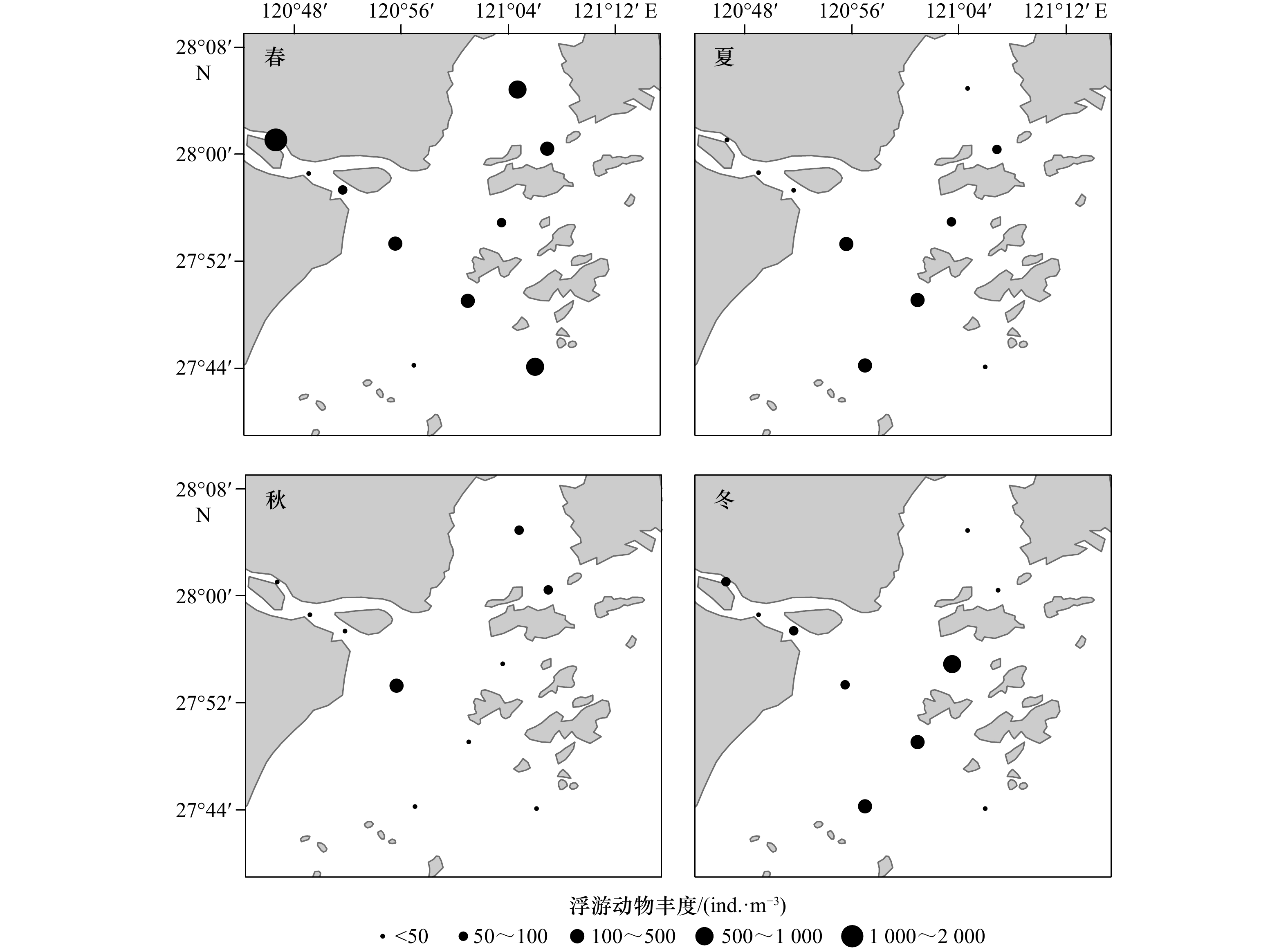
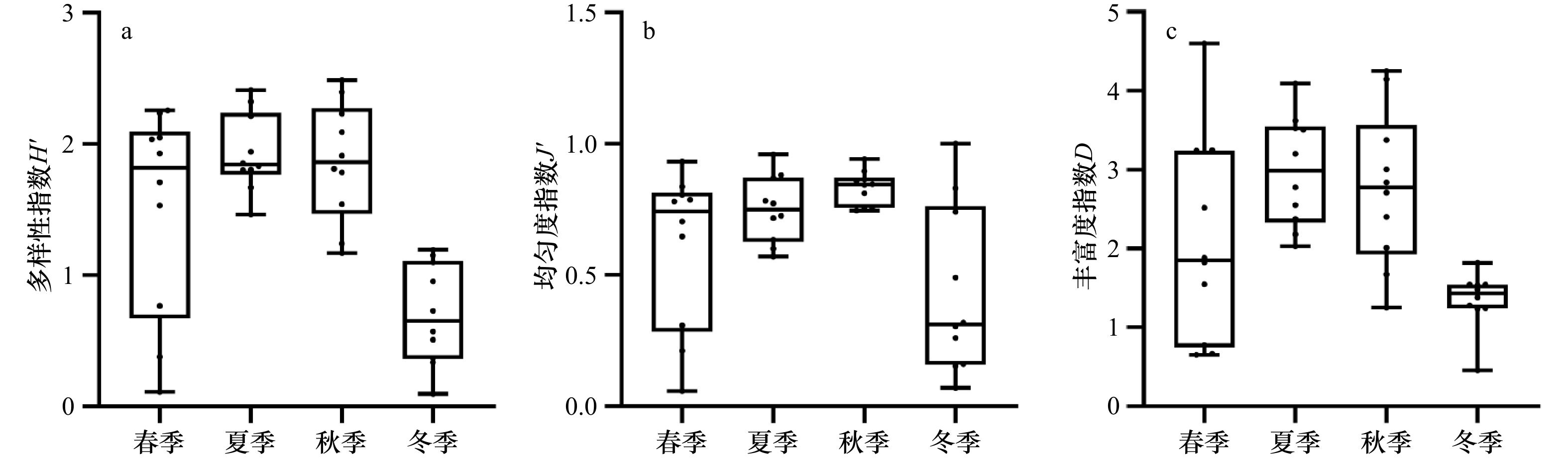
摘要: 为探究瓯江口海域浮游动物群落结构与环境因子的相关性,分别于2021年3月(冬季)、5月(春季)、8月(夏季)、11月(秋季)对瓯江口海域的浮游动物及海水温度、盐度、叶绿素a浓度等环境因子进行了4个航次的调查。结果显示,本次调查共鉴定出浮游动物78种,其中包括16种浮游幼虫,隶属于8门14大类,夏季物种数最丰富(47种),冬季物种数最低(23种),优势种(Y ≥ 0.02)有17种,其中桡足类占8种,如中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus)、中华华哲水蚤(Sinocalanus sinensis)、太平洋纺锤水蚤(Acartia pacifica)和背针胸刺水蚤(Centropages dorsispinatus)等。浮游动物的年平均丰度为(162.95 ± 310.96)ind./m3,年平均生物量为(118.85 ± 62.80)mg/m3,存在明显的季节变化差异,春季丰度和生物量最高,秋季最低;冬季丰度比夏季高,生物量低于夏季。浮游动物Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')、Pielou均匀度指数(J')和浮游动物Margalef丰富度指数(D)年平均值分别为1.500 ± 0.702、0.656 ± 0.270和2.301 ± 1.087。Spearman相关性分析和典范对应分析结果表明,海水温度、盐度、叶绿素a浓度和浮游植物丰度是影响瓯江口海域浮游动物优势丰度的重要环境因素。这为瓯江口环境季节变化对浮游动物的影响研究提供科学参考依据,为瓯江口生物资源的可持续发展提供基础资料和理论依据。Abstract: In order to explore the relationship between zooplankton community structure and environmental factors in the Oujiang River Estuary, four voyages were conducted in March (winter), May (spring), August (summer) and November (autumn) in 2021 to investigate the zooplankton and other environmental factors such as sea temperature, salinity and chlorophyll a concentration in the Oujiang River Estuary sea area. The results show that 78 species of zooplankton are identified, including 16 species of larva, it belongs to 8 classes and 14 categories , with the highest number of species in summer (47 species) and the lowest number in winter (23 species). The dominant species (Y ≥ 0.02) include Calanus sinicus, Sinocalanus sinensis, Acartia pacifica, and Centropages dorsispinatus, 17 species. The average annual abundance of zooplankton is (162.95 ± 310.96) ind./m3, and the average annual biomass is (118.85 ± 62.80) mg/m3. The abundance and biomass of zooplankton are the highest in spring and the lowest in autumn. The abundance in winter is higher than that in summer, and the biomass is lower than that in summer. The average annual Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H'), Pielou evenness index (J') and Margalef richness index (D) are 1.500 ± 0.702, 0.656 ± 0.270 and 2.301 ± 1.087, respectively. Spearman correlation analysis and canonical correspondence analysis show that sea temperature, salinity, Chl a concentration and phytoplankton abundance are important environmental factors affecting the dominant abundance of zooplankton in the Oujiang River Estuary. It provides scientific reference for the study on the influence of seasonal environmental changes on zooplankton in the Oujiang River Estuary, and provides basic data and theoretical basis for the sustainable development of biological resources in the Oujiang River Estuary.
-
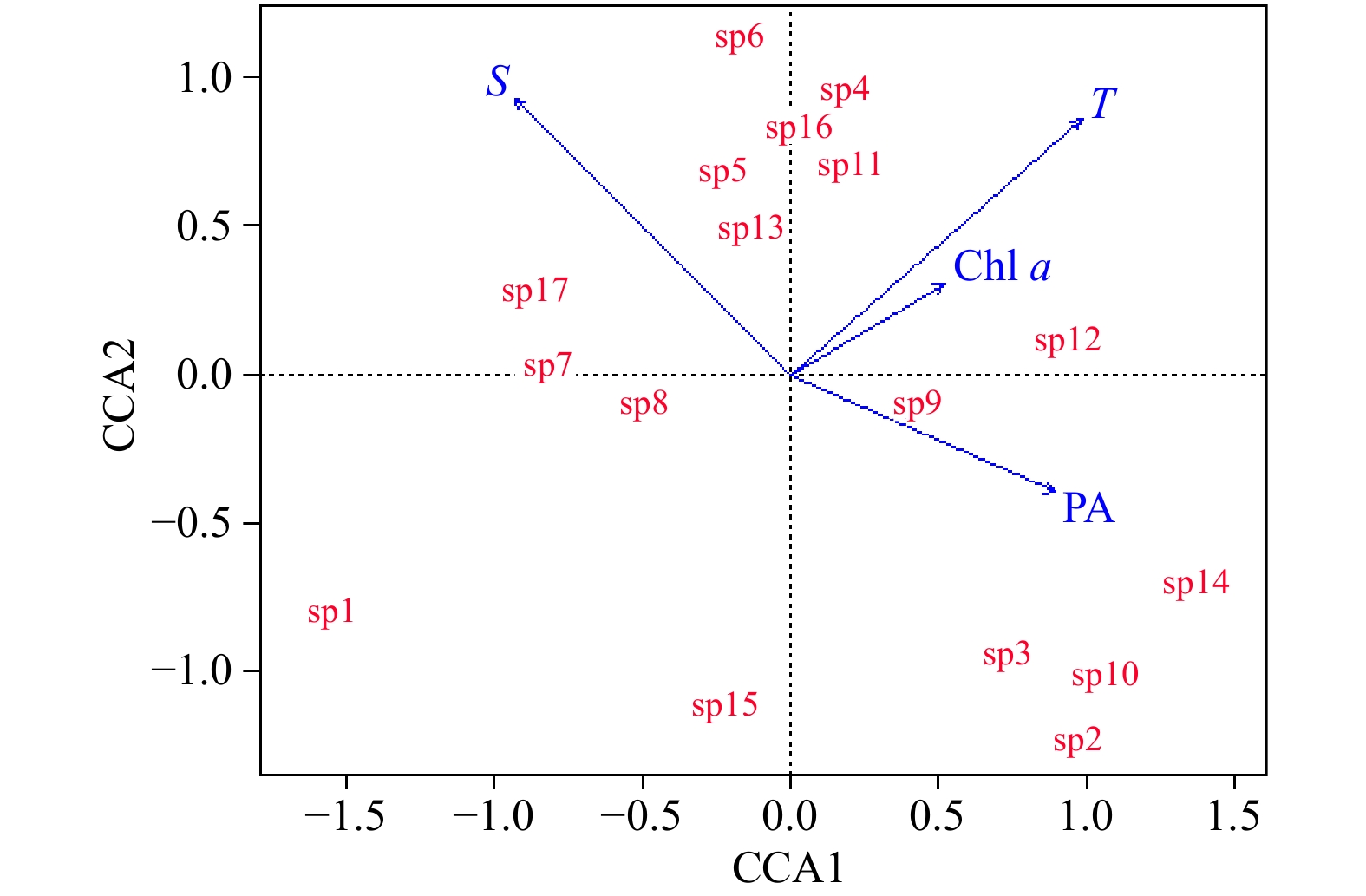
图 7 瓯江口海域浮游动物优势种丰度与环境因子的CCA分析
T:海水温度;S:盐度;Chl a:叶绿素a浓度;PA:浮游植物丰度;sp1:中华哲水蚤;sp2:中华华哲水蚤;sp3:虫肢歪水蚤;sp4:太平洋纺锤水蚤;sp5:背针胸刺水蚤;sp6:精致针刺水蚤;sp7:亚强真哲水蚤;sp8:中华胸刺水蚤;sp9:钩虾(未定种);sp10:糠虾幼体;sp11:磷虾类带叉幼体;sp12:短尾类溞状幼体;sp13:箭虫幼体;sp14:长额刺糠虾;sp15:短额刺糠虾;sp16:百陶箭虫;sp17:异体住囊虫
Fig. 7 CCA analysis of zooplankton abundance and environmental factors in the Oujiang River Estuary sea area
T: Sea water temperature; S: salinity; Chl a: chlorophyll a concentration; PA: phytoplankton abundance; sp1: Calanus sinicus; sp2: Sinocalanus sinensis; sp3: Tortanus vermiculus; sp4: Acartia pacifica; sp5: Centropages dorsispinatus; sp6: Euchaeta concinna; sp7: Eucalanus subcrassus; sp8: Centropages sinensis; sp9: Gammarus sp.; sp10: Mysidacea larva; sp11: Furcilia larva; sp12: Brachyura zoea; sp13: Sagitta larva; sp14: Acanthomysis longirostris; sp15: Acanthomysis brevirostris; sp16: Sagitta bedoti; sp17: Oikopleura dioica
表 1 瓯江口海域浮游动物优势种的季节分布和平均丰度
Tab. 1 Seasonal distribution and average abundance of dominant zooplankton species in the Oujiang River Estuary sea area
序号 种名 冬季 春季 夏季 秋季 优势度 平均丰度/(ind.·m−3) 优势度 平均丰度/(ind.·m−3) 优势度 平均丰度/(ind.·m−3) 优势度 平均丰度/(ind.·m−3) sp1
中华哲水蚤
Calanus sinicus0.96 280.2 ± 435.5 0.03 304.1 ± 958.5 − − − − sp2
中华华哲水蚤
Sinocalanus sinensis/ / 0.03 145.3 ± 407.5 − − − − sp3
虫肢歪水蚤
Tortanus vermiculus/ / 0.02 90.4 ± 278.2 − − / / sp4
太平洋纺锤水蚤
Acartia pacifica/ / − − 0.38 44.3 ± 57.8 0.04 2.9 ± 4.6 sp5
背针胸刺水蚤
Centropages dorsispinatus/ / / / 0.04 5.1 ± 5.4 0.08 6.8 ± 7.8 sp6
精致真刺水蚤
Euchaeta concinna/ / / / 0.02 3.7 ± 5.9 − − sp7
亚强真哲水蚤
Eucalanus subcrassus/ / / / − − 0.14 7.8 ± 15.3 sp8
中华胸刺水蚤
Centropages sinensis/ / / / − − 0.05 6.9 ± 20.4 sp9
钩虾(未定种)
Gammarus sp.− − 0.17 483.2 ± 848.7 − − / / sp10
糠虾幼体
Mysidacea larva/ / 0.10 463.2 ± 1 146.4 0.02 6.1 ± 11.9 − − sp11
磷虾类带叉幼体
Furcilia larva− − 0.02 57.6 ± 140.1 − − − − sp12
短尾类溞状幼体
Brachyura zoea− − − − 0.04 5.3 ± 7.0 − − sp13
箭虫幼体
Sagitta larva− − − − − − 0.02 1.7 ± 1.9 sp14
长额刺糠虾
Acanthomysis longirostris/ / 0.04 191.7 ± 568.1 − − − − sp15
短额刺糠虾
Acanthomysis brevirostris/ / − − / / 0.02 2.3 ± 3.9 sp16
百陶箭虫
Sagitta bedoti/ / − − 0.05 8.6 ± 13.1 − − sp17
异体住囊虫
Oikopleura dioica/ / / / − − 0.03 2.4 ± 4.2 注:sp表示种类;“−”表示此物种不是优势种(Y < 0.02);“/”表示未出现该物种。 表 2 瓯江口海域浮游动物丰度与环境因子的Sperman相关性分析
Tab. 2 Sperman correlation analysis of zooplankton abundance and environmental factors in Oujiang River Estuary sea area
相关系数 桡足类 端足类 浮游幼虫 糠虾类 毛颚类 被囊类 叶绿素a浓度 0.619** 0.112 0.501** 0.443** 0.138 0.225 水温 0.499** 0.211 0.577** 0.156 0.475** −0.045 盐度 −0.217 −0.487** −0.337* −0.558** 0.217 0.163 浮游植物丰度 0.371* 0.477** 0.571** 0.241 0.283 −0.141 注: “*”表示显著相关(p < 0.05),“**”表示极显著相关(p < 0.01)。 -
[1] 陈学超, 朱丽岩, 黄瑛, 等. 南黄海浮游动物群落结构研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(10): 41−49. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160428005Chen Xuechao, Zhu Liyan, Huang Ying, et al. Community structure of the zooplankton in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(10): 41−49. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160428005 [2] Yıldız İ, Feyzioglu A M. Distribution of mesozooplankton along to Anatolian coast in Black Sea over autumn period[J]. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 2016, 45(2): 269−276. [3] 姜会超, 刘宁, 高继庆, 等. 烟台四十里湾浮游动物群落特征及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(4): 1318−1327.Jiang Huichao, Liu Ning, Gao Jiqing, et al. Zooplankton community structure in Sishili Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(4): 1318−1327. [4] Baars M A, Fransz H G. Grazing pressure of copepods on the phytoplankton stock of the central North Sea[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1984, 18(1/2): 120−142. [5] 庞碧剑, 蓝文陆, 黎明民, 等. 北部湾近岸海域浮游动物群落结构特征及季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19): 7014−7024.Pang Bijian, Lan Wenlu, Li Mingmin, et al. Community structure and seasonal variation of zooplankton in coastal Beibu Gulf[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(19): 7014−7024. [6] Suzuki K, Tsuda A, Kiyosawa H, et al. Grazing impact of microzooplankton on a diatom bloom in a mesocosm as estimated by pigment-specific dilution technique[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2002, 271(1): 99−120. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00038-2 [7] Fullgrabe L, Grosjean P, Gobert S, et al. Zooplankton dynamics in a changing environment: a 13-year survey in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2020, 159: 104962. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.104962 [8] 张才学, 龚玉艳, 孙省利, 等. 2010年夏季雷州半岛沿岸海域浮游动物群落结构特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4): 91−99.Zhang Caixue, Gong Yuyan, Sun Xingli, et al. Zooplankton community in the coastal zone of Leizhou Peninsula in summer 2010[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(4): 91−99. [9] 叶文建, 杜萍, 寿鹿, 等. 舟山海域大中型浮游动物群落时空变化及受控要素[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(1): 254−267.Ye Wenjian, Du Ping, Shou Lu, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of marco and mesozooplankton communities and the controlling factors around Zhoushan Archipelago[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(1): 254−267. [10] 陈雷, 徐兆礼, 姚炜民, 等. 瓯江口春季营养盐、 浮游植物和浮游动物的分布[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(3): 1571−1577. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.056Chen Lei, Xu Zhaoli, Yao Weimin, et al. The distribution of nutrients, phytoplankton and zooplankton in spring of the Oujiang River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(3): 1571−1577. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.056 [11] 黄小平, 黄良民. 河口最大浑浊带浮游植物生态动力过程研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(9): 1527−1533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.09.023Huang Xiaoping, Huang Liangmin. Progress in researches on dynamical processes of phytoplankton ecology in maximum turbidity zone of estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(9): 1527−1533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.09.023 [12] 李娟, 温周瑞, 李庚辰, 等. 太湖梅梁湾和贡湖湾浮游甲壳动物群落结构及其与环境因子的相互关系[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(S1): 81−90.Li Juan, Wen Zhourui, Li Gengchen, et al. Relationship between crustacean zooplankton community structure and aquatic environmental factors of Meiliang and Gonghu bay in lake Taihu[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2014, 23(S1): 81−90. [13] 高倩, 徐兆礼. 瓯江口水域夏、秋季浮游动物数量时空分布特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 2009, 16(3): 372−380. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2009.03.009Gao Qian, Xu Zhaoli. Distribution pattern of zooplankton in the Oujiang Estuary during summer and autumn[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2009, 16(3): 372−380. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2009.03.009 [14] 高倩, 徐兆礼. 瓯江口夏、秋季浮游动物种类组成及其多样性[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(10): 2048−2055.Gao Qian, Xu Zhaoli. Species composition and diversity of zooplankton in Oujiang River Estuary in summer and autumn[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(10): 2048−2055. [15] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋调查规范: 第6部分 海洋生物调查: GB/T 12763.6−2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for oceanographic survey: Part 6 marine biological survey: GB/T 12763.6−2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [16] Pianka E R. Ecology of the agamid lizard Amphibolurus isolepis in western Australia[J]. Copeia, 1971, 1971(3): 527−536. [17] 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 1989, 8(4): 13−15.Xu Zhaoli, Chen Yaqu. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1989, 8(4): 13−15. [18] Burks A W, Shannon C E, Weaver W. The mathematical theory of communication[J]. The Philosophical Review, 1951, 60(3): 398−400. doi: 10.2307/2181879 [19] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋监测规范: 第7部分 近海污染生态调查和生物监测: GB 17378.7−2007 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. The specification for marine monitoring: Part 7 ecological survey for offshore pollution and biological monitoring: GB 17378.7−2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [20] 张群, 许旭明, 陈倩. 潮白河流域水库浮游动物群落季节变化特征及其驱动因素[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(2): 290−300.Zhang Qun, Xu Xuming, Chen Qian. Seasonal variation and drivers of zooplankton community in reservoirs of Chaobai river basin[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2023, 59(2): 290−300. [21] 翁学传, 王从敏. 关于台湾暖流水的研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 1989, 19(S1): 159−168.Weng Xuechuan, Wang Congmin. A study on Taiwan warm current water[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 1989, 19(S1): 159−168. [22] Dagg M J. Ingestion of phytoplankton by the micro-and mesozooplankton communities in a productive subtropical estuary[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1995, 17(4): 845−857. doi: 10.1093/plankt/17.4.845 [23] 付菲雨, 卜心宇, 沈盎绿, 等. 西北太平洋亚热带海域浮游动物种类组成与分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(2): 544−550.Fu Feiyu, Bu Xinyu, Shen Anglü, et al. Composition and distribution of zooplankton species in the subtropical areas of the northwestern Pacific Ocean[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(2): 544−550. [24] 陈小庆, 俞存根, 胡颢琰, 等. 舟山渔场及邻近海域浮游动物数量分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(7): 1834−1844.Chen Xiaoqing, Yu Cungen, Hu Haoyan, et al. Distribution characteristic of zooplankton quantitative in Zhoushan Fishing Ground and its adjacent area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(7): 1834−1844. [25] 林义, 邹清, 王航俊, 等. 温州沿岸海域春、夏季浮游动物群落特征及与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2021, 38(6): 51−59.Lin Yi, Zou Qing, Wang Hangjun, et al. Characteristics of zooplankton community structure and its response to environment factors in the Wenzhou coastal waters during spring and summer[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2021, 38(6): 51−59. [26] 邹清, 姚炜民, 张淑敏. 乐清湾2009年夏季浮游动物种类组成和数量分布[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(2): 266−275.Zou Qing, Yao Weimin, Zhang Shumin. Species composition and quantitative distribution of zooplankton in Yueqing Bay during the summer of 2009[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(2): 266−275. [27] 张才学, 周凯, 孙省利, 等. 深圳湾浮游动物的群落结构及季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(11): 2686−2692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.11.029Zhang Caixue, Zhou Kai, Sun Xingli, et al. Community structure and seasonal variation of the zooplankton in Shenzhen Bay[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(11): 2686−2692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.11.029 [28] Pu Xinming, Sun Song, Yang Bo, et al. The combined effects of temperature and food supply on Calanus sinicus in the southern Yellow Sea in summer[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2004, 26(9): 1049−1057. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbh097 [29] Huang Yousong, Liu Guangxing, Chen Xiaofeng. Molecular phylogeography and population genetic structure of the planktonic copepod Calanus sinicus Brodsky in the coastal waters of China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(10): 74−84. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0542-2 [30] 黄加祺, 郑重. 温度和盐度对厦门港几种桡足类存活率的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1986, 17(2): 161−167.Huang Jiaqi, Zheng Zhong. The effects of temperature and salinity on the survival of some copepods from Xiamen Harbour[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1986, 17(2): 161−167. [31] 王媛媛, 李捷, 石洪华, 等. 庙岛群岛南部海域浮游生物群落特征初步分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2016, 40(6): 30−40. doi: 10.11759/hykx20151006001Wang Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Shi Honghua, et al. Preliminary analysis of the characteristics of plankton community in southern waters of Miaodao Archipelago[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(6): 30−40. doi: 10.11759/hykx20151006001 [32] 张冬融, 徐兆礼, 徐佳奕, 等. 杭州湾不同水域秋季浮游动物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(9): 2859−2866.Zhang Dongrong, Xu Zhaoli, Xu Jiayi, et al. Zooplankton community structure in relation to influencing factors in different parts of Hangzhou Bay in autumn[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(9): 2859−2866. [33] 王桂忠, 李少菁, 陈峰, 等. 厦门港海区两种常见纺锤水蚤卵的生物学和季节演替[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 1994, 33(S1): 135−140.Wang Guizhong, Li Shaojing, Chen Feng, et al. Studies on the egg biology and seasonal succession of two common species of Acartia from Xiamen waters[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 1994, 33(S1): 135−140. [34] 左涛, 王俊, 王秀霞. 莱州湾桡足类胸刺水蚤(Centropages)的种类季节更替和生态分布[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(2): 327−335.Zuo Tao, Wang Jun, Wang Xiuxia. Seasonal species succession and ecological distribution of Copepod Centropages in Laizhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(2): 327−335. [35] 袁骐, 王云龙. 东海北部肥胖箭虫和百陶箭虫空间分布参数的特征[J]. 海洋渔业, 2007, 29(3): 240−244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2007.03.008Yuan Qi, Wang Yunlong. On the parametric features of the spatial distribution of Sagitta enflata and Sagitta bedoti in the northern part of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2007, 29(3): 240−244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2007.03.008 [36] 孙鲁峰, 孙岳, 徐兆礼. 椒江口海域浮游动物群落季节变化特征[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2014, 23(1): 131−138.Sun Lufeng, Sun Yue, Xu Zhaoli. The study on the seasonal variations of zooplankton community in Jiaojiang coastal waters[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2014, 23(1): 131−138. [37] 郑敬云, 李孟国, 麦苗, 等. 瓯江口水文泥沙特征分析[J]. 水道港口, 2008, 29(1): 1−7.Zheng Jingyun, Li Mengguo, Mai Miao, et al. Hydrographic and sediment analyses of the Oujiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2008, 29(1): 1−7. [38] 徐佳奕, 徐兆礼. 三沙湾浮游动物生态类群演替特征[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5): 1413−1424. doi: 10.5846/stxb201207241050Xu Jiayi, Xu Zhaoli. Seasonal succession of zooplankton in Sansha Bay, Fujian[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 1413−1424. doi: 10.5846/stxb201207241050 [39] Devreker D, Souissi S, Seuront L. Effects of chlorophyll concentration and temperature variation on the reproduction and survival of Temora longicornis (Copepoda, Calanoida) in the eastern English Channel[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2005, 318(2): 145−162. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2004.12.011 [40] Lenz P H, Hower A E, Hartline D K. Temperature compensation in the escape response of a marine copepod, Calanus finmarchicus (Crustacea)[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 2005, 209(1): 75−85. doi: 10.2307/3593143 [41] 郑白雯, 曹文清, 林元烧, 等. 北部湾北部生态系统结构与功能研究Ⅰ. 浮游动物种类组成及其时空变化[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(6): 154−161.Zheng Baiwen, Cao Wenqing, Lin Yuanshao, et al. Ecosystem structure and function in northern Beibu Gulf Ⅰ. The temporal and spatial variation of species composition on zooplankton[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(6): 154−161. [42] 付菲雨, 韩霈武, 方舟, 等. 西北太平洋春、冬季浮游动物优势种水平分布与影响因子的关系[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2022, 37(3): 489−496.Fu Feiyu, Han Peiwu, Fang Zhou, et al. Distribution and relationship with influential factors of dominant zooplankton species in the Northwest Pacific Ocean in spring and winter[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2022, 37(3): 489−496. [43] 朱延忠, 陈洪举, 刘光兴. 福建沙埕港浮游动物群落特征及影响因子[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 38(6): 943−950.Zhu Yanzhong, Chen Hongju, Liu Guangxing. Study on the community characteristics of zooplankton and influential factors in Shacheng Harbor, Fujian Province[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2008, 38(6): 943−950. -




 下载:
下载: