Multi-scale impacts on beach ecosystem of beach nourishment: a review
-
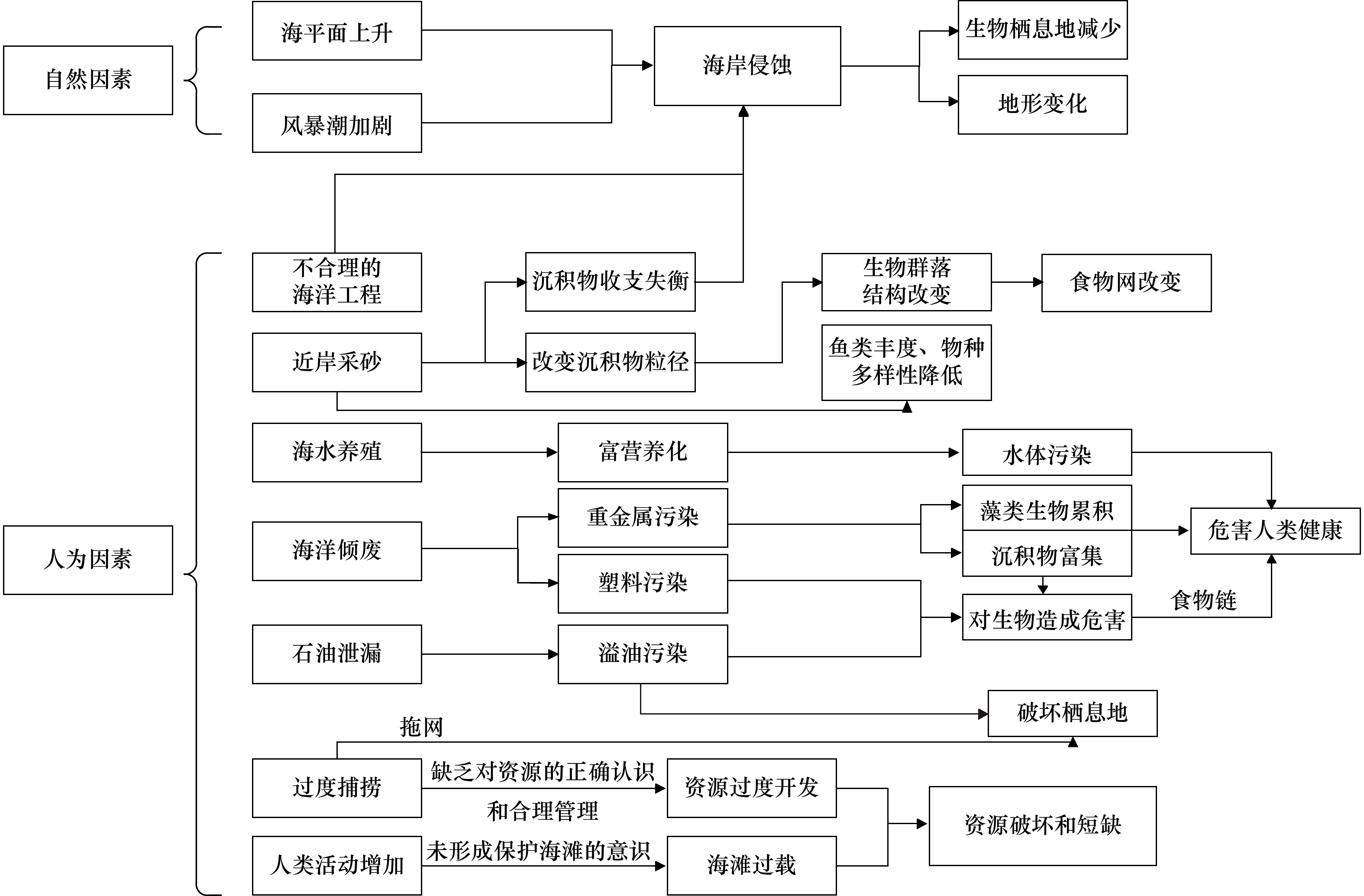
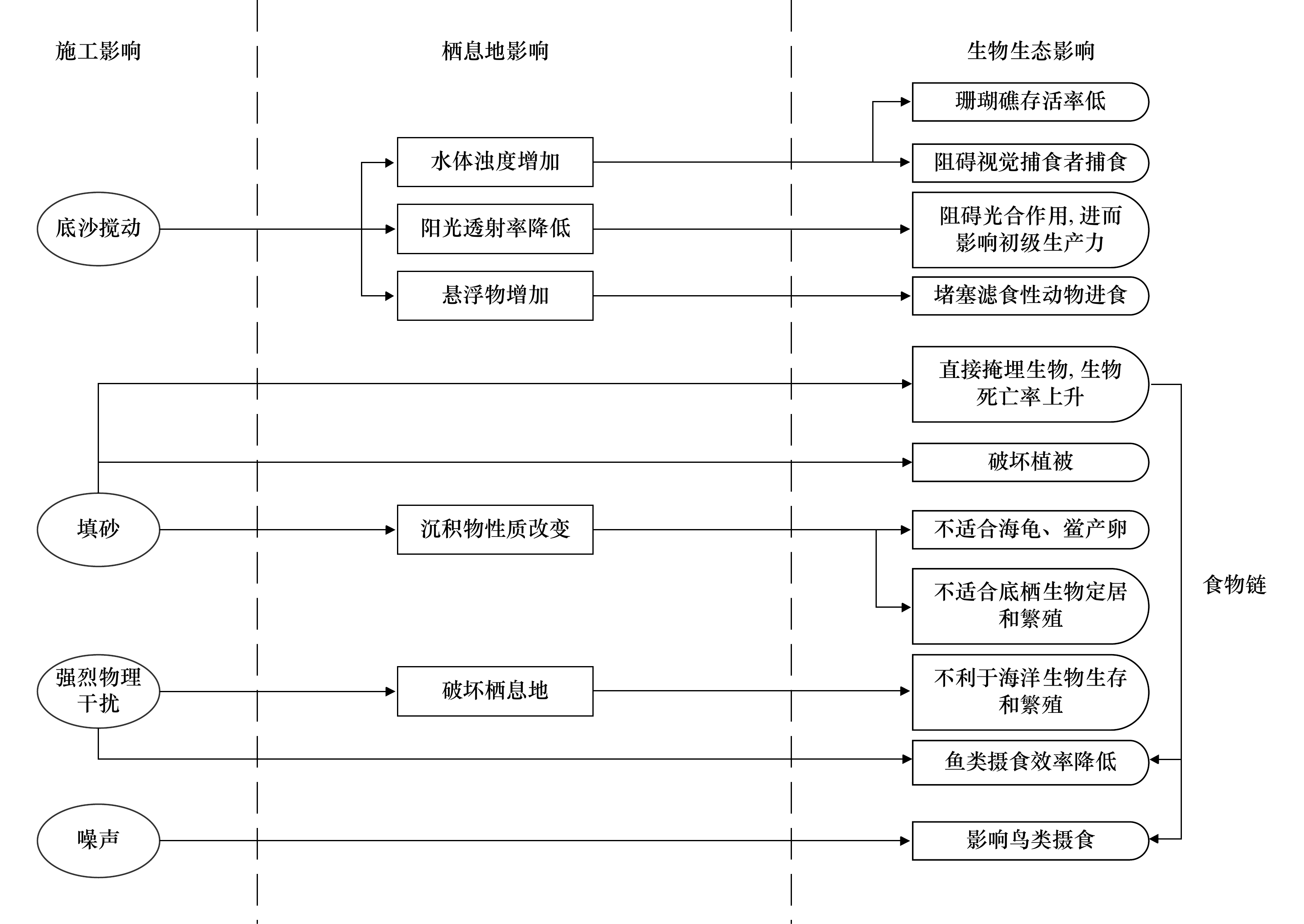
摘要: 海滩是常见且脆弱的滨海生态系统,具有极大的生态服务功能。受气候变化和人类活动的多重影响,海滩生态系统受损严重。海滩养护是利用人工补沙的方式对海滩地貌进行修复,是抵御海岸侵蚀和改善海滩环境的有效措施,以往的养护往往忽略了对海滩生态系统的影响,许多研究表明海滩养护对海滩生态系统会产生多方面、多尺度的复杂影响。本文在总结前人研究的基础上,梳理出海滩生态系统的构成、特点和功能,分析了海滩生态受损的基本特征,对海滩养护对海滩生态系统多尺度影响过程及影响机制进行了重点述评,并从降低负面生态影响角度给出了海滩养护技术优化方法,以支撑海滩生态系统适应性管理和可持续利用。Abstract: Beach is a common and vulnerable coastal ecosystem with huge ecological service functions. Due to the multiple impacts of climate change and human activities, beach ecosystem has been seriously damaged. Beach nourishment is an effective approach to prevent coastal erosion and improve the beach environment by using sand replenishment to restore beach morphology. Previous nourishments have often neglected the impacts on beach ecosystem. Many studies show that beach nourishment have multifaceted, multi-scale and complex impacts on beach ecosystem. Based on reviewing previous researches, the compositions, characteristics and functions of beach ecosystem are summarized. The basic characteristics of beach ecological damage, the impact process and mechanism of beach nourishment on beach ecosystem at various scales are analyzed. Then, some adaptive measures for beach nourishment are suggested from the perspective of reducing negative ecological impacts, which would support coastal management and sustainable utilization of beach.
-
Key words:
- beach ecosystem /
- beach nourishment /
- ecological impacts
-
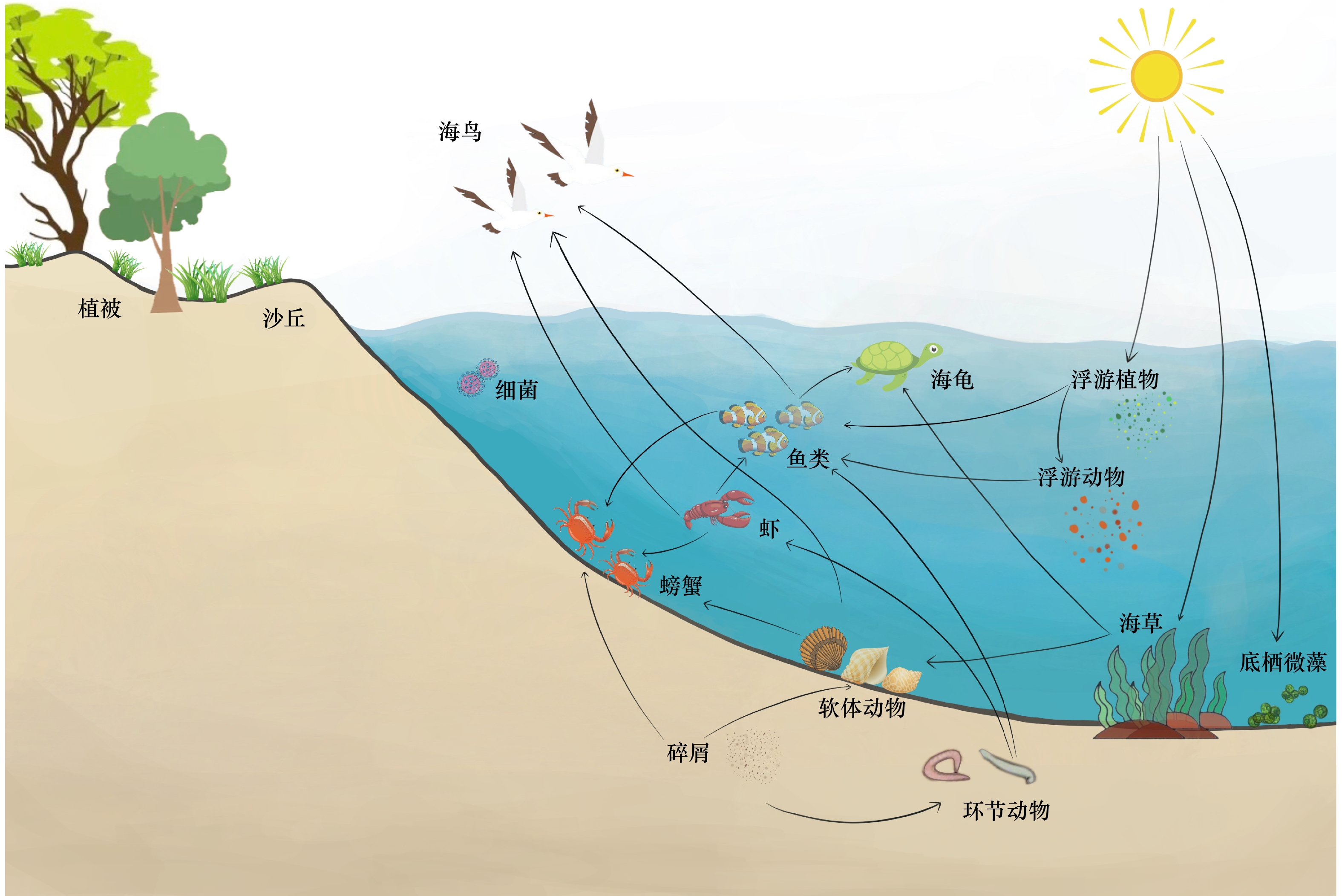
功能分类 生态系统服务功能 沙丘 海滩 激浪带 供给 (生物) 为了营养目的原位养殖的动物 

用于营养的野生植物(陆生和水生,包括真菌、藻类) 
直接使用或加工的野生植物纤维及其他原料(不包括遗传物质) 

用于营养的野生动物(陆生和水生) 


直接使用或加工的野生动物纤维及其他原料(不包括遗传物质) 

为维持或建立种群而收集的种子、孢子和其他植物材料 
为维持或建立种群而收集的动物材料 

供给 (非生物) 可饮用的地表水 
用于原料的地下水(非饮用目的) 
用于能源的海水 
可饮用的地下水 
用于营养目的的矿物质 
用作原料的矿物质 

用于营养目的的非矿物质或生态系统物质 


用于原料的非矿物质 

太阳能 

调节和维持(生物) 微生物、藻类、动植物的生物修复 


微生物、藻类、动植物的过滤/封存/储存/积累 


气味减少 


噪声衰减 
视觉遮蔽 
控制侵蚀速率 
质量运动的缓冲和衰减 
水文循环和水流调节(包括防洪和海岸保护) 


防风 
授粉(或在海洋环境中的配子传播) 


种子传播 
保持幼小种群和栖息地(包括基因库的保护) 


风化过程及其对泥土质量的影响 


泥土分解固定过程及其对泥土质量的影响 

通过生物过程调节海水的化学条件 


大气和海洋化学组分的调节 


调节温度和湿度,包括通风和蒸发作用 

调节和维持(非生物) 淡水和海洋生态系统的稀释 

通过其他化学或物理手段的调节(如过滤、封存、储存或积累) 


调节和维持(非生物) 通过非生物结构或过程对损害的调节 
质量流动 


液体流动 


气体流动 
通过无机的自然的化学或物理过程维持或调节 


其他:种子、幼体和配子通过物理过程传播 


文化 (生物) 通过主动或沉浸式互动,实现促进健康、恢复或享受的活动 


通过被动或观察互动,实现促进健康、恢复或享受的活动 


能够进行科学调查或创造传统生态知识的活动 


教育和培训 


文化或遗产上有共鸣的活动 


审美体验 


具有象征意义的元素 


具有神圣或宗教意义的元素 


用于娱乐或代表意义的元素 


存在价值 


选择价值或遗赠价值 


文化 (非生物) 能够进行主动或被动的物理和经验的相互作用 


能够进行思维的相互作用 


能够进行精神的、象征性的和其他的相互作用 


具有存在、选择或遗产价值的自然特征 


注:颜色条带越长,表示该服务功能供应越多。 表 2 典型海滩养护案例
Tab. 2 Typical beach nourishment cases
养护工程 生态影响 恢复时间 恢复程度 参考文献 澳大利亚新南威尔士州
博塔尼湾海滩养护工程结束后采样无Exoediceros fossor生物;沉积物变化不大,生物恢复在1年内完成 1年 恢复在几周内开始,以时空相互作用为标准,恢复在1年内完成 文献[91] 澳大利亚东部棕榈
海滩养护工程完成5个月后,沉积物粒度恢复,但只限于海滩的中层和上层,下层沉积物会变粗。养护的影响大小在
潮间带梯度上是不均匀的,对靠近沙丘的
海滩上层影响要大得多5个月 海滩的上层没有恢复,仍然是生物稀少的。在中层和下层,恢复正在进行,物种丰富度恢复完全,但丰度恢复不完全 文献[92] 雷洛萨海滩沙丘恢复 降低了海岸侵蚀的影响,海滩变得更平坦;人工沙丘的潮间带动物群落密度较潮上带的更高(F = 3.56,p = 0.063),在某种程度上沙丘恢复工程有利于潮间带生物。对比天然沙丘,欧洲沙蚤(Talitrus saltator)的丰度在重建沙丘处明显降低(F = 7.63,p = 0.007) 4年 沙丘重建的影响在第3年仍然可见,
但在第4年完全消失文献[7] 美国加利福尼亚州圣迭戈县8个海滩补沙工程 补沙后1个月,所有无脊椎动物的密度都有所降低,特别是多毛类,减少了2/3。沙蟹(Emerita analoga)在补沙后4个月大量繁殖,在补沙地方变得更常见 1年3个月 补沙15个月后,补沙对生物多样性指标
的影响消失文献[61] 表 3 海滩养护填砂沉积物性质
Tab. 3 Beach nourishment sediment properties
沉积物性质 选择 影响 参考文献 粒径 接近或略粗于
天然砂粒径与稳定性有关,填砂粒径细于天然砂可能会导致生物缺乏氧气而窒息死亡,干滩面积减小;
粗于天然砂可能会阻碍鸟类和鱼类进食,并导致潮间带淤积文献[21, 97] 泥球 尽量少 与海水浊度有关,浊度升高会阻碍视觉捕食者的捕食,对邻近珊瑚礁生态系统造成不利影响 文献[73] 贝壳碎片 尽量少 影响海滩潮间带底栖动物的掘穴能力,并可能导致较低的生物密度 文献[66] 化学毒性 无化学毒性的砂 细粒沉积物可能被重金属或合成有机化合物污染,可能对沉降的幼体或海滩无脊椎动物
的后期生命阶段产生毒性文献[98] 材料 硅酸盐等耐磨损材料 耐磨损材料能保证更长的耐久性,并防止近岸水浑浊 文献[96] 颜色 与天然砂相同 既保护景观,也避免对地表或地下生活和筑巢的动物造成影响 文献[75] -
[1] 杨燕雄, 张甲波, 刘松涛. 秦皇岛海滩养护工程的实践与方法[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(3): 1−15.Yang Yanxiong, Zhang Jiabo, Liu Songtao. What we have learnt from the beach nourishment project in Qinhuangdao[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(3): 1−15. [2] 戚洪帅, 刘根, 蔡锋, 等. 海滩修复养护技术发展趋势与前景[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(1): 111−125.Qi Hongshuai, Liu Gen, Cai Feng, et al. Development trend and prospect of beach nourishment technology[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 111−125. [3] Amaral A C Z, Corte G N, Filho J S R, et al. Brazilian sandy beaches: characteristics, ecosystem services, impacts, knowledge and priorities[J]. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 2016, 64(sp2): 5−16. [4] 张朝晖, 王宗灵, 朱明远. 海洋生态系统服务的研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2007, 26(6): 925−932.Zhang Zhaohui, Wang Zongling, Zhu Mingyuan. Research progress on marine ecosystem services[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26(6): 925−932. [5] Defeo O, McLachlan A, Schoeman D S, et al. Threats to sandy beach ecosystems: a review[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2009, 81(1): 1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2008.09.022 [6] Defeo O, McLachlan A, Armitage D, et al. Sandy beach social–ecological systems at risk: regime shifts, collapses, and governance challenges[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2021, 19(10): 564−573. doi: 10.1002/fee.2406 [7] Nourisson D H, Bessa F, Scapini F, et al. Macrofaunal community abundance and diversity and talitrid orientation as potential indicators of ecological long-term effects of a sand-dune recovery intervention[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2014, 36: 356−366. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.08.005 [8] Semeoshenkova V, Newton A. Overview of erosion and beach quality issues in three southern European countries: Portugal, Spain and Italy[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2015, 118: 12−21. [9] Ma Zhijun, Melville D S, Liu Jianguo, et al. Rethinking China’s new great wall[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6212): 912−914. doi: 10.1126/science.1257258 [10] 陈雪初, 戴禹杭, 孙彦伟, 等. 大都市海岸带生态整治修复技术研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(3): 477−484.Chen Xuechu, Dai Yuhang, Sun Yanwei, et al. Research progress and prospect of eco-realignment and restoration technologies for metropolitan coastal zone[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(3): 477−484. [11] 李亚娟, 马春, 毛天宇. 生态修复工程在港口建设中的应用[J]. 科技视界, 2014(26): 68, 122.Li Yajuan, Ma Chun, Mao Tianyu. Application of ecological restoration project in port construction[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2014(26): 68, 122. [12] 朱嘉, 刘建辉, 蔡晓琼. 珠江口外伶仃岛海滩修复研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2014, 31(11): 36−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2014.11.009Zhu Jia, Liu Jianhui, Cai Xiaoqiong. Research on beach restoration of Wailingding Island, Zhujiang River Estuary[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2014, 31(11): 36−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2014.11.009 [13] 蔡锋, 刘根. 我国海滩养护修复的发展与技术创新[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2019, 38(4): 452−463.Cai Feng, Liu Gen. Beach nourishment development and technological innovations in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 452−463. [14] 朱君, 蔡锋, 刘建辉, 等. 海滩养护修复过程中拦沙堤的应用[J]. 海洋工程, 2021, 39(6): 152−165.Zhu Jun, Cai Feng, Liu Jianhui, et al. Application of groin system in beach nourishment[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2021, 39(6): 152−165. [15] James R J. From beaches to beach environments: linking the ecology, human-use and management of beaches in Australia[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2000, 43(6): 495−514. [16] Micallef A, Williams A T. Theoretical strategy considerations for beach management[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2002, 45(4/5): 261−275. [17] 姜欢欢, 温国义, 周艳荣, 等. 我国海洋生态修复现状、存在的问题及展望[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2013, 30(1): 35−38, 112.Jiang Huanhuan, Wen Guoyi, Zhou Yanrong, et al. Current situation, problems and prospects of marine ecological restoration in China[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2013, 30(1): 35−38, 112. [18] 沈国英, 黄凌风, 郭丰, 等. 海洋生态学[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.Shen Guoying, Huang Lingfeng, Guo Feng, et al. Marine Ecology[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. [19] Corte G N, Checon H H, Esmaeili Y S, et al. Evaluation of the effects of urbanization and environmental features on sandy beach macrobenthos highlights the importance of submerged zones[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 182: 113962. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113962 [20] Speybroeck J, Bonte D, Courtens W, et al. Beach nourishment: an ecologically sound coastal defence alternative? A review[J]. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 2006, 16(4): 419−435. doi: 10.1002/aqc.733 [21] de Schipper M A, Ludka B C, Raubenheimer B, et al. Beach nourishment has complex implications for the future of sandy shores[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2021, 2(1): 70−84. [22] 尤龙辉, 林捷, 谭芳林, 等. 福建省岩石性海岸、潮间沙石海滩生态系统服务及其价值研究[J]. 防护林科技, 2016(10): 10−14.You Longhui, Lin Jie, Tan Fanglin, et al. Evaluation of ecosystem services and value of rocky coast and sandy beach wetland in Fujian Province[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2016(10): 10−14. [23] 黎树式, 林俊良, 黄鹄, 等. 广西海滩侵蚀原因与修复[J]. 北部湾大学学报, 2019, 34(12): 30−37.Li Shushi, Lin Junliang, Huang Hu, et al. Causes of beach erosion and its restoration in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Beibu Gulf University, 2019, 34(12): 30−37. [24] Costa L L, Fanini L, Zalmon I R, et al. Cumulative stressors impact macrofauna differentially according to sandy beach type: a meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 307: 114594. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114594 [25] Harris L, Campbell E E, Nel R, et al. Rich diversity, strong endemism, but poor protection: addressing the neglect of sandy beach ecosystems in coastal conservation planning[J]. Diversity and Distributions, 2014, 20(10): 1120−1135. doi: 10.1111/ddi.12226 [26] Jaramillo E, McLachlan A, Coetzee P. Intertidal zonation patterns of macroinfauna over a range of exposed sandy beaches in South-central Chile[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1993, 101: 105−117. doi: 10.3354/meps101105 [27] McLachlan A, Jaramillo E, Defeo O, et al. Adaptations of bivalves to different beach types[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 1995, 187(2): 147−160. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(94)00176-E [28] Heymans J J, McLachlan A. Carbon budget and network analysis of a high-energy beach/surf-zone ecosystem[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1996, 43(4): 485−505. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1996.0083 [29] Dugan J E, Hubbard D M, Page H M, et al. Marine macrophyte wrack inputs and dissolved nutrients in beach sands[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2011, 34(4): 839−850. doi: 10.1007/s12237-011-9375-9 [30] Checon H H, Corte G N, Esmaeili Y S, et al. The efficacy of benthic indices to evaluate the ecological quality and urbanization effects on sandy beach ecosystems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 856: 159190. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159190 [31] Harris L R, Defeo O. Sandy shore ecosystem services, ecological infrastructure, and bundles: new insights and perspectives[J]. Ecosystem Services, 2022, 57: 101477. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2022.101477 [32] Schlacher T A, Schoeman D S, Dugan J, et al. Sandy beach ecosystems: key features, sampling issues, management challenges and climate change impacts[J]. Marine Ecology, 2008, 29(S1): 70−90. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0485.2007.00204.x [33] Barbier E B, Hacker S D, Kennedy C, et al. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services[J]. Ecological Monographs, 2011, 81(2): 169−193. doi: 10.1890/10-1510.1 [34] Sardá R. Ecosystem services in the Mediterranean Sea: the need for an economic and business oriented approach[M]//Hughes T B. Mediterranean Sea: Ecosystems, Economic Importance and Environmental Threats. New York: Nova Publishers, 2013: 1−34. [35] 张明慧, 孙昭晨, 梁书秀, 等. 海岸整治修复国内外研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2017, 36(4): 635−640.Zhang Minghui, Sun Zhaochen, Liang Shuxiu, et al. Progress of coastal environment repairing and cleaning engineering research and its prospect[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(4): 635−640. [36] 李广雪, 宫立新, 杨继超, 等. 山东滨海沙滩侵蚀状态与保护对策[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(5): 35−46.Li Guangxue, Gong Lixin, Yang Jichao, et al. Beach erosion along the coast of Shandong Province and protection countermeasures[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(5): 35−46. [37] Cai Feng, Su Xianze, Liu Jianhui, et al. Coastal erosion in China under the condition of global climate change and measures for its prevention[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(4): 415−426. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.05.034 [38] 吕永龙, 苑晶晶, 李奇锋, 等. 陆源人类活动对近海生态系统的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(5): 1183−1191.Lü Yonglong, Yuan Jingjing, Li Qifeng, et al. Impacts of land-based human activities on coastal and offshore marine ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(5): 1183−1191. [39] 聂华欣. 辽东湾近海污染问题与治理研究[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2022.Nie Huaxin. Research on offshore pollution problems and management in Liaodong Bay[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2022. [40] 金信飞. 浅析海洋污染与海洋渔业资源保护[J]. 工程技术研究, 2020, 2(11): 31−32.Jin Xinfei. Analysis of marine pollution and marine fishery resources protection[J]. Engineering and Technological Research, 2020, 2(11): 31−32. [41] Wang Ying, Wang Juying, Mu Jingli, et al. Aquatic predicted no-effect concentration for three polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and probabilistic ecological risk assessment in Liaodong Bay of the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(1): 148−158. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1597-x [42] Kalantzi I, Papageorgiou N, Sevastou K, et al. Metals in benthic macrofauna and biogeochemical factors affecting their trophic transfer to wild fish around fish farm cages[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 470−471: 742−753. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.020 [43] Defeo O, Castrejón M, Pérez-Castañeda R, et al. Co-management in Latin American small-scale shellfisheries: assessment from long-term case studies[J]. Fish and Fisheries, 2016, 17(1): 176−192. doi: 10.1111/faf.12101 [44] Wiese F K, Ryan P C. The extent of chronic marine oil pollution in southeastern Newfoundland waters assessed through beached bird surveys 1984−1999[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 46(9): 1090−1101. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00250-9 [45] Ko J Y, Day J W. A review of ecological impacts of oil and gas development on coastal ecosystems in the Mississippi Delta[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2004, 47(11/12): 597−623. [46] Dayton P K, Thrush S F, Agardy M T, et al. Environmental effects of marine fishing[J]. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 1995, 5(3): 205−232. doi: 10.1002/aqc.3270050305 [47] Thomson E E. Impacts of summer hypoxia on benthic fauna and implications for fisheries productivity in the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina[D]. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina, 1998. [48] 崔晓菁. 中国海洋资源开发现状与海洋综合管理策略[J]. 管理观察, 2019(17): 63−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2877.2019.17.025Cui Xiaojing. Current situation of marine resources exploitation and comprehensive marine management strategy in China[J]. Management Observer, 2019(17): 63−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2877.2019.17.025 [49] 王圣洁, 刘锡清, 戴勤奋, 等. 中国海砂资源分布特征及找矿方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3): 83−89.Wang Shengjie, Liu Xiqing, Dai Qinfen, et al. Distribution characteristics of marine aggregate resources and potential prospect in China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 83−89. [50] 曹雪晴, 张勇, 何拥军, 等. 中国近海建筑用海砂勘查回顾与面临的问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(3): 121−125.Cao Xueqing, Zhang Yong, He Yongjun, et al. Retrospect and discussion of surveys for construction sand in China offshore area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(3): 121−125. [51] Peduzzi P. Sand, rarer than one thinks[J]. Environmental Development, 2014, 11: 208−218. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2014.04.001 [52] Hwang S W, Lee H G, Choi K H, et al. Impact of sand extraction on fish assemblages in Gyeonggi Bay, Korea[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2014, 30(6): 1251−1259. [53] Rangel-Buitrago N, Neal W, Pilkey O, et al. The global impact of sand mining on beaches and dunes[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2023, 235: 106492. [54] Masalu D C P. Coastal erosion and its social and environmental aspects in Tanzania: a case study in illegal sand mining[J]. Coastal Management, 2002, 30(4): 347−359. doi: 10.1080/089207502900255 [55] Thornton E B, Sallenger A, Sesto J C, et al. Sand mining impacts on long-term dune erosion in southern Monterey Bay[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 229(1/2): 45−58. [56] McLachlan A. Physical factors in benthic ecology: effects of changing sand particle size on beach fauna[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1996, 131: 205−217. doi: 10.3354/meps131205 [57] Smith V H, Schindler D W. Eutrophication science: where do we go from here?[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2009, 24(4): 201−207. [58] Thushari G G N, Senevirathna J D M. Plastic pollution in the marine environment[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6(8): e04709. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04709 [59] Peterson C H, Bishop M J. Assessing the environmental impacts of beach nourishment[J]. BioScience, 2005, 55(10): 887−896. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2005)055[0887:ATEIOB]2.0.CO;2 [60] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 海滩养护与修复技术指南: HY/T 255−2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Technical guide for beach nourishment and restoration: HY/T 255−2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2019. [61] Wooldridge T, Henter H J, Kohn J R. Effects of beach replenishment on intertidal invertebrates: a 15-month, eight beach study[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 175: 24−33. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.03.018 [62] Peterson C H, Bishop M J, D’Anna L M, et al. Multi-year persistence of beach habitat degradation from nourishment using coarse shelly sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 487: 481−492. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.046 [63] 蔡锋. 中国海滩养护技术手册[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015.Cai Feng. Chinese Beach Nourishment Manual[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2015. [64] Cooke B C, Jones A R, Goodwin I D, et al. Nourishment practices on Australian sandy beaches: a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 113: 319−327. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.09.025 [65] Bird E, Lewis N. Beach Renourishment[M]. Cham: Springer, 2015. [66] Peterson C H, Summerson H C, Thomson E, et al. Synthesis of linkages between benthic and fish communities as a key to protecting essential fish habitat[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 2000, 66(3): 759−774. [67] Dean R G. Beach Nourishment: Theory and Practice[M]. New Jersey: World Scientific, 2002. [68] Menn I, Junghans C, Reise K. Buried alive: Effects of beach nourishment on the infauna of an erosive shore in the North Sea[J]. Senckenbergiana Maritima, 2003, 32(1/2): 125−145. [69] McLachlan A, Brown A C. The Ecology of Sandy Shores[M]. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006. [70] Courtenay Jr W R, Harrema D J, Thompson M J, et al. Ecological monitoring of beach erosion control projects, Broward County, Florida, and adjacent areas[R]. Ft. Belvoir, VA: US Army Corps of Engineers, 1974. [71] 雷刚, 刘根, 蔡锋. 厦门岛会展中心海滩养护及其对我国海岸防护的启示[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2013, 32(3): 305−315. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.03.002Lei Gang, Liu Gen, Cai Feng. Enlightenment to China’s coastal protection from the coast beach nourishment at Huizhan Zhongxin of Xiamen Island[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 305−315. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.03.002 [72] Medina J R, Tintoré J, Duarte C M. Las praderas de Posidonia oceanica y la regeneración de playas[J]. Revista de Obras Publicas, 2001, 148(3409): 31−43. [73] Benfield M C, Minello T J. Relative effects of turbidity and light intensity on reactive distance and feeding of an estuarine fish[J]. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 1996, 46(2): 211−216. doi: 10.1007/BF00005223 [74] Manning L M, Peterson C H, Bishop M J. Dominant macrobenthic populations experience sustained impacts from annual disposal of fine sediments on sandy beaches[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2014, 508: 1−15. doi: 10.3354/meps10870 [75] Saengsupavanich C, Pranzini E, Ariffin E H, et al. Jeopardizing the environment with beach nourishment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 868: 161485. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161485 [76] Fisher L, Banks K, Gilliam D S, et al. Real-time coral stress observations before, during, and after beach nourishment dredging offshore SE Florida[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Coral Reef Symposium. [S.l.: s.n.]: 2008. [77] Convertino M, Donoghue J F, Chu-Agor M L, et al. Anthropogenic renourishment feedback on shorebirds: a multispecies Bayesian perspective[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2011, 37(8): 1184−1194. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.02.019 [78] Martin K L M, Adams L C. Effects of repeated sand replenishment projects on runs of a beach-spawning fish, the California grunion[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(3): 178. doi: 10.3390/jmse8030178 [79] Montague C L. Recovering the sand deficit from a century of dredging and jetties along Florida’s Atlantic coast: a reevaluation of beach nourishment as an essential tool for ecological conservation[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2008, 24(4): 899−916. [80] Nelson D A, Dickerson D D. Effects of beach nourishment on sea turtles[C]//Proceedings of the 1st Beach Preservation Technology Conference. Tallahassee, Florida: Florida Shore & Beach Preservation Association, Inc. , 1988. [81] Raymond P W. The effects of beach restoration on marine Turtles Nesting in South Brevard County, Florida[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 1984. [82] Burney C, Mattison C. The effects of egg relocation and beach nourishment on the nesting and hatching of Caretta caretta in Broward County, Florida, 1991. [C]//Proceedings of the Fifth Annual National Conference on Beach Preservation Technology. Tallahassee, Florida: Florida Shore and Beach Preservation Assessment, 1992: 395−407. [83] Grain D A, Bolten A B, Bjorndal K A. Effects of beach nourishment on sea turtles: review and research initiatives[J]. Restoration Ecology, 1995, 3(2): 95−104. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-100X.1995.tb00082.x [84] Holloman K T, Godfrey M H. 2006 Sea turtle monitoring project report Bogue Banks, North Carolina[R]. Raleigh: North Carolina Wildlife Resources Commission, 2008. [85] Rumbold D G, Davis P W, Perretta C. Estimating the effect of beach nourishment on Caretta caretta (loggerhead sea turtle) nesting[J]. Restoration Ecology, 2001, 9(3): 304−310. doi: 10.1046/j.1526-100x.2001.009003304.x [86] Leewis L, van Bodegom P M, Rozema J, et al. Does beach nourishment have long-term effects on intertidal macroinvertebrate species abundance?[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2012, 113: 172−181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.07.021 [87] Peterson C H, Bishop M J, Johnson G A, et al. Exploiting beach filling as an unaffordable experiment: benthic intertidal impacts propagating upwards to shorebirds[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2006, 338(2): 205−221. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2006.06.021 [88] Adriaanse L A, Coosen J. Beach and dune nourishment and environmental aspects[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1991, 16(1): 129−146. doi: 10.1016/0378-3839(91)90056-M [89] Roig F X, Rodríguez-Perea A, Martín-Prieto J A, et al. Soft management of beach-dune systems as a tool for their sustainability[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2009(S56): 1284−1288. [90] 魏伟, 张一康, 张忠起, 等. 借用自然力量应对极端风暴的韧性设计——珠海香炉湾沙滩景观带[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(12): 80−84.Wei Wei, Zhang Yikang, Zhang Zhongqi, et al. Resilient design by natural methods in response to extreme storms: the landscape belt of Xianglu Bay beach in Zhuhai[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(12): 80−84. [91] Jones A R, Murray A, Lasiak T A, et al. The effects of beach nourishment on the sandy-beach amphipod Exoediceros fossor: impact and recovery in Botany Bay, New South Wales, Australia[J]. Marine Ecology, 2008, 29(S1): 28−36. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0485.2007.00197.x [92] Schlacher T A, Noriega R, Jones A, et al. The effects of beach nourishment on benthic invertebrates in eastern Australia: impacts and variable recovery[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 435−436: 411−417. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.071 [93] Zeiler M, Figge K, Griewatsch K, et al. Regenerierung von materialentnahmestellen in Nord-und Ostsee[J]. Die Küste, 2004, 68: 67−98. [94] Greene K. Beach nourishment: a review of the biological and physical impacts[R]. Washington: Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission, 2002. [95] De Jong M F, Baptist M J, Lindeboom H J, et al. Short-term impact of deep sand extraction and ecosystem-based landscaping on macrozoobenthos and sediment characteristics[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 97(1/2): 294−308. [96] Pranzini E, Anfuso G, Muñoz-Perez J J. A probabilistic approach to borrow sediment selection in beach nourishment projects[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2018, 139: 32−35. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2018.05.001 [97] Quammen M L. Influence of subtle substrate differences on feeding by shorebirds on intertidal mudflats[J]. Marine Biology, 1982, 71(3): 339−343. doi: 10.1007/BF00397050 [98] Foteinis S, Kallithrakas-Kontos N G, Synolakis C. Heavy metal distribution in opportunistic beach nourishment: a case study in Greece[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2013, 2013: 472149. [99] McLachlan A, Defeo O. The Ecology of Sandy Shores[M]. 3rd ed. London: Academic Press, 2018. [100] Stive M J F, De Schipper M A, Luijendijk A P, et al. A new alternative to saving our beaches from sea-level rise: the sand engine[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2013, 29(5): 1001−1008. [101] Van Egmond E M, Van Bodegom P M, Berg M P, et al. A mega-nourishment creates novel habitat for intertidal macroinvertebrates by enhancing habitat relief of the sandy beach[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 207: 232−241. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.03.003 [102] Rosov B, Bush S, Briggs T R, et al. The state of understanding the impacts of beach nourishment activities on infaunal communities[J]. Shore & Beach, 2016, 84(3): 4−8. [103] Rakocinski C F, Heard R W, LeCroy S E, et al. Responses by macrobenthic assemblages to extensive beach restoration at Perdido Key, Florida, U. S. A.[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1996, 12(1): 326−353. [104] Janssen G, Mulder S. Zonation of macrofauna across sandy beaches and surf zones along the Dutch coast[J]. Oceanologia, 2005, 47(2): 265−282. [105] 李发明, 聂光裕, 周军, 等. 粤东海岸带生态系统现状及其生态保护修复[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2021, 38(10): 75−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.10.013Li Faming, Nie Guangyu, Zhou Jun, et al. Status of coastal ecosystem and its ecological restoration in the east of Guangdong Province[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2021, 38(10): 75−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.10.013 [106] Nordstrom K F. Beach and Dune Restoration[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021. [107] Kindeberg T, Almström B, Skoog M, et al. Toward a multifunctional nature-based coastal defense: a review of the interaction between beach nourishment and ecological restoration[J]. Nordic Journal of Botany, 2023, 2023(1): e03751. doi: 10.1111/njb.03751 [108] Cooke B C, Morton J K, Baldry A, et al. Backshore nourishment of a beach degraded by off-road vehicles: ecological impacts and benefits[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 724: 138115. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138115 [109] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 海滩后滨沙地植被修复技术方法: HY/T 0304−2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Technology method of vegetation restoration in backshore sandy landforms: HY/T 0304−2021[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. [110] Charbonneau B R, Cochran C, Avenarius C. What we know and what we think we know: Revealing misconceptions about coastal management for sandy beaches along the U. S. Atlantic Seaboard[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 245: 131−142. [111] McLachlan A. Ecology of coastal dune fauna[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 1991, 21(2): 229−243. doi: 10.1016/S0140-1963(18)30684-0 [112] Stienen E W M, Schekkerman H. Statistische analyse van de verspreiding en de broedresultaten van kustbroedvogels in het Deltagebied: relaties met habitatkenmerken, predatiedruk en toerisme[R]. Wageningen: Alterra, 2000. [113] Jones K, Hanna E. Design and implementation of an ecological engineering approach to coastal restoration at Loyola Beach, Kleberg County, Texas[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2004, 22(4/5): 249−261. -




 下载:
下载: