Seasonal variations of dissolved Mn concentration in the surface water of the Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area
-
摘要: 锰(Mn)是海洋中的生命必需痕量元素。河口位于河流和海洋的交界区域,其对Mn的改造作用会影响陆源Mn向海输送的生物地球化学过程。本研究使用自动固相萃取−电感耦合等离子体联用技术对2019年9月(秋季)、2021年3月(春季)和2021年7月(夏季)长江口及其邻近水域的表层溶解Mn浓度进行了测定和分析。结果显示,溶解Mn的平均浓度和河口行为表现出了季节性差异:夏季的溶解Mn浓度最高,表现为先移除后添加的分布特征;秋季的溶解Mn浓度次之,表现为添加型分布;春季的溶解Mn浓度最低,表现为保守型分布。显著性分析结果表明,长江携带的溶解Mn仅在淡水端元浓度值较高的季节会显著影响长江口及其邻近水域溶解Mn的分布;当长江淡水端元浓度值较低时,长江口溶解Mn则受多种生物地球化学过程的共同主导。长江口的中低盐度海水中高悬浮颗粒物浓度是造成该区域溶解Mn移除的重要因素,而高盐度海水中溶解Mn的添加机制则有待进一步研究。Abstract: Manganese (Mn) is an essential trace element for the marine ecosystem. As the transitional zone between rivers and oceans, estuaries have a significant effect on dissolved Mn and its terrigenous input. In this study, the distribution of dissolved Mn, investigated in the surface water of Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area during September 2019 (autumn), March 2021 (spring) and July 2021 (summer), was analyzed by automatic solid phase extraction and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The results indicated that the average concentration and estuarine behaviors of dissolved Mn showed seasonal variations between the three cruises: the maximum average concentration occurred in summer and dissolved Mn was removed firstly and then added with the increase of salinity; the medium average concentration occurred in autumn and dissolved Mn was mainly removed with the increase of salinity; the minimum average concentration occurred in spring and dissloved Mn was mainly conservative with the increase of salinity. The results of significance test indicated that only in the season when the fresh water had high concentrations, dissloved Mn carried by the Changjiang River had significant influence on the distribution of dissolved Mn in the Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area; the distribution of dissolved Mn was co-dominated by a variety of biogeochemical processes in the season when the concentrations were low in the fresh water. The high suspended particulate matter concentrations were the important factor of the removal of dissolved Mn in the Changjiang Estuary’s water with medium-low salinity. And the addition mechanism of dissolved Mn in water with high salinity needs further vestigation.
-
1. 引言
锰(Mn)是海洋中具有重要生态生理效应的痕量金属之一,其广泛存在于水体、岩石和土壤之中,在地壳中的质量分数约为0.07%,于地壳元素中排名第12位[1]。Mn是海洋中的生命必需元素,在海洋生态系统和全球碳循环中起着至关重要的作用:其能够以锰簇(4Mn-Ca)的形式参与光合作用,在光系统II中和酪氨酸残基Yz结合生成放氧复合体[2];其含量在类囊体所需金属中仅次于铁,排名第2位[2];此外,Mn还可以参与生成超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase, SOD)并储存于线粒体之中[3],SOD是清除活性氧物质( Reactive Oxygen Species, ROS)和减轻细胞损伤的重要物质[4–5]。海水中Mn的分布受到其源汇格局以及自身生物地球化学特征的调控。由于Mn的风化产物在水中的溶解度低且停留时间较短,因此溶解Mn在海洋中的浓度较低[4]。全球海洋的表层溶解Mn浓度普遍在0.1~25.0 nmol/L之间[6]。海洋中溶解Mn的来源主要有河流输入[7]、大气沉降[8]、沉积物的溶出以及海底热液的输送[9–11]等过程,其汇主要有化学清除、颗粒物的吸附和生物的吸收利用等过程[12]。
河流输入是海洋中溶解Mn的重要来源,在全球大洋中,由河流输入的Mn年通量约为137.0 Mmol [13]。河口是连接河流和海洋的重要交界区域,也是陆海连续系统的关键组成部分,影响着河流中溶解Mn的向海输送过程。溶解Mn在不同河口的界面行为特征存在差异[14],例如:在英国的比尤利(Beaulieu)河口,溶解Mn表现为保守型分布[15];在美国的特拉华(Delaware)河口,溶解Mn受絮凝过程的影响,整体表现出移除型分布[16];而在美国的皮科尼克(Peconic)河口的中盐度区域,溶解Mn由于受到悬浮颗粒物(Suspend Particulate Matter, SPM)的解吸作用以及沉积物的释放,表现出添加型分布[17];溶解Mn在河口也会表现出季节性差异,如在美国的哈得孙(Hudson)河口,由于春季流量高,Mn在河口的停留时间短暂,溶解Mn浓度低于秋季[18]。因此,甄别河口溶解Mn的调控因素有助于提升对Mn在海洋生物地球化学过程及大洋库存中的认识。
长江是世界第三大河,年径流量约为900 km3,年泥沙通量约为500 Mt [19],是东海近90%淡水的输入源[20]。长江口溶解Mn的分布受其源汇格局和生物地球化学过程的影响。前人研究观测到长江口溶解Mn的分布具有时空变异性,而水团的影响以及SPM对Mn的吸附作用是该变异性的重要来源。长江口及其邻近水域受多种水团的影响,其中包含了长江冲淡水、台湾暖流和黑潮等[21],水文环境复杂,温盐性质有明显的区域性差异。长江冲淡水具有低盐度、高SPM含量的特点,在春季和夏季,长江冲淡水主要向东和东北方向延伸,而在秋季,长江冲淡水向南扩散的趋势则会加强[22];台湾暖流具有高温度、高盐度、低SPM含量的特征,其从台湾海峡流经东海陆架区域中部,在夏季,受到西南季风的影响,台湾暖流会变强[23];黑潮具有高盐度、低SPM浓度的特点,其会沿着台湾东北部向北持续侵入至东海陆架区域[24]。前人通过比对长江冲淡水−台湾暖流−黑潮的三端元理论稀释线,发现河口区域对溶解Mn的移除行为,并通过溶解Mn浓度与SPM含量的显著负相关关系进一步揭示了SPM的吸附作用也是该时空变异性的重要来源[23, 25]。SPM通过吸附/解吸作用影响溶解Mn在水中的存在形式,其中吸附作用被认为是决定长江口溶解Mn分布的关键因素之一:杨亭亭等[25]认为在春季和夏季,SPM是该区域溶解Mn的主要汇之一,并推测来自长江口上游的溶解Mn被截留在了SPM含量较高的区域;Wang等[23]通过模拟长江口环境的简单混合试验对SPM的吸附作用进行进一步的研究,结果同样表明吸附过程对长江口溶解Mn的行为起着重要的作用。但在其他河口的观测则发现了SPM可能是溶解Mn的来源:如在皮科尼克河口和哈得孙河口的中低盐度端,SPM的解吸作用是溶解Mn添加的主要原因,而随着盐度的增加,SPM对溶解Mn的作用又逐渐转为吸附[17, 26]。在前人的观测中,长江溶解Mn的端元值分别为28.2 nmol/L、49.5 nmol/L和65.5 nmol/L,在徐六泾观测到的长江溶解Mn浓度变化范围为7.2~82.9 nmol/L[23],该变化范围跨度高达1个数量级,而已有的研究尚未考虑到当淡水端元溶解Mn浓度输入值较低时,长江口区域溶解Mn的行为以及SPM对溶解Mn的作用。
本研究将借助对3个季节的观测,探讨当淡水端元溶解Mn输入值较低时,长江口及其邻近水域溶解Mn的行为变化,并结合温盐、溶解氧浓度、叶绿素浓度和营养盐浓度等环境参数,讨论溶解Mn在长江口及其邻近水域的季节分布差异和生物地球化学规律。
2. 材料与方法
2.1 研究区域和样品的采集
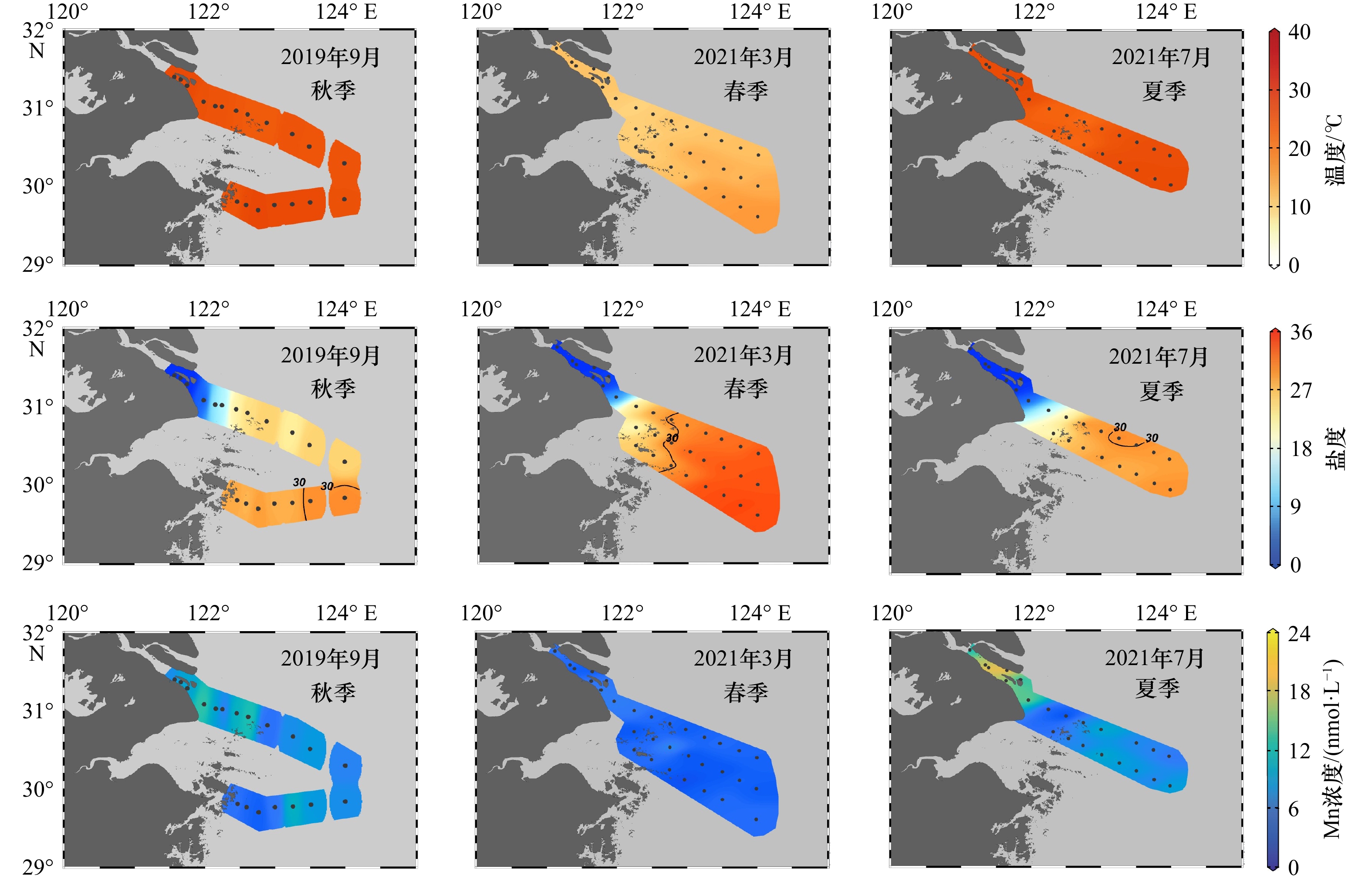
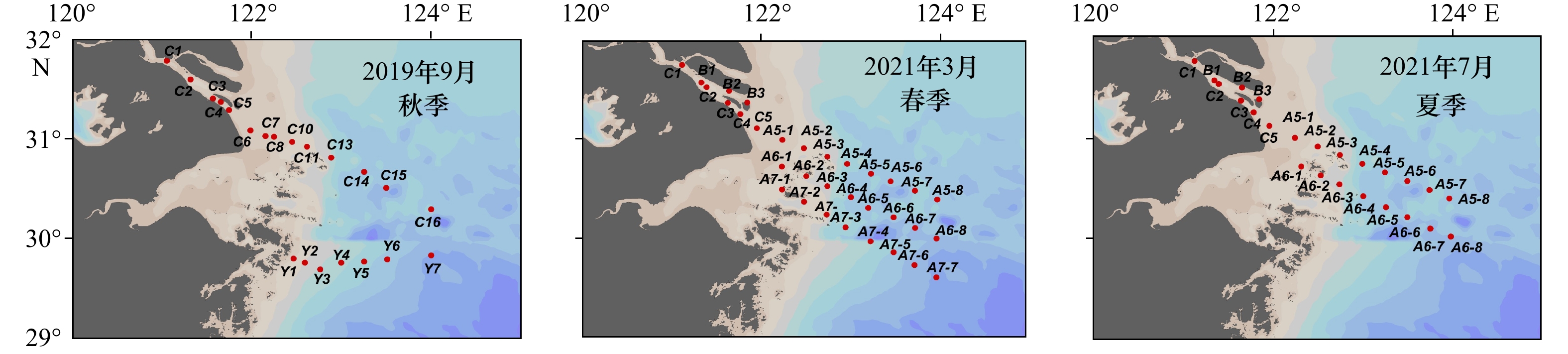
通过搭载同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室共享航次(KECES-2019)和国家自然科学基金委员会共享航次,乘坐“浙渔科2”号和“润江1”号科考船对长江口及其邻近水域进行考察,分别在2019年9月(秋季)获得表层水样21个,2021年3月(春季)获得表层水样32个,2021年7月(夏季)获得表层水样24个(图1)。
表层水样的采集装置为实验室自制简易痕量金属采集器。操作方法如下:用凯夫拉绳将5 kg的硅胶包裹重锤固定于酸洗后的4 L高密度聚乙烯(Nalgene)瓶下方约2 m处,当温盐深仪(CTD)下放时,在位于水流上游的船头处释放采水器,采水瓶最终需保持在水深约0.5 m处,待采水器充满海水后拉上甲板,盖上瓶盖。在船上搭建的洁净环境下,使用蠕动泵经囊式过滤器(AcroPak®0.2 µm, Pall)过滤海水,然后将过滤完的水样装入经过酸洗的60 mL低密度聚乙烯瓶中,使用3层自封袋将其密封后常温保存。
2.2 溶解Mn浓度数据分析
本研究采用Ge等[27]的方法,应用固相萃取电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)检测溶解Mn浓度。具体步骤如下:使用Fisher Optima级盐酸酸化样品至pH约为2,摇匀后静置3个月;为避免样品中金属浓度过高对seaFAST系统产生污染,控制Optima级盐酸和Milli-Q水的体积比为1∶1 000,配制出pH = 2的盐酸溶液,根据样品的盐度(S)进行稀释操作,如S < 1的样品稀释100倍,1 ≤ S < 15的样品稀释20倍,S ≥ 15的样品稀释10倍;然后用seaFAST分离并富集样品中的溶解Mn。seaFAST的步骤简述如下:按比例混合Optima级别的氨水和醋酸得到缓冲液(pH约为6),将10 mL样品加入定量环中,让样品和缓冲液在线混合后进入预浓缩柱,从而使溶解Mn被螯合树脂选择性吸附;将超纯水和缓冲溶液在线混合后通过预富集柱去除干扰离子和未被螯合的离子最终进入废液;使用0.5 mL的0.5 nmol/L Optima级硝酸在预富集柱中将被分析物洗脱至LDPE样品板的样品槽中;最后使用PerkinElmer PE5000多重四级杆ICP-MS进行分析。
本研究中所有操作均在上海交通大学千级洁净实验室中进行,样品前处理在内置高效过滤网(High Efficiency Particulate Air Filter)的百级洁净台中完成,实验用具均为Trace Metal级。此外,本研究所使用低密度聚乙烯小瓶、聚乙烯离心管以及4 × 12的5 mL低密度聚乙烯背板购自ESI,小瓶、离心管和背板均经过以下清洗步骤:首先用2% Citranox清洁剂浸泡器材24 h,浸泡完毕后用Milli-Q水冲洗7次;然后将器材浸泡在10%的盐酸中7 d,浸泡完毕后用Milli-Q水冲洗7次,冲洗完成后用3层自封袋密封储存。
用实验室采自西太平洋表层的质控海水(LEMON)为基体,分别配制溶解Mn浓度为0 μg/L、0.001 μg/L、0.005 μg/L、0.01 μg/L、0.05 μg/L、0.10 μg/L、0.20 μg/L、0.50 μg/L的标准曲线进行方法流程定量。本方法的准确性经过严格的验证,Mn浓度的方法检出限为0.003 nmol/L,对加拿大国家研究委员会(National Research Council, Canada)认证的参考物质进行方法准确度的验证结果如下:SLEW-3的推荐值为(1.61 ± 0.22)µg/L,本研究的测试值为(1.44 ± 0.04)µg/L;SLRs-6的推荐值为(2.12 ± 0.10)µg/L,本研究的测试值为(1.88 ± 0.10)µg/L;CASS-6 的推荐值为(2.18 ± 0.08)µg/L,本研究的测试值为(2.09 ± 0.03)µg/L; NASS-7的推荐值为(0.75 ± 0.06)µg/L,本研究的测试值为(0.70 ± 0.03)µg/L。本方法获得的测试值与推荐值基本相符。
2.3 环境参数
本研究的环境参数有温度、盐度、悬浮颗粒物含量、营养盐浓度、叶绿素浓度以及溶解氧浓度,参数均来自同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室和国家自然科学基金委员会的共享航次数据。
2.4 相关性分析方法
本研究拟用皮尔逊相关性分析比较溶解Mn浓度与各环境参数之间的关系,较好的相关性能够反映两个变量之间存在生物地球化学行为上的相似。皮尔逊相关性分析常用于鉴别两个变量x与y之间的亲密度,其中相关性r的数学表达式为
$$ r\,=\,\frac{\displaystyle\sum _{i\ =\ 1}^{n}({x}_{i}-\bar{x})}{\sqrt{{\displaystyle\sum _{i\ =\ 1}^{n}({x}_{i}-\bar{x})^{2}}{\displaystyle\sum_{i\ =\ 1}^{n}({y}_{i}-\bar{y})^{2}}}} \text{,} $$ (1) 式中,
$ {x}_{i} $ 和$ {y}_{i} $ 表示各变量的观测值;$ \bar{x} $ 和$ \bar{y} $ 表示各变量的平均值;n则表示各变量的个数。|r| ≤ 1,当|r|越接近1时,x和y的线性相关度越高,当r = −1时,两变量呈完全负线性相关关系;当r = 1时,两变量呈完全正线性相关关系;当r = 0时,两变量不存在相关关系。
r是通过样本的数据计算而来,其可靠性受样本的随机性和数目等因素的影响,因此需要引入显著性p对r的可靠性进行检验,p < 0.01表示为极显著,0.01 < p < 0.05表示为显著,p ≥ 0.05表示为不显著。根据式(2)以及t分布表可以得出显著性p的值,其中n为样本数目。
$$ t=\left|r\right|\sqrt{\frac{n-2}{1-{r}^{2}}}~t(n-2) . $$ (2) 3. 结果与讨论
3.1 长江口及其邻近水域表层水体中溶解Mn浓度的季节分布特征
长江口及其邻近水域表层水体中盐度、温度和溶解Mn浓度的季节分布如图2和表1所示。调查期间,秋季和夏季的温盐性质相似,而春季则与秋夏两个季节有明显差异。平均盐度的季节变化表现为:春季(23.6 ± 13.4)> 秋季(18.9 ± 11.6)≈ 夏季(18.5 ± 13.2);平均温度(单位:℃)表现为:秋季(28.0 ± 1.0)≈ 夏季(27.3 ± 1.8)> 春季(12.8 ± 1.7)。本文采用咸淡水划分模式探讨溶解Mn浓度的季节分布特征和控制因素,划分方式如下:以盐度1和30为界限,将研究区域划分为淡水(S < 1)、冲淡水(1 ≤ S ≤ 30)和海水(S > 30)[28-29]。在相同的调查季节,不同水域间并未观测到温度存在显著性差异(邓肯检验,p > 0.05)。
表 1 长江口及其邻近水域表层水体的盐度、温度和溶解Mn浓度Table 1. Salinity, temperature and dissolved Mn concentration in the surface of the Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area季节 水域 盐度 温度/℃ 溶解Mn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 样本数 范围 均值 样本数 范围 均值 样本数 范围 均值 秋季 全水域 24 0.0~32.1 18.9 ± 11.6 21 26.4~29.5 28.0 ± 1.0 21 3.8~12.9 7.8 ± 2.5 淡水 5 0.0~0.1 0.04 ± 0.05 5 28.7~28.9 28.8 ± 0.1 5 6.2~9.7 8.0 ± 1.3 冲淡水 16 2.8~29.5 22.6 ± 7.0 14 26.4~29.5 27.7 ± 1.0 14 3.8~12.9 7.7 ± 2.9 海水 3 30.4~30.6 31.0 ± 0.8 2 27.6~29.0 28.3 ± 0.7 2 7.3~8.3 7.8 ± 0.5 春季 全水域 32 0.2~34.8 23.6 ± 13.4 32 10.1~17.0 12.8 ± 1.7 31 2.7~15.7 4.4 ± 1.0 淡水 5 0.2~0.3 0.2 ± 0.02 5 12.1~12.7 12.4 ± 0.2 5 3.1~5.5 4.5 ± 1.0 冲淡水 10 1.0~29.6 19.2 ± 11.0 10 10.1~12.3 12.3 ± 0.6 10 3.2~6.1 4.9 ± 1.0 海水 17 30.4~34.8 33.1 ± 1.4 17 11.4~17.0 13.8 ± 1.8 16 2.7~7.0 4.1 ± 0.9 夏季 全水域 24 0.1~31.4 18.5 ± 13.2 24 22.9~28.8 27.3 ± 1.8 22 2.0~20.5 9.7 ± 5.0 淡水 7 0.1~0.2 0.1 ± 0.01 7 28.4~28.6 28.5 ± 0.07 6 10.9~20.5 16.0 ± 3.7 冲淡水 14 2.8~30.0 25.0 ± 7.4 14 23.9~28.8 27.0 ± 1.7 14 2.0~15.4 7.4 ± 3.2 海水 3 30.1~31.4 30.8 ± 0.6 3 22.9~28.0 26.2 ± 2.3 2 6.9~7.7 7.3 ± 0.4 溶解Mn的平均浓度(单位:nmol/L)在长江口及其邻近水域表现出了显著的季节性差异(邓肯检验,p < 0.05),具体表现为:夏季(9.7 ± 5.0) > 秋季(7.8 ± 2.5) >春季(4.4 ± 1.0)。但对水域的显著性分析结果则表明:只有在夏季,淡水溶解Mn浓度显著高于冲淡水和海水(邓肯检验,p < 0.05),其他季节中,溶解Mn在不同水体中的浓度差异并不显著(邓肯检验,p > 0.05)。基于本研究中3个季节的调查,可以说明长江携带的溶解Mn仅在淡水端元浓度值较高的季节会对长江口及其邻近水域的溶解Mn分布产生显著影响;当长江淡水端元浓度值较低时,颗粒物吸附解吸、生物消耗、氧化还原以及底界面等生物地球化学过程或将共同主导长江口及其邻近水域溶解Mn的分布,而长江淡水对溶解Mn分布的主导作用不强。如表2所示,对比2011−2021年长江口至东海区域溶解Mn浓度的历史数据[23, 25],可知长江口及其邻近水域溶解Mn除了季节差异之外,还具有明显的年际差异,而本研究中3个季节溶解Mn的浓度均位于较低水平,这与长江口淡水端元浓度值的高时间变异性[25]和长江口生物地球化学过程的共同影响有关。
表 2 长江口至东海区域中表层盐度和溶解Mn浓度的历史数据对比Table 2. The comparison of historical salinity and dissolved Mn concentrations in the surface from the Changjiang River Estuary to the East China Sea研究区域 时间 纬度 经度 盐度(平均值) 溶解Mn浓度(平均值)/(nmol·L−1) 参考文献 长江口表层水 2021年3月 29°~32°N 120°~125°E 0.2~34.8
(23.6)2.7~15.7
(4.4)本研究 2021年7月 29°~32°N 120°~125°E 0.1~31.4
(18.5)2.0~20.5
(9.7)2019年9月 29°~32°N 120°~125°E 0.0~32.1
(18.9)3.8~12.9
(7.8)长江口表层水 2012年3月 29°~33°N 120°~124°E 0.2~33.9
(25.1)2.5~55.1
(11.5)文献[25] 2012年7月 29°~33°N 120°~124°E 0.1~32.3
(23.2)4.2~74.1
(16.5)长江口、东海表层水 2011年5月 23°~34°N 120°~128°E 24.4~34.6
(32.2)2.6~21.8
(7.7)文献[23] 2011年8月 27°~34°N 120°~128°E 21.5~33.8
(29.6)4.2~15.5
(9.6)2011年11月 29°~32°N 120°~128°E 24.3~33.8
(31.1)2.5~13.9
(6.5)东海表层水 2015年10月 26°~32°N 120°~128°E 20.4~34.9
(32.4)2.2~10.7
(6.1)文献[30] 表3结合本研究数据比较了世界部分河流、河口、边缘海及大洋的表层溶解Mn浓度。本研究中淡水区域的Mn浓度变化也具有明显的时间变异性,其范围为3.1~20.5 nmol/L,与Wang等[23]在徐六泾观测到的长江溶解Mn浓度范围相符。长江口淡水端元的溶解Mn浓度比世界其他河流低,例如哥伦比亚河、哈得孙河和珠江的溶解Mn浓度最高分别可以达240.0 nmol/L、1 460.0 nmol/L和512.3 nmol/L。作为河口中溶解Mn的输入源,河流中溶解Mn的浓度一般不低于河口,例如长江和哥伦比亚河的溶解Mn浓度高于河口,而哈得孙河的溶解Mn浓度则与河口区域相近。整体上,世界范围内溶解Mn的分布受到其源汇格局的影响:在河口和边缘海,由于靠近陆地,具有丰富的陆源输入,溶解Mn浓度会出现高值;在黑海等缺氧水体中,高价态的Mn氧化物容易被还原成Mn(II),再加上底层沉积物的释放,溶解Mn浓度同样出现高值[31];而在远离陆源输入的开阔大洋,溶解Mn浓度则主要表现为低值。
表 3 世界部分河流、河口、边缘海及大洋的表层溶解Mn浓度Table 3. Surface dissolved Mn concentrations of rivers, estuaries, marginal seas and oceans in the world类别 采样区域 溶解Mn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 参考文献 河流 长江 3.1~20.5 本研究 长江 7.2~82.9 文献[15] 哥伦比亚河 60.0~240.0 文献[7] 哈得孙河 33.0~1 460.0 文献[26] 珠江 1.5~512.3 文献[32] 河口 长江口咸水 2.0~15.4 本研究 哥伦比亚河口 12. 0~40.0 文献[33] 哈得孙河河口 33.0~1 640.0 文献[26] 杰克逊港口 24.5~1 172.7 文献[34] 长江口海水 2.7~8.3 本研究 边缘海 东海 1.5~21.8 文献[30] 南海 1.8~16.2 文献[35] 威德尔海 0.2~0.4 文献[36] 马尾藻海 0.7~4.3 文献[37] 大洋 西北太平洋 1.2~2.6 文献[38] 南大洋 0.04~0.6 文献[39] 3.2 长江口溶解Mn行为的季节变化和驱动因素
长江口及其邻近水域水文环境复杂,其接收了大量来自长江输送的陆源物质,长江携带的淡水与黑潮水在此混合[22],仅考虑物理混合的情况下使用两端元混合模型,可获得溶解Mn在长江口分布的理论稀释线。如图3所示,选择本研究划分的长江淡水区域作为淡水端元,选用黑潮表层水作为海水端元,黑潮表层水参考端元值的溶解Mn浓度为3.4 nmol/L,盐度为34.7[23]。对比本研究的实际观测数据和理论稀释线,溶解Mn在长江口及其邻近水域表现出了季节性行为差异。其中,秋季溶解Mn浓度整体位于理论稀释线上方,表现为添加型分布,且在中高盐度(S > 18)添加作用明显;春季溶解Mn浓度与盐度的关系与理论稀释线基本吻合,表现为保守型分布;夏季溶解Mn表现出先移除后添加的趋势,当S < 22时表现为移除型分布,当S ≥ 22时表现为添加型分布。
如表4所示,从季节分布来看,长江口溶解Mn在夏季和秋季主要受到长江径流的影响,都与盐度显示出了负相关关系。夏季,溶解Mn浓度与叶绿素浓度的正相关关系,表明包括Mn在内的陆源输送物质对初级生产的促进作用[31];秋季,溶解Mn浓度与溶解氧浓度表现出负相关关系,和溶解无机氮浓度则表现出正相关关系,这表明了影响溶解Mn浓度分布的原因较为复杂,可能与陆源输送、耗氧再生、氧化还原和底界面输送等过程有关[40–42]。研究表明,长江口及其邻近水域存在上升流,底界面能够通过上升流向长江口表层水供应营养盐[43]。但由于数据限制,本研究无法定量分析该过程对长江口溶解Mn浓度的影响。
表 4 各季节溶解 Mn 浓度与其他环境因子的皮尔逊相关性Table 4. Pearson correlation between dissolved Mn concentration and other environmental factors in different seasons季节 盐度 温度 溶解无机氮浓度 磷酸盐浓度 硅酸盐浓度 叶绿素浓度 溶解氧浓度 悬浮颗粒物含量 春季 −0.33 −0.25 0.33 0.16 0.29 0.20 −0.12 0.38 夏季 −0.36* −0.25 0.35 0.27 0.30 0.53** −0.15 0.18 秋季 −0.74** 0.51* 0.60* 0.028 0.35 0.039 −0.57** −0.26 注:**指相关性在0.01级别上显著(双尾检验);*指相关性在0.05级别上显著(双尾检验)。 3.3 悬浮颗粒物对长江口溶解Mn浓度分布的影响
前人的研究提出了水体中SPM在调控长江口区域溶解Mn分布的关键作用,特别是在高淡水端元的年际对溶解Mn的移除效应显著[23, 25]。类似的,本文尝试寻找SPM对长江口及其邻近水域溶解Mn分布的影响。根据
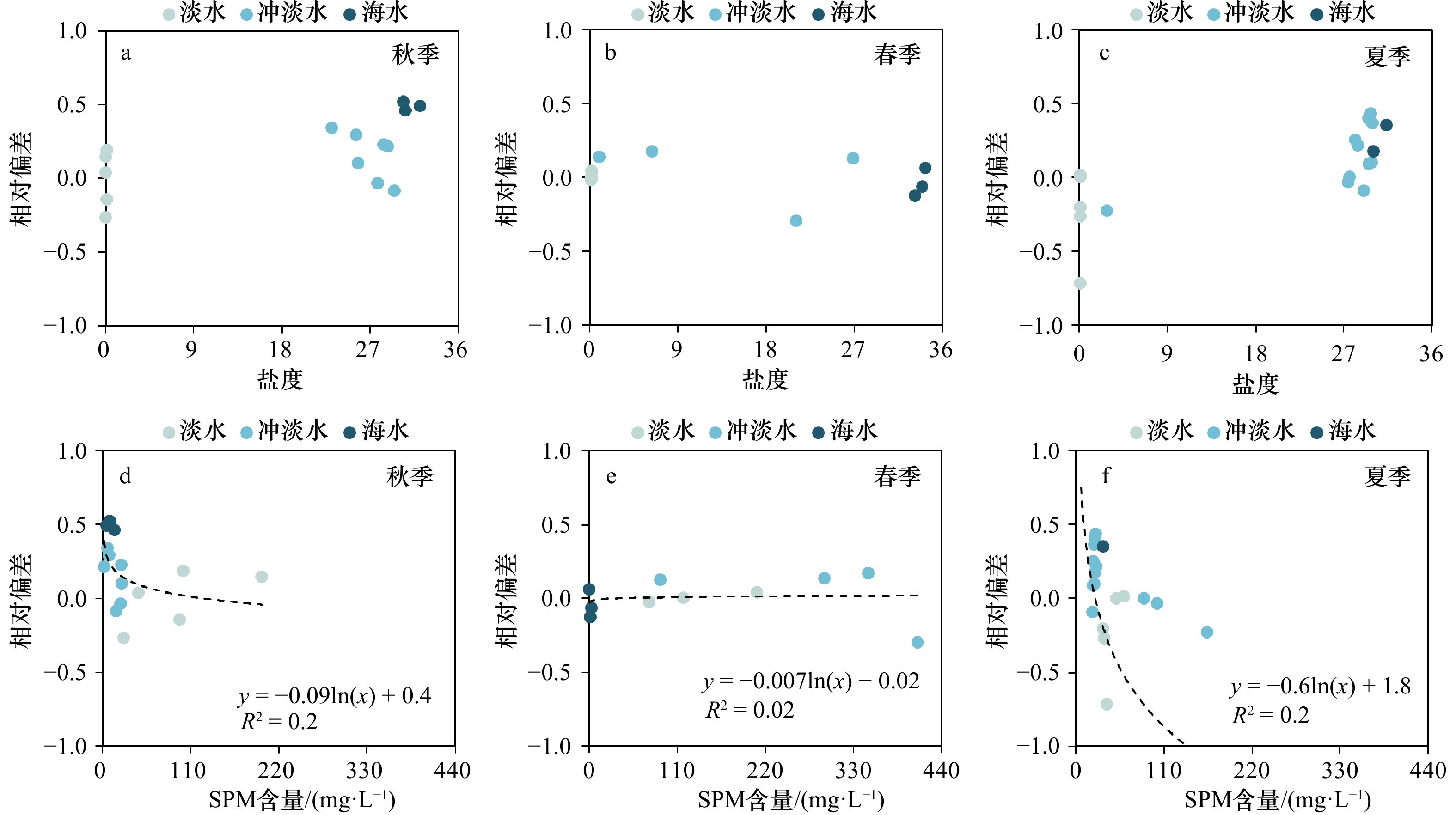
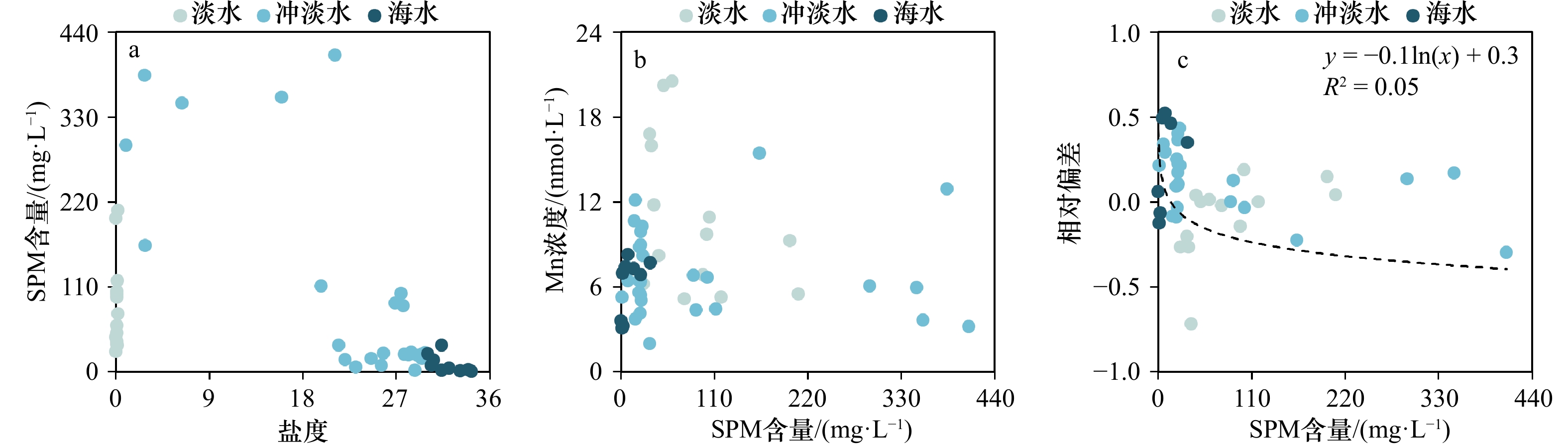
$ {S}_{ \mathrm{a}}=x{S}_{ \mathrm{C}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{W}}+y{S}_{ \mathrm{K}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{W}} $ 和$ x+y=1 $ 分别计算出长江冲淡水(Changjiang Diluted Water, CDW)和黑潮表层水(Kuroshio Surface Water, KSW)在混合过程中各自所占比例x和y,其中$ {S}_{ \mathrm{a}} $ 为实测盐度,$ {{S}}_{ \mathrm{C}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{W}} $ 为本研究中淡水端元的平均盐度,$ {S}_{ \mathrm{K}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{W}} $ 为黑潮表层水的平均盐度34.7[22]。再根据公式$ {C}_{{\mathrm{e}}}=x{C}_{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{W}}+y{C}_{\mathrm{K}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{W}} $ ,计算理论浓度$ {C}_{{\mathrm{e}}} $ ,其中$ {C}_{{\mathrm{CDW}}} $ 为本研究中溶解Mn在淡水端元的平均浓度,$ {C}_{\mathrm{K}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{W}} $ 为黑潮表层水溶解Mn平均浓度3.4 nmol/L,再计算理论值与实际值的相对偏差。溶解Mn的估算相对偏差$ {C}_{\mathbf{\delta }} $ = ($ {C}_{\mathrm{a}}-{C}_{\mathrm{e}} $ )/$ {C}_{\mathrm{a}} $ ,$ {C}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为实际测得的溶解Mn浓度值。如图4所示,春季观测的相对偏差均接近于0,表明溶解Mn的添加或移除行为在春季并不明显,这也对应了溶解Mn浓度在春季整体上保守型的分布特征,表明水团混合可能是春季溶解Mn浓度分布的主导因素。在秋季和夏季,相对偏差的负值主要出现在淡水和中低盐度的冲淡水区域,相对偏差与SPM的负相关关系表明出高SPM含量下表层溶解Mn被移除的趋势,这也与前人观测到长江口最大浑浊带区域中SPM对溶解Mn的显著移除现象一致[23, 25]。而相对偏差的正值则主要出现在夏秋两季的高盐度、低SPM含量区域。
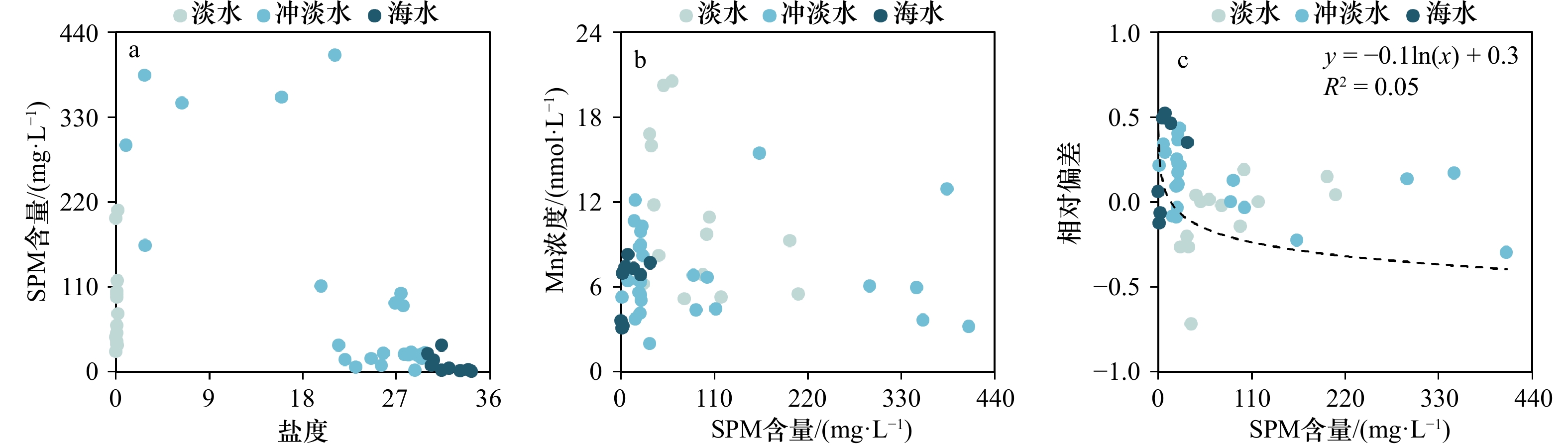
为探讨溶解Mn浓度与不同SPM含量的关系,图5展示了3个季节SPM含量与盐度、溶解Mn浓度与SPM含量以及相对偏差与SPM含量的关系,从中发现在低SPM含量、高盐度区域相对偏差主要表现为正值,即溶解Mn出现添加行为,这与前人在长江口的观测存在差异[25];而相同之处在于,随SPM含量增加,相对偏差趋近稳定并接近于0。本文观测到溶解Mn在低SPM含量、高盐度区域的添加现象可能主要由于春秋两季的淡水端元低浓度以及其他Mn添加过程有关。长江口SPM含量的极大值出现在中低盐度区域,在秋季和夏季最高分别可达198.9 mg/L和348.0 mg/L,而溶解Mn浓度的低值同样出现在长江口的中低盐度区域(图3),这证明SPM在中低盐度区域可通过吸附作用将部分溶解Mn截留在该区域[44]。随着盐度的增加,水体中Cl−相应增加,SPM表面附着的Cl−数目以及对溶解Mn的吸附能力也随之增加,且Mn2+对位点的吸附能力强于一般海水阳离子,因此由SPM解吸的溶解Mn也相应减少 [17-18]。高盐度水域SPM含量迅速降低,使得SPM对溶解Mn的吸附能力减弱,而对于本研究观测到高盐度水域溶解Mn的添加过程需要进一步的研究。相较于长江口, Conwy河口中SPM对溶解Mn分布的影响与其类似,即在SPM含量的高值区对溶解Mn起到移除的作用[45];而在皮科尼克河口和哈得孙河口,SPM却是溶解Mn的重要来源,即SPM通过解吸作用使溶解Mn表现为添加型分布 [24, 26]。SPM在不同河口对溶解Mn的不同作用或与河流以及悬浮颗粒物的性质差异有关。本文验证了长江口高浊度中低盐度海区SPM对Mn的移除效应,然而跨越长江口最大浑浊带高盐度水域溶解Mn的添加行为机制需要进一步的研究。
4. 结论
通过比较长江口秋季、夏季和春季的表层溶解Mn浓度及其影响因素,得出以下结论。
(1)长江口及其邻近水域的表层溶解Mn浓度存在显著的季节性差异,其中夏季的溶解Mn浓度最高,表现为先移除后添加的分布特征;秋季的溶解Mn浓度次之,表现为添加型分布;春季的溶解Mn浓度最低,表现为保守型分布。
(2)由长江携带的溶解Mn仅在淡水端元浓度值较高的季节会对长江口及其邻近水域的溶解Mn分布产生显著影响;而当淡水端元浓度值较低时,长江口及其邻近水域的溶解Mn则受颗粒物吸附解吸、生物消耗、氧化还原、底界面等多种生物地球化学过程的共同主导。
(3)在秋季和夏季,溶解Mn在中低盐度、高SPM含量区域表现出了移除的趋势,验证了长江口的高浊度中低盐度海区中SPM对Mn的移除效应,然而长江口最大浑浊带之外的高盐度水域中溶解Mn的添加机制还需要进一步研究。
-
表 1 长江口及其邻近水域表层水体的盐度、温度和溶解Mn浓度
Tab. 1 Salinity, temperature and dissolved Mn concentration in the surface of the Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area
季节 水域 盐度 温度/℃ 溶解Mn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 样本数 范围 均值 样本数 范围 均值 样本数 范围 均值 秋季 全水域 24 0.0~32.1 18.9 ± 11.6 21 26.4~29.5 28.0 ± 1.0 21 3.8~12.9 7.8 ± 2.5 淡水 5 0.0~0.1 0.04 ± 0.05 5 28.7~28.9 28.8 ± 0.1 5 6.2~9.7 8.0 ± 1.3 冲淡水 16 2.8~29.5 22.6 ± 7.0 14 26.4~29.5 27.7 ± 1.0 14 3.8~12.9 7.7 ± 2.9 海水 3 30.4~30.6 31.0 ± 0.8 2 27.6~29.0 28.3 ± 0.7 2 7.3~8.3 7.8 ± 0.5 春季 全水域 32 0.2~34.8 23.6 ± 13.4 32 10.1~17.0 12.8 ± 1.7 31 2.7~15.7 4.4 ± 1.0 淡水 5 0.2~0.3 0.2 ± 0.02 5 12.1~12.7 12.4 ± 0.2 5 3.1~5.5 4.5 ± 1.0 冲淡水 10 1.0~29.6 19.2 ± 11.0 10 10.1~12.3 12.3 ± 0.6 10 3.2~6.1 4.9 ± 1.0 海水 17 30.4~34.8 33.1 ± 1.4 17 11.4~17.0 13.8 ± 1.8 16 2.7~7.0 4.1 ± 0.9 夏季 全水域 24 0.1~31.4 18.5 ± 13.2 24 22.9~28.8 27.3 ± 1.8 22 2.0~20.5 9.7 ± 5.0 淡水 7 0.1~0.2 0.1 ± 0.01 7 28.4~28.6 28.5 ± 0.07 6 10.9~20.5 16.0 ± 3.7 冲淡水 14 2.8~30.0 25.0 ± 7.4 14 23.9~28.8 27.0 ± 1.7 14 2.0~15.4 7.4 ± 3.2 海水 3 30.1~31.4 30.8 ± 0.6 3 22.9~28.0 26.2 ± 2.3 2 6.9~7.7 7.3 ± 0.4 表 2 长江口至东海区域中表层盐度和溶解Mn浓度的历史数据对比
Tab. 2 The comparison of historical salinity and dissolved Mn concentrations in the surface from the Changjiang River Estuary to the East China Sea
研究区域 时间 纬度 经度 盐度(平均值) 溶解Mn浓度(平均值)/(nmol·L−1) 参考文献 长江口表层水 2021年3月 29°~32°N 120°~125°E 0.2~34.8
(23.6)2.7~15.7
(4.4)本研究 2021年7月 29°~32°N 120°~125°E 0.1~31.4
(18.5)2.0~20.5
(9.7)2019年9月 29°~32°N 120°~125°E 0.0~32.1
(18.9)3.8~12.9
(7.8)长江口表层水 2012年3月 29°~33°N 120°~124°E 0.2~33.9
(25.1)2.5~55.1
(11.5)文献[25] 2012年7月 29°~33°N 120°~124°E 0.1~32.3
(23.2)4.2~74.1
(16.5)长江口、东海表层水 2011年5月 23°~34°N 120°~128°E 24.4~34.6
(32.2)2.6~21.8
(7.7)文献[23] 2011年8月 27°~34°N 120°~128°E 21.5~33.8
(29.6)4.2~15.5
(9.6)2011年11月 29°~32°N 120°~128°E 24.3~33.8
(31.1)2.5~13.9
(6.5)东海表层水 2015年10月 26°~32°N 120°~128°E 20.4~34.9
(32.4)2.2~10.7
(6.1)文献[30] 表 3 世界部分河流、河口、边缘海及大洋的表层溶解Mn浓度
Tab. 3 Surface dissolved Mn concentrations of rivers, estuaries, marginal seas and oceans in the world
类别 采样区域 溶解Mn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 参考文献 河流 长江 3.1~20.5 本研究 长江 7.2~82.9 文献[15] 哥伦比亚河 60.0~240.0 文献[7] 哈得孙河 33.0~1 460.0 文献[26] 珠江 1.5~512.3 文献[32] 河口 长江口咸水 2.0~15.4 本研究 哥伦比亚河口 12. 0~40.0 文献[33] 哈得孙河河口 33.0~1 640.0 文献[26] 杰克逊港口 24.5~1 172.7 文献[34] 长江口海水 2.7~8.3 本研究 边缘海 东海 1.5~21.8 文献[30] 南海 1.8~16.2 文献[35] 威德尔海 0.2~0.4 文献[36] 马尾藻海 0.7~4.3 文献[37] 大洋 西北太平洋 1.2~2.6 文献[38] 南大洋 0.04~0.6 文献[39] 表 4 各季节溶解 Mn 浓度与其他环境因子的皮尔逊相关性
Tab. 4 Pearson correlation between dissolved Mn concentration and other environmental factors in different seasons
季节 盐度 温度 溶解无机氮浓度 磷酸盐浓度 硅酸盐浓度 叶绿素浓度 溶解氧浓度 悬浮颗粒物含量 春季 −0.33 −0.25 0.33 0.16 0.29 0.20 −0.12 0.38 夏季 −0.36* −0.25 0.35 0.27 0.30 0.53** −0.15 0.18 秋季 −0.74** 0.51* 0.60* 0.028 0.35 0.039 −0.57** −0.26 注:**指相关性在0.01级别上显著(双尾检验);*指相关性在0.05级别上显著(双尾检验)。 -
[1] Sun Yao, Gao Ruohan, Li Zhiwei, et al. Composition and evolution of continental crust at orogenic belts: constraints from a 3-D crustal model of Southeast China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2022, 127(12): e2022JB025057. doi: 10.1029/2022JB025057 [2] Landing W M, Bruland K W. Manganese in the North Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 49(1): 45−56. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90149-1 [3] Kitayama K, Kitayama M, Osafune T, et al. Subcellular localization of iron and manganese superoxide dismutase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyceae)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 1999, 35(1): 136−142. doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3510136.x [4] 任景玲, 张桂玲, 刘素美, 等. 海洋中锰的生物地球化学循环研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(3): 432−440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.03.014Ren Jingling, Zhang Guiling, Liu Sumei, et al. Review on the study of biogeochemical cycle of manganese in the oceans[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(3): 432−440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.03.014 [5] Dau H, Haumann M. Eight steps preceding O-O bond formation in oxygenic photosynthesis—A basic reaction cycle of the photosystem II manganese complex[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2007, 1767(6): 472−483. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2007.02.022 [6] Shiller A M. Manganese in surface waters of the Atlantic Ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1997, 24(12): 1495−1498. doi: 10.1029/97GL01456 [7] Aguilar-Islas A M, Bruland K W. Dissolved manganese and silicic acid in the Columbia River plume: a major source to the California current and coastal waters off Washington and Oregon[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2006, 101(3/4): 233−247. [8] Baker A R, Jickells T D, Witt M, et al. Trends in the solubility of iron, aluminium, manganese and phosphorus in aerosol collected over the Atlantic Ocean[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2006, 98(1): 43−58. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2005.06.004 [9] Burdige D J. The biogeochemistry of manganese and iron reduction in marine sediments[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1993, 35(3): 249−284. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(93)90040-E [10] Boyle E A, Bergquist B A, Kayser R A, et al. Iron, manganese, and lead at Hawaii Ocean Time-series station ALOHA: temporal variability and an intermediate water hydrothermal plume[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(21): 5165−5166. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.006 [11] Delgadillo-Hinojosa F, Segovia-Zavala J A, Huerta-Díaz M A, et al. Influence of geochemical and physical processes on the vertical distribution of manganese in Gulf of California waters[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2006, 53(8): 1301−1319. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2006.06.002 [12] SCOR Working Group. GEOTRACES—An international study of the global marine biogeochemical cycles of trace elements and their isotopes[J]. Geochemistry, 2007, 67(2): 85−131. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2007.02.001 [13] van Hulten M, Middag R, Dutay J C, et al. Manganese in the west Atlantic Ocean in the context of the first global ocean circulation model of manganese[J]. Biogeosciences, 2017, 14(5): 1123−1152. doi: 10.5194/bg-14-1123-2017 [14] Zhang Zhouling, Cao Zhimian, Grasse P, et al. Dissolved silicon isotope dynamics in large river estuaries[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 273: 367−382. [15] Moore R M, Burton J D, Williams P J L, et al. The behaviour of dissolved organic material, iron and manganese in estuarine mixing[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(6): 919−926. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90229-1 [16] Church T M. Biogeochemical factors influencing the residence time of microconstituents in a large tidal estuary, Delaware Bay[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1986, 18(2/4): 393−406. [17] Wilke R J, Dayal R. The behavior of iron, manganese and silicon in the Peconic River Estuary, New York[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1982, 15(5): 577−586. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(82)90009-9 [18] Li Yuanhui, Burkhardt L, Teraoka H. Desorption and coagulation of trace elements during estuarine mixing[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(10): 1879−1884. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90371-5 [19] Yang Shilun, Xu Kehui, Milliman J D, et al. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: impact from natural and anthropogenic changes[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12581. doi: 10.1038/srep12581 [20] Sun Xueshi, Fan Dejiang, Liu Ming, et al. Persistent impact of human activities on trace metals in the Yangtze River Estuary and the East China Sea: evidence from sedimentary records of the last 60 years[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 654: 878−889. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.439 [21] 李伟, 王玉衡, 汪嘉宁, 等. 2011年春、夏季黄、东海水团与水文结构分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 615−623. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203032032Li Wei, Wang Yuheng, Wang Jianing, et al. Distributions of water masses and hydrographic structures in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in spring and summer 2011[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 615−623. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203032032 [22] Li Wei, Wang Yuheng, Wang Jianing, et al. Distributions of water masses and hydrographic structures in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in spring and summer 2011[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 615−623. [23] Wang Zhaowei, Ren Jingling, Jiang Shuo, et al. Geochemical behavior of dissolved manganese in the East China Sea: seasonal variation, estuarine removal, and regeneration under suboxic conditions[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2016, 17(2): 282−299. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006128 [24] Zhang Jing, Liu Sumei, Ren Jingling, et al. Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2007, 74(4): 449−478. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.04.019 [25] 杨亭亭, 任景玲, 王召伟, 等. 长江口及邻近海域溶解态锰的分布及影响因素[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(2): 260−270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.02.011Yang Tingting, Ren Jingling, Wang Zhaowei, et al. Distributions and influence factors of dissolved manganese in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent area[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2016, 34(2): 260−270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.02.011 [26] Yang Min, Sañudo-Wilhelmy S A. Cadmium and manganese distributions in the Hudson River Estuary: interannual and seasonal variability[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 160(3/4): 403−418. [27] Ge Yuncong, Zhang Ruifeng, Jiang Ziyuan, et al. Determination of Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in seawater by isotope dilution automatic solid-phase extraction-ICP-MS[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2022, 41(8): 129−136. doi: 10.1007/s13131-022-2016-2 [28] 李健华. 近海与河口区域沉积层与上覆水体间水动力的数学模型及特性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.Li Jianhua. Study on hydrodynamic mathematical model and its characteristics between sediment and overlying water in the offshore and estuarine areas[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018. [29] 苏育嵩, 李凤岐, 王凤钦. 渤、黄、东海水型分布与水系划分[J]. 海洋学报, 1996, 18(6): 1−7.Su Yusong, Li Fengqi, Wang Fengqin. Water pattern distribution and water system division in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1996, 18(6): 1−7. [30] Zhang Yuan, Li Lei, Ren Jingling, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of dissolved manganese in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2021, 234: 104002. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2021.104002 [31] Peers G, Price N M. A role for manganese in superoxide dismutases and growth of iron-deficient diatoms[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2004, 49(5): 1774−1783. doi: 10.4319/lo.2004.49.5.1774 [32] Zhang Jing. Biogeochemistry of Chinese estuarine and coastal waters: nutrients, trace metals and biomarkers[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2002, 3(1/3): 65−76. [33] Klinkhammer G P, Chin C S, Wilson C, et al. Distributions of dissolved manganese and fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Columbia River Estuary and plume as determined by in situ measurement[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1997, 56(1/2): 1−14. [34] Hatje V, Apte S C, Hales L T, et al. Dissolved trace metal distributions in Port Jackson Estuary (Sydney Harbour), Australia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 46(6): 719−730. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00061-4 [35] Wang Zhaowei, Ren Jingling, Zhang Ruifeng, et al. Physical and biological controls of dissolved manganese on the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2019, 167: 25−33. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2018.07.006 [36] Dellwig O, Bosselmann K, Kölsch S, et al. Sources and fate of manganese in a tidal basin of the German Wadden Sea[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2007, 57(1): 1−18. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2006.07.006 [37] Sunda W G, Huntsman S A. Effect of sunlight on redox cycles of manganese in the southwestern Sargasso Sea[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1988, 35(8): 1297−1317. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(88)90084-2 [38] Yakushev E, Pakhomova S, Sørenson K, et al. Importance of the different manganese species in the formation of water column redox zones: observations and modeling[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2009, 117(1/4): 59−70. [39] Middag R, de Baar H J W, Laan P, et al. Dissolved manganese in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2011, 58(25/26): 2661−2677. [40] Yemenicioglu S, Erdogan S, Tugrul S. Distribution of dissolved forms of iron and manganese in the Black Sea[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2006, 53(17/19): 1842−1855. [41] Minakawa M, Noriki S, Tsunogai S. Manganese in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Geochemical Journal, 1996, 30(1): 41−55. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.30.41 [42] Thamdrup B, Glud R N, Hansen J W. Manganese oxidation and in situ manganese fluxes from a coastal sediment[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(11): 2563−2570. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90032-9 [43] 王保栋. 长江口及邻近海域富营养化状况及其生态效应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2006.Wang Baodong. Eutrophication status and its ecological effects in the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent coastal waters[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2006. [44] 窦衍光. 长江口邻近海域沉积物粒度和元素地球化学特征及其对沉积环境的指示[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2007.Dou Yanguang. Characteristics of sediment granularity, element geochemistry and their significance for identifying sedimentary environment in the contiguous sea areas of Changjiang River Estuary[D]. Qingdao: The First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2007. [45] Zhou J L, Liu Y P, Abrahams P W. Trace metal behaviour in the Conwy Estuary, North Wales[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 51(5): 429−440. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00853-6 -






 下载:
下载:
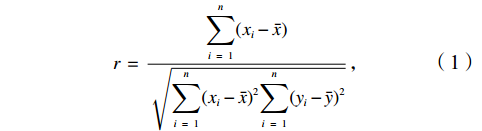
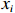
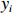
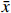
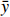
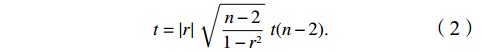


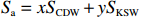
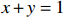
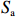
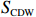
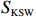
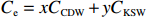
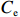
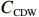
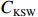
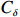
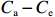
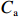
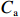


 下载:
下载: