Preliminary study on the trophic relationship of dominant fishes in coral reefs of Weizhou Island in autumn
-
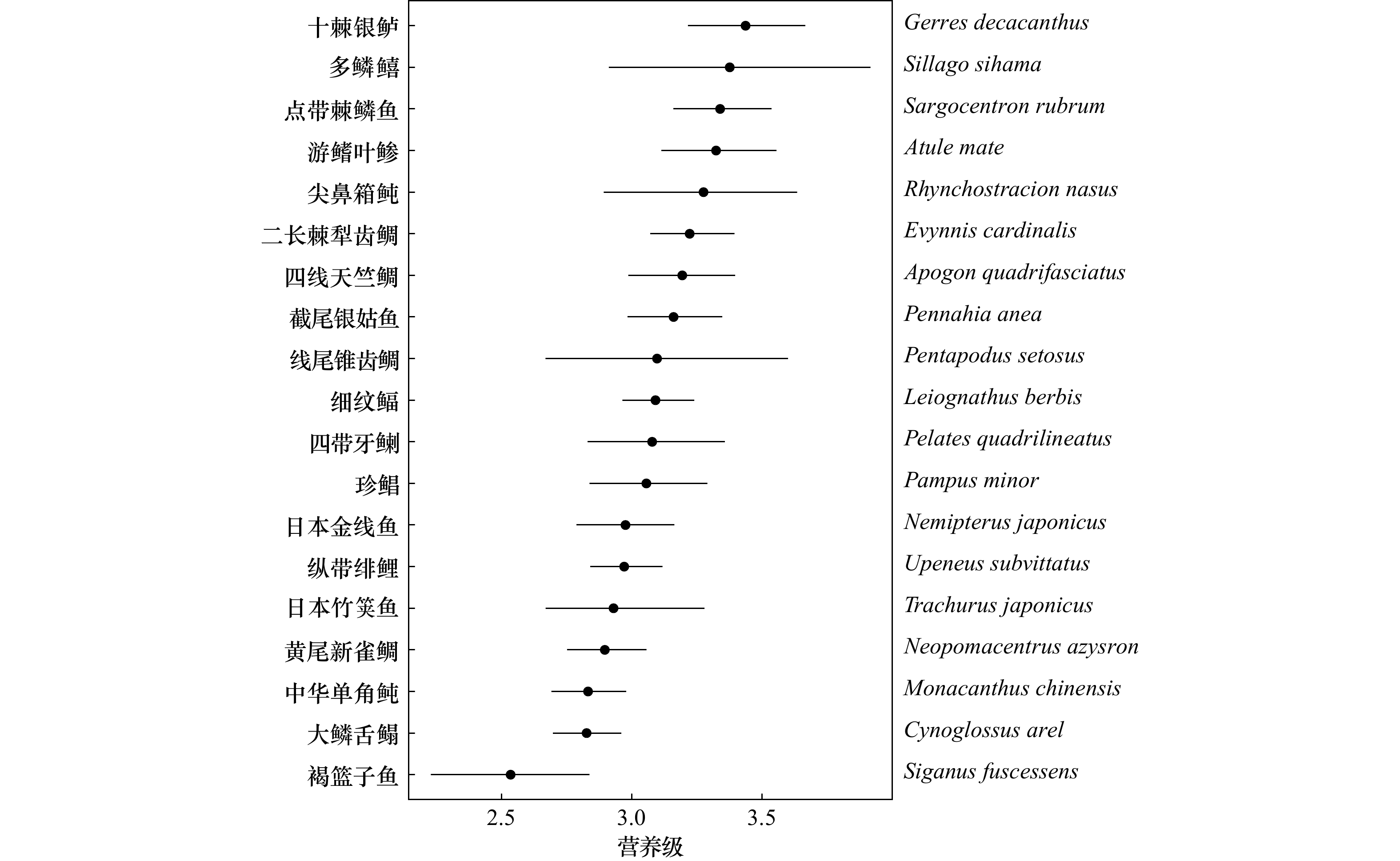
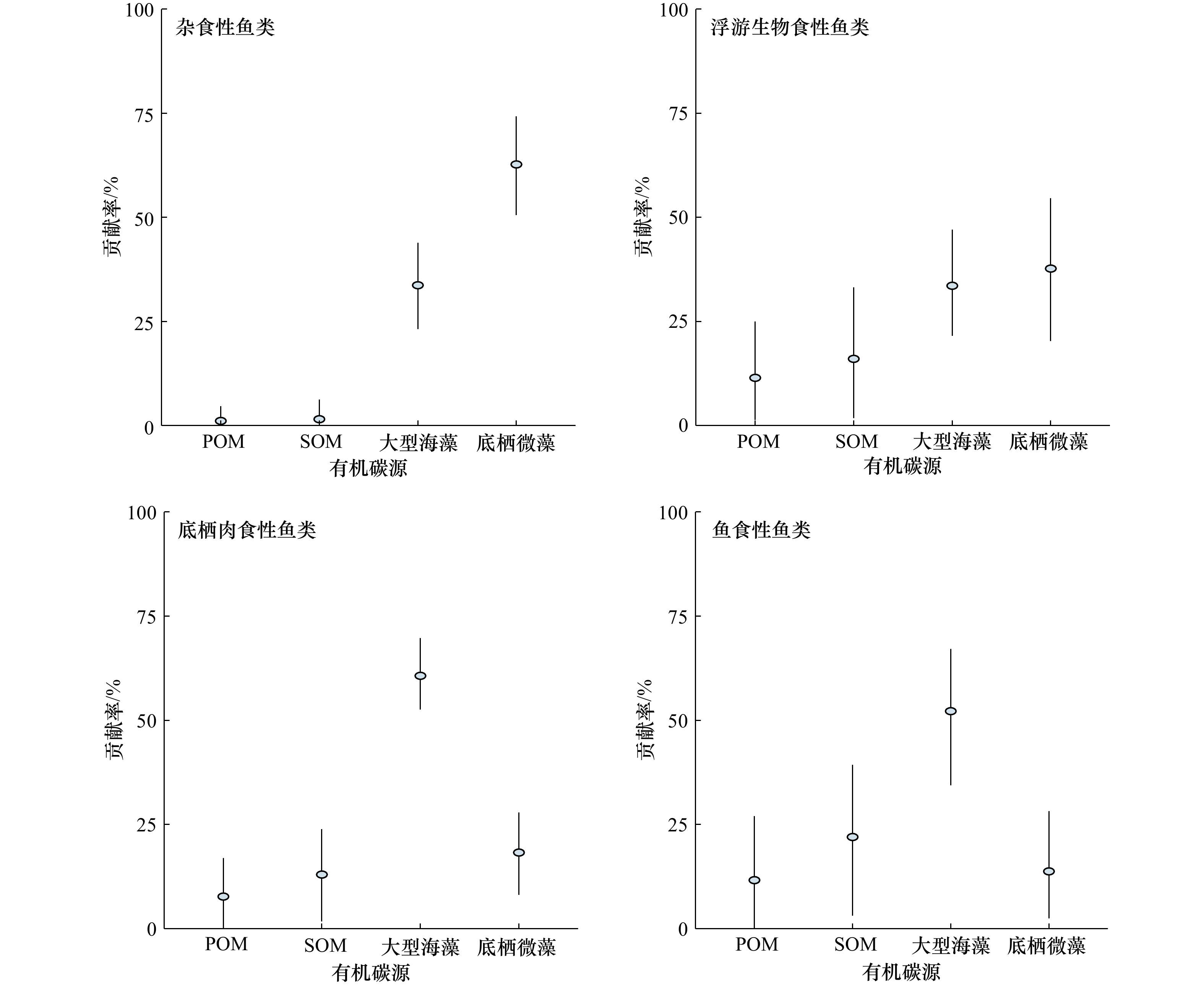
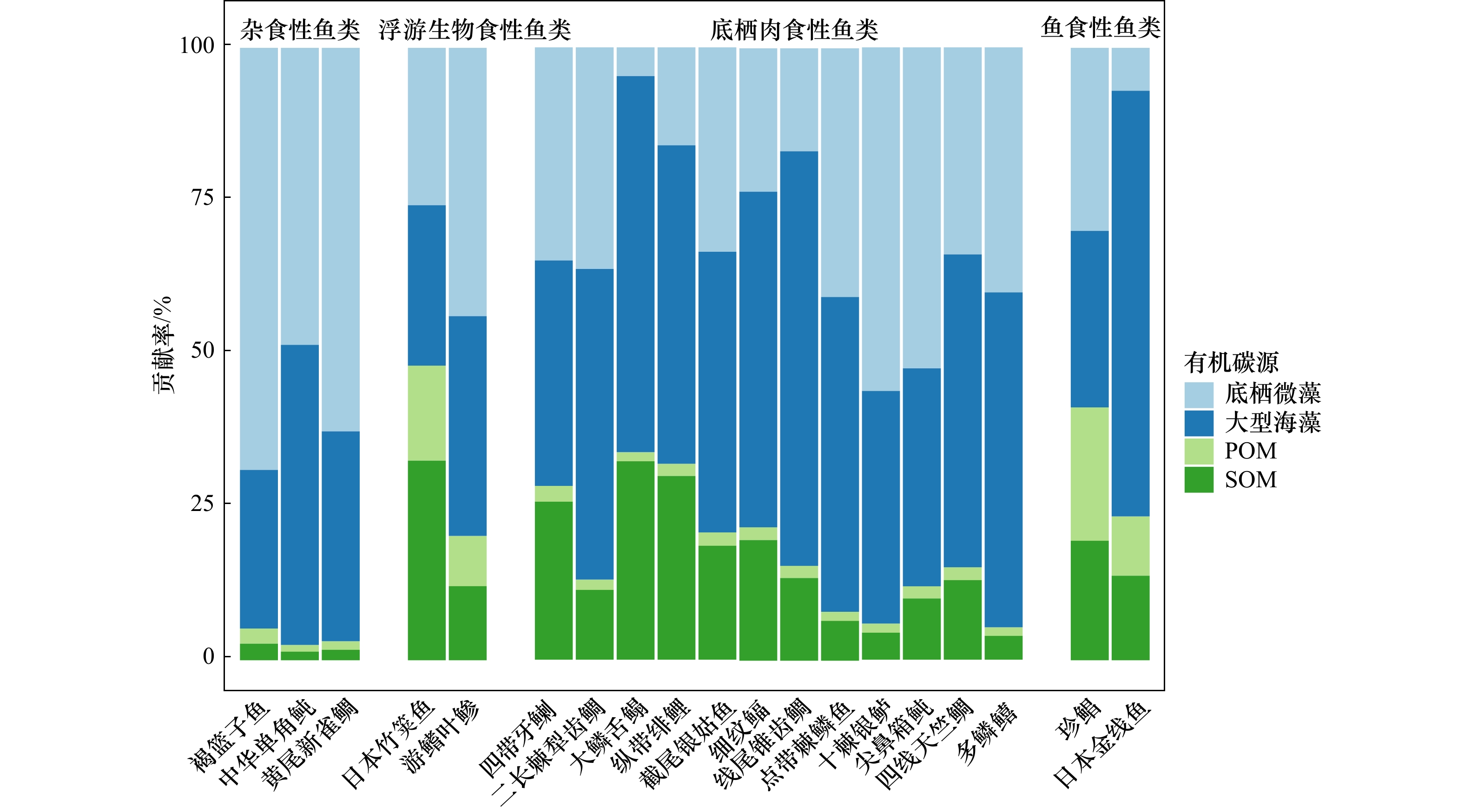
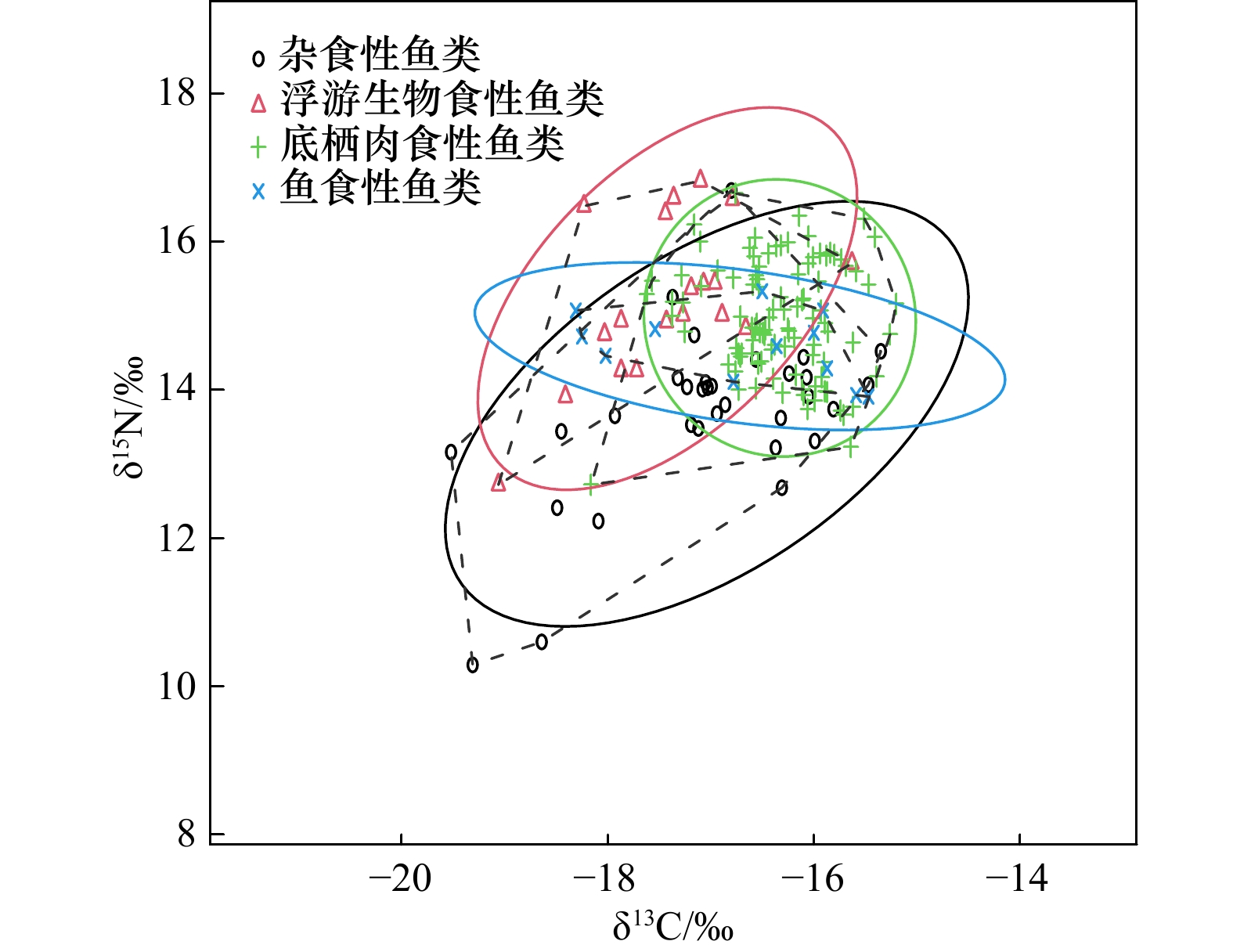
摘要: 本研究利用碳、氮稳定同位素(δ13C、δ15N)技术,估算了秋季涠洲岛珊瑚礁主要鱼类的营养级(TL)和主要碳源,结合6个群落营养结构量化指标,初步分析秋季涠洲岛珊瑚礁主要鱼类的营养关系。结果表明,不同鱼类之间的δ13C和δ15N值差异显著(p < 0.01),其中,δ13C值介于−18.3‰~−15.4‰,δ15N值介于12.9‰~16.3‰。鱼类TL介于2.5~3.4,平均TL为3.0 ± 0.8,显示涠洲岛的鱼类以肉食性为主。涠洲岛鱼类的有机碳源比较复杂,但大型海藻和底栖微藻是驱动鱼类食物网的关键碳源。鱼类群落的食源多样性水平和营养级长度(CR和NR)分别为2.35和3.09。凸多边形总面积(TA)、平均离心距离(CD)、平均最近相邻距离(MNND)和最近相邻距离的标准差(SDNND)分别为4.48、0.89、0.40和0.29,表明涠洲岛珊瑚礁鱼类群落的营养结构具有营养冗余程度较高,但食物链较短和营养多样性低等特征。以上结果表明,涠洲岛珊瑚礁生态系统食物网结构不完整,未来有必要开展适当的管控和修复措施恢复涠洲岛珊瑚礁生态系统的结构和功能。Abstract: Here, stable carbon and nitrogen isotope (δ13C and δ15N) techniques are used to estimate the trophic levels (TL) and main carbon sources of the dominant fish in the coral reefs of Weizhou Island in autumn. Combined with the six quantitative indicators of community trophic structure, the trophic relationship of the dominant fish in the coral reefs of Weizhou Island in autumn is preliminarily analyzed. The results show that the δ13C and δ15N values of different fishes are significantly different (p < 0.01). The δ13C values are between −18.3‰ and −15.4‰, and the δ15N values are between 12.9‰ and 16.3‰. The trophic levels of fish ranged from 2.5 to 3.4, with an average values of 3.0 ± 0.8, indicating that fish in Weizhou Island are mainly carnivorous. The organic carbon sources of fish in Weizhou Island are complex, but macroalgae and benthic microalgae are the key carbon sources fuelling fish food webs. The food source diversity level and trophic level length (CR and NR) of fish community are 2.35 and 3.09, respectively. The total area (TA), mean centrifugal distance (CD), mean nearest neighbor distance (MNND) and standard deviation of nearest neighbor distance (SDNND) are 4.48, 0.89, 0.40 and 0.29, respectively. These above indicators suggest that the trophic structure of coral reef fish community in Weizhou Island has a high degree of nutritional redundancy, but the food chain is short and the nutritional diversity is low. The coral reef ecosystem in Weizhou Island is incomplete in food web structure. In the future, it is necessary to carry out appropriate control and restoration measures to restore the structure and function of the coral reef ecosystem in Weizhou Island.
-
表 1 涠洲岛珊瑚礁鱼类的4个营养类群
Tab. 1 Four trophic guilds of fishes in coral reefs of the Weizhou Island
营养类群 摄食类型 鱼类物种 平均营养级 1 杂食性鱼类 褐篮子鱼(Siganus fuscessens)、中华单角鲀(Monacanthus chinensis)、黄尾新雀鲷(Neopomacentrus azysron) 2.7 ± 0.2 2 浮游生物食性鱼类 日本竹䇲鱼(Trachurus japonicus)、游鳍叶鲹(Atule mate) 3.2 ± 0.2 3
底栖肉食性鱼类
四带牙䱨(Pelates quadrilineatus)、二长棘犁齿鲷(Evynnis cardinalis)、大鳞舌鳎(Cynoglossus arel)、纵带绯鲤(Upeneus subvittatus)、截尾银姑鱼(Pennahia anea)、细纹鲾(Leiognathus berbis)、线尾锥齿鲷(Pentapodus setosus)、点带棘鳞鱼(Sargocentron rubrum)、十棘银鲈(Gerres decacanthus)、尖鼻箱鲀(Rhynchostracion nasus)、四线天竺鲷(Apogon quadrifasciatus)、多鳞鱚(Sillago sihama) 3.1 ± 0.1 4 鱼食性鱼类 珍鲳(Pampus minor)、日本金线鱼(Nemipterus japonicus) 3.0 ± 0.2 表 2 2021年秋季涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域鱼类及其潜在有机碳源的稳定同位素信息
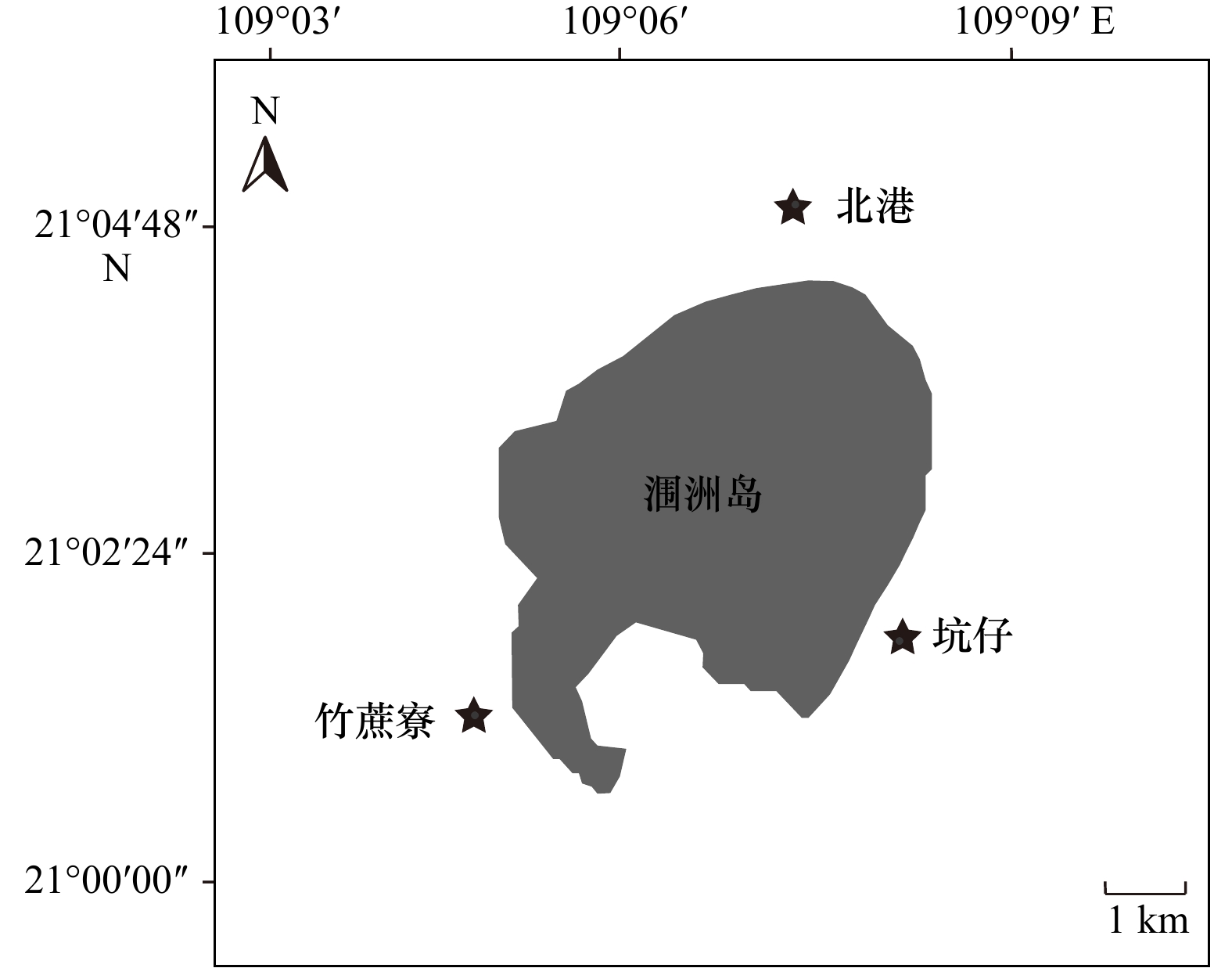
Tab. 2 Stable isotope information of fishes and their potential carbon sources in the Weizhou Island coral reef in the autumn of 2021
物种 北港 坑仔 竹蔗寮 δ13C/‰ δ15N/‰ 样品数 体长/mm δ13C/‰ δ15N/‰ 样品数 体长/mm δ13C/‰ δ15N/‰ 样品数 体长/mm 有机碳源 悬浮颗粒有机物 −23.3 ± 0.8 7.1 ± 1.4 3 −22.2 ± 0.1 7.0 ± 1.5 3 −22.1 ± 0.5 5.5 ± 1.2 4 沉积颗粒有机物 −19.3 ± 0.2 6.7 ± 0.7 6 −20.0 ± 0.5 5.2 ± 1.9 5 −19.8 ± 0.4 6.3 ± 0.4 6 团扇藻 −15.7 ± 0.6 8.8 ± 0.3 3 −14.6 ± 0.4 7.7 ± 0.4 5 −14.6 ± 0.3 7.0 ± 1.0 3 钙化红藻 −16.3 ± 0.3 9.6 ± 0.4 2 −16.0 ± 0.4 8.8 ± 0.4 4 −14.8 ± 0.3 8.0 ± 0.3 4 藻席 −15.9 9.0 1 −16.6 8.1 1 −17.6 9.3 1 底栖微藻 −18.4 ± 0.4 9.2 ± 1.0 5 −18.3 ± 0.1 10.5 ± 1.4 5 −19.6 ± 0.2 10.0 ± 0.8 5 鱼类 四带牙䱨
Pelates quadrilineatus−17.3 ± 0.9 14.4 ± 1.4 3 107.7 ± 16.0 −16.5 15.7 1 117.0 −17.0 ± 0.6 15.0 ± 0.6 5 106.2 ± 7.8 二长棘犁齿鲷
Evynnis cardinalis−16.2 ± 0.4 15.1 ± 0.5 6 98.9 ± 9.5 −16.2 ± 0.4 16.0 ± 0.3 4 80.3 ± 1.9 −16.4 ± 0.2 15.2 ± 0.5 6 79.0 ± 4.6 大鳞舌鳎
Cynoglossus arel−16.1 ± 0.3 14.3 ± 0.3 6 247.9 ± 18.1 −16.1 ± 0.1 13.9 ± 0.1 3 255.0 ± 13.2 −15.7 ± 0.2 13.8 ± 0.3 6 239.0 ± 22.8 褐篮子鱼
Siganus fuscessens−17.4 ± 1.5 12.9 ± 2.6 5 131.2 ± 23.7 −18.1 ± 1.0 12.9 ± 0.6 6 153.4 ± 15.5 −16.7 ± 0.4 13.5 ± 0.3 2 188.5 ± 13.4 纵带绯鲤
Upeneus subvittatus−16.0 ± 0.3 14.4 ± 0.6 4 102.0 ± 7.2 −16.6 ± 0.1 14.4 ± 0.2 6 102.5 ± 6.4 −16.5 ± 0.2 14.7 ± 0.4 6 102.3 ± 9.5 中华单角鲀
Monacanthus chinensis−15.9 ± 0.8 14.0 ± 0.4 4 89.8 ± 7.4 −16.1 14.2 1 95.0 −16.7 ± 0.4 14.0 ± 0.2 3 97.8 ± 7.9 黄尾新雀鲷
Neopomacentrus azysron−17.4 15.3 1 49.0 −16.4 ± 0.5 14.2 ± 0.3 4 49.5 ± 4.7 −17.2 ± 0.1 14.1 ± 0.4 6 49.2 ± 2.6 游鳍叶鲹
Atule mate−17.3 ± 0.5 16.2 ± 0.5 6 108.5 ± 12.4 −16.9 ± 0.7 15.0 ± 0.5 6 105.0 ± 20.2 − − − 截尾银姑鱼
Pennahia anea−16.6 ± 0.1 15.0 ± 0.8 2 150.5 ± 0.7 −16.5 ± 0.5 15.2 ± 0.3 6 115.7 ± 12.3 − − − 珍鲳
Pampus minor−18.3 15.1 1 96.0 −17.9 ± 0.4 14.7 ± 0.2 3 84.0 ± 2.0 − − − 细纹鲾
Leiognathus berbis−16.1 ± 0.2 14.9 ± 0.1 6 63.8 ± 3.9 −17.4 15.2 1 54.0 − − − 线尾锥齿鲷
Pentapodus setosus−15.9 ± 0.1 15.2 ± 1.0 2 161.0 ± 24.0 −15.4 ± 0.3 14.7 ± 0.1 2 153.5 ± 16.3 − − − 点带棘鳞鱼
Sargocentron rubrum−16.0 ± 0.5 15.8 ± 0.2 3 83.3 ± 44.2 −16.4 ± 0.1 15.7 ± 0.4 2 142.5 ± 17.7 − − − 日本金线鱼
Nemipterus japonicus−16.6 ± 0.3 14.4 ± 0.3 2 106.0 ± 0.1 − − − −15.9 ± 0.4 14.6 ± 0.5 6 116.6 ± 12.9 十棘银鲈
Gerres decacanthus−15.5 16.3 1 148.0 − − − −16.9 ± 0.3 16.0 ± 0.2 3 54.0 ± 4.4 日本竹䇲鱼
Trachurus japonicus−17.9 ± 0.7 14.5 ± 0.9 6 141.0 ± 7.1 − − − −18.2 13.9 1 130.0 尖鼻箱鲀
Rhynchostracion nasus−16.4 16.1 1 102.0 − − − −17.3 ± 0.3 15.4 ± 0.3 3 105.3 ± 20.4 四线天竺鲷
Apogon quadrifasciatus− − − −16.6 ± 0.2 14.5 ± 0.3 4 60.8 ± 7.9 −16.1 ± 0.2 15.8 ± 0.2 6 73.5 ± 11.8 多鳞鱚
Sillago sihama− − − −15.6 ± 0.5 15.5 ± 0.5 2 137.5 ± 36.1 −16.4 ± 0.5 16.2 ± 0.7 2 146.0 ± 0.1 注:“−”代表物种未在该站位出现。 表 3 涠洲岛珊瑚礁不同站位之间主要鱼类及其有机碳源δ13C、δ15N值的统计检验
Tab. 3 Statistical analysis of δ13C and δ15N values of the dominant fishes and their organic carbon sources among stations in coral reefs of the Weizhou Island
物种 δ13C δ15N F p F p POM 4.992 0.045 1.544 0.278 SOM 4.136 0.041 2.099 0.162 大型海藻 1.529 0.240 3.444 0.112 底栖微藻 32.006 0.001 2.030 0.174 四带牙䱨 0.396 0.689 0.738 0.517 二长棘犁齿鲷 0.744 0.494 1.879 0.215 大鳞舌鳎 1.265 0.223 2.568 0.133 褐篮子鱼 1.273 0.322 0.084 0.920 纵带绯鲤 1.988 0.186 1.543 0.250 中华单角鲀 2.805 0.104 0.137 0.875 黄尾新雀鲷 1.098 0.264 1.813 0.242 表 4 不同研究区鱼类群落的营养结构指标
Tab. 4 The indicators for trophic structure of fish communities in different study areas
-
[1] 余克服. 珊瑚礁科学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.Yu Kefu. Introduction to the Science of Coral Reefs[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. [2] Briand M J, Bonnet X, Guillou G, et al. Complex food webs in highly diversified coral reefs: insights from δ13C and δ15N stable isotopes[J]. Food Webs, 2016, 8: 12−22. doi: 10.1016/j.fooweb.2016.07.002 [3] Qin Qiang, Zhang Fubin, Liu Fei, et al. Food web structure and trophic interactions revealed by stable isotope analysis in the midstream of the Chishui River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Water, 2021, 13(2): 195. doi: 10.3390/w13020195 [4] 陈俊伊, 王康, 郭钰伦, 等. 基于稳定同位素技术的保安湖食物网结构特征研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2022, 46(5): 699−706.Chen Junyi, Wang Kang, Guo Yulun, et al. Food web structure of the Bao’an Lake based on stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes analysis[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2022, 46(5): 699−706. [5] 刘小琳, Rutakumwa E S, 徐靖昂, 等. 舟山外海重要海洋动物的碳氮稳定同位素特征和食物网营养结构[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(5): 415−423.Liu Xiaolin, Rutakumwa E S, Xu Jing’ang, et al. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope characteristics and nutrient structure of food web of important marine animals near Zhoushan Islands[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2021, 40(5): 415−423. [6] Wyatt A S J, Waite A M, Humphries S. Stable isotope analysis reveals community-level variation in fish trophodynamics across a fringing coral reef[J]. Coral Reefs, 2012, 31(4): 1029−1044. doi: 10.1007/s00338-012-0923-y [7] Kolasinski J, Nahon S, Rogers K, et al. Stable isotopes reveal spatial variability in the trophic structure of a macro-benthic invertebrate community in a tropical coral reef[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2016, 30(3): 433−446. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7443 [8] 王腾, 刘永, 李纯然, 等. 南沙美济礁海域隆背笛鲷繁殖和食性的初步研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2022, 18(6): 78−84. doi: 10.12131/20210379Wang Teng, Liu Yong, Li Chunran, et al. A preliminary study on reproduction and feeding habits of Lutjanus gibbus from Meiji Reef of Nansha[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2022, 18(6): 78−84. doi: 10.12131/20210379 [9] Fey P, Parravicini V, Bănaru D, et al. Multi-trophic markers illuminate the understanding of the functioning of a remote, low coral cover Marquesan coral reef food web[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 20950. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00348-w [10] Bradley C J, Longenecker K, Pyle R L, et al. Compound-specific isotopic analysis of amino acids reveals dietary changes in mesophotic coral-reef fish[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2016, 558: 65−79. doi: 10.3354/meps11872 [11] Carreón-Palau P L, Parrish C C, Del Angel-rodríguez A, et al. Revealing organic carbon sources fueling a coral reef food web in the Gulf of Mexico using stable isotopes and fatty acids[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2013, 58(2): 593−612. doi: 10.4319/lo.2013.58.2.0593 [12] Letourneur Y, Lison de Loma T, Richard P, et al. Identifying carbon sources and trophic position of coral reef fishes using diet and stable isotope (δ15N and δ13C) analyses in two contrasted bays in Moorea, French Polynesia[J]. Coral Reefs, 2013, 32(4): 1091−1102. doi: 10.1007/s00338-013-1073-6 [13] Morillo-Velarde P S, Briones-Fourzán P, Álvarez-Filip L, et al. Habitat degradation alters trophic pathways but not food chain length on shallow Caribbean coral reefs[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 4109. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22463-x [14] Miller S D, Zgliczynski B J, Fox M D, et al. Niche width expansion of coral reef fishes along a primary production gradient in the remote central Pacific[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2019, 625: 127−143. doi: 10.3354/meps13023 [15] Zhu Yiou, Newman S P, Reid W D K, et al. Fish stable isotope community structure of a Bahamian coral reef[J]. Marine Biology, 2019, 166(12): 160. doi: 10.1007/s00227-019-3599-9 [16] 朱文涛, 秦传新, 马鸿梅, 等. 大亚湾珊瑚礁生态系统简化食物网的稳定同位素[J]. 水产学报, 2020, 44(7): 1112−1123.Zhu Wentao, Qin Chuanxin, Ma Hongmei, et al. Stable isotope analysis of simple food web in coral reef ecosystem of Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2020, 44(7): 1112−1123. [17] 尹洪洋, 朱文涛, 马文刚, 等. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场区域夏季食物网研究[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(8): 3241−3253.Yin Hongyang, Zhu Wentao, Ma Wengang, et al. The summer food web in the marine ranch area of Wuzhizhou Island in Sanya, Hainan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 3241−3253. [18] 王腾, 刘永, 李纯厚, 等. 永兴岛附近海域珊瑚礁鱼类群落结构特征[J]. 水生生物学报, 2023, 47(4): 674−683.Wang Teng, Liu Yong, Li Chunhou, et al. Characteristics of fish community structure in coral reefs adjacent to Yongxing Island of Xisha islands[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2023, 47(4): 674−683. [19] 梁文, 周浩郎, 王欣, 等. 涠洲岛西南部海域造礁石珊瑚的群落结构特征分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(11): 123−135.Liang Wen, Zhou Haolang, Wang Xin, et al. Studies on scleractinian coral community structure characteristics in the southwest seawaters of the Weizhou Island[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(11): 123−135. [20] 龙雅婷, 余克服, 王瑞, 等. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁的发育过程及其与气候的对应关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1): 184−193. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021103101Long Yating, Yu Kefu, Wang Rui, et al. Development of coral reefs around Weizhou Island and its bearing on climate[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 184−193. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021103101 [21] 史敬文, 张瑞杰, 韩民伟, 等. 北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁区多介质环境中多环芳烃的污染特征与生态风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20221207.014.Shi Jingwen, Zhang Ruijie, Han Minwei, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the multi-media environment of Weizhou Island, Beibu Bay[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20221207.014. [22] Xu Shendong, Zhang Zhinan, Yu Kefu, et al. Spatial variations in the trophic status of Favia palauensis corals in the South China Sea: insights into their different adaptabilities under contrasting environmental conditions[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(6): 839−852. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9774-0 [23] 李邢凡, 曹超, 蔡锋. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁系统特征及台风对其影响[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2019, 36(11): 49−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.11.008Li Xingfan, Cao Chao, Cai Feng. Coral reef system characteristic and typhoon influence in Weizhou Island[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2019, 36(11): 49−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.11.008 [24] 何精科, 黄振鹏. 广西涠洲岛珊瑚分布状况研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2019, 36(1): 57−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.01.011He Jingke, Huang Zhenpeng. The distribution of corals in Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Marine Development and Management, 2019, 36(1): 57−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.01.011 [25] 刘静, 吴仁协, 康斌, 等. 北部湾鱼类图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.Liu Jing, Wu Renxie, Kang Bin, et al. Fishes of Beibu Gulf[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [26] 赖廷和, 何斌源. 广西北部湾海洋硬骨鱼类图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.Lai Tinghe, He Binyuan. Marine Osteichthyes Fishes in Guangxi Beibu Gulf of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [27] 徐步欣. 海南不同区域海草床底栖食物网表征分析[D]. 三亚: 海南热带海洋学院, 2022.Xu Buxin. Characterization of benthic food webs in different seagrass beds regions of Hainan[D]. Sanya: Hainan Tropical Ocean University, 2022. [28] Lin Jinlan, Liu Xinming, Lai Tinghe, et al. Trophic importance of the seagrass Halophila ovalis in the food web of a Hepu seagrass bed and adjacent waters, Beihai, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 125: 107607. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107607 [29] 杨璐, 曹文清, 林元烧, 等. 夏季北部湾九种经济鱼类的食性类型及营养生态位初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(2): 66−75. doi: 10.11978/2014133Yang Lu, Cao Wenqing, Lin Yuanshao, et al. Preliminary study on feeding habits and trophic niche of nine economic fish species in Beibu Gulf in summer[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(2): 66−75. doi: 10.11978/2014133 [30] 陈颖涵. 北部湾主要鱼类食性的初步研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2013.Chen Yinghan. Preliminary study on the feeding habit of dominant fish species in Beibu Gulf[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2013. [31] Quezada-Romegialli C, Jackson A L, Hayden B, et al. Trophicposition, an R package for the Bayesian estimation of trophic position from consumer stable isotope ratios[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2018, 9(6): 1592−1599. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13009 [32] Post D M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions[J]. Ecology, 2002, 83(3): 703−718. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[0703:USITET]2.0.CO;2 [33] Layman C A, Arrington D A, Montaña C G, et al. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure?[J]. Ecology, 2007, 88(1): 42−48. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2007)88[42:CSIRPF]2.0.CO;2 [34] Jackson A L, Inger R, Parnell A C, et al. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER-Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 2011, 80(3): 595−602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2011.01806.x [35] Vander Zanden M J, Rasmussen J B. Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2001, 46(8): 2061−2066. doi: 10.4319/lo.2001.46.8.2061 [36] Parnell A C, Inger R, Bearhop S, et al. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(3): e9672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009672 [37] 张宇洋, 董建宇, 孙昕, 等. 基于稳定同位素技术的灵山岛及周边海域渔业生物群落营养结构分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(8): 40−51.Zhang Yuyang, Dong Jianyu, Sun Xin, et al. Trophic structure of fishery assemblage in surrounding waters of Lingshan Island based on stable isotope analysis[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 2022, 52(8): 40−51. [38] 陆亚楠, 张瑞, 张虎, 等. 应用稳定同位素技术研究江苏近海食物网营养结构的季节性变化[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(2): 1−10.Lu Ya’nan, Zhang Rui, Zhang Hu, et al. Seasonal variation in the trophic structure of food webs in coastal waters of Jiangsu Province based on stable isotope techniques[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(2): 1−10. [39] 黄佳兴, 龚玉艳, 徐姗楠, 等. 南海中西部渔场主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(1): 76−84.Huang Jiaxing, Gong Yuyan, Xu Shannan, et al. Characteristics of stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes of major fishery organisms in the fishing ground of central western South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(1): 76−84. [40] 张文博, 黄洪辉, 李纯厚, 等. 华南典型海湾主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2019, 15(5): 9−14. doi: 10.12131/20180173Zhang Wenbo, Huang Honghui, Li Chunhou, et al. Study on carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of main fishery species in typical gulf, southern China[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2019, 15(5): 9−14. doi: 10.12131/20180173 [41] 张镇, 董建宇, 孙昕, 等. 莱州芙蓉岛人工鱼礁区大型底栖动物营养结构特征研究[J]. 水产学报, 2023, 47(9): 62−75.Zhang Zhen, Dong Jianyu, Sun Xin, et al. Trophic structure of macrobenthos in artificial reef area of Furong Island, Laizhou Bay[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2023, 47(9): 62−75. [42] Zheng Xinqing, Como S, Magni P, et al. Spatiotemporal variation in environmental features and elemental/isotopic composition of organic matter sources and primary producers in the Yundang Lagoon (Xiamen, China)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(13): 13126−13137. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04720-2 [43] Hilting A K, Currin C A, Kosaki R K. Evidence for benthic primary production support of an apex predator-dominated coral reef food web[J]. Marine Biology, 2013, 160(7): 1681−1695. doi: 10.1007/s00227-013-2220-x [44] 陈玲, 王凯, 周曦杰, 等. 岛礁水域海藻场食物网基准生物的选择[J]. 海洋渔业, 2016, 38(4): 364−373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2016.04.003Chen Ling, Wang Kai, Zhou Xijie, et al. Investigation on food web’s isotopic baseline in typical reef ecosystem-seaweed bed[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2016, 38(4): 364−373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2016.04.003 [45] Pan Ke, Zheng Xinqing, Liu Xinming, et al. Nitrogen cycling in a tropical coral reef ecosystem under severe anthropogenic disturbance in summer: insights from isotopic compositions[J]. Water Research, 2021, 207: 117824. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117824 [46] Skinner C, Pei Yude, Morimoto N, et al. Stable isotopes elucidate body-size and seasonal fluctuations in the feeding strategies of planktivorous fishes across a semi-enclosed tropical embayment[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2022, 10: 942968. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.942968 [47] 梁鑫, 彭在清. 广西涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域水质环境变化研究与评价[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2018, 35(1): 114−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.01.020Liang Xin, Peng Zaiqing. Analysis and appraisal of seawater quality in coral reef water, Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2018, 35(1): 114−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.01.020 [48] 2021年广西壮族自治区生态环境状况公报[N]. 广西日报, 2022−06−02(6).Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region ecological environment status bulletin in 2021[N]. Guangxi Daily, 2022−06−02(6). [49] 邹琦, 吴志强, 黄亮亮, 等. 广西涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域鱼类物种组成的调查分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(1): 1−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2020.01.001Zou Qi, Wu Zhiqiang, Huang Liangliang, et al. Coral reef fish species composition in Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2020, 51(1): 1−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2020.01.001 [50] 罗峥力, 杨长平, 王良明, 等. 北部湾北部沿岸海域鱼类资源时空分布特征及多样性变化[J]. 南方农业学报, 2023, 54(6): 1847−1851.Luo Zhengli, Yang Changping, Wang Liangming, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and diversity of fish resources in the coastal waters of northern Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2023, 54(6): 1847−1851. [51] 黄晖, 马斌儒, 练健生, 等. 广西涠洲岛海域珊瑚礁现状及其保护策略研究[J]. 热带地理, 2009, 29(4): 307−312, 318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2009.04.001Huang Hui, Ma Binru, Lian Jiansheng, et al. Status and conservation strategies of the coral reef in Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Tropical Geography, 2009, 29(4): 307−312, 318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2009.04.001 [52] 李永振, 陈丕茂. 南沙群岛重要珊瑚礁水域鱼类资源数量分布[J]. 水产学报, 2004, 28(6): 651−656.Li Yongzhen, Chen Pimao. Quantitative distribution of fish resources in main coral reef waters of Nansha Islands[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2004, 28(6): 651−656. [53] 倪勇, 伍汉霖. 江苏鱼类志[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006: 503−504.Ni Yong, Wu Hanlin. Fishes of Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2006: 503−504. [54] McMahon K W, Thorrold S R, Houghton L A, et al. Tracing carbon flow through coral reef food webs using a compound-specific stable isotope approach[J]. Oecologia, 2016, 180(3): 809−821. doi: 10.1007/s00442-015-3475-3 [55] Du Jianguo, Zheng Xinqing, Peristiwady T, et al. Food sources and trophic structure of fishes and benthic macroinvertebrates in a tropical seagrass meadow revealed by stable isotope analysis[J]. Marine Biology Research, 2016, 12(7): 748−757. doi: 10.1080/17451000.2016.1183791 [56] Cao D, Cao W, Yu K, et al. Evaluation of anthropogenic influences on the Luhuitou fringing reef via spatial and temporal analyses (from isotopic values)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(5): 4431−4443. doi: 10.1002/2017JC012871 [57] Zheng Xinqing, Huang Lingfeng, Huang Bangqin, et al. Factors regulating population dynamics of the amphipod Ampithoe valida in a eutrophic subtropical coastal lagoon[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 32(6): 56−65. doi: 10.1007/s13131-013-0322-4 [58] Zheng Xinqing, Huang Lingfeng, Lin Rongcheng, et al. Roles of epiphytes associated with macroalgae in benthic food web of a eutrophic coastal lagoon[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 110: 201−209. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.10.013 [59] Zheng Xinqing, Como S, Huang Lingfeng, et al. Temporal changes of a food web structure driven by different primary producers in a subtropical eutrophic lagoon[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2020, 161: 105128. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.105128 [60] 于婉君. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁区的底质特征及其对珊瑚分布的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2022.Yu Wanjun. Substrate characteristics of the area of Weizhou Island reef and its effects on the distribution of coral[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022. [61] Qin Chuanxin, Chen Pimao, Sarà G, et al. Ecological implications of purple sea urchin (Heliocidaris crassispina, Agassiz, 1864) enhancement on the coastal benthic food web: evidence from stable isotope analysis[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2020, 158: 104957. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.104957 -




 下载:
下载: