Research on automatic identification method of mangrove based on CU-Net model: Taking the Qi’ao Island in Zhuhai City, Guangdong Province as an example
-
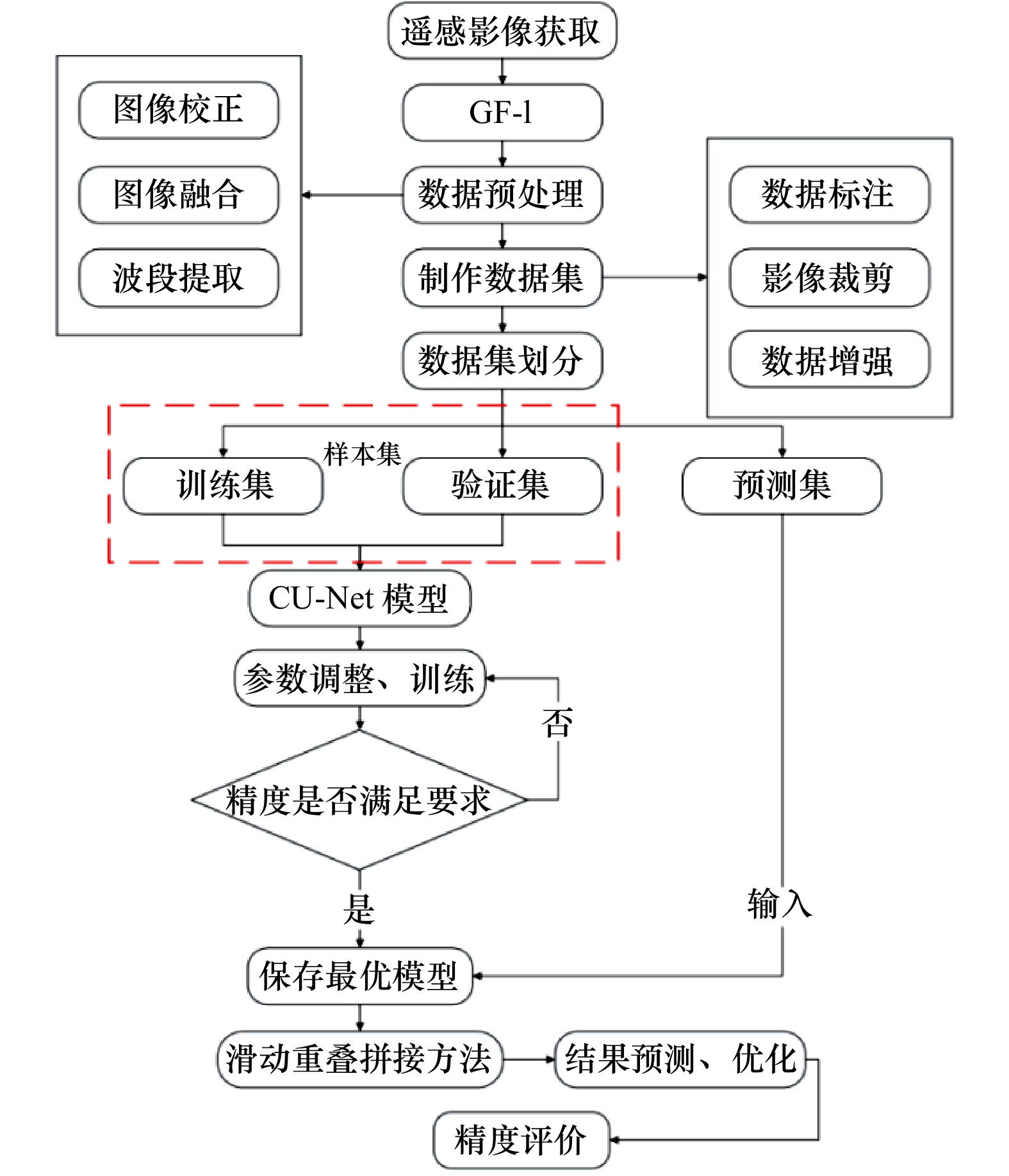
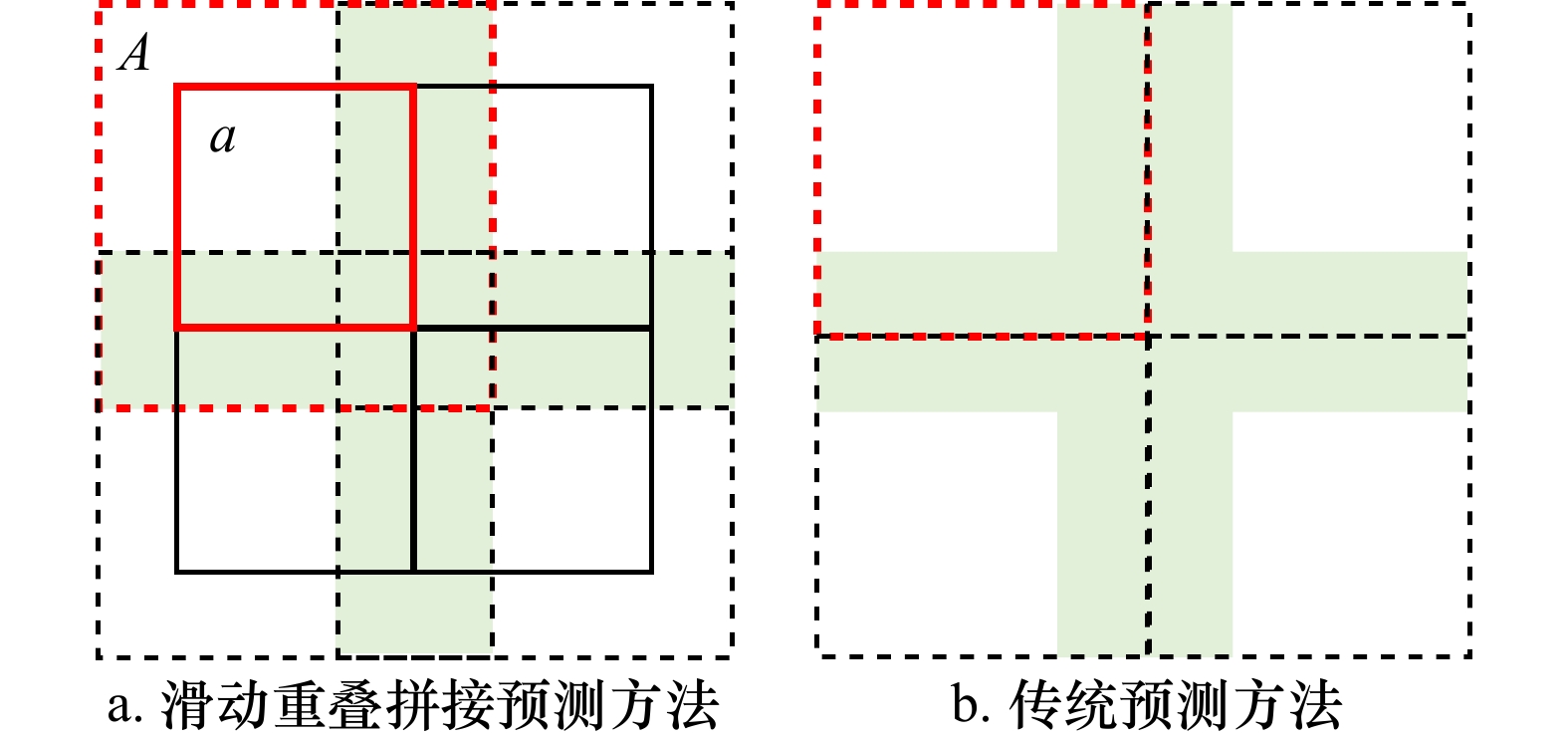
摘要: 红树林对维护生物多样性以及生态平衡等具有重要意义。因此,高效、精确地提取红树林植被信息以及实时对其进行监测十分必要。本文提出了一种高分辨率遥感影像红树林像素级精确提取的深度学习方法。针对红树林遥感分类精度不高的问题,通过强化图像中心信息,弱化边缘信息的方法引入CLoss损失函数,添加Dropout、Batch Normalization层构建了适用于红树林识别的CU-Net模型,采用滑动重叠拼接方法构建了新的预测模型,有效解决了预测结果边缘信息不足以及有拼接痕迹的问题。将本文方法的识别结果与U-Net、SegNet、DenseNet模型的预测结果以及传统的SVM、RF方法进行对比,结果表明,本文模型相较于其他深度学习模型泛化能力更强,识别效果更好,在两个测试区域的平均总体精度、平均交并比分别达到了94.43%、88.12%,平均F1-分数在红树林和普通树木的精度分别达到了95.96%、90.49%,精度明显高于传统的SVM、RF方法,也高于其他几种神经网络方法,验证了该模型在红树林识别领域的有效性,可为高分辨率遥感红树林识别领域提供一条新的思路。Abstract: Mangroves are important for maintaining biodiversity as well as ecological balance. Therefore, it is necessary to extract mangrove vegetation information efficiently and accurately and to monitor it in real time. A deep learning method for pixel-level accurate extraction of mangroves from high-resolution remote sensing images is presented in this paper. For the problem of low accuracy of mangrove remote sensing classification, CU-Net model for mangrove identification is constructed by introducing CLoss loss function by strengthening image center information and weakening edge information, and adding Dropout and Batch Normalization layers. And a new prediction model is constructed by sliding overlap splicing method, which effectively solves the problem of insufficient edge information and splicing traces in the prediction results. The recognition results of the proposed method are compared with the prediction results of U-Net, SegNet and DenseNet models as well as the traditional SVM and RF methods. The results show that the proposed model has stronger generalization ability and better recognition effect compared with other deep learning models. In the two test areas, the average OA and MIoU reach 94.43% and 88.12%, respectively. The average F1-score in mangrove and ordinary trees reach 95.96% and 90.49%, respectively. The accuracy is significantly higher than that of traditional SVM and RF methods, as well as several other neural networks. The effectiveness of the model in the field of mangrove recognition is verified, which can provide a new idea for the field of high resolution remote sensing mangrove recognition.1) ① a图审图号为GS(2019)3266号。
-
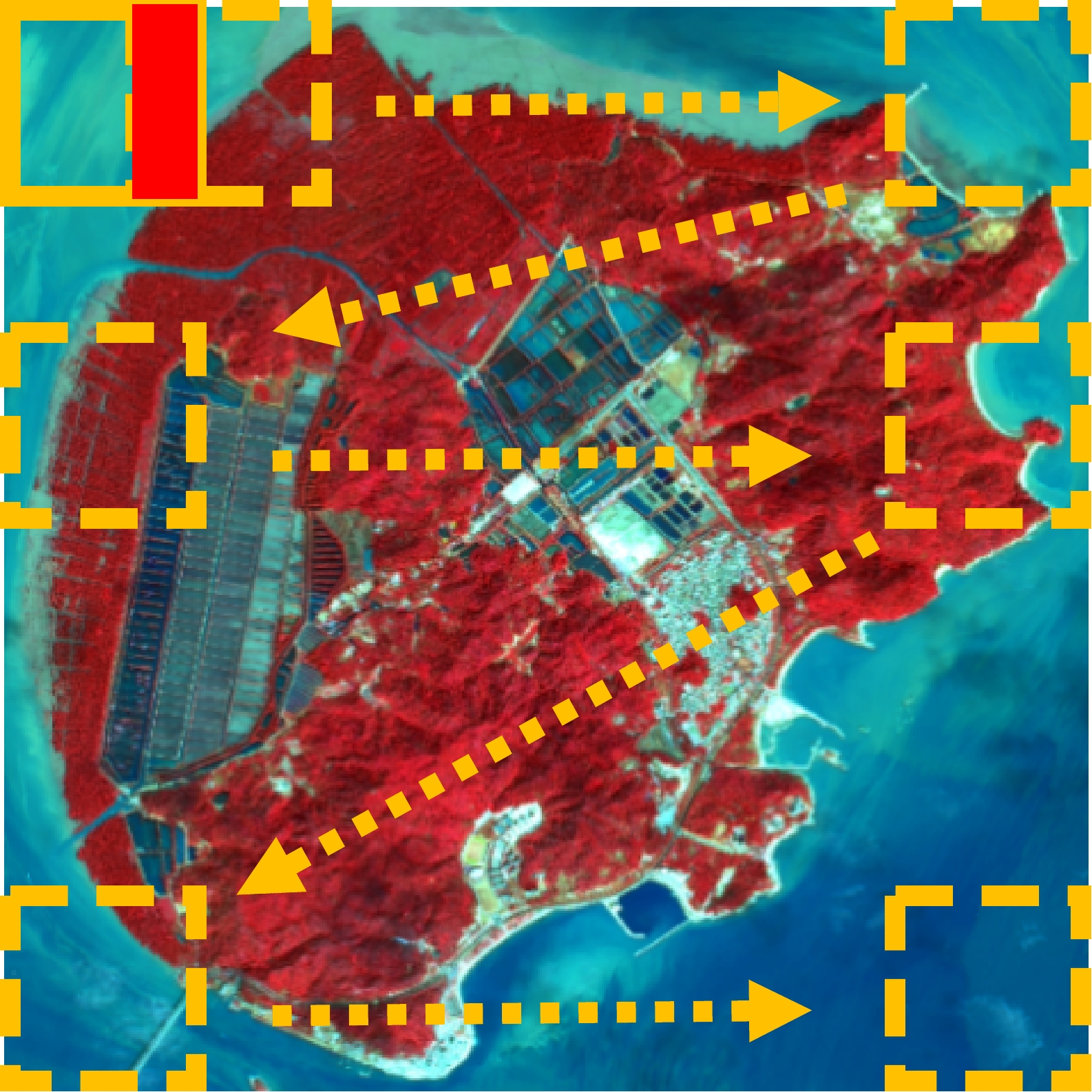
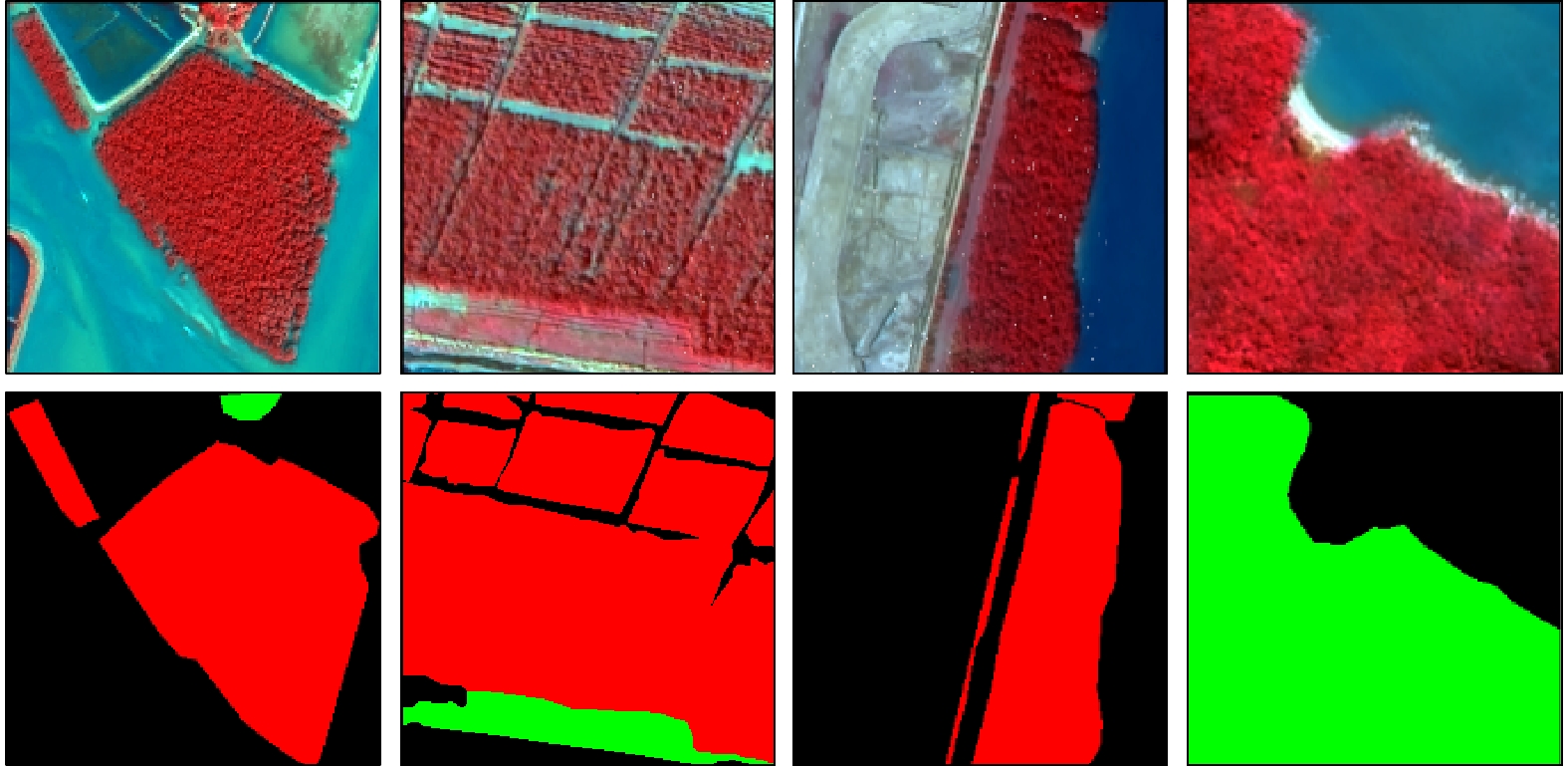
图 1 研究区地理位置及区域遥感影像①
Fig. 1 Geographic location of the study area and regional remote-sensing images
表 1 GF-1卫星影像参数
Tab. 1 GF-1 satellite image parameters
载荷 谱段号 谱段范围/μm 空间分辨率/m 幅宽/km 全色相机 1 0.45~0.90 2 60 多光谱相机 2 0.45~0.52 8 60 3 0.52~0.59 8 60 4 0.63~0.69 8 60 5 0.77~0.89 8 60 表 2 网络训练参数设置
Tab. 2 Network training parameters setting
参数 具体设置 批处理大小 16 学习率 0.000 1 训练次数 300 优化器 Adam 表 3 测试区域1的精度评价结果
Tab. 3 Test area 1 precision evaluation results
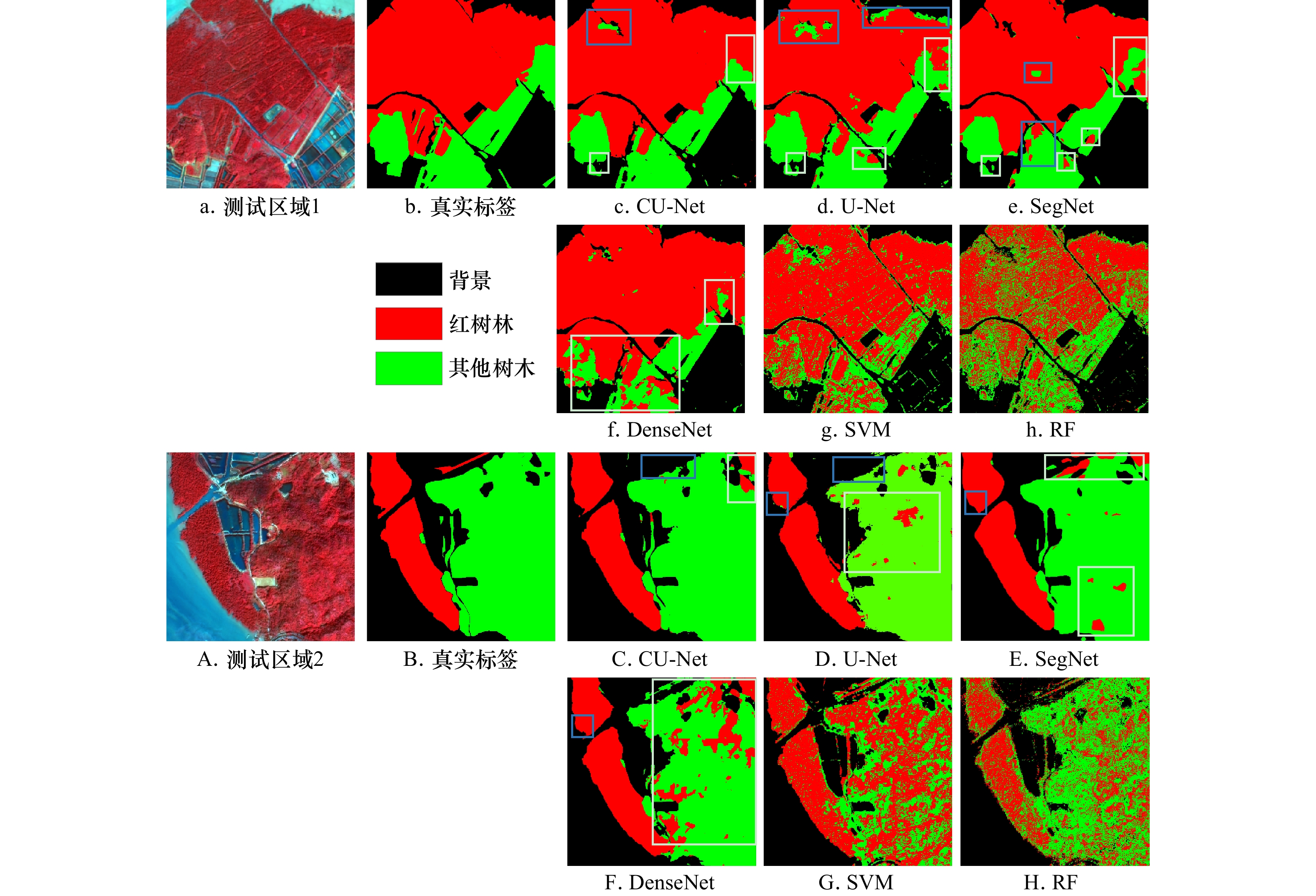
测试区 CU-Net U-Net SegNet DenseNet SVM RF 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 总体精度/% 94.00 91.54 92.01 88.33 79.80 73.91 平均交并比/% 87.21 83.35 83.36 76.18 65.31 60.59 F1-分数/% 95.78 89.16 93.39 84.29 94.42 85.26 91.13 72.09 83.46 54.81 75.45 54.60 表 4 测试区域2的精度评价结果
Tab. 4 Test area 2 precision evaluation results
测试区 CU-Net U-Net SegNet DenseNet SVM RF 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 红树林 其他树木 总体精度/% 94.86 91.28 92.59 86.67 64.38 72.69 平均交并比/% 89.03 83.77 84.74 75.03 51.60 57.30 F1-分数/% 96.14 91.82 91.05 88.61 92.15 92.32 86.68 74.85 46.99 55.33 48.62 71.86 -
[1] Lee S Y, Primavera J H, Dahdouh-Guebas F, et al. Ecological role and services of tropical mangrove ecosystems: a reassessment[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2014, 23(7): 726−743. doi: 10.1111/geb.12155 [2] Giri C, Ochieng E, Tieszen L L, et al. Status and distribution of mangrove forests of the world using Earth observation satellite data[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2011, 20(1): 154−159. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-8238.2010.00584.x [3] Field C D. Rehabilitation of mangrove ecosystems: an overview[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1999, 37(8−12): 383−392. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(99)00106-X [4] 甄佳宁, 廖静娟, 沈国状. 1987以来海南省清澜港红树林变化的遥感监测与分析[J]. 湿地科学, 2019, 17(1): 44−51.Zhen Jianing, Liao Jingjuan, Shen Guozhuang. Remote sensing monitoring and analysis on the dynamics of mangrove forests in Qinglan Habor of Hainan Province since 1987[J]. Wetland Science, 2019, 17(1): 44−51. [5] Vaiphasa C, De Boer W F, Skidmore A K, et al. Impact of solid shrimp pond waste materials on mangrove growth and mortality: a case study from Pak Phanang, Thailand[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2007, 591(1): 47−57. doi: 10.1007/s10750-007-0783-6 [6] 冯家莉, 刘凯, 朱远辉, 等. 无人机遥感在红树林资源调查中的应用[J]. 热带地理, 2015, 35(1): 35−42.Feng Jiali, Liu Kai, Zhu Yuanhui, et al. Application of unmanned aerial vehicles to mangrove resources monitoring[J]. Tropical Geography, 2015, 35(1): 35−42. [7] 罗丹, 李正会, 王德智, 等. 海口市东寨港红树林面积动态变化分析[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2013, 24(2): 97−99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2013.02.042Luo Dan, Li Zhenghui, Wang Dezhi, et al. Analysis on dynamic change of mangrove area in Dongzhai Port, Haikou City[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2013, 24(2): 97−99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2013.02.042 [8] 李春干, 代华兵. 红树林空间分布信息遥感提取方法[J]. 湿地科学, 2014, 12(5): 580−589. doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2014.05.007Li Chungan, Dai Huabing. Extraction of mangroves spatial distribution using remotely sensed data[J]. Wetland Science, 2014, 12(5): 580−589. doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2014.05.007 [9] 梁超, 刘利, 刘建强, 等. 基于HY-1C CZI影像光谱指数重构数据MNF变换的红树林提取[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(4): 104−112.Liang Chao, Liu Li, Liu Jianqiang, et al. Extracting mangrove information using MNF transformation based on HY-1C CZI spectral indices reconstruction data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(4): 104−112. [10] Jia Mingming, Wang Zongming, Wang Chao, et al. A new vegetation index to detect periodically submerged mangrove forest using single-tide sentinel-2 imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(17): 2043. doi: 10.3390/rs11172043 [11] Muhsoni F F, Sambah A B, Mahmudi M, et al. Comparison of different vegetation indices for assessing mangrove density using sentinel-2 imagery[J]. International Journal of GEOMATE, 2018, 14(45): 42−51. [12] Baloloy A B, Blanco A C, Ana R R C S, et al. Development and application of a new mangrove vegetation index (MVI) for rapid and accurate mangrove mapping[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 166: 95−117. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.06.001 [13] Manna S, Raychaudhuri B. Retrieval of leaf area index and stress conditions for Sundarban mangroves using Sentinel-2 data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(3): 1019−1039. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1655174 [14] 徐芳, 张英, 翟亮, 等. 基于Sentinel-2的潮间红树林提取方法[J]. 测绘通报, 2020(2): 49−54.Xu Fang, Zhang Ying, Zhai Liang, et al. Extraction method of intertidal mangrove by using Sentinel-2 images[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2020(2): 49−54. [15] 刘凯, 龚辉, 曹晶晶, 等. 基于多类型无人机数据的红树林遥感分类对比[J]. 热带地理, 2019, 39(4): 492−501.Liu Kai, Gong Hui, Cao Jingjing, et al. Comparison of mangrove remote sensing classification based on multi-type UAV data[J]. Tropical Geography, 2019, 39(4): 492−501. [16] 李想, 刘凯, 朱远辉, 等. 基于资源三号影像的红树林物种分类研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2018, 33(2): 360−369.Li Xiang, Liu Kai, Zhu Yuanhui, et al. Study on mangrove species classification based on ZY-3 image[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2018, 33(2): 360−369. [17] Ballanti L, Blesius L, Hines E, et al. Tree species classification using hyperspectral imagery: a comparison of two classifiers[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(6): 445. doi: 10.3390/rs8060445 [18] Wing B M, Ritchie M W, Boston K, et al. Prediction of understory vegetation cover with airborne Lidar in an interior ponderosa pine forest[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 124: 730−741. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.06.024 [19] Mondal P, Liu Xue, Fatoyinbo T E, et al. Evaluating combinations of sentinel-2 data and machine-learning algorithms for mangrove mapping in West Africa[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 2928. doi: 10.3390/rs11242928 [20] 蒙良莉. 基于哨兵多源遥感数据的红树林信息提取算法研究[D]. 南宁: 南宁师范大学, 2020.Meng Liangli. Mangrove information extraction algorithm based on multi-source remote sensing data of sentinel[D]. Nanning: Nanning Normal University, 2020. [21] Carranza-García M, García-Gutiérrez J, Riquelme J C. A framework for evaluating land use and land cover classification using convolutional neural networks[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 274. doi: 10.3390/rs11030274 [22] 黄亦其, 刘琪, 赵建晔, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的红树林物种无人机监测研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2020, 41(2): 141−146, 189.Huang Yiqi, Liu Qi, Zhao Jianye, et al. Research on unmanned aerial surveillance of mangrove species based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2020, 41(2): 141−146, 189. [23] Lassalle G, Ferreira M P, La Rosa L E C, et al. Deep learning-based individual tree crown delineation in mangrove forests using very-high-resolution satellite imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 189: 220−235. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.05.002 [24] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich: Springer, 2015: 234−241. [25] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston: IEEE, 2015: 3431−3440. [26] Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929−1958. [27] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: PMLR, 2015: 448−456. [28] Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Fort Lauderdale: JMLR, 2011: 315−323 -





 下载:
下载: