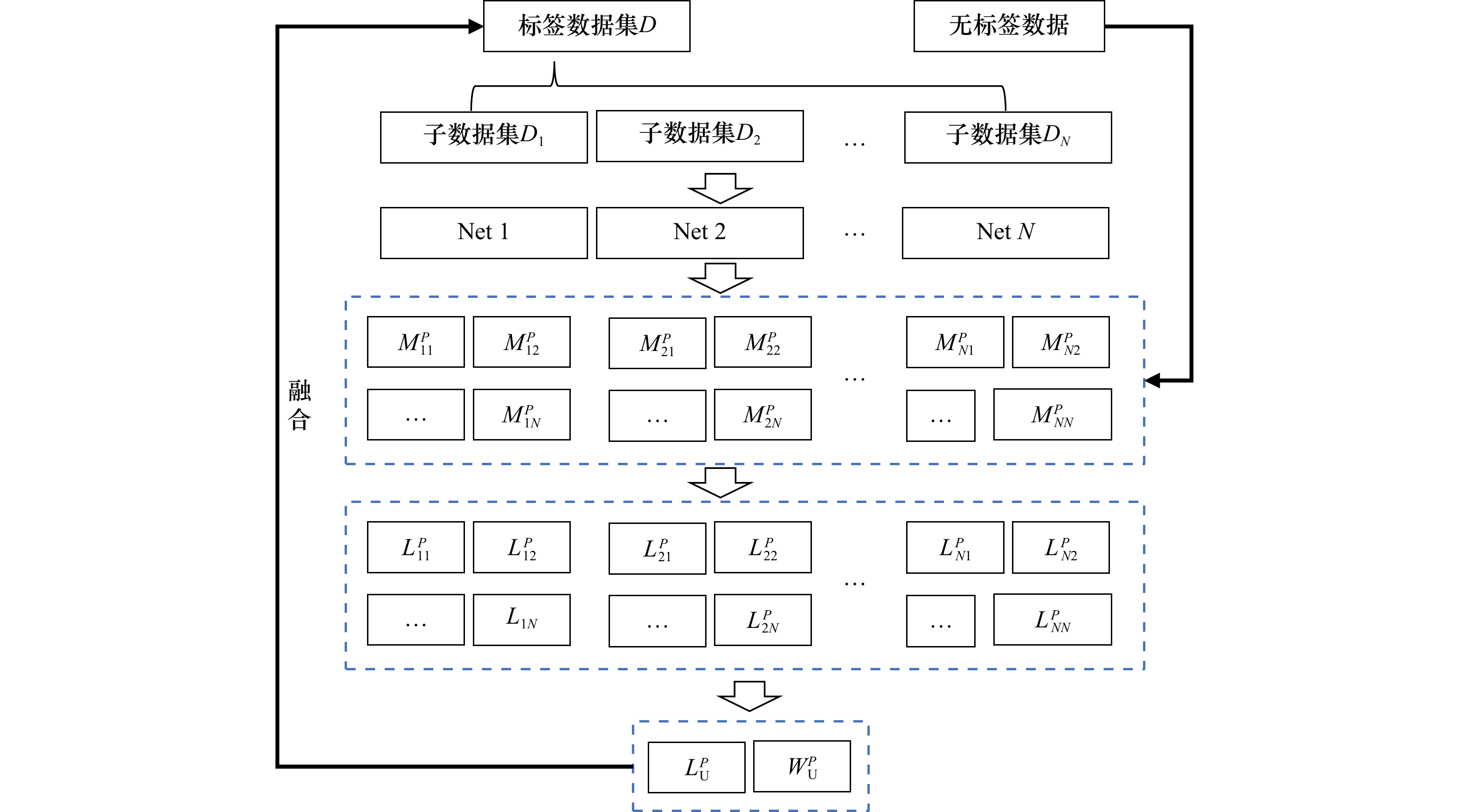
A semi-supervised coral reef substrate classification method based on soft and hard collaborative decision making
-
摘要: 珊瑚礁底质分类对海洋资源开发和海洋生态环境保护起到至关重要的作用。目前,深度学习语义分割方法在遥感图像分类领域应用广泛,但在底质分类方面的研究较少。由于基于全监督深度学习的方法中逐像素标注标签的成本较高,不适用于大规模、高频次的底质分类工作,基于半监督的深度学习方法能够有效利用已标注标签为无标签数据产生伪标签,从而有效降低人工成本,然而现有半监督方法的性能易受伪标签噪声的干扰。针对以上问题,本文提出了一种基于软硬协作决策的半监督底质分类方法。首先,利用多模型联合决策生成高质量的伪标签;然后,提出了一种能够顾及伪标签像素置信度的损失函数来指导模型进行训练;最后,采用软硬协作的决策方式得到精确的底质分类结果。在美属维尔京群岛圣克罗伊岛北部的巴克岛礁和夏威夷群岛的中途岛东南约400 km处的珍珠与爱马仕环礁的浅层底栖生物栖息地地图数据集上评估了本文方法的精度,实验结果表明,本文提出的方法与全监督学习方法精度相当,比主流的语义分割方法精度平均高3.08%,能够有效服务于珊瑚礁底质调查工作。Abstract: Coral reef substrate classification plays a crucial role in marine resource development and marine ecological protection. At present, deep learning semantic segmentation methods are widely used in the field of remote sensing image classification, but less research has been conducted in substrate classification. Due to the high cost of pixel-by-pixel labeling in the fully supervised deep learning-based method, it is not suitable for large-scale and high-frequency substrate classification work. The semi-supervised deep learning-based method can effectively use the labeled labels to generate pseudo-labels for unlabeled data, thus effectively reducing the labor cost, however, the performance of the existing semi-supervised method is vulnerable to the interference of pseudo-label noise. To address the above problems, this paper proposes a semi-supervised substrate classification method based on soft and hard collaborative decision making. First, a high quality Pseudo tag is generated using joint decision making of multiple models; then, a loss function (Collaboration Choice of decision Confidence Loss function, 3CLoss) is proposed to take into account the confidence of Pseudo tag pixels and guide the model for training; finally, a soft and hard collaborative decision making approach is used to obtain accurate substrate classification results. The accuracy of this paper was evaluated on the shallow benthic habitat atlas datasets of Buck Island Reef in the northern part of St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands, and Pearl and Hermes Atolls, about 400 km southeast of Midway Island, Hawaiian Islands, and the experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed method is comparable to that of the fully supervised learning method, and 3.08% higher than that of the mainstream semantic segmentation methods on average, which can effectively serve the coral reef substrate survey.
-
表 1 BIRNM数据集底质分类类型描述
Tab. 1 Description of substrate classification types in the BIRNM dataset
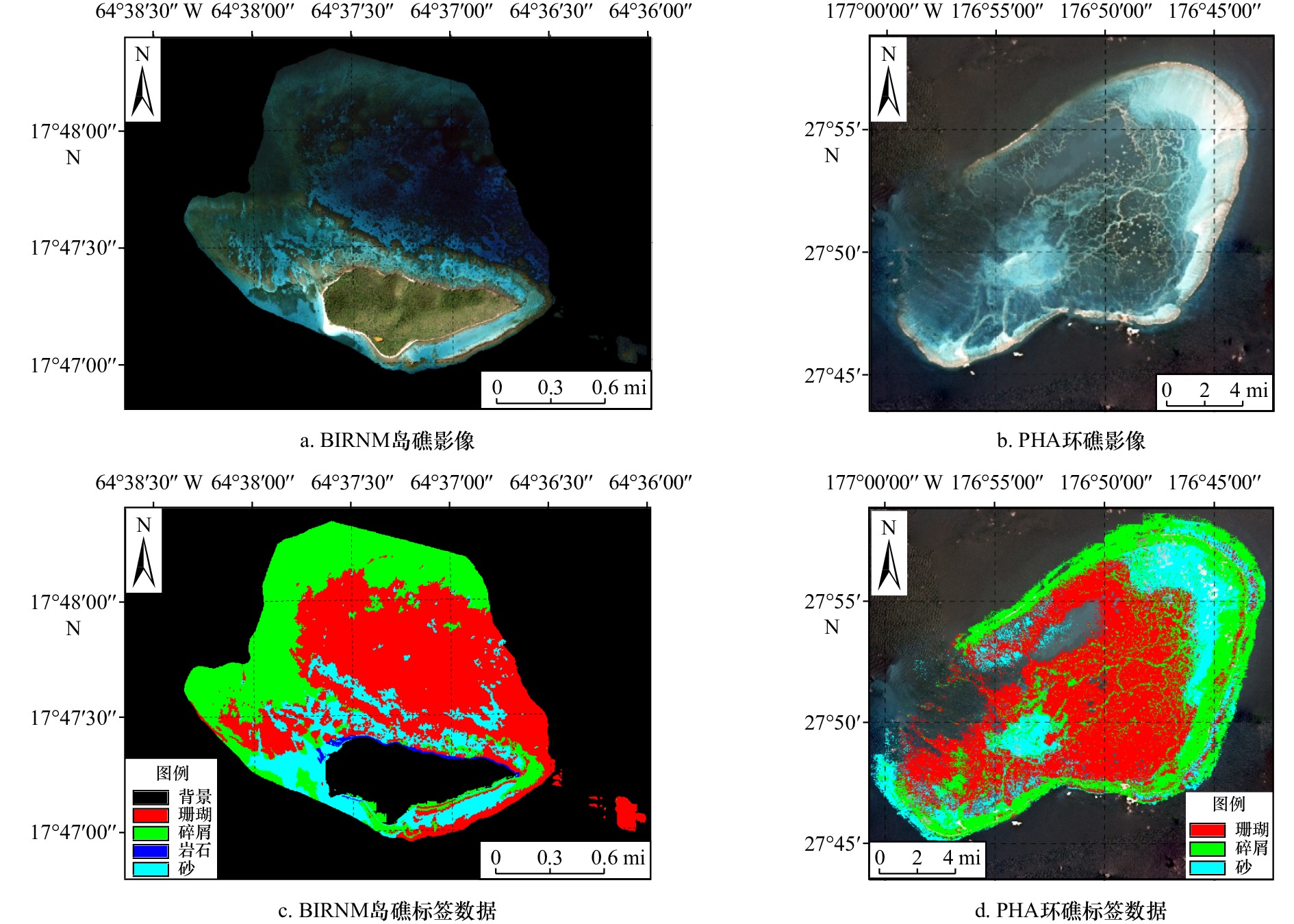
类别 描述 卫星 水下 珊瑚 连续的、高浮雕式的珊瑚形成,形状各异,包括平行于大陆架边缘的线性珊瑚 

碎屑 死去的、不稳定的珊瑚瓦砾,经常被丝状物或其他大型藻类所占据。这种底质经常出现在礁顶,珊瑚礁碎石可以在宽阔的近海沙地上以低密度聚集的方式出现 

岩石 从岛屿基岩延伸到海上的固体碳酸盐块的聚集,或从原生床剥离和运输的松散碳酸盐碎片,根据温特沃斯标准,单个巨石的直径在0.25~3 m之间 

砂 粗糙的沉积物,通常存在于海流或波浪能量影响的区域。颗粒大小在
1/16~256 mm不等

表 2 巴克岛礁数据集半监督实验结果
Tab. 2 Results of semi-supervised experiments on the Buck Island dataset
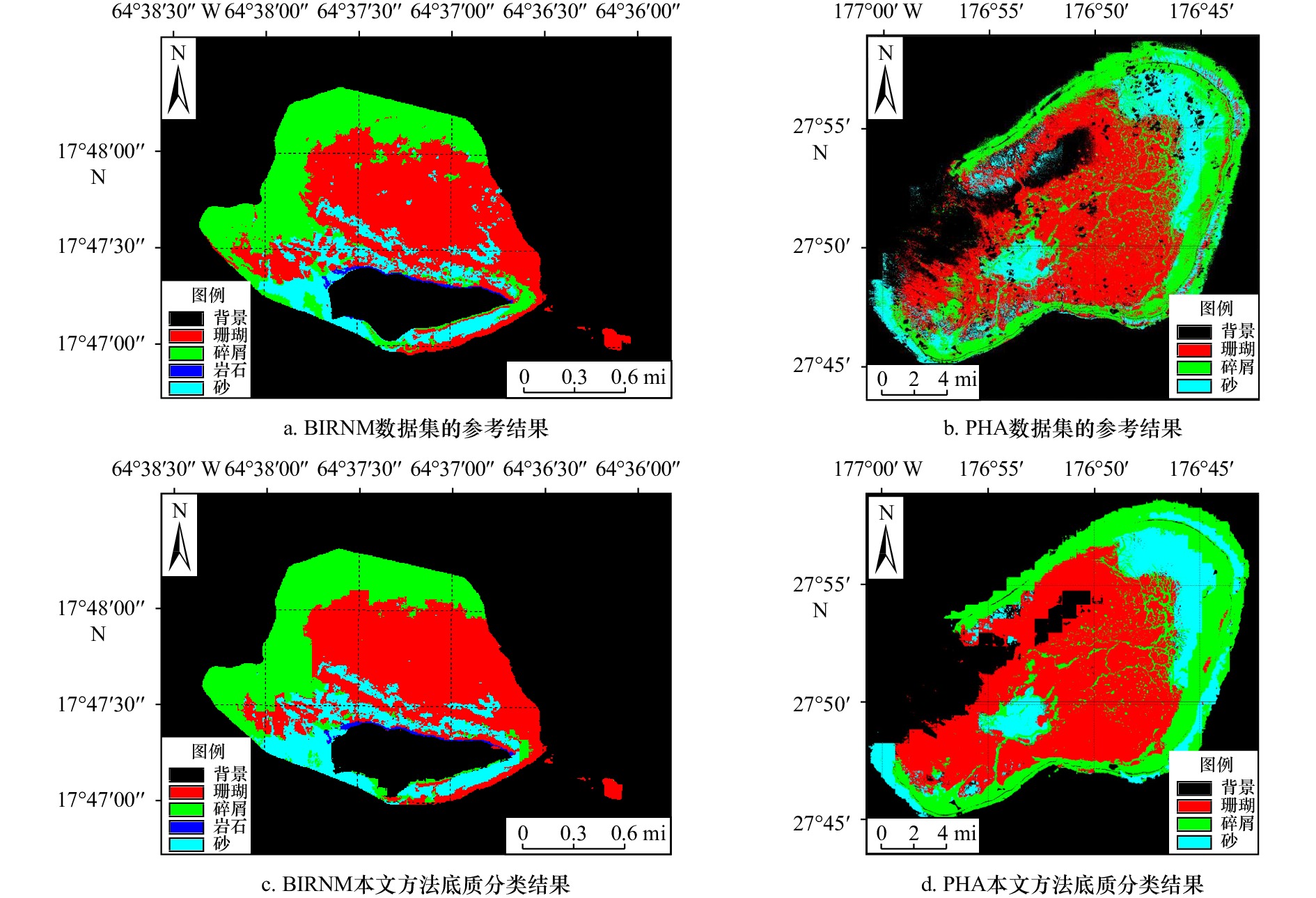
方法 背景 珊瑚 碎屑 岩石 砂 mIoU Lawin 0.930 0 0.853 2 0.729 8 0.367 0 0.740 0 0.723 3 SegFormer 0.942 8 0.863 1 0.689 5 0.513 1 0.762 5 0.754 2 PanopticDeep 0.930 4 0.851 2 0.679 0 0.442 5 0.713 8 0.718 3 本文方法 0.939 5 0.869 1 0.726 1 0.539 9 0.784 7 0.771 9 表 3 珍珠与爱马仕环礁半监督实验结果
Tab. 3 Results of semi-supervised experiments on the Pearl and Hermes Atoll
方法 背景 珊瑚 碎屑 砂 mIoU Lawin 0.874 1 0.675 5 0.528 5 0.452 1 0.632 5 SegFormer 0.872 5 0.661 2 0.523 1 0.437 1 0.623 5 PanopticDeep 0.866 6 0.672 6 0.497 5 0.443 1 0.619 9 本文方法 0.875 3 0.684 2 0.557 7 0.472 1 0.647 3 表 4 3CLoss对实验精度的影响
Tab. 4 3CLoss effect on experimental accuracy
方法 Loss 背景 珊瑚 碎屑 岩石 砂 mIoU 本文方法 3CLoss 0.939 5 0.869 1 0.726 1 0.539 9 0.784 7 0.771 9 本文方法 Cross Entropy Loss 0.942 7 0.859 8 0.713 7 0.477 9 0.746 4 0.748 1 表 5 迭代次数对平均交并比的影响
Tab. 5 Effect of number of iterations on mIoU
迭代次数 背景 珊瑚 碎屑 岩石 砂 mIoU 1 0.935 3 0.867 0 0.729 8 0.545 0 0.774 2 0.770 3 2 0.939 5 0.869 1 0.726 1 0.539 9 0.784 7 0.771 9 3 0.937 8 0.866 9 0.733 8 0.531 8 0.772 1 0.768 4 表 6 本文方法与全监督语义分割方法对比结果
Tab. 6 Comparison results between the method in this paper and the fully supervised semantic segmentation method
方法 监督方法 mIoU(BIRNM) mIoU(PHA) Lawin 全监督 0.759 6 0.633 5 SegFormer 全监督 0.770 6 0.638 1 PanopticDeep 全监督 0.743 8 0.624 7 本文方法 半监督 0.771 9 0.647 3 -
[1] 逄岩, 许枫, 刘佳. 基于Gammatone滤波器组时频谱和卷积神经网络的海底底质分类[J]. 应用声学, 2021, 40(4): 510−517. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2021.04.003Pang Yan, Xu Feng, Liu Jia. Seabed sediment classification based on Gammatone filter banks time-frequency spectrum and convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2021, 40(4): 510−517. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2021.04.003 [2] Gregr E J, Haggarty D R, Davies S C, et al. Comprehensive marine substrate classification applied to Canada’s Pacific shelf[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(10): e0259156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259156 [3] Reshitnyk L, Costa M, Robinson C, et al. Evaluation of WorldView-2 and acoustic remote sensing for mapping benthic habitats in temperate coastal Pacific waters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 153: 7−23. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.07.016 [4] Wicaksono P, Aryaguna P A. Analyses of inter-class spectral separability and classification accuracy of benthic habitat mapping using multispectral image[J]. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 2020, 19: 100335. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100335 [5] Dempster A P, Laird N M, Rubin D B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 1977, 39(1): 1−22. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1977.tb01600.x [6] Pillay T, Cawthra H C, Lombard A T. Characterisation of seafloor substrate using advanced processing of multibeam bathymetry, backscatter, and sidescan sonar in Table Bay, South Africa[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 429: 106332. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106332 [7] Blaschke T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2010, 65(1): 2−16. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2009.06.004 [8] Furey T S, Cristianini N, Duffy N, et al. Support vector machine classification and validation of cancer tissue samples using microarray expression data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2000, 16(10): 906−914. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.10.906 [9] Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5−32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [10] 万佳馨, 任广波, 马毅. 基于WorldView-2和GF-2遥感影像的赵述岛礁坪底质变化研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(10): 43−54.Wan Jiaxin, Ren Guangbo, Ma Yi. Study on substrate changes of Zhaoshu reef flat based on WorldView-2 and GF-2 remote sensing images[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(10): 43−54. [11] 逄今朝, 任广波, 施祺, 等. 基于底质类型变化监测的2005−2018年西沙永乐群岛珊瑚礁白化分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(6): 92−106.Pang Jinzhao, Ren Guangbo, Shi Qi, et al. Analysis of coral reef bleaching in Yongle Islands of Xisha from 2005 to 2018 based on sediment types change monitoring[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(6): 92−106. [12] 董娟, 任广波, 胡亚斌, 等. 基于高分辨率遥感的珊瑚礁地貌单元体系构建和分类方法——以8波段Worldview-2影像为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(4): 116−129.Dong Juan, Ren Guangbo, Hu Yabin, et al. Construction and classification of coral reef geomorphic unit system based on high-resolution remote sensing: using 8-band Worldview-2 Image as an example[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 116−129. [13] 李晓敏, 马毅, 吕喜玺. 南海珊瑚岛礁遥感分类体系和解译标志[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(5): 23−30. doi: 10.11759/hykx20201110003Li Xiaomin, Ma Yi, Lü Xixi. Establishing a remote sensing classification system and interpretation marks for the coral islands and reefs in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(5): 23−30. doi: 10.11759/hykx20201110003 [14] Wan Jiaxin, Ma Yi. Multi-scale spectral-spatial remote sensing classification of coral reef habitats using CNN-SVM[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2020, 102(S1): 11−20. [15] Huang Rongyong, Zhang Huiya, Yu Kefu. Analysis on the live coral cover around Weizhou Island using MODIS data[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(19): 4309. doi: 10.3390/s19194309 [16] 谭琨, 王雪, 杜培军. 结合深度学习和半监督学习的遥感影像分类进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(11): 1823−1841. doi: 10.11834/jig.190348Tan Kun, Wang Xue, Du Peijun. Research progress of the remote sensing classification combining deep learning and semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(11): 1823−1841. doi: 10.11834/jig.190348 [17] King A, Bhandarkar S M, Hopkinson B M. A comparison of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of coral reef survey images[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 1394−1402. [18] Li Jiwei, Knapp D E, Fabina N S, et al. A global coral reef probability map generated using convolutional neural networks[J]. Coral Reefs, 2020, 39(6): 1805−1815. doi: 10.1007/s00338-020-02005-6 [19] Wang Mengqiu, Hu Chuanmin. Satellite remote sensing of pelagic Sargassum macroalgae: the power of high resolution and deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 264: 112631. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112631 [20] 耿艳磊, 陶超, 沈靖, 等. 高分辨率遥感影像语义分割的半监督全卷积网络法[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(4): 499−508.Geng Yanlei, Tao Chao, Shen Jing, et al. High-resolution remote sensing image semantic segmentation based on semi-supervised full convolution network method[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(4): 499−508. [21] 李鑫伟, 李彦胜, 张永军. 弱监督深度语义分割网络的多源遥感影像水体检测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(12): 3015−3026.Li Xinwei, Li Yansheng, Zhang Yongjun. Weakly supervised deep semantic segmentation network for water body extraction based on multi-source remote sensing imagery[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(12): 3015−3026. [22] Xie Enze, Wang Wenhai, Yu Zhiding, et al. SegFormer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021, 34: 12077−12090. [23] Cheng Bowen, Collins M D, Zhu Yukun, et al. Panoptic-deeplab: A simple, strong, and fast baseline for bottom-up panoptic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. New York: IEEE, 2020: 12475−12485. [24] Yan Haotian, Zhang Chuang, Wu Ming. Lawin transformer: improving semantic segmentation transformer with multi-scale representations via large window attention[EB/OL]. (2022–01–05)[2022–08–15]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.01615. -




 下载:
下载: