Study on the structural evolution and dynamic balance of the shoal and channel in the Huangmaohai Estuary of the Zhujiang River
-
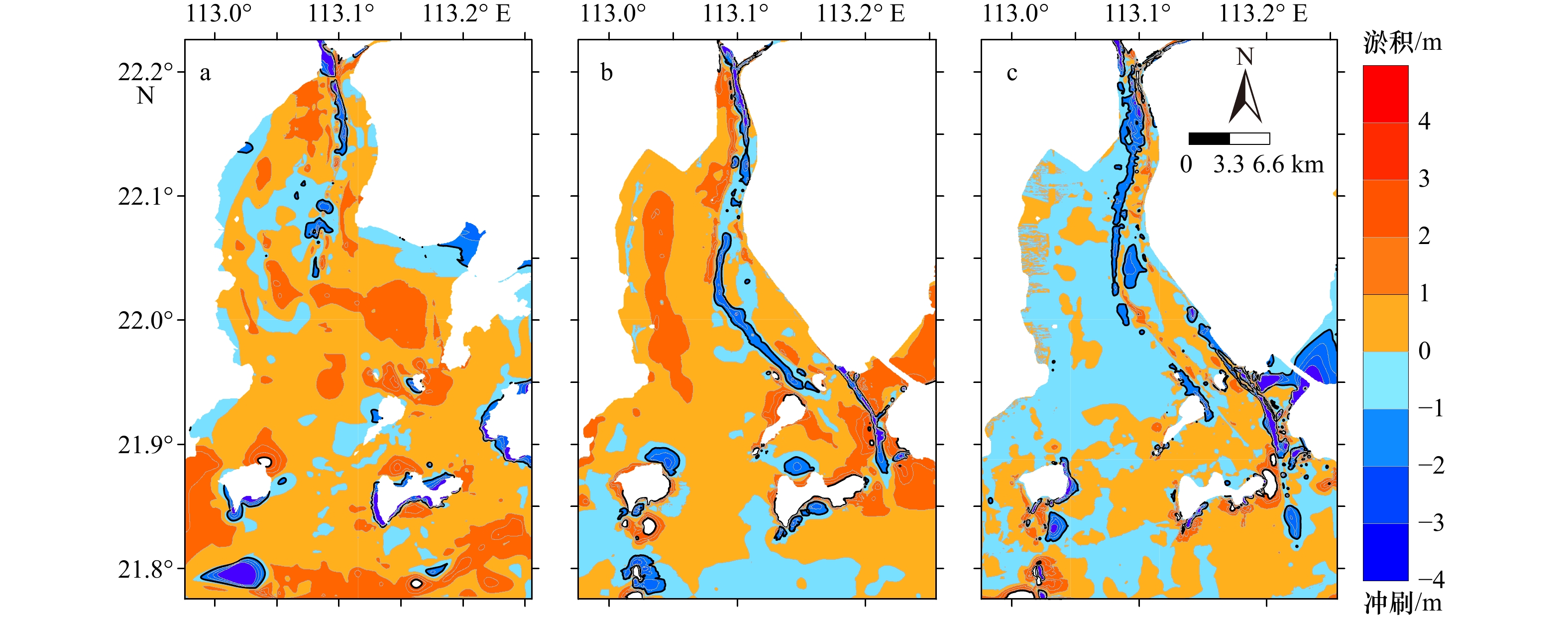
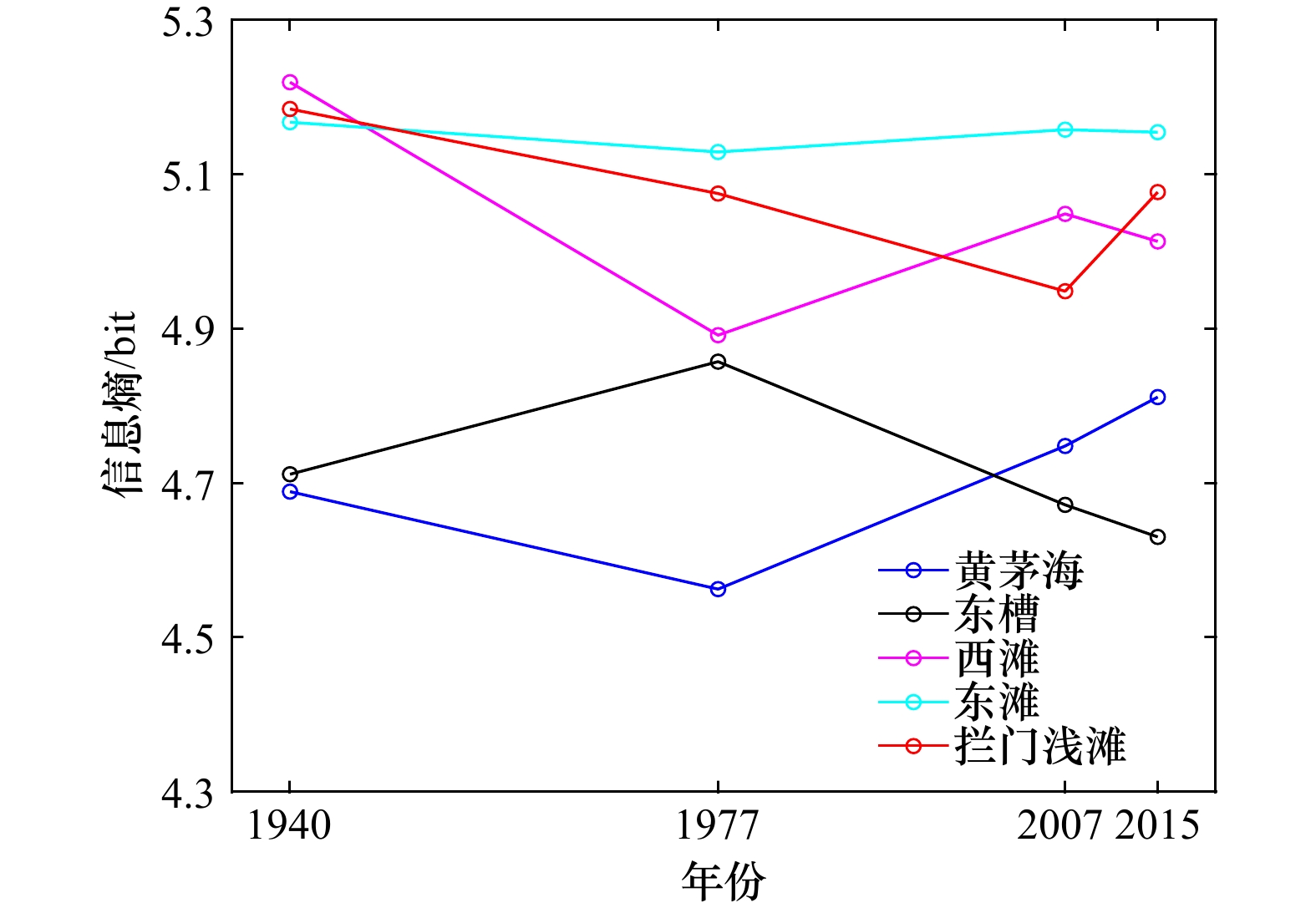
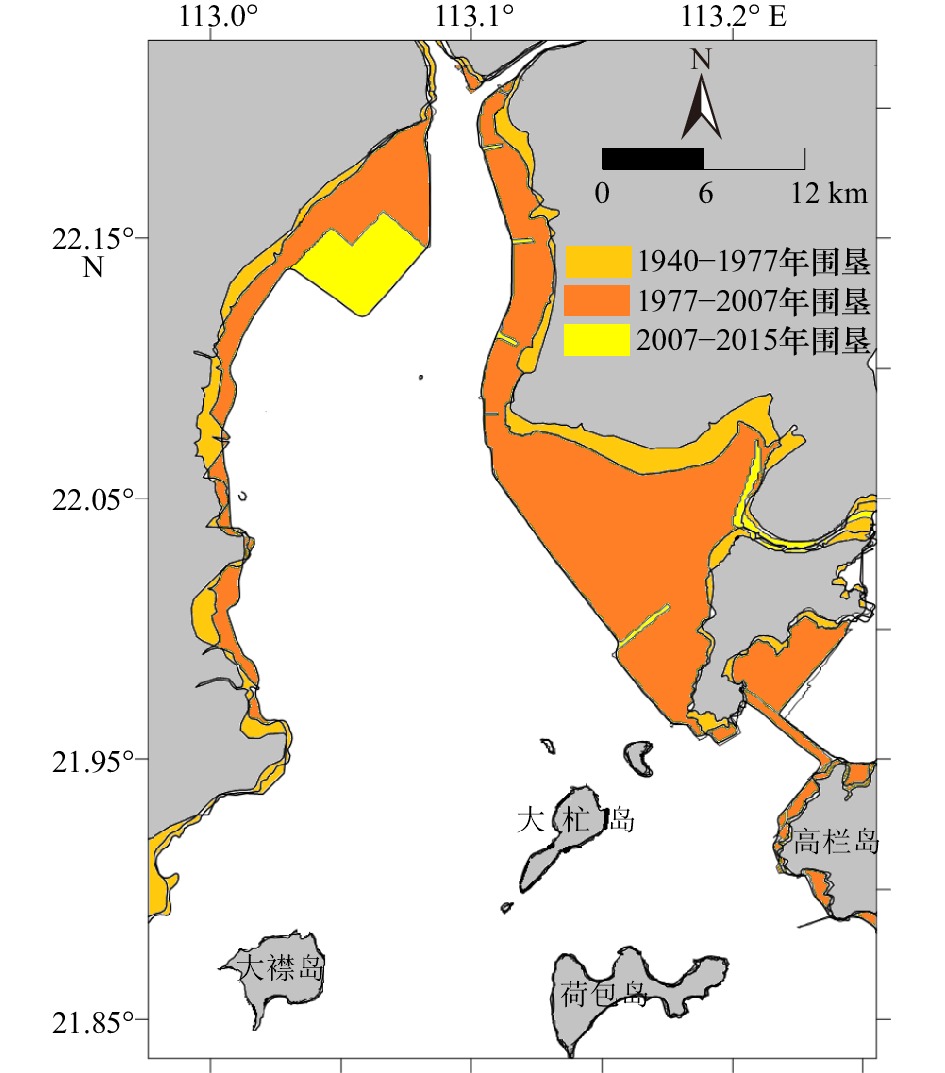
摘要: 河口湾常由滩、槽地貌系统组合而成,其滩槽结构演变及动态平衡既是河口海岸研究的重要科学问题,又是河口规划治理与港口航道建设的理论基石。本文以黄茅海河口湾为研究靶区,采用“动力−沉积−地貌”的研究思路,基于不同历史年代的海图资料,运用地貌信息熵等分析方法,研究黄茅海河口湾滩槽结构的系统演变特征及动态平衡机制,主要发现包括:(1)黄茅海河口湾半个多世纪以来的地貌演变,大致以2007年为转折点,经历由淤积到冲刷的状态转换,其在1940–2007年呈淤积状态,年均淤积率为1.4 cm/a,在2007–2015年呈冲刷状态,年均冲刷率为1.2 cm/a。(2)黄茅海河口湾的滩槽结构发生转换,在2003–2007年之间由“三滩两槽”的结构转换为“两滩一槽”的结构,受围垦和疏浚工程影响,滩槽分异趋于加强,呈现浅滩淤浅、深槽刷深的演变特征。(3)黄茅海河口湾地貌信息熵熵值先减后增,从缓慢淤积相对稳定的有序状态向人为干预下冲淤格局变化及滩槽演变的不确定性增加转换;滩槽结构的稳态存在差异,浅滩相对于深槽显示出更高的不确定性。(4)人类活动将滩槽结构的原有稳态打破,疏浚工程使得东槽的活力提升,促进深槽自适应重构平衡向有序方向发展。西滩和东滩经历围垦等人类活动干扰平衡,浅滩失稳呈无序演变。Abstract: Estuarine bay is a special geomorphological system, which is often charactered with the combination of shoals and channels. Its evolution and shifting balance of shoal-channel structure are not only the frontier hotspots of estuarine and coastal researches, but also the theoretical cornerstone of estuarine management and port waterway construction. Based on the nautical bathymetry data of different historical ages, using geomorphological information entropy and other analytical methods, this paper studies the phylogenetic evolution characteristics and shifting balance mechanism of the shoal-channel structure in Huangmaohai Estuary Bay (HEB), and the main findings include: (1) The geomorphological evolution of HEB has undergone a transition from siltation to erosion during 1940 to 2007. The average annual siltation rate was 1.4 cm/a. From then on, till 2015, the bay had shifted to erosion period and the average annual erosion rate was 1.2 cm/a. (2) The structure of shoal and channel in HEB was converted, and the structure of "three shoals and two channels" was transformed into the structure of "two shoals and one channel" between 2003 and 2007, and the elevation differentiation between shoals and channels tended to be enlarged due to the impact of reclamation in the shallow coasts and dredging projects in channels. As a result, the shallow shoals became shallower and the channels were deeper. (3) The entropy value of geomorphological information of HEB decreased first and then increased, indicating HEB it changed from the relatively stable mode of slow siltation to the abrupt changing mode, in which the uncertainty of the shoal-channel evolution was induced by human intervention; moreover, the steady states of the shoal and channel are different. The shoals showed higher uncertainty than the deep channel. (4) Human activities disturbed the original steady state of the shoal-channel structure, and the dredging project will enhance the vitality of the East Channel and promote the adaptive reconstruction in the deep channel to evolve in an orderly direction. The West Shoal and the East Shoal have undergone a disturbance balance of human activities such as reclamation, and the shoal instability has shown a disorderly evolution.
-
表 1 海图相关说明及水深资料
Tab. 1 Chart related descriptions and water depth information
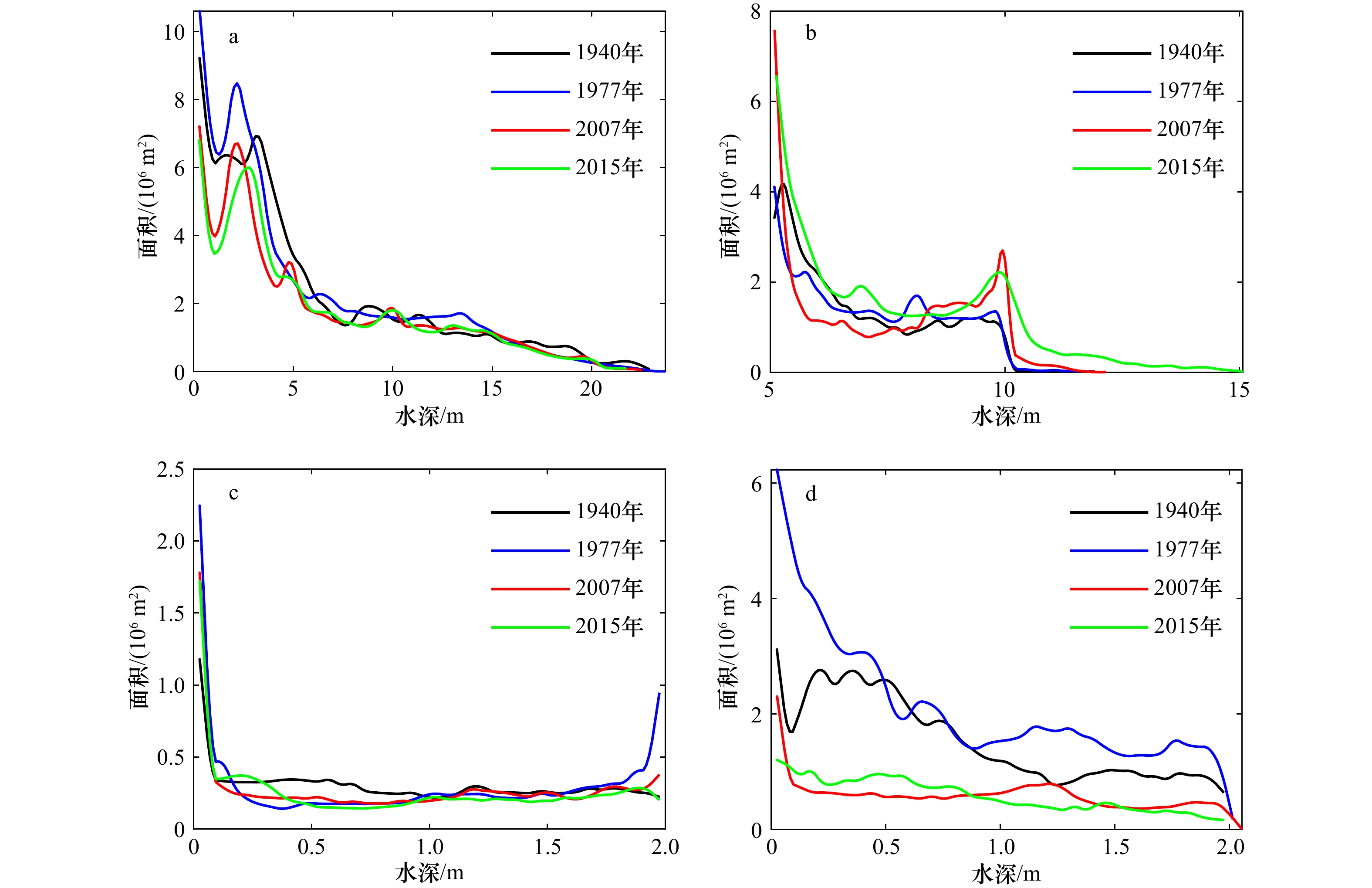
序号 年份 海图名称 比例尺 测量时期 坐标系和投影 基准面 1 1940 上川岛至澳门港 1∶100 000 1938–1940年 2000国家大地坐标系墨卡托投影 略最低低潮面 2 1977 香港至上川岛 1∶150 000 1977年 2000国家大地坐标系墨卡托投影 黄海平均海面 3 2007 澳门港至珠海港 1∶75 000 2007年 2000国家大地坐标系墨卡托投影 理论最低潮面 4 2015 小蒲台岛至小襟岛 1∶75 000 2015年 2000国家大地坐标系墨卡托投影 1985国家基准高程 表 2 黄茅海河口湾及不同地貌单元的年代际冲淤变化
Tab. 2 Interdecadal erosion changes in Huangmaohai Estuary and different geomorphological units
区域 1940–
1977年1977–
2007年2007–
2015年西滩 冲刷量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) –0.35 –0.05 –1.26 面积/(108 m2) 0.48 0.19 0.72 淤积量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 1.08 2.26 0.78 面积/(108 m2) 0.90 1.02 0.61 净冲淤 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 0.72 2.21 –0.49 年均变化率/(cm·a−1) 0.52 1.82 –0.37 东滩 冲刷量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) –0.77 –0.007 –1.12 面积/(108 m2) 0.39 0.02 0.12 淤积量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 0.59 0.49 0.89 面积/(108 m2) 0.27 0.24 0.16 净冲淤 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) –0.17 0.49 –0.23 年均变化率/(cm·a−1) –0.26 1.94 –0.82 东槽 冲刷量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) –0.16 –0.35 –3.17 面积/(108 m2) 0.06 0.09 0.22 淤积量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 0.41 1.00 1.74 面积/(108 m2) 0.27 0.23 0.13 净冲淤 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 0.25 0.65 –1.43 年均变化率/(cm·a−1) 0.76 2.07 –4.04 拦门浅滩 冲刷量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) –0.14 –0.21 –2.87 面积/(108 m2) 0.17 0.11 0.75 淤积量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 2.36 1.65 0.62 面积/(108 m2) 1.25 0.87 0.26 净冲淤 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 2.22 1.44 –2.25 年均变化率/(cm·a−1) 1.56 1.47 –2.22 黄茅海 冲刷量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) –6.02 –3.47 –28.79 面积/(108 m2) 2.22 2.06 3.89 淤积量 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 14.27 15.87 19.15 面积/(108 m2) 7.02 5.80 4.00 净冲淤 年均体积/(106 m3·a−1) 8.25 12.40 –9.54 年均变化率/(cm·a−1) 1.18 1.58 –1.21 注:正值表示淤积,负值表示冲刷。 表 3 黄茅海河口湾冲刷量及东槽浚深量估算
Tab. 3 Huangmaohai Estuary erosion volume and East Channel dredging volume estimation
时期 黄茅海冲刷量/
(106 m3)东槽浚深量/
(106 m3)浚深占冲刷量之比/% 1940–1977 222.74 – – 1977–2007 104.1 56.76 54.5 2007–2015 230.32 39.62 17.2 注:−代表不统计。 -
[1] 李春初. 论河口体系及其自动调整作用——以华南河流为例[J]. 地理学报, 1997, 52(4): 67−74.Li Chunchu. On the estuarine system and its automatic adjustment[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1997, 52(4): 67−74. [2] 易小兵, 王世俊, 李春初. 珠江河口界面特征与河口管理理念[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(4): 86−92.Yi Xiaobing, Wang Shijun, Li Chunchu. Estuary boundary characteristics of the Pearl River Estuary and their effects on the management idea[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26(4): 86−92. [3] McManus J. Deltaic responses to changes in river regimes[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2002, 79(3/4): 155−170. [4] Syvitski J P M. Deltas at risk[J]. Sustainability Science, 2008, 3(1): 23−32. doi: 10.1007/s11625-008-0043-3 [5] Blum M D, Roberts H H. Drowning of the Mississippi Delta due to insufficient sediment supply and global sea-level rise[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(7): 488−491. doi: 10.1038/ngeo553 [6] Liu Feng, Yuan Lirong, Yang Qingshu, et al. Hydrological responses to the combined influence of diverse human activities in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. CATENA, 2014, 113: 41−55. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2013.09.003 [7] Giosan L, Syvitski J, Constantinescu S, et al. Climate change: protect the world’s deltas[J]. Nature, 2014, 516(7529): 31−33. doi: 10.1038/516031a [8] 姚鹏. 人类活动对珠江口伶仃洋年代际动力地貌演变的贡献研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2019.Yao Peng. Decadal varibility of Lingdingyang Bay morphodynamics: the role of human activities[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2019. [9] Gao Guandong, Wang Xiaohua, Bao Xianwen. Land reclamation and its impact on tidal dynamics in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 151: 285−294. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.07.017 [10] Lin Lei, Liu Zhe, Xie Lian, et al. Dynamics governing the response of tidal current along the mouth of Jiaozhou Bay to land reclamation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(4): 2958−2972. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010434 [11] Wu Ziyin, Saito Y, Zhao Di’neng, et al. Impact of human activities on subaqueous topographic change in Lingding Bay of the Pearl River Estuary, China, during 1955−2013[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 37742. doi: 10.1038/srep37742 [12] 应强, 何杰, 辛文杰. 巨型人工采砂坑对伶仃洋自然演变的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2019, 30(6): 915−922.Ying Qiang, He Jie, Xin Wenjie. Influence of giant artificial sand pits on the natural evolution of Lingding Bay[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2019, 30(6): 915−922. [13] Walther R, Schaguene J, Hamm L, et al. Coupled 3D modeling of turbidity maximum dynamics in the Loire Estuary, France[J]. Coastal Engineering Proceedings, 2012, 1(33): 22. [14] Van Maren D S, Oost A P, Wang Z B, et al. The effect of land reclamations and sediment extraction on the suspended sediment concentration in the Ems Estuary[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 376: 147−157. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.03.007 [15] 吴超羽. 珠江三角洲千年尺度演变的动态平衡及其唯象判据探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(7): 22−37.Wu Chaoyu. A preliminary study on the phenomenological relation between morphodynamic equilibrium and geomorphic information entropy in the evolution of the Zhujiang River Delta[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(7): 22−37. [16] van Wesenbeeck B K. Thresholds and shifts: consequences of habitat modification in salt-marsh pioneer zones[D]. Groningen: University of Groningen, 2007. [17] Möllmann C, Folke C, Edwards M, et al. Marine regime shifts around the globe: theory, drivers and impacts[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2015, 370(1659): 20130260. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0260 [18] van de Koppel J, Gascoigne J C, Theraulaz G et al. Experimental evidence for spatial self-organization and its emergent effects in mussel bed ecosystems[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5902): 739−742. doi: 10.1126/science.1163952 [19] von Elverfeldt K. System Theory in Geomorphology: Challenges, Epistemological Consequences and Practical Implications[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2012: 1−142. [20] 李炎. 均衡态: 动力−沉积−地貌系统的跨尺度联系[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(7): 38−42.Li Yan. The equilibrium status: a cross-scale linkage for hydrodynamics, sedimentology, and geomorphology[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(7): 38−42. [21] 艾南山. 侵蚀流域系统的信息熵[J]. 水土保持学报, 1987, 1(2): 1−8.Ai Nanshan. Comentropy in erosional-drainage-system[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1987, 1(2): 1−8. [22] Tejedor A, Longjas A, Edmonds D A, et al. Entropy and optimality in river deltas[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(44): 11651−11656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708404114 [23] 贾良文, 罗军, 任杰. 珠江口黄茅海拦门沙演变及成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(5): 120−127.Jia Liangwen, Luo Jun, Ren Jie. The analysis of the evolution of a sand bar and its formation in the Huangmao Bay of the Zhujiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(5): 120−127. [24] 俞丰华, 余顺超, 丁晓英. 珠江河口近30年演变趋势分析[J]. 人民珠江, 2011, 32(1): 14−17.Yu Fenghua, Yu Shunchao, Ding Xiaoying. Analysis of evolution trend of Pearl River Estuary in the past 30 years[J]. Pearl River, 2011, 32(1): 14−17. [25] 李举国, 董兆英, 周丽华. 黄茅海拦门沙演变及回淤分析[R]. 广州: 广东省航道局总工室, 1994: 4.Li Juguo, Dong Zhaoying, Zhou Lihua. Evolution and sedimentation analysis of barrier sand in Huangmaohai Estuary[R]. Guangzhou: General Engineering Office of Guangdong Provincial Navigation Bureau, 1994: 4. [26] 罗军, 张淑雯. 黄茅海二维水动力模拟[J]. 中国水运, 2014, 14(3): 204−206.Luo Jun, Zhang Shuwen. Two-dimensional hydrodynamic simulation of Huangmaohai[J]. China Water Transport, 2014, 14(3): 204−206. [27] Van der Wal D, Pye K. The use of historical bathymetric charts in a GIS to assess morphological change in estuaries[J]. The Geographical Journal, 2003, 169(1): 21−31. doi: 10.1111/1475-4959.04943 [28] Elias E P L, Cleveringa J, Buijsman M C, et al. Field and model data analysis of sand transport patterns in Texel tidal inlet (The Netherlands)[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2006, 53(5/6): 505−529. [29] Jaffe B E, Smith R E, Foxgrover A C. Anthropogenic influence on sedimentation and intertidal mudflat change in San Pablo Bay, California: 1856−1983[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2007, 73(1/2): 175−187. [30] Zhang Wei, Xu Yang, Hoitink A J F, et al. Morphological change in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 363: 202−219. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.02.012 [31] Mei Xuefei, Dai Zhijun, Wei Wen, et al. Secular bathymetric variations of the north channel in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary, China, 1880–2013: causes and effects[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 303: 30−40. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.11.014 [32] Xie Dongfeng, Pan Cunhong, Wu Xiuguang, et al. Local human activities overwhelm decreased sediment supply from the Changjiang River: continued rapid accumulation in the Hangzhou Bay-Qiantang Estuary system[J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 392: 66−77. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.08.013 [33] Burrough P A, McDonnell R A. Principles of Geographical Information Systems[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. [34] Dai Zhijun, Liu J T, Wei Wen, et al. Detection of the Three Gorges Dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6600. doi: 10.1038/srep06600 [35] Shannon C E. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27(4): 623−656. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x [36] 丁晓瑛, 许祥向, 余顺超, 等. 基于DEM的黄茅海滩槽演变分析[C]//中国海洋工程学会. 第十二届中国海岸工程学术讨论会论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 547−551.Ding Xiaoying, Xu Xiangxiang, Yu Shunchao, et al. Evolution analysis of Huangmao beach trough based on DEM[C]//Chinese Society of Ocean Engineering. Proceedings of the 12th China Coastal Engineering Symposium. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2005: 547−551. [37] 胡煌昊, 徐阳, 官明开, 等. 珠江河口水下三角洲冲淤演变分析[J]. 水道港口, 2016, 37(6): 593−598.Hu Huanghao, Xu Yang, Guan Mingkai, et al. Analysis on morphological evolution of underwater delta in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2016, 37(6): 593−598. [38] 申其国, 谢凌峰, 解鸣晓, 等. 珠江三角洲河口湾航道整治研究[J]. 水道港口, 2019, 40(3): 286−292.Shen Qiguo, Xie Lingfeng, Xie Mingxiao, et al. Research on channel regulation in Pearl River Delta estuaries[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2019, 40(3): 286−292. [39] 何杰, 辛文杰. 崖门出海航道疏浚工程潮流泥沙变化数值模拟[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2009(3): 1−4.He Jie, Xin Wenjie. Numerical simulation of tidal current and sediment for dredging project in Yamen Sea Channel[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2009(3): 1−4. [40] 陈惠珍. 崖门出海航道整治研究[J]. 中国水运, 2000(12): 35−36.Chen Huizhen. Research on regulation of Yamen Channel leading to sea[J]. China Water Transport, 2000(12): 35−36. [41] Gong Wenping, Jia Liangwen, Shen Jian, et al. Sediment transport in response to changes in river discharge and tidal mixing in a funnel-shaped micro-tidal estuary[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 76: 89−107. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.006 [42] 严静, 韦惺. 珠江黄茅海河口地貌形态变化及其动力响应[J/OL]. 热带海洋学报, (2022–06–16)[2022–07–14]. http://www.jto.ac.cn/CN/10.11978/2022106.Yan Jing, Wei Xing. Geomorphological changes and dynamic responses of the Huangmaohai Estuary of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, (2022–06–16)[2022–07–14]. http://www.jto.ac.cn/CN/10.11978/2022106. [43] 罗军. 十年至百年尺度黄茅海地形演变及成因研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2010.Luo Jun. Cause analysis of morphological evolution of Huangmaosea Estuary in the decade to century-scale[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2010. [44] 贾良文, 文艺. 珠江口黄茅海枯季表层沉积物特性及输移研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2013(1): 60−66.Jia Liangwen, Wen Yi. Study of characteristics and transport pattern of surface sediment during dry seasons in Huangmao Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2013(1): 60−66. [45] 赵狄能. 珠江河口三角洲近165年演变及对人类活动响应研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.Zhao Di’neng. Morphological evolution of the Pearl River Delta in the past 165 years and its response to human activities[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. [46] 储南洋. 人类活动影响下珠江口伶仃洋滩槽演变研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2020.Chu Nanyang. The evolution of Lingding Bay channel-shoal system under anthropogenic influence[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2020. -





 下载:
下载: