Temporal and spatial evolution and genetic mechanism of shallow continental shelf sandbodies in the northwestern Zhusan Depression
-
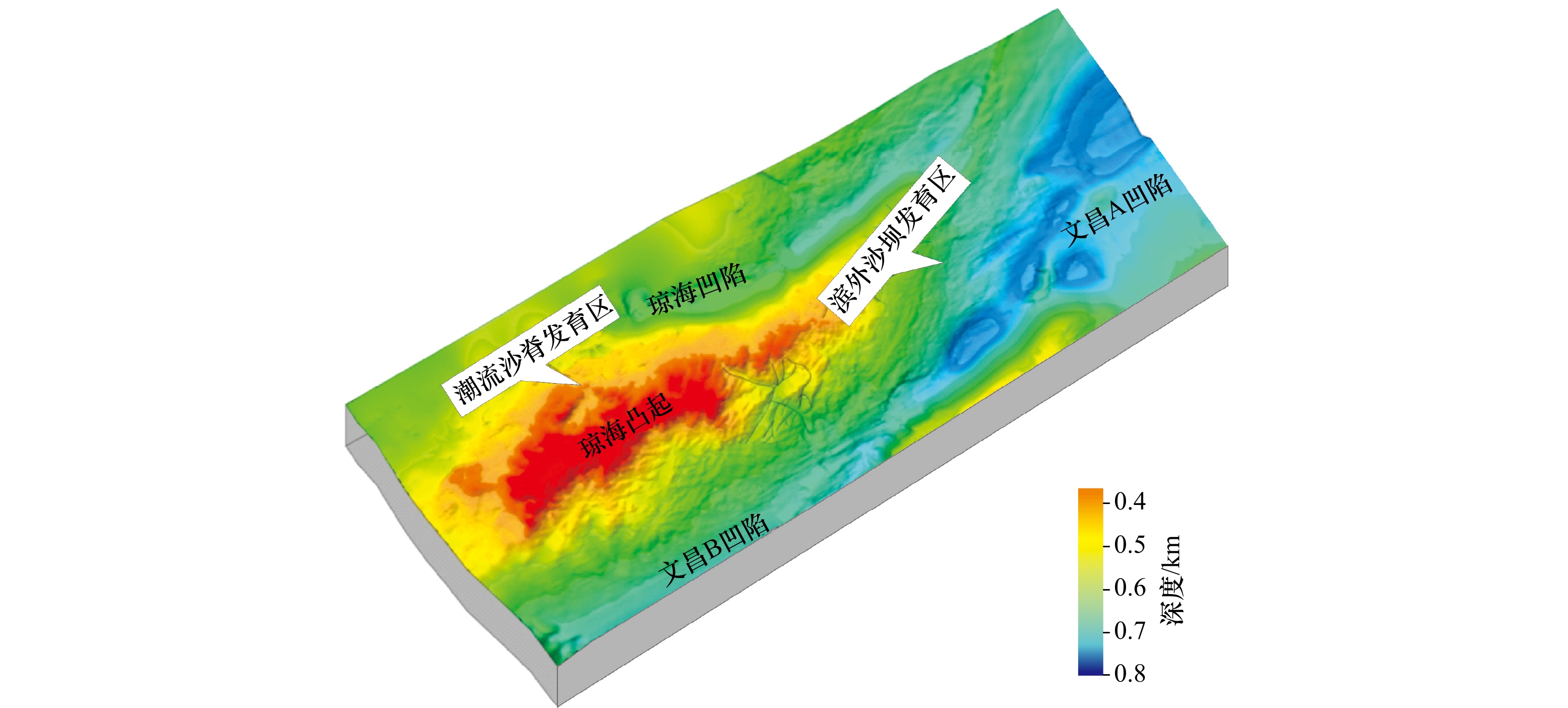
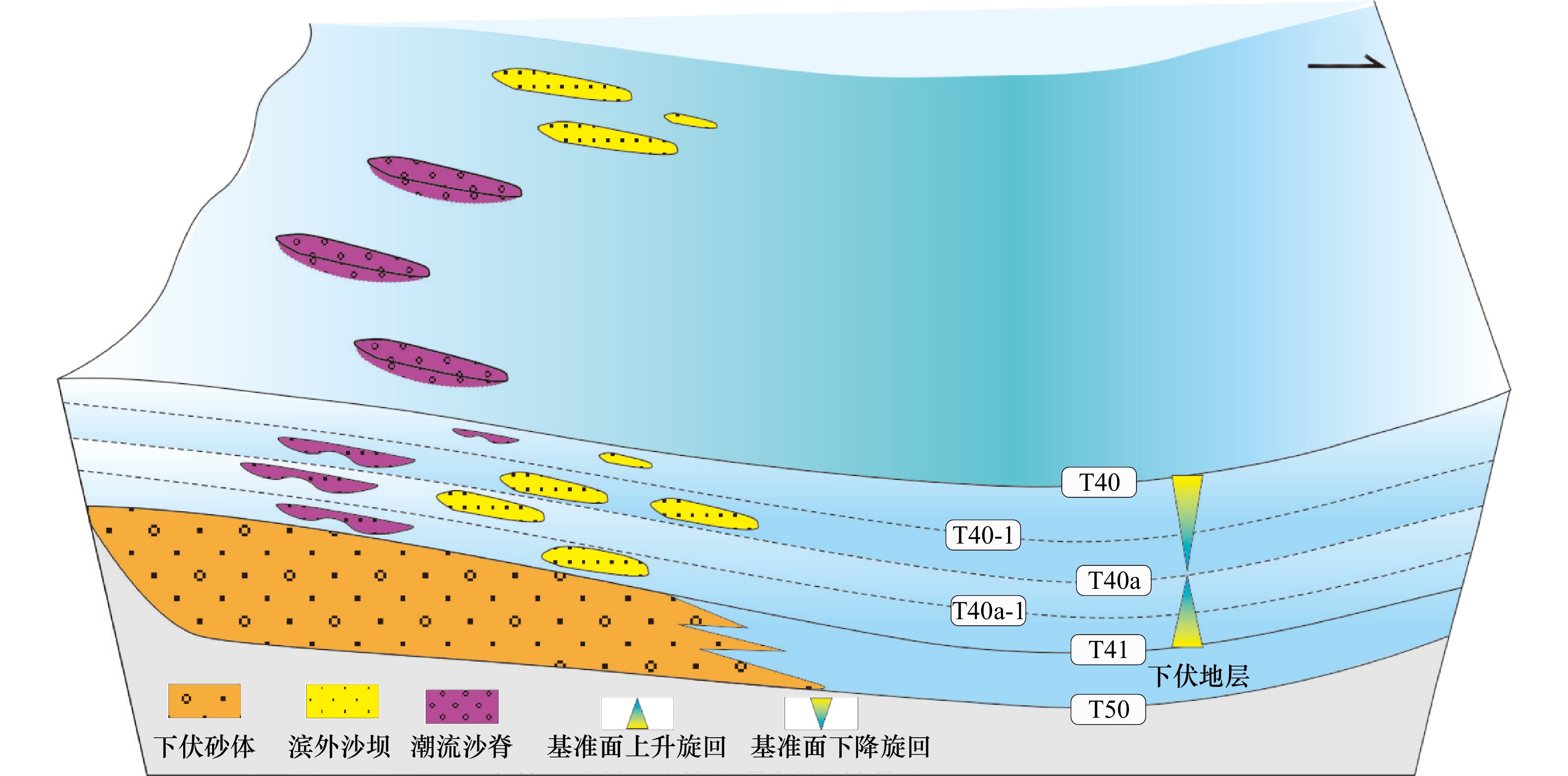
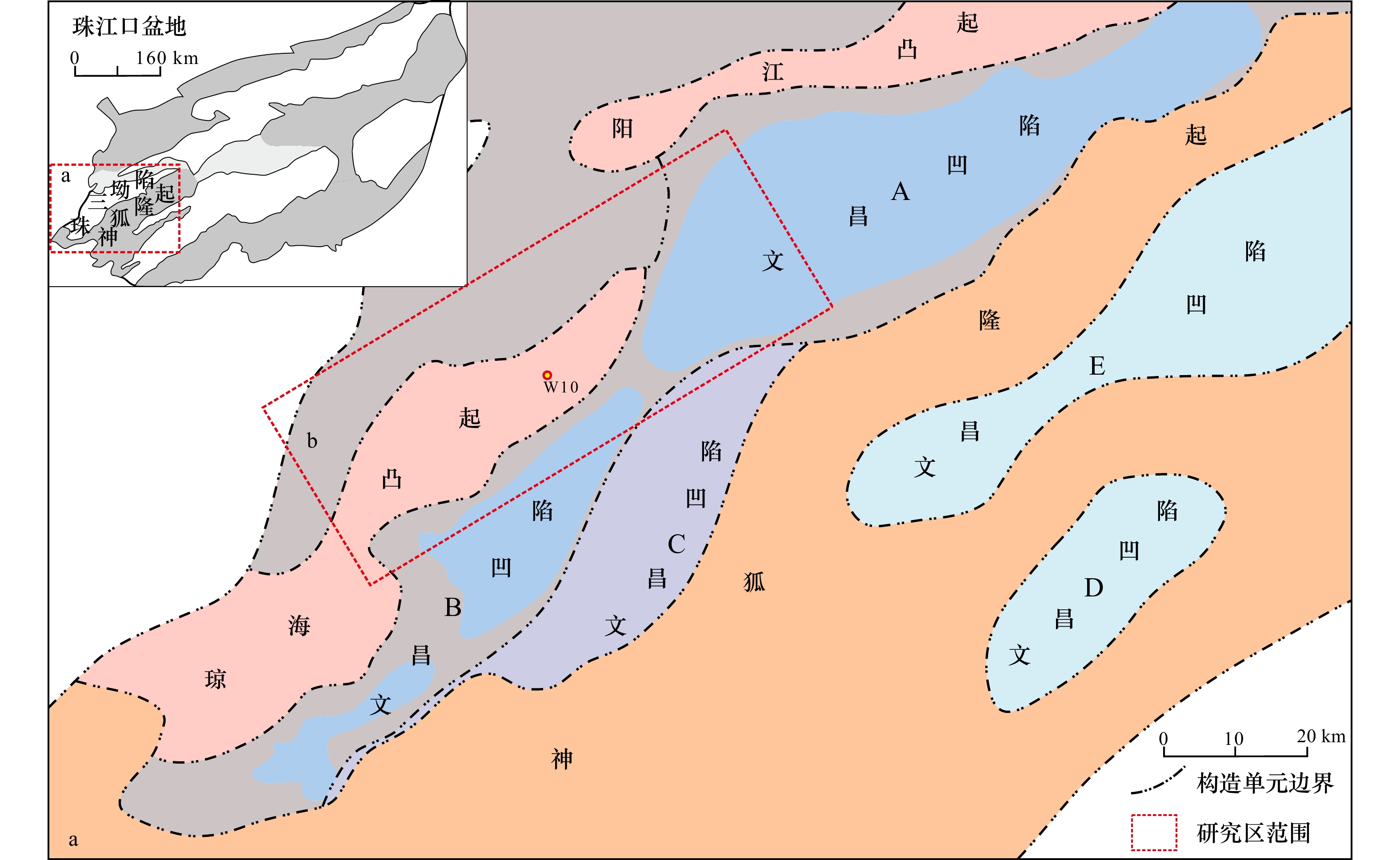
摘要: 为阐明珠三坳陷西北部珠江组一段上亚段浅海陆架砂体成因机制,综合地质与地球物理数据,首先搭建了五级层序地层格架,并以此为约束,开展浅海陆架砂体识别与定量描述,剖析其时空演化规律,进而讨论其成因机制。结果表明:(1)研究区珠江组一段上亚段可划分为4个五级层序,自下向上编号为FS4、FS3、FS2与FS1;(2)研究区发育潮流沙脊与滨外沙坝两种类型陆架砂体,两者整体呈NW−SE向展布,潮流沙脊主要分布于研究区西部,滨外沙坝则集中于东部;(3)FS4、FS3与FS2 3个五级层序中,潮流沙脊与滨外沙坝均呈现较大规模与较多数量,最上部FS1五级层序中,规模与数量达到最小;(4)沉积基准面(水动力)、同沉积地貌、沉积物碎屑供给等因素共同影响了潮流沙脊与滨外沙坝的发育规模、展布特征与时空演化规律等,综合构成了珠三坳陷西北部浅海陆架砂体的成因机制。Abstract: In order to clarify the genetic mechanism of shallow continental shelf sandbodies in the upper submember of the first member of Zhujiang Formation in the northwestern Zhusan Depression, with integrated use of geological and geophysical data, the five-order sequence framework was established firstly, inside of which, the shallow continental shelf sandbodies were identified and quantitatively described, and the temporal and spatial evolution of the shallow continental shelf sandbodies were analyzed, and the genetic mechanism was discussed. The results show that: (1) The upper submember of the first member of Zhujiang Formation in the study area can be divided into four five-order sequences, which were numbered as FS4, FS3, FS2 and FS1 from bottom to top. (2) There are two types of shelf sand bodies: tidal sand ridge and offshore sand bar, which are distributed in NW−SE direction. Tidal sand ridges are mainly distributed in the west of the study area, while offshore sand bars are concentrated in the east. (3) In the three five-order sequences FS4, FS3 and FS2, the scale and quantity of both tidal sand rdiges and offshore sand bars are relatively large, while in the upper five-order sequence FS1, the scale and quantity present poor. (4) Sedimentary base level (hydrodynamic condition), synsedimentary geomorphology and sediment debris supply jointly affected the development scale, distribution characteristics and temporal and spatial evolution of tidal sand ridges and offshore sand bars, which comprehensively constituted the genetic mechanism of shallow continental shelf sand bodies in the northwestern Zhusan Depression.
-
表 1 珠江组一段上亚段浅海陆架砂体沉积特征及演化
Tab. 1 Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of shallow-sea shelf sandbodies in the upper submember of the first member of Zhujiang Formation
五级旋回 浅海陆架砂体发育规模 长/km 宽/km 厚/m 长/宽 FS1 2.4~8.7 1.1~3.5 20~40 2.2~2.5 FS2 4.4~15.7 1.3~6.2 40~60 2.7~3.2 FS3 4.7~16.4 1.5~5.4 40~60 3.1~3.3 FS4 4.2~18.5 2.9~9.4 40~60 1.7~2.2 -
[1] 张功成, 米立军, 吴时国, 等. 深水区——南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(2): 15−21.Zhang Gongcheng, Mi Lijun, Wu Shiguo, et al. Deepwater area–the new prospecting targets of northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 15−21. [2] 张功成, 梁建设, 徐建永, 等. 中国近海潜在富烃凹陷评价方法与烃源岩识别[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(1): 13−19, 102.Zhang Gongcheng, Liang Jianshe, Xu Jianyong, et al. An evaluation method of potential hydrocarbon-rich sags and their source rock identification offshore China[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(1): 13−19, 102. [3] 范春花, 王英民, 刘豪. 浅海陆架沉积特征研究综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(2): 29−34.Fan Chunhua, Wang Yingmin, Liu Hao. A review of shallow continental shelf sedimentary characteristics[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(2): 29−34. [4] Song Guangzeng, Wang Hua, Gan Huajun, et al. Paleogene tectonic evolution controls on sequence stratigraphic patterns in the central part of deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2014, 25(2): 275−288. doi: 10.1007/s12583-014-0433-7 [5] Song Guangzeng, Wang Hua, Wang Zhenfeng, et al. Sequence stratigraphic architectures and responses to syndepositional tectonic evolution in the Paleogene Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea[J]. International Geology Review, 2020, 62(7/8): 1036−1056. [6] 张功成, 陈莹, 杨海长, 等. 恩平组岩性地层圈闭——白云凹陷深水区天然气勘探新领域[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(6): 1−9.Zhang Gongcheng, Chen Ying, Yang Haizhang, et al. Stratigraphic-lithologic traps in the Enping Formation: a new exploration field in deep water area of the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(6): 1−9. [7] 张磊岗, 屈红军, 陈硕, 等. 浅海砂质碎屑流沉积特征与模式: 以莺歌海盆地东方1-1气田莺二段为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 140−150.Zhang Leigang, Qu Hongjun, Chen Shuo, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model of shallow sea sandy debrisflow: a case study of Ying Ⅱ member in the Dongfang 1-1 Gas Field, Yinggehai Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 140−150. [8] Posamentier H W. Ancient shelf ridges-a potentially significant component of the transgressive systems tract: case study from offshore northwest Java[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(1): 75−106. [9] Lee H J, Jeon C K, Lim H S. Transgressive shelf sands around the Korean Peninsula: a brief review[J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2020, 55(4): 465−475. doi: 10.1007/s12601-020-0035-5 [10] 刘建兴, 石学法, 吴永华, 等. 东海外陆架厚层砂质沉积岩石磁学特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2020, 38(3): 435−445.Liu Jianxing, Shi Xuefa, Wu Yonghua, et al. Rock-magnetic properties of thick sandy sediments on the outer continental shelf of East China Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2020, 38(3): 435−445. [11] 路月. 东海陆架—冲绳海槽不同沉积单元表层沉积物组成特征及环境指示意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.Lu Yue. Surface sediment composition and environmental indication significance of different sedimentary units in the East China Sea shelf-Okinawa Trough[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019. [12] Liu Zhenxia, Xia Dongxing, Berne S, et al. Tidal deposition systems of China’s continental shelf, with special reference to the eastern Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 145(3/4): 225−253. [13] 李伟, 左倩媚, 刘平, 等. 珠江口盆地文昌凹陷浅海陆架砂体沉积特征及油气勘探意义[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(33): 94−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.33.013Li Wei, Zuo Qianmei, Liu Ping, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of continental shelf sand bodies and their significance for the oil-gas exploration in Wenchang Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(33): 94−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.33.013 [14] 李俊良, 王海荣, 张建新, 等. 珠江口盆地西部珠江组潮流砂脊的分布、形态和水动力机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(5): 671−677. doi: 10.11743/ogg20100517Li Junliang, Wang Hairong, Zhang Jianxin, et al. Distribution, geometry and hydrodynamic mechanism of tidal sand ridges in the Zhujiang Formation, the western Zhujiangkou Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(5): 671−677. doi: 10.11743/ogg20100517 [15] 谢辉, 周蒂, 石红才, 等. 珠江口盆地−琼东南盆地深水区新生代构造沉积演化对比分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(3): 48−61.Xie Hui, Zhou Di, Shi Hongcai, et al. Comparative study on the Cenozoic tectonic and sedimentary evolution in the deep water areas of the Zhujiang River Estuary Basin and the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(3): 48−61. [16] 施和生, 杜家元, 梅廉夫, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州运动及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3): 447−461. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.02Shi Hesheng, Du Jiayuan, Mei Lianfu, et al. Huizhou movement and its significance in Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 447−461. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.02 [17] 马明, 漆家福, 张远泽, 等. 珠江口盆地新生代沉降特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(2): 269−289.Ma Ming, Qi Jiafu, Zhang Yuanze, et al. An analysis of subsidence characteristics and affecting factors in the Pearl River Mouth Basin in Cenozoic[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2): 269−289. [18] 张功成, 贾庆军, 王万银, 等. 南海构造格局及其演化[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(10): 4194−4215. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0698Zhang Gongcheng, Jia Qingjun, Wang Wanyin, et al. On tectonic framework and evolution of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(10): 4194−4215. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0698 [19] 胡阳, 吴智平, 何敏, 等. 珠江口盆地新近纪构造特征与演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(3): 433−441.Hu Yang, Wu Zhiping, He Min, et al. Neogene tectonic characteristics and evolution of Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China[J]. Geological Journal of China University, 2018, 24(3): 433−441. [20] 邵磊, 雷永昌, 庞雄, 等. 珠江口盆地构造演化及对沉积环境的控制作用[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(9): 1177−1181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2005.09.007Shao Lei, Lei Yongchang, Pang Xiong, et al. Tectonic evolution and its controlling for sedimentary environment in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2005, 33(9): 1177−1181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2005.09.007 [21] 庞雄, 陈长民, 邵磊, 等. 白云运动: 南海北部渐新统—中新统重大地质事件及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(2): 145−151.Pang Xiong, Chen Changmin, Shao Lei, et al. Baiyun movement, a great tectonic event on the Oligocene-Miocene boundary in the northern South China Sea and its implications[J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(2): 145−151. [22] Han Jianhui, Xu Guoqiang, Li Yangyang, et al. Evolutionary history and controlling factors of the shelf breaks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 179−189. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.06.009 [23] 钟泽红, 徐万兴, 刘芳, 等. 珠江口盆地西部珠三坳陷珠江组沉积演化[J]. 世界地质, 2018, 37(4): 1122−1136, 1166.Zhong Zehong, Xu Wanxing, Liu Fang, et al. Sedimentary evolution of Zhujiang Formation in Zhu III depression, West Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Global Geology, 2018, 37(4): 1122−1136, 1166. [24] 刘琼, 于水, 陈全红, 等. 北非撒哈拉地台三叠系TAGI组基准面旋回充填样式及有利储层预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 118−122. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0216Liu Qiong, Yu Shui, Chen Quanhong, et al. Base-levelcycle sequence filling types and favorable reservoir prediction of Triassic TAGI on Sahara Platform, North Africa[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 118−122. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0216 [25] 祝彦贺, 王英民, 吕延防, 等. 松辽盆地北部西斜坡青山口组四级层序划分及变化特征分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2006, 18(6): 376−381, 385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.06.004Zhu Yanhe, Wang Yingmin, Lü Yanfang, et al. Fourth-order sequence division and its variation in Qingshankou Formation of the west slope, the northern Songliao Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2006, 18(6): 376−381, 385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.06.004 [26] Lü Dawei, Song Ying, Shi Longqing, et al. The complex transgression and regression history of the northern margin of the Palaeogene Tarim Sea (NW China), and implications for potential hydrocarbon occurrences[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 112: 104041. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104041 [27] 李珊珊, 彭松, 邓勇, 等. 珠江口盆地西部渐新世以来钙质超微化石年代地层研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2015, 32(3): 308−316.Li Shanshan, Peng Song, Deng Yong, et al. Calcareous nannofossil chronostratigraphy in the western Pearl River Mouth Basin since the Oligocene[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2015, 32(3): 308−316. [28] 李学杰, 陈芳, 陈超云, 等. 南海西部浮游有孔虫含量与水深关系定量研究[J]. 古地理学报, 2004, 6(4): 442−447. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2004.04.005Li Xuejie, Chen Fang, Chen Chaoyun, et al. Quantitative research on relationship between planktonic foraminifera content and water depth in western South China Sea[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2004, 6(4): 442−447. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2004.04.005 -




 下载:
下载: