Flow structure decomposition and baroclinic M4 constituent current exploration in estuarine zone
-
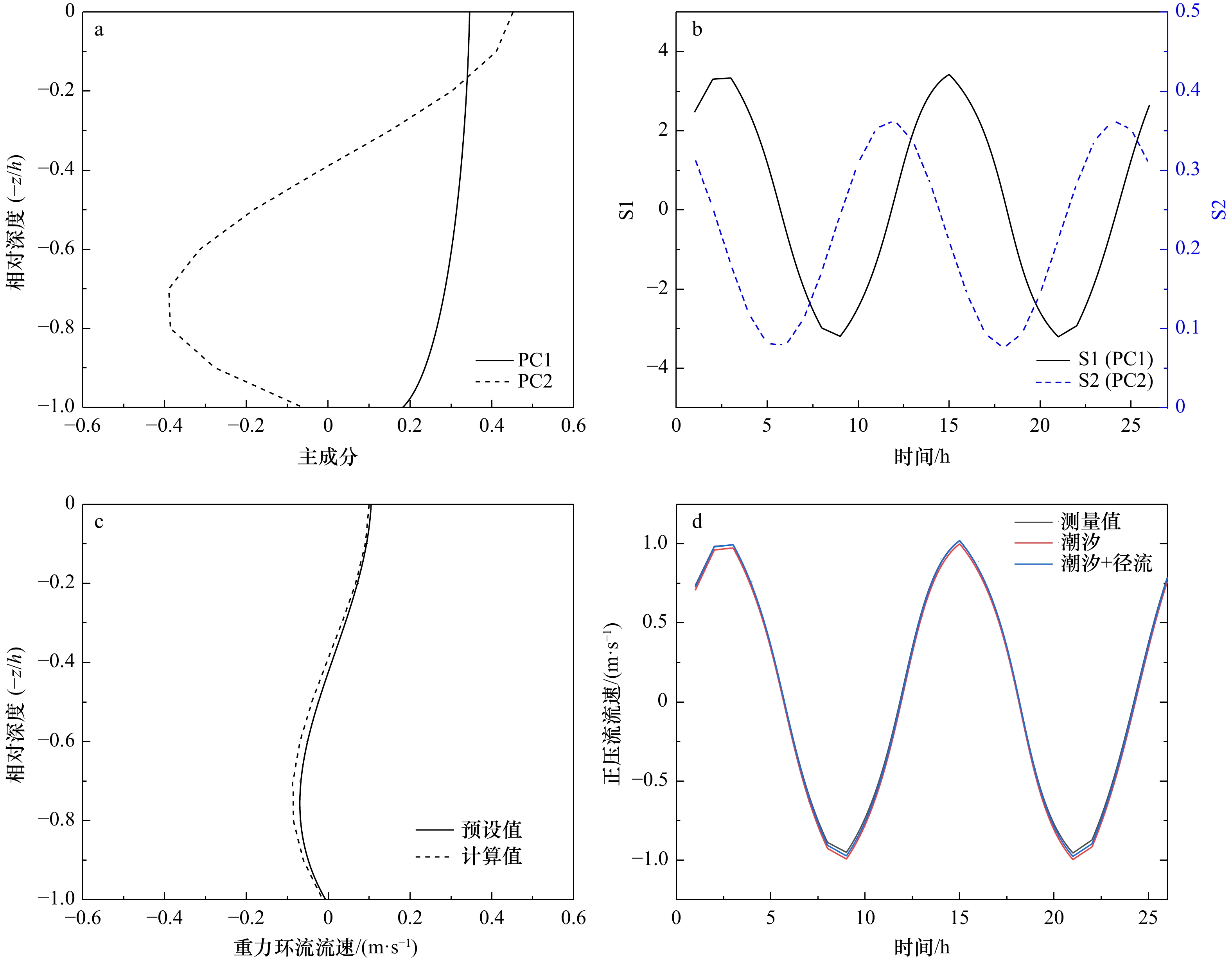
摘要: 河口水流是河口生态环境、河道演变、物质输运等物理过程的根本动力。由于径流、潮波、地形以及气象等因素的影响,河口水流呈现复杂的三维结构。其中既包括淡水注入形成的余流,也包括周期性的潮流、风生流、斜压流及河口非线性作用导致的流动等。为探究河口水流的组成及其潮内变化,基于瓯江口实测资料,利用主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis, PCA)法对河口水流进行分解,探讨了PCA法对河口水流的分解性能及斜压分潮流的高频特征。研究认为,PCA法在河口水流结构研究中既可采用原始数据操作亦可用标准化的数据进行计算。PCA法可分解出斜压成分(河口重力环流型结构),但不能将正压成分(径流和潮流)分开,径流和潮流二者综合作用的结果体现在主成分的得分之中。主成分的取舍应根据水流结构和累计解释方差综合判断,不宜仅依据累计解释方差。河口斜压流动具有明显的高频特征,近似呈1/4日分潮的周期。Abstract: Estuarine flow is the fundamental driving of physical processes such as estuarine ecological environment, river evolution and material transport. Due to the runoff, tide, topography and meteorology, the estuarine flow presents a complex three-dimensional structure, including not only the residual flow induced by fresh water injection, but also the periodical tidal current, wind-driven flow, baroclinic flow and the residual flow caused by estuarine nonlinearity. In order to explore the composition and intra-tidal variation of estuarine flow, based on the field data in the Oujiang River Estuary, the estuarine flow is decomposed by principal component analysis (PCA) method, and the decomposition performance of PCA method for estuarine flow and high-frequency characteristics of baroclinic overtide are deeply discussed. The results show that PCA method can operate original data or standardized data in the study of estuarine flow structure. PCA method can decompose baroclinic components (estuarine gravitational circulation structure), but cannot separate barotropic components (runoff and tidal current). The coupled effect of runoff and tidal current is reflected in the score of principal components. The filter of principal components should employ conjoint judgment of flow structure and cumulative interpretation variance, rather than only cumulative interpretation variance. The estuarine baroclinic flow has clearly high-frequency characteristics, which approximates quarter-diurnal.
-
Key words:
- baroclinic /
- PCA /
- M4 constituent /
- Oujiang River Estuary /
- estuarine gravitational circulation
-
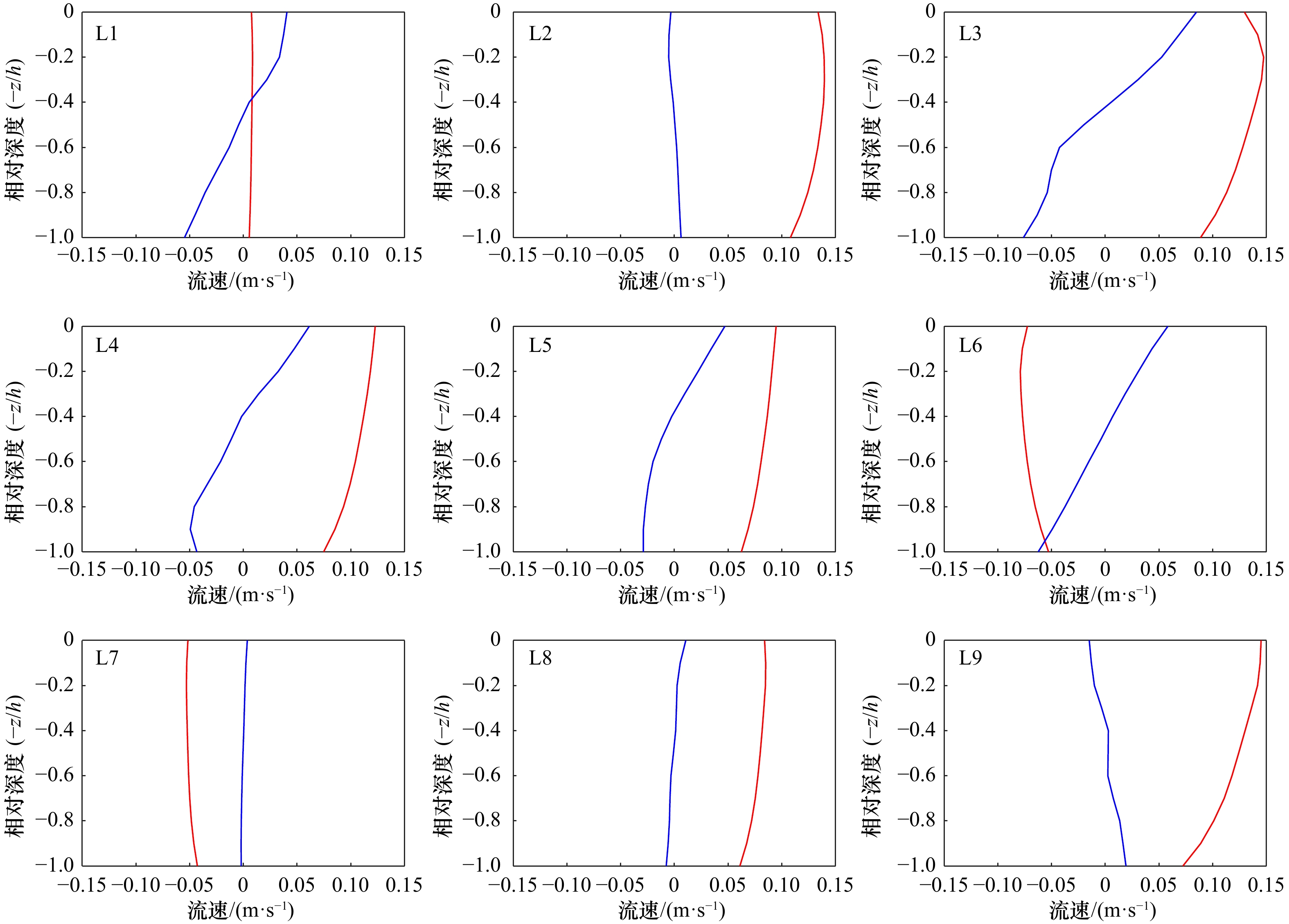
表 1 瓯江口流速测点PCA的主成分累计解释方差(%)
Tab. 1 PCA cumulative variance (%) of velocity measurement sites in the Oujiang River Estuary
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 L8 L9 PC1 99.53 99.69 99.05 99.65 99.70 99.57 99.69 99.71 98.66 PC2 0.40 0.18 0.72 0.23 0.24 0.26 0.24 0.22 0.66 PC3 0.04 0.09 0.14 0.09 0.04 0.13 0.04 0.05 0.38 -
[1] Hansen D V, Rattray M. Gravitational circulation in straits and estuaries[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1965, 23(2): 104−122. [2] Cheng Peng, Valle-Levinson A, De Swart H E. A numerical study of residual circulation induced by asymmetric tidal mixing in tidally dominated estuaries[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011, 116(C1): C01017. [3] Cheng Peng, Mao Jianshan, Yu Fengling, et al. A numerical study of residual flow induced by eddy viscosity-shear covariance in a tidally energetic estuary[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 230: 106446. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.106446 [4] Wei Xiaoyan, Schuttelaars H M, Williams M E, et al. Unraveling interactions between asymmetric tidal turbulence, residual circulation, and salinity dynamics in short, periodically weakly stratified estuaries[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2021, 21(5): 1395−1416. [5] Li Chunyan, Valle-Levinson A, Wong K C, et al. Separating baroclinic flow from tidally induced flow in estuaries[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1998, 103(C5): 10405−10417. doi: 10.1029/98JC00582 [6] 魏登云, 张文俊. 主成分分析法应用中原始数据的标准化辨析[J]. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(2): 189−194. doi: 10.14182/J.cnki.1001-2443.2018.02.015Wei Dengyun, Zhang Wenjun. Standardization of raw data in the application of principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 2018, 41(2): 189−194. doi: 10.14182/J.cnki.1001-2443.2018.02.015 [7] Stacey M T, Burau J R, Monismith S G. Creation of residual flows in a partially stratified estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2001, 106(C8): 17013−17037. doi: 10.1029/2000JC000576 [8] Jay D A, Musiak J D. Internal tidal asymmetry in channel flows: origins and consequences[M]//Pattiaratchi C. Estuaries and Coastal Seas. Washington, D C: American Geophysical Union, 1996, 50: 211−249. [9] 黄嘉佑, 李庆祥. 气象数据统计分析方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2015.Huang Jiayou, Li Qingxiang. Statistical Analysis Methods of Meteorological Data[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2015. [10] 邹志利. 海岸动力学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009.Zou Zhili. Coastal Hydrodynamics[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2009. [11] Ianniello J P. Tidally induced residual currents in estuaries of variable breadth and depth[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1977, 9(5): 962−974. [12] Pawlowicz R, Beardsley B, Lentz S. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2002, 28(8): 929−937. -




 下载:
下载: