Nutritional environment and influencing factors of seawater and surface sediments in the Jiaozhou Bay
-
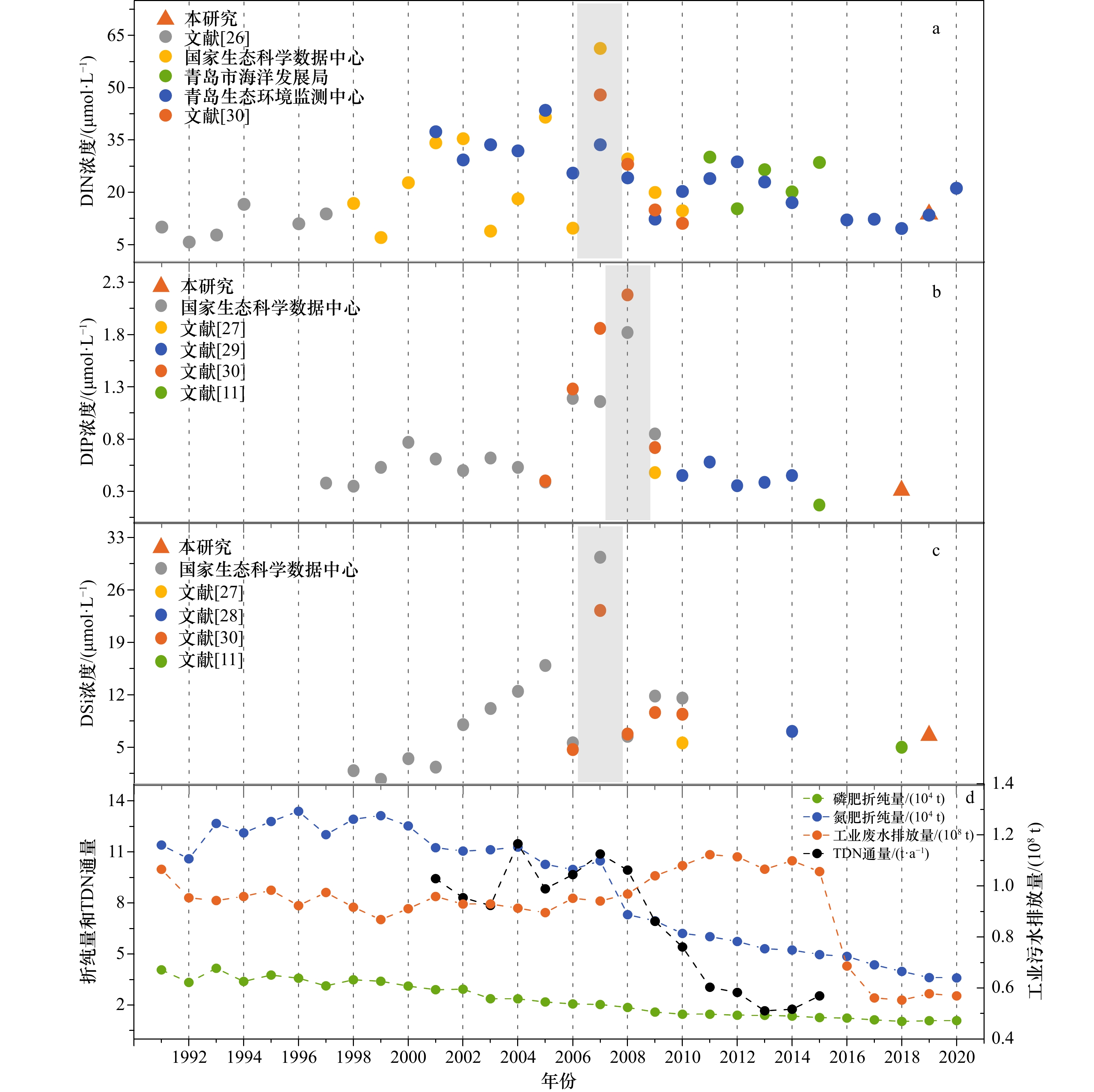
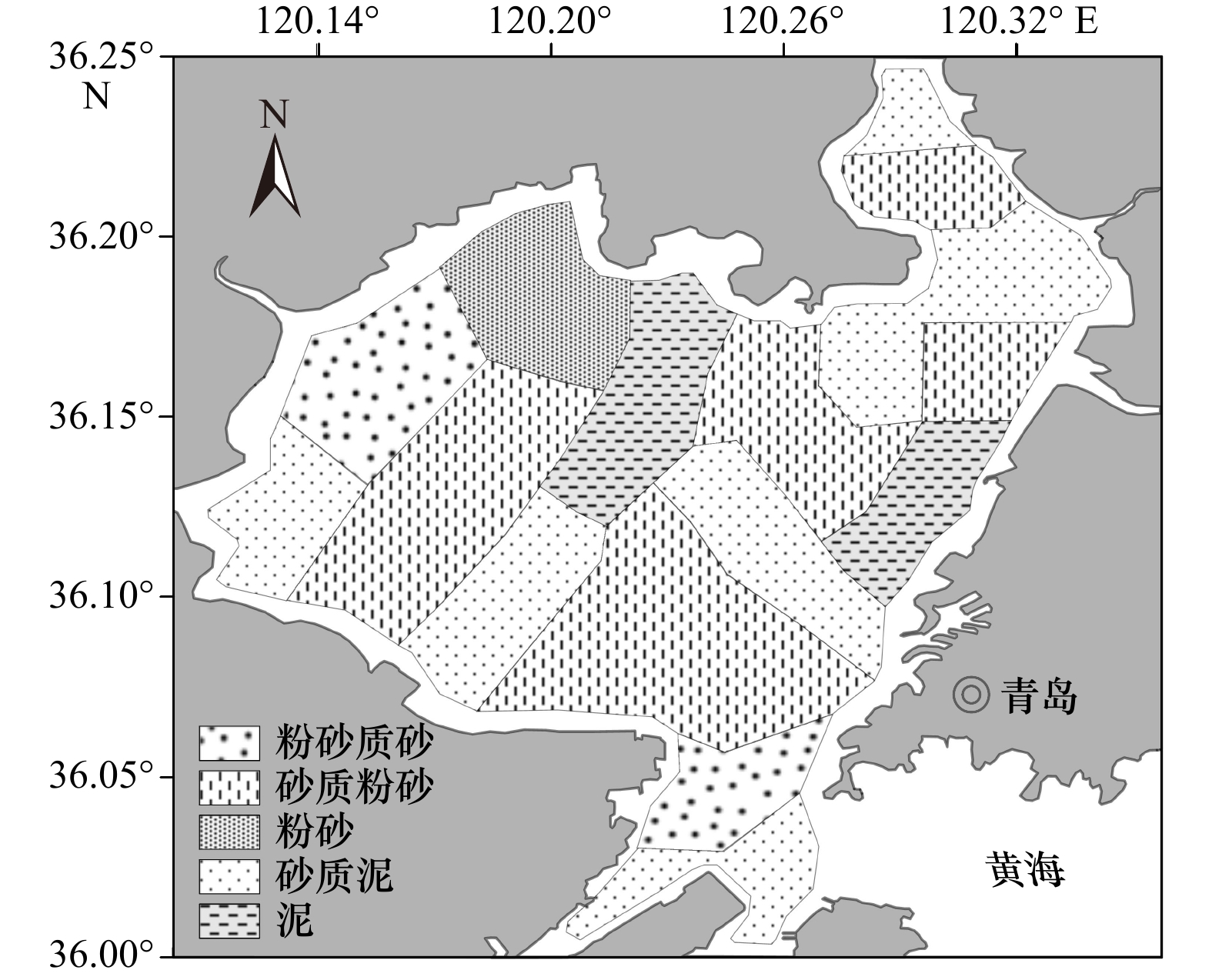
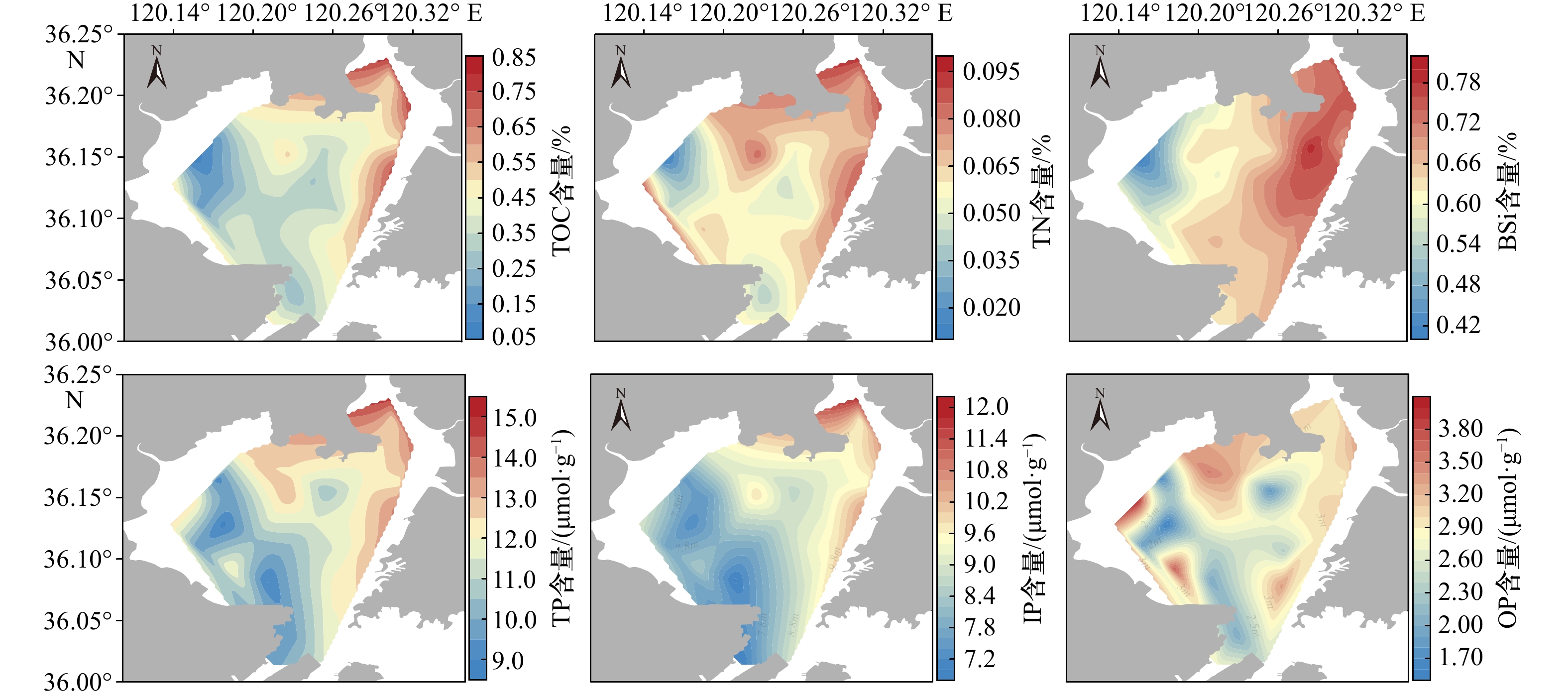
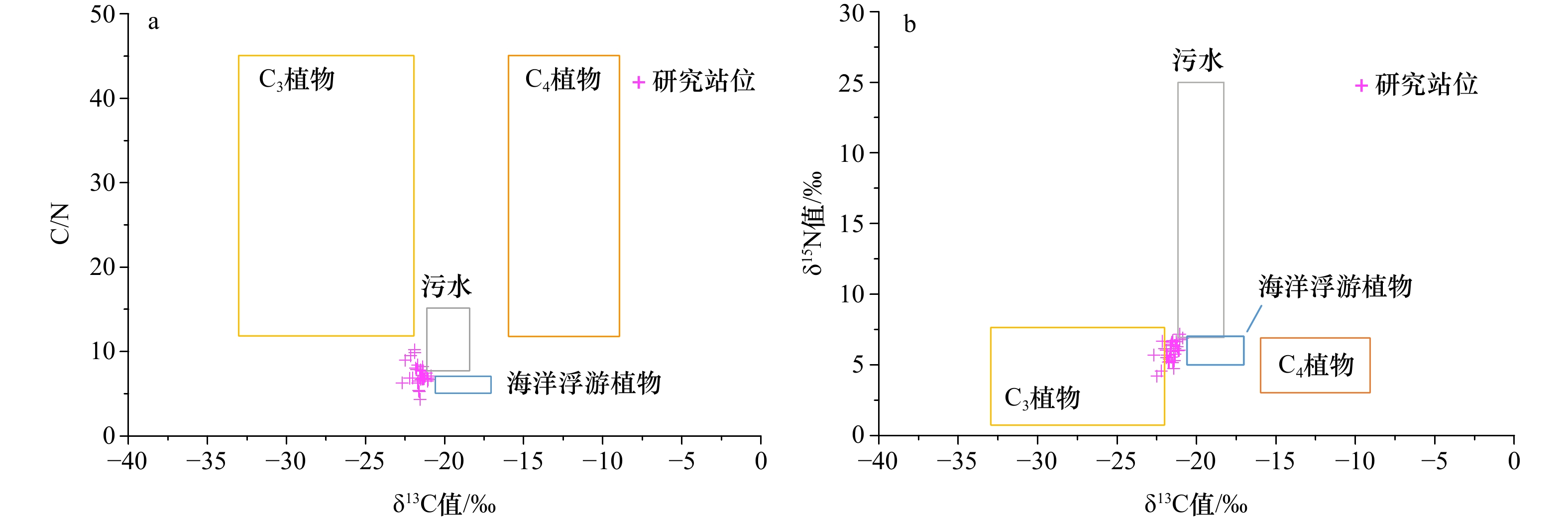
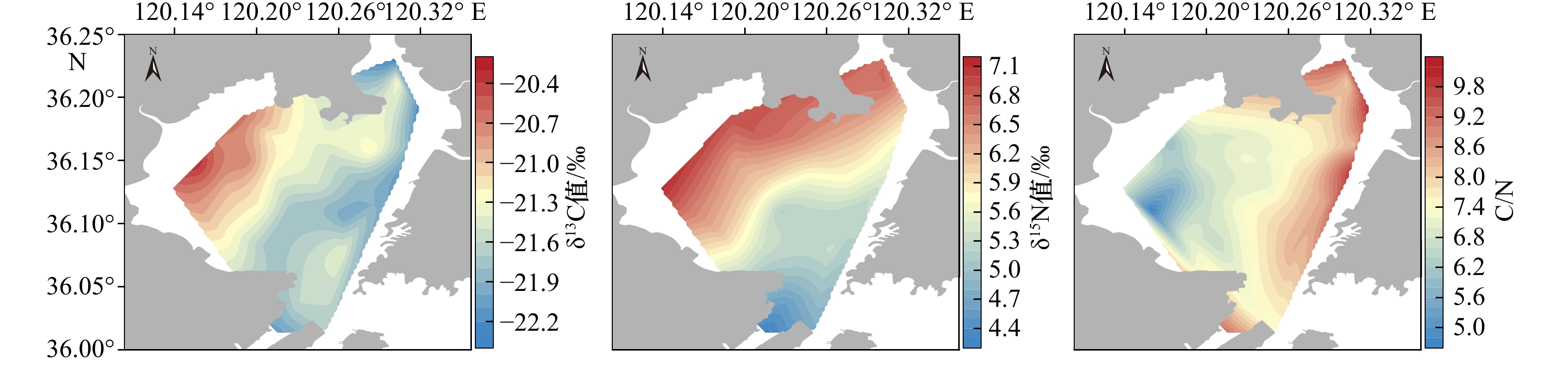
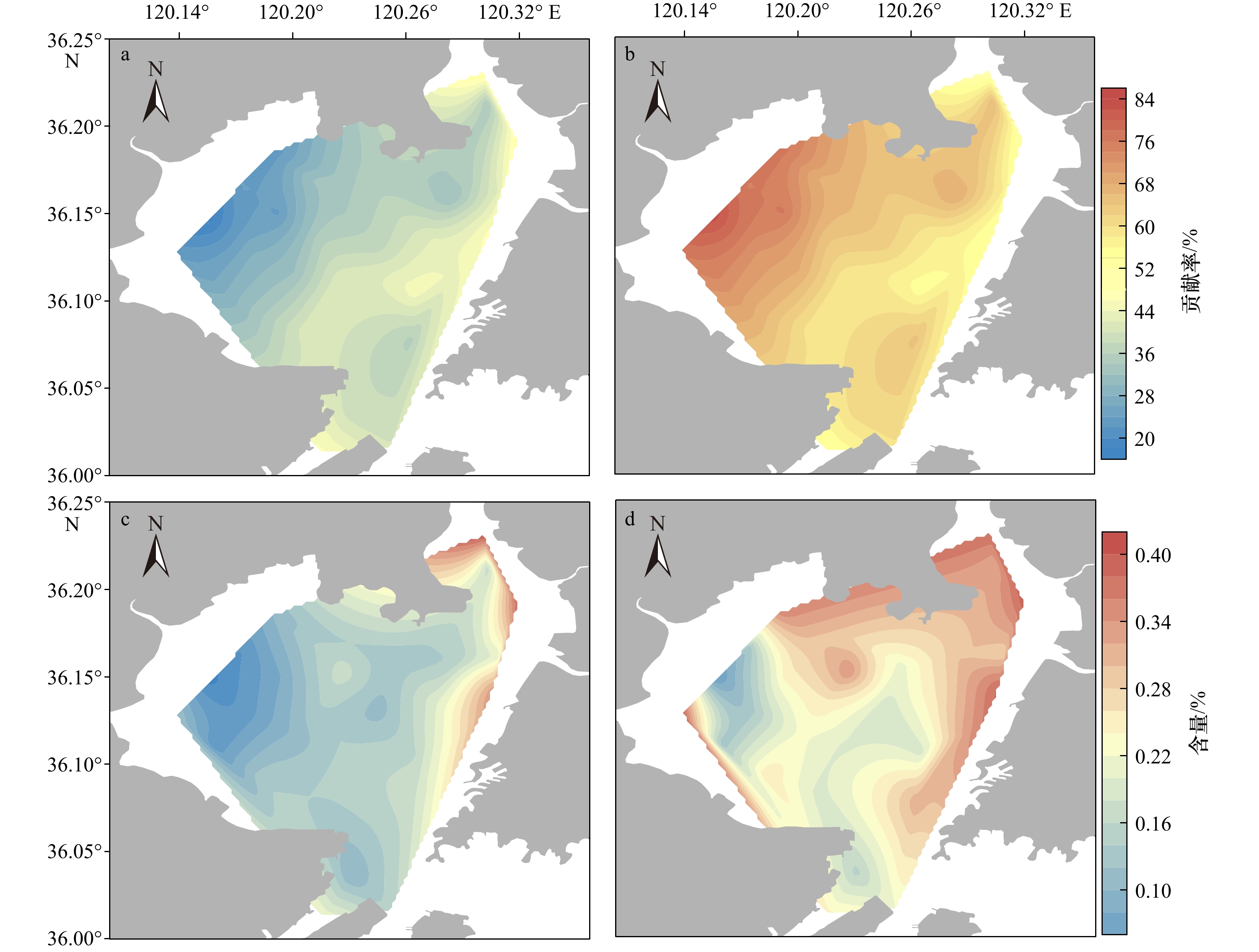
摘要: 为了解胶州湾水体和表层沉积物营养环境状况及其主要影响因素,于2019年8月在胶州湾30个站位点采集了海水和表层沉积物样品,并于2021年5月在胶州湾沿岸采集了18个站位点的水样,对水体溶解无机态营养盐浓度和组成以及表层沉积物中总有机碳、总氮、总磷及生物硅含量和碳、氮稳定同位素(δ13C、δ15N)进行了分析。结果表明,胶州湾内水体和沿岸水体中溶解无机氮、溶解无机磷和溶解硅酸盐浓度空间分布相近,高值均位于湾东北部,主要受到河流输入和沿岸污水排放的影响,低值主要出现在湾中部和湾口处。结合近30年来的历史数据分析发现,胶州湾夏季营养盐浓度在1990−2008年期间呈持续上升的趋势,政府实施的污染物总量控制措施以及河流径流量下降使得2006年以来营养盐浓度呈现下降的趋势,该变化在空间上主要体现为大沽河氮、磷输入量的减少及其对应的湾西部营养盐高值的消失。胶州湾氮、磷营养盐输入的不平衡使得“磷限制”在2000年后逐渐加剧。胶州湾表层沉积物中总有机碳、总氮、总磷含量高值均集中于东北部和东部沿岸,结合生物硅和水体营养盐含量分析显示,这主要是河流与排污输入及其带来的高初级生产力造成的,沉积物生源要素与水体营养盐在空间分布上存在较好的耦合关系。沉积物粒度较粗对有机质保存的不利影响以及湾口较强的水动力作用共同导致了湾西部、中部以及湾口的生源要素含量较低。δ13C以及二端元混合模型显示,胶州湾表层沉积物有机质来源总体以海源为主,平均占比为64%,东部沿岸受陆源输入影响较明显。δ15N的空间分布显示,胶州湾表层沉积物中氮元素受到了海水养殖与污水排放的共同影响。水体和沉积物营养环境现状共同表明,对东北部河流和沿岸污水排放的控制是后期胶州湾污染治理的关键。Abstract: Seawater and surface sediment samples at 30 stations in the Jiaozhou Bay (JZB) and river water and coastal water samples at 18 stations along the JZB were collected in August 2019 and May 2021, respectively. Dissolved inorganic nutrient concentrations and structure in the water and the contents of total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), biogenic silica (BSi), and stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen (δ13C, δ15N) in surface sediments were analyzed to clarify the present nutritional environment of seawater and surface sediment and its main influencing factors in the JZB. The results show that the spatial distribution of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP), and dissolved silicate (DSi) in seawater is consistent with that in the coastal water of JZB. The high values that occur northeast of the bay are mainly caused by river input and sewage discharge, and the low values mainly occur at the center and bay mouth. Combined with the analysis of historical data, we found that the nutrient concentrations of JZB in summer continued to rise from 1990 to 2008 and then declined since 2006 because of the declining nutrient loadings related to the implementation of total pollutant load control management and freshwater loadings from surrounding rivers. The decreased nutrient loadings were mainly found in rivers such as the Dagu River, causing the disappearance of high concentrations in the western region after 2010. The phosphorus limitation accelerated after 2000 as a result of the imbalanced input of nitrogen and phosphorus. The high values of TOC, TN, and TP in the surface sediments of JZB are concentrated along the northeast and east coasts, combined with BSi and water nutrient analysis, which is mainly caused by the river input and sewage discharge and the high primary productivity they bring. Sediment biogenic elements are well coupled with water column nutrients in spatial distribution. The adverse effect of coarse sediment grain size on the preservation of organic matter and the strong hydrodynamic effect of the bay mouth jointly lead to the low content of biogenic elements in the west, middle, and mouth of the bay. The δ13C and two-endmember mixing model show that the source of organic matter in the surface sediments of JZB is mainly marine-derived, accounting for an average of 64%. The eastern coast is obviously affected by terrestrial input. The spatial distribution of δ15N shows that the nitrogen in the surface sediment of JZB is jointly affected by mariculture and sewage discharge. The current situation of the water body and sediment nutrient environments shows that the control of sewage discharge from the northeast river and the coastal area is the key to the later pollution control of JZB.
-
表 1 相关性分析结果
Tab. 1 Correlation analysis results
TOC TN TP IP OP BSi C/N δ13C δ15N OCM DIN DIP DSi TOC 1 0.934 1** 0.741 6** 0.785 8** 0.409 1* 0.693 7** 0.826 0** −0.632 0** 0.116 4 0.923 1** 0.446 2* 0.559 1** 0.405 5* TN 1 0.672 2** 0.701 0** 0.390 7* 0.634 2** 0.596 3** −0.474 5** 0.306 6 0.964 3** 0.318 2 0.396 6* 0.335 9 TP 1 0.934 2** 0.774 2** 0.442 8* 0.658 5** −0.262 0 0.291 2 0.722 0** 0.505 4** 0.564 3** 0.450 2* IP 1 0.497 4** 0.556 8** 0.669 9** −0.413 0* 0.276 0 0.708 2** 0.562 1** 0.655 8** 0.463 4** OP 1 0.089 9 0.412 7 0.094 8 0.217 6 0.498 8 0.230 3 0.207 4 0.271 1 BSi 1 0.660 7** −0.756 3** −0.192 7 0.575 4** 0.305 5 0.398 0* 0.137 7 C/N 1 −0.734 7** −0.263 9 0.694 4** 0.431 1* 0.560 5** 0.323 4 δ13C 1 0.495 6** −0.345 2 −0.147 7 −0.311 4 −0.012 2 δ15N 1 0.327 8 0.332 4 0.255 6 0.381 2* OCM 1 0.379 5* 0.435 8* 0.412 5* DIN 1 0.958 9** 0.884 3** DIP 1 0.847 8** DSi 1 黏土占比 0.579 3** 0.731 7** 0.384 5* 0.368 5 0.281 4 0.601 9** 粉砂占比 0.422 3* 0.592 9** 0.250 0 0.248 9 0.166 4 0.461 4* 砂占比 −0.489 4** −0.656 7** −0.305 2 −0.298 6 −0.212 6 −0.523 2** 中值粒径 −0.409 5* −0.512 6** −0.310 2 −0.280 7 −0.256 0 −0.355 9 注:*代表0.05显著水平(双尾); **代表0.01显著水平(双尾)。 -
[1] Howarth R W, Anderson D B, Cloern J E, et al. Nutrient pollution of coastal rivers, bays, and seas[R]. Washington: Ecology Society of America, 2020: 1−16. [2] Kemp W M, Boynton W R, Adolf J E, et al. Eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay: historical trends and ecological interactions[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2005, 303: 1−29. doi: 10.3354/meps303001 [3] Matsuoka K. Eutrophication process recorded in dinoflagellate cyst assemblages-a case of Yokohama Port, Tokyo Bay, Japan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 231(1): 17−35. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00087-X [4] Rabalais N N, Turner R E, Gupta B K S, et al. Sediments tell the history of eutrophication and hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Ecological Applications, 2007, 17(S5): S129−S143. doi: 10.1890/06-0644.1 [5] Glibert P M. Eutrophication, harmful algae and biodiversity-challenging paradigms in a world of complex nutrient changes[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 124(2): 591−606. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.04.027 [6] Boesch D F. Barriers and bridges in abating coastal eutrophication[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2019, 6: 123. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00123 [7] Liu Dongyan, Sun Jun, Zhang Jing, et al. Response of the diatom flora in Jiaozhou Bay, China to environmental changes during the last century[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2008, 66(3/4): 279−290. [8] 孙晓霞, 孙松, 吴玉霖, 等. 胶州湾网采浮游植物群落结构的长期变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2011, 42(5): 639−646. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201105003003Sun Xiaoxia, Sun Song, Wu Yulin, et al. Long-term changes of phytoplankton community structure in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2011, 42(5): 639−646. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201105003003 [9] Li Keqiang, He Jian, Li Junlong, et al. Linking water quality with the total pollutant load control management for nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 85: 57−66. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.10.019 [10] 孙晓霞, 孙松, 赵增霞, 等. 胶州湾营养盐浓度与结构的长期变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2011, 42(5): 662−669. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201105006006Sun Xiaoxia, Sun Song, Zhao Zengxia, et al. Long-term changes in nutrient concentration and structure in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2011, 42(5): 662−669. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201105006006 [11] 徐菡悦, 王保栋, 辛明, 等. 胶州湾营养盐的长期变化及其生态效应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2020, 38(2): 276−286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.02.008Xu Hanyue, Wang Baodong, Xin Ming, et al. Long-term changes of nutrients and their ecological effects in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2020, 38(2): 276−286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.02.008 [12] Kang Xuming, Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao, et al. The sources and composition of organic matter in sediments of the Jiaozhou Bay: implications for environmental changes on a centennial time scale[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(11): 68−78. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1076-1 [13] Wang Yueqi, Song Jinming, Duan Liqin, et al. Historical reconstructions of sedimentary organic matter sources and phytoplankton evolution in the Jiaozhou Bay based on sterols and carbon isotope[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 165: 112109. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112109 [14] Yuan Yuan, Song Dehai, Wu Wen, et al. The impact of anthropogenic activities on marine environment in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China: a review and a case study[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2016, 8: 287−296. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2016.01.004 [15] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937−968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211 [16] 彭亚君, 王玉珏, 刘东艳, 等. 酸化过程对海洋沉积物中有机碳同位素分析的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(12): 85−92.Peng Yajun, Wang Yujue, Liu Dongyan, et al. Acid treatment effects on the carbon stable isotope values of marine sediments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(12): 85−92. [17] Aspila K I, Agemian H, Chau A S Y. A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments[J]. The Analyst, 1976, 101(1200): 187−197. doi: 10.1039/an9760100187 [18] DeMaster D J. The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(10): 1715−1732. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90006-5 [19] Shultz D J, Calder J A. Organic carbon 13C/12C variations in estuarine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1976, 40(4): 381−385. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(76)90002-8 [20] Wan Yi, Hu Jianying, An Lihui, et al. Determination of trophic relationships within a Bohai Bay food web using stable δ15N and δ13C analysis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(10): 1021−1025. doi: 10.1360/04wd0283 [21] Yang Liyang, Wu Ying, Zhang Jing, et al. Burial of terrestrial and marine organic carbon in Jiaozhou Bay: different responses to urbanization[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2011, 11(3): 707−714. doi: 10.1007/s10113-010-0202-9 [22] Yu Xue, Zhang Junlong, Kong Fanlong, et al. Identification of source apportionment and its spatial variability of dissolved organic matter in Dagu River-Jiaozhou Bay Estuary based on the isotope and fluorescence spectroscopy analysis[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102: 528−537. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.004 [23] 青岛市海洋发展局. 2011−2015青岛市海洋环境质量公报[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://ocean.qingdao.gov.cn/sitesearch/index.html?siteid=39&keyword=%E5%85%AC%E6%8A%A5Qingdao Municipal Marine Development Bureau. 2011−2015 Marine Environmental Quality Bulletin of Qingdao [EB/OL].[2021−12−01]. http://ocean.qingdao.gov.cn/sitesearch/index.html?siteid=39&keyword=%E5%85%AC%E6%8A%A5 [24] 青岛市生态环境局, 青岛生态环境监测中心. 2001−2020青岛市环境状况公报[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://mbee.qingdao.gov.cn:8082/m2/ZWGKNew/TreeModulList.aspx?m=35Qingdao Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment, Qingdao Environmental Monitoring Center. 2001−2020 Environmental Status Bulletin of Qingdao[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://mbee.qingdao.gov.cn:8082/m2/ZWGKNew/TreeModulList.aspx?m=35 [25] 赵永芳, 赵增霞, 孙晓霞. 1997−2010年胶州湾水体营养盐结构及浮游植物生长限制因子数据集[J]. 中国科学数据, 2020, 5(1): 27−36.Zhao Yongfang, Zhao Zengxia, Sun Xiaoxia. A dataset of nutrient structure and limiting factors of phytoplankton growth in Jiaozhou Bay from 1997 to 2010[J]. China Scientific Data, 2020, 5(1): 27−36. [26] Shen Zhiliang. Historical changes in nutrient structure and its influences on phytoplantkon composition in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2001, 52(2): 211−224. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2000.0736 [27] 王玉珏, 刘哲, 张永, 等. 2010−2011年胶州湾叶绿素a与环境因子的时空变化特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(4): 103−116.Wang Yujue, Liu Zhe, Zhang Yong, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of chlorophyll a and environmental factors in Jiaozhou Bay in 2010−2011[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(4): 103−116. [28] 高磊, 曹婧, 张蒙蒙, 等. 2014年胶州湾营养盐结构特征变化及富营养化评价[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2016, 35(4): 66−73.Gao Lei, Cao Jing, Zhang Mengmeng, et al. Assessment on the change of nutrient structure and eutrophication in the Jiaozhou Bay in 2014[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2016, 35(4): 66−73. [29] 汪进生, 张晓红, 王晓彤. 十二五胶州湾海水水质状况分析评价[J]. 科学技术创新, 2019(23): 9−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2019.23.006Wang Jinsheng, Zhang Xiaohong, Wang Xiaotong. Analysis and evaluation of seawater quality in Jiaozhou Bay during the 12th Five-Year Plan period[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2019(23): 9−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2019.23.006 [30] 赵增霞, 孙晓霞, 赵永芳, 等. 2006−2010年胶州湾水文和化学环境因子监测数据集[J]. 中国科学数据, 2020, 5(2): 79−86.Zhao Zengxia, Sun Xiaoxia, Zhao Yongfang, et al. A dataset of monitoring hydrological and chemical environmental factors in the Jiaozhou Bay during 2006−2010[J]. China Scientific Data, 2020, 5(2): 79−86. [31] 青岛市统计局. 1990−2021青岛统计年鉴[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://qdtj.qingdao.gov.cn/tongjisj/tjsj_tjnj/Qingdao Municipal Statistics Bureau. 1990−2021 Qingdao Statistical Yearbook[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://qdtj.qingdao.gov.cn/tongjisj/tjsj_tjnj/ [32] Meyers P A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 27(5/6): 213−250. [33] Goñi M A, Teixeira M J, Perkey D W. Sources and distribution of organic matter in a river-dominated estuary (Winyah Bay, SC, USA)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 57(5/6): 1023−1048. [34] Rao Zhiguo, Guo Wenkang, Cao Jiantao, et al. Relationship between the stable carbon isotopic composition of modern plants and surface soils and climate: a global review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 165: 110−119. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.12.007 [35] Pancost R D, Boot C S. The palaeoclimatic utility of terrestrial biomarkers in marine sediments[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 92(1/4): 239−261. [36] Andrews J E, Greenaway A M, Dennis P F. Combined carbon isotope and C/N ratios as indicators of source and fate of organic matter in a poorly flushed, tropical estuary: Hunts Bay, Kingston Harbour, Jamaica[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 46(5): 743−756. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0305 [37] McClelland J W, Valiela I, Michener R H. Nitrogen-stable isotope signatures in estuarine food webs: a record of increasing urbanization in coastal watersheds[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1997, 42(5): 930−937. doi: 10.4319/lo.1997.42.5.0930 [38] Gao Xuelu, Yang Yuwei, Wang Chuanyuan. Geochemistry of organic carbon and nitrogen in surface sediments of coastal Bohai Bay inferred from their ratios and stable isotopic signatures[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(6): 1148−1155. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.03.028 [39] 宋金明, 袁华茂, 李学刚, 等. 胶州湾的生态环境演变与营养盐变化的关系[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(8): 106−117.Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao, Li Xuegang, et al. Ecological environment evolution and nutrient variations in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(8): 106−117. [40] 宋金明, 袁华茂, 吴云超, 等. 营养物质输入通量及海湾环境演变过程[M]//黄小平, 黄良民, 宋金明, 等. 营养物质对海湾生态环境影响的过程与机理. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 1−159.Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao, Wu Yunchao, et al. Nutrients influx and environmental evolution process of the bays[M]//Huang Xiaoping, Huang Liangmin, Song Jinming, et al. Process and Mechanism of Nutrient Effects on Gulf Ecological Environment. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 1−159. [41] Lu Dongliang, Yang Nannan, Liang Shengkang, et al. Comparison of land-based sources with ambient estuarine concentrations of total dissolved nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay (China)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 180: 82−90. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.06.032 [42] 青岛市气象局. 2019年夏季青岛市生态质量气象评价[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://www.qingdao.gov.cn/n172/n24624151/n24632715/n24638046/n24638060/190920143831304534.html.Qingdao Municipal Meteorological Bureau. 2019 Meteorological evaluation of ecological quality in Qingdao[EB/OL]. [2021−12−01]. http://www.qingdao.gov.cn/n172/n24624151/n24632715/n24638046/n24638060/190920143831304534.html. [43] Liu Sumei, Ye Xiwen, Zhang Jing, et al. The silicon balance in Jiaozhou Bay, North China[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2008, 74(1/2): 639−648. [44] 王有霄, 钟萍丽, 于格, 等. 胶州湾氮、磷非点源污染负荷估算及时空分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(2): 85−97.Wang Youxiao, Zhong Pingli, Yu Ge, et al. Estimation of N, P non-point source pollution loads and analysis of spatial and temporal characteristies in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(2): 85−97. [45] Guo Shujin, Zhu Mingliang, Zhao Zengxia, et al. Spatial-temporal variation of phytoplankton community structure in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019, 37(5): 1611−1624. doi: 10.1007/s00343-019-8249-z [46] 沈志良, 陆家平, 刘兴俊, 等. 胶州湾水域的营养盐[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 1994(35): 115−129.Shen Zhiliang, Lu Jiaping, Liu Xingjun, et al. Nutrients in Jiaozhou Bay waters[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 1994(35): 115−129. [47] 康美华. 胶州湾生源要素的时空分布特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Kang Meihua. Studies on the seasonal and spatial distributions of biogenic elements in the Jiaozhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [48] Dortch Q, Whitledge T E. Does nitrogen or silicon limit phytoplankton production in the Mississippi River plume and nearby regions?[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1992, 12(11): 1293−1309. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(92)90065-R [49] Justić D, Rabalais N N, Turner R E, et al. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1995, 40(3): 339−356. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(05)80014-9 [50] Nelson D M, Brzezinski M A. Kinetics of silicic acid uptake by natural diatom assemblages in two Gulf Stream warm-core rings[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1990, 62(3): 283−292. [51] 高磊, 张蒙蒙, 姚海燕, 等. 近年来胶州湾营养盐结构与限制变化的探讨[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2018, 40(6): 61−68. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2018.06.009Gao Lei, Zhang Mengmeng, Yao Haiyan, et al. An analysis of nutrient structure and limitation changes in Jiaozhou Bay in recent years[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2018, 40(6): 61−68. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2018.06.009 [52] 宋金明, 李学刚. 海洋沉积物/颗粒物在生源要素循环中的作用及生态学功能[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(10): 1−13.Song Jinming, Li Xuegang. Ecological functions and biogenic element cycling roles of marine sediment/particles[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(10): 1−13. [53] Canfield D E. Factors influencing organic carbon preservation in marine sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 114(3/4): 315−329. [54] Ke Zhixin, Chen Danting, Liu Jiaxing, et al. The effects of anthropogenic nutrient inputs on stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in suspended particulate organic matter in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2020, 208: 104244. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2020.104244 [55] 杨世民, 刘任茜, 陈文卿. 2018年胶州湾浮游植物群落结构[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(9): 72−80.Yang Shimin, Liu Renxi, Chen Wenqing. The phytoplankton community in Jiaozhou Bay in 2018[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2020, 50(9): 72−80. [56] 于宇, 宋金明, 李学刚, 等. 沉积物生源要素对水体生态环境变化的指示意义[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(5): 1623−1632. doi: 10.5846/stxb201101170088Yu Yu, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang, et al. Indicative significance of biogenic elements to eco-environmental changes in waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(5): 1623−1632. doi: 10.5846/stxb201101170088 [57] Kang Xuming, Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao, et al. Phosphorus speciation and its bioavailability in sediments of the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2017, 188: 127−136. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.02.029 [58] 佘晨阳, 贾文东, 李铁, 等. 胶州湾表层沉积物中磷的形态及特征研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2021, 43(6): 179−186. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2021.06.024She Chenyang, Jia Wendong, Li Tie, et al. Chemical forms of phosphorus and their characteristics in surface sediments in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2021, 43(6): 179−186. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2021.06.024 [59] Zhang He, Xin Ming, Wang Baodong, et al. Spatiotemporal variations in phosphorus concentrations in the water and sediment of Jiaozhou Bay and sediment phosphorus release potential[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150540. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150540 [60] Boesch D F, Brinsfield R B, Magnien R E. Chesapeake Bay eutrophication: scientific understanding, ecosystem restoration, and challenges for agriculture[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2001, 30(2): 303−320. doi: 10.2134/jeq2001.302303x [61] Liu Ke, Xiao Xiaotong, Zhang Daolai, et al. Quantitative estimates of organic carbon contributions to the river-estuary-marine system in the Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 129: 107929. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107929 [62] Weldrick C K, Jelinski D E. Resource subsidies from multi-trophic aquaculture affect isotopic niche width in wild blue mussels (Mytilus edulis)[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2016, 157: 118−123. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.01.001 -





 下载:
下载: