Characterizing the circulation flow structure in the Modaomen Estuary of the Zhujiang River
-
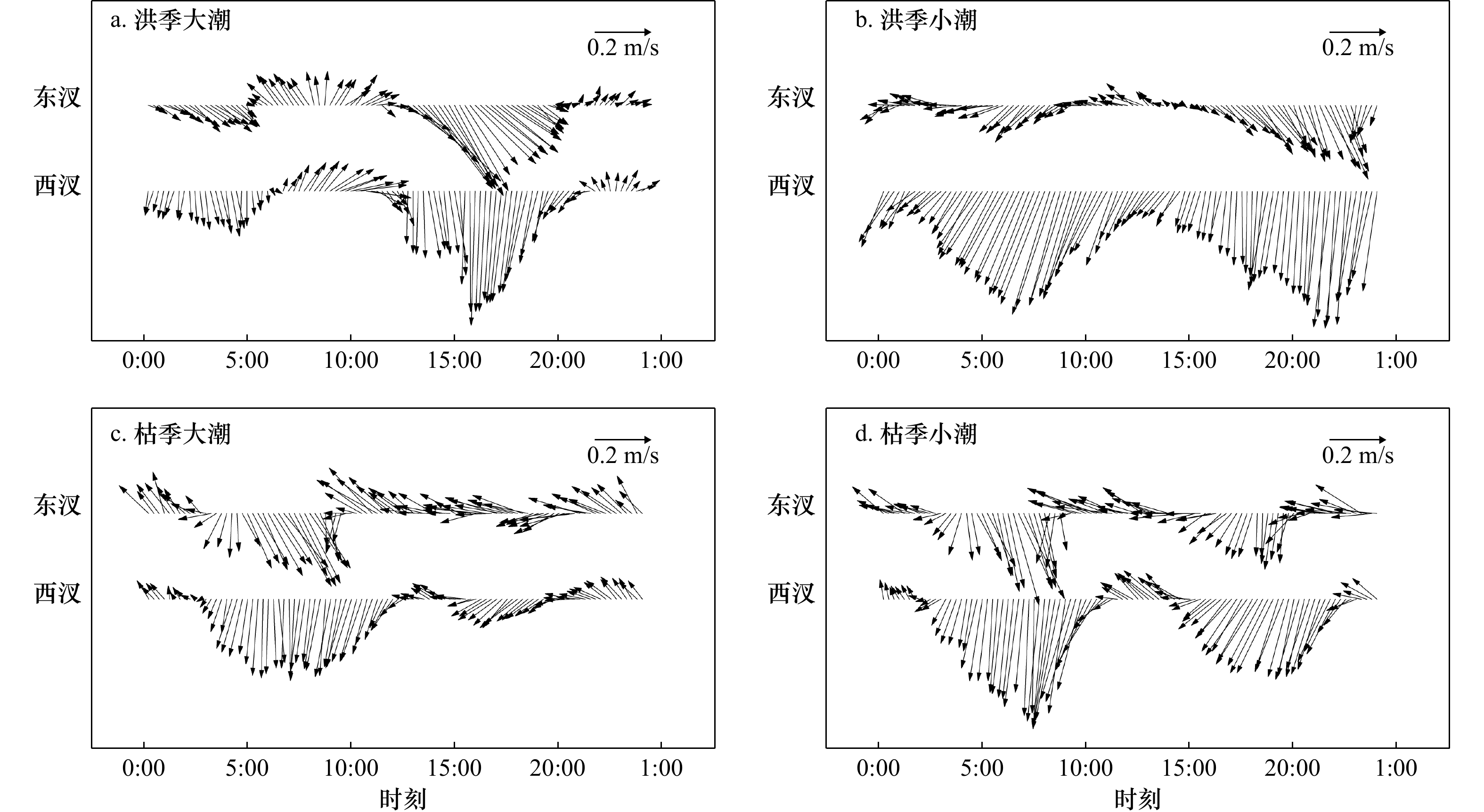
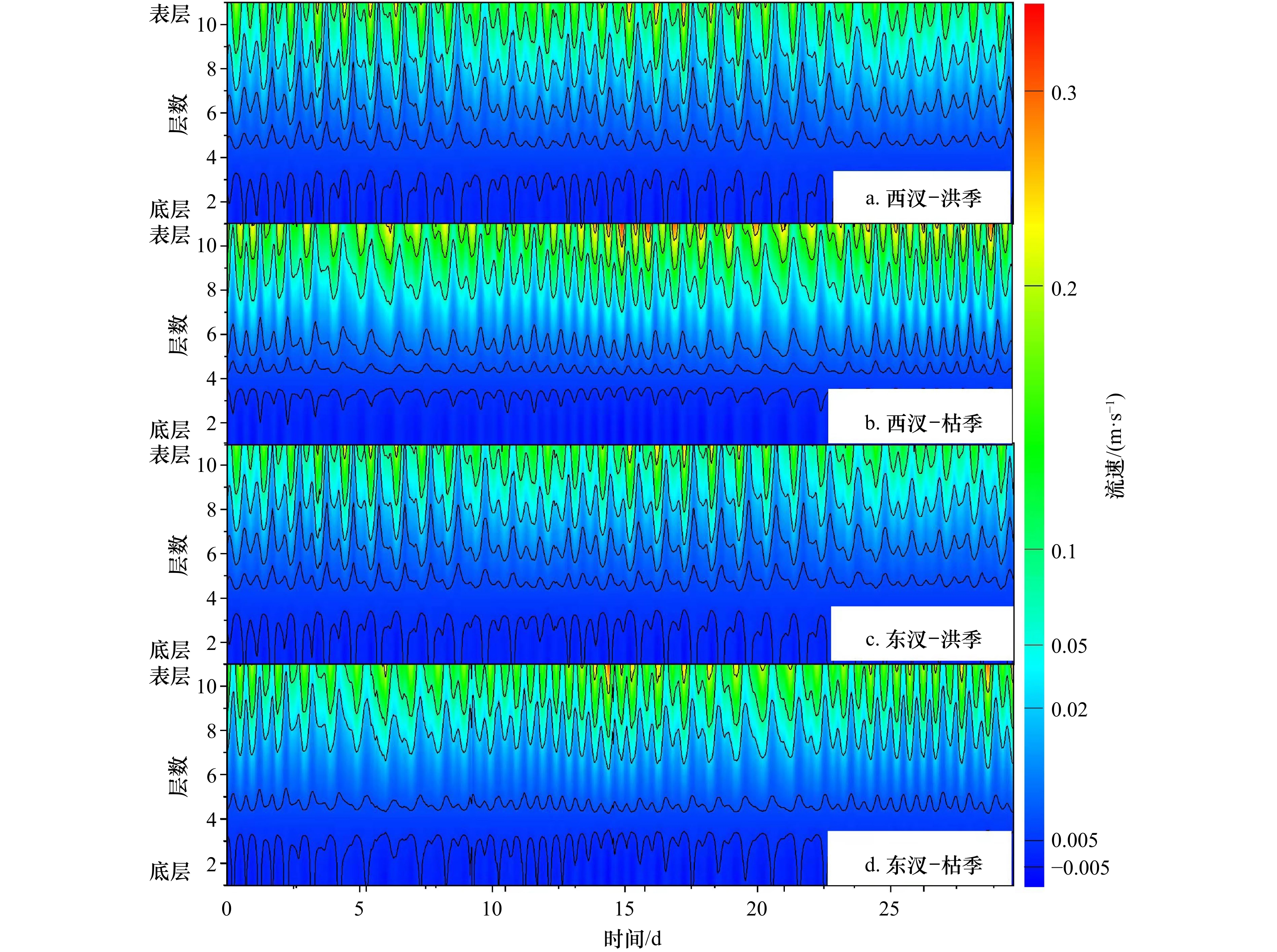
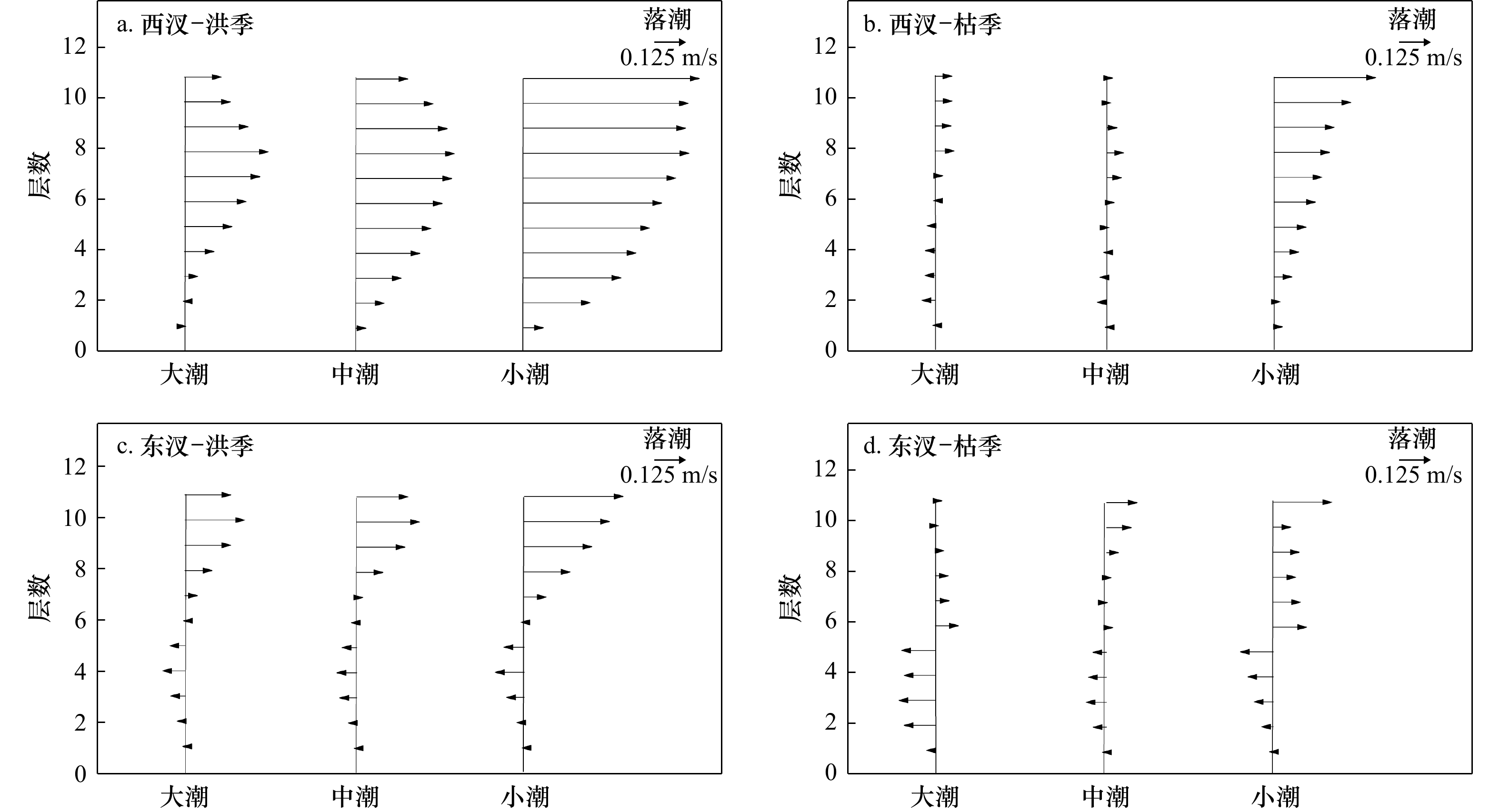
摘要: 河口环流结构关系到物质输运、泥沙沉积和地貌变化等物理过程。根据2019年磨刀门河口原型观测平台洪枯季连续观测分层潮流资料,统计洪枯季、大小潮河口东、西汊的涨落潮流及历时变化特征,利用理论方法解析河口东西汊平面环流和重力环流结构,进一步引入混合参数研究河口纵向环流中的潮汐应变环流。研究发现枯季东、西汊在转潮时刻存在东涨西落的平面环流结构,洪季平面环流特征较不明显;枯季重力环流强度整体略大于洪季,西汊重力环流强于东汊,表层向海环流流速可达0.2~0.25 m/s,而底层向陆环流流速相对较小。洪季大潮期由潮不对称性驱动的潮汐应变环流相对较大,进而增强了纵向环流的强度。河口垂向余流结构同样表现洪枯季、大小潮的变化规律。洪季余流整体较大,西汊在小潮期表层余流流速超过0.6 m/s,而东汊余流则明显呈现表层向海、底层向陆的分布特征,枯季余流整体较小,表明其对物质输运和河口地形塑造作用较弱。Abstract: The structure of circulation flow is related to physical processes such as material transport, sediment deposition and landform evolution. According to the continuous stratified tidal current data derived by the prototype observation platform of Modaomen Estuary in flood and dry seasons in 2019, the flow characteristic during the spring and neap tide at wet and dry seasons in the east and west branches were analyzed. Theoretical methods were used to explore plane circulation and gravity circulation structure in the east and west branches. Besides, the longitudinal circulation with the tidal strain circulation was explained by the mixed parameter. Plane circulation flow structure with ebb at west branch and rise at east branch during the dry season was found. Moreover, gravitational circulation at dry season was generally larger than that at wet season, and the gravitational circulation at west branch was stronger than the east branch, with 0.2–0.25 m/s surface velocity and much lower bottom velocity. The tidal strain circulation driven by the tidal asymmetry at wet season spring tide was relatively higher, which tends to favor the magnitude of vertical circulation. Additionally, the muti-layer residual current also displays seasonal and tidal variations. The residual current at wet season was relatively larger than the dry season, with the surface residual flow velocity more than 0.6 m/s during the neap tide at west branch. However, the downstream residual current at surface and upstream residual current at bottom was found at east branch. Much lower residual current velocity was found at dry season, indicating that the impact on the substance transport and morphological evolution was lower.
-
表 1 测站位置表
Tab. 1 The field measured sites
测站 纬度 经度 水深/m A8 22°04′35.98″N 113°28′13.01″E 6 A9 22°03′28.70″N 113°34′35.28″E 3 A10 22°02′14.99″N 113°31′59.00″E 4.2 表 2 珠江口原型观测站磨刀门水域测站平均流速和流向
Tab. 2 The statistical data of average flow velocity and direction at Modaomen based on the prototype observation platform in Zhujiang River Estuary
测站 潮型 全年 枯季 洪季 流速/
(m·s−1)流向/
(°)流速/
(m·s−1)流向/
(°)流速/
(m·s−1)流向/
(°)A8 落潮 0.51 154 0.48 155 0.53 153 涨潮 0.27 334 0.29 334 0.24 337 A9 落潮 0.29 146 0.26 152 0.31 141 涨潮 0.2 293 0.2 294 0.21 292 A10 落潮 0.43 196 0.39 204 0.45 191 涨潮 0.23 350 0.26 334 0.22 367 平均 落潮 0.41 165 0.38 170 0.43 162 涨潮 0.23 326 0.25 321 0.22 332 -
[1] 时钟, 熊龙兵, 倪智慧, 等. 潮汐河口环流、湍流、混合与层化的物理学[J]. 海岸工程, 2019, 38(1): 1−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2019.01.001Shi Zhong, Xiong Longbing, Ni Zhihui, et al. The physics of circulation, turbulence, mixing and stratification in tidal estuaries[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2019, 38(1): 1−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2019.01.001 [2] Kearney W S, Fagherazzi S. Salt marsh vegetation promotes efficient tidal channel networks[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12287. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12287 [3] Wu Yao, Zhang Wei, Zhu Yuliang, et al. Intra-tidal division of flow and suspended sediment at the first order junction of the Pearl River network[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 209: 169−182. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.05.030 [4] 杨名名, 吴加学, 张乾江, 等. 珠江黄茅海河口洪季侧向余环流与泥沙输移[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(1): 31−45.Yang Mingming, Wu Jiaxue, Zhang Qianjiang, et al. Lateral residual circulation and sediment transport during the flood season in the Huangmaohai Estuary, Pearl River[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(1): 31−45. [5] 高抒. 潮汐汊道形态动力过程研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2008, 23(12): 1237−1248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.12.002Gao Shu. Morphodynamic processes of tidal inlets: a review[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2008, 23(12): 1237−1248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.12.002 [6] He Yong, Wu Yao, Lu Chen, et al. Morphological change of the mouth bar in relation to natural and anthropogenic interferences[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2019, 175: 42−52. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2019.01.015 [7] 易侃, 龚文平. 伶仃洋河口横向环流[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(3): 1−14.Yi Kan, Gong Wenping. Lateral circulation in the Lingding Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(3): 1−14. [8] Fraccascia S, Winter C, Ernstsen V B, et al. Residual currents and bedform migration in a natural tidal inlet (Knudedyb, Danish Wadden Sea)[J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 271: 74−83. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.07.017 [9] Geyer W R, MacCready P. The estuarine circulation[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 46: 175−197. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010313-141302 [10] Valle-Levinson A, Lwiza K M M. The effects of channels and shoals on exchange between the Chesapeake Bay and the adjacent ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1995, 100(C9): 18551−18563. doi: 10.1029/95JC01936 [11] Kasai A, Hill A E, Fujiwara T, et al. Effect of the Earth’s rotation on the circulation in regions of freshwater influence[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2000, 105(C7): 16961−16969. doi: 10.1029/2000JC900058 [12] Wong K C. On the nature of transverse variability in a coastal plain estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1994, 99(C7): 14209−14222. doi: 10.1029/94JC00861 [13] 朱磊. 河势变化下河口环流结构及变异研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018.Zhu Lei. Alteration of estuarine circulation under the influence of morphological evolution[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018. [14] 蔡华阳, 杨昊, 郭晓娟, 等. 珠江磨刀门河口径潮动力耦合条件下余水位的多时空尺度分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(7): 55−65.Cai Huayang, Yang Hao, Guo Xiaojuan, et al. Investigation of temporal-spatial distribution patterns of residual water level under the influence of tide-river interaction in the Modaomen Estuary, Zhujiang River[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(7): 55−65. [15] 杨士瑛, 鲍献文, 陈长胜, 等. 夏季粤西沿岸流特征及其产生机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(6): 1−8.Yang Shiying, Bao Xianwen, Chen Changsheng, et al. Analysis on characteristics and mechanism of current system in west coast of Guangdong Province in the summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2003, 25(6): 1−8. [16] Officer C B. Physical Oceanography of Estuaries (and Associated Coastal Waters)[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. , 1976. [17] Schwing F B, Kjerfve B, Sneed J E. Nearshore coastal currents on the South Carolina continental shelf[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1983, 88(C8): 4719−4729. doi: 10.1029/JC088iC08p04719 [18] Buschman F A, Hoitink A J F, van der Vegt M, et al. Subtidal flow division at a shallow tidal junction[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(12): W12515. [19] Holleman R C, Geyer W R, Ralston D K. Stratified turbulence and mixing efficiency in a salt wedge estuary[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2016, 46(6): 1769−1783. doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-15-0193.1 [20] 张丽芬, 杨作升, 张凡, 等. 长江河口南槽纵向余环流: 径流、潮汐和地形耦合机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 64(12): 2129−2143. doi: 10.1007/s11430-021-9813-7Zhang Lifen, Yang Zuosheng, Zhang Fan, et al. Longitudinal residual circulation in the south passage of Yangtze Estuary: combined influences from runoff, tide and bathymetry[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(12): 2129−2143. doi: 10.1007/s11430-021-9813-7 -





 下载:
下载: