Distribution and ecological characteristics of seagrass bed of Mashanli sea area in Rongcheng
-
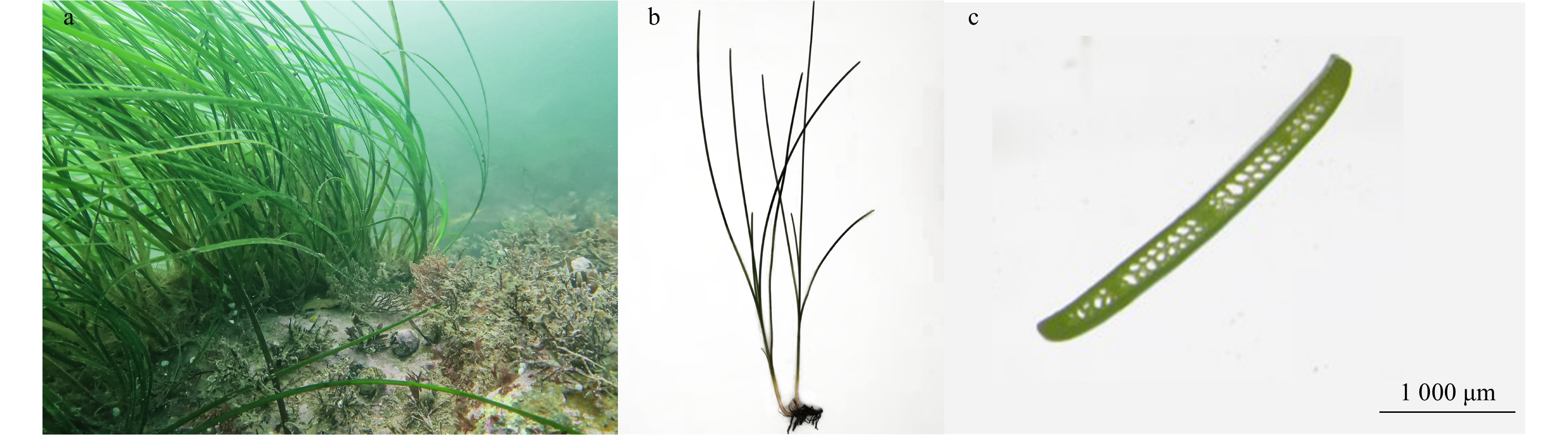
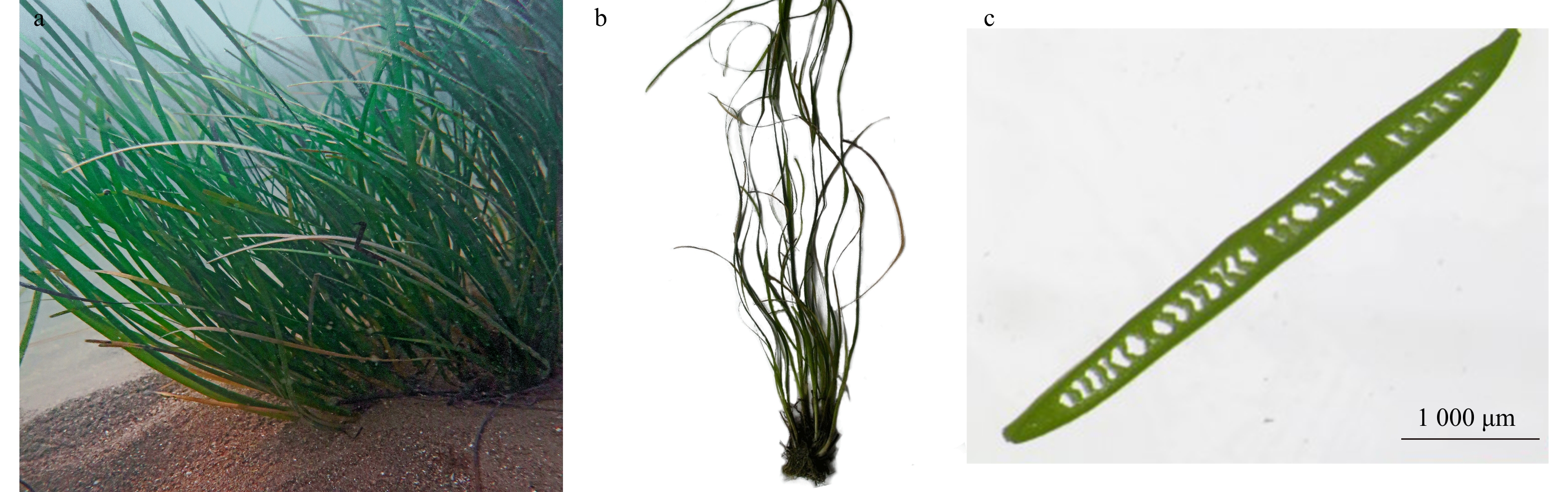
摘要: 海草床是滨海三大典型生态系统之一,具有极其重要的环境改善、资源养护和减灾防灾等生态功能,亦是全球重要的碳库。2016年8月,通过对荣成马山里海域的现场调查,发现了面积为58.26 hm2的海草床,其海草的种类为红纤维虾形草(Phyllospadix iwatensis)和丛生鳗草(Zostera caespitosa)。红纤维虾形草分布面积为54.50 hm2,占该海域海草床总面积的93.5%,分为北部和南部2个带状区域,平均茎枝密度为(368.0±18.2)shoots/m2,平均生物量(干重,下同)为(297.0±41.5)g/m2。丛生鳗草分布面积为3.76 hm2,占海草床总面积的6.5%,呈现斑块状分布,与红纤维虾形草交错而生,平均茎枝密度为(691.2±17.1)shoots/m2,平均生物量为(534.0±70.7)g/m2。马山里海域海草床主要分布在平均水深为(2.8±0.3) m的以岩礁为主的底质上。海草的生长状况存在显著的空间差异,与水温呈现显著的正相关,与水深和陆源污染物存在显著的负相关。结合历史资料,发现该海域海草床退化现象较严重,其主要威胁因素是人为干扰,主要包括渔业生产、养殖活动和陆源污染输入。建议合理规划周边海域的养殖规模和密度、加强陆源污染物管控和开展海草床生态修复工程,以期为温带海草床的有效保护和科学管理提供参考。Abstract: Seagrass bed is one of the three typical coastal ecosystems, which plays an important role in environmental improvement, resource conservation, and mitigation of environment degradation caused by natural disasters. It is also important as a global carbon stock. In August 2016, a field survey was conducted in the sea area of Mashanli of Rongcheng. A seagrass bed with an area of 58.26 hm2 was found, consisting of Phyllospadix iwatensis and Zostera caespitosa meadows. The P. iwatensis meadow was composed of two belt regions south and north of the bed, occupying an area of 54.50 hm2 and accounting for 93.5% of the seagrass bed. The P. iwatensis shoot density was (368.0±18.2) shoots/m2 and the biomass was (297.0±41.5) g/m2. While the Z. caespitosa generally formed dense patches within the P. iwatensis meadows, and occupied an area of 3.76 hm2, accounting for 6.5% of the seagrass bed. The shoot density of Z. caespitosa was (691.2±17.1) shoots/m2, and the biomass was (534.0±70.7) g/m2. The water depth in the seagrass bed was (2.8±0.3) m, and the seabed was mainly rocky, with some sediments covering on the rocky beds. The growth of the seagrasses showed significant spatial variation, which was positively correlated with the water temperature, and negatively correlated with water depth and terrestrial pollutants. By comparing with historical data, it was found that the degradation of seagrass beds in Mashanli sea area was severe. Anthropogenic activities are the main causes of seagrass degradation, including fishing and aquaculture activities, as well as the pollution of land-based sources. Therefore, it is suggested that rationally planning the scale and density of aquaculture in surrounding area, strengthening the control of terrestrial pollutants, and carrying out ecological restoration projects of seagrass beds will promote the effective protection and scientific management of seagrass beds in temperate zone.
-
Key words:
- seagrass bed /
- seagrass species /
- distribution area /
- ecological characteristics /
- Mashanli sea area
-
图 7 海草形态学指标与环境因子间的相关性分析
SH. 株高;LSL. 叶鞘长;AB. 单株地上生物量;UB. 单株地下生物量;WD. 水深;WT. 水温;DO. 溶解氧含量;SWT. 透明度;OM. 有机质含量;A. 海草形态学指标之间的相关性;B. 环境因子指标之间的相关性;C. 海草形态学指标与环境因子指标之间的相关性;*代表p<0.05, **代表p<0.01
Fig. 7 Correlation analysis among morphological indexes of seagrass and environmental factors
SH. Shoot height; LSL. leaf sheath length; AB. aboveground bio mass per plant; UB. underground bio mass per plant; WD. water depth; WT. water temperature; DO. dissolved oxygen content; SWT. transparency; OM. organic matter content; the data on the left and right sides are the normalized canonical correlation coefficient of the variables; A. correlation between morphological indexes of seagrasses; B. correlation between environmental factors; C. correlation between morphological indexes of seagrasses and environmental factors; * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01
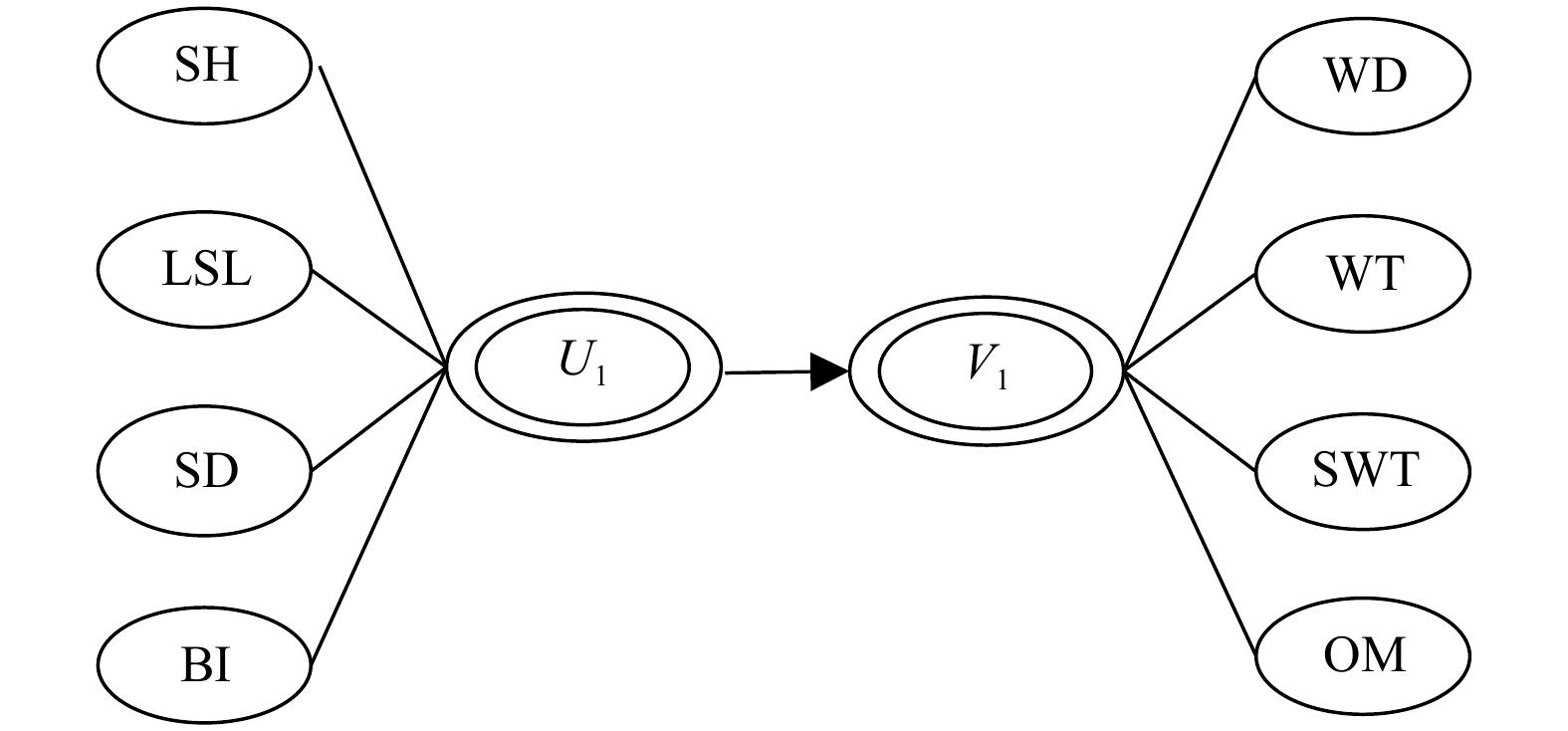
图 8 U1、V1典型结构示意图
U1. 生态学指标第一典型变量;V1. 海区环境指标第一典型变量;SH. 株高;LSL. 叶鞘长;SD. 茎枝密度;BI. 单株干重;WD. 水深;WT. 水温;SWT. 透明度;OM. 有机质含量
Fig. 8 Canonical correlation structure diagram of U1 and V1
U1. The first canonical variable of morphological indexes; V1. the first canonical variable of marine environmental factors; SH. shoot height; LSL. leaf sheath length; SD. shoot density; BI. dry weight per plant; WD. water depth; WT. water temperature; SWT. transparency; OM. organic matter content
图 9 变量典型载荷分析(a)和变量交叉载荷分析(b)
SH. 株高;LSL. 叶鞘长;SD. 茎枝密度;BI. 单株干重;WD. 水深;WT. 水温;SWT. 透明度;OM. 有机质含量
Fig. 9 Variable typical load analysis (a) and variable cross load analysis (b)
SH. Shoot height; LSL. leaf sheath length; SD. shoot density; BI. dry weight per plant; WD. water depth; WT. water temperature; SWT. transparency; OM. organic matter content
表 1 马山里海域海草形态学指标统计
Tab. 1 Statistics of morphological indexes of seagrasses in the Mashanli sea area
海草种类 站位 株高/cm 叶鞘长/cm 叶鞘宽/cm 叶宽/cm 最大根长/cm 红纤维虾形草 PW1 81.8±3.2 7.5±1.5 0.29±0.02 0.23±0.01 0.36±0.06 PW2 90.0±4.1 14.7±2.3 0.31±0.03 0.27±0.02 1.08±0.09 PW3 90.8±2.3 16.0±2.5 0.30±0.02 0.28±0.02 1.75±0.06 PW4 96.0±3.3 13.3±1.9 0.23±0.04 0.23±0.01 0.98±0.05 PW5 87.6±3.8 12.5±1.8 0.29±0.03 0.25±0.02 1.13±0.07 平均值 89.2±4.2 12.8±2.7 0.28±0.03 0.25±0.02 1.06±0.10 丛生鳗草 ZC1 68.3±4.5 13.3±0.56 0.37±0.03 0.33±0.02 6.10±0.62 ZC2 80.8±5.2 15.2±0.33 0.45±0.02 0.39±0.03 7.74±0.58 ZC3 87.1±7.2 16.1±0.84 0.44±0.02 0.41±0.03 8.10±0.71 ZC4 88.7±6.4 16.1±0.75 0.44±0.03 0.39±0.02 8.60±0.67 ZC5 67.3±7.3 14.7±0.64 0.43±0.01 0.38±0.03 6.15±0.84 平均值 78.4±8.3 15.1±0.94 0.42±0.02 0.38±0.03 7.34±0.94 注:站位位置见图6。 表 2 马山里海域海草床主要环境因子
Tab. 2 The main environmental factors of the seagrass beds in the Mashanli sea area
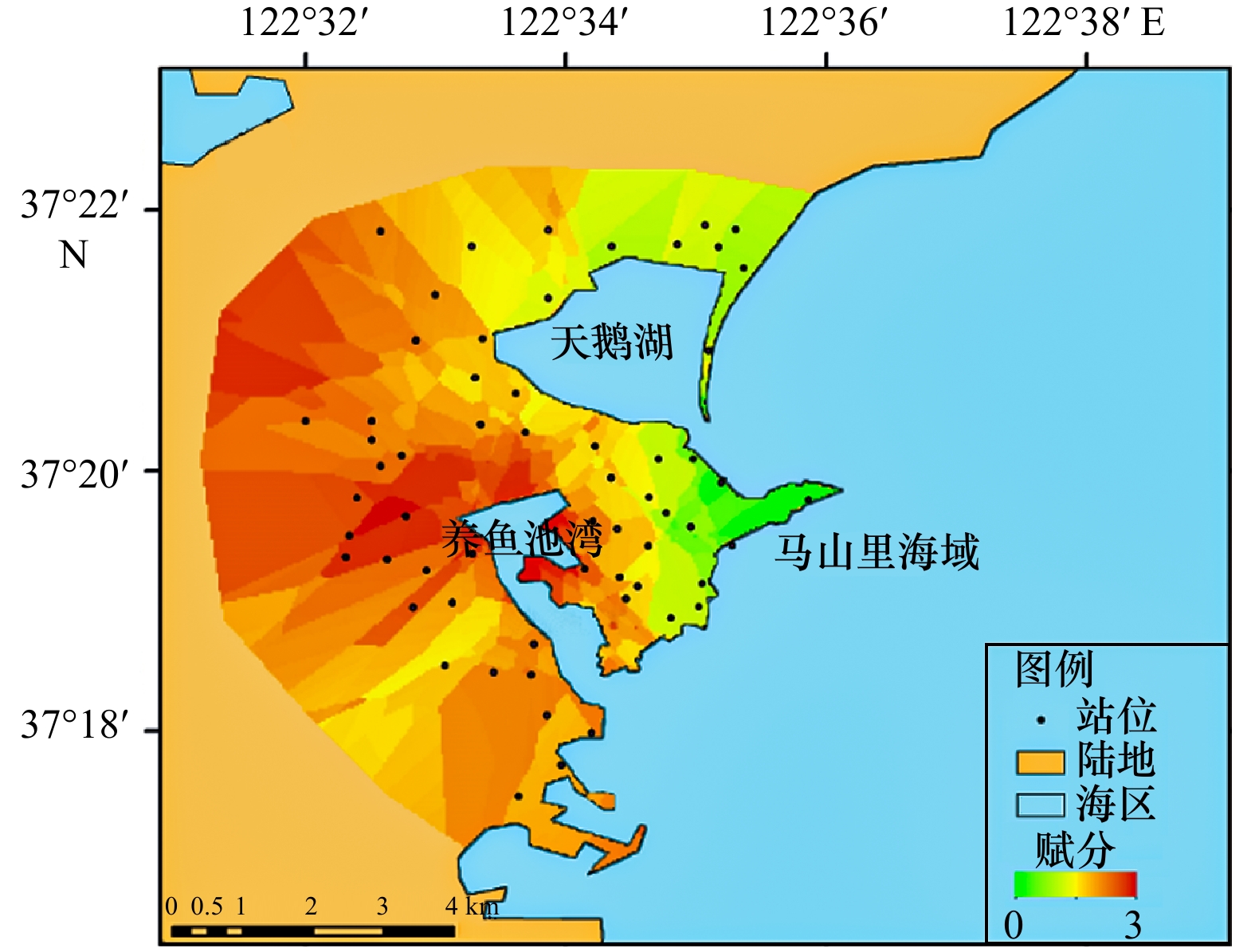
海草种类 站位 水深/m 水温/℃ 盐度 溶解氧含量/(mg·L−1) pH 透明度/m 底质类型 沉积物有机质含量/% 红纤维虾形草 PW1 2.9 23.5 31.6 8.5 7.3 1.6 礁石 1.13 PW2 2.5 23.5 31.3 8.7 7.5 1.6 礁石 1.19 PW3 2.9 23.4 31.5 8.5 7.7 1.8 礁石 1.17 PW4 2.3 23.5 31.3 8.4 7.3 1.9 礁石 1.11 PW5 2.5 23.6 31.6 8.7 7.5 1.4 礁石 1.18 平均值 2.6±0.2 23.5±0.1 31.5±0.1 8.6±0.1 7.5±0.1 1.6±0.2 礁石 1.16±0.03 丛生鳗草 ZC1 2.9 23.3 31.9 10.3 7.3 1.9 cS 1.09 ZC2 3.0 22.9 31.9 10.7 7.4 1.7 cS 1.05 ZC3 2.9 23.0 31.9 10.0 7.4 1.8 cS 1.06 ZC4 3.2 23.0 31.9 11.2 7.2 1.6 cS 1.15 ZC5 3.1 23.1 31.9 10.7 7.3 1.6 cS 1.11 平均值 3.0±0.1 23.1±0.1 31.9±0 10.6±0.4 7.3±0.1 1.7±0.2 cS 1.09±0.04 注:cS为黏土质砂;站位位置见图6。 表 3 环境类型及赋分标准
Tab. 3 Environment type and assignment standard
类型 自然保护区 耕地 居民区 工厂(养殖场) 赋分 0 1 2 3 -
[1] McKenzie L J, Yoshida R L, Aini J W, et al. Seagrass ecosystem contributions to people’s quality of life in the Pacific Island countries and territories[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 167: 112307. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112307 [2] 庄武艺, J·谢佩尔. 海草对潮滩沉积作用的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 1991, 13(2): 230−239.Zhuang Wuyi, Champey J. Effects of seagrass on tidal flat sedimentation[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1991, 13(2): 230−239. [3] 邱广龙, 林幸助, 李宗善, 等. 海草生态系统的固碳机理及贡献[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(6): 1825−1832.Qiu Guanglong, Lin Xingzhu, Li Zongshan, et al. Seagrass ecosystems: contributions to and mechanisms of carbon sequestration[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(6): 1825−1832. [4] Waycott M, Duarte C M, Carruthers T J B, et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(30): 12377−12381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905620106 [5] Short F T, Polidoro B, Livingstone S R, et al. Extinction risk assessment of the world’s seagrass species[J]. Biological Conservation, 2011, 144(7): 1961−1971. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2011.04.010 [6] 郑凤英, 邱广龙, 范航清, 等. 中国海草的多样性、分布及保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5): 517−526.Zheng Fengying, Qiu Guanglong, Fan Hangqing, et al. Diversity, distribution and conservation of Chinese seagrass species[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(5): 517−526. [7] 叶春江, 赵可夫. 高等植物大叶藻研究进展及其对海洋沉水生活的适应[J]. 植物学通报, 2002, 19(2): 184−193.Ye Chunjiang, Zhao Kefu. Advances in the study on the marine higher plant eelgrass (Zostera marina L. ) and its adaptation to submerged life in seawater[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2002, 19(2): 184−193. [8] 李洪辰, 张沛东, 李文涛, 等. 黄海镆铘岛海域海草床数量分布及其生态特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(4): 46−51. doi: 10.11759/hykx20180803001Li Hongchen, Zhang Peidong, Li Wentao, et al. Quantitative distribution and ecological characteristics of seagrass beds in the coastal area of Moye Island, Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(4): 46−51. doi: 10.11759/hykx20180803001 [9] 郭栋, 张沛东, 张秀梅, 等. 山东近岸海域海草种类的初步调查研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2010(2): 17−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.02.004Guo Dong, Zhang Peidong, Zhang Xiumei, et al. Preliminary investigation and study on seagrass species of inshore areas in Shandong Province[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2010(2): 17−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.02.004 [10] 李政, 李文涛, 杨晓龙, 等. 威海双岛湾海域海草分布及其生态特征[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(2): 176−183.Li Zheng, Li Wentao, Yang Xiaolong, et al. Distribution and ecological characteristics of seagrass in Shuangdao Bay, Weihai[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(2): 176−183. [11] 李政, 李文涛, 杨晓龙, 等. 威海荣成桑沟湾海域海草床分布现状及其生态特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(10): 52−59.Li Zheng, Li Wentao, Yang Xiaolong, et al. Distribution and ecological characteristics of seagrass beds in Rongcheng Sanggou Bay, Weihai[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(10): 52−59. [12] 吴沅珈, 张宏科. 广西合浦海草床变化情况及保护对策[J]. 中国科技信息, 2018(22): 68−69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8972.2018.22.025Wu Yuanjia, Zhang Hongke. Changes of seagrass beds and conservation strategies in Hepu, Guangxi Province[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2018(22): 68−69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8972.2018.22.025 [13] 吴钟解, 陈石泉, 蔡泽富, 等. 海南岛海草床分布变化及恢复建议[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(4): 542−549. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200130Wu Zhongjie, Chen Shiquan, Cai Zefu, et al. Analysis of distribution change and restoration suggestion of the seagrass beds in Hainan Island[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(4): 542−549. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200130 [14] 岳世栋, 徐少春, 张玉, 等. 中国温带海域新发现较大面积(大于50 ha)海草床: Ⅳ烟台沿海海草分布现状及生态特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(10): 61−70.Yue Shidong, Xu Shaochun, Zhang Yu, et al. New discovery of larger seagrass beds with area >50 ha in the temperate waters of China: Ⅳ distribution status and ecological characteristics of seagrass in the coastal waters of Yantai[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(10): 61−70. [15] 周毅, 张晓梅, 徐少春, 等. 中国温带海域新发现较大面积(大于50 ha)的海草床: Ⅰ黄河河口区罕见大面积日本鳗草海草床[J]. 海洋科学, 2016, 40(9): 95−97. doi: 10.11759/hykx20151218001Zhou Yi, Zhang Xiaomei, Xu Shaochun, et al. New discovery of larger seagrass beds with areas >50 ha in temperate waters of China: an unusual large seagrass (Zostera japonica) bed in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(9): 95−97. doi: 10.11759/hykx20151218001 [16] 周毅, 许帅, 徐少春, 等. 中国温带海域新发现较大面积(大于0.5 km2)海草床: Ⅱ声呐探测技术在渤海唐山沿海海域发现中国面积最大的鳗草海草床[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(8): 50−55. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190318003Zhou Yi, Xu Shuai, Xu Shaochun, et al. New discovery of larger seagrass beds with areas >0.50 km2 in temperate waters of China: Ⅱ the largest Zostera marina bed in China discovered in the coastal waters of Tangshan in the Bohai Sea by sonar detection technology[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(8): 50−55. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190318003 [17] 刘慧, 黄小平, 王元磊, 等. 渤海曹妃甸新发现的海草床及其生态特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(7): 1677−1683.Liu Hui, Huang Xiaoping, Wang Yuanlei, et al. Newly discovered seagrass bed and its ecological characteristics in the coastal area of Caofeidian, Bohai Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(7): 1677−1683. [18] 杨贵福. 獐子岛近海海草的群落特征和大叶藻营养动态分析[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2014.Yang Guifu. Community ecological characteristics of seagrass and trophical dynamical analysis of Zostera marina L. in littoral of Zhangzi Island[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2014. [19] Xu Shaochun, Qiao Yongliang, Xu Shuai, et al. Diversity, distribution and conservation of seagrass in coastal waters of the Liaodong Peninsula, North Yellow Sea, northern China: implications for seagrass conservation[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 167: 112261. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112261 [20] 周毅, 徐少春, 许帅, 等. 中国温带海域新发现较大面积(大于50 ha)海草床: Ⅲ渤海兴城−觉华岛海域大面积海草床鳗草种群动力学及补充机制[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(4): 943−951. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200100032Zhou Yi, Xu Shaochun, Xu Shuai, et al. New discovery of larger seagrass beds with areas >50 ha in temperate waters of China: Ⅲ population dynamics and recruitment mechanism of Zostera marina in the Xingcheng-Juehuadao coastal waters of Bohai Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(4): 943−951. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200100032 [21] 宁秋云, 何斌源, 赖廷和. 广西竹山海草生态修复工程效果评估[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2020(12): 304−306.Ning Qiuyun, He Binyuan, Lai Tinghe. Effect evaluation of ecological restoration of seagrass in Zhushan, Guangxi Province[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2020(12): 304−306. [22] 范航清, 彭胜, 石雅君, 等. 广西北部湾沿海海草资源与研究状况[J]. 广西科学, 2007, 14(3): 289−295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2007.03.026Fan Hangqing, Peng Sheng, Shi Yajun, et al. The situations of seagrass resources and researches along Guangxi coasts of Beibu Gulf[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2007, 14(3): 289−295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2007.03.026 [23] 黄小平, 江志坚, 张景平, 等. 广东沿海新发现的海草床[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(1): 132−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.01.020Huang Xiaoping, Jiang Zhijian, Zhang Jingping, et al. Newly discovered seagrass beds in the coastal seas of Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(1): 132−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.01.020 [24] 钟超, 孙凯峰, 廖岩, 等. 广东流沙湾海草分布现状及其与不同养殖生境的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(4): 521−527. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190406Zhong Chao, Sun Kaifeng, Liao Yan, et al. Distribution status of seagrass and its relationship with different habitat types in Liusha Bay of Guangdong Province[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(4): 521−527. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190406 [25] 陈石泉, 庞巧珠, 蔡泽富, 等. 海南黎安港海草床分布特征、健康状况及影响因素分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(11): 57−64.Chen Shiquan, Pang Qiaozhu, Cai Zefu, et al. Analysis of distribution characteristics, health status, and influencing factors of seagrass bed in Li’an Lagoon, Hainan Island[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(11): 57−64. [26] 陈石泉, 林国尧, 蔡泽富, 等. 海南东寨港海草资源分布特征及影响因素[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2019, 15(4): 53−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3290.2019.04.13Chen Shiquan, Lin Guoyao, Cai Zefu, et al. Patterns and impacting factors of the distribution of the seagrass resources in Dongzhai Harbour of Hainan[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 2019, 15(4): 53−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3290.2019.04.13 [27] 陈石泉, 吴钟解, 陈晓慧, 等. 海南岛南部海草资源分布现状调查分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(6): 106−113.Chen Shiquan, Wu Zhongjie, Chen Xiaohui, et al. Investigation and analysis of the distribution status of seagrass resources in the southern part of Hainan Island[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(6): 106−113. [28] 黄小平, 黄良民, 李颖虹, 等. 华南沿海主要海草床及其生境威胁[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(S2): 136−142. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-9136-5Huang Xiaoping, Huang Liangmin, Li Yinghong, et al. Main seagrass beds and threats to their habitats in the coastal sea of South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(S2): 136−142. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-9136-5 [29] 赵东波. 常用沉积物粒度分类命名方法探讨[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2009, 25(8): 41−44, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2009.08.009Zhao Dongbo. Discussion on general methods of the grain-size classification and nomenclature of sediments[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2009, 25(8): 41−44, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2009.08.009 [30] 程鹏, 高抒, 李徐生. 激光粒度仪测试结果及其与沉降法、筛析法的比较[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(3): 449−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.03.023Cheng Peng, Gao Shu, Li Xusheng. Evaluation of a wide range laser particle size analyses and comparison with pipette and sieving methods[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(3): 449−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.03.023 [31] 钱宝, 刘凌, 肖潇. 土壤有机质测定方法对比分析[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(1): 34−38.Qian Bao, Liu Ling, Xiao Xiao. Comparative tests on different methods for content of soil organic matter[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 39(1): 34−38. [32] Turner T. Complexity of early and middle successional stages in a rocky intertidal surfgrass community[J]. Oecologia, 1983, 60(1): 56−65. doi: 10.1007/BF00379320 [33] Larkum A W D, Orth R J, Duarte C M. Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2006. [34] Lee S Y, Choi C I, Suh Y, et al. Seasonal variation in morphology, growth and reproduction of Zostera caespitosa on the southern coast of Korea[J]. Aquatic Botany, 2005, 83(4): 250−262. doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.03.003 [35] 江鑫, 潘金华, 韩厚伟, 等. 底质与水深对大叶藻和丛生大叶藻分布的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2012, 27(2): 101−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9957.2012.02.002Jiang Xin, Pan Jinhua, Han Houwei, et al. Effects of substrate and water depth on distribution of sea weeds Zostera marina and Z. caespitosa[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2012, 27(2): 101−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9957.2012.02.002 [36] Yabe T, Ikusima I, Tsuchiya T. Production and population ecology of Phyllospadix iwatensis Makino. I. leaf growth and biomass in an intertidal zone[J]. Ecological Research, 1995, 10(3): 291−299. doi: 10.1007/BF02347855 [37] 杨芳, 贺达汉. 生境破碎化对生物多样性的影响[J]. 生态科学, 2006, 25(6): 564−567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2006.06.020Yang Fang, He Dahan. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity[J]. Ecologic Science, 2006, 25(6): 564−567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2006.06.020 [38] 武晶, 刘志民. 生境破碎化对生物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(7): 1946−1952.Wu Jing, Liu Zhimin. Effect of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(7): 1946−1952. [39] Sweatman J L, Layman C A, Fourqurean J W. Habitat fragmentation has some impacts on aspects of ecosystem functioning in a sub-tropical seagrass bed[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2017, 126: 95−108. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2017.02.003 [40] Jaeger J A G. Landscape division, splitting index, and effective mesh size: new measures of landscape fragmentation[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2000, 15(2): 115−130. doi: 10.1023/A:1008129329289 [41] Forman R T T. Some general principles of landscape and regional ecology[J]. Landscape Ecology, 1995, 10(3): 133−142. doi: 10.1007/BF00133027 [42] Lee K S, Park S R, Kim Y K. Effects of irradiance, temperature, and nutrients on growth dynamics of seagrasses: a review[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2007, 350(1/2): 144−175. [43] Ralph P J, Durako M J, Enríquez S, et al. Impact of light limitation on seagrasses[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2007, 350(1/2): 176−193. [44] 柳杰, 张沛东, 郭栋, 等. 环境因子对海草生长及光合生理影响的研究进展[J]. 水产科学, 2012, 31(2): 119−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2012.02.013Liu Jie, Zhang Peidong, Guo Dong, et al. Research advancement in effects of environmental factors on growth and photosynthetic physiology of sea weed[J]. Fisheries Science, 2012, 31(2): 119−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2012.02.013 [45] Dawes C J, Andorfer J, Rose C, et al. Regrowth of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum into propeller scars[J]. Aquatic Botany, 1997, 59(1/2): 139−155. [46] Frank J S, Timothy J L, David W C, et al. Scarring of Florida’s seagrasses: assessment and management options[R]. Florida: Florida Department of Environmental Protection, 1995. [47] 李诗奇, 张彦浩, 李政, 等. 大叶藻对氮磷营养盐的吸收动力学特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(7): 772−781. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0335Li Shiqi, Zhang Yanhao, Li Zheng, et al. Uptake kinetics of nitrogen and phosphorus by Zostera marina[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(7): 772−781. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0335 [48] 陈玉, 韩秋影, 郑凤英, 等. 东楮岛海草组织碳氮含量特征及环境影响因素[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学学报), 2016, 46(5): 56−64.Chen Yu, Han Qiuying, Zheng Fengying, et al. Carbon and nitrogen content characteristics in seagrass tissues and environmental effects in Dongchu Island[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(5): 56−64. [49] 李诗奇, 李政, 王仙宁, 等. 植物对氮磷元素吸收利用的生理生态学过程研究进展[J]. 山东农业科学, 2019, 51(3): 151−157.Li Shiqi, Li Zheng, Wang Xianning, et al. Advances in research of physiological and ecological process of nitrogen and phosphorus absorption and utilization in plant[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 51(3): 151−157. [50] Ramı́rez-Garcı́a P, Terrados J, Ramos F, et al. Distribution and nutrient limitation of surfgrass, Phyllospadix scouleri and Phyllospadix torreyi, along the Pacific coast of Baja California (México)[J]. Aquatic Botany, 2002, 74(2): 121−131. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3770(02)00050-5 [51] 柳杰. 不同环境条件对天鹅湖大叶藻生长及光合色素含量的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.Liu Jie. Effects of different environmental conditions on the growth and photosynthetic pigment contents of Zostera marina L. in Swan Lake[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2011 [52] 黄驰, 张景平, 江志坚, 等. 海草对营养盐的吸收过程及其与附生藻类的竞争机制[J]. 渔业研究, 2017, 39(3): 222−228.Huang Chi, Zhang Jingping, Jiang Zhijian, et al. Nutrients uptake processes of seagrass and its competition with epiphytic algae[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2017, 39(3): 222−228. [53] 高亚平, 蒋增杰, 杜美荣, 等. 除草剂扑草净和阿特拉津对海草与大型藻类的毒性比较[J]. 水生生物学报, 2017, 41(4): 930−934. doi: 10.7541/2017.116Gao Yaping, Jiang Zengjie, Du Meirong, et al. Comparison of the herbicide atrazine and prometryn’s toxicity on seagrass and seaweed[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2017, 41(4): 930−934. doi: 10.7541/2017.116 [54] 李磊, 黄小平. 重金属在海草中累积及其对海草生长的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(9): 1897−1904.Li Lei, Huang Xiaoping. Research advances in heavy metals accumulation in seagrass and its effects on seagrass growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(9): 1897−1904. [55] 刘燕山, 郭栋, 张沛东, 等. 北方澙湖大叶藻植株枚订移植法的效果评估与适宜性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(2): 176−183. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0017Liu Yanshan, Guo Dong, Zhang Peidong, et al. Assessing establishment success and suitability analysis of Zostera marina transplants using staple method in northern lagoons[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(2): 176−183. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0017 [56] 张倩, 柳杰, 张沛东, 等. 不同水流流速对大叶藻移植植株存活、生长及光合色素含量的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(6): 806−812.Zhang Qian, Liu Jie, Zhang Peidong, et al. Effects of different current velocities on survival, growth and photosynthetic pigment contents of Zostera marina transplants[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(6): 806−812. [57] 程冉, 侯鑫, 王欢, 等. 红纤维虾形草移植植株存活、生长和生理对不同水动力条件的响应[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2022, 43(2): 21−31.Cheng Ran, Hou Xin, Wang Huan, et al. Survival, growth, and physiological responses of surfgrass transplants to different hydrodynamic regimes[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2022, 43(2): 21−31. -





 下载:
下载: