Behavioral response to tidal replacement of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
-
摘要: 潮汐更替对潮间带生物的生理和行为影响显著,底内动物可以通过行为过程建立适宜的微环境适应潮间带环境变化。本实验运用行为学观测装置研究了双齿围沙蚕对潮汐更替的行为响应特征。实验设置3个温度梯度(15℃、20℃和25℃)和4个时间段(T1: 退潮前、T2: 退潮后、T3: 涨潮30 min内和T4: 涨潮30 min后),每个处理组设6个重复。结果显示,在同一时间段内,随着温度的升高,双齿围沙蚕的径向起伏频率、径向起伏泵水速率、轴向爬行速度和头尾对调次数呈增大的趋势,头尾对调一次的时间逐渐缩短。同一温度下,双齿围沙蚕在T3时间段内的径向起伏频率、轴向爬行速度、径向起伏泵水速率、径向起伏泵水效率、轴向爬行时间和头尾对调次数均高于其他时间段,头尾对调一次的时间均有短于其他时间段的趋势;T1和T4时间段内的所有运动指标均无显著差异(p>0.05)。20℃时,双齿围沙蚕在T3时间段比T1时间段的径向起伏频率和泵水速率的增幅均高于15℃和25℃时。同一时间段内,双齿围沙蚕径向起伏时间的最大值和轴向爬行时间的最小值均出现在20℃。15℃和20℃时,双齿围沙蚕在T1和T3时间段内的轴向爬行速度均无显著差异(p>0.05)。但是在25℃时,T3时间段内双齿围沙蚕的轴向爬行速度显著高于T1时间段(p<0.05)。结果表明,双齿围沙蚕的运动强度随温度升高而增强,在水温为20℃时,其在沉积物中的运动状态较佳。退潮后双齿围沙蚕轴向爬行运动较为缓慢;刚涨潮时,双齿围沙蚕的运动强度显著增加;涨潮30 min后,双齿围沙蚕的运动逐渐恢复到与退潮前相近的状态。双齿围沙蚕可以通过一系列运动行为应对潮汐更替产生的不利条件。Abstract: Tidal replacement has a significant impact on the physiology and behavior of intertidal organisms. Infauna can establish a suitable microenvironment to adapt to intertidal environment through the behavioral process. In this experiment, the behavioral response of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube to tidal alternation were studied by behavioral observation device. Three temperature grades (15℃, 20℃ and 25℃) and four time periods (T1: before ebb tide, T2: after ebb tide, T3: within 30 minutes after rising tide and T4: 30 minutes after rising tide) were set up for the experiment, with six replications for each experimental group. The results showed that at the same time period, the radial undulation frequency, radial undulation pumping rate, axial crawling velocity and the frequency of head-tail exchange of P. aibuhitensis Grube tended to increase with the increase of temperature, while the time of head-tail exchange tended to decrease. At the same temperature, the radial undulation frequency, axial crawling velocity, radial undulation pumping rate, radial undulation pumping efficiency, axial crawling time and the frequency of head-tail exchange of P. aibuhitensis Grube in T3 were higher than those of other time periods, while the time of one head-tail exchange was lower. There was no significant difference in all behavioral indexes between T1 and T4 (p>0.05). At 20℃, the radial undulation frequency and pumping rate of P. aibuhitensis Grube in T3 were higher than T1. At the same time period, the radial undulation time and axial crawling time of P. aibuhitensis Grube were at the maximum and minimum at 20℃, respectively. There was no significant difference in axial crawling velocity of P. aibuhitensis Grube at 15℃ and 20℃ in T1 and T3. However, at 25℃, the axial crawling velocity in T3 was significantly higher than T1 (p<0.05). The results indicate that the motion intensity of P. aibuhitensis Grube increased with the increase of temperature. The motion state of P. aibuhitensis Grube was better at 20℃. After ebb tide, it is an important time for P. aibuhitensis Grube to forage for sediment, and its axial crawling motion is relatively slow. At the beginning of the rising tide, the motion intensity of P. aibuhitensis Grube increased significantly. 30 minutes after the rising tide, the motion of P. aibuhitensis Grube gradually returns to a state similar to that before the ebb tide. P. aibuhitensis Grube can deal with the adverse effects of tidal replacement through a series of behaviors.
-
Key words:
- infauna /
- polychaete /
- behavior /
- tidal replacement /
- bioturbation
-
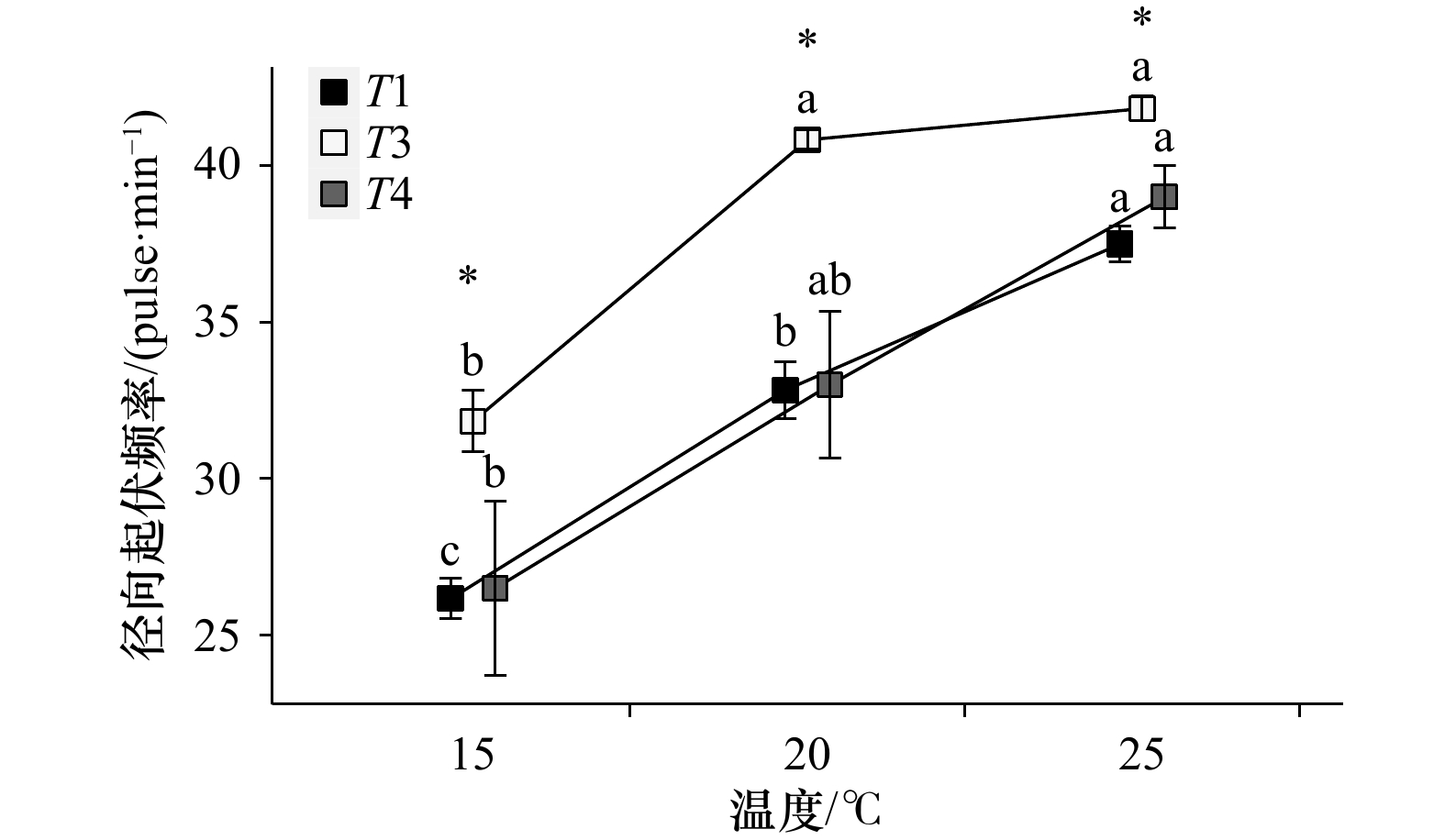
图 1 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕径向起伏频率的影响
图中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);*代表同一温度不同时间段间存在显著差异(p<0.05);T1、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后3个时间段;误差棒的长度代表标准误差(SE)的大小
Fig. 1 The influence of temperature and time periods on the radial undulating frequency of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
Data with different letters are significantly different among different temperature at the same time period (p<0.05); data with * are significantly different among different time periods at the same temperature (p<0.05); T1, T3 and T4 represent before ebb tide, within 30 min after rising tide and 30 min after rising tide respectively; error bars represent 1 SE
图 2 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕轴向爬行速度的影响
图中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);*代表同一温度不同时间段间存在显著差异(p<0.05);T1、T2、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、退潮后、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后4个时间段;误差棒的长度代表标准误差(SE)的大小
Fig. 2 The influence of temperature and time periods on the axial crawling velocity of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
Data with different letters are significantly different among different temperature at the same time period (p<0.05); data with * are significantly different among different time periods at the same temperature (p<0.05); T1, T2, T3 and T4 represent before ebb tide, after ebb tide, within 30 min after rising tide and 30 min after rising tide respectively; error bars represent 1 SE
图 3 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕径向起伏泵水速率的影响
图中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);T1、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后3个时间段;误差棒的长度代表标准误差(SE)的大小
Fig. 3 The influence of temperature and time periods on the pumping rate of radial undulating motion of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
Data with different letters are significantly different among different temperature at the same time period (p<0.05); T1, T3 and T4 represent before ebb tide, within 30 min after rising tide and 30 min after rising tide respectively; error bars represent 1 SE
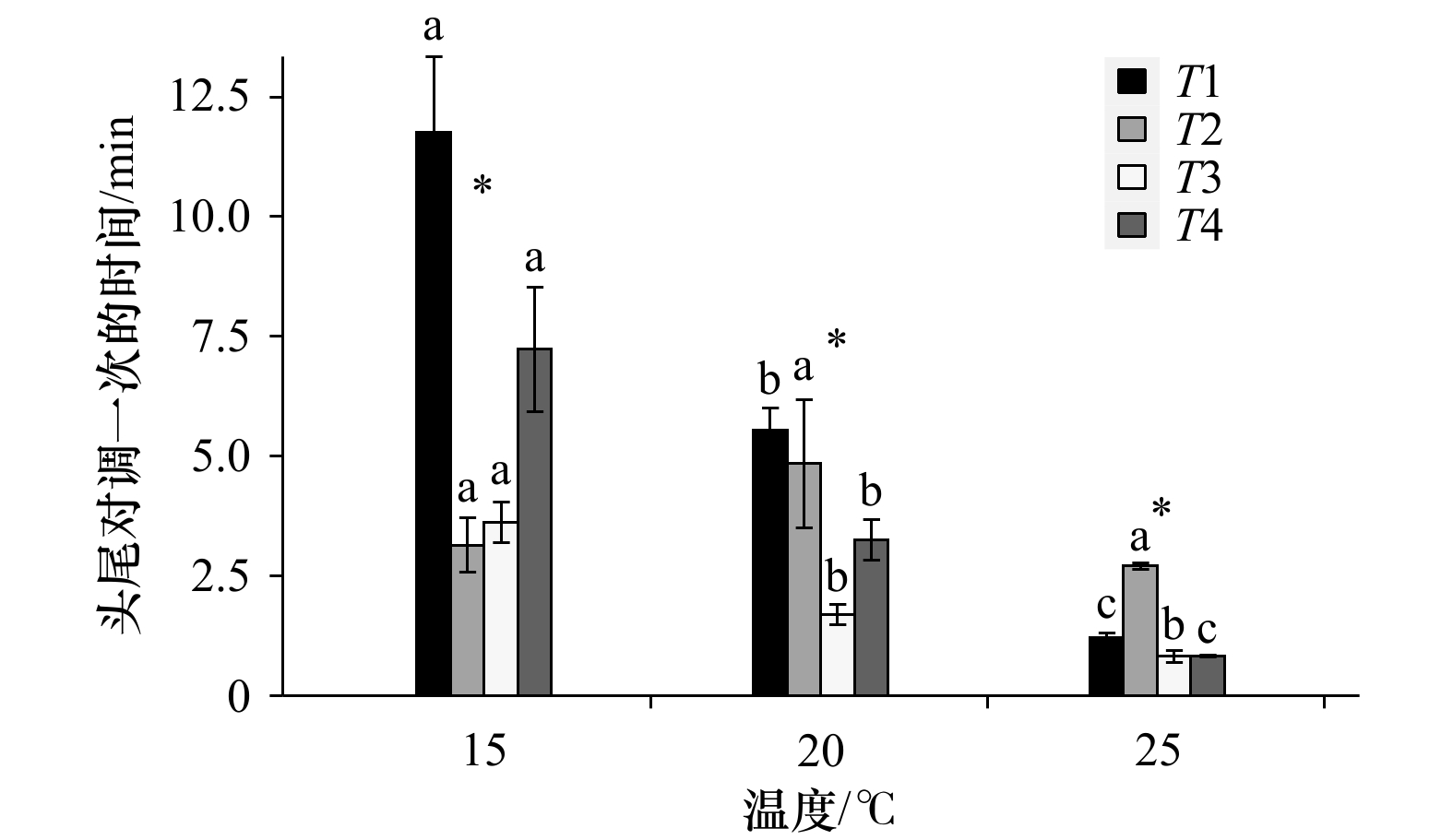
图 4 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕头尾对调一次时间的影响
图中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);*代表同一温度不同时间段间存在显著差异(p<0.05);T1、T2、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、退潮后、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后4个时间段;误差棒的长度代表标准误差(SE)的大小
Fig. 4 The influence of temperature and time periods on the time of head-tail exchange of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
Data with different letters are significantly different among different temperature at the same time period (p<0.05); data with * are significantly different among different time periods at the same temperature (p<0.05); T1, T2, T3 and T4 represent before ebb tide, after ebb tide, within 30 min after rising tide and 30 min after rising tide respectively; error bars represent 1 SE
表 1 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕径向起伏泵水效率(单位:mL/pulse)的影响
Tab. 1 The influence of temperature and time periods on the pumping efficiency (unit: mL/pulse) of radial undulating motion of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
温度/℃ 时间段 T1 T3 T4 15 0.17±0b 0.19±0.01c 0.17±0.02a 20 0.21±0.01a 0.23±0a 0.21±0a 25 0.21±0a 0.21±0b 0.20±0.01a 注:表中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);T1、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后3个时间段。 表 2 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕头尾对调次数的影响
Tab. 2 The influence of temperature and time periods on the frequency of head-tail exchange of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
温度/℃ 时间段 T1 T2 T3 T4 15 0.43±0.13b 0.17±0.07b 1.14±0.26a 0.14±0.09b 20 0.92±0.20b 0.17±0.04b 1.00±0.37a 0.42±0.15ab 25 1.92±0.30a 0.50±0.11a 1.17±0.31a 1.17±0.33a 注:表中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);T1、T2、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、退潮后、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后4个时间段。 表 3 温度和时间段对双齿围沙蚕运动时间(单位:min)的影响
Tab. 3 The influence of temperature and time periods on motion time (unit: min) of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube
运动类型 温度/℃ 时间段 T1 T2 T3 T4 径向起伏 15 13.79±1.68b − 13.00±2.23b 14.49±2.05a 20 25.01±1.22a − 22.92±0.71a 21.66±2.19a 25 20.12±3.60ab − 19.08±1.24a 17.51±1.60a 轴向爬行 15 11.80±1.96ab 10.64±1.03a 21.44±2.23a 12.07±0.80a 20 6.83±0.73b 3.67±0.46b 15.36±1.86a 12.21±1.85a 25 14.09±0.46a 9.50±2.00a 17.84±2.20a 15.83±0.39a 注:表中不同字母代表同一时间段不同温度间差异显著(p<0.05);T1、T2、T3和T4分别代表退潮前、退潮后、涨潮30 min内和涨潮30 min后4个时间段;在干露状态时(T2),双齿围沙蚕无径向起伏运动,因此−代表无数据。 -
[1] 朱明远, 杨宇, 吴宝铃. 温度和月相对多齿围沙蚕的群浮诱导[J]. 动物学报, 1993, 39(2): 222−225. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-7302.1993.02.021Zhu Mingyuan, Yang Yu, Wu Baoling. Induction of swarming of Perinereis nuntia savigny by temperature and lunar timing[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 1993, 39(2): 222−225. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-7302.1993.02.021 [2] Marinelli R L. Effects of burrow ventilation on activities of a terebellid polychaete and silicate removal from sediment pore waters[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1994, 39(2): 303−317. doi: 10.4319/lo.1994.39.2.0303 [3] 郑忠明, 顾小英, 蒋霞敏, 等. 若干生态因子对双齿围沙蚕生长发育的影响[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2000, 19(4): 378−380, 387.Zheng Zhongming, Gu Xiaoying, Jiang Xiamin, et al. Effects of several ecological factors on the growth of Perineries aibuhitensis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2000, 19(4): 378−380, 387. [4] Lohrer A M, Thrush S F, Gibbs M M. Bioturbators enhance ecosystem function through complex biogeochemical interactions[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7012): 1092−1095. doi: 10.1038/nature03042 [5] 徐孟飘, 东培华, 马骏, 等. 大小潮作用对潮滩沉积物层理影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(10): 70−80.Xu Mengpiao, Dong Peihua, Ma Jun, et al. The effects of spring-neap tide on sediment bedding on tidal flats: a numerical study[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(10): 70−80. [6] 褚言皓, 吴文娟, 李鹏, 等. 黄河口悬浮泥沙时空动态及其驱动机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(6): 150−163. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2022059Chu Yanhao, Wu Wenjuan, Li Peng, et al. Temporal and spatial dynamics of suspended sediment and its driving mechanism in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(6): 150−163. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2022059 [7] Koo B J, Kwon K K, Hyun J H. Effect of environmental conditions on variation in the sediment-water interface created by complex macrofaunal burrows on a tidal flat[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2007, 58(4): 302−312. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2007.07.002 [8] Seo J, Koo B J. Spring-neap variation on sediment reworking with organic matter contents by a polychaete, Perinereis aibuhitensis, in the intertidal sediments of the Gomso Bay, Korea[J]. Marine Biology, 2019, 166(10): 124. doi: 10.1007/s00227-019-3572-7 [9] Esselink P, Zwarts L. Seasonal trend in burrow depth and tidal variation in feeding activity of Nereis diversicolor[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1989, 56(3): 243−254. [10] Riisgård H U, Larsen P S. Water pumping and analysis of flow in burrowing zoobenthos: an overview[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 2005, 39(2): 237−258. doi: 10.1007/s10452-004-1916-x [11] 孙瑞平, 杨德渐. 中国动物志: 无脊椎动物. 第三十三卷: 环节动物门: 多毛纲(二): 沙蚕目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 180−183.Sun Ruiping, Yang Dejian. Fauna Sinica. Invertebrata 33. Annelida. Polychaeta II. Neridida[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 180−183. [12] 房景辉, 孟珊, 袁伟, 等. 温度对不同规格双齿围沙蚕运动行为特征的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(10): 1251−1262.Fang Jinghui, Meng Shan, Yuan Wei, et al. Effects of temperature on the motion behavior of Perinereis aibuhitensis of different sizes[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(10): 1251−1262. [13] Fang Jinghui, Zhang Jihong, Jiang Zengjie, et al. Environmental remediation potential of Perinereis aibuhitensis (Polychaeta) based on the effects of temperature and feed types on its carbon and nitrogen budgets[J]. Marine Biology Research, 2016, 12(6): 583−594. doi: 10.1080/17451000.2016.1177653 [14] 刘毅, 张继红, 吴文广, 等. 不同温度条件下黑足鲍干露耐受能力和生化响应的模拟研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 2020, 27(11): 1316−1324.Liu Yi, Zhang Jihong, Wu Wenguang, et al. Dry exposure stress tolerance and physiological response of black abalone Haliotis iris at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2020, 27(11): 1316−1324. [15] 王玲, 陈爱华, 赵啸, 等. 温度和体重对双齿围沙蚕呼吸和排泄的影响[J]. 大连水产学院学报, 2004, 19(3): 176−181.Wang Ling, Chen Aihua, Zhao Xiao, et al. Effect of temperature and body weight on respiration and excretion in Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 2004, 19(3): 176−181. [16] 潘洋. 刺参运动节律行为的数量化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2015.Pan Yang. Quantitative research on motor behavioral rhythms of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka)[D]. Qingdao: The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [17] 陈松波. 不同温度条件下鲤鱼摄食节律与呼吸代谢的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2004.Chen Songbo. Studies on feeding rhythm and respiratory metabolism of common carp at different temperature[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2004. [18] 张倩. 水流、水温及体重对团头鲂(Megalobrama amblycephala)幼鱼游泳行为及标准代谢的影响[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2013.Zhang Qian. Effects of water flow, water temperature and body weight on swimming behavior and standard metabolism of juvenile fish of Megalobrama amblycephala[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2013. [19] 李信书, 彭永兴, 阎斌伦, 等. 不同水交换条件对双齿围沙蚕生长的影响[J]. 水产养殖, 2006, 27(6): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2006.06.001Li Xinshu, Peng Yongxing, Yan Binlun, et al. Effects of exchange model of water on the growth of Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 2006, 27(6): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2006.06.001 [20] 冯善聪, 黄国强, 赖祖鹏, 等. 双齿围沙蚕对温度、盐度和干露的耐受性研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2014, 36(1): 109−114.Feng Shancong, Huang Guoqiang, Lai Zupeng, et al. Tolerance studies on the temperature, salinity and desiccation in Perinereis aibuhitensis[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2014, 36(1): 109−114. [21] 孟珊. 双齿围沙蚕应对典型环境变化的行为特征[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2020.Meng Shan. Behavior characteristics of Perinereis aibuhitensis in response to the changes of typical environment[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2020. [22] 尚玉昌. 动物行为学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2005.Shang Yuchang. Animal Behavior[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2005. [23] Kristensen E, Kostka J E. Macrofaunal burrows and irrigation in marine sediment: microbiological and biogeochemical interactions[M]//Kristensen E, Haese R R, Kostka J E. Interactions Between Macro- and Microorganisms in Marine Sediments. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2005: 125−57. -




 下载:
下载: