Differences of eDNA metabarcoding fragments in relative fish species resolution
-
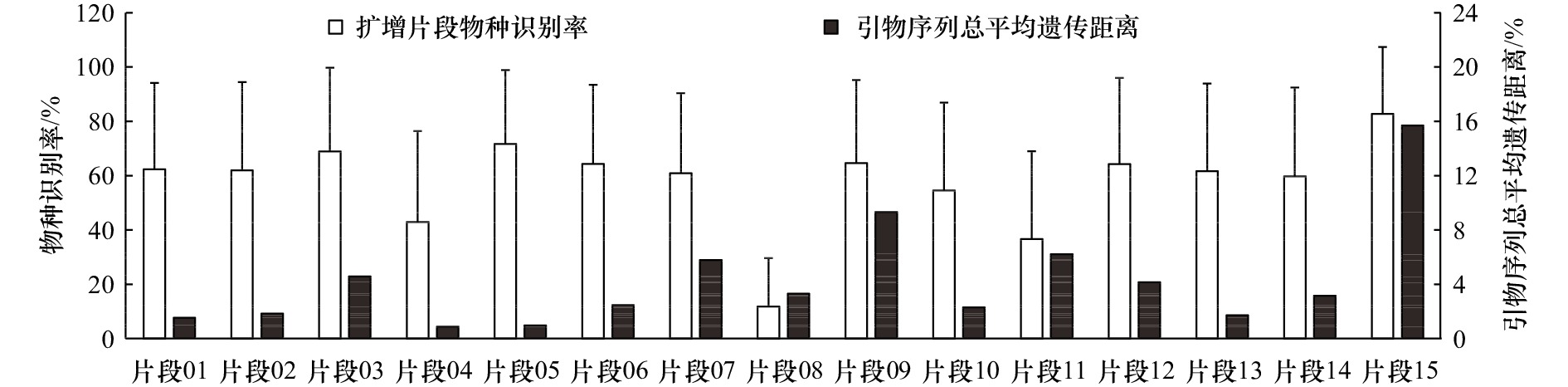
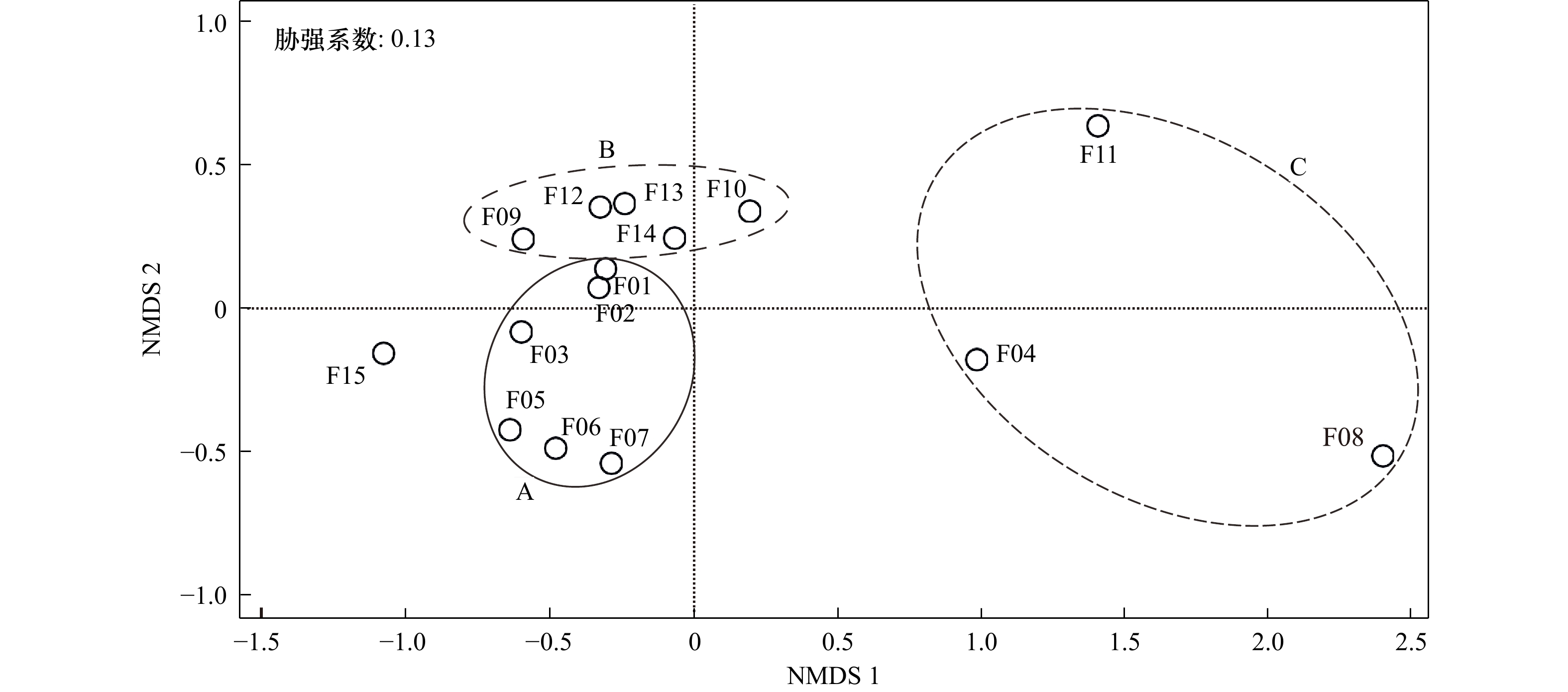
摘要: 已知的鱼类环境DNA(eDNA)metabarcoding片段均未被针对性考察其对近缘物种的适用性,实际使用过程中存在“物种丢失”风险。为筛选出物种识别率最高的片段,本研究比较了15个主流片段对106属(共935种)鱼类的识别差异。研究结果如下:(1)蛋白质编码基因(COI,片段15)的物种识别率最高,但其引物通用性最差;片段09、片段11、片段07、片段03、片段12的引物序列总平均遗传距离也较大,均存在eDNA低效扩增的风险;(2)片段长度影响物种识别率,核糖体基因中片段05、片段06、片段01、片段02及片段13的物种识别率较高;(3)非度量多维尺度分析(NMDS)显示,不同基因、同一基因不同片段的识别结果存在较大差异,应考虑多片段、多基因组合应用;片段01与片段02、片段05与片段06等在NMDS图上距离较近,存在相互替代性;(4)物种类群影响识别结果,eDNA研究仍需要进一步开发高识别率片段。综合物种识别率、引物通用性、NMDS分析等多方面因素,本研究推荐2×150 bp测序平台使用片段01(MiFish-U)、2×250 bp测序平台使用片段05(Ac12S),辅以片段13(Vert-16S-eDNA)等进行近缘鱼类多样性调查。本研究旨在为提高鱼类eDNA调查结果准确性提供一定技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 环境DNA metabarcoding /
- 近缘鱼类识别 /
- 12S /
- 扩增长度 /
- 多片段
Abstract: The applicability of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding fragments to relative fish species had not been compared. There was a risk of “species loss” in diversity surveys. In order to screen out the best fragments, we compared the resolution rate differences of 15 eDNA metabarcoding fragments in 106 genera (a total of 935 species). The results were as follows: (1) the protein-coding gene (COI, fragment 15) had the highest resolution rate, but the universality of its corresponding primer pairs was the worst; the overall mean distance based on primer pair sequence of fragment 09, fragment 11, fragment 07, fragment 03 and fragment 12 were obviously large, suggesting their eDNA amplification efficiency were possibly low. (2) The resolution rates were significantly affected by the length of fragments, and the fragment 05, fragment 06, fragment 01, fragment 02 and fragment 13 of ribosomal genes had a higher resolution rate except fragment 15. (3) Non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis (NMDS) showed that there were great differences among different genes and different fragments belonging to the same gene. Therefore, the combination application of multi-fragment and multi-gene should be considered; besides, fragment 01 and fragment 02, and fragment 05 and fragment 06 were close to each other in the NMDS plot. They function of fish resolution were overlapped. (4) Species groups affected the resolution results, and eDNA studies stilled need to develop fragments with higher resolution rates. Based on the resolution rate of relative species, the universality of primer pairs and NMDS analysis, this study recommended fragment 01 (Mifish-U) for 2×150 bp sequencing platform and fragment 05 (Ac12S) for 2×250 bp sequencing platform, supplemented by fragment 13 (Vert-16S-eDNA) to investigate the diversity of relative fish. This study provided some support for improving the accuracy of fish eDNA survey results.-
Key words:
- eDNA metabarcoding /
- relative fish species resolution /
- 12S /
- amplicon length /
- multi-fragments
-
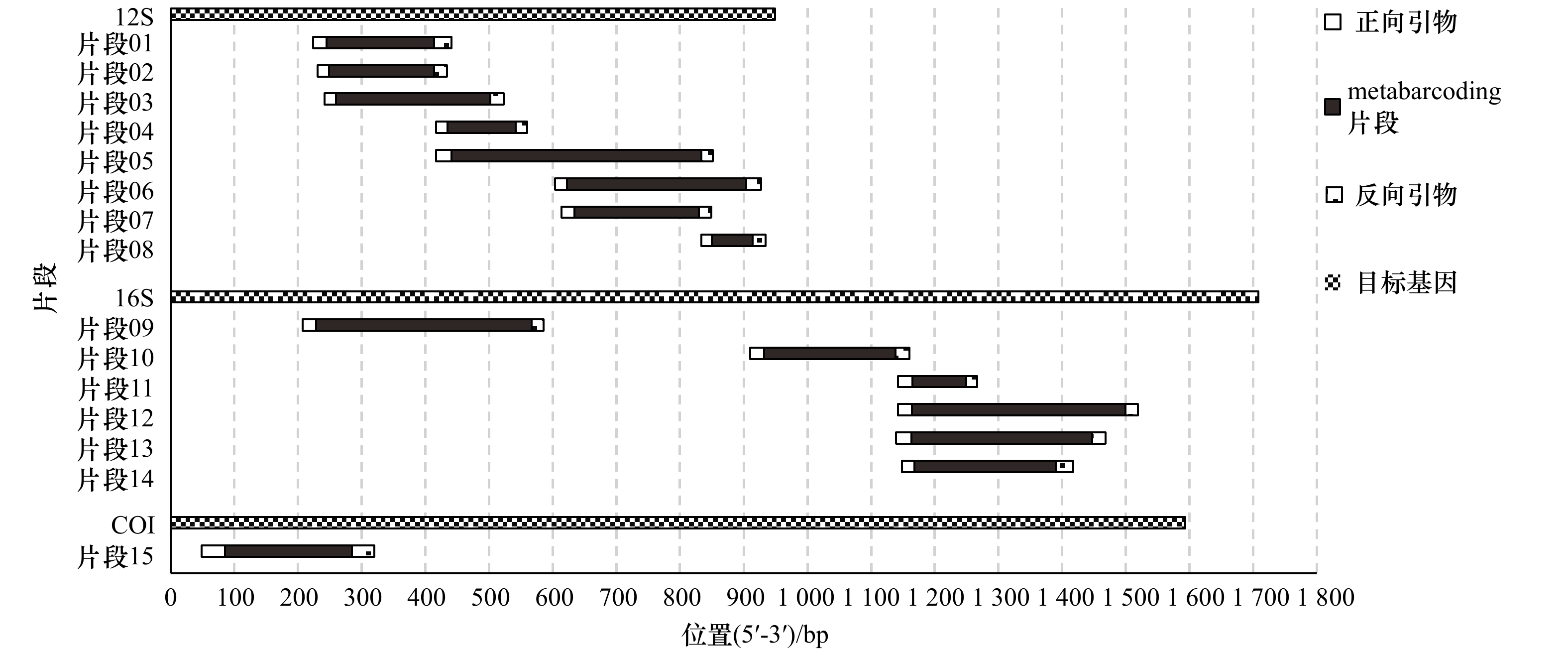
图 1 本研究中15个鱼类eDNA metabarcoding片段和对应引物在目标基因上的位置
以花鳗鲡(Anguilla marmorata)线粒体基因序列(GenBank登录号:NC006540)为标注模板
Fig. 1 Locations of the 15 fish eDNA metabarcoding fragments and primer pairs on the target mitochondrial genes
Sequence of the marbled eel (Anguilla marmorata) (GenBank accession number: NC006540) was used as template
表 1 本研究中15个鱼类eDNA metabarcoding片段简介
Tab. 1 Summary of 15 fish eDNA metabarcoding fragments analyzed in this study
metabarcoding片段 对应引物名称 目标基因 长度/bp 引物序列(5'-3') 设计者 片段01 MiFish-U 12S 169 For-GTCGGTAAAACTCGTGCCAGC Miya等[4] Rev-CATAGTGGGGTATCTAATCCCAGTTTG 片段02 Tele02 12S 165 For-AAACTCGTGCCAGCCACC Taberlet等[16] Rev-GGGTATCTAATCCCAGTTTG 片段03 Am12S 12S 242 For-AGCCACCGCGGTTATACG Evans等[17] Rev-CAAGTCCTTTGGGTTTTAAGC 片段04 12S-V5 12S 107 For-ACTGGGATTAGATACCCC Riaz等[18] Rev-TAGAACAGGCTCCTCTAG 片段05 Ac12S 12S 392 For-ACTGGGATTAGATACCCCACTATG Evans等[17] Rev-GAGAGTGACGGGCGGTGT 片段06 AcMDB07 12S 282 For-GCCTATATACCGCCGTCG Bylemans等[19] Rev-GTACACTTACCATGTTACGACTT 片段07 NeoFish_3 12S 196 For-CGCCGTCGCAAGCTTACCCT Milan等[20] Rev-AGTGACGGGCGGTGTGTGC 片段08 Tele01 12S 64 For-ACACCGCCCGTCACTCT Valentini等[8] Rev-CTTCCGGTACACTTACCATG 片段09 Ac16S 16S 339 For-CCTTTTGCATCATGATTTAGC Evans等[[17] Rev-CAGGTGGCTGCTTTTAGGC 片段10 L2513/H2714 16S 206 For-GCCTGTTTACCAAAAACATCAC Kitano等[21] Rev-CTCCATAGGGTCTTCTCGTCTT 片段11 Fish16S 16S 84 For-CGAGAAGACCCTWTGGAGCTTIAG Shaw等[22] Rev-GGTCGCCCCAACCRAAG 片段12 Ve16S 16S 335 For-CGAGAAGACCCTATGGAGCTTA Evans等[17] Rev-AATCGTTGAACAAACGAACC 片段13 Vert-16S-eDNA 16S 284 For-AGACGAGAAGACCCYDTGGAGCTT Vences等[5] Rev-GATCCAACATCGAGGTCGTAA 片段14 Fish16S F/D-2R 16S 222 For-GACCCTATGGAGCTTTAGAC DiBattista等[23] Rev-CGCTGTTATCCCTADRGTAACT 片段15 PS1 COI 199 For-ACCTGCCTGCCGTATTTGGYGCYTGRGCCGGRATAGT Balasingham等[6] Rev-ACGCCACCGAGCCARAARCTYATRTTRTTYATTCG 注:片段长度以花鳗鲡(Anguilla marmorata)(GenBank登录号:NC006540)为参考。 表 2 metabarcoding片段对各类群的识别率
Tab. 2 The species resolution rates of metabarcoding fragments for different groups
物种类群 物种数 识别率/% 片段 01 片段 02 片段 03 片段 04 片段 05 片段 06 片段 07 片段 08 片段 09 片段 10 片段 11 片段12 片段 13 片段 14 片段15 全部片段 鱊属 Acheilognathus 14 71.43 71.43 85.71 71.43 85.71 85.71 71.43 57.14 71.43 85.71 57.14 85.71 85.71 71.43 100 77.14±11.83 鲟属 Acipenser 15 13.33 20 26.67 13.33 46.67 33.33 40 6.67 33.33 0 33.33 6.67 13.33 6.67 73.33 24.44± 19.46 光唇鱼属 Acrossocheilus 16 56.25 50 62.5 50 87.5 75 62.5 6.25 68.75 43.75 50 62.5 50 43.75 100 57.92± 21.45 黑头鱼属 Alepocephalus 7 57.14 14.29 28.57 0 28.57 28.57 28.57 0 28.57 14.29 14.29 28.57 42.86 28.57 100 29.52± 24.43 西鲱属 Alosa 6 50 0 0 0 33.33 33.33 33.33 0 0 66.67 16.67 16.67 16.67 16.67 100 25.56± 28.78 双锯鱼属 Amphiprion 10 70 50 60 20 60 50 30 10 60 60 30 80 60 50 40 48.67± 19.22 鳗鲡属 Anguilla 17 29.41 35.29 64.71 0 76.47 70.59 76.47 41.18 64.71 47.06 35.29 76.47 64.71 52.94 88.24 54.9± 23.5 细鲫属 Aphyocypris 5 60 60 60 20 60 40 40 0 100 80 60 100 80 100 100 64± 30.43 旗鳉属 Aphyosemion 8 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 12.5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 94.17± 22.59 深海鳐属 Bathyraja 8 12.5 25 50 12.5 25 12.5 12.5 0 12.5 12.5 0 25 25 37.5 50 20.83±15.43 鲫属 Carassius 5 0 0 0 0 60 20 20 0 60 40 0 40 0 0 60 20±25.07 真鲨属 Carcharhinus 14 64.29 71.43 100 78.57 100 100 100 50 85.71 35.71 14.29 50 64.29 71.43 100 72.38±26.57 刺尻鱼属 Centropyge 16 75 75 87.5 31.25 62.5 56.25 62.5 12.5 87.5 37.5 0 50 50 62.5 100 56.67±27.8 九棘鲈属 Cephalopholis 5 100 100 100 40 100 60 60 0 40 40 60 100 100 100 100 73.33±32.66 鳢属 Channa 8 62.5 62.5 62.5 62.5 62.5 62.5 62.5 25 75 75 75 75 75 75 50 64.17±13.25 红鳍鲌属 Chanodichthys 5 20 20 20 20 60 60 0 0 100 60 0 100 60 60 100 45.33±36.62 燕鳐属 Cheilopogon 8 37.5 37.5 25 0 25 50 50 0 62.5 25 12.5 12.5 25 12.5 75 30±22.06 鲮属 Cirrhinus 5 60 60 60 40 100 100 100 0 60 60 20 60 40 40 60 57.33±28.15 胡子鲇属 Clarias 6 66.67 16.67 33.33 33.33 83.33 33.33 33.33 0 66.67 33.33 0 66.67 66.67 33.33 100 44.44±29.32 花鳅属 Cobitis 11 81.82 81.82 81.82 81.82 72.73 81.82 81.82 9.09 63.64 81.82 63.64 81.82 81.82 81.82 100 75.15±20.17 鲚属 Coilia 6 16.67 50 50 16.67 66.67 100 66.67 0 50 66.67 33.33 33.33 16.67 16.67 100 45.56±30.52 白鲑属 Coregonus 14 7.14 7.14 0 0 21.43 35.71 21.43 7.14 0 0 0 0 0 0 7.14 7.14±10.8 兵鲶属 Corydoras 6 33.33 33.33 33.33 16.67 50 50 66.67 16.67 50 50 16.67 0 0 0 66.67 32.22±23.12 杜父鱼属 Cottus 12 50 75 100 50 83.33 50 41.67 8.33 83.33 83.33 41.67 83.33 66.67 100 100 67.78±26.7 舌鳎属 Cynoglossus 12 100 100 100 83.33 100 100 100 83.33 100 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 100 92.22±8.61 长吻鳐属 Dipturus 8 0 12.5 37.5 12.5 50 37.5 37.5 0 50 12.5 0 25 25 25 62.5 25.83±19.75 盘属 Discogobio 5 40 40 60 40 60 40 60 0 20 40 0 40 60 40 60 40±20 塘鳢属 Eleotris 6 66.67 66.67 100 100 100 100 100 0 100 100 66.67 66.67 66.67 66.67 100 80±27.6 Enteromius属 5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 40 100 100 100 100 80 100 100 94.67±15.98 石斑鱼属 Epinephelus 22 90.91 90.91 90.91 50 90.91 90.91 90.91 36.36 72.73 90.91 22.73 81.82 68.18 63.64 90.91 74.85±22.52 扁鳉属 Epiplatys 7 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 0 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 71.43 66.67±18.44 镖鲈属 Etheostoma 10 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 40 100 70 90 100 100 100 100 93.33±16.76 底鳄鳉属 Fundulopanchax 5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 20 100 100 60 100 100 100 100 92±22.42 底鳉属 Fundulus 5 60 60 60 20 100 100 100 0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 80±32.95 南乳鱼属 Galaxias 5 100 100 100 60 100 100 100 0 100 60 60 100 100 100 100 85.33±28.75 墨头鱼属 Garra 10 100 100 100 50 100 100 100 30 80 100 50 100 100 100 100 87.33±23.74 骨尾鱼属 Gila 5 40 20 60 20 60 40 40 0 60 60 20 60 60 60 100 46.67±24.69 露齿鲨属 Glyphis 8 25 12.5 25 0 37.5 37.5 37.5 0 25 25 25 25 25 37.5 25 24.17±12.01 纹胸属 Glyptothorax 11 18.18 18.18 63.64 18.18 36.36 27.27 36.36 9.09 54.55 9.09 27.27 54.55 54.55 63.64 81.82 38.18±22.59 颌须属 Gnathopogon 6 33.33 66.67 100 100 100 66.67 66.67 0 100 50 16.67 33.33 33.33 33.33 66.67 57.78±32.65 鳅鮀属 Gobiobotia 6 100 50 100 50 100 100 100 0 66.67 66.67 16.67 83.33 83.33 66.67 100 72.22±31.91 裸鲤属 Gymnocypris 8 37.5 37.5 37.5 0 12.5 12.5 0 0 12.5 37.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 0 25 16.67±14.69 海猪鱼属 Halichoeres 5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 20 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 94.67±20.66 鳠属 Hemibagrus 5 60 60 60 80 60 40 60 0 60 60 20 60 60 60 60 53.33±19.52 䱻属 Hemibarbus 7 42.86 42.86 42.86 28.57 42.86 28.57 14.29 0 42.86 28.57 14.29 42.86 42.86 42.86 100 37.14±22.13 海马属 Hippocampus 18 88.89 88.89 88.89 55.56 66.67 66.67 61.11 27.78 100 77.78 55.56 100 100 100 100 78.52±22.11 刺蝶鱼属 Holacanthus 5 40 40 60 40 60 60 60 0 40 20 20 40 40 40 60 41.33±17.67 下鱵属 Hyporhamphus 5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 40 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 96±15.49 野鲮属 Labeo 20 70 70 80 35 90 80 75 10 60 30 25 55 40 50 80 56.67±24.1 兔头鲀属 Lagocephalus 8 100 100 100 75 100 100 100 25 100 75 75 62.5 75 62.5 100 83.33±21.99 太阳鱼属 Lepomis 6 100 100 100 50 100 100 100 0 100 100 66.67 100 100 100 100 87.78±28.5 薄鳅属 Leptobotia 6 50 16.67 66.67 50 66.67 50 33.33 0 33.33 16.67 50 33.33 33.33 33.33 50 38.89±18.55 䱀属 Liobagrus 9 66.67 77.78 77.78 11.11 77.78 55.56 66.67 0 33.33 33.33 33.33 100 100 100 77.78 60.74±31.95 笛鲷属 Lutjanus 13 84.62 84.62 100 100 100 100 84.62 23.08 100 69.23 30.77 100 100 100 100 85.13±25.42 狼绵鳚属 Lycodes 5 60 60 60 40 60 60 60 0 100 40 20 60 60 60 100 56±25.3 虹银汉鱼属 Melanotaenia 6 100 100 50 0 66.67 33.33 33.33 0 66.67 0 50 33.33 100 66.67 100 53.33±36.84 小鳔属 Microphysogobio 14 64.29 64.29 85.71 64.29 71.43 50 35.71 7.14 85.71 35.71 35.71 57.14 71.43 57.14 100 59.05±23.76 泥鳅属 Misgurnus 5 100 100 100 20 60 60 40 0 60 60 0 60 100 60 100 61.33±35.02 假鳃鳉属 Nothobranchius 8 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 12.5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 94.17±22.59 美洲鱥属 Notropis 10 100 80 100 60 100 100 80 10 100 60 70 100 100 100 100 84±25.58 沙塘鳢属 Odontobutis 6 100 100 100 100 100 100 66.67 33.33 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 93.33±18.69 太平洋鲑属 Oncorhynchus 8 37.5 62.5 100 37.5 100 75 75 0 37.5 0 0 50 50 50 100 51.67±34.68 白甲鱼属 Onychostoma 11 81.82 63.64 45.45 18.18 63.64 63.64 54.55 27.27 54.55 72.73 0 81.82 54.55 45.45 63.64 52.73±22.85 马口鱼属 Opsariichthys 5 100 120 100 40 60 60 20 0 60 60 40 100 100 100 100 70.67±35.35 罗非鱼属 Oreochromis 9 66.67 66.67 66.67 33.33 44.44 11.11 44.44 0 55.56 22.22 22.22 44.44 33.33 22.22 77.78 40.74±22.88 青鳉属 Oryzias 10 80 80 80 80 80 80 80 80 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 89.33±10.33 纹唇鱼属 Osteochilus 5 80 100 100 80 100 100 100 0 100 100 80 100 100 100 100 89.33±26.04 鲳属 Pampus 7 28.57 57.14 28.57 14.29 28.57 28.57 28.57 0 28.57 28.57 14.29 14.29 14.29 14.29 42.86 24.76±13.73 属 Pareuchiloglanis 5 60 60 60 20 60 100 60 0 60 100 60 60 60 60 100 61.33±26.69 鱥属 Phoxinus 7 100 100 100 57.14 100 71.43 71.43 0 71.43 71.43 14.29 100 100 100 100 77.14±32.31 花鳉属 Poecilia 5 20 20 20 20 60 20 40 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 60 26.67±14.47 多鳍鱼属 Polypterus 10 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 40 100 80 60 100 100 100 100 92±18.21 原唇齿脂鲤属 Prochilodus 5 20 20 20 0 20 0 40 0 0 0 0 40 40 40 20 17.33±16.68 拟鲿属 Pseudobagrus 12 41.67 58.33 75 33.33 58.33 58.33 58.33 16.67 66.67 8.33 8.33 33.33 25 25 83.33 43.33±24.03 拟腹吸鳅属 Pseudogastromyzon 9 33.33 55.56 55.56 0 55.56 55.56 55.56 0 77.78 55.56 44.44 100 77.78 55.56 77.78 53.34±26.96 多刺鱼属 Pungitius 7 71.43 100 100 28.57 100 57.14 57.14 0 28.57 28.57 0 71.43 71.43 42.86 100 57.14±34.99 鳐属 Raja 6 16.67 16.67 33.33 16.67 66.67 16.67 16.67 0 50 66.67 16.67 66.67 66.67 66.67 66.67 38.89±25.72 波鱼属 Rasbora 7 100 100 100 71.43 100 71.43 100 14.29 71.43 100 57.14 71.43 71.43 71.43 100 80±24.03 吻鰕虎鱼属 Rhinogobius 5 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 93.33±25.82 鳑鲏属 Rhodeus 10 80 80 80 30 80 80 60 20 100 80 50 100 100 80 100 74.67±24.75 红点鲑属 Salvelinus 12 8.33 8.33 25 8.33 25 25 25 0 16.67 8.33 0 8.33 0 8.33 58.33 15±15.17 鳈属 Sarcocheilichthys 9 55.56 44.44 55.56 11.11 55.56 55.56 33.33 0 55.56 33.33 0 44.44 33.33 44.44 55.56 38.52±20.08 沙丁鱼属 Sardinella 6 100 100 100 66.67 100 50 66.67 33.33 50 66.67 66.67 100 100 66.67 100 77.78±23.29 蛇属 Saurogobio 7 100 100 100 71.43 100 71.43 71.43 0 71.43 71.43 14.29 100 100 100 100 78.1±31.88 南鳅属 Schistura 11 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 54.55 100 100 63.64 100 100 100 100 94.55±14.5 裸裂尻鱼属 Schizopygopsis 7 14.29 14.29 14.29 0 14.29 28.57 14.29 0 28.57 0 0 42.86 42.86 42.86 71.43 21.91±20.82 裂腹鱼属 Schizothorax 26 11.54 11.54 15.38 7.69 23.08 23.08 11.54 3.85 15.38 7.69 0 11.54 3.85 11.54 30.77 12.56±8.15 马鲛鱼属 Scomberomorus 6 66.67 66.67 66.67 33.33 66.67 66.67 66.67 33.33 100 66.67 100 66.67 66.67 66.67 100 68.89±19.79 平鲉属 Sebastes 19 31.58 31.58 31.58 10.53 36.84 47.37 26.32 0 10.53 15.79 0 26.32 15.79 15.79 68.42 24.56±18.09 瓢鳍虾虎鱼属 Sicyopterus 18 33.33 33.33 44.44 22.22 50 66.67 50 33.33 83.33 33.33 33.33 66.67 55.56 66.67 88.89 50.74±20.13 篮子鱼属 Siganus 6 33.33 33.33 33.33 16.67 100 66.67 66.67 0 66.67 16.67 0 16.67 0 0 33.33 32.22±30.52 鱚属 Sillago 6 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 50 100 100 66.67 100 100 100 100 94.44±15 鲶属 Silurus 6 66.67 66.67 66.67 50 100 100 66.67 16.67 66.67 50 50 66.67 66.67 100 100 68.89±23.46 鳜属 Siniperca 7 57.14 42.86 100 28.57 42.86 28.57 28.57 0 42.86 28.57 14.29 14.29 14.29 14.29 28.57 32.38±23.82 金线鲃属 Sinocyclocheilus 14 85.71 85.71 85.71 35.71 78.57 78.57 64.29 28.57 50 57.14 21.43 64.29 57.14 78.57 85.71 63.81±21.84 银属 Squalidus 7 42.86 28.57 57.14 42.86 100 57.14 57.14 14.29 57.14 28.57 14.29 42.86 28.57 28.57 100 46.67±26.16 扁鲨属 Squatina 5 60 60 60 20 60 60 60 0 20 40 40 60 60 60 100 50.67±23.74 疯鲿属 Tachysurus 8 75 75 75 25 100 100 100 0 75 37.5 0 75 50 50 75 60.83±33.03 东方鲀属 Takifugu 16 0 6.25 6.25 6.25 37.5 25 12.5 12.5 12.5 18.75 6.25 31.25 25 31.25 62.5 19.58±16.34 田中鳑鲏属 Tanakia 6 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 16.67 100 100 33.33 100 100 100 100 90±26.58 鲀属 Tetraodon 5 100 100 100 60 60 60 60 0 100 100 0 100 60 60 100 70.67±34.53 棱鳀属 Thryssa 6 100 100 100 66.67 100 100 100 0 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 91.11±26.63 金枪鱼属 Thunnus 9 0 11.11 11.11 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1.48±3.91 茴鱼属 Thymallus 10 20 20 40 0 30 50 20 0 30 20 10 20 30 10 60 24±16.82 结鱼属 Tor 7 71.43 71.43 100 0 71.43 42.86 57.14 0 28.57 57.14 28.57 71.43 57.14 28.57 100 52.38±30.86 高原鳅属 Triplophysa 21 47.62 47.62 80.95 42.86 71.43 71.43 61.9 4.76 66.67 52.38 19.05 47.62 47.62 47.62 80.95 52.7±21.1 全部物种 935 62.3±31.84 61.95±32.54 68.9±30.81 42.92±33.46 71.62±27.3 64.34±29.13 60.89±29.48 11.79±17.79 64.6±30.65 54.58±32.28 36.71±32.27 64.2±31.8 61.6±32.35 59.71±32.78 82.76±24.66 -
[1] 姜维, 赵虎, 邓捷, 等. 环境DNA分析技术—一种水生生物调查新方法[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2016, 37(5): 1−7.Jiang Wei, Zhao Hu, Deng Jie, et al. Detection of aquatic species using environmental DNA[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2016, 37(5): 1−7. [2] 陈炼, 吴琳, 刘燕, 等. 环境DNA metabarcoding及其在生态学研究中的应用[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(15): 4573−4582.Chen Lian, Wu Lin, Liu Yan, et al. Application of environmental DNA metabarcoding in ecology[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(15): 4573−4582. [3] Zhang Shan, Zhao Jindong, Yao Meng. A comprehensive and comparative evaluation of primers for metabarcoding eDNA from fish[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 11(12): 1609−1625. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13485 [4] Miya M, Sato Y, Fukunaga T, et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2015, 2(7): 150088. doi: 10.1098/rsos.150088 [5] Vences M, Lyra M L, Perl R G B, et al. Freshwater vertebrate metabarcoding on Illumina platforms using double-indexed primers of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 2016, 8(3): 323−327. doi: 10.1007/s12686-016-0550-y [6] Balasingham K D, Walter R P, Mandrak N E, et al. Environmental DNA detection of rare and invasive fish species in two Great Lakes tributaries[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2018, 27(1): 112−127. doi: 10.1111/mec.14395 [7] 陈治. 浙江近海鱼类多样性eDNA调查方法的建立与应用[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2019.Chen Zhi. Establishment and application of eDNA method for fish diversity survey around Zhejiang coastal area[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2019. [8] Valentini A, Taberlet P, Miaud C, et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2016, 25(4): 929−942. doi: 10.1111/mec.13428 [9] 程馨雨, 陶捐, 武瑞东, 等. 淡水鱼类功能生态学研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(3): 810−822.Cheng Xinyu, Tao Juan, Wu Ruidong, et al. Functional ecology of freshwater fish: research progress and prospects[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(3): 810−822. [10] 李高俊, 顾党恩, 蔡杏伟, 等. 海南岛“两江一河”淡水土著鱼类的种类组成与分布现状[J]. 淡水渔业, 2020, 50(6): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.06.003Li Gaojun, Gu Dang’en, Cai Xingwei, et al. The species composition and distribution of indigenous freshwater fishes of three main rivers in Hainan Island[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2020, 50(6): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.06.003 [11] 申志新, 李高俊, 蔡杏伟, 等. 海南省淡水野生鱼类多样性演变及保护建议[J]. 中国水产, 2018, 11(6): 56−60.Shen Zhixin, Li Gaojun, Cai Xingwei, et al. The evolution and protection of freshwater fish species in Hainan Province[J]. China Fisheries, 2018, 11(6): 56−60. [12] 魏亚男, 王晓梅, 姚鹏程, 等. 比较不同DNA条形码对中国海岸带耐盐植物的识别率[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(10): 1095−1104. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017164Wei Ya’nan, Wang Xiaomei, Yao Pengcheng, et al. Comparison of species resolution rates of DNA barcoding for Chinese coastal halo-tolerant plants[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2017, 25(10): 1095−1104. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017164 [13] Kruskal J B. Nonmetric multidimensional scaling: a numerical method[J]. Psychometrika, 1964, 29(2): 115−129. doi: 10.1007/BF02289694 [14] Newmaster S G, Fazekas A J, Steeves R A D, et al. Testing candidate plant barcode regions in the Myristicaceae[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2008, 8(3): 480−490. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.02002.x [15] 魏观渊, 黄桂芳. 厦门湾春、秋季鱼类群落结构及其多样性[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(8): 1060−1068.Wei Guanyuan, Huang Guifang. Fish community structure and species diversity during spring and autumn in the Xiamen Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(8): 1060−1068. [16] Taberlet P, Bonin A, Zinger L, et al. Environmental DNA—for Biodiversity Research and Monitoring[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2018: 206. [17] Evans N T, Olds B P, Renshaw M A, et al. Quantification of mesocosm fish and amphibian species diversity via environmental DNA metabarcoding[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2016, 16(1): 29−41. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12433 [18] Riaz T, Shehzad W, Viari A, et al. ecoPrimers: inference of new DNA barcode markers from whole genome sequence analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(21): e145. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr732 [19] Bylemans J, Gleeson D M, Hardy C M, et al. Toward an ecoregion scale evaluation of eDNA metabarcoding primers: a case study for the freshwater fish biodiversity of the Murray-Darling Basin (Australia)[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2018, 8(17): 8697−8712. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4387 [20] Milan D T, Mendes I S, Damasceno J S, et al. New 12S metabarcoding primers for enhanced Neotropical freshwater fish biodiversity assessment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 17966. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74902-3 [21] Kitano T, Umetsu K, Tian Wei, et al. Two universal primer sets for species identification among vertebrates[J]. International Journal of Legal Medicine, 2007, 121(5): 423−427. doi: 10.1007/s00414-006-0113-y [22] Shaw J L A, Clarke L J, Wedderburn S D, et al. Comparison of environmental DNA metabarcoding and conventional fish survey methods in a river system[J]. Biological Conservation, 2016, 197: 131−138. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2016.03.010 [23] DiBattista J D, Coker D J, Sinclair-Taylor T H, et al. Assessing the utility of eDNA as a tool to survey reef-fish communities in the Red Sea[J]. Coral Reefs, 2017, 36(4): 1245−1252. doi: 10.1007/s00338-017-1618-1 [24] Hebert P D N, Cywinska A, Ball S L, et al. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 2003, 270(1512): 313−321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2218 [25] Collins R A, Bakker J, Wangensteen O S, et al. Non-specific amplification compromises environmental DNA metabarcoding with COI[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2019, 10(11): 1985−2001. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13276 [26] Menning D, Simmons T, Talbot S. Using redundant primer sets to detect multiple native Alaskan fish species from environmental DNA[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 2020, 12(1): 109−123. doi: 10.1007/s12686-018-1071-7 [27] Jennings W B, Ruschi P A, Ferraro G, et al. Barcoding the Neotropical freshwater fish fauna using a new pair of universal COI primers with a discussion of primer dimers and M13 primer tails[J]. Genome, 2019, 62(2): 77−83. doi: 10.1139/gen-2018-0145 [28] Sultana S, Ali M E, Hossain M A M, et al. Universal mini COI barcode for the identification of fish species in processed products[J]. Food Research International, 2018, 105: 19−28. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.10.065 [29] Gantner S, Andersson A F, Alonso-Sáez L, et al. Novel primers for 16S rRNA-based archaeal community analyses in environmental samples[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2011, 84(1): 12−18. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2010.10.001 [30] Freeland J R. The importance of molecular markers and primer design when characterizing biodiversity from environmental DNA[J]. Genome, 2017, 60(4): 358−374. doi: 10.1139/gen-2016-0100 [31] Deiner K, Renshaw M A, Li Yiyuan, et al. Long-range PCR allows sequencing of mitochondrial genomes from environmental DNA[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2017, 8(12): 1888−1898. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12836 [32] 李渊. 鲳属鱼类形态学和遗传学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Li Yuan. Studies on morphology and genetics of Pampus species[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [33] Lockwood S F, Bickham J W. Genetic stock assessment of spawning Arctic cisco (Coregonus autumnalis) populations by flow cytometric determination of DNA content[J]. Cytometry, 1991, 12(3): 260−267. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120309 [34] Shubina E A, Ponomareva E V, Gritsenko O F. Genetic structure of the Salvelinus genus chars from reservoirs of the Kuril Islands[J]. Biochemistry (Moscow), 2007, 72(12): 1331−1348. doi: 10.1134/S0006297907120073 [35] 张辉. 西北太平洋两种卵胎生鱼类(许氏平鲉和褐菖鲉)的分子系统地理学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.Zhang Hui. Molecular phylogeography of two marine ovoviviparous fishes in Northwestern Pacific[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013. [36] 潘晓哲. 中、日斑鰶耳石形态及线粒体基因组研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Pan Xiaozhe. Otolith morphological study and analysis of the mitochondrial genome of Chinese and Japanese dotted gizzard shad (Konosirus punctatus)[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [37] 张艳春. 大口鳒Psettodes erumei线粒体全序列的研究和鲽形目鱼类系统进化分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009.Zhang Yanchun. Analysis of the mitoehondrial genome of Psettodes erumei and phylogenetic analyses of flatfishes[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. [38] 林小婉. 新疆额尔齐斯河北极茴鱼线粒体全基因组测定及遗传多样性分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2021.Lin Xiaowan. Analysis of complete genome mitochondrial sequence and genetic diversity of Thymallus arcticus arcticus (pallas) in Xinjiang[D]. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2021. [39] Evans N T, Lamberti G A. Freshwater fisheries assessment using environmental DNA: a primer on the method, its potential, and shortcomings as a conservation tool[J]. Fisheries Research, 2018, 197: 60−66. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2017.09.013 [40] Hänfling B, Handley L L, Read D S, et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of lake fish communities reflects long-term data from established survey methods[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2016, 25(13): 3101−3119. doi: 10.1111/mec.13660 -
 补充材料.rar
补充材料.rar

-




 下载:
下载: