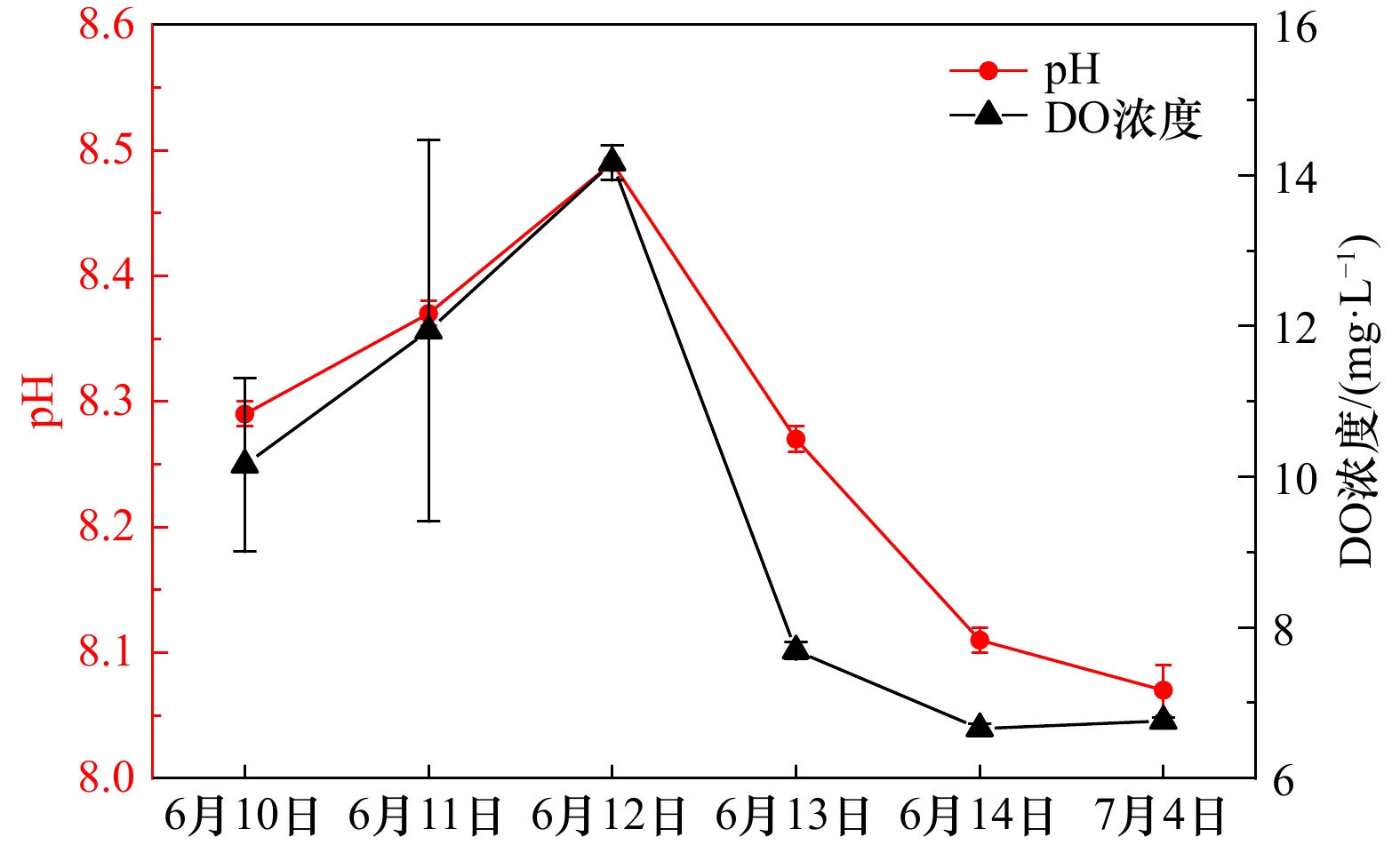
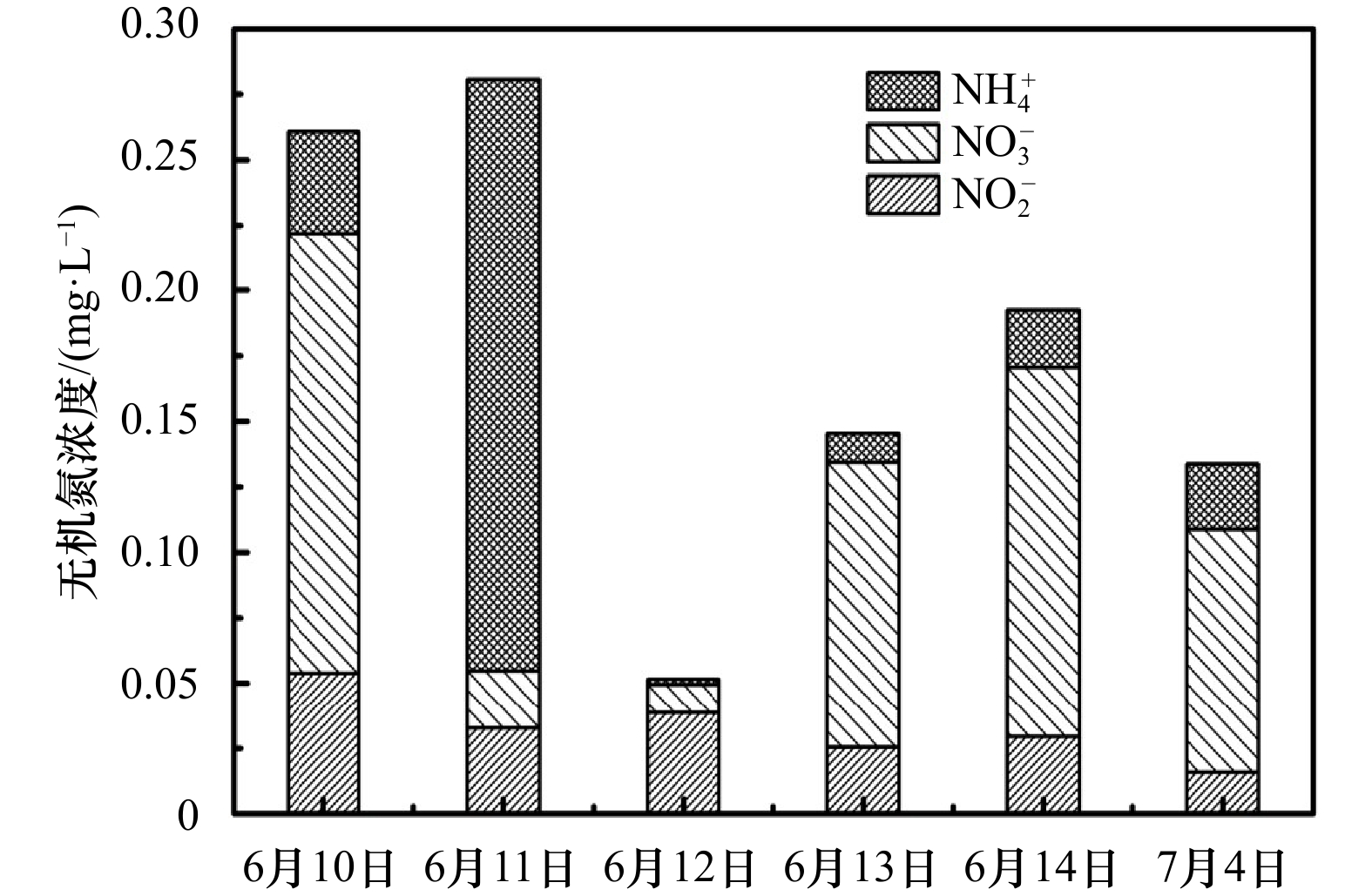
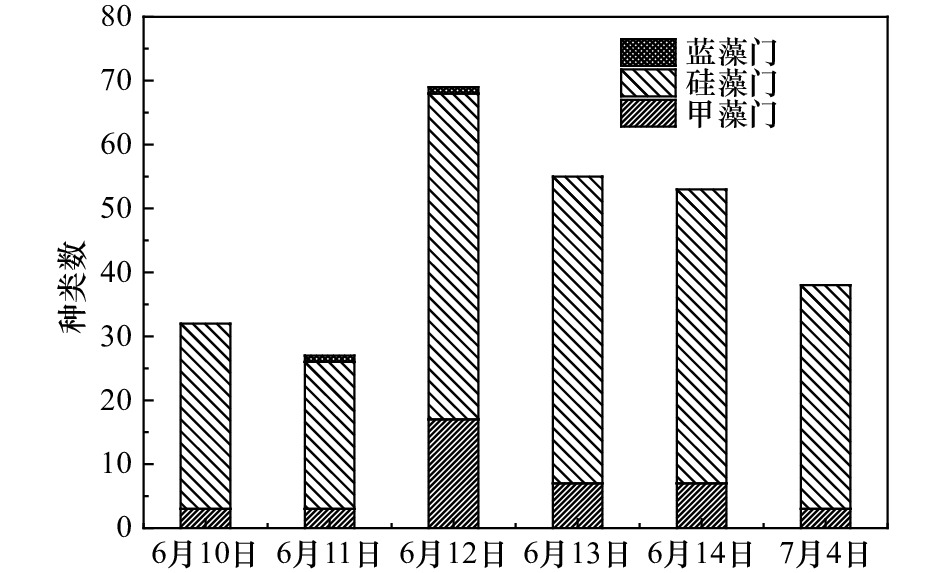
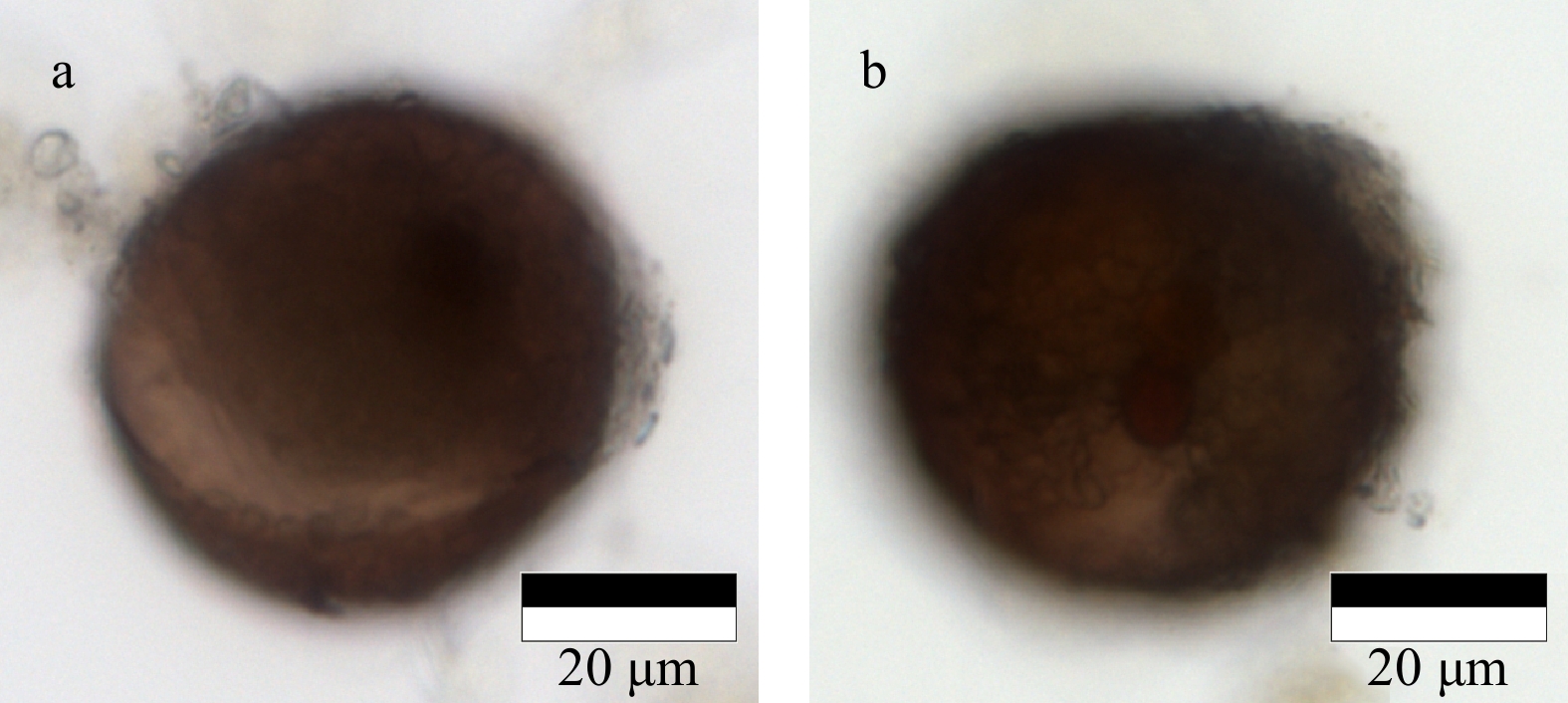
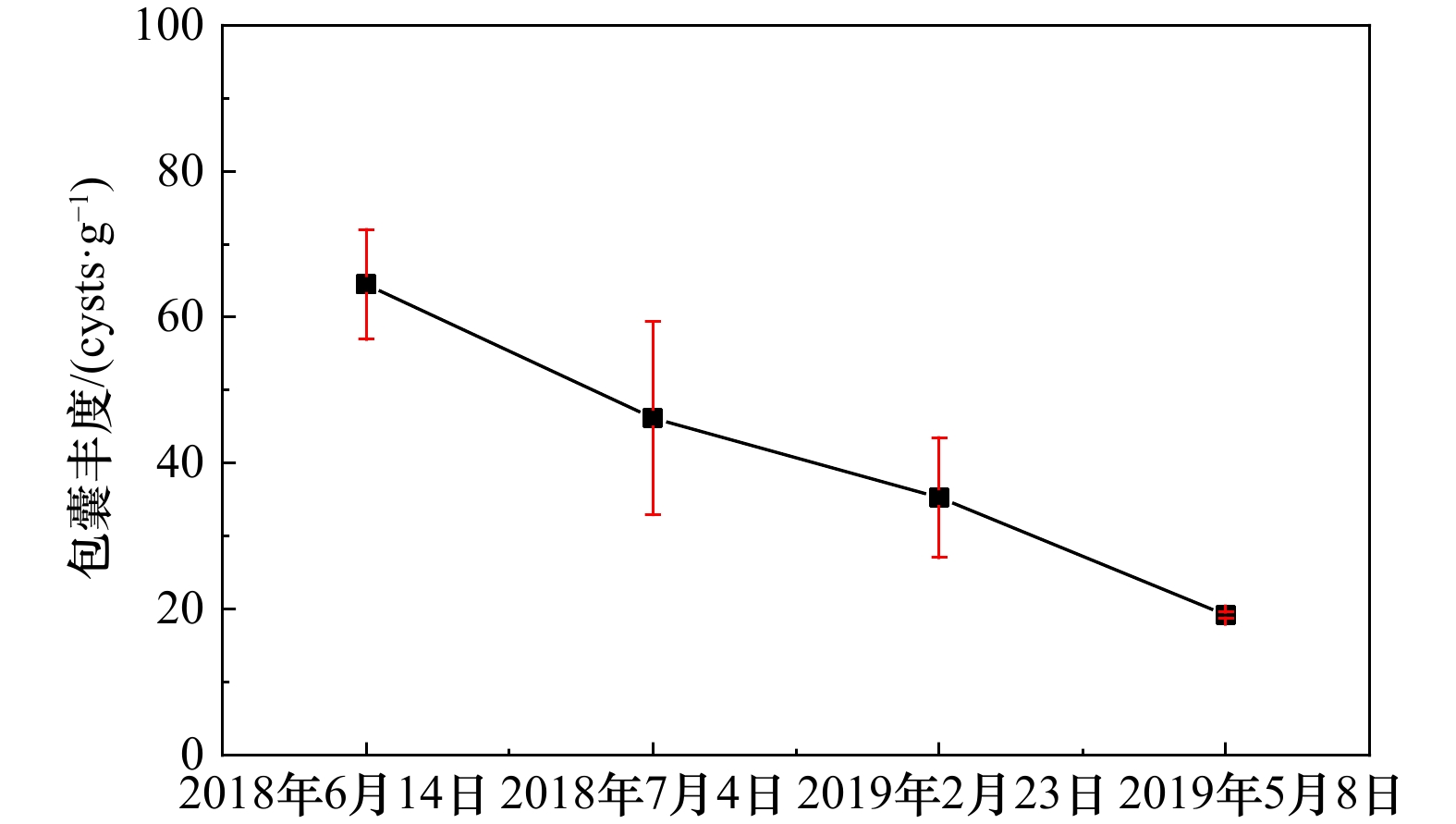
| [1] |
李冠国, 范振刚. 海洋生态学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011: 343.Li Guanguo, Fan Zhengang. Marine Ecology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2011: 343.
|
| [2] |
李雪丁. 近20年福建沿海赤潮的发生特点[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(4): 601−610. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200120Li Xueding. Occurrence characteristics of the red tide in Fujian coastal waters during the last two decades[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(4): 601−610. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200120
|
| [3] |
高养春, 董燕红, 李海涛, 等. 有害甲藻包囊的分类鉴定研究进展[J]. 生物安全学报, 2016, 25(4): 238−254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2016.04.002Gao Yangchun, Dong Yanhong, Li Haitao, et al. Research progress on identification of harmful dinoflagellate cysts: a review[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2016, 25(4): 238−254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2016.04.002
|
| [4] |
丁光茂, 张树峰. 2012年三沙湾米氏凯伦藻赤潮的生态特征及成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(6): 104−112.Ding Guangmao, Zhang Shufeng. Ecological characteristics and the causes of Karenia mikimotoi bloom in the Sansha Bay in 2012[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(6): 104−112.
|
| [5] |
郭皓, 丁德文, 林凤翱, 等. 近20 a我国近海赤潮特点与发生规律[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2015, 33(4): 547−558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.04.013Guo Hao, Ding Dewen, Lin Fengxiang, et al. Characteristics and patterns of red tide in China coastal waters during the last 20 a[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2015, 33(4): 547−558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.04.013
|
| [6] |
张文. 不同环境因子对有害赤潮生物链状裸甲藻的生长和产毒的影响[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2009.Zhang Wen. Effect of different environment factors on the growth and toxin production of toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum Graham[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2009.
|
| [7] |
王朝晖. 中国典型近海海域甲藻包囊分布及其与富营养化和赤潮生消关系研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2007.Wang Zhaohui. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in Chinese typical coastal areas and its relationships with eutrophication and algal bloom[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2007.
|
| [8] |
陈火荣. 2017年福建海域链状裸甲藻赤潮事件应急处置与思考[J]. 渔业研究, 2018, 40(4): 308−314.Chen Huorong. Emergency treatment and reflection of red tide event of Gymnodinium catenatum in Fujian sea area in 2017[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2018, 40(4): 308−314.
|
| [9] |
颜利, 蒋金龙, 詹兴旺, 等. 泉州湾表层水主要化学要素含量和富营养化指数的时空变化特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 2012, 31(4): 459−465.Yan Li, Jiang Jinlong, Zhan Xingwang, et al. Characters of spatiotemporal variations of chemical elements content and eutrophication index in surface water of Quanzhou Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2012, 31(4): 459−465.
|
| [10] |
国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 12763−2007 海洋调查规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 12763−2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2007.
|
| [11] |
国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB 17378−2007 海洋监测规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. GB 17378−2007 The specification for marine monitoring[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2007.
|
| [12] |
王朝晖. 中国沿海甲藻包囊与赤潮研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2007.Wang Zhaohui. Study of Dinoflagellate Cysts and Red Tide in Coastal Areas of China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2007.
|
| [13] |
陆欣鑫. 华南沿海典型海域甲藻包囊地理分布及环境指示作用研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2017.Lu Xinxin. Biogeological distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from southern Chinese coast and their roles as a signal of environmental changes[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2017.
|
| [14] |
郭皓. 我国海域赤潮甲藻包囊形态与分布特征研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2016.Guo Hao. Studies on the characteristics of the morphology and distribution of red-tide dinoflagellate cysts in China[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2016.
|
| [15] |
黄海燕, 陆斗定, 夏平, 等. 2006年冬季长江口海域表层沉积物中甲藻包囊的分类学研究[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(11): 5902−5911. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.11.019Huang Haiyan, Lu Douding, Xia Ping, et al. Taxonomic study of dinoflagellate cysts in Changjiang Estuary in the winter of 2006[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(11): 5902−5911. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.11.019
|
| [16] |
黄琳. 东、黄海海域沉积物中甲藻包囊的生态分布特征及其与海区污染关系研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2012.Huang Lin. Ecological distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediments of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea and its relationships with marine pollution[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2012.
|
| [17] |
Blackburn S I, Hallegraeff G M, Bolch C J. Vegetative reproduction and sexual life cycle of the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum from Tasmania, Australia[J]. Journal of Phycology, 1989, 25(3): 577−590. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.1989.tb00264.x
|
| [18] |
许翠娅. 泉州湾春、夏季浮游植物的生态特征[J]. 福建水产, 2001(4): 64−69.Xu Cuiya. Ecological characteristics of phytoplankton in Quanzhou Bay in spring and summer[J]. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 2001(4): 64−69.
|
| [19] |
江兴龙, 宋立荣. 泉州湾赤潮藻类优势种演替影响因子探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2009, 40(6): 761−767. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.06.014Jiang Xinglong, Song Lirong. The influence factors on dominant red-tide algal species succession in Quanzhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2009, 40(6): 761−767. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.06.014
|
| [20] |
李涛, 刘胜, 黄良民, 等. 大亚湾一次赤潮生消期间浮游植物群落变化研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(3): 18−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.03.003Li Tao, Liu Sheng, Huang Liangmin, et al. Studies on phytoplankton community change at Daya Bay during a red tide[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(3): 18−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.03.003
|
| [21] |
庞勇, 聂瑞, 吕松辉. 珠江口双胞旋沟藻Cochlodinium geminatum赤潮生消过程的环境特征初步分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(2): 286−293.Pang Yong, Nie Rui, Lü Songhui. Preliminary environmental analysis of the evolution of Cochlodinium geminatum bloom in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(2): 286−293.
|
| [22] |
邓华, 管卫兵, 曹振轶, 等. 2012年福建沿海大规模米氏凯伦藻赤潮暴发的水文气象原因探讨[J]. 海洋学研究, 2016, 34(4): 28−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2016.04.004Deng Hua, Guan Weibing, Cao Zhenyi, et al. Analysis of hydrological and meteorological factors causing Karenia mikimotoi bloom in 2012 along Fujian coast[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2016, 34(4): 28−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2016.04.004
|
| [23] |
Liu Minlu, Gu Haifeng, Krock B, et al. Toxic dinoflagellate blooms of Gymnodinium catenatum and their cysts in Taiwan Strait and their relationship to global populations[J]. Harmful Algae, 2020, 97: 101868. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101868
|
| [24] |
Zheng Chongrong, Li Guangyi, Chen Jingwu, et al. Potential effects of some environmental factors on a dinoflagellate red tide caused by Gymnodinium catenatum in Shenhu Bay in 2017[J]. Meteorological and Environment Research, 2019, 10(4): 26−30.
|
| [25] |
Hallegraeff G M, Steffensen D A, Wetherbee R. Three estuarine Australian dinoflagellates that can produce paralytic shellfish toxins[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1988, 10(3): 533−541. doi: 10.1093/plankt/10.3.533
|
| [26] |
Figueroa R I, Bravo I, Ramilo I, et al. New life-cycle stages of Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae): laboratory and field observations[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2008, 52(1): 13−23.
|
| [27] |
程军利, 张鹰, 张东, 等. 海州湾赤潮发生期生态环境要素分析[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2009, 27(2): 217−223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.012Cheng Junli, Zhang Ying, Zhang Dong, et al. Analysis of ecological environment elements during the red tide occurring in Haizhou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2009, 27(2): 217−223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.012
|
| [28] |
高铭琪. 石狮市近岸海域水质分析与评价[J]. 渔业研究, 2017, 39(6): 493−501.Gao Mingqi. Analysis and evaluation of water quality in Shishi inshore waters[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2017, 39(6): 493−501.
|
| [29] |
丁光茂, 洪华生, 王大志. 东海原甲藻和链状亚历山大藻对硝酸盐和氨盐的生理响应[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 49(1): 95−101.Ding Guangmao, Hong Huasheng, Wang Dazhi. Physiological response of Prorocentrum donghaiense and Alexandrium tamarense to nitrate and ammonium[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2010, 49(1): 95−101.
|
| [30] |
Bravo I, Fraga S, Figueroa R I, et al. Bloom dynamics and life cycle strategies of two toxic dinoflagellates in a coastal upwelling system (NW Iberian Peninsula)[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2010, 57(3/4): 222−234.
|
| [31] |
Bolch C J S, Hallegraeff G M. Dinoflagellate cysts in recent marine sediments from Tasmania, Australia[J]. Botanica Marina, 1990, 33(2): 173−192.
|
| [32] |
潘俊, 李瑞香, 李艳, 等. 秋季南黄海表层沉积物中甲藻包囊分布[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(1): 41−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.006Pan Jun, Li Ruixiang, Li Yan, et al. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from the southern Yellow Sea in autumn[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2010, 28(1): 41−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.006
|
| [33] |
李光毅, 郑崇荣, 吴惠锴, 等. 湄洲湾海域甲藻包囊的时空分布初步调查[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(8): 115−126.Li Guangyi, Zheng Chongrong, Wu Huikai, et al. A preliminary investigation of spatial and temporal distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the Meizhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(8): 115−126.
|
| [34] |
Figueroa R I, Bravo I, Garcés E, et al. Nuclear features and effect of nutrients on Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae) sexual stages[J]. Journal of Phycology, 2006, 42(1): 67−77. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00181.x
|




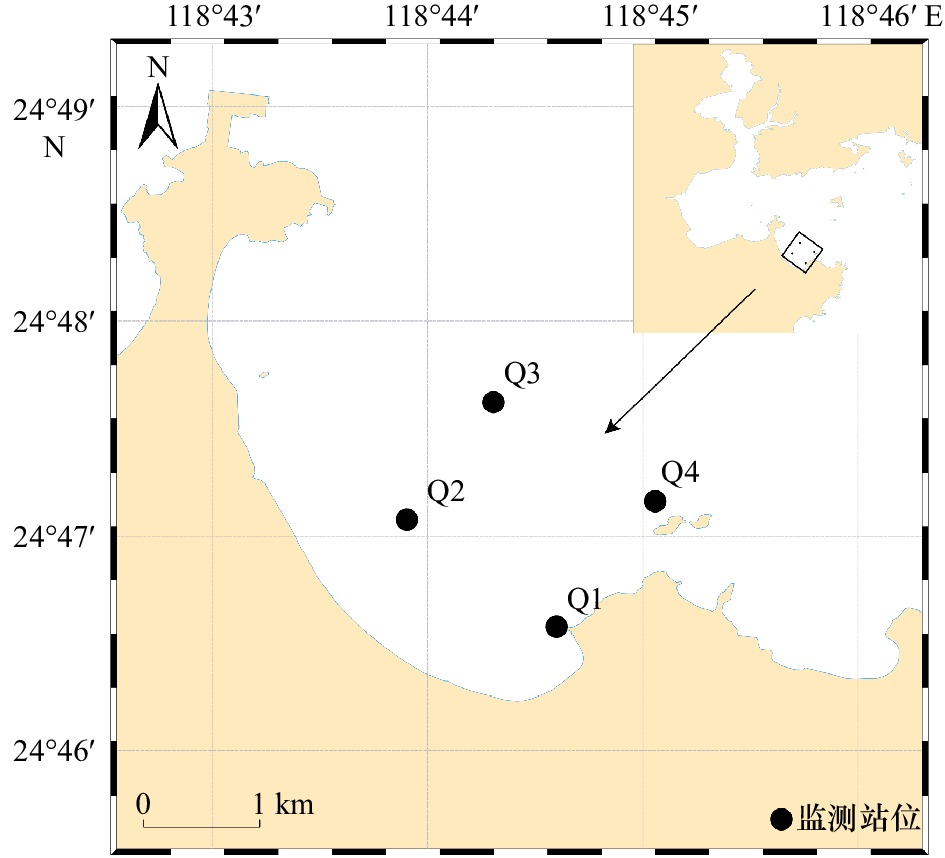
 下载:
下载: