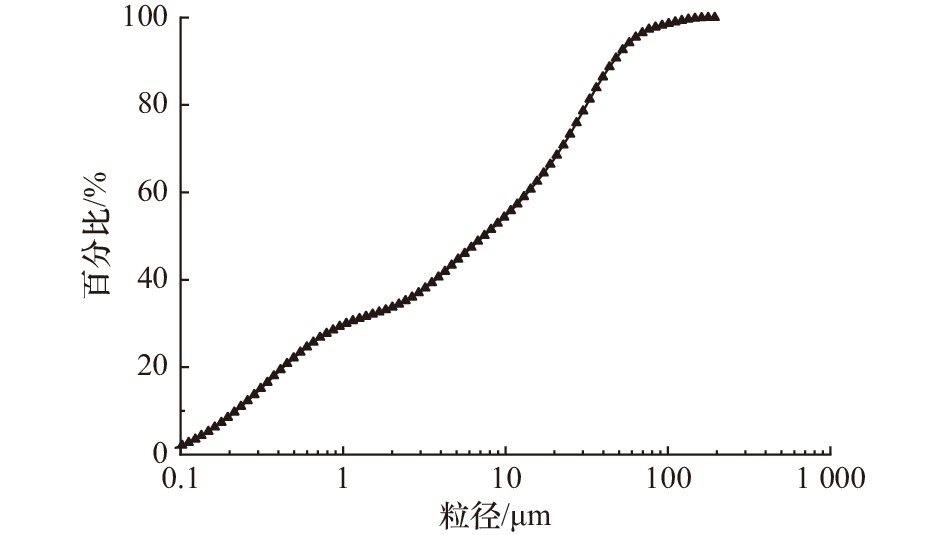
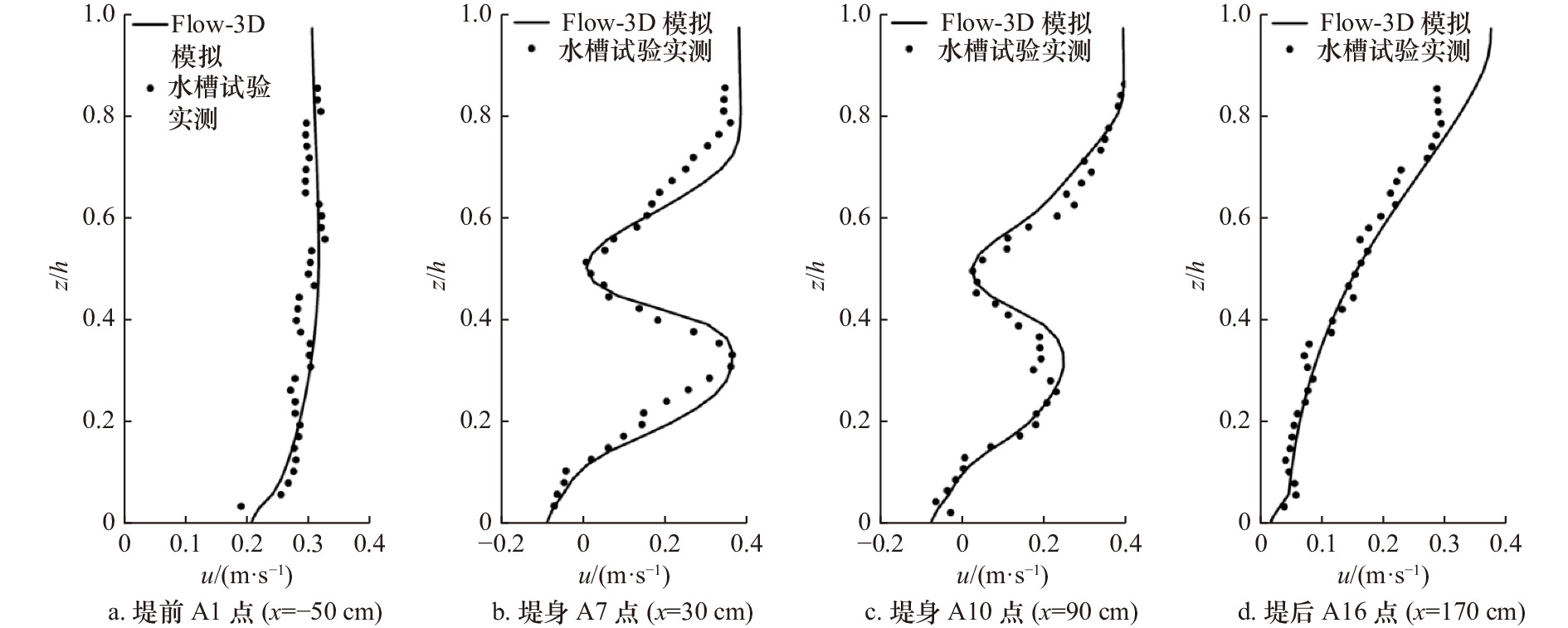
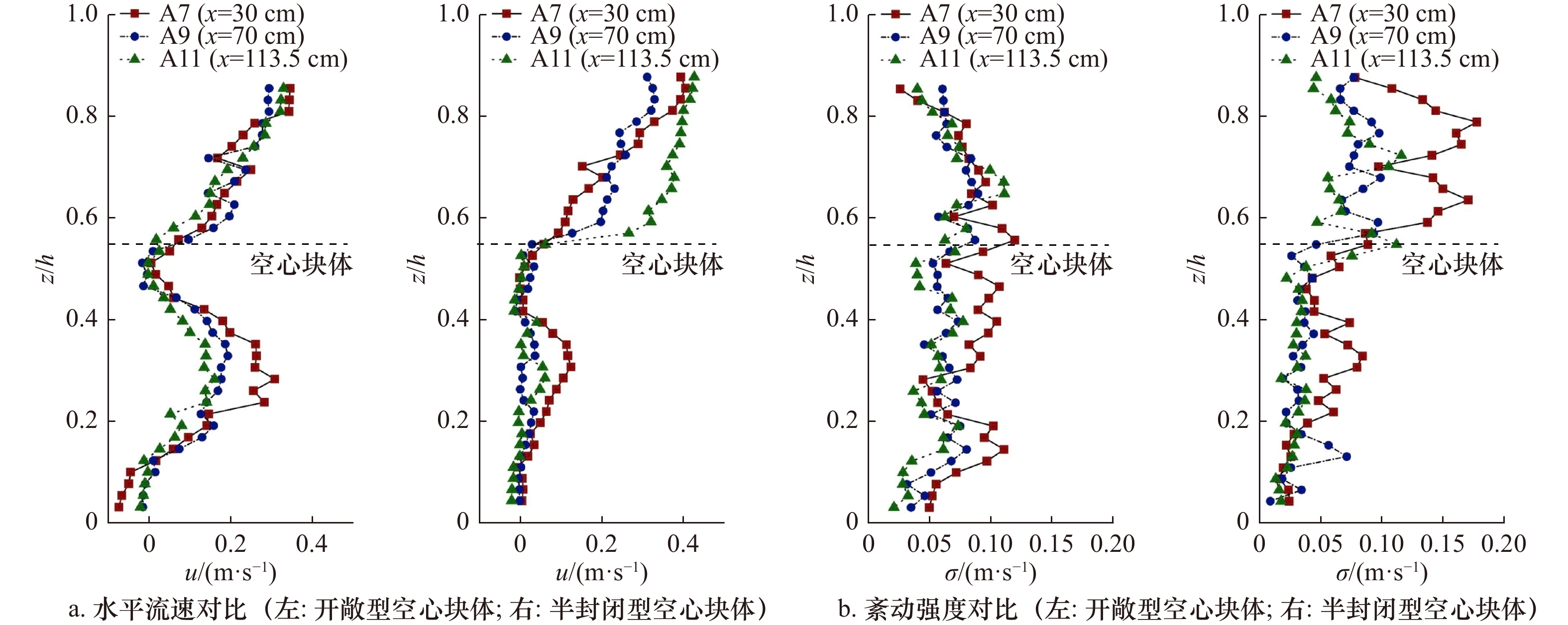
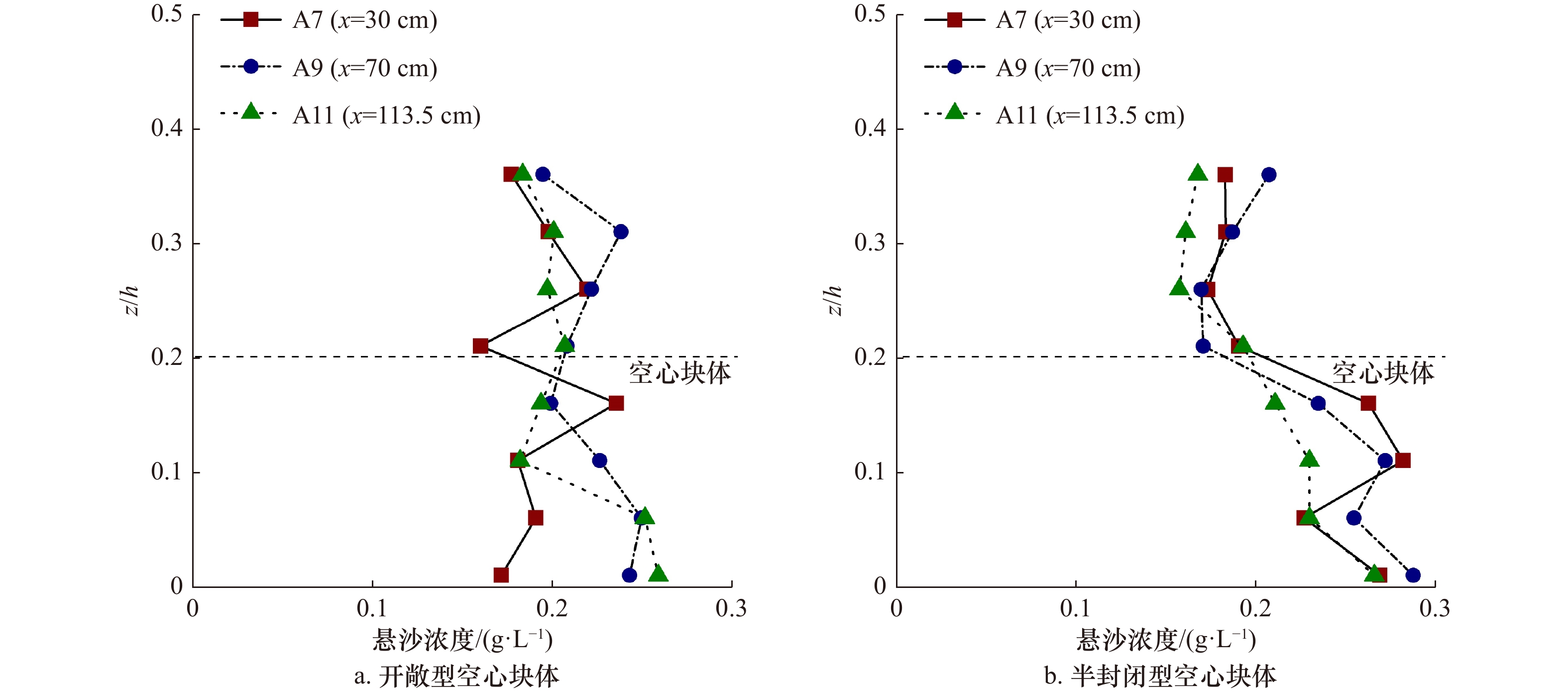
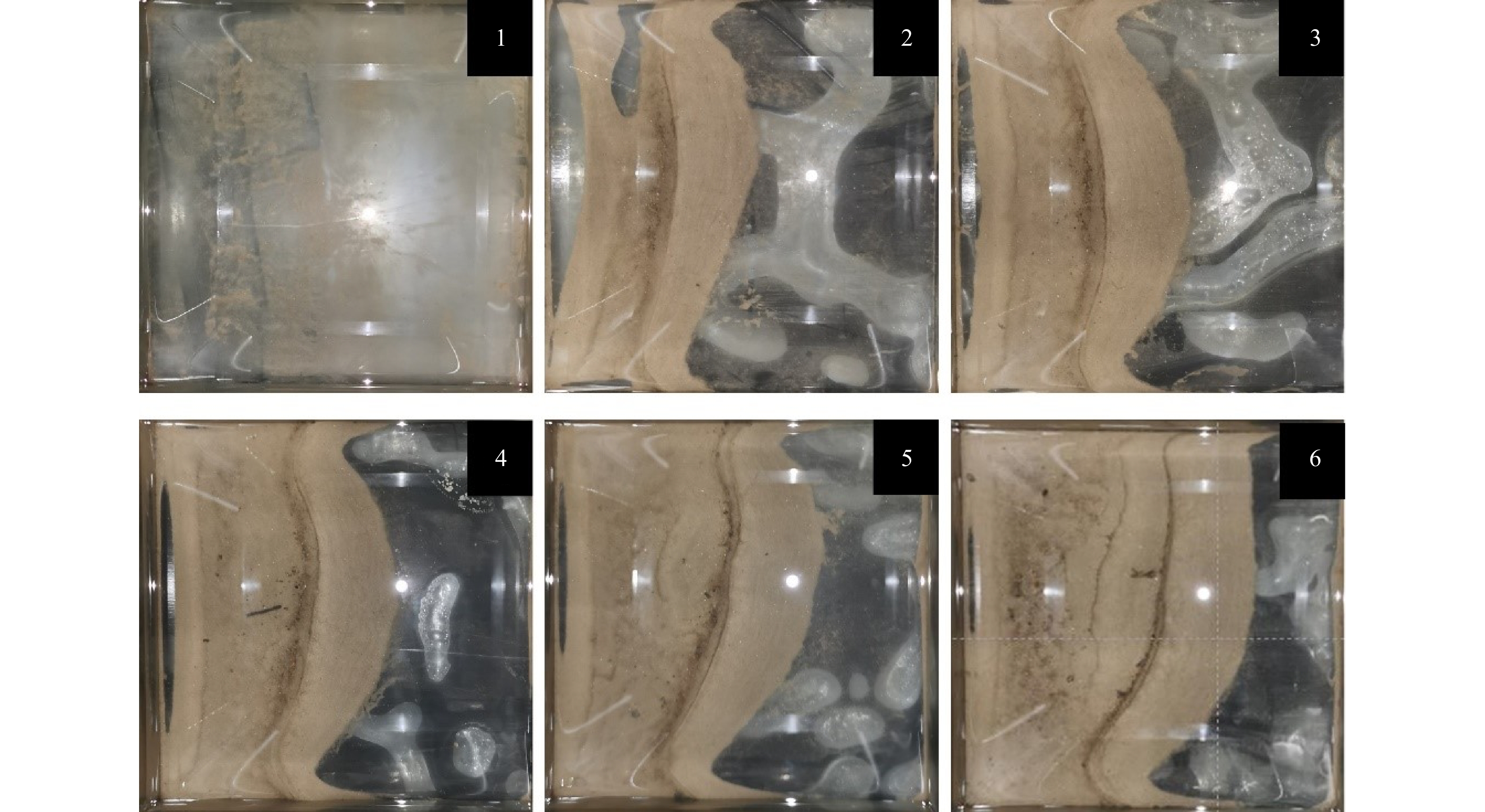
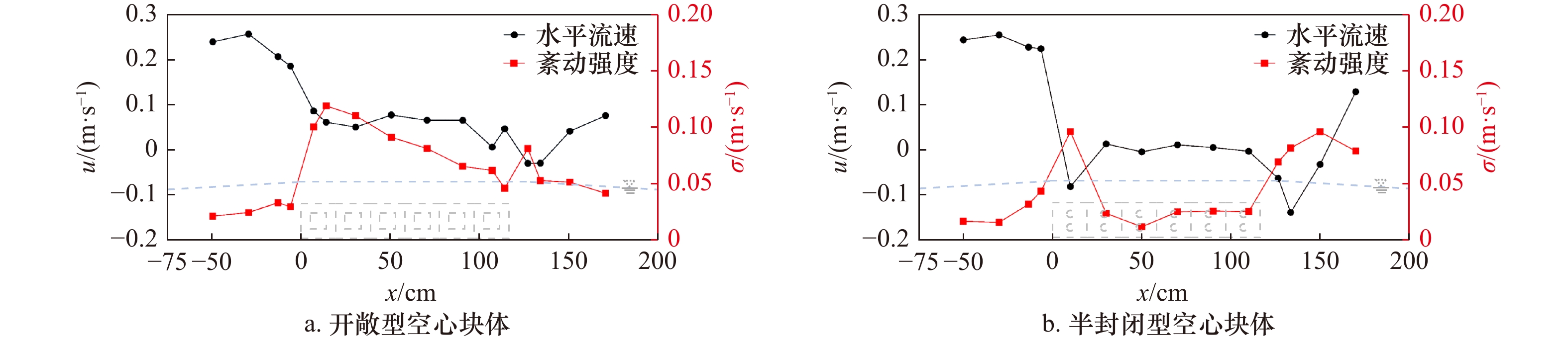
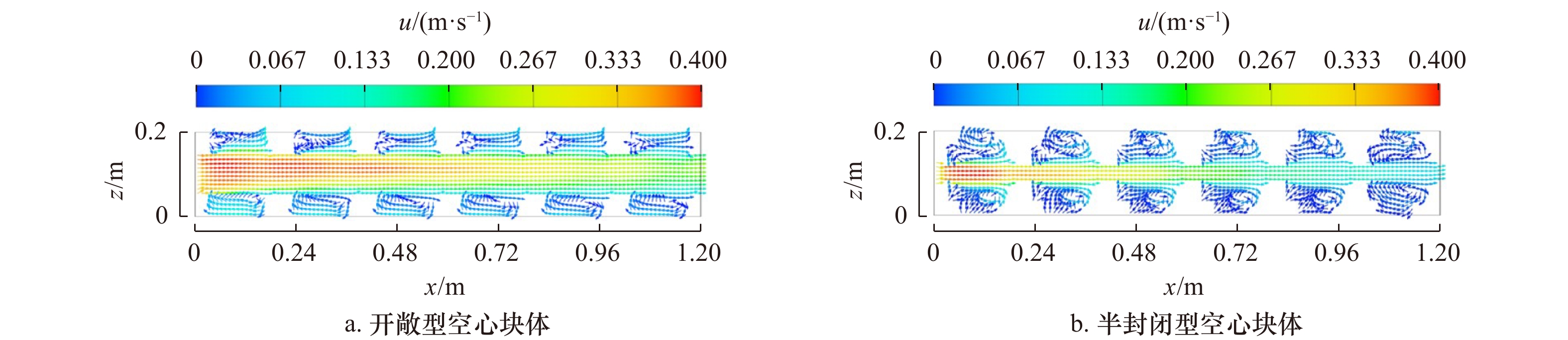
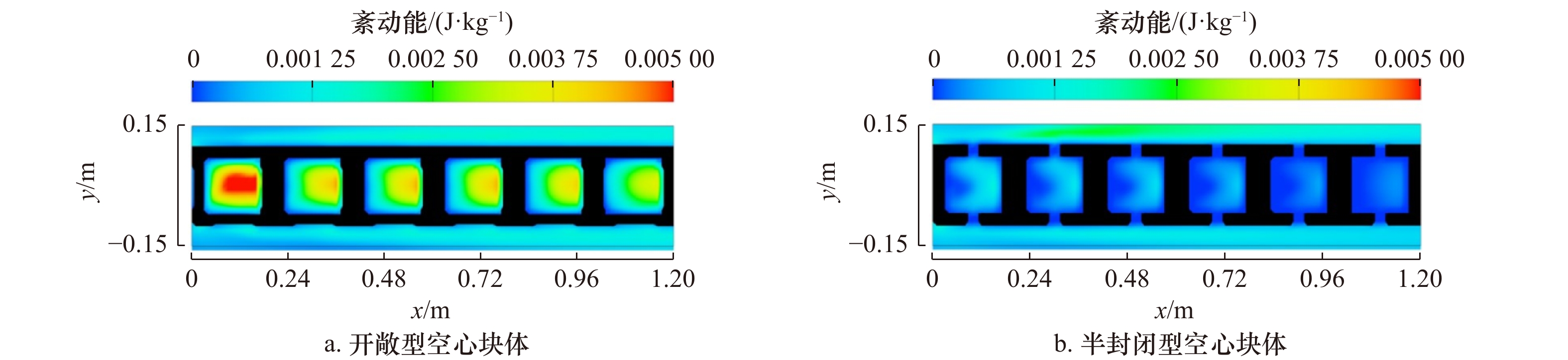
Study on flow and sediment dynamics and deposition characteristics of hollow block
-
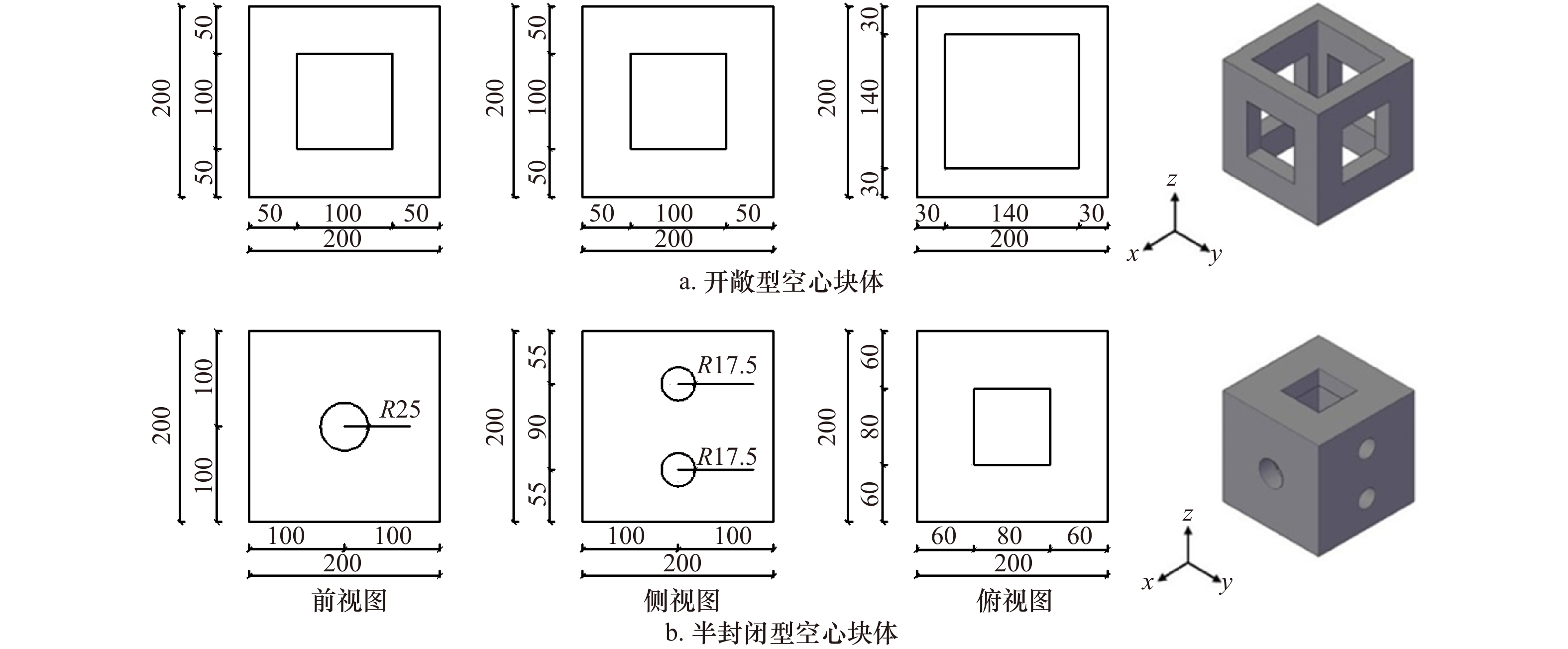
摘要: 空心块体具有良好的阻水和促淤功能,近年来被广泛用于生态修复工程。本文结合水槽试验及Flow-3D数值模拟,分析了开敞型和半封闭型空心块体的阻水效应和泥沙淤积特性。结果表明:空心块体的开孔率对内部水流流速、紊动强度起主导作用,开孔率较小的半开敞型空心块体减速、制紊效果更强;开敞型和半封闭型空心块体近底层悬沙浓度分别增大56%和75%,两者均有利于促进泥沙在块体内部淤积,近底层水流紊动越强,泥沙淤积形态差异越大;空心块体所营造的低流速、泥沙微淤、内外连通的水沙环境是大型底栖生物的生境需求,半封闭型空心块体内部的低紊动水流结构更有利于大型底栖生物的栖息、繁衍。Abstract: Hollow blocks have good water blocking and siltation promotion functions, and have been widely used in ecological restoration projects in recent years. In this paper, combined with flume experiment and Flow-3D numerical simulation, the water blocking effect and sedimentation characteristics of open and semi-closed hollow blocks are analyzed. The results show that the permeability of the hollow block plays a leading role in the internal flow velocity and turbulence intensity, and the semi-open hollow block with small permeability has a better effect in slowing down and turbulence control. The suspended sediment concentration near the bottom of open and semi-closed hollow blocks increases by 56% and 75%, respectively. Both of them can promote the deposition of sediment in the block. The environment of low flow velocity, sediment micro-deposition and water and sediment connected inside and outside by hollow blocks is the habitat requirement of macrobenthos, the structure of low turbulent flow inside the semi-enclosed hollow block is more favorable for the habitat and reproduction of macrobenthos.
-
Key words:
- hollow block /
- flume experiment /
- Flow-3D /
- flow and sediment dynamic /
- deposition
-
表 1 空心块体透水能力参数
Tab. 1 Hollow block water permeability parameter
结构型式 透水截面面积/cm2 总透水面积S0/cm2 开孔率S0/S x轴方向 y轴方向 z轴方向 开敞型 100 100 196 792 33% 半封闭型 19.6 19.2 顶面64
底面196337.6 14% 注:S为包含结构体外轮廓总面积S=20$ \text{×} $20$ \text{×} $6=2 400 (cm²)。 表 2 长江口目标生物生境需求指标[20]
Tab. 2 Target biological habitat demand indicators for the Changjiang River Estuary[20]
生物类别 代表性物种 生境需求指标 双壳类 河蚬、黑龙江河篮蛤、
彩虹明樱蛤等河蚬、黑龙江河篮蛤一般栖息在底质0~5 cm深度;彩虹明樱蛤栖息深度一般在4~15 cm 甲壳类 中华绒螯蟹等 中华绒螯蟹在南槽水域主要为抱卵蟹和蚤状幼体,抱卵蟹适应流速不大于1.5 m/s,
蚤状幼体适应流速不大于0.7 m/s,幼蟹介于两者之间多毛类 沙蚕 沙蚕栖息深度在0~30 cm,基本生活在沉积底质内,
受水流作用影响相对较小 -
[1] 范航清, 何斌源, 王欣, 等. 生态海堤理念与实践[J]. 广西科学, 2017, 24(5): 427−434, 440.Fan Hangqing, He Binyuan, Wang Xin, et al. The conception and practices of ecological sea dyke[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2017, 24(5): 427−434, 440. [2] Mitsch W J, Jørgensen S E. Ecological Engineering: An Introduction to Ecotechnology[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 1989. [3] 李泽龙, 孙林云, 唐磊, 等. 河口海岸保滩促淤方式及水沙机理研究综述[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2018, 38(11): 1−8. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs201811001Li Zelong, Sun Linyun, Tang Lei, et al. Review on beach protection and deposition promotion and water and sediment transport mechanism in estuaries and coastal area[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2018, 38(11): 1−8. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs201811001 [4] Ido S, Shimrit P F. Blue is the new green-ecological enhancement of concrete based coastal and marine infrastructure[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 84: 260−272. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.09.016 [5] Heatherington C, Bishop M J. Spatial variation in the structure of mangrove forests with respect to seawalls[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 2012, 63(10): 926−933. doi: 10.1071/MF12119 [6] 杨芳丽, 耿嘉良, 付中敏, 等. 长江中游航道整治中生态技术应用探讨[J]. 人民长江, 2012, 43(24): 68−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.24.018Yang Fangli, Geng Jialiang, Fu Zhongmin, et al. Exploration on application of eco-technology in waterway regulation project at midstream of Yangtze River[J]. Yangtze River, 2012, 43(24): 68−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.24.018 [7] 张为, 李义天, 王秀英, 等. 透水结构促淤试验研究[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2005, 37(6): 31−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3087.2005.06.007Zhang Wei, Li Yitian, Wang Xiuying, et al. Experimental study on deposition promotion of permeable structure[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2005, 37(6): 31−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3087.2005.06.007 [8] 吴龙华, 周春天, 严忠民, 等. 架空率、杆件长宽比对四面六边透水框架群减速促淤效果的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2003(3): 74−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2003.03.017Wu Longhua, Zhou Chuntian, Yan Zhongmin, et al. Effects of overhead ratio and pole’s length-width ratio on deceleration and accretion promotion of tetrahedron-like penetrating frames[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2003(3): 74−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2003.03.017 [9] 崔勇, 关长涛, 万荣, 等. 布设间距对人工鱼礁流场效应影响的数值模拟[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2011, 33(2): 59−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2011.02.008Cui Yong, Guan Changtao, Wan Rong, et al. Numerical simulation on influence of disposal space on effects of flow field around artificial reefs[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2011, 33(2): 59−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2011.02.008 [10] Harris L E. Submerged reef structures for habitat enhancement and shoreline erosion abatement[J]. Coastal Engineering Technical Note, 2001(9): 1–16. [11] Moreira J, Chapman M G, Underwood A J. Maintenance of chitons on seawalls using crevices on sandstone blocks as habitat in Sydney Harbour, Australia[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2007, 347(1/2): 134−143. [12] Temmerman S, Meire P, Bouma T J, et al. Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7478): 79−83. doi: 10.1038/nature12859 [13] 杨培思, 蔡德所, 莫崇勋. 基于FLOW-3D的竖缝式鱼道水力特性研究[J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 43(4): 1675−1683.Yang Peisi, Cai Desuo, Mo Chongxun. Study on hydraulic characteristics of vertical-slot fishways based on FLOW3D[J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 43(4): 1675−1683. [14] 侯勇俊, 熊烈, 何环庆, 等. 基于FLOW-3D的三维数值波流水槽的构建及应用研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(9): 111−116. doi: 10.11759/hykx20140902003Hou Yongjun, Xiong Lie, He Huanqing, et al. Three-dimensional wave-current numerical model and application based on FLOW-3D[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(9): 111−116. doi: 10.11759/hykx20140902003 [15] 王小明, 程永舟, 常留红, 等. 梯形透水潜坝三维水流特性的数值模拟[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2017, 37(5): 51−56. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2017.05.009Wang Xiaoming, Cheng Yongzhou, Chang Liuhong, et al. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional flow characteristics of trapezoidal permeable submerged dam[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2017, 37(5): 51−56. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2017.05.009 [16] Colby B R, Hembree C H. Computations of total sediment discharge, Niobrara river near Cody, Nebraska[J]. Science, 1954, 119(3097): 657−658. doi: 10.1126/science.119.3097.657.b [17] Van Rijn L C. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas[M]. Amsterdam: Aqua Publications, 1993. [18] Nielsen P, Teakle I A L. Turbulent diffusion of momentum and suspended particles: a finite-mixing-length theory[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2004, 16(7): 2342−2348. doi: 10.1063/1.1738413 [19] Larsson P. Transport of PCBs from aquatic to terrestrial environments by emerging chironomids[J]. Environmental Pollution Series A, Ecological and Biological, 1984, 34(3): 283−289. doi: 10.1016/0143-1471(84)90123-5 [20] 李亚, 陈海峰, 黄明毅, 等. 新型聚氨酯碎石空心块体生态堤结构构建[J]. 水运工程, 2020(11): 132−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2020.11.023Li Ya, Chen Haifeng, Huang Mingyi, et al. Structure creation of new type of ecological embankment made of PPM hollow block[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2020(11): 132−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2020.11.023 -




 下载:
下载: