Variations of suspended sediment concentration of the Mississippi River delivered from land into sea
-
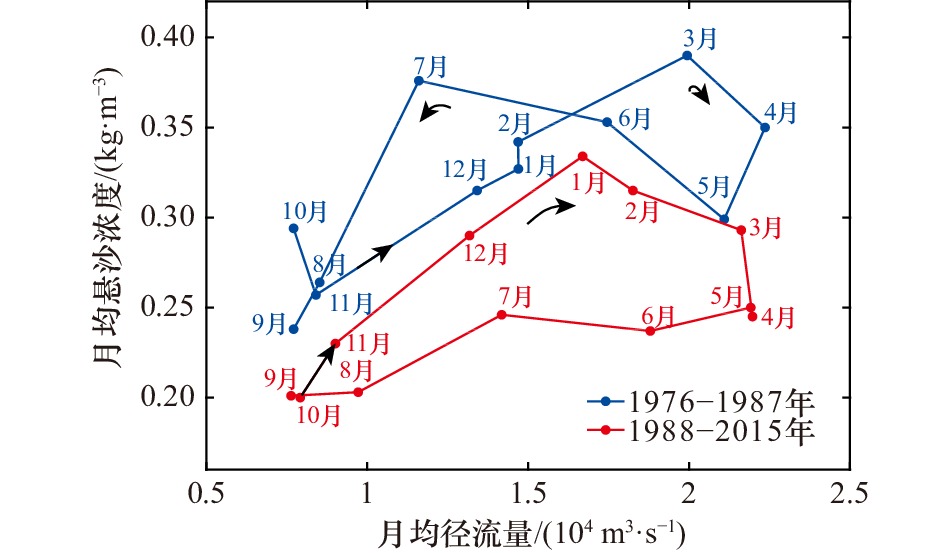
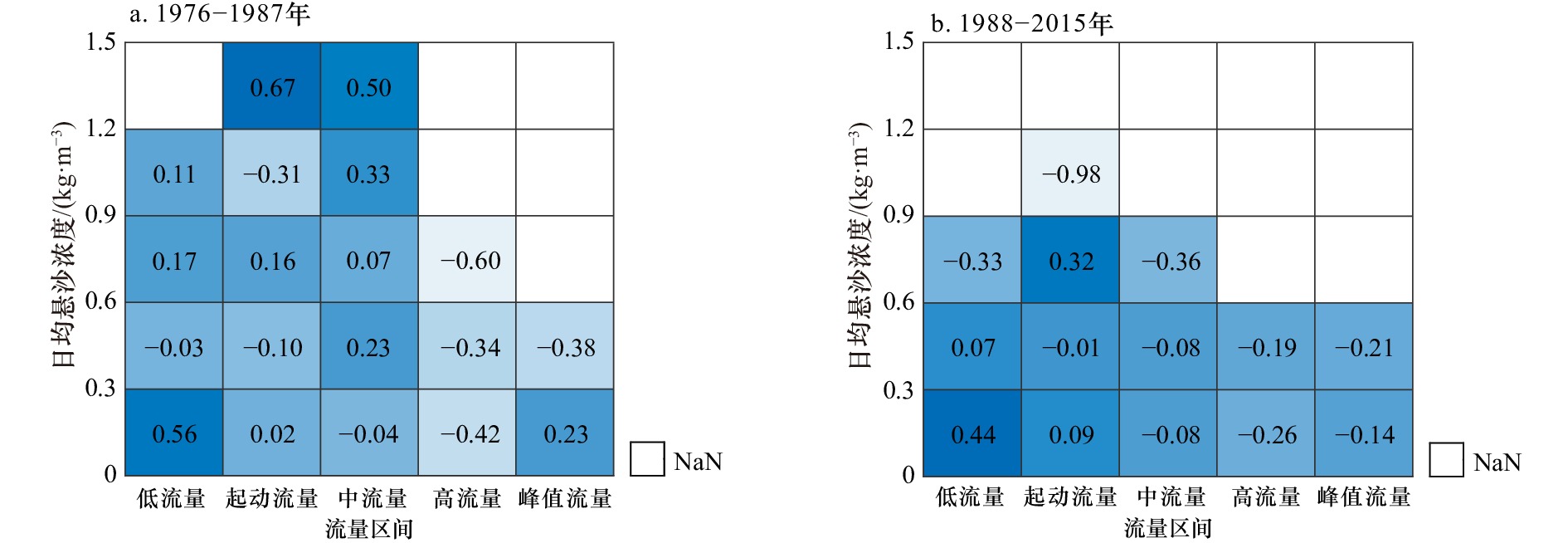
摘要: 河流入海水体悬沙浓度的变化直接反映该流域人类活动和自然应力的影响。基于密西西比河塔伯特兰丁站长期水文资料,本文采用百分位法、Mann-Kendall法等统计方法对近40年密西西比河入海水体悬沙浓度进行分析,探究密西西比河通过“鸟足状”三角洲进入墨西哥湾的水体悬沙浓度变化过程及其可能影响因素。结果表明:(1)在1976−2015年期间,密西西比河入海水体悬沙浓度展现阶段性下降趋势,其中第一时期即1976−1987年期间,入海水体悬沙浓度相对较高,平均值为0.33 kg/m3;第二时期即1988−2015年期间,悬沙浓度较低且平均值为0.25 kg/m3。(2)密西西比河日径流量与悬沙浓度之间的关系符合高斯分布。与1976−1987年相比,1988−2015年期间水沙关系曲线较为扁平,日均超过0.60 kg/m3的高悬沙浓度事件明显减少。在低流量及起动流量阶段,悬沙浓度随着流量的增加而增加,在流量接近20 000 m3/s时,悬沙浓度达到最大值,流量高于20 000 m3/s后,悬沙浓度反而随着流量增加而减小。同时,密西西比河月均水沙关系在1976−1987年期间呈双绳套样,1988−2015年期间则呈现“先沙后水”的顺时针单一型绳套样。(3)分洪工程建设及土壤保持措施是影响密西西比河入海水体悬沙浓度的主要原因。其中,工程建设减少了河道沿程沉积物物源,土壤保持措施使土地侵蚀减少,从而使得悬沙浓度保持较低水平。此外,极端水文事件对密西西比河入海悬沙浓度的影响较小。Abstract: The change of fluvial suspended sediment concentration (SSC) to the sea directly reflects the effects of riverine anthropogenic activities and natural force. Based on long-term hydrological data at Tarbert Landing Station of the Mississippi River (MR), statistical means, such as percentile method and Mann-Kendall method are used to detect change process of SSC from the MR entering the Gulf of Mexico in recent 40 years, and associated possible influencing factors. The results show that: (1) SSC from the MR entering the Gulf of Mexico is characterized by a staged decline from 1976 to 2015, in the first stage from 1976 to 1987, the SSC is relatively high with an average value of 0.33 kg/m3; in the second stage from 1988 to 2015, the SSC is much lower with a mean value of 0.25 kg/m3. (2) The relationship between daily SSC and runoff of MR follows Gaussian distribution. Compared with the first stage (1976−1987), the rating curve between SSC and runoff in the second stage (1988−2015) is relatively flat, when the number of high daily SSC event over 0.60 kg/m3 reduces significantly. SSC increases with the runoff in low-action flows and reaches the maximum when the runoff approaches 20 000 m3/s, but decreases with the runoff thereafter. The rating curve between monthly SSC and water discharge of the MR exhibits “double-loop” shape during 1976−1987, but presents clockwise “single loop” with “sediment before water” during 1988−2015. (3) Flood diversion project construction and soil conservation measures dominate the fluvial SSC from the MR into the Gulf of Mexico. The construction of flood diversion engineering reduces the sediment source along the river channel, and the soil conservation measures repress the land erosion, which have combined to keep the SSC at a relatively low level. In addition, SSC in the MR presents minor response to extreme hydrological events.
-
图 1 研究区域
a. 密西西比河流域;b. 密西西比河地理位置;c. 旧河控制结构;d. 1984年旧河控制结构;e. 1988年旧河控制结构;f. 1990年旧河控制结构
Fig. 1 The study area
a. Mississippi River Basin; b. the location of Mississippi River; c. old river control structure; d. old river control structure in 1984; e. old river control structure in 1988; f. old river control structure in 1990
表 1 平水年、洪水年、枯水年水文参数
Tab. 1 Hydrological parameters in normal year, flood year and dry year
水文年类型 年份 年均流量
/(m3·s−1)年均悬沙通量/(108 t·a−1) 年均悬沙浓度/(kg·m−3) 平水年 1978 14 137 1.71 0.38 1982 13 755 1.84 0.42 1986 14 045 1.62 0.37 1999 15 083 1.68 0.35 洪水年 1979 18 905 1.94 0.33 1983 19 477 1.98 0.32 1993 20 401 1.87 0.29 1997 18 793 1.57 0.26 2005 19 194 1.17 0.19 2010 19 019 1.83 0.31 枯水年 1988 10 595 0.80 0.24 2000 8 989 0.73 0.26 2006 8 459 0.70 0.26 2012 11 780 0.90 0.24 -
[1] Walling D E. Human impact on land-ocean sediment transfer by the world’s rivers[J]. Geomorphology, 2006, 79(3/4): 192−216. [2] Dai Zhijun, Liu J T, Wei Wen, et al. Detection of the Three Gorges Dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6600. [3] Dai Zhijun, Fagherazzi S, Mei Xuefei, et al. Decline in suspended sediment concentration delivered by the Changjiang (Yangtze) River into the East China Sea between 1956 and 2013[J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 268: 123−132. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.06.009 [4] Syvitski J P M, Peckham S D, Hilberman R, et al. Predicting the terrestrial flux of sediment to the global ocean: a planetary perspective[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 162: 5−24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812878106 [5] 程天文, 赵楚年. 我国主要河流入海径流量、输沙量及对沿岸的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 1985, 7(4): 460−471.Cheng Tianwen, Zhao Chunian. Runoff, sediment transport and coastal impact of major rivers in China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1985, 7(4): 460−471. [6] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 392. [7] Syvitski J P M, Vörösmarty C J, Kettner A J, et al. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5720): 376−380. doi: 10.1126/science.1109454 [8] 李彩虹, 于泉洲, 宫雪, 等. 1980年代以来黄河下游含沙量变化的遥感研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2020, 45(2): 165−170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2020.02.033Li Caihong, Yu Quanzhou, Gong Xue, et al. Remote sensing monitoring of sediment content variation in lower reach of Yellow River since 1980s[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2020, 45(2): 165−170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2020.02.033 [9] 陆永军, 季荣耀, 王志力, 等. 珠江三角洲网河区低水位时空变化规律[J]. 水科学进展, 2019, 30(6): 800−809.Lu Yongjun, Ji Rongyao, Wang Zhili, et al. Spatial-temporal variation of low water level in the channel network system of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2019, 30(6): 800−809. [10] Zhan Weikang, Wu Jie, Wei Xing, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of the suspended sediment concentration in the Pearl River Estuary observed by MODIS during 2003–2015[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2019, 172: 22−32. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2018.11.007 [11] Fu K D, He D M, Lu X X. Sedimentation in the Manwan reservoir in the upper Mekong and its downstream impacts[J]. Quaternary International, 2008, 186(1): 91−99. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.09.041 [12] Kummu M, Vans O. Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the lower Mekong River[J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3/4): 275−293. [13] Arisanty D, Saputra A N. Remote sensing studies of suspended sediment concentration variation in barito delta[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2017, 98: 012058. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/98/1/012058 [14] 周金城, 胡辉敏, 黎振强. 密西西比河流域水质协同治理及对长江流域治理的启示[J]. 武陵学刊, 2021, 46(1): 52−58.Zhou Jincheng, Hu Huimin, Li Zhenqiang. Water quality cooperative management in Mississippi River basin and its enlightenment to the Yangtze River basin[J]. Journal of Wuling, 2021, 46(1): 52−58. [15] Han Guoqi, Ma Zhimin, Chen Nan, et al. Coastal sea level projections with improved accounting for vertical land motion[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 16085. doi: 10.1038/srep16085 [16] 任美锷. 人类活动对密西西比河三角洲最近演变的影响[J]. 地理学报, 1989, 44(2): 221−229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.02.011Ren Meie. Man’s impact on the coastal zone of the Mississippi River Delta[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1989, 44(2): 221−229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.02.011 [17] Meade R H, Moody J A. Causes for the decline of suspended-sediment discharge in the Mississippi River system, 1940–2007[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2010, 24(1): 35−49. [18] Joshi S, Xu Y J. Assessment of suspended sand availability under different flow conditions of the lowermost Mississippi River at tarbert landing during 1973–2013[J]. Water, 2015, 7(12): 7022−7044. doi: 10.3390/w7126672 [19] 丁喜桂, Mendelssohn I A, 王吉松. 美国密西西比河三角洲湿地流失的原因及修复措施[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(2): 61−65.Ding Xigui, Mendelssohn I A, Wang Jisong. Wetland loss in Mississippi River Delta complex: causes and remediation[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(2): 61−65. [20] Wass P D, Leeks G J L. Suspended sediment fluxes in the Humber catchment, UK[J]. Hydrological Processes, 1999, 13(7): 935−953. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(199905)13:7<935::AID-HYP783>3.0.CO;2-L [21] Horowitz A J, Elrick K A, Smith J J. Estimating suspended sediment and trace element fluxes in large river basins: methodological considerations as applied to the NASQAN programme[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2001, 15(7): 1107−1132. doi: 10.1002/hyp.206 [22] Siakeu J, Oguchi T, Aoki T, et al. Change in riverine suspended sediment concentration in central Japan in response to late 20th century human activities[J]. CATENA, 2004, 55(2): 231−254. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00120-6 [23] Rovira A, Batalla R J. Temporal distribution of suspended sediment transport in a Mediterranean basin: the Lower Tordera (NE SPAIN)[J]. Geomorphology, 2006, 79(1/2): 58−71. [24] 夏骥, 肖永芹. 密西西比河开发经验及对长江流域发展的启示[J]. 重庆社会科学, 2006(5): 22−26.Xia Ji, Xiao Yongqin. Exploitation experiences of Mississippi River & the revelation for the development of Yangtze basin[J]. Chongqing Social Sciences, 2006(5): 22−26. [25] Xu Y J. Long-term sediment transport and delivery of the largest distributary of the Mississippi River, the Atchafalaya, USA[M]//Banasik K, Horowitz A, Owens P N, et al. Sediment Dynamics for a Changing Future. Wallingford: IAHS Press, 2010. [26] Copeland R R, Thomas W A. Lower Mississippi River tarbert landing to east jetty sedimentation study: numerical model investigation[R]. New Orleans, Louisiana: US Army Engineer District, 1992. [27] Rosen T, Xu Y J. Recent decadal growth of the Atchafalaya River Delta complex: effects of variable riverine sediment input and vegetation succession[J]. Geomorphology, 2013, 194: 108−120. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.04.020 [28] Hulme M. Intergovernmental panel on climate change (IPCC)[C]//International Encyclopedia of Geography: People, the Earth, Environment and Technology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2016. [29] Bonsal B R, Zhang X, Vincent L A, et al. Characteristics of daily and extreme temperatures over Canada[J]. Journal of Climate, 2001, 14(9): 1959−1976. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<1959:CODAET>2.0.CO;2 [30] 魏凤英. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1999.Wei Fengying. Modern Climate Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Technology[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1999. [31] Gao Jinjuan, Dai Zhijun, Mei Xuefei, et al. Interference of natural and anthropogenic forcings on variations in continental freshwater discharge from the Red River (Vietnam) to sea[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380−381: 133−142. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.01.007 [32] Greenwood J A, Landwehr J M, Matalas N C, et al. Probability weighted moments: definition and relation to parameters of several distributions expressable in inverse form[J]. Water Resources Research, 1979, 15(5): 1049−1054. doi: 10.1029/WR015i005p01049 [33] Mouri G, Ros F C, Chalov S. Characteristics of suspended sediment and river discharge during the beginning of snowmelt in volcanically active mountainous environments[J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 213: 266−276. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.02.001 [34] White M J, Santhi C, Kannan N, et al. Nutrient delivery from the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico and effects of cropland conservation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 69(1): 26−40. doi: 10.2489/jswc.69.1.26 [35] Mize S V, Murphy J C, Diehl T H, et al. Suspended-sediment concentrations and loads in the lower Mississippi and Atchafalaya rivers decreased by half between 1980 and 2015[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 564: 1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.05.068 [36] Knox J C. Historical valley floor sedimentation in the upper Mississippi valley[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 1987, 77(2): 224−244. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8306.1987.tb00155.x [37] Alexander J S, Wilson R C, Green W R. A brief history and summary of the effects of river engineering and dams on the Mississippi River system and delta[R]. Reston, Virginia: U. S. Geological Survey, 2012. [38] Tweel A W, Turner R E. Watershed land use and river engineering drive wetland formation and loss in the Mississippi River birdfoot delta[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2012, 57(1): 18−28. doi: 10.4319/lo.2012.57.1.0018 [39] Mossa J. Discharge-sediment dynamics of the lower Mississippi River[J]. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions, 1988, 38: 303−314. [40] Mossa J. Sediment dynamics in the lowermost Mississippi River[J]. Engineering Geology, 1996, 45(1/4): 457−479. [41] 谢云, 赵莹, 张玉平, 等. 美国土壤侵蚀调查的历史与现状[J]. 中国水土保持, 2013(10): 53−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2013.10.015Xie Yun, Zhao Ying, Zhang Yuping, et al. History and current situation of soil erosion survey in the United States[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2013(10): 53−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2013.10.015 [42] Morang A, Rosati J D, King D B. Regional sediment processes, sediment supply, and their impact on the Louisiana coast[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2013, 63(S1): 141−165. [43] Misir V, Arya D S, Murumkar A R. Impact of ENSO on river flows in Guyana[J]. Water Resources Management, 2013, 27(13): 4611−4621. doi: 10.1007/s11269-013-0430-0 [44] Wood P A. Controls of variation in suspended sediment concentration in the River Rother, West Sussex, England[J]. Sedimentology, 1977, 24(3): 437−445. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1977.tb00131.x -





 下载:
下载: