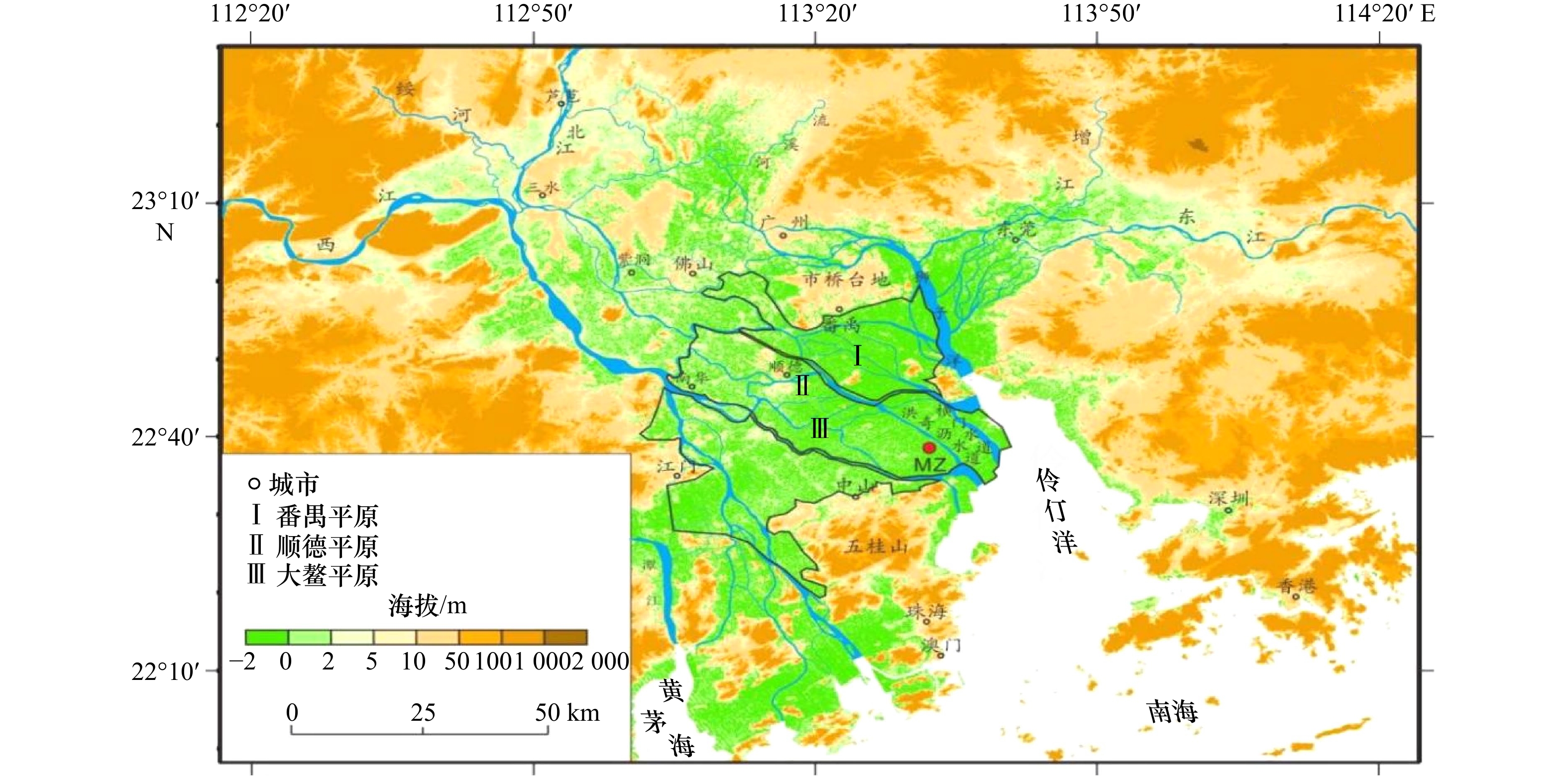
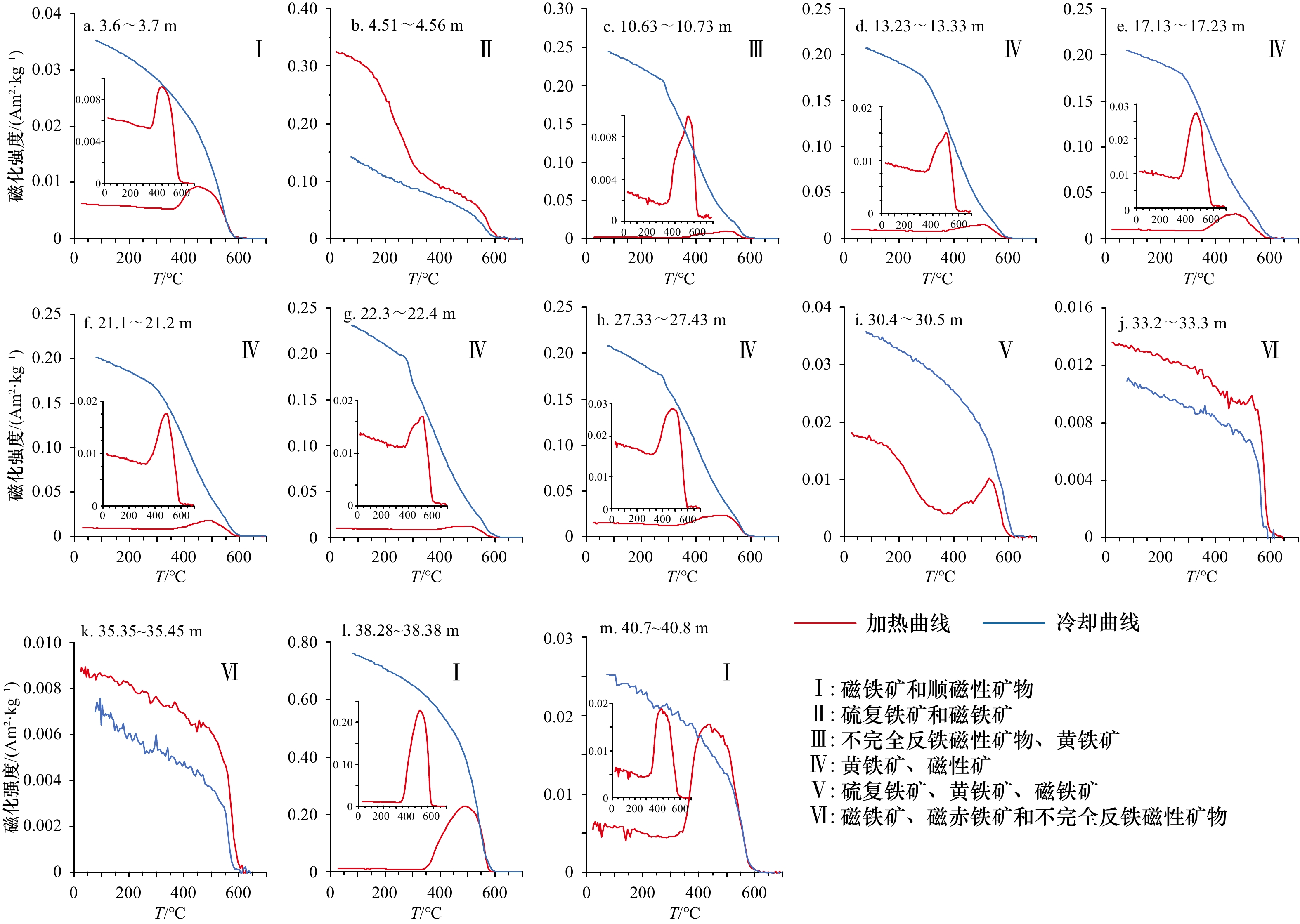
Magnetic characteristics and early diagenesis of Holocene sediments in the Zhujiang River Delta
-
摘要: 磁性矿物的早期成岩作用是沉积物埋藏后的重要过程,辨别早期成岩作用,才能更好地解释地层的矿物磁性变化。本研究对珠江三角洲顺德平原全新世钻孔MZ孔进行沉积相和室温磁性分析,并辅以热磁分析鉴定磁性矿物,以探讨钻孔不同深度和沉积相的早期成岩作用阶段。结果表明,MZ孔全新世地层自下而上包括感潮河道、河口湾和三角洲相。室温磁性特征与沉积相缺乏明显关联,表现出强烈的早期成岩作用。此外,全新世晚期岩芯磁性特征还受人类活动影响。该孔早期成岩作用以磁性矿物溶解和形成自生黄铁矿为主。在三角洲前缘相的上部和河口湾相底部保存了硫复铁矿。根据矿物组合推测以4.51~4.56 m和30.4~30.5 m两个深度为代表的硫复铁矿形成机制不同,即三角洲前缘相中硫复铁矿可能形成于早期成岩作用的硫酸盐还原阶段,而河口湾相的硫复铁矿形成于甲烷厌氧氧化阶段,后者的含量随着深度增加逐渐增多。上述现象说明,沉积环境可以通过影响有机质和硫酸根离子的供应量,决定磁性矿物所达到的早期成岩作用阶段。Abstract: Magnetic mineral diagenesis is an important early diagenetic process after the burial of sediments and its proper identification is the precondition of interpretations for the mineral magnetic properties in the sediments. This study carried out analyses of sedimentary facies, room temperature magnetic and thermomagnetic properties in a Holocene Core MZ collected in the Shunde Plain of the Zhujiang River Delta to identify the vertical changes in the assemblage of magnetic minerals, so as to explore the early diagenetic stages and possible linkage to the sedimentary facies. The results show that the Holocene sedimentary sequence of Core MZ includes tidal channel, embayment, and deltaic successions from bottom upward. The magnetic properties at room temperature lack correlation with sedimentary facies and demonstrate features of strong early diagenesis. In addition, the magnetic properties of the late Holocene sediments were strongly influenced by the human activities. The early diagenesis mainly includes the dissolution of magnetic minerals and the formation of authigenic pyrite. Greigite was also identified in the upper section of the delta-front succession and the bottom of embayment succession. The concentration of greigite increases with depth in the embayment succession. According to the magnetic mineral assemblages, we infer different formation mechanism of greigite in the two successions. We suggest that the greigite in the delta-front facies was formed in the sulfate reduction stage of early diagenesis, whilst it was formed in the anaerobic oxidation stage of methane in the embayment facies. These phenomena indicate that sedimentary environment has impacts on the early diagenetic stage of magnetic minerals by controlling the availability of organic matter and sulfate.
-
图 1 稳态早期成岩作用分带及磁性矿物浓度变化的概念模型图(修改自文献[26-27])
红色为磁铁矿,灰色为硫复铁矿。SD、PSD、MD、SP分别为单畴态、假单畴态、多畴态以及超顺磁态颗粒;SMTZ为硫酸盐-甲烷转换带
Fig. 1 Steady mtate redox zones of early diagenesis and associated changes in the concentrations of magnetic minerals (refer to references [26-27])
Magnetite is red, greigite is gray. SD, PSD, MD and SP are single-domain, pseudosingle-domain, multi-domain and superparamagnetic particles. SMTZ is sulfate-methane transition zone
表 1 珠江三角洲顺德平原MZ孔测年结果及校正(校正年龄取概率大于0.8的区间)
Tab. 1 AMS14C ages and calibrations for Core MZ in the Shunde Plain of Zhujiang River Delta (the calibrated ages are selected with a probability of more than 0.8)
深度/m 标高/m 测年材料 常规年龄/a BP 校正年龄/cal. a BP 实验室编号 2σ 中值 概率 6.52 −6.1 植物 380±30 318~503 445 1.000 Beta-548917 7.78 −7.36 植物 1 100±30 955~1 063 1 000 0.961 Beta-548918 10.39 −9.97 木头 2 880±30 2 921~3 078 3 010 0.899 Beta-548919 11.80 −11.38 贝壳 2 590±30 1 993~2 388 2 205 1.000 Beta-548920 17.43 −17.01 贝壳 2 690±30 2 117~2 565 2 335 1.000 Beta-548921 18.44 −18.02 贝壳 3 010±30 2 516~2 918 2 730 1.000 Beta-548923 21.74 −21.32 贝壳 5 420±30 5 524~5 891 5 695 1.000 Beta-548924 21.88 −21.46 植物 7 820±30 8 534~8 649 8 595 0.968 Beta-548925 22.14 −21.72 植物 4 950±30 5 598~5 732 5 660 1.000 Beta-548926 30.06 −29.64 植物 8 780±30 9 658~9 908 9 785 0.963 Beta-548927 31.30 −30.88 木头 8 850±30 9 766~10 154 9 970 1.000 Beta-548928 42.73 −42.31 贝壳 10 980±30 12 813~12 998 12 880 0.915 Beta-548929 44.20 −43.78 贝壳 11 180±30 13 081~13 162 13 110 1.000 Beta-548930 表 2 MZ孔磁性单元的磁参数特征值
Tab. 2 Characteristic values of magnetic parameters in each unit of Core MZ
磁性参数 磁性单元及沉积相类型 A单元
(三角洲前缘)B单元
(三角洲
前缘−斜坡)C单元
(斜坡−前三
角洲)D单元
(前三角洲)E单元
(河口湾)F单元
(河口湾)G单元
(感潮河道−河床)χ/
(10−8 m3·kg−1)范围 119.7~395.4 11.5~71.2 7.1~26.4 17.5~28.0 13.0~30.4 16.1~93.2 3.9~73.5 平均值 202.1 52.2 13.8 21.9 20.8 34.1 22.2 标准差 73.3 15.4 7.6 2.3 3.9 18.0 11.0 SIRM/
(10−6 Am2·kg−1)范围 10 461.3~30 448.1 905.2~28 471.9 341.0~3 542.4 1 636.0~4 355.8 1 711.9~4 217.1 1 955.8~18 601.5 1 007.5~27 547.1 平均值 17 272.3 6 909.8 1 466.5 2 607.6 2 792.0 7 210.8 2 959.0 标准差 5 966.5 5 625.4 1 295.6 690.5 623.9 5 291.8 3 697.6 χfd /% 范围 5~9.71 0~7.0 0~1.9 0~1.6 0~9.72 0~3.7 0~2.7 平均值 6.8 4.2 0.3 0.2 0.9 0.7 0.5 标准差 1.2 2.1 0.7 0.4 2.0 0.9 0.7 χarm/
(10−8 m3·kg−1)范围 467.3~1 842.4 11.9~1 756.8 1.5~20.9 33.0~404.0 200.6~521.2 60.3~338.2 22.8~266.8 平均值 940.6 356.9 5.8 145.6 346.1 198.6 83.5 标准差 320.6 403.5 6.8 101.2 83.5 86.7 49.7 χarm/χ 范围 3.3~7.2 0.2~67.1 0.1~3.0 1.6~18.5 11.2~21.9 1.1~13.4 1.7~14.0 平均值 4.8 8.4 0.7 6.6 16.7 6.8 4.0 标准差 1.0 15.0 1.0 4.5 2.7 3.2 2.3 (χarm/SIRM)/
(10−5 mA−1)范围 33.1~88.4 2.1~594.3 0.9~61.4 16.1~134.8 85.9~162.6 10.8~70.5 9.7~91.9 平均值 56.5 74.9 12.5 52.5 124.6 35.3 32.2 标准差 14.7 133.4 21.9 27.5 15.9 17.3 12.6 SIRM/χ 范围 7.7~10.0 7.8~50.7 4.8~13.6 9.1~19.2 8.4~14.7 5.0~60.9 6.6~37.5 平均值 8.6 13.0 8.7 11.9 13.4 24.4 12.7 标准差 0.8 9.5 3.6 2.7 1.1 16.2 5.8 HIRM/
(10−6 Am2·kg−1)范围 66.1~1 241.4 121.0~698.4 25.9~256.2 129.5~231.5 73.6~236.0 6.5~721.2 9.3~372.1 平均值 595.6 318.5 129.6 196.2 165.3 195.8 131.7 标准差 319.5 126.2 84.9 21.0 40.4 155.5 69.8 S−20/% 范围 53.3~75.7 50.8~80.1 61.1~73.8 56.5~81.5 81.1~568.7 59.8~98.8 53.6~97.8 平均值 58.7 57.1 69.3 62.3 63.0 73.8 66.4 标准差 7.5 7.8 4.2 6.4 4.2 11.0 8.7 S−40/% 范围 75.1~86.9 50.5~76.7 53.0~68.4 52.6~73.9 59.8~82.8 51.9~98.8 53.5~98.5 平均值 79.2 70.1 58.1 63.8 64.6 63.6 62.0 标准差 3.4 5.1 6.0 4.1 4.6 10.4 7.5 S−100/% 范围 90.0~95.3 64.3~91.3 69.0~88.4 80.5~88.6 86.2~95.8 81.1~99.6 75.3~100.0 平均值 92.2 87.7 77.9 84.4 87.8 88.3 86.3 标准差 1.4 6.0 7.6 2.1 1.5 3.5 3.5 S−300/% 范围 95.4~99.6 81.7~97.6 83.3~94.1 89.2~95.4 92.5~97.7 91.2~99.9 88.7~99.7 平均值 96.6 94.2 89.2 92.1 94.0 96.1 94.5 标准差 1.2 3.3 3.8 1.6 0.9 2.5 2.1 注:磁参数特征值包括最大值、最小值、平均值和标准差。 -
[1] Thompson R, Oldfield F. Environmental Magnetism[M]. London: Allen & Unwin, 1986. [2] Oldfield F. Environmental magnetism—a personal perspective[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(1): 73−85. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90031-O [3] Bloemendal J, King J W, Hall F R, et al. Rock magnetism of Late Neogene and Pleistocene deep-sea sediments: relationship to sediment source, diagenetic processes, and sediment lithology[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1992, 97(B4): 4361−4375. doi: 10.1029/91JB03068 [4] Verosub K L, Roberts A P. Environmental magnetism: past, present, and future[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1995, 100(B2): 2175−2192. doi: 10.1029/94JB02713 [5] Liu Qingsong, Roberts A P, Larrasoaña J C, et al. Environmental magnetism: principles and applications[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2012, 50(4): RG4002. [6] 张卫国, 贾铁飞, 陆敏, 等. 长江口水下三角洲Y7柱样磁性特征及其影响因素[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(6): 1063−1071. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.06.022Zhang Weiguo, Jia Tiefei, Lu Min, et al. Magnetic properties of core Y7 from subaqueous delta of the Changjiang estuary and their influencing factors[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(6): 1063−1071. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.06.022 [7] 马鸿磊, 张卫国, 胡忠行, 等. 长江口外CX21柱样的磁性特征及其影响因素[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2012(3): 120−129,153.Ma Honglei, Zhang Weiguo, Hu Zhongxing, et al. Magnetic properties of the core CX21 off the Yangtze Estuary and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2012(3): 120−129,153. [8] 王永红, 张卫国, 刘修锦, 等. 黄河三角洲不同气候条件下沉积物中胶黄铁矿的形成[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(10): 2193−2201.Wang Yonghong, Zhang Weiguo, Liu Xiujin, et al. Formation of greigite under different climate conditions in the Yellow River delta[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 44(10): 2193−2201. [9] 刘修锦, 王永红, 李广雪, 等. 基于磁学和粒度参数的黄河三角洲刁口叶瓣地区全新世以来的地层演化[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(3): 518−526.Liu Xiujin, Wang Yonghong, Li Guangxue, et al. Stratigraphy evolution of the Diaokou Lobe area in the Huanghe Delta since Holocene: implication from grain size and magnetic properties[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(3): 518−526. [10] Chen Ting, Wang Zhanghua, Wu Xuxu, et al. Magnetic properties of tidal flat sediments on the Yangtze coast, China: early diagenetic alteration and implications[J]. The Holocene, 2015, 25(5): 832−843. doi: 10.1177/0959683615571425 [11] 白雪莘, 张卫国, 董艳, 等. 长江三角洲全新世地层中潮滩沉积磁性特征及其古环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(6): 1165−1175.Bai Xuexin, Zhang Weiguo, Dong Yan, et al. Magnetic properties of Holocene tidal flats in the Yangtze Delta and their paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(6): 1165−1175. [12] Pan Dadong, Chen Ting, Zhan Qing, et al. Mineral magnetic properties of Holocene sediments in the subaqueous Yangtze delta and the implications for human activity and early diagenesis[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 459: 133−143. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.05.010 [13] Yang Xiaoqiang, Grapes R, Zhou Houyun, et al. Magnetic properties of sediments from the Pearl River Delta, South China: paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(1): 56−66. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0151-4 [14] 欧阳婷萍, 万洪富, 张金兰, 等. 珠江三角洲农业土壤磁化率空间分布特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(6): 1199−1206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.06.13Ouyang Tingping, Wan Hongfu, Zhang Jinlan, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of magnetic susceptibility of agricultural soils and analysis of its influencing factors for the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(6): 1199−1206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.06.13 [15] Chu Nanyang, Yang Qingshu, Liu Feng, et al. Distribution of magnetic properties of surface sediment and its implications on sediment provenance and transport in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 424: 106162. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106162 [16] 杨小强, 李华梅, 余素华. 从SX97孔分析深圳沿海近3万年来海平面及气候变迁[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(2): 146−154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.02.007Yang Xiaoqiang, Li Huamei, Yu Suhua. Sea-level fluctuations and paleoclimatic evolution histories from Core SX97 in Shenzhen region of South China during about 30 ka BP[J]. Geochimica, 2003, 32(2): 146−154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.02.007 [17] 曹玲珑, 王建华, 王晓静, 等. 珠江口全新世沉积物粒度与磁化率的变化特征及其所反映的气候环境变化[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2012(1): 167−175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2012.01.022Cao Linglong, Wang Jianhua, Wang Xiaojing, et al. Holoceneediments of the Pearl River Estuary changes in grain size and magnetic susceptibility and as reflected in climate changes[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2012(1): 167−175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2012.01.022 [18] 彭杰, 杨小强, 黄文娅, 等. 珠江三角洲全新世海平面升降及其对全球变化的响应[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 53(6): 63−72.Peng Jie, Yang Xiaoqiang, Huang Wenya, et al. Sea-level fluctuations and response to global changes during the Holocene in the Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2014, 53(6): 63−72. [19] Karlin R, Levi S. Diagenesis of magnetic minerals in recent haemipelagic sediments[J]. Nature, 1983, 303(5915): 327−330. doi: 10.1038/303327a0 [20] Snowball I, Thompson R. A stable chemical remanence in Holocene sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1990, 95(B4): 4470−4479. [21] Roberts A P, Turner G M. Diagenetic formation of ferrimagnetic iron sulphide minerals in rapidly deposited marine sediments, South Island, New Zealand[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 115(1/4): 257−273. [22] Roberts A P, Reynolds R L, Verosub K L, et al. Environmental magnetic implications of Greigite (Fe3S4) Formation in a 3 m. y. lake sediment record from Butte Valley, northern California[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1996, 23(20): 2859−2862. doi: 10.1029/96GL02831 [23] Robinson S G, Sahota J T S, Oldfield F. Early diagenesis in North Atlantic abyssal plain sediments characterized by rock-magnetic and geochemical indices[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 163(1/4): 77−107. [24] Liu Jian, Zhu Rixiang, Roberts A P, et al. High-resolution analysis of early diagenetic effects on magnetic minerals in post-middle-Holocene continental shelf sediments from the Korea Strait[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2004, 109(B3): B03103. [25] Demory F, Oberhänsli H, Nowaczyk N R, et al. Detrital input and early diagenesis in sediments from Lake Baikal revealed by rock magnetism[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2005, 46(1/4): 145−166. [26] Rowan C J, Roberts A P, Broadbent T. Reductive diagenesis, magnetite dissolution, greigite growth and paleomagnetic smoothing in marine sediments: a new view[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 277(1/2): 223−235. [27] Roberts A P. Magnetic mineral diagenesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 151: 1−47. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.09.010 [28] Froelich P N, Klinkhammer G P, Bender M L, et al. Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(7): 1075−1090. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90095-4 [29] Beal E J, House C H, Orphan V J. Manganese- and iron-dependent marine methane oxidation[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5937): 184−187. doi: 10.1126/science.1169984 [30] 刘喜停, 李安春, 马志鑫, 等. 沉积过程对自生黄铁矿硫同位素的约束[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(1): 124−137.Liu Xiting, Li Anchun, Ma Zhixin, et al. Constraint of sedimentary processes on the sulfur isotope of authigenic pyrite[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(1): 124−137. [31] Liu Xiting, Li Anchun, Fike D A, et al. Environmental evolution of the East China Sea inner shelf and its constraints on pyrite sulfur contents and isotopes since the last deglaciation[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 429: 106307. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106307 [32] Liu Jianxing, Shi Xuefa, Liu Qingsong, et al. Authigenic iron sulfides indicate sea-level change on the continental shelf: an illustration from the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2021, 126(3): e2020JB021222. [33] Liu Xiting, Zhang Mingyu, Li Anchun, et al. Depositional control on carbon and sulfur preservation onshore and offshore the Oujiang Estuary: implications for the C/S ratio as a salinity indicator[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2021, 227: 104510. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2021.104510 [34] Ran Yong, Zhang Yulong. Sources, early diagenesis, and structure of organic matter in the Pearl River Delta[M]// He Zhongqi, Wu Fengchang. Labile Organic Matter-Chemical Compositions, Function, and Significance in Soil and the Environment. Madison: Soil Science Society of America, 2015: 337−367. [35] 王建华, 郑卓, 吴超羽. 潮汕平原晚第四纪沉积相与古环境演变[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 36(1): 95−100.Wang Jianhua, Zheng Zhuo, Wu Chaoyu. Sedimentary facies and paleoenvironmental evolution of the late Quaternary in the Chao Shan Plain, East Guangdong[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1997, 36(1): 95−100. [36] Zhang Chaosheng, Wang Lijun. Multi-element geochemistry of sediments from the Pearl River system, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2001, 16(9/10): 1251−1259. [37] 吴超羽, 任杰, 包芸, 等. 珠江河口“门”的地貌动力学初探[J]. 地理学报, 2006, 61(5): 537−548. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.05.010Wu Chaoyu, Ren Jie, Bao Yun, et al. A preliminary study on the morphodynamic evolution of the ‘Gate’of the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2006, 61(5): 537−548. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.05.010 [38] 吴超羽, 何志刚, 任杰, 等. 珠江三角洲中部子平原形成演变机理研究——以大鳌平原为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(5): 814−827. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.023Wu Chaoyu, He Zhigang, Ren Jie, et al. A physical study on the evolution of the sub-deltaic plains in the mid Zhujiang River delta: a case study of Da’ao sub-delta[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(5): 814−827. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.023 [39] Zong Y, Yu F, Huang G, et al. Sedimentary evidence of Late Holocene human activity in the Pearl River delta, China[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2010, 35(9): 1095−1102. doi: 10.1002/esp.1970 [40] Zong Yongqiang, Huang Kangyou, Yu Fengling, et al. The role of sea-level rise, monsoonal discharge and the palaeo-landscape in the early Holocene evolution of the Pearl River delta, southern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 54: 77−88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.002 [41] Fu Shuqing, Xiong Haixian, Zong Yongqiang, et al. Reasons for the low sedimentation and slow progradation in the Pearl River delta, southern China, during the middle Holocene[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 423: 106133. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106133 [42] Yoneda M, Uno H, Shibata Y, et al. Radiocarbon marine reservoir ages in the western Pacific estimated by pre-bomb molluscan shells[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B:Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2007, 259(1): 432−437. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2007.01.184 [43] Southon J, Kashgarian M, Fontugne M, et al. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian ocean and Southeast Asia[J]. Radiocarbon, 2002, 44(1): 167−180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778 [44] Bloemendal J, Lamb B, King L. Paleoenvironmental implications of rock-magnetic properties of Late Quaternary sediment cores from the eastern equatorial Atlantic[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1988, 3(1): 61−87. [45] 张卫国, 俞立中, 许羽. 环境磁学研究的简介[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1995, 10(3): 95−105.Zhang Weiguo, Yu Lizhon, Xu Yu. Brief reviews on environmental maguetism[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1995, 10(3): 95−105. [46] Maher B A. Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1988, 94(1): 83−96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1988.tb03429.x [47] Evans M E, Heller F, Bloemendal J, et al. Natural magnetic archives of past global change[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 1997, 18(2): 183−196. [48] 谢红霞. 长江口潮滩芦苇与互花米草中重金属累积的比较研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2006.Xie Hongxia. A comparative study on heavy metal accumulation in Phragmites australis and Spartina alterniflora in tidal flat of Yangtze Estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2006. [49] Stober J C, Thompson R. An investigation into the source of magnetic minerals in some Finnish lake sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1979, 45(2): 464−474. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90145-6 [50] Snowball I F. Magnetic hysteresis properties of greigite (Fe3S4) and a new occurrence in Holocene sediments from Swedish Lappland[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1991, 68(1/2): 32−40. [51] Roberts A P. Magnetic properties of sedimentary greigite (Fe3S4)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 134(3/4): 227−236. [52] Passier H F, De Lange G J, Dekkers M J. Magnetic properties and geochemistry of the active oxidation front and the youngest sapropel in the eastern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2001, 145(3): 604−614. doi: 10.1046/j.0956-540x.2001.01394.x [53] Roberts A P, Chang Liao, Rowan C J, et al. Magnetic properties of sedimentary greigite (Fe3S4): an update[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2011, 49(1): RG1002. [54] Dunlop D, Özdemir Ö, Fuller M D. Rock magnetism: fundamentals and frontiers[J]. Physics Today, 1998, 51(9): 64−66. doi: 10.1063/1.882466 [55] Basavaiah N, Babu J L V M, Gawali P B, et al. Late Quaternary environmental and sea level changes from Kolleru Lake, SE India: inferences from mineral magnetic, geochemical and textural analyses[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 371: 197−208. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.12.018 [56] Hoffmann V. Greigite (Fe3S4): magnetic properties and first domain observations[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1992, 70(3/4): 288−301. [57] Torii M, Fukuma K, Horng C S, et al. Magnetic discrimination of pyrrhotite- and greigite-bearing sediment samples[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1996, 23(14): 1813−1816. doi: 10.1029/96GL01626 [58] 李海燕, 张世红. 黄铁矿加热过程中的矿相变化研究——基于磁化率随温度变化特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2005, 48(6): 1384−1391. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.06.022Li Haiyan, Zhang Shihong. Detection of mineralogical changes in pyrite using measurements of temperature-dependence susceptibilities[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(6): 1384−1391. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.06.022 [59] 王磊, 潘永信, 李金华, 等. 黄铁矿热转化矿物相变过程的岩石磁学研究[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 2008, 38(9): 1068−1077.Wang Lei, Pan Yongxin, Li Jinhua, et al. Petromagnetic study of pyrite thermal transformation mineral transformation process[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2008, 38(9): 1068−1077. [60] Ferrow E A, Sjöberg B A. Oxidation of pyrite grains: a mössbauer spectroscopy and mineral magnetism study[J]. Hyperfine Interactions, 2005, 163(1/4): 95−108. [61] Liu Xiuming, Hesse P, Rolph T, et al. Properties of magnetic mineralogy of Alaskan loess: evidence for pedogenesis[J]. Quaternary International, 1999, 62(1): 93−102. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(99)00027-0 [62] Zhou L P, Oldfield F, Wintle A G, et al. Partly Pedogenic origin of magnetic variations in Chinese loess[J]. Nature, 1990, 346(6286): 737−739. doi: 10.1038/346737a0 [63] Jia Jia, Xia Dunsheng, Wang Bo, et al. Magnetic investigation of Late Quaternary loess deposition, Ili area, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 250: 84−92. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.06.018 [64] Chen Huixian, Wang Jianhua, Khan N S, et al. Early and late Holocene paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the Pearl River estuary, South China Sea using foraminiferal assemblages and stable carbon isotopes[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 222: 112−125. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.04.002 [65] Liu Yan, He Zhongfa, Wang Zhanghua. Magnetic properties of Holocene core ZK9 in the subaqueous Yangtze delta and their mechanisms and implications[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2013, 7(3): 331−340. doi: 10.1007/s11707-013-0375-x [66] 梁方仲. 中国历代户口、田地、田赋统计: 上册[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 2008.Liang Fangzhong. Statistics of Registered Residents, Farmlands, Land Tax in Chinese History[M]. Beijing: Zhong Hua Book Company, 2008. [67] Hu Dengke, Clift P D, Böning P, et al. Holocene evolution in weathering and erosion patterns in the Pearl River delta[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(7): 2349−2368. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20166 [68] Yu Fengling, Zong Yongqiang, Lloyd J M, et al. Bulk organic δ13C and C/N as indicators for sediment sources in the Pearl River delta and estuary, southern China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 87(4): 618−630. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.02.018 [69] Zong Yongqiang, Zheng Zhuo, Huang Kangyou, et al. Changes in sea level, water salinity and wetland habitat linked to the late agricultural development in the Pearl River delta plain of China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 70: 145−157. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.03.020 [70] Garming J F L, Bleil U, Riedinger N. Alteration of magnetic mineralogy at the sulfate–methane transition: analysis of sediments from the Argentine continental slope[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2005, 151(3/4): 290−308. [71] Riedinger N, Pfeifer K, Kasten S, et al. Diagenetic alteration of magnetic signals by anaerobic oxidation of methane related to a change in sedimentation rate[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(16): 4117−4126. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.02.004 [72] März C, Hoffman J, Bleil U, et al. Diagenetic changes of magnetic and geochemical signals by anaerobic methane oxidation in sediments of the Zambezi deep-sea fan (SW Indian Ocean)[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 255(3/4): 118−130. [73] Poulton S W, Krom M D, Raiswell R. A revised scheme for the reactivity of iron (oxyhydr) oxide minerals towards dissolved sulfide[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(18): 3703−3715. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.03.012 [74] Peng Xiaotong, Guo Zixiao, Chen Shun, et al. Formation of carbonate pipes in the northern Okinawa Trough linked to strong sulfate exhaustion and iron supply[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 205: 1−13. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.02.010 [75] Canfield D E, Berner R A. Dissolution and pyritization of magnetite in anoxie marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(3): 645−659. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90076-7 [76] 罗祎, 苏新, 蒋少涌, 等. 东太平洋水合物海岭钻井沉积物铁硫化物的磁学特征及其意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(5): 235−247.Luo Yi, Su Xin, Jiang Shaoyong, et al. The magnetic properties of iron sulfide minerals from Hydrate Ridge cores, East Pacific and their significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(5): 235−247. [77] Kao S J, Horng C S, Roberts A P, et al. Carbon-sulfur-iron relationships in sedimentary rocks from southwestern Taiwan: influence of geochemical environment on greigite and pyrrhotite formation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 203(1/2): 153−168. [78] Aben F M, Dekkers M J, Bakker R R, et al. Untangling inconsistent magnetic polarity records through an integrated rock magnetic analysis: a case study on Neogene sections in East Timor[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(6): 2531−2554. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005294 [79] Tarduno J A. Temporal trends of magnetic dissolution in the pelagic realm: gauging paleoproductivity?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 123(1/3): 39−48. [80] Yamazaki T, Abdeldayem A L, Ikehara K. Rock-magnetic changes with reduction diagenesis in Japan Sea sediments and preservation of geomagnetic secular variation in inclination during the last 30, 000 years[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2003, 55(6): 327−340. doi: 10.1186/BF03351766 [81] Dillon M, Bleil U. Rock magnetic signatures in diagenetically altered sediments from the Niger deep-sea fan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2006, 111(B3): B03105. -





 下载:
下载: