Temporal and spatial dynamics of suspended sediment and its driving mechanism in the Yellow River Estuary
-
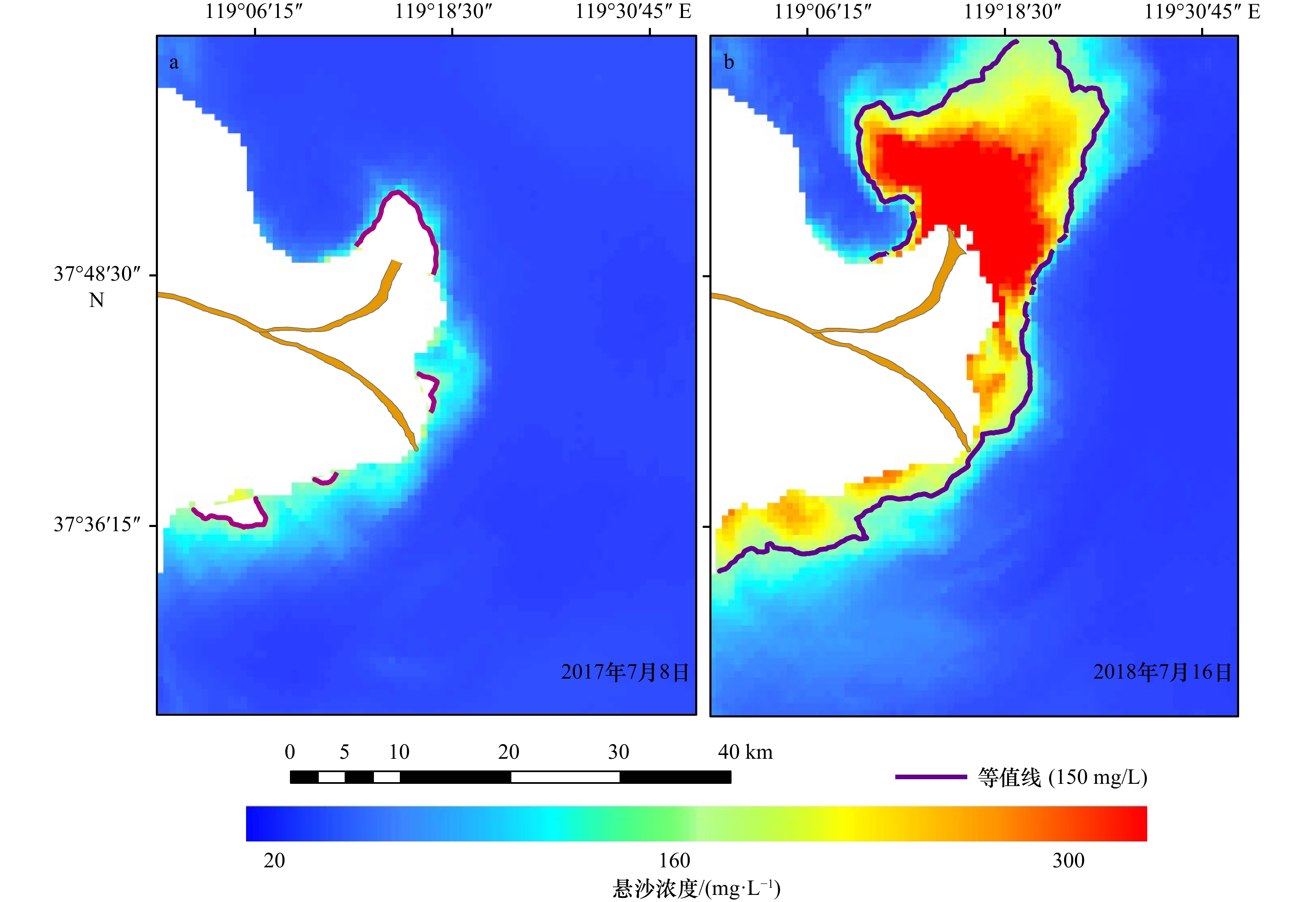
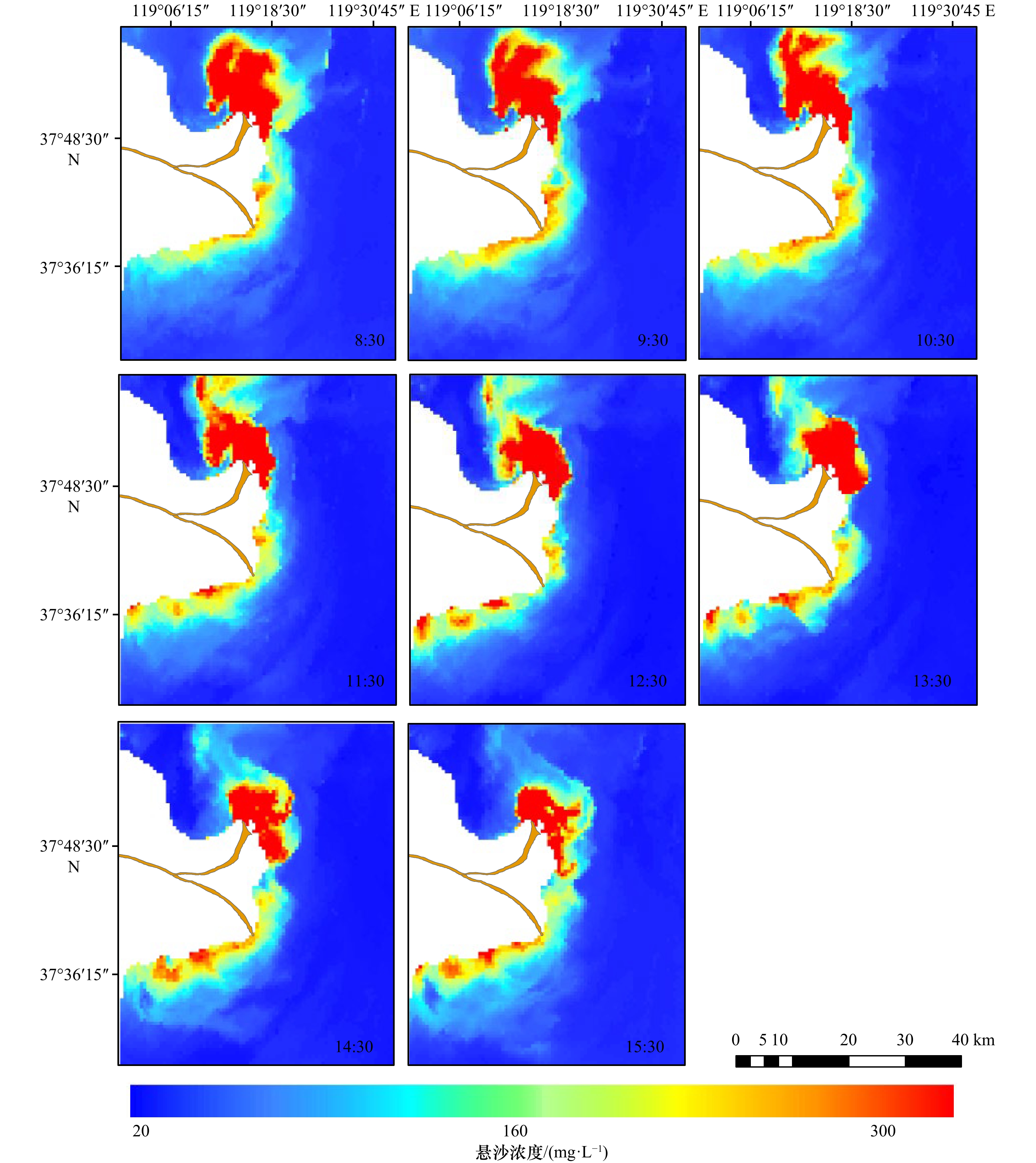
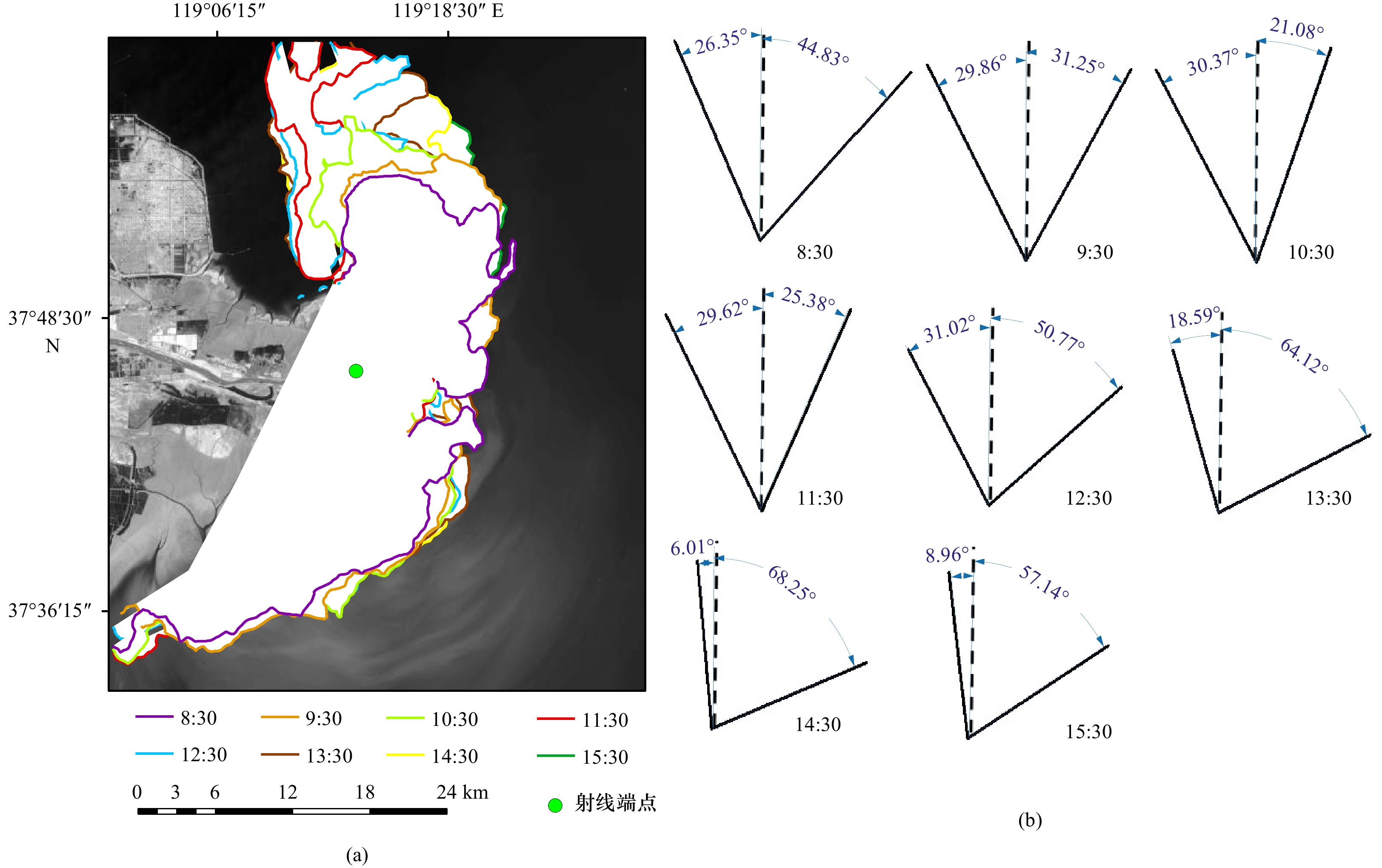
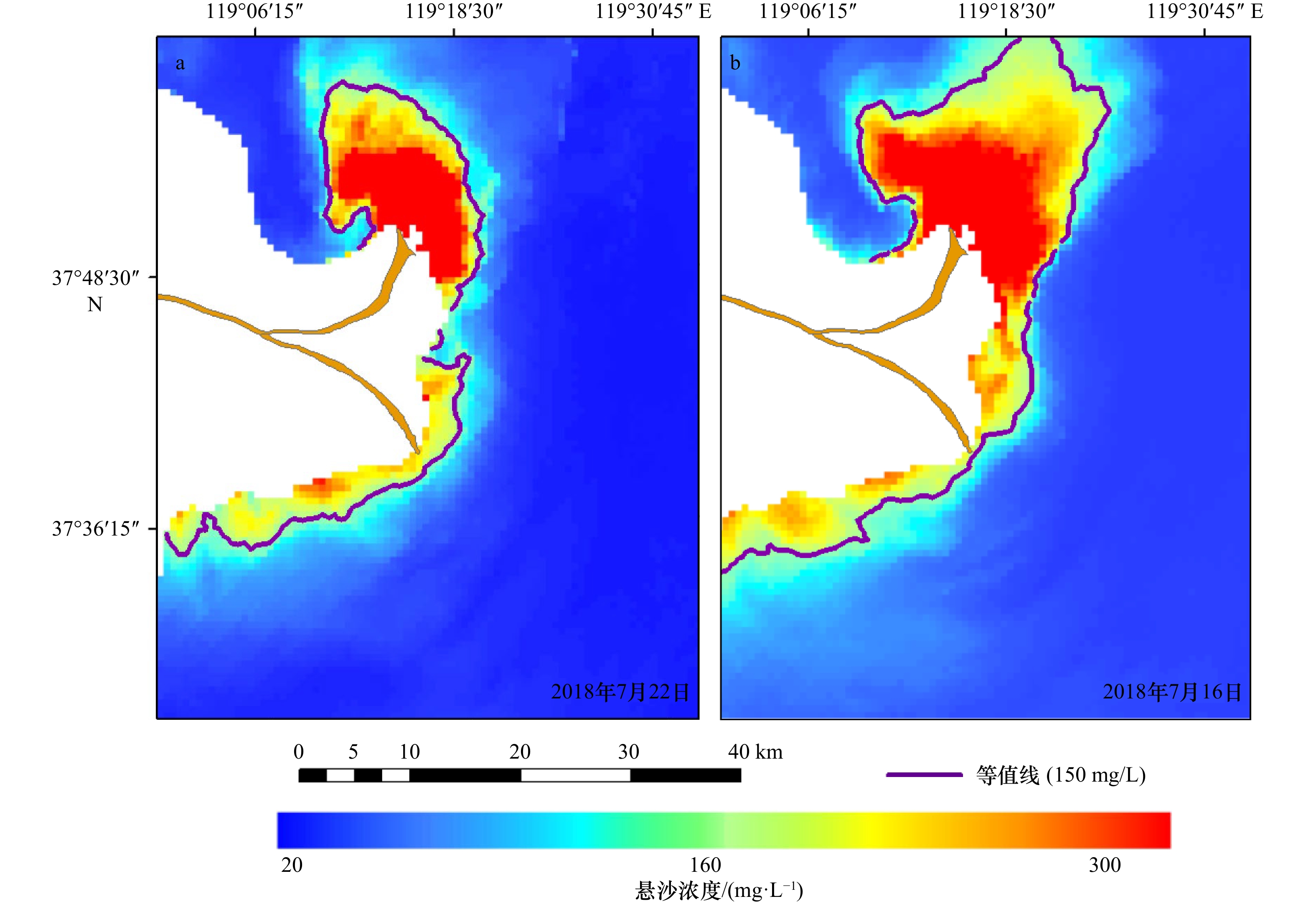
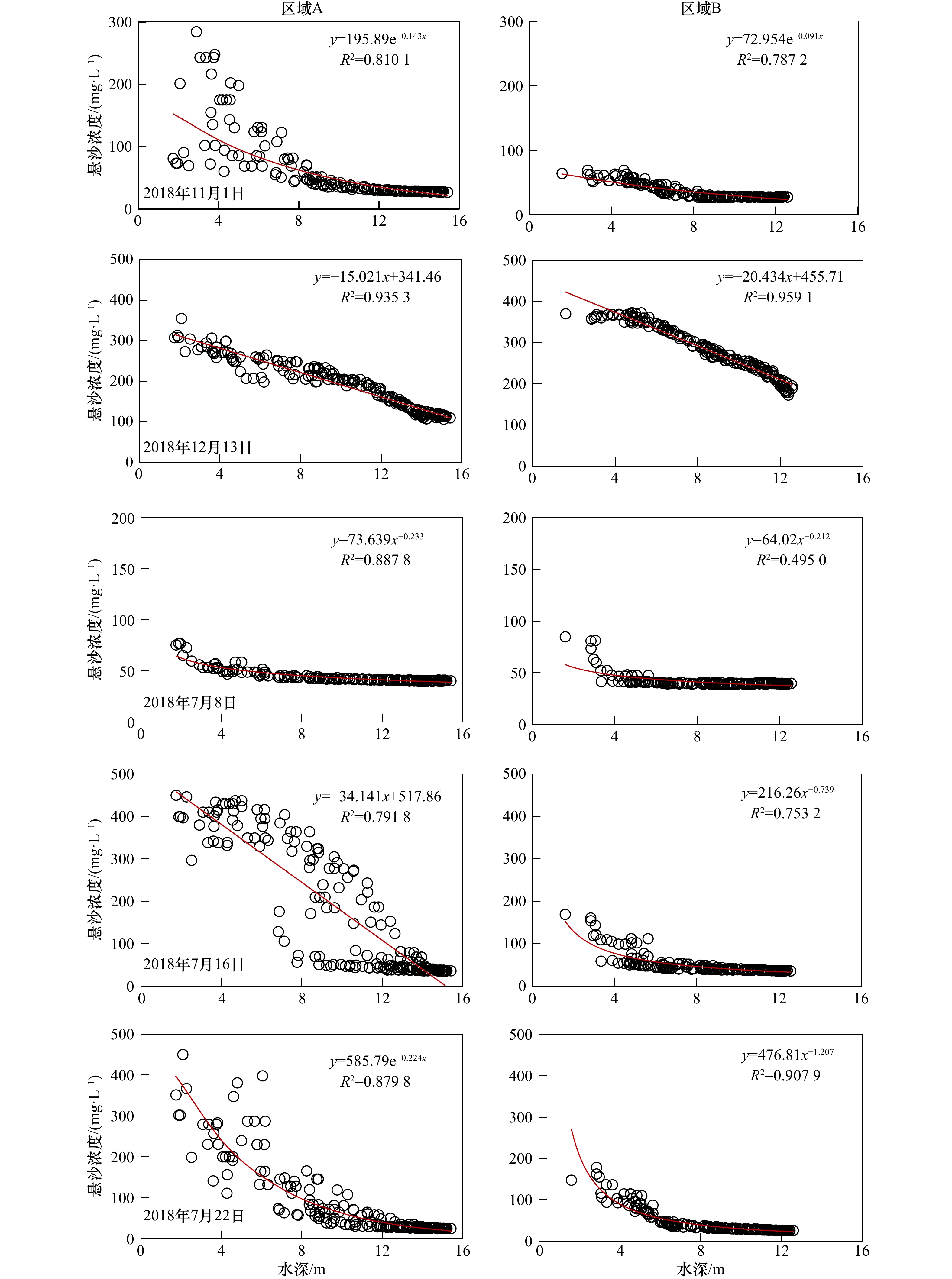
摘要: 受径流输沙、风浪、潮汐等影响,河口近岸海域悬浮泥沙具有显著的时空变化。本文基于小时分辨率的GOCI遥感影像,利用最优遥感反演算法,结合空间分析和统计方法,深入研究黄河口及邻近海域悬沙时空动态特征及驱动机制。结果表明,径流输沙对悬沙浓度的影响以河口近岸区为主,高径流输沙对悬沙浓度分布影响可达距岸约20 km,并向孤东近岸方向扩散。大风可引起清水沟老河口区泥沙强烈再悬浮,形成高浓度悬沙区。涨落潮对小时尺度的悬沙浓度影响显著,并影响悬沙的南北扩散。大潮悬沙浓度变化和扩散范围均大于小潮,潮流流速不同是造成该差异的主要原因。水深与悬沙浓度之间存在较明显的负相关关系,根据不同驱动因素的差异,悬沙浓度随着水深的增加呈现出指数型、幂函数型、线性3种关系。Abstract: Affected by fluvial sediment discharge, wind waves and tides, etc., suspended sediment in estuaries and adjacent waters has significant temporal and spatial changes. Based on the GOCI remote sensing images at hourly resolution, this paper uses the optimal remote sensing inversion algorithm, combined with spatial analysis and statistical methods to deeply study the temporal and spatial dynamic characteristics and driving mechanism of suspended sediment in the Yellow River Estuary and adjacent waters. The results show that the impact of fluvial sediment discharge on the concentration of suspended sediment is concentrated in the nearshore area of the estuary. The impact of high fluvial sediment discharge on the distribution of suspended sediment concentration can reach about 20 km offshore and spread to the Gudong nearshore area. Strong winds can cause intensive resuspension of sediment near the old river mouth of Qingshuigou, forming a high-concentration suspended sediment area. The flood and ebb tides have a significant impact on the hourly-scale suspended sediment concentration, and affect the dispersal of suspended sediment from north to south. The variation and dispersal range of the suspended sediment concentration in the spring tide are larger than that of the neap tide due to different tidal flow velocities. There is an obvious negative correlation between water depth and suspended sediment concentration. According to the difference of driving factors, the suspended sediment concentration present exponential, power function, and linear relationships with the increase of water depth.
-
Key words:
- GOCI /
- suspended sediment /
- temporal and spatial dynamics /
- driving factors
-
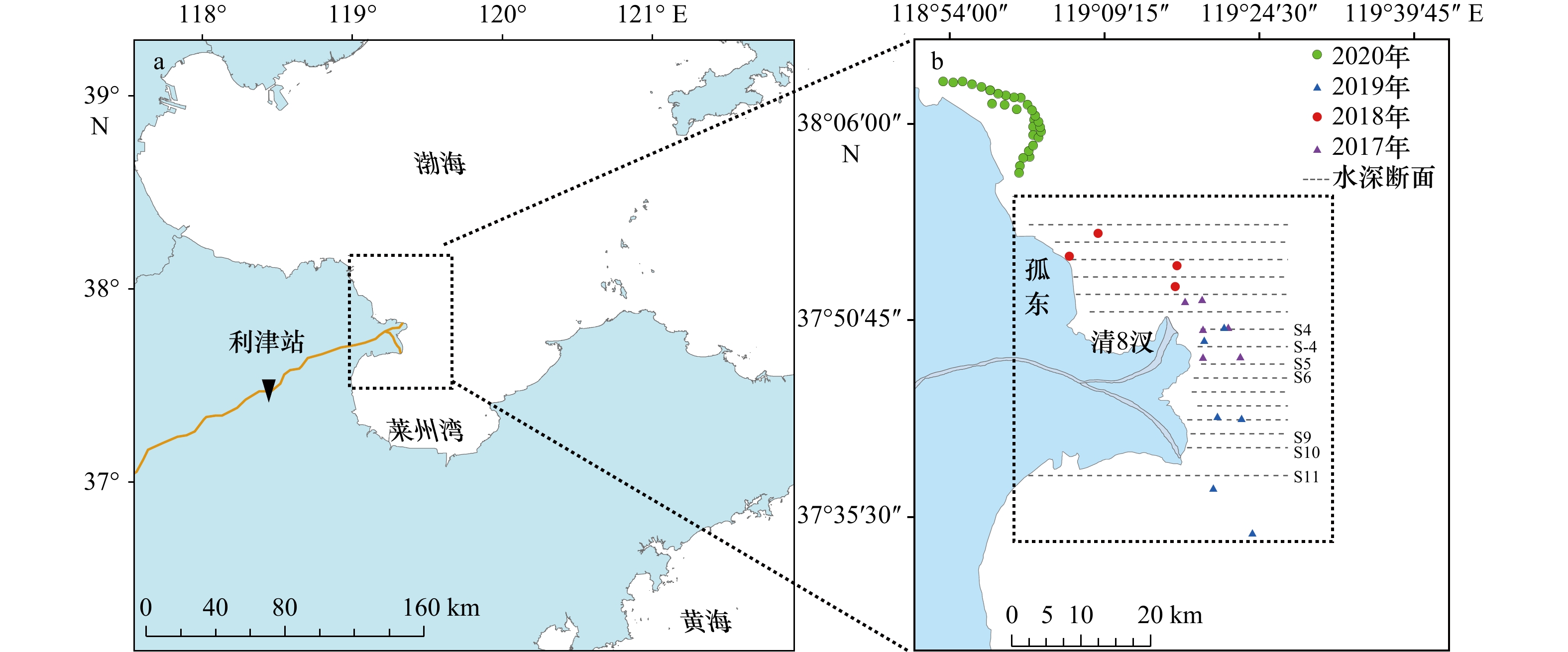
表 1 悬沙浓度实测数据
Tab. 1 Measured data of suspended sediment concentration
日期 数据量/个 悬沙浓度范围/(mg·L−1) 2017年8月6日 14 2.2~47.8 2017年8月7日 12 1.4~248.5 2017年8月8日 6 3.6~48.6 2018年8月25日 10 10.9~195.26 2018年8月26日 11 3.6~405.07 2018年8月27日 8 4.2~34.4 2019年7月12日 10 10~40 2019年7月15日 6 10~80 2020年9月6日 7 9.7~46.9 表 2 所用GOCI影像信息
Tab. 2 GOCI imagery information used in this study
成像日期 可用影像/景 成像日期 可用影像/景 2017年7月8日 8 2018年8月27日 5 2017年8月6日 8 2018年8月30日 8 2017年8月7日 8 2018年11月1日 8 2017年8月8日 8 2018年12月13日 8 2017年8月9日 8 2019年7月11日 8 2018年7月16日 8 2019年7月12日 8 2018年7月22日 8 2018年7月15日 3 2018年8月25日 8 2018年7月16日 8 2018年8月26日 4 2020年9月6日 8 表 3 悬沙浓度反演模型列表
Tab. 3 List of suspended sediment concentration inversion models
算法 模型 适用地区 YOC SSC=100.649+25.623(Rrs555+Rrs660)-0.646(Rrs490/Rrs555) 黄海、东海 Case2 SSC=100.08832+1.627(Rrs745/Rrs555)+1.121(Rrs680/Rrs490) 韩国近岸海域 余佳算法 SSC=0.6358exp(87.65Rrs555) 黄海、渤海 Li算法 SSC=101.019(Rrs660/Rrs555)+10.394Rrs490+0.835 黄河口近岸海域 表 4 不同情景下高浓度悬沙(不小于150 mg/L)情况
Tab. 4 High-concentration suspended sediment (no less than 150 mg/L) under different scenarios
情景 径流量/(m³·s−1) 日输沙量/(104 t) 面积/km² 最大值/(mg·L−1) 最大扩散范围/km 高径流输沙 2520.00 481.00 316.00 1377.62 17.14 低径流输沙 440.00 3.10 25.00 386.34 2.77 微风(2.1 m/s) 770.00 11.81 23.50 1501.33 5.31 大风(8.9 m/s) 370.00 2.45 783.00 1692.60 21.56 大潮(1.12 m) 2520.00 481.00 316.00 1377.62 17.14 小潮(0.49 m) 3490.00 1079.00 196.25 1365.80 13.55 注:“情景”列括号内分别是微风、大风情况下的风速和大、小潮的潮差。 -
[1] Meire P, Ysebaert T, Van Damme S, et al. The Scheldt estuary: a description of a changing ecosystem[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2005, 540(1/3): 1−11. [2] Wang Houjie, Wu Xiao, Bi Naishuang, et al. Impacts of the dam-orientated water-sediment regulation scheme on the lower reaches and delta of the Yellow River (Huanghe): a review[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2017, 157: 93−113. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.08.005 [3] van der Wal D, van Kessel T, Eleveld M A, et al. Spatial heterogeneity in estuarine mud dynamics[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2010, 60(3): 519−533. doi: 10.1007/s10236-010-0271-9 [4] Van der Molen J, Ruardij P, Greenwood N. A 3D SPM model for biogeochemical modelling, with application to the northwest European continental shelf[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2017, 127: 63−81. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2016.12.003 [5] Fu Yutao, Chen Shenliang, Ji Hongyu, et al. The modern Yellow River Delta in transition: causes and implications[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 436: 106476. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106476 [6] Zhang Xiaohe, Fichot C G, Baracco C, et al. Determining the drivers of suspended sediment dynamics in tidal marsh-influenced estuaries using high-resolution ocean color remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 240: 111682. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111682 [7] van der Wegen M. Numerical modeling of the impact of sea level rise on tidal basin morphodynamics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 2013, 118(2): 447−460. doi: 10.1002/jgrf.20034 [8] Mariotti G, Fagherazzi S, Wiberg P L, et al. Influence of storm surges and sea level on shallow tidal basin erosive processes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010, 115(C11): C11012. doi: 10.1029/2009JC005892 [9] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1−21. doi: 10.1086/628741 [10] 刘锋, 陈沈良, 彭俊, 等. 近60年黄河入海水沙多尺度变化及其对河口的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(3): 313−323. doi: 10.11821/xb201103003Liu Feng, Chen Shenliang, Peng Jun, et al. Multi-scale variability of flow discharge and sediment load of Yellow River to sea and its impacts on the estuary during the past 60 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(3): 313−323. doi: 10.11821/xb201103003 [11] 王俊杰, 拾兵, 巴彦斌. 近70年黄河入海水沙通量演变特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(3): 52−62,69.Wang Junjie, Shi Bing, Ba Yanbin. Evolution characteristics of runoff and sediment fluxes of Yellow River into Bohai Sea in recent 70 years[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(3): 52−62,69. [12] 王开荣. 黄河调水调沙对河口及其三角洲的影响和评价[J]. 泥沙研究, 2005(6): 29−33. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2005.06.004Wang Kairong. Impact and evaluation of water and sediment regulation in the Yellow River on the estuary and its delta[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2005(6): 29−33. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2005.06.004 [13] 毕乃双, 杨作升, 王厚杰, 等. 黄河调水调沙期间黄河入海水沙的扩散与通量[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2): 27−34.Bi Naishuang, Yang Zuosheng, Wang Houjie, et al. Characteristics of dispersal of the Yellow River Water and sediment to the sea during water-sediment regulation period of the Yellow River and its dynamic mechanism[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2): 27−34. [14] 韩其为. 小浪底水库初期运用及黄河调水调沙研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2008(3): 1−18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2008.03.001Han Qiwei. Study on preliminary operation of Xiaolangdi Reservoir and flow-sediment regulation of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2008(3): 1−18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2008.03.001 [15] 乔淑卿, 石学法, 白亚之, 等. 黄河口及邻近渤海海域悬浮体和沉积物中有机碳、氮的分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(2): 354−362.Qiao Shuqing, Shi Xuefa, Bai Yazhi, et al. Distribution of organic carbon, nitrogen in suspended and surface sediments and their controlling factors off the Huanghe (Yellow River) Mouth and the nearby Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(2): 354−362. [16] 刘锋, 陈沈良, 周永东, 等. 黄河2009年调水调沙期间河口水动力及悬沙输移变化特征[J]. 泥沙研究, 2010(6): 1−8.Liu Feng, Chen Shenliang, Zhou Yongdong, et al. Effect of water-sediment regulation in Yellow River on hydrodynamics and suspended sediment transport in its estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2010(6): 1−8. [17] 王海龙, 李国胜. 黄河入海泥沙在渤海中悬移输送季节变化的数值研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2009, 40(2): 129−137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.02.004Wang Hailong, Li Guosheng. Numerical simulation on seasonal transportation of suspended sediment from Huanghe (Yellow) River to Bohai Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2009, 40(2): 129−137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.02.004 [18] 王厚杰, 杨作升, 毕乃双. 黄河口泥沙输运三维数值模拟Ⅰ—黄河口切变锋[J]. 泥沙研究, 2006(2): 1−9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.02.001Wang Houjie, Yang Zuosheng, Bi Naishuang. 3-D simulation of the suspended sediment transport in the Yellow River mouth I: shear front off the Yellow River mouth[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2006(2): 1−9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.02.001 [19] 李国胜, 王海龙, 董超. 黄河入海泥沙输运及沉积过程的数值模拟[J]. 地理学报, 2005, 60(5): 707−716. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.05.001Li Guosheng, Wang Hailong, Dong Chao. Numerical simulations on transportation and deposition of SPM introduced from the Yellow River to the Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2005, 60(5): 707−716. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.05.001 [20] 冯秀丽, 吴世强, 林霖, 等. 黄河三角洲埕岛近岸海域悬浮泥沙运动[J]. 海洋科学, 2003, 27(12): 66−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2003.12.017Feng Xiuli, Wu Shiqiang, Lin Lin, et al. Offshore supended sediment transport in Huanghe Delta Chengdao marine area[J]. Marine Sciences, 2003, 27(12): 66−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2003.12.017 [21] 李广雪. 黄河入海泥沙扩散与河海相互作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(3): 1−10.Li Guangxue. Suspended sediment dispersal and interaction of river-sea off the Yellow River mouth[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(3): 1−10. [22] 黄海军, 李成治, 郭建军. 黄河口海域悬沙光谱特征的研究[J]. 海洋科学, 1994, 18(5): 40−44.Huang Haijun, Li Chengzhi, Guo Jianjun. A study on the spectral feature of suspended matter in the Huanghe River delta area[J]. Marine Sciences, 1994, 18(5): 40−44. [23] 樊辉, 黄海军, 唐军武. 黄河口水体光谱特性及悬沙浓度遥感估测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2007, 32(7): 601−604.Fan Hui, Huang Haijun, Tang Junwu. Spectral signature of waters in Huanghe Estuary and estimation of suspended sediment concentration from remote sensing data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2007, 32(7): 601−604. [24] 刘振宇, 崔廷伟, 李佳, 等. 黄河口悬浮物浓度Landsat 8 OLI多波段反演研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(4): 1579−1585.Liu Zhenyu, Cui Tingwei, Li Jia, et al. Suspended particle concentration retrieval in Yellow River Estuary using multi-band of Landsat 8 OLI[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(4): 1579−1585. [25] Zhang Minwei, Dong Qing, Cui Tingwei, et al. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River estuary from Landsat TM and ETM + imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 146: 136−147. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.09.033 [26] Qiu Zhongfeng, Xiao Cong, Perrie W, et al. Using Landsat 8 data to estimate suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(1): 276−290. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012412 [27] Shi Wei, Wang Menghua. Satellite views of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2012, 104: 30−45. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2012.05.001 [28] 张永强. 莱州湾风暴潮过程增水、波浪、风暴潮流数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2010.Zhang Yongqiang. The numerical study of storm surge, wave and tide in Laizhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: The First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2010. [29] 胡春宏, 吉祖稳, 王涛. 黄河口海洋动力特性与泥沙的输移扩散[J]. 泥沙研究, 1996(4): 2−11.Hu Chunhong, Ji Zuwen, Wang Tao. Characteristics of ocean dynamics and sediment diffusion in the Yellow River estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1996(4): 2−11. [30] 黄海军, 樊辉. 黄河三角洲潮滩潮沟近期变化遥感监测[J]. 地理学报, 2004, 59(5): 723−730. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.05.010Huang Haijun, Fan Hui. Change detection of tidal flats and tidal creeks in the Yellow River delta using Landsat TM/ETM+ images[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004, 59(5): 723−730. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.05.010 [31] 陈沈良, 谷硕, 姬泓宇, 等. 新入海水沙情势下黄河口的地貌演变[J]. 泥沙研究, 2019, 44(5): 60−66.Chen Shenliang, Gu Shuo, Ji Hongyu, et al. Processes of the Yellow River Mouth on new water and sediment condition[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2019, 44(5): 60−66. [32] Ryu J H, Han H J, Cho S, et al. Overview of geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) and GOCI data processing system (GDPS)[J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2012, 47(3): 223−233. doi: 10.1007/s12601-012-0024-4 [33] Ruddick K G, Ovidio F, Rijkeboer M. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters[J]. Applied Optics, 2000, 39(6): 897−912. doi: 10.1364/AO.39.000897 [34] Fettweis M, Nechad B, Van den Eynde D. An estimate of the suspended particulate matter (SPM) transport in the southern North Sea using SeaWiFS images, in situ measurements and numerical model results[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2007, 27(10/11): 1568−1583. [35] Kowalczuk P, Darecki M, Zabłocka M, et al. Validation of empirical and semi-analytical remote sensing algorithms for estimating absorption by coloured dissolved organic matter in the Baltic Sea from SeaWiFS and MODIS imagery[J]. Oceanologia, 2010, 52(2): 171−196. doi: 10.5697/oc.52-2.171 [36] Choi J K, Park Y J, Lee B R, et al. Application of the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) to mapping the temporal dynamics of coastal water turbidity[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 146: 24−35. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.05.032 [37] Higa H, Sugahara S, Salem S I, et al. An estimation method for blue tide distribution in Tokyo Bay based on sulfur concentrations using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 235: 106615. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106615 [38] Choi J, Pak Y J, Ahn J H, et al. GOCI, the world’s first geostationary ocean color observation satellite, for the monitoring of temporal variability in coastal water turbidity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C9): C09004. [39] Li Peng, Ke Yinghai, Wang Dawei, et al. Human impact on suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary, China: evidence from remote sensing data fusion using an improved spatiotemporal fusion method[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 750: 141612. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141612 [40] Siswanto E, Tang J W, Yamaguchi H, et al. Empirical ocean-color algorithms to retrieve chlorophyll-a, total suspended matter, and colored dissolved organic matter absorption coefficient in the Yellow and East China Seas[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2011, 67(5): 627−650. doi: 10.1007/s10872-011-0062-z [41] Choi J K, Park Y J, Ryu J H. Retrieval of suspended sediment concentration in the coastal waters of yellow sea from Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI)[C]//Proceeding of International Symposium of Remote Sensing. Korean Society of Remote Sensing, 2013: 809−812. [42] 余佳. 黄海悬浮体分布及季节性变化[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Yu Jia. Seasonal variation and distribution of suspended sediment in the Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [43] 李阳东, 吴珍瑜, 常亮. 基于GOCI影像进行渤海表层悬浮泥沙浓度估算的新方法[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(3): 80−88.Li Yangdong, Wu Zhenyu, Chang Liang. A novel method for the estimation of suspended sediment concentration in Bohai Sea based on GOCI images[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(3): 80−88. [44] Li Peng, Ke Yinghai, Bai Junhong, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary, China during the past two decades based on time-series Landsat and Sentinel-2 data[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 149: 110518. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110518 [45] Long C M, Pavelsky T M. Remote sensing of suspended sediment concentration and hydrologic connectivity in a complex wetland environment[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2013, 129: 197−209. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.10.019 -




 下载:
下载: