Isolation, purification and analysis of antialgal activities of antialgal compounds from Laminaria japonica
-
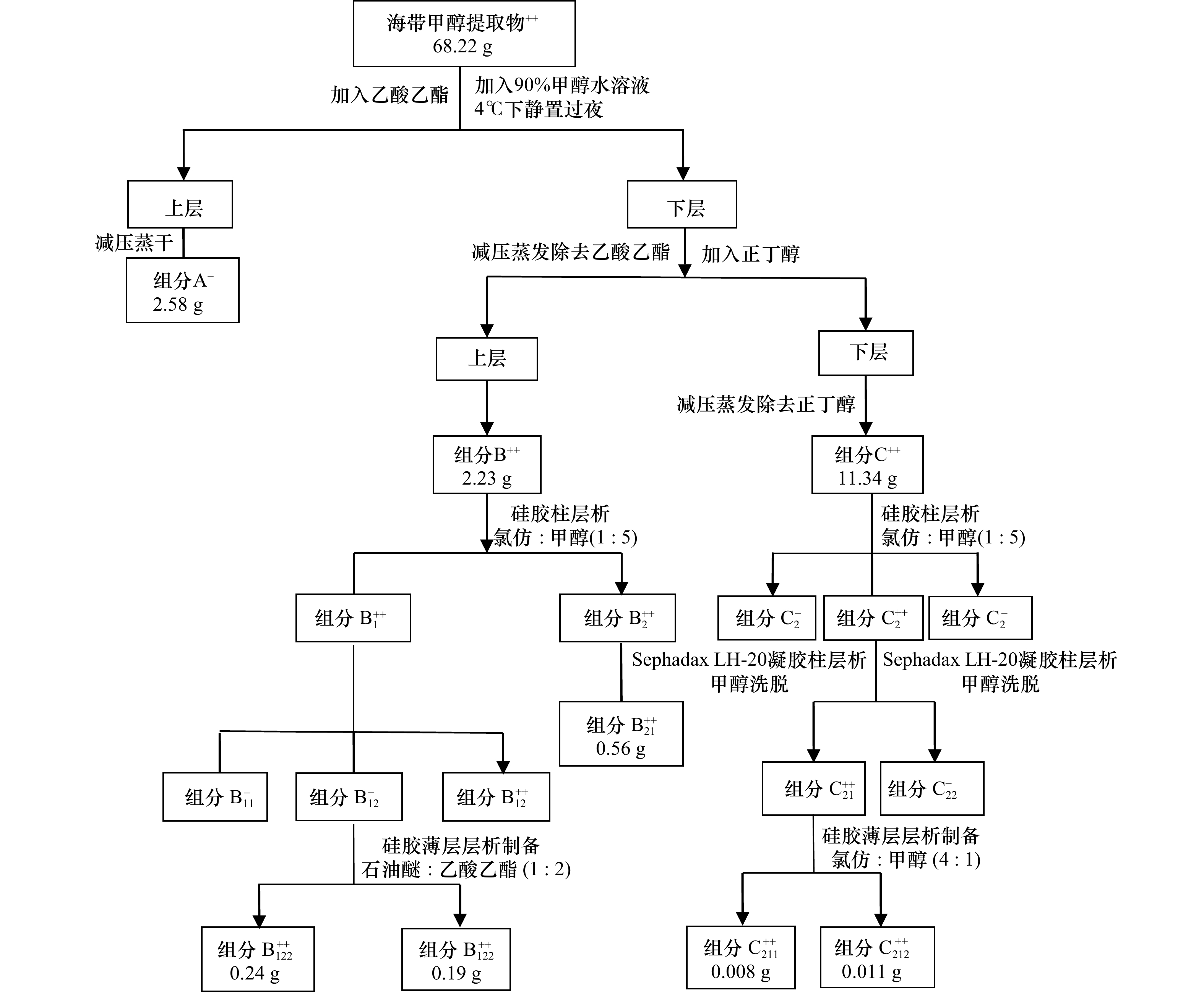
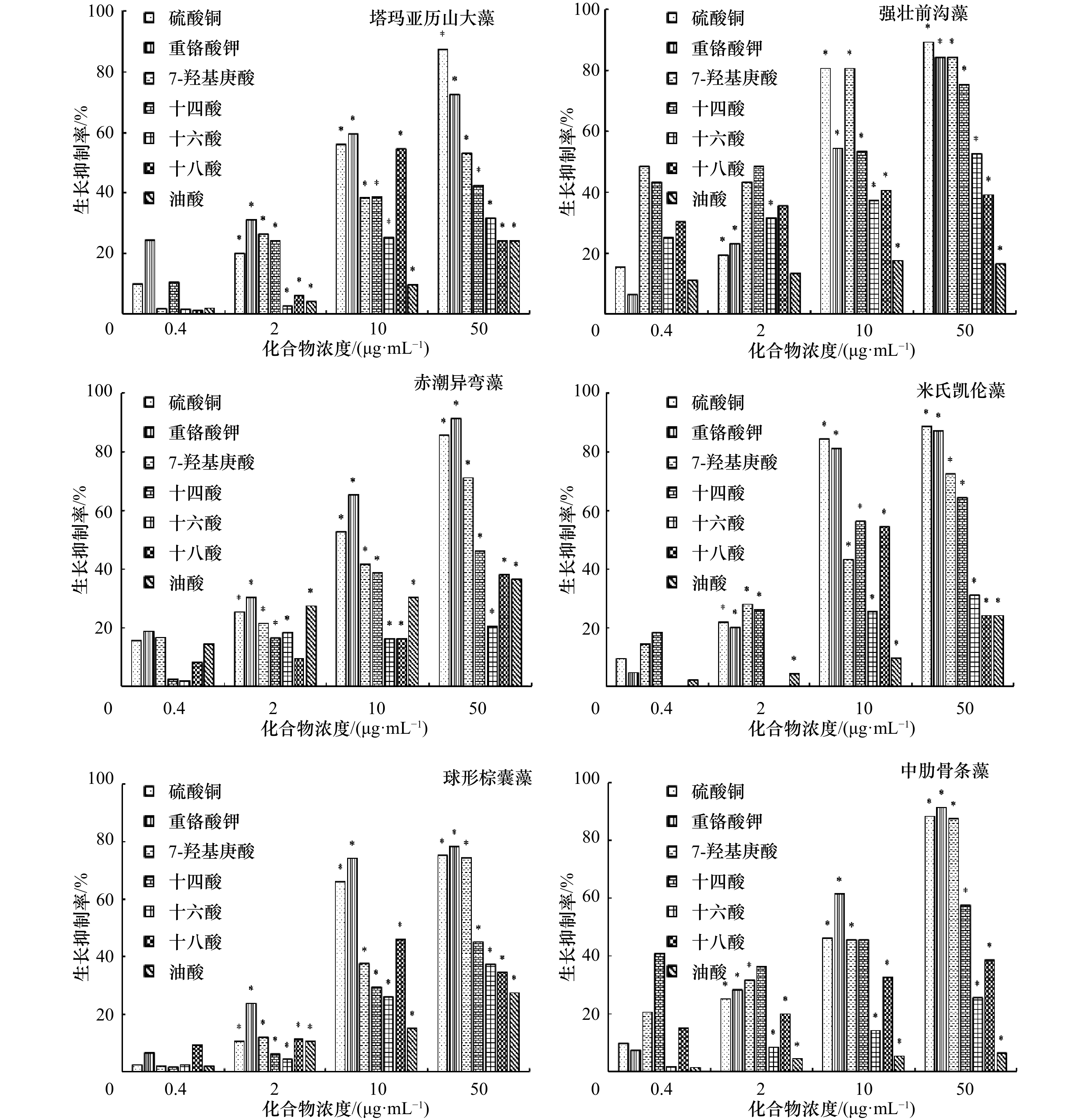
摘要: 以2 000 g海带为原料、米氏凯伦藻为测试微藻,采用甲醇浸提、液液萃取、硅胶柱层析、Sephadax LH-20凝胶柱层析和硅胶薄层层析等分离方法,纯化可能具有抑藻活性的化合物,制备到5个薄层纯样品,B21(1.39 g)、B131(0.51 g)、B132(0.48 g)、C211(0.016 g)和C212(0.020 g)。经鉴定,B21、B131、B132、C211和C212依次为7-羟基庚酸、十四酸、十六酸、十八酸和油酸,均是第一次从海带中分离获得。此5种脂肪酸对塔玛亚历山大藻、强壮前沟藻、赤潮异弯藻、米氏凯伦藻、球形棕囊藻和中肋骨条藻的生长表现出选择性抑制作用,其中7-羟基庚酸具有较为广泛的抑藻活性。除塔玛亚力山大藻之外,在浓度为50 μg/mL时,7-羟基庚酸对其他5种赤潮微藻生长的抑制作用与硫酸铜和重铬酸钾对它们生长的抑制作用接近,生长抑制率超过71%(第4天);十四酸在浓度为50 μg/mL时对强壮前沟藻、米氏凯伦藻和中肋骨条藻生长也有明显的抑制作用,第4天时对它们的生长抑制率在57%以上。在此基础上,第一次确定了7-羟基庚酸、十四酸、十六酸和十八酸对强壮前沟藻、赤潮异弯藻、米氏凯伦藻、球形棕囊藻和中肋骨条藻生长的半抑制效应浓度(EC50~96 h),7-羟基庚酸对塔玛亚历山大藻生长的EC50~96 h也是第一次被确定。与硫酸铜和重铬酸钾对每种赤潮微藻生长的EC50~96 h比较,7-羟基庚酸和十四酸在抑制强壮前沟藻上具有明显的抑藻优势。Abstract: Using 2 000 g kelp as raw material and Karenia mikimotoi as the test microalgae, methanol extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, silica gel column chromatography, sephadax LH-20 gel column chromatography and silica gel thin layer chromatography are used to purify compounds that might inhibit algal activity. Five samples with thin layer purity, B21 (1.39 g), B131 (0.51 g), B132 (0.48 g), C211 (0.016 g) and C212 (0.020 g), are prepared. Structural identification shows that B21, B131, B132, C211 and C212 are 7-hydroxyheptanic acid, tetradecanoic acid, hexadecanoic acid, octadecanoic acid, and oleic acid, respectively. They are isolated from Laminaria japonica for the first time. The results show that these five compounds have selective inhibition effects on the growth of six species of red tide microalgae (Alexandrium tamarense, Amphidinium carterae, Heterosigma akashiwo, Karenia mikimotoi, Phaeocystis globsa, and Skeletonema costatum). Among them, 7-hydroxyheptanoic acid has a wide range of antialgal activities. Except for Alexandrium tamarense, at the concentration of 50 μg/mL, the growth inhibition of 7-hydroxyheptanic acid against the other five species of red tide microalgae is close to that of copper sulfate and potassium dichromate, and the growth inhibition is more than 71% (the 4th day). Tetradecanoic acid also shows obvious inhibition on the growth of Amphidinium carterae, Karenia mikimotoi, and Skeletonema costatum. On 4th day, the growth inhibition of tetradecanoic acid for the three species of red tide microalgae is more than 57%. Furthermore, EC50−96 h values of 7-hydroxyheptanic acid, tetradecanoic acid, hexadecanoic acid, and octadecanoic acid for Amphidinium carterae, Heterosigma akashiwo, Karenia mikimotoi, Phaeocystis globsa, and Skeletonema costatum are obtained for the first time, respectively. EC50−96 h value of 7-hydroxyheptanic acid for Alexandrium tamarense is also determined for the first time. It is found that 7-hydroxyheptanic acid and tetradecanoic acid has the advantage of inhibiting Amphidinium carterae.
-
Key words:
- antialgal compound /
- isolation /
- Laminaria japonica /
- purification /
- red tide microalgae
-
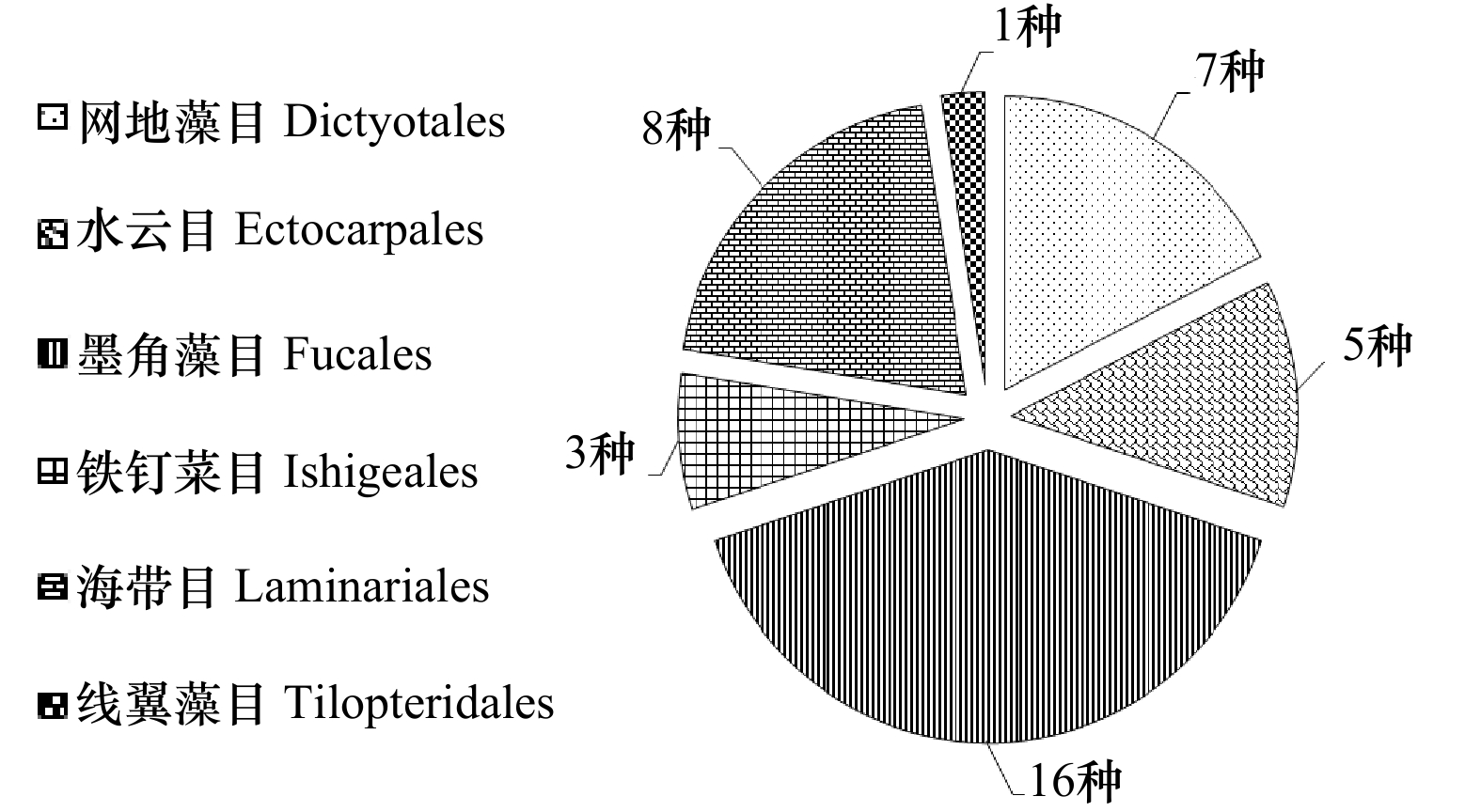
图 1 可抑制赤潮微藻的大型褐藻的目类归属分布
数据来源于1960−2019年Web of Science、Springer、Google Scholar和CNKI数据库收录的研究
Fig. 1 Distribution of brown marine macroalgae with antialgal activity against red tide microalgae according the orders
Data extracted from related studies in Web of Science, Springer, Google Scholar and CNKI between 1960 and 2019
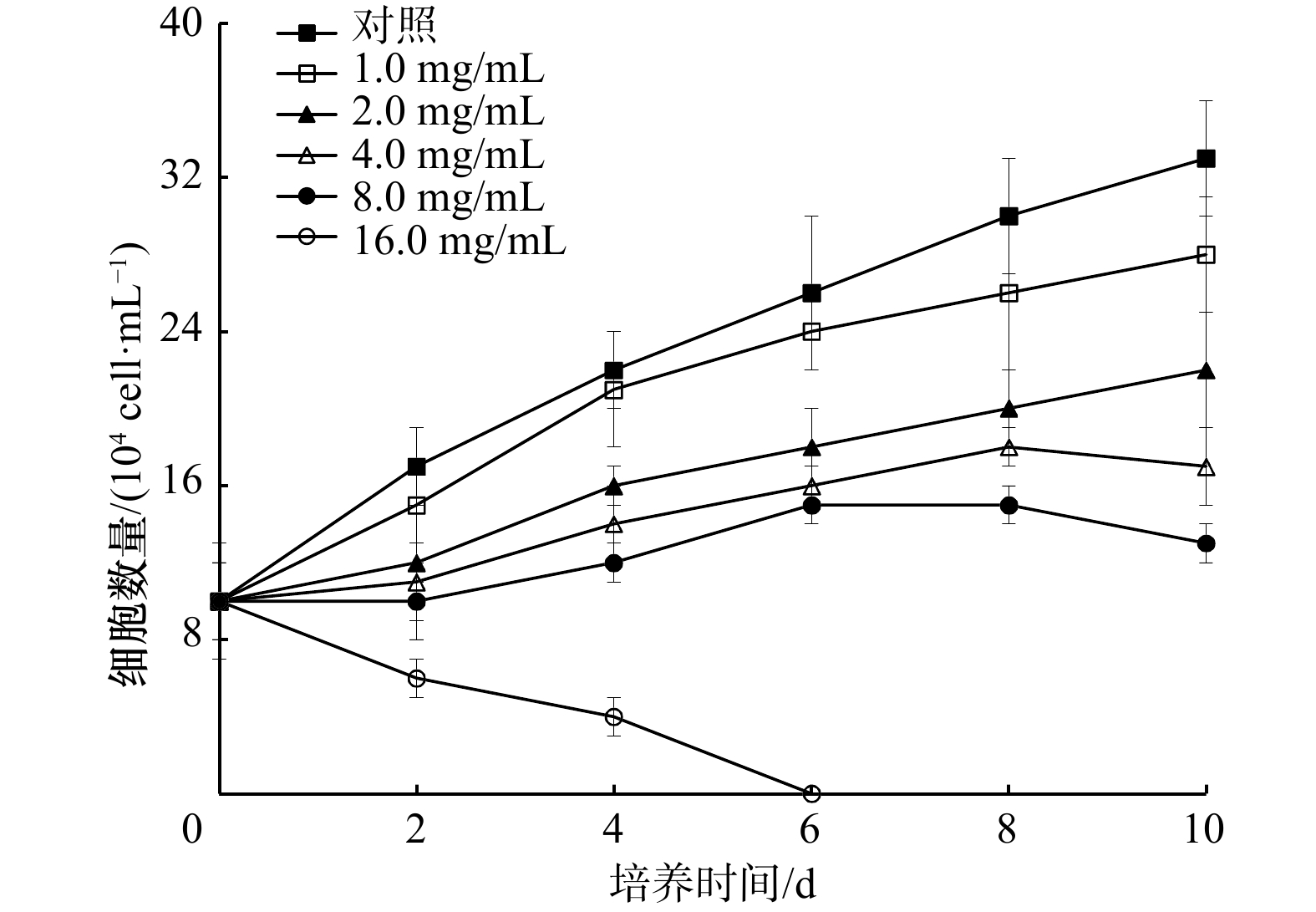
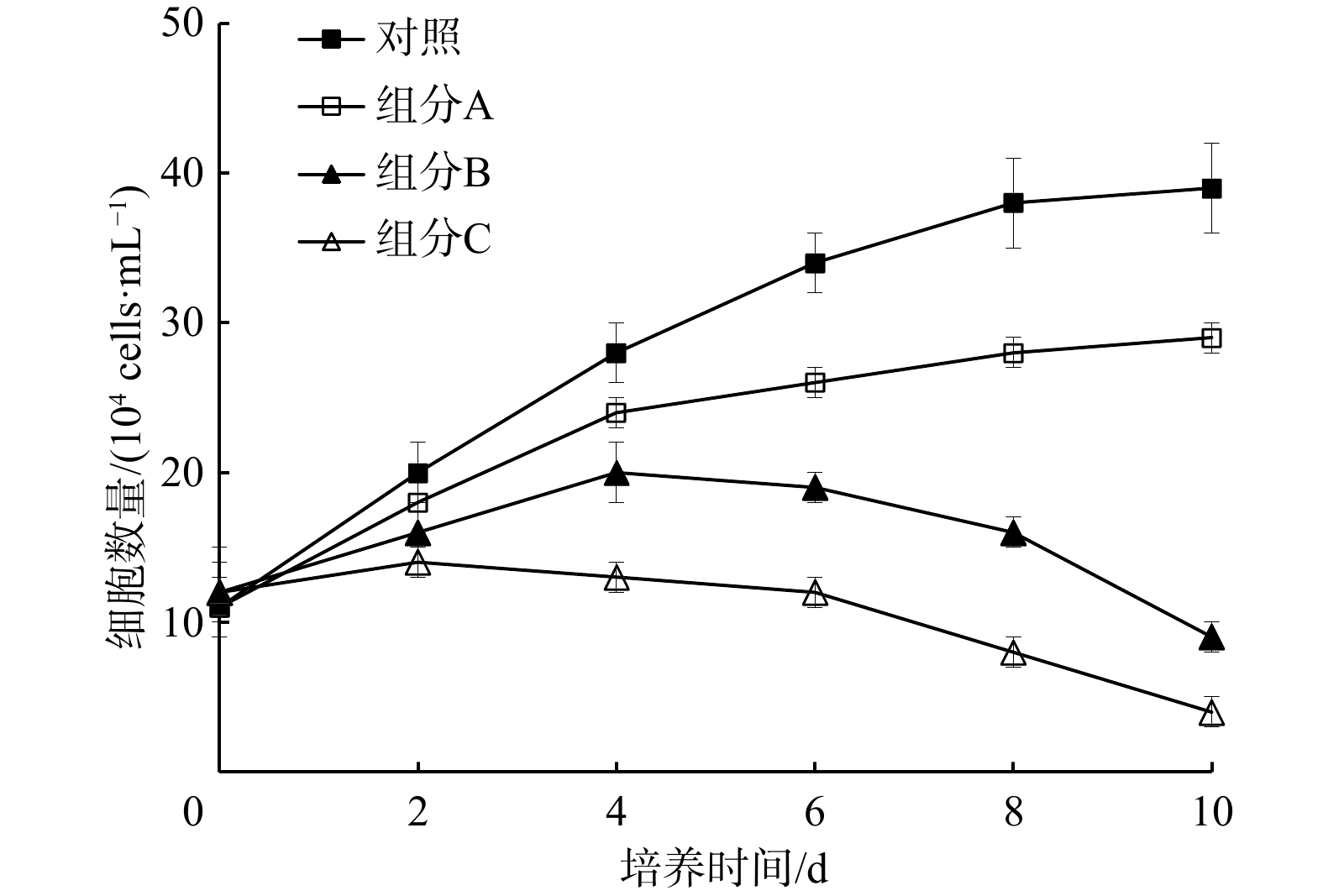
表 1 组分B和组分C的分离纯化过程中抑藻活性检测
Tab. 1 Antialgal activity test of the fractions B and C in the isolation and purification process
浓度 组分B 组分C 硅胶柱层析分离(3.0 cm×40 cm) 硅胶柱层析分离(5.0 cm×80 cm) 1.0 mg/mL(Sephadax LH-20凝胶柱层析
(2.0 cm2×25 cm))组分${\rm B}_1^{++} $ 组分${\rm B}_2^{++} $ 组分${\rm C}_1^{-} $ 组分${\rm C}_2^{++} $ 组分${\rm C}_3^{-} $ 0.25 mg/mL(硅胶薄层层析制备) ${\rm{B}}_{11}^- $、${\rm{B}}_{12}^- $、${\rm{B}}_{13}^{++} $ ${\rm{B}}_{21}^{++} $ ${\rm{C}}_{21}^{++} $、${\rm{C}}_{22}^{-} $ 0.05 mg/mL ${\rm{B}}_{131}^{++} $、${\rm{B}}_{132}^{++} $ ${\rm{C}}_{211}^{++} $、${\rm{C}}_{212}^{++} $ 注:−表示没有抑藻活性;+表示微弱的抑藻活性,生长抑制率为20%~50%;++表示强烈的抑藻活性,生长抑制率大于50%。 表 2 不同化合物对6种赤潮微藻生长的半抑制效应浓度(EC50~96 h,单位:μg/mL)
Tab. 2 Different compounds isolated from Laminaria japonica for the six species of red tide microalgae (EC50−96 h,unit:μg/mL)
藻类 硫酸铜 7-羟基庚酸 十四酸 十六酸 十八酸 油酸 塔玛亚历山大藻 6.76 7.39 10.6 36.8 115.4 − 强壮前沟藻 4.16 2.19 3.54 54.4 − − 赤潮异弯藻 6.42 13.9 15.4 37.3 154.3 − 米氏凯伦藻 4.43 11.1 11.4 12.6 215.9 − 球形棕囊藻 11.2 18.5 20.1 95.9 361.0 − 中肋骨条藻 6.99 18.0 18.5 32.5 292.6 − 注:−表示没有计算得出。 -
[1] Anderson D M, Cembella A D, Hallegraeff G M. Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2012, 4: 143−176. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120308-081121 [2] 周名江, 朱明远. “我国近海有害赤潮发生的生态学、海洋学机制及预测防治”研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(7): 673−679. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.07.003Zhou Mingjiang, Zhu Mingyuan. Progress of the project “ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms in China”[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(7): 673−679. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.07.003 [3] 李赟辉, 吴婷, 杨维东, 等. 十种黄酮类化合物对两种赤潮藻的抑制作用[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(1): 72−75.Li Yunhui, Wu Ting, Yang Weidong, et al. Inhibitory effects of ten flavonoids against two harmful algae[J]. Journal of Jinan University (Natural Science), 2012, 33(1): 72−75. [4] 俞志明, 邹景忠, 马锡年. 一种提高粘土矿物去除赤潮生物能力的新方法[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1994, 25(2): 226−232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.02.020Yu Zhiming, Zou Jingzhong, Ma Xinian. A new method to improve the capability of clays for removing red tide organisms[J]. Oceanologia ET Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25(2): 226−232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.02.020 [5] Wang Xiulin, Gong Liangyu, Liang Shengkang, et al. Algicidal activity of rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Harmful Algae, 2005, 4(2): 433−443. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2004.06.001 [6] Nagasaki K, Tarutani K, Yamaguchi M. Growth characteristics of Heterosigma akashiwo virus and its possible use as a microbiological agent for red tide control[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(3): 898−902. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.3.898-902.1999 [7] Zheng Xiaowei, Zhang Bangzhou, Zhang Jinlong, et al. A marine algicidal actinomycete and its active substance against the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(20): 9207−9215. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4617-8 [8] 刘伯雅, 魏东芝, 鲁思然, 等. 灵菌红素对有害藻类的除藻活性研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(4): 477−482.Liu Boya, Wei Dongzhi, Lu Siran, et al. Algicidal activity of prodigiosin against harmful algae[J]. China Environmental Science, 2010, 30(4): 477−482. [9] Sun Yingying, Zhou Wenjing, Wang Hui, et al. Antialgal compounds with antialgal activity against the common red tide microalgae from a green algae Ulva pertusa[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 157: 61−66. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.051 [10] Sun Yingying, Dong Shasha, Zhou Wenjing, et al. A comprehensive review of secondary metabolites with antialgal activity from marine macroalgae against red tide microalgae[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2019, 93(S1): 475−488. [11] 张鑫洋, 刘天浩, 梅齐诚, 等. 来源于海洋天然产物的抑藻剂探究[J]. 山东化工, 2020, 49(18): 49−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020.18.019Zhang Xinyang, Liu Tianhao, Mei Qicheng, et al. Research on algae inhibitors derived from marine natural products[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(18): 49−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020.18.019 [12] Ohsawa N, Ogata Y, Okada N, et al. Physiological function of bromoperoxidase in the red marine alga, Corallina pilulifera: production of bromoform as an allelochemical and the simultaneous elimination of hydrogen peroxide[J]. Phytochemistry, 2001, 58(5): 683−692. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00259-X [13] 卢慧明. 大型海藻龙须菜化学成分及其对中肋骨条藻化感作用研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2011.Lu Huiming. Chemical constituents of the seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis and their allelopathic effects on Skeletonema costatum[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan Univesity, 2011. [14] Kim J Y, Alamsjah M A, Hamada A, et al. Algicidal diterpenes from the brown alga Dictyota dichotoma[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2006, 70(10): 2571−2574. doi: 10.1271/bbb.60281 [15] Hirao S, Tara K, Kuwano K, et al. Algicidal activity of glycerolipids from brown alga Ishige sinicola toward red tide microalgae[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2012, 76(2): 372−374. doi: 10.1271/bbb.110645 [16] Sun Yingying, Xing Jingzeng, Zhang Jianshuo, et al. Sesquiterpenoids with antialgal activity against the common red tide microalgae from marine macroalga Porphyra yezoensis[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(8): 7844−7859. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0958-2 [17] Chowdhury M T H, Bangoura I, Kang J Y, et al. Comparison of Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis for phlorotannin extraction[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2014, 35(4): 713−719. [18] Nagayama K, Shibata T, Fujimoto K, et al. Algicidal effect of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome on red tide microalgae[J]. Aquaculture, 2003, 218(1/4): 601−611. [19] 李凤超. 海带和厚叶解曼藻中防污活性物质的提取及性能研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Li Fengchao. Extraction and performance investigation of antifouling compounds produced by Laminaria and Kjellmaniella crassifolia[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [20] Jeong J H, Jin H J, Sohn C H, et al. Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2000, 12(1): 37−43. doi: 10.1023/A:1008139129057 [21] 安蓁. 大型海藻及纳米材料对赤潮中肋骨条藻的抑制作用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.An Zhen. The research of inhibitory effect on red tide Skeletonema costatum by macroalgae and nanomaterials[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2008. [22] Alamsjah M A, Hirao S, Ishibashi F, et al. Isolation and structure determination of algicidal compounds from Ulva fasciata[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2005, 69(11): 2186−2192. doi: 10.1271/bbb.69.2186 [23] Suzuki Y, Takabayashi T, Kawaguchi T, et al. Isolation of an allelopathic substance from the crustose coralline algae, Lithophyllum spp., and its effect on the brown Alga, Laminaria religiosa miyabe (phaeophyta)[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 1998, 225(1): 69−77. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(97)00208-6 [24] Marklund S, Marklund G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1974, 47(3): 469−474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x [25] Wang Haifeng, Niu Youhong, Zhang Guoying, et al. A unified synthesis of cyclic ethers or lactones via Pd-catalyzed intramolecular O-functionalization of sp3 C-H bonds[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2016, 57(41): 4544−4548. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.08.086 [26] 李宁新, 范青飞, 宋启示. 傣药石梓皮和接骨草的化学成分研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2017, 29: 11−17.Li Ningxin, Fan Qingfei, Song Qishi. Chemical constituents from bark of Gmelina arborea and Sambucus chinensis[J]. Natural Product Research Development, 2017, 29: 11−17. [27] 任冰如, 夏冰, 李维林, 等. 乌韭的化学成分研究(II) [J]. 中草药, 2009, 40(1): 104-106.Ren Bingru, Xia Bing, Li Weilin, et al. Chemical constituents of Stenoloma chusanum[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2009, 40(1): 104-106. [28] Yang Nianyun, Wang Liuying, Zhang Yiwen. Immunological activities of components from leaves of Liriodendron chinensis[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicines, 2015, 7(3): 279−282. doi: 10.1016/S1674-6384(15)60051-X [29] 陈路, 刘远俊, 黄菲菲, 等. 国产巴西人参醋酸乙酯部位化学成分研究[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(6): 1255−1260. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.06.004Chen Lu, Liu Yuanjun, Huang Feifei, et al. Chemical constituents from ethyl acetate extracts of domestic Pfaffia glomerata[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2018, 49(6): 1255−1260. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.06.004 [30] Sun Yingying, Meng Kun, Su Zhenxia, et al. Isolation and purification of antialgal compounds from the red alga Gracilaria lemaneiformis for activity against common harmful red tide microalgae[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(5): 4964−4972. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8256-y [31] 尹玉丽. 两类植物化感物质对赤潮藻生长的影响研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2007.Yi Yuli. Studies on inhibitive effect of two kinds allelochemicals on HABs algae[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2007. [32] OECD. Test No. 201: Freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test[M]//OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Paris: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, 1981. [33] El Amrani Zerrifi S, El Khalloufi F, Oudra B, et al. Seaweed bioactive compounds against pathogens and microalgae: potential uses on pharmacology and harmful algae bloom control[J]. Marine Drugs, 2018, 16(2): 55. doi: 10.3390/md16020055 [34] Ben Gharbia H, Yahia O K D, Cecchi P, et al. New insights on the species-specific allelopathic interactions between macrophytes and marine HAB dinoflagellates[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(11): e0187963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187963 [35] Złoch I, Śliwińska-Wilczewska S, Kucharska M, et al. Allelopathic effects of Chara species (C. aspera, C. baltica, and C. canescens) on the bloom-forming picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp.[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(36): 36403−36411. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3579-5 [36] Chiang I Z, Huang Wenya, Wu J T. Allelochemicals of Botryococcus braunii (Chlorophyceae)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 2004, 40(3): 474−480. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2004.03096.x [37] Kakisawa H, Asari F, Kusumi T, et al. An allelopathic fatty acid from the brown alga Cladosiphon okamuranus[J]. Phytochemistry, 1988, 27(3): 731−735. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(88)84084-6 [38] Oh M Y, Lee S B, Jin D H, et al. Isolation of algicidal compounds from the red alga Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2010, 22(4): 453−458. doi: 10.1007/s10811-009-9478-x [39] 崔峰. 浒苔对赤潮微藻的化感抑制作用以及化感物质的结构鉴定[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2014.Cui Feng. Studies on allelopathy effects of Ulva prolifera on red tide microalgae and allelochemicals identification[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2014. [40] 高红, 周飞飞, 唐洪杰, 等. 黄海绿潮浒苔提取物的化感效应及化感物质的分离鉴定[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(12): 11−20.Gao Hong, Zhou Feifei, Tang Hongjie, et al. Allelopathy of extracts of Ulva prolifera on green tides in the Yellow Sea and the identification of the allelochemicals[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(12): 11−20. [41] 金浩良. 肠浒苔中抑藻活性物质的分离鉴定及其对赤潮藻的影响[D]. 宁波: 宁波大学, 2011.Jin Haoliang. Studies on the inhibition activity of Ulva intestinalis on red tide microalgae and the isolation and identification of the algicidal compounds[D]. Ningbo: Ningbo University, 2011. [42] 王国蕊. 海洋酸化对大型海藻活性代谢产物影响的研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2018.Wang Guorui. Effects of ocean acidification on active metabolites of macroalgae[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2018. [43] 张庭廷, 郑春艳, 何梅, 等. 脂肪酸类物质的抑藻效应及其构效关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 2009, 29(3): 274−279. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2009.03.009Zhang Tingting, Zheng Chunyan, He Mei, et al. Inhibition on algae of fatty acids and the structure-effect relationship[J]. China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(3): 274−279. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2009.03.009 [44] 何宗祥, 张庭廷. 四种十八碳脂肪酸抑藻时效关系分析的数学模型设计[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(23): 7235−7243.He Zongxiang, Zhang Tingting. Mathematical model design of time-effect relationship analysis about the inhibition of four eighteen-cabon fatty acids on toxic Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(23): 7235−7243. [45] 姜闻新, 贾永, 王从彦, 等. 软脂酸和硬脂酸对铜绿微囊藻生长的抑制作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(2): 291−295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.02.007Jiang Wenxin, Jia Yong, Wang Congyan, et al. The inhibitory effects of palmitic acid and stearic acid on Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(2): 291−295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.02.007 [46] 罗万芬, 曾仁权. 几种长链脂肪酸对铜绿微囊藻生长的影响研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 37(8): 92−95.Luo Wanfen, Zeng Renquan. Studies of some long chain fatty acids on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 37(8): 92−95. [47] Kamaya Y, Kurogi Y, Suzuki K. Acute toxicity of fatty acids to the freshwater green alga Selenastrum capricornutum[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2003, 18(5): 289−294. doi: 10.1002/tox.10127 [48] 夏钰妹, 孙雪, 徐年军, 等. α-亚麻酸对赤潮异弯藻生长的抑制作用[J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(5): 880−885. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.05.017Xia Yumei, Sun Xue, Xu Nianjun, et al. Inhibitory effects of α-linolenic acid on the red tide microalgae Heterosigma akashiwo[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(5): 880−885. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.05.017 [49] 王平平. 亚麻酸对赤潮异弯藻和米氏凯伦藻化感效应及细胞凋亡机制的研究[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学, 2015.Wang Pingping. Allelopathic effect and the apoptotic mechanisms of linolenic acid on Heterosigma akashiwo and Karenia mikimotoi[D]. Qufu: Qufu Normal University, 2015. [50] Agafonov A, Gritsenko E, Belosludtsev K, et al. A permeability transition in liposomes induced by the formation of Ca2+/palmitic acid complexes[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes, 2003, 1609(2): 153−160. doi: 10.1016/S0005-2736(02)00666-1 [51] 尚忠林, 孙大业. 植物细胞内的钙通道[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2002, 38(6): 625−630.Shang Zhonglin, Sun Daye. Calcium channels in plant cells[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2002, 38(6): 625−630. [52] Sokolov Y, Mirzabekov T, Martin D W, et al. Membrane channel formation by antimicrobial protegrins[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes, 1999, 1420(1/2): 23−29. [53] 娄亚迪. 海洋赤潮藻生长过程中碳源的作用机制[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2020.Lou Yadi. Carbon mechanism on the growth of marine blooms microalgae[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2020. [54] Liu Yuxin, Liu Yu, Jiao Dian, et al. Synthesis and release of fatty acids under the interaction of Ulva pertusa and Heterosigma akashiwo by stable isotope analysis[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 210: 111852. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111852 [55] Zhao Yan, Tang Xuexi, Zhao Xiaowei, et al. Effect of various nitrogen conditions on population growth, temporary cysts and cellular biochemical compositions of Karenia mikimotoi[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0171996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171996 [56] 杨秋婵, 赵玲, 尹平河, 等. 溶藻活性物质对棕囊藻溶藻及其脂肪酸影响的模拟[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(9): 3255−3261.Yang Qiuchan, Zhao Ling, Yin Pinghe, et al. Effects of algicidal substance on Phaeocystis globosa and its fatty acids by the simulation experiment[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(9): 3255−3261. [57] Ni Lixiao, Jie Xiaoting, Wang Peifang, et al. Characterization of unsaturated fatty acid sustained-release microspheres for long-term algal inhibition[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 120: 383−390. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.098 -




 下载:
下载: