Retrieving shallow bathymetry by integrating spatial autocorrelation features with machine learning
-
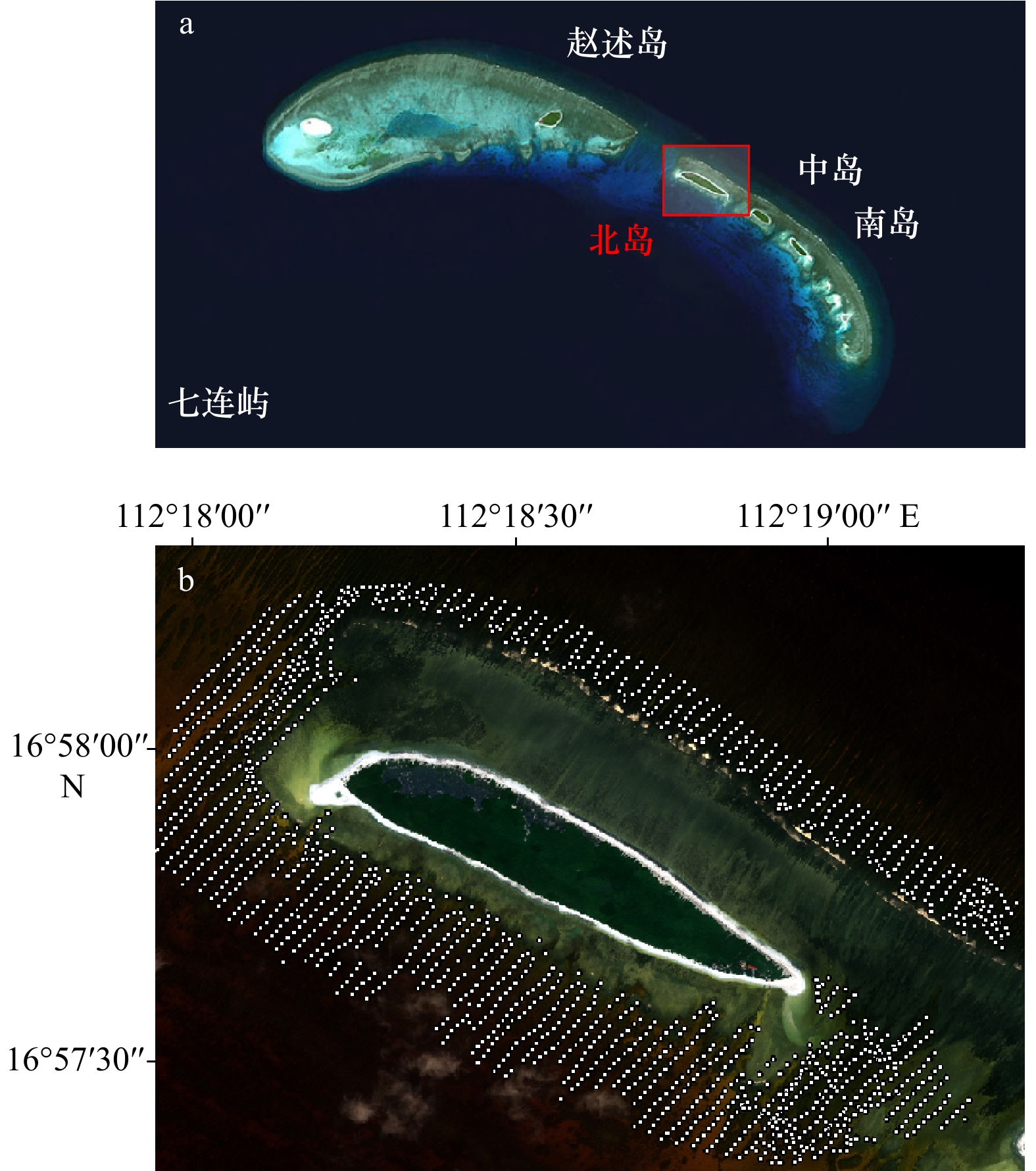
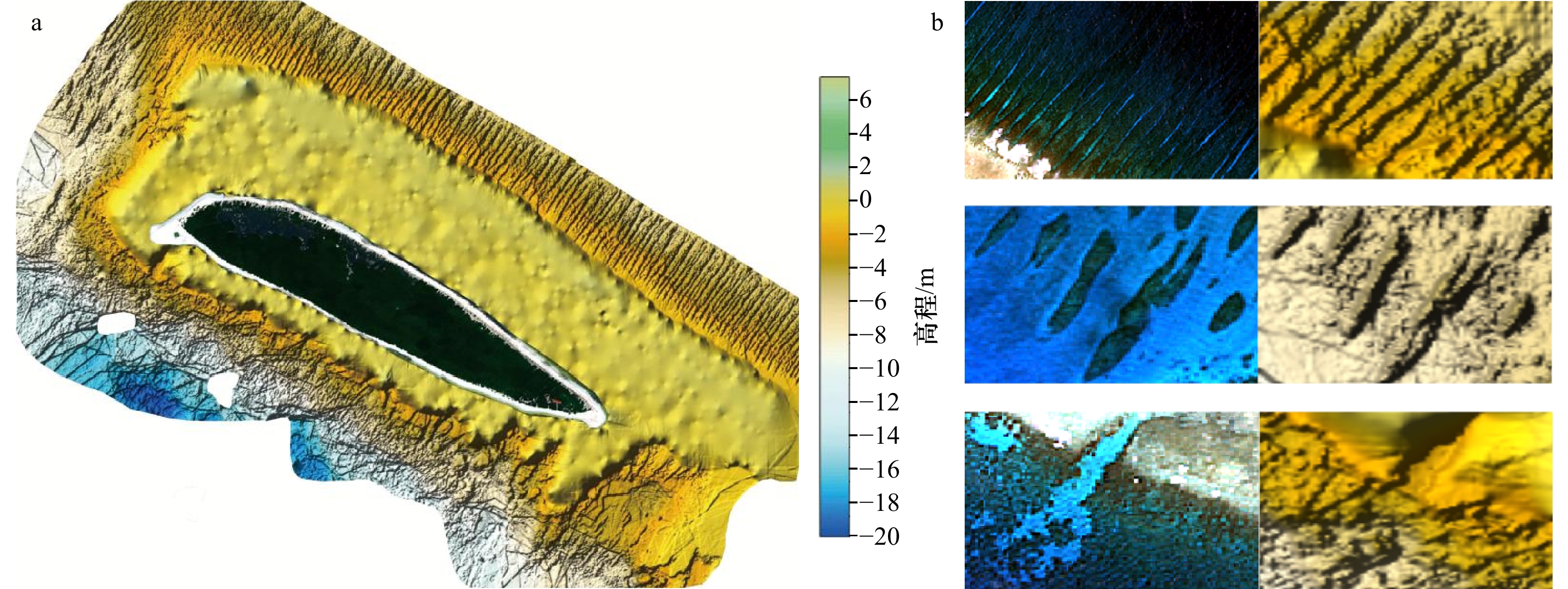
摘要: 基于多光谱影像的水深反演方法是获取近岸水深信息的高效手段,然而反演精度低一直是制约其广泛应用的瓶颈。本文聚焦于实测水深与多光谱数据自身的空间自相关特性,提出在机器学习框架下将学习样本的空间自相关特征与统计互相关特征相结合,以提高水深反演精度。西沙北岛海域的实验结果表明:在实测数据量较小的情况下,相比传统机器学习,顾及自相关特征的新方法可获得18%的精度提升;而当实测数据量充足时,精度提升可达到27%。结果表明,将数据源的空间自相关特征融入机器学习算法中,可显著提升多光谱水深反演结果的精确性,进而为浅海海洋研究提供有效数据支撑。Abstract: Retrieving shallow water depth based on multispectral satellite imagery is highly cost-effective. However, the extensive application of satellite-derived bathymetry has been restricted by its low prediction accuracy. To improve about the accuracy of the retrieved bathymetry, spatial autocorrelation features within the in situ depth measurements and the multi-spectral image are focused in this research. To this end, we develop a machine learning method combining with spatial autocorrelation features and statistical intercorrelation features of learned samples. The experimental results of Xisha Beidao show that compared with the traditional machine learning, the accuracy of the new method is improved by 18% when the number of in situ depths is small. On the contrary, when the number of in situ depths is large, an improvement of 27% in root mean square error is achieved. This demonstrates that incorporating the spatial autocorrelation features of data sources into the machine learning can significantly improve the prediction accuracy, and then provide effective data support for shallow ocean research.
-
Key words:
- bathymetry retrieval /
- random forest /
- machine learning /
- spatial autocorrelation
-
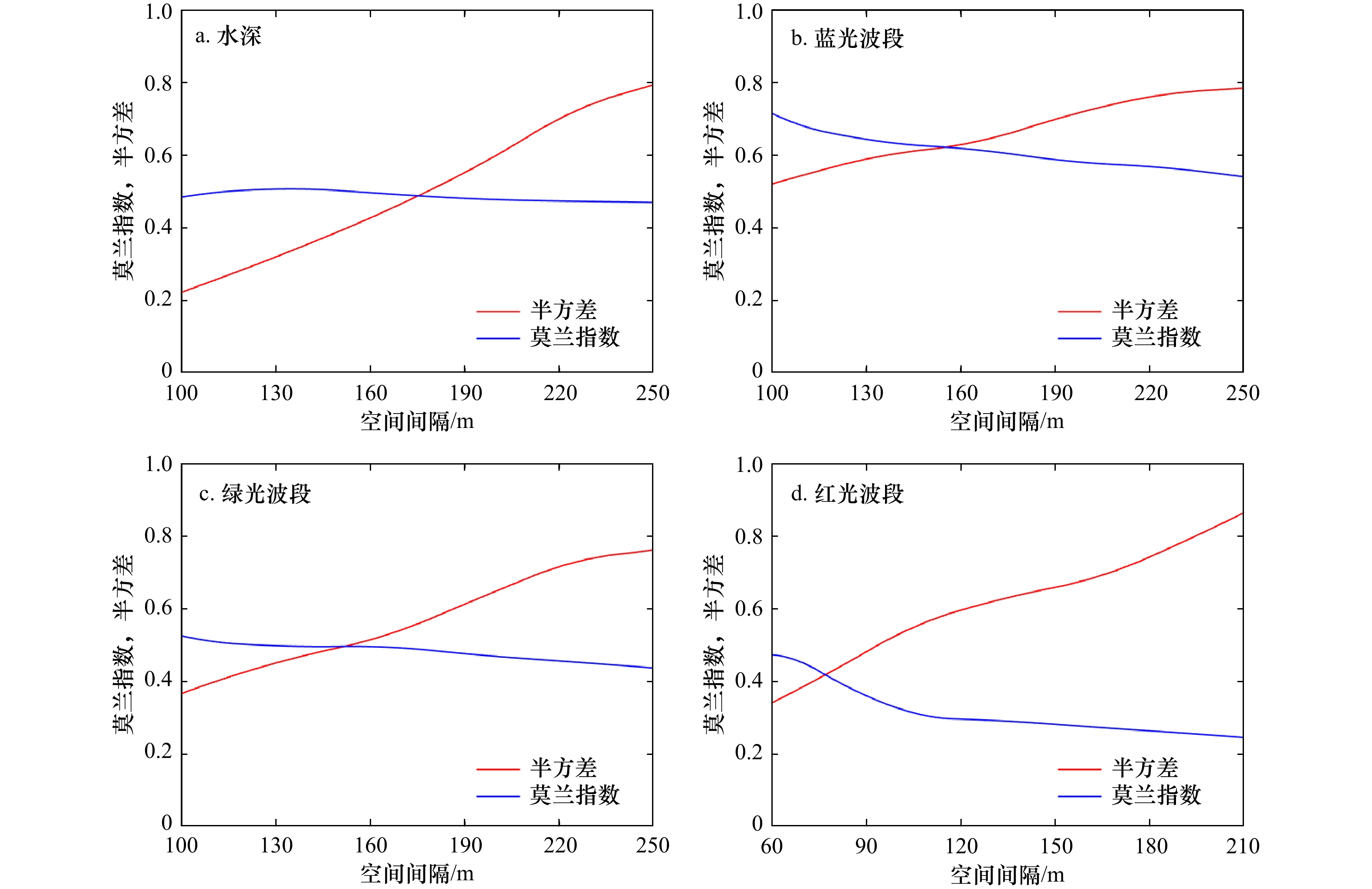
表 1 研究区变量的全局莫兰指数、Z值和P值
Tab. 1 Global Moran’s I, normalized Z value and P value of variables in the study area
环境变量 莫兰指数 Z值 P值 水深 0.511 8.853 0.001 蓝光波段 0.631 10.967 0.001 绿光波段 0.501 8.954 0.001 红光波段 0.301 5.531 0.001 表 2 验证数据测试精度对比
Tab. 2 Accuracy comparison of different methods
方法 均方根误差/m 平均绝对误差/m 决定系数 对数比值模型 2.067 1.608 0.797 普通克里金模型 1.894 1.487 0.845 随机森林模型 1.635 1.058 0.888 空间自相关随机森林模型 1.338 0.998 0.923 -
[1] 刘经南, 赵建虎. 多波束测深系统的现状和发展趋势[J]. 海洋测绘, 2002, 22(5): 3−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2002.05.001Liu Jingnan, Zhao Jianhu. Status and development tendency of multi-beam bathymetric system[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2002, 22(5): 3−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2002.05.001 [2] 赵建虎, 欧阳永忠, 王爱学. 海底地形测量技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1786−1794. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170276Zhao Jianhu, Ouyang Yongzhong, Wang Aixue. Status and development tendency for seafloor terrain measurement technology[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1786−1794. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170276 [3] Richard Z, Daniel I, David R, et al. Habitat classification of temperate marine macroalgal communities using bathymetric LiDAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(3): 2154−2175. doi: 10.3390/rs6032154 [4] 杨必胜, 梁福逊, 黄荣刚. 三维激光扫描点云数据处理研究进展、挑战与趋势[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1509−1516. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170351Yang Bisheng, Liang Fuxun, Huang Ronggang. Progress, challenges and perspectives of 3D LiDAR point cloud processing[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1509−1516. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170351 [5] 蒋兴伟, 林明森, 张有广, 等. 海洋遥感卫星及应用发展历程与趋势展望[J]. 卫星应用, 2018(5): 10−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9030.2018.05.005Jiang Xingwei, Lin Mingsen, Zhang Youguang, et al. Development and prospect of ocean remote sensing satellite and its application[J]. Satellite Application, 2018(5): 10−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9030.2018.05.005 [6] Hodul M, Bird S, Knudby A, et al. Satellite derived photogrammetric bathymetry[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2018, 142(8): 268−277. [7] Lyzenga D R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features[J]. Applied Optics, 1978, 17(3): 379−383. doi: 10.1364/AO.17.000379 [8] 马毅, 张杰, 张靖宇, 等. 浅海水深光学遥感研究进展[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2018, 36(3): 5−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.03.001Ma Yi, Zhang Jie, Zhang jingyu, et al. Progress in shallow water depth mapping from optical remote sensing[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2018, 36(3): 5−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.03.001 [9] Lyzenga D R, Malinas N P, Tanis F J. Multispectral bathymetry using a simple physically based algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(8): 2251−2259. [10] 陈启东, 邓孺孺, 秦雁, 等. 广东飞来峡库区水深遥感[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 51(1): 122−127.Chen Qidong, Deng Ruru, Qin Yan, et al. Water depth extraction from remote sensing image in Feilaixia Reservoir[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2012, 51(1): 122−127. [11] Figueiredo I N, Pinto L, Gonalves G. A modified Lyzenga’s model for multispectral bathymetry using Tikhonov regularization[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 53−57. [12] Stumpf R P, Holderied K, Sinclair M. Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2003, 48(1/2): 547−556. [13] Liang Jian, Zhang Jie, Ma Yi. A spatial resolution effect analysis of remote sensing bathymetry[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(7): 102−109. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1088-x [14] 陈本清, 杨燕明, 罗凯. 基于高分一号卫星多光谱数据的岛礁周边浅海水深遥感反演[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(2): 70−78.Chen Benqing, Yang Yanming, Luo Kai. Retrieval of island shallow water depth from the GaoFen-1 multi-spectral imagery[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(2): 70−78. [15] 陈琛, 马毅, 张靖宇. GF-1 WFV图像经验模分解的光谱保真性与水深遥感探测[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(4): 51−60.Chen Chen, Ma Yi, Zhang Jingyu. Spectral fidelity and water depth remote sensing detection of EMD of GF-1 WFV images[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(4): 51−60. [16] Xia H, Li X, Zhang H, et al. A Bathymetry mapping approach combining log-ratio and semianalytical models using four-band multispectral imagery without ground data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2695−2709. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2953381 [17] 王燕红, 陈义兰, 周兴华, 等. 基于多项式回归模型的岛礁遥感浅海水深反演[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(3): 121−128.Wang Yanhong, Chen Yilan, Zhou Xinghua, et al. Research on reef bathymetry using remote sensing based on polynomial regression model[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(3): 121−128. [18] Wang Yanjiao, Zhang Peiqun, Dong Wenjie, et al. Study on remote sensing of water depths based on BP artificial neural network[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2007, 9(1): 26−35. [19] 王锦锦, 马毅, 张靖宇. 基于模糊隶属度的多核SVR遥感水深融合探测[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(1): 130−136. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2018.01.020Wang Jinjin, Ma Yi, Zhang Jingyu. Multiple kernel support vector regression based on fuzzy membership for remote sensing water depth fusion detection[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(1): 130−136. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2018.01.020 [20] 朱金山, 纪轩禹, 宋珍珍. 基于支持向量机和BP神经网络的水深反演研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2019, 42(6): 11−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2019.06.004Zhu Jinshan, Ji Xuanyu, Song Zhenzhen. Water depth inversion based on support vector machine and BP neural network[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2019, 42(6): 11−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2019.06.004 [21] 温开祥, 李勇, 王华, 等. 基于遥感和机器学习的内陆水体水深反演技术[J]. 热带地理, 2020, 40(2): 314−322. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003237Wen Kaixiang, Li Yong, Wang Hua, et al. Estimating inland water depth based on remote sensing and machine learning technique[J]. Tropical Geography, 2020, 40(2): 314−322. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003237 [22] 刘光孟, 汪云甲, 张海荣, 等. 空间分析中几种插值方法的比较研究[J]. 地理信息世界, 2011, 9(3): 41−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2011.03.008Liu Guangmeng, Wang Yunjia, Zhang Hairong, et al. Comparative study of several lnterpolation methods on spatial analysis[J]. Geomatics World, 2011, 9(3): 41−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2011.03.008 [23] 印兴耀, 刘永社. 储层建模中地质统计学整合地震数据的方法及研究进展[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2002, 37(4): 423−430. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2002.04.020Yin Xingyao, Liu Yongshe. Methods and development of integrating seismic data in reservoir model-building[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2002, 37(4): 423−430. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2002.04.020 [24] 何红艳, 郭志华, 肖文发. 降水空间插值技术的研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 10(15): 1187−1191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2005.10.016He Hongyan, Guo Zhihua, Xiao Wenfa. Review on spatial interpolation techniques of rainfall[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 10(15): 1187−1191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2005.10.016 [25] Su H, Liu H, Wu Q. Prediction of water depth from multispectral satellite imagery-the regression Kriging alternative[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(12): 2511−2515. [26] Brunsdon C, Fotheringham A S, Charlton M E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity spatial[J]. Geographical Analysis, 2010, 28(4): 281−298. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-4632.1996.tb00936.x [27] Zhang K, Wang X, Wu Z, et al. Improving statistical uncertainty estimate of satellite-derived bathymetry by accounting for depth-dependent uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, PP(99): 1−9. [28] Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5−32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [29] Ham J, Chen Y, Crawford M M, et al. Investigation of the random forest framework for classification of hyperspectral data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(3): 492−501. [30] Stumpf A, Kerle N. Object-oriented mapping of landslides using random forests[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(10): 2564−2577. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.05.013 [31] 邱耀炜, 沈蔚, 纪茜. 随机森林模型在遥感水深反演中的应用[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2019, 38(5): 98−103.Qiu Yaowei, Shen Wei, Ji Qian. Satellite-derived bathymetry using random forest model[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2019, 38(5): 98−103. [32] 朱钟正, 苏伟. 基于局部空间统计分析的SPOT 5影像分类[J]. 遥感学报, 2011, 15(5): 957−972. doi: 10.11834/jrs.2011162Zhu Zhongzheng, Su Wei. The analysis of the classification of SPOT 5 image based on local spatial statistics[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2011, 15(5): 957−972. doi: 10.11834/jrs.2011162 [33] 张涛, 方宏, 韦玉春, 等. 顾及空间自相关性的高分遥感影像中建设用地的变化检测[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(4): 212−225.Zhang Tao, Fang Hong, Wei Yuchun, et al. Detection of the construction land change in fine spatial resolution remote sensing imagery coupling spatial autocorrelation[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35(4): 212−225. [34] Behrens T, Schmidt K, Viscarra R, et al. Spatial modelling with Euclidean distance fields and machine learning[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 69(5): 757−770. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12687 [35] Anselin L. Local indicator of spatial association-LISA[J]. Geographical Analysis, 1995, 27(2): 93−115. [36] 张松林, 张昆. 全局空间自相关Moran指数和G系数对比研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 46(4): 93−97. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2007.04.021Zhang Songlin, Zhang Kun. Comparison between general Moran’s index and Getis-Ord general G of spatial autocorrelation[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2007, 46(4): 93−97. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2007.04.021 [37] Carr J R, De Miranda F P. The semivariogram in comparison to the co-occurrence matrix for classification of image texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(6): 1945−1952. [38] Hedley J D, Harborne A R, Mumby P J. Technical note: Simple and robust removal of sun glint for mapping shallow-water benthos[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2005, 26(10): 2107−2112. doi: 10.1080/01431160500034086 -





 下载:
下载: