Study on the community structure of zooplankton in the sea area near the north operation area in the Lanshan Port of Rizhao Port in spring and autumn
-
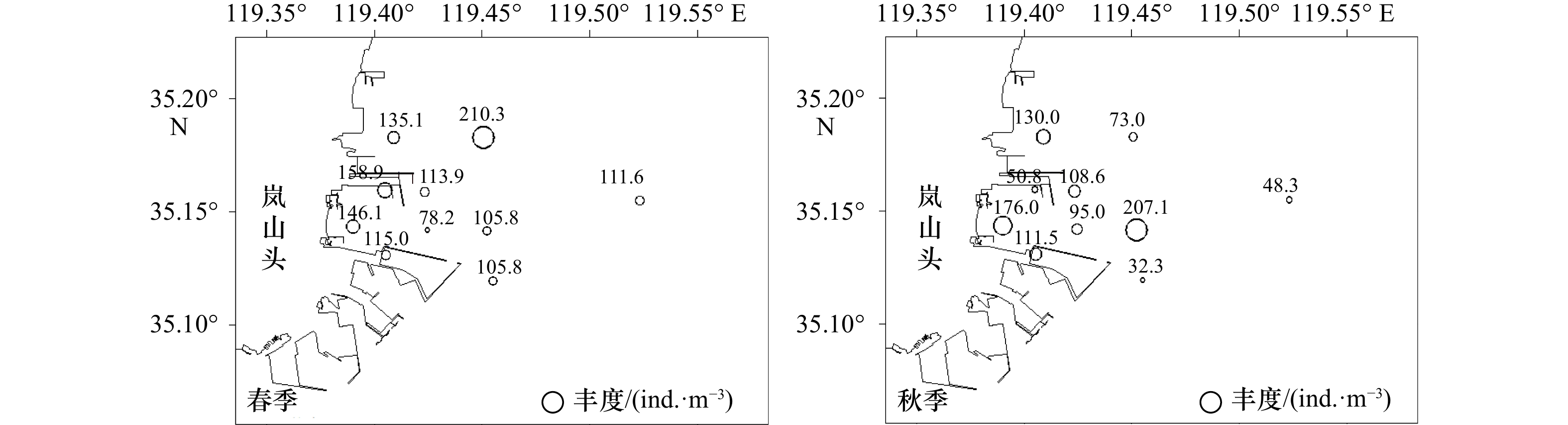
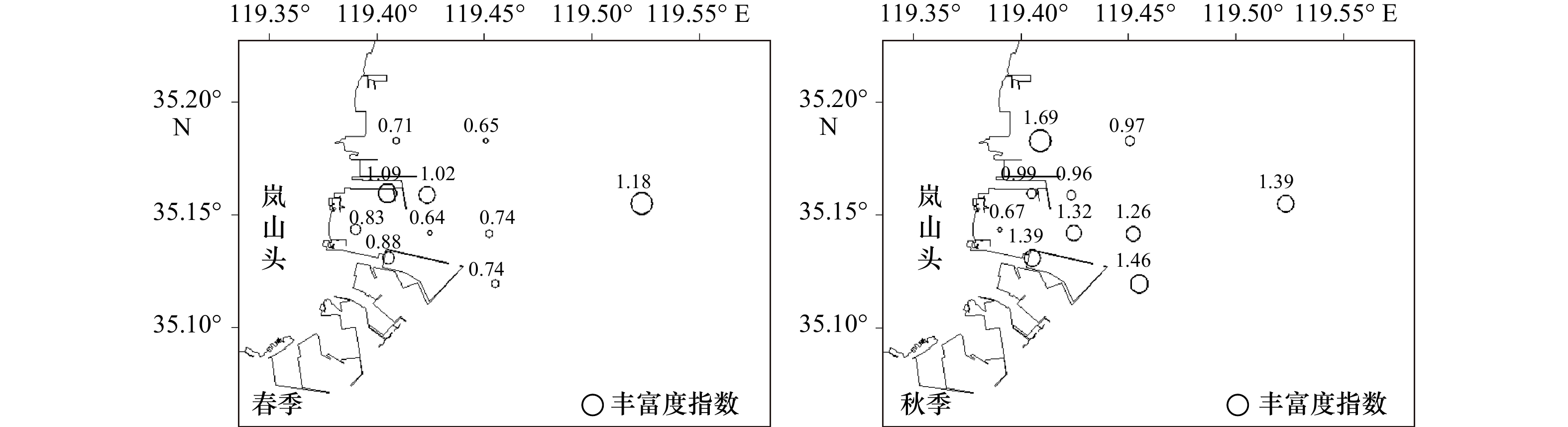
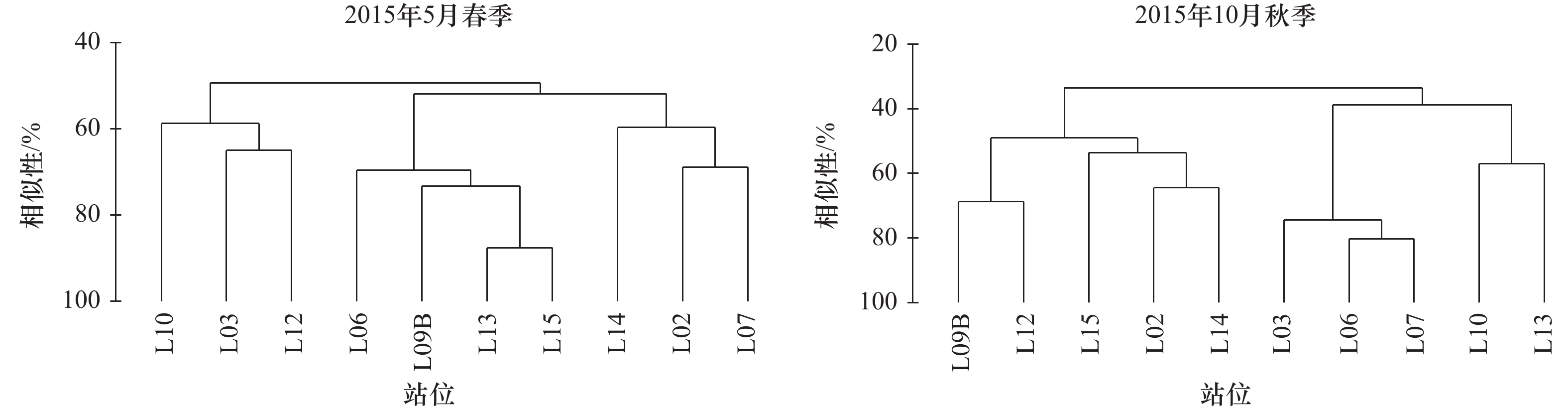
摘要: 以2015年5月(春季)和10月(秋季)在日照岚山港北作业区邻近海域进行的浮游动物调查数据为例,分析了该海域浮游动物的群落结构特征。调查海域两季共发现浮游动物成体20种,浮游幼虫7类,其中春季成体12种,浮游幼虫4类,秋季成体19种,浮游幼虫6类;春、秋两季调查浮游动物平均丰度分别为128.1 ind./m3、103.3 ind./m3;平均生物量(湿重)分别为1 129.9 mg/m3、954.3 mg/m3;平均多样性指数分别为2.39、2.01;平均丰富度指数分别为0.85、1.21;平均均匀度指数分别为0.87、0.62;春季调查优势种为强壮箭虫(Sagitta crassa)、中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus)、真刺唇角水蚤(Labibocera euchaeta)、太平洋纺锤水蚤(Acartia pacifica)、球型侧腕水母(Pleurobrachia globosa),秋季调查优势种为太平洋纺锤水蚤、小齿海樽(Doliolum denticulatum)、强壮箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤;聚类分析表明,调查海域浮游动物可划分为3个群落。本研究可为深入研究该海域浮游动物群落结构提供重要的基础数据。Abstract: Based on the investigation data of zooplankton in the sea area near the north operation area in the Lanshan Port of Rizhao Port in May (spring) and October (autumn) 2015, the community structure characteristics of zooplankton was analysed in this paper. The results showed that 20 species and 7 taxa of zooplankton were found in the two seasons, including 12 species and 4 taxa in spring and 19 species and 6 taxa in autumn, the average abundance of zooplankton were 128.1 ind./m3 in spring and 103.3 ind./m3 in autumn, the average biomass (wet weight) were 1 129.9 mg/m3 and 954.3 mg/m3, the average Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H'), Margalef’s species richness diversity (D) and Pielou’s evenness index (J) were 2.39, 0.85, 0.87 in spring, respectively, and 2.01, 1.21, 0.62 in autumn, respectively. In spring, the dominant species were Sagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Labibocera euchaeta, Acartia pacifica, Pleurobrachia globosa, while in autumn, the dominant species were Acartia pacifica, Doliolum denticulatum, Sagitta crassa, Labibocera euchaeta. Cluster analysis showed that the zooplankton in the investigation area could be divided into three groups. This study could provide important basic data for further study of zooplankton community structure in the coastal waters of Rizhao.
-
Key words:
- Lanshan Port of Rizhao Port /
- zooplankton /
- community structure /
- diversity /
- dominant species
-
表 1 浮游动物种类名录表
Tab. 1 List of zooplankton species
序号 中文名 拉丁文名或英文名 类群 春季 秋季 1 半球美螅水母 Clytia hemisphaerica 腔肠动物 − + 2 薮枝螅水母 Obelia spp. 腔肠动物 + + 3 黑球真唇水母 Eucheilota menoni 腔肠动物 + + 4 锡兰和平水母 Eirene ceylonensis 腔肠动物 + + 5 瓜水母 Beroe sp. 栉水母 + + 6 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 栉水母 + + 7 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 节肢动物 − + 8 瘦尾胸刺水蚤 Centropages tenuiremis 节肢动物 − + 9 双刺唇角水蚤 Labibocera bipinnata 节肢动物 + + 10 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica 节肢动物 + + 11 汤氏长足水蚤 Calanopia thompsoni 节肢动物 − + 12 近缘大眼剑水蚤 Corycaeus affinis 节肢动物 − + 13 小拟哲水蚤 Paracalanus parvus 节肢动物 − + 14 真刺唇角水蚤 Labibocera euchaeta 节肢动物 + + 15 中华哲水蚤 Calanus sinicus 节肢动物 + + 16 左突唇角水蚤 Labibocera sinilobata 节肢动物 − + 17 强壮箭虫 Sagitta crassa 毛颚动物 + + 18 萨利扭鳃樽 Thalia democratica 尾索动物 + − 19 小齿海樽 Doliolum denticulatum 尾索动物 − + 20 异体住囊虫 Oikopleura dioica 尾索动物 + + 21 桡足类幼体 Copepoda larva 浮游幼虫 − + 22 蔓足类无节幼虫 Nauplius larva(Cirripedia) 浮游幼虫 + − 23 短尾类溞状幼体 Zoea larva(Brachyura) 浮游幼虫 + + 24 多毛类幼体 Polychaeta larva 浮游幼虫 + + 25 腹足类幼体 Gastropoda larva 浮游幼虫 − + 26 海星幼体 Echinopluteus larva 浮游幼虫 − + 27 长尾类幼体 Macrura larva 浮游幼虫 + + 注:+代表出现;−代表未出现。 表 2 浮游动物种类组成
Tab. 2 Taxa composition of zooplankton
类群 春季 秋季 种类数 百分比/% 种类数 百分比/% 节肢动物 4 25 10 40 腔肠动物 3 19 4 16 栉水母 2 13 2 8 毛颚动物 1 6 1 4 尾索动物 2 13 2 8 浮游幼虫 4 25 6 24 合计 16 100 25 100 表 3 浮游动物优势种及其优势度
Tab. 3 Dominant species and its dominances of zooplankton
优势种 春季 秋季 出现频率 优势度指数(Y) 出现频率 优势度指数(Y) 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 0.70 0.03 − − 中华哲水蚤 Calanus sinicus 1.00 0.24 − − 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica 0.70 0.05 0.90 0.34 真刺唇角水蚤 Labibocera euchaeta 0.80 0.15 1.00 0.05 强壮箭虫 Sagitta crassa 1.00 0.28 1.00 0.14 小齿海樽 Doliolum denticulatum − − 0.90 0.19 注:−代表未出现。 表 4 调查海域浮游动物多样性指数
Tab. 4 The diversity index of zooplankton in monitoring areas
站位 春季 秋季 多样性指数(H') 均匀度(J) 阈值(Dv) 等级描述 多样性指数(H') 均匀度(J) 阈值(Dv) 等级描述 L02 1.86 0.72 1.3 多样性一般 3.03 0.85 2.6 多样性丰富 L03 2.10 0.81 1.7 多样性较好 1.07 0.38 0.4 多样性差 L06 2.58 0.81 2.1 多样性较好 1.79 0.64 1.1 多样性一般 L07 2.69 0.90 2.4 多样性较好 1.57 0.56 0.9 多样性一般 L09B 2.56 0.81 2.1 多样性较好 1.94 0.56 1.1 多样性一般 L10 2.65 0.95 2.5 多样性较好 0.85 0.33 0.3 多样性差 L12 2.28 0.98 2.2 多样性较好 2.09 0.63 1.3 多样性一般 L13 2.37 0.92 2.2 多样性较好 2.40 0.67 1.6 多样性较好 L14 2.49 0.89 2.2 多样性较好 2.55 0.74 1.9 多样性较好 L15 2.37 0.92 2.2 多样性较好 2.81 0.84 2.4 多样性较好 平均 2.39 0.87 2.1 多样性较好 2.01 0.62 1.4 多样性一般 -
[1] 陈学超, 朱丽岩, 黄瑛, 等. 南黄海浮游动物群落结构研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(10): 41−49. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160428005Chen Xuechao, Zhu Liyan, Huang Ying, et al. Community structure of the zooplankton in the Southern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(10): 41−49. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160428005 [2] 于洋, 孟娜, 王建勇, 等. 绿潮暴发对浮游动物群落结构影响研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2019, 36(3): 57−63.Yu Yang, Meng Na, Wang Jianyong, et al. Impacts of green tide outbreaks on zooplankton community structure[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2019, 36(3): 57−63. [3] 毕晓欣, 毕立海, 刘冲, 等. 山东省近岸海域浮游动物的生态特征分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(4): 136−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.04.045Bi Xiaoxin, Bi Lihai, Liu Chong, et al. Ecological characteristics of zooplankton of inshore areas in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(4): 136−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.04.045 [4] 张亮, 宋春丽, 王岚, 等. 日照港岚山港区附近海域秋季浮游动物群落结构特征[J]. 广西科学, 2020, 27(2): 203−210.Zhang Liang, Song Chunli, Wang Lan, et al. Community structure characteristics of zooplankton in the sea area near Lanshan Port of Rizhao Port in autumn[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2020, 27(2): 203−210. [5] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 17378.7−2007, 海洋监测规范 第7部分: 近海污染生态调查和生物监测[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 17378.7−2007, The specification for marine monitoring—Part7: Ecological survey for offshore pollution and biological monitoring[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008. [6] 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 1989, 8(4): 13−15,19.Xu Zhaoli, Chen Yaqu. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1989, 8(4): 13−15,19. [7] Shannon C E, Weaver W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication[M]. Urbana: The University of Illinois Press, 1949. [8] Margalef R. Information theory in ecology[J]. General Systematics, 1958(3): 36−71. [9] Pielou E C. An Introduction to Mathematical Ecology[M]. New York: Wiley, 1969: 1−286. [10] 陆家昌, 姜发军, 许铭本, 等. 2015年冬季钦州湾浮游动物死体对海洋生态系统的影响[J]. 广西科学, 2016, 23(4): 325−330.Lu Jiachang, Jiang Fajun, Xu Mingben, et al. Effects of zooplankton carcasses in Qinzhou Bay during winter 2015 on marine ecosystem[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2016, 23(4): 325−330. [11] 陈清潮, 黄良民, 尹健强, 等. 南沙群岛海区浮游动物多样性研究[M]//中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队. 南沙群岛及其邻近海区海洋生物多样性研究I. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1994: 42−50.Chen Qingchao, Huang Liangmin, Yin Jianqiang, et al. Studies on the zooplanktonic biodiversities in the waters around Nansha Islands[M]//Nansha Comprehensive Scientific Investigation Team, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Studies on Marine Biodiversity of the Nansha Islands and Neighbouring Waters I. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1994: 42−50. [12] 左涛. 东、黄海浮游动物群落结构研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2003.Zuo Tao. Community structure of zooplankton in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003. [13] 王云龙, 沈新强, 李纯厚, 等. 中国大陆架及邻近海域浮游生物[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2005.Wang Yunlong, Shen Xinqiang, Li Chunhou, et al. Plankton in the Chinese Mainland and Adjacent Waters[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2005. [14] 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室. 全国海洋综合调查报告第八册[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, 1964: 48−51, 113−117.Comprehensive Marine Survey Office of Ocean Group Science and Technology Committee in People’s Republic of China. The National Comprehensive Marine Survey Report Volume 8[R]. Beijing: Comprehensive Marine Survey Office of Ocean Group Science and Technology Committee in People’s Republic of China, 1964: 48−51, 113−117. [15] 王晓, 姜美洁, 刘萍, 等. 秋季南黄海浮游动物分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(10): 125−134.Wang Xiao, Jiang Meijie, Liu Ping, et al. Distribution pattern of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the South Yellow sea in autumn[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(10): 125−134. [16] 姜会超, 刘宁, 高继庆, 等. 烟台四十里湾浮游动物群落特征及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(4): 1318−1327.Jiang Huichao, Liu Ning, Gao Jiqing, et al. Zooplankton community structure in Sishili Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(4): 1318−1327. [17] 郑重, 李少菁, 许振祖. 海洋浮游生物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984: 139−491.Zheng Zhong, Li Shaojing, Xu Zhenzu. Marine Plankton Biology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984: 139−491. [18] 柳丽华, 左涛, 陈瑞盛, 等. 2004年秋季长江口海域浮游植物的群落结构和多样性[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2007, 28(3): 112−119.Liu Lihua, Zuo Tao, Chen Ruisheng, et al. Community structure and diversity of phytoplankton in the estuary of Yangtze River in autumn[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 2007, 28(3): 112−119. [19] 庞碧剑, 覃秋荣, 蓝文陆. 生物多样性指数在生态评价中的实用性分析——以北部湾为例[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2019, 35(2): 91−99.Pang Bijian, Qian Qiurong, Lan Wenlu. Practicability of ecological evaluation by biodiversity index: a case study of the Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2019, 35(2): 91−99. [20] 纪莹璐, 王尽文, 张亮, 等. 日照岚山港邻近海域大型底栖动物群落结构及季节变化[J]. 生态科学, 2020, 39(5): 151−160.Ji Yinglu, Wang Jinwen, Zhang Liang, et al. Community structure and seasonal changes of macrobenthos in the adjacent waters of Lanshan Harbour[J]. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(5): 151−160. [21] 陈清潮, 陈亚瞿, 胡雅竹. 南黄海和东海浮游生物群落的初步探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 1980, 2(2): 149−157.Chen Qingchao, Chen Yaqu, Hu Yazhu. Preliminary study on the plankton communities in the Southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1980, 2(2): 149−157. [22] 姜会超, 陈海刚, 宋秀凯, 等. 莱州湾金城海域浮游动物群落结构及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(22): 7308−7319.Jiang Huichao, Chen Haigang, Song Xiukai, et al. Zooplankton community structure in Jincheng area of Laizhou Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(22): 7308−7319. [23] 罗鸣, 苗素英, 于红兵, 等. 春末海南万宁海域浮游动物群落结构研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2013, 37(11): 79−84.Luo Ming, Miao Suying, Yu Hongbing, et al. Community structure of zooplankton in the offshore water of wanning at the end of spring[J]. Marine Sciences, 2013, 37(11): 79−84. [24] 时永强, 左涛, 袁伟, 等. 夏季崂山湾浮游动物群落结构及空间分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(5): 990−997. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20170200035Shi Yongqiang, Zuo Tao, Yuan Wei, et al. Community structure and spatial distribution of zooplankton in Laoshan Bay in summer[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(5): 990−997. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20170200035 [25] 杨杰青, 欧阳珑玲, 唐峰华, 等. 海南西北部近岸海域浮游动物群落结构与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2020, 27(2): 236−249.Yang Jieqing, Ouyang Longling, Tang Fenghua, et al. Relationship between the zooplankton community structure and environmental factors offshore of northwest Hainan Island, China[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2020, 27(2): 236−249. -




 下载:
下载: