The genesis, accumulation model and exploration significance of Y gas field in X Sag, East China Sea Basin
-
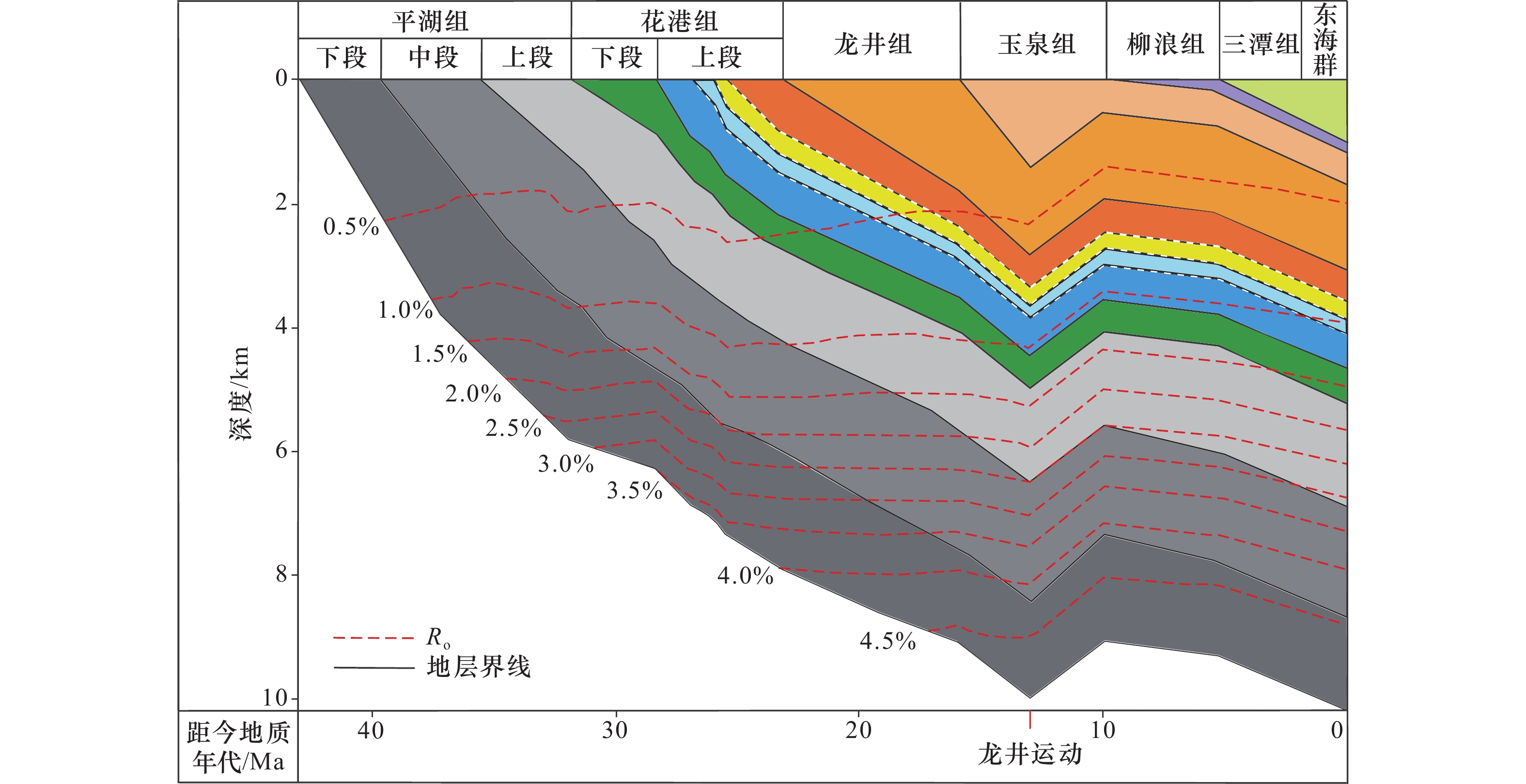
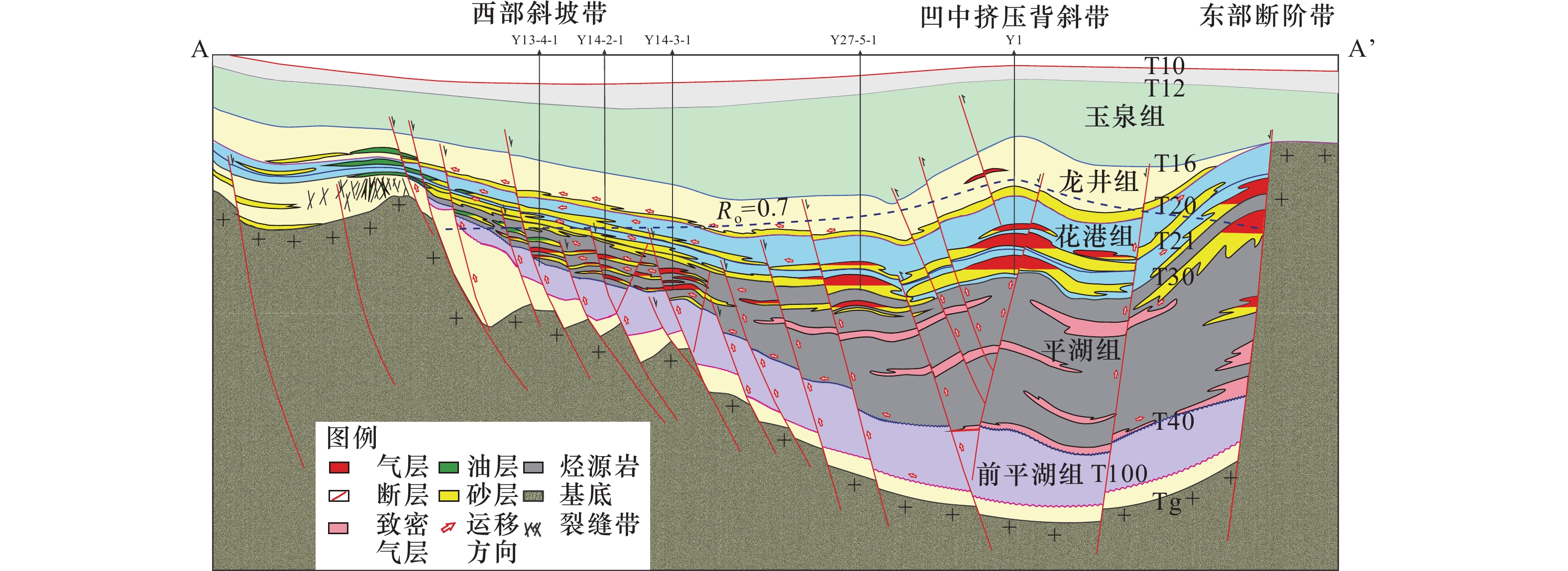
摘要: 本文旨在厘清东海盆地X凹陷Y气田天然气成因,建立成藏模式,以指导下步勘探部署。本文从天然气组分、烷烃气碳同位素、轻烃、凝析油生物标志化合物等分析入手,系统研究了油气成因类型及来源,并结合构造演化史、生烃史分析,建立了Y气田成藏模式,提出了大中型气田的勘探方向。主要认识如下:(1)天然气组分碳同位素、轻烃和埋藏史分析表明,Y气田天然气为凹中始新统平湖组烃源岩在龙井运动期(距今13 Ma)生成的高成熟煤型气;(2)凝析油姥鲛烷/植烷、规则甾烷等特征,反映了凹中区平湖组烃源岩发育于弱氧化−弱还原潮坪、潟湖沉积环境,生烃母质中存在一定数量的低等水生生物;(3)Y气田具有“凹中区平湖组烃源岩、花港组大型水道砂储集体、挤压构造作用”时空耦合的成藏模式,明确了凹中挤压背斜带是X凹陷大中型气田勘探的主攻方向。Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to clarify the genesis of natural gas of Y gas field, and establish accumulation model to guide the next exploration deployment in X Sag, East China Sea Basin. Based on the analyses of natural gas composition, carbon isotope of alkane gas, light hydrocarbon and biomarker compound of condensate oil, this paper systematically studies the genetic types and sources of oil and gas, establishes the reservoir accumulation model of Y large and medium-sized gas field, and puts forward the exploration direction of large and medium-sized gas field. The analyses of carbon isotope, light hydrocarbon and burial history show that the natural gas in Y gas field is highly mature coal type gas generated by the source rocks of middle Eocene Pinghu formation in the sag during the Longjing movement period (13 Ma BP). The characteristics of pristane/phytane and regular sterane of condensate oil reflect that the source rocks of middle Eocene Pinghu formation in the central sag are developed in tidal flat and lagoon sedimentary environment with weak oxidation weak reduction, and there are a certain number of lower aquatic organisms in the hydrocarbon generating parent material. Y gas field has a spatiotemporal coupling reservoir accumulation model of “Pinghu formation source rock, Huagang formation large channel sand reservoir and Mid-Miocene compressional tectonism” in the central sag. It is clear that the compressional anticline belt in the central sag is the main exploration direction of large and medium-sized gas fields in X Sag.
-
表 1 东海盆地X凹陷Y气田天然气组分与烷烃气碳同位素特征
Tab. 1 Natural gas composition and carbon isotope characteristics of the Y gas field of X sag in the East China Sea Basin
区带 井号 井段/m 测试层号 地层 天然气组分/% 干燥系数 碳同位素δ13C/‰ C1 C2-5 N2 CO2 C1/ΣC1+ C1 C2 C3 C4 X凹陷凹中
背斜带Y1 3769~3799 DST1 花港组H3b下部 92.98 3.15 1.61 2.15 0.967 −30.9 −24 −24 −23.1 Y1 3709~3739 DST2 花港组H3b中上部 93.49 3.15 1.19 2.04 0.967 −29.8 −23.8 −23.6 −19.1 Y1 3177~3181, 3186~3199 DST4 花港组H1 94.45 3.00 1.47 0.93 0.969 −29.9 −23.5 −22.7 −19.5 Y2 4240~4352 DST1 花港组H5 87.12 5.96 1.45 5.36 0.936 −30.4 −25.3 −23.3 −23.4 Y2 3673~3700 DST2 花港组H3a 92.88 3.16 1.25 2.49 0.967 −27.7 −23.3 −22.7 −22.8 表 2 X凹陷Y气田和北部湾等盆地天然气C7轻烃组成
Tab. 2 Compositions of C7 light hydrocarbon serial of natural gas in Y gas field of X Sag and Beibu Gulf Basin
盆地 井名 地层 天然气C7轻烃组成 甲基环己烷
指数甲苯/
苯甲基环己烷
(MCH)含量/%正庚烷
(nC7)含量/%二甲基环戊烷
(ΣDMCP)含量/%东海 Y1 渐新统花
港组71.90 18.30 9.80 0.719 2.7 Y1 70.49 18.06 11.46 0.704 9 2.08 Y2 69.90 18.77 11.33 0.699 2.77 南海北部湾 W1 始新统流
沙港组33.3 25.9 40.7 0.333 * W2 渐新统涠
洲组34.8 30.4 34.8 0.348 * W3 35.71 32.14 32.14 0.357 1 * 鄂尔多斯 榆
211下二叠统
山西组70.4 16.8 12.8 0.704 * 四川 须二
Z2三叠系须
家河组73 15 12 0.73 * 注∶甲基环己烷指数=MCH/(MCH+nC7+ΣDMCP),*表示甲苯/苯比值未知。 表 3 东海盆地X凹陷烃源岩、凝析油饱和烃色谱−质谱参数表
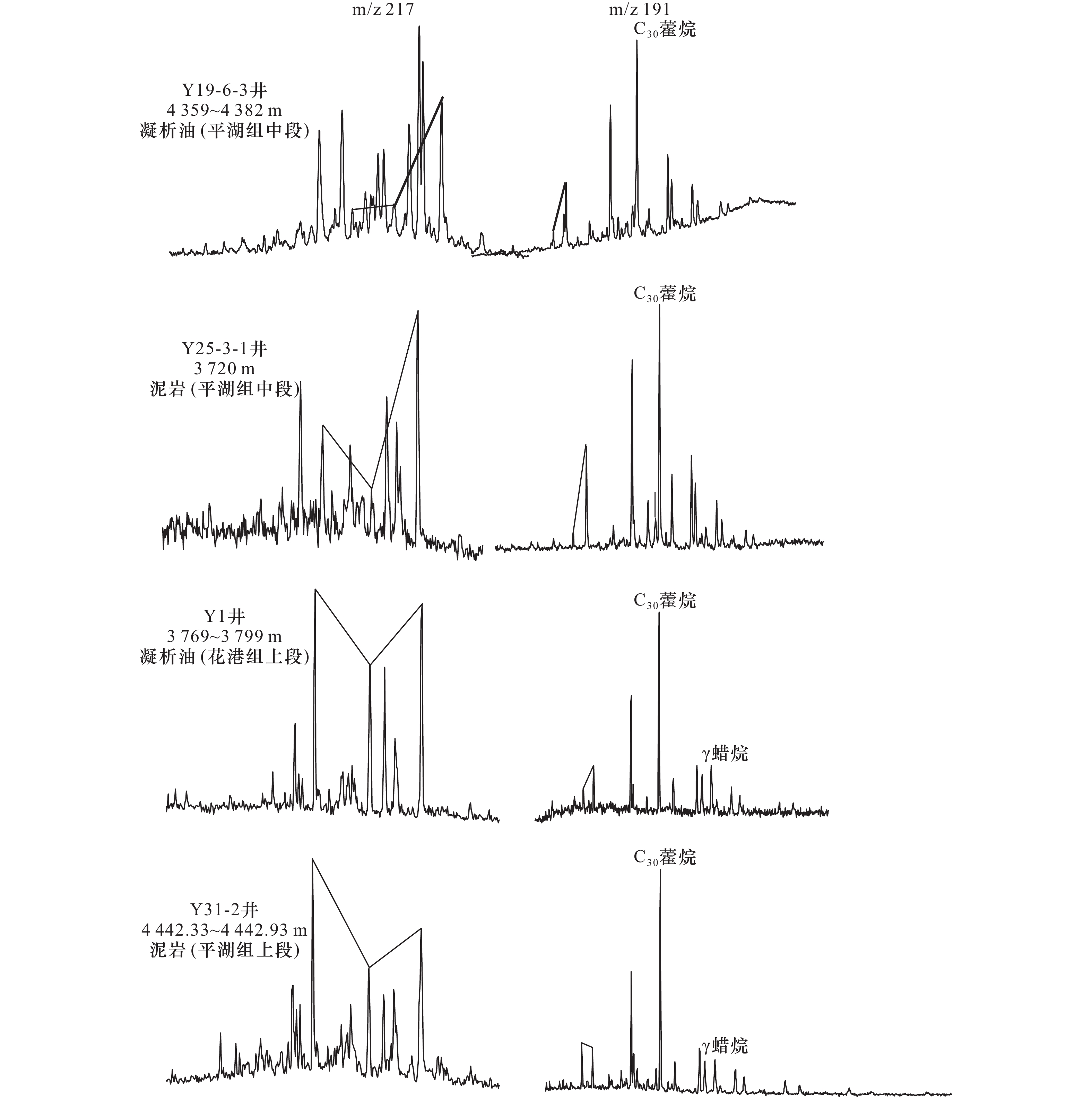
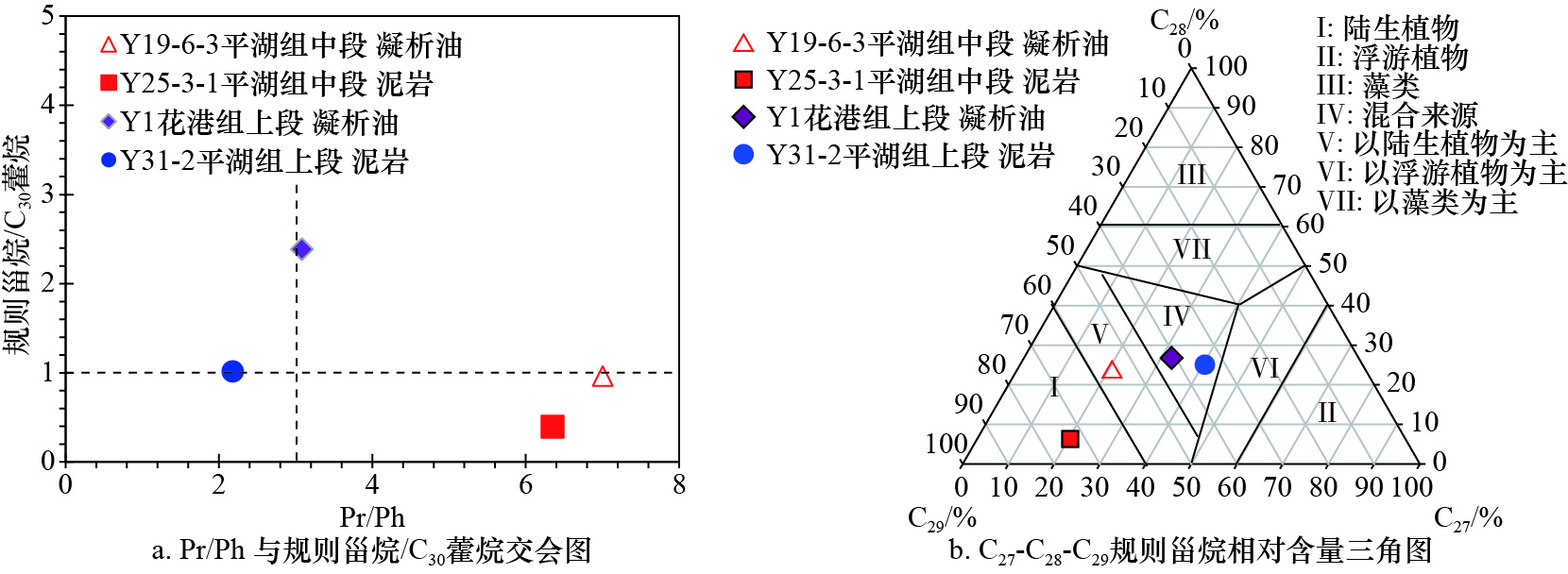
Tab. 3 Source rocks and condensate chromatographic-mass spectrometry parameter of X Sag in the East China Sea Basin
区带 井号 井段/m 样品
类型地层 Pr/Ph 规则甾烷/
C30藿烷甾烷
C27/%甾烷
C28/%甾烷
C29/%甾烷C27/C29 Ts/Tm 奥利烷/
C30藿烷伽马蜡烷/
C30藿烷西部斜坡带 Y19-6-3 4 359~4 382 凝析油 平湖组中段 7 0.97 21.06 23.20 55.73 0.389 0.26 0.15 / Y25-3-1 3 720 泥岩 平湖组中段 6.35 0.40 20.37 6.33 73.29 0.28 0.16 0.12 / 凹中挤压背斜带 Y1 3 760~3 799 凝析油 花港组上段 3.08 2.39 32.32 26.79 40.89 0.79 0.56 / 0.25 Y31-2 4 442.33~4 442.93 泥岩 平湖组上段 2.18 1.02 40.45 25.07 34.48 1.17 1.10 0.10 0.15 表 4 Y气田天然气成熟度与等效烃源岩埋深
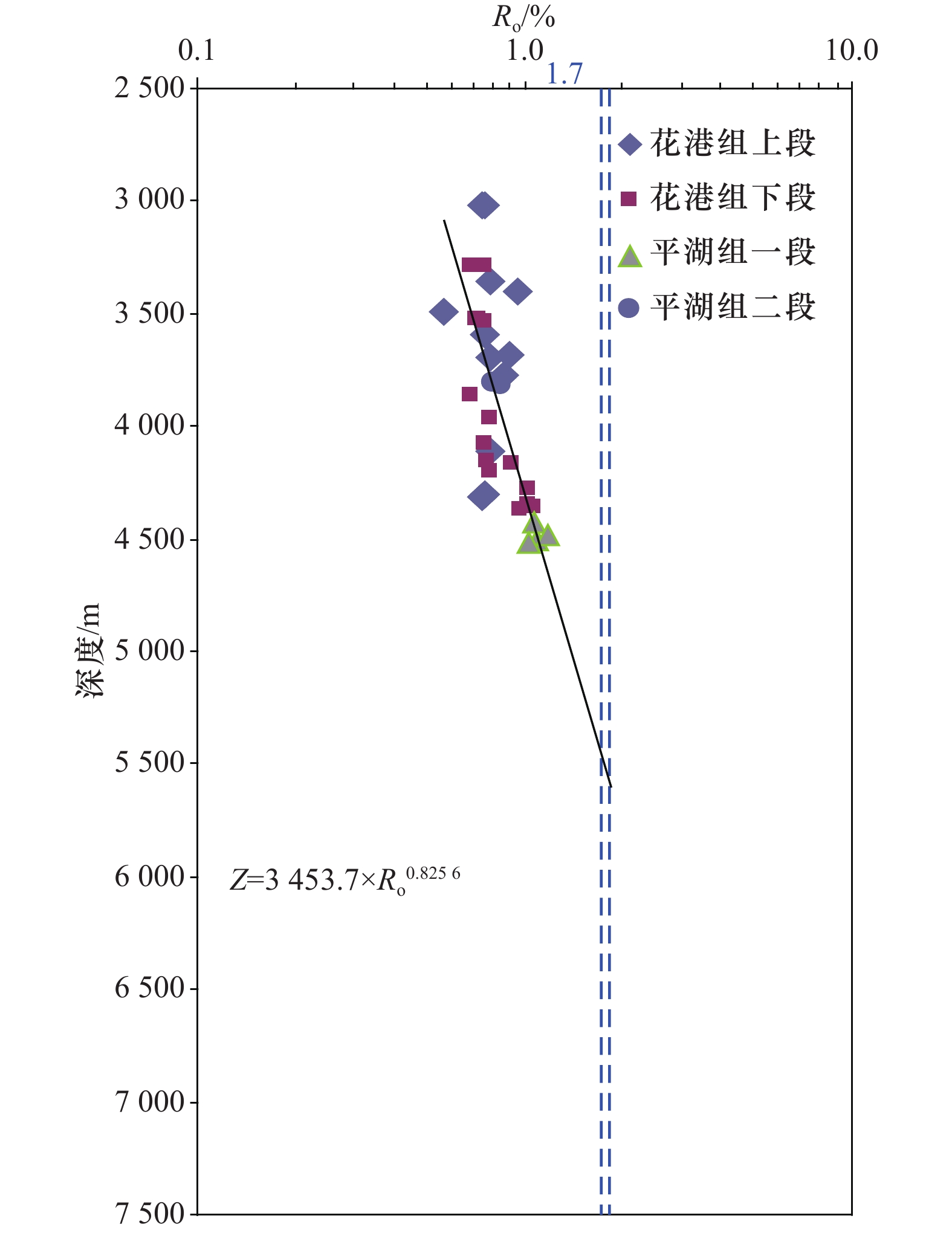
Tab. 4 The maturity of natural gas and equivalent burial depth of source rock of Y gas field
井号 甲烷碳同位素δ13C1/‰ *天然气成熟度Ro/% **烃源岩埋深Z/m Y1 −30.9 1.70 5 344 Y1 −29.8 1.77 5 537 Y1 −29.9 1.76 5 520 Y2 −30.4 1.73 5 431 Y3 −27.7 1.92 5 927 注∶*δ13C1=58.67×lg(Ro)−44.37[29],**Z=3453.7×Ro0.8256。 -
[1] Engebretson D C, Cox A, Gordon R G. Relative motions between oceanic and continental plates in the Pacific Basin[J]. Geological Society of America, 1985, 206(9): 1−60. [2] Northrup C J, Royden L H, Burchfiel B C. Motion of the Pacific plate relative to Eurasia and its potential relation to Cenozoic extension along the eastern margin of Eurasia[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(8): 719−722. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0719:MOTPPR>2.3.CO;2 [3] 董树文, 张岳桥, 陈宣华, 等. 晚侏罗世东亚多向汇聚构造体系的形成与变形特征[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(3): 306−317. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.005Dong Shuwen, Zhang Yueqiao, Chen Xuanhua, et al. The formation and deformational characteristics of East Asia multi-direction convergent tectonic system in late Jurassic[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(3): 306−317. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.005 [4] 张建培, 张田, 唐贤君. 东海陆架盆地类型及其形成的动力学环境[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(11): 2033−2043.Zhang Jianpei, Zhang Tian, Tang Xianjun. Basin type and dynamic environment in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11): 2033−2043. [5] 杨传胜, 杨长清, 杨艳秋, 等. 东海陆架盆地中生界残留分布特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(11): 86−95.Yang Chuansheng, Yang Changqing, Yang Yanqiu, et al. Characteristics of mesozoic strata in the East China Sea Shelf Basin and their geotectonic implications[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(11): 86−95. [6] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 等. 西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造−岩浆响应[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(16): 1550−1593. doi: 10.1360/N972017-01113Li Sanzhong, Suo Yanhui, Li Xiyao, et al. Mesozoic plate subduction in West Pacific and tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(16): 1550−1593. doi: 10.1360/N972017-01113 [7] Zhu Weilin, Zhong Kai, Fu Xiaowei, et al. The formation and evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin: A new view[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 190: 89−111. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.009 [8] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 孙晶, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代演化与动力学转换过程[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 2019, 49(1): 139−153.Yang Changqing, Yang Chuansheng, Sun Jing, et al. Mesozoic evolution and dynamics transition in Southern Shelf Basin of the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(1): 139−153. [9] 周心怀. 西湖凹陷地质认识创新与油气勘探领域突破[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(1): 1−12.Zhou Xinhuai. Geological understanding and innovation in Xihu Sag and breakthroughs in oil and gas exploration[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(1): 1−12. [10] 李晓龙, 许长海, 高顺莉, 等. 东海晚中生代岩浆弧与陆缘汇聚作用: 碎屑锆石U-Pb年代约束[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(2): 480−490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.02.009Li Xiaolong, Xu Changhai, Gao Shunli, et al. Late Mesozoic magmatic arc of continental margin: Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb data, East China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(2): 480−490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.02.009 [11] 刘金水, 许怀智, 蒋一鸣, 等. 东海盆地中、新生代盆架结构与构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 675−691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.001Liu Jinshui, Xu Huaizhi, Jiang Yiming, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic basin structure and tectonic evolution in the East China sea Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 675−691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.001 [12] 武法东, 陆永潮, 陈平, 等. 东海西湖凹陷渐新统花港组海绿石的发现及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(3): 160−163.Wu Fadong, Lu Yongchao, Chen Ping, et al. The discovery and significance of glauconites in the Huagang formation of the Oligocene, Xihu Depression, East China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(3): 160−163. [13] 戴金星, 邹才能, 张水昌, 等. 无机成因和有机成因烷烃气的鉴别[J]. 中国科学 D辑:地球科学, 2008, 51(12): 1737−1749. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0133-1Dai Jinxing, Zou Caineng, Zhang Shuichang, et al. Discrimination of abiogenic and biogenic alkane gases[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(12): 1737−1749. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0133-1 [14] 沈平, 徐永昌, 王先彬, 等. 气源岩和天然气地球化学特征及成气机理研究[M]. 兰州: 甘肃科学技术出版社, 1991: 39−122.Shen Ping, Xu Yongchang, Wang Xianbin, et al. Geochemical Characteristics of Source Rocks and Natural Gas and Gas Generating Mechanism[M]. Lanzhou: Gansu Science and Technology Press, 1991: 39−122. [15] 徐永昌. 天然气成因理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 97−1016.Xu Yongchang. Theory of Natural Gas Genesis and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 97−1016. [16] 徐永昌. 天然气中的幔源稀有气体[J]. 地学前缘, 1996, 3(3/4): 63−71.Xu Yongchang. The mantle noble gas of natural gases[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1996, 3(3/4): 63−71. [17] Jenden P D, Hilton D R, Kaplan I R, et al. Abiogenic hydrocarbons and mantle helium in oil and gas fields[M]//Howell D G. The Future of Energy Gases. Washington, DC: U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 1993: 31−56. [18] 戴金星. 中国含油气盆地的无机成因气及其气藏[J]. 天然气工业, 1995, 15(3): 22−27.Dai Jinxing. Abiogenic gas in oil-gas bearing basins in China and its reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1995, 15(3): 22−27. [19] 戴金星, 石昕, 卫延召. 无机成因油气论和无机成因的气田(藏)概略[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(6): 5−10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2001.06.002Dai Jinxing, Shi Xin, Wei Yanzhao. Summary of the abiogenic origin theory and the abiogenic gas pools (fields)[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22(6): 5−10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2001.06.002 [20] 董伟良, 黄保家. 南海莺−琼盆地煤型气的鉴别标志及气源判识[J]. 天然气工业, 2000, 20(1): 23−27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2000.01.006Dong Weiliang, Huang Baojia. Identification marks and source discrimination of the coal-type gas in YGH and QDN basins of South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2000, 20(1): 23−27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2000.01.006 [21] 何家雄, 陈伟煌, 李明兴. 莺−琼盆地天然气成因类型及气源剖析[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(6): 398−405.He Jiaxiong, Chen Weihuang, Li Mingxing. Genetic types of natural gas and source rock in Ying-Qiong Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(6): 398−405. [22] 朱俊章, 施和生, 庞雄, 等. 白云凹陷天然气生成与大中型气田形成关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(2): 213−221.Zhu Junzhang, Shi Hesheng, Pang Xiong, et al. Discussion on natural gas generation and giant-medium size gas field formation in Baiyun Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(2): 213−221. [23] 庄新兵, 邹华耀, 李楠, 等. 秦南地区天然气成因与油气勘探潜力分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(3): 680−688.Zhuang Xinbing, Zou Huayao, Li Nan, et al. Origin of natural gas and exploration potential of hydrocarbon, Qinnan Area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(3): 680−688. [24] Schoell M. Genetic characterization of natural gases[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1983, 67(12): 2225−2238. [25] 杨柳. 中国海域新生代聚煤规律与控煤模式[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2017.Yang Liu. Cenozoic coal accumulation regularity and controlling pattern in China offshore[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017. [26] Galimov E M. Sources and mechanisms of formation of gaseous hydrocarbons in sedimentary rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 71(1/3): 77−95. [27] 胡惕麟, 戈葆雄, 张义纲, 等. 源岩吸附烃和天然气轻烃指纹参数的开发和应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 1990, 12(4): 375−394, 450. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199004375Hu Tilin, Ge Baoxiong, Zhang Yigang, et al. The development and application of fingerprint parameters for hydrocarbons absorbed by source rocks and light hydrocarbons in natural gas[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1990, 12(4): 375−394, 450. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199004375 [28] 戴金星. 利用轻烃鉴别煤成气和油型气[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1993, 20(5): 26−32.Dai Jinxing. Identification of coal formed gas and oil type gas by light hydrocarbons[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1993, 20(5): 26−32. [29] 程熊, 侯读杰, 赵喆, 等. 西湖凹陷天然气成因及来源分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3): 50−60.Cheng Xiong, Hou Dujie, Zhao Zhe, et al. Analysis on the genesis and source of natural gas in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(3): 50−60. [30] 张迎朝, 徐新德, 王立锋, 等. 南海北部超压低渗气藏成藏过程与成藏模式——以莺歌海盆地XF区XF13-1超压气田为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(9): 1679−1688.Zhang Yingzhao, Xu Xinde, Wang Lifeng, et al. The accumulation process and model of overpressured low permeability gas pool in the north of South China Sea: A case study of XF13-1 overpressured gas field in XF Area of the Yinggehai Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geosciences, 2015, 26(9): 1679−1688. [31] 张迎朝, 徐新德, 甘军, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区L18气田上新统地层圈闭气田形成条件及成藏模式[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(3): 120−132.Zhang Yingzhao, Xu Xinde, Gan Jun, et al. Formation condition and accumulation of Pliocene strata-trapped gas field L18 in the deepwater area of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(3): 120−132. [32] 夏青松, 黄成刚, 陆江. 沉积盆地中油气充注与储集层成岩作用的响应关系[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2019, 41(2): 185−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2019.02.005Xia Qingsong, Huang Chenggang, Lu Jiang. Response relationship between hydrocarbon charging and diagenesis of reservoirs in sedimentary basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2019, 41(2): 185−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2019.02.005 [33] 纪友亮, 高崇龙, 刘玉瑞, 等. 高邮凹陷阜一段油气充注对储层物性演化的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(1): 133−139.Ji Youliang, Gao Chonglong, Liu Yurui, et al. Influence of hydrocarbon charging to the reservoir property in 1st member of funning formation in Gaoyou Depression[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2015, 43(1): 133−139. -





 下载:
下载: