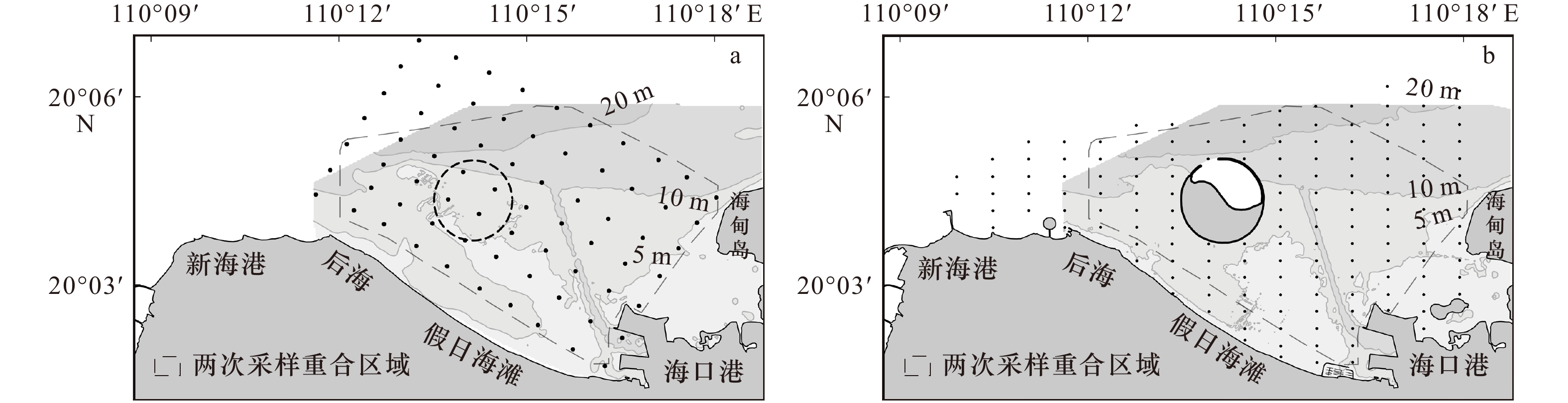
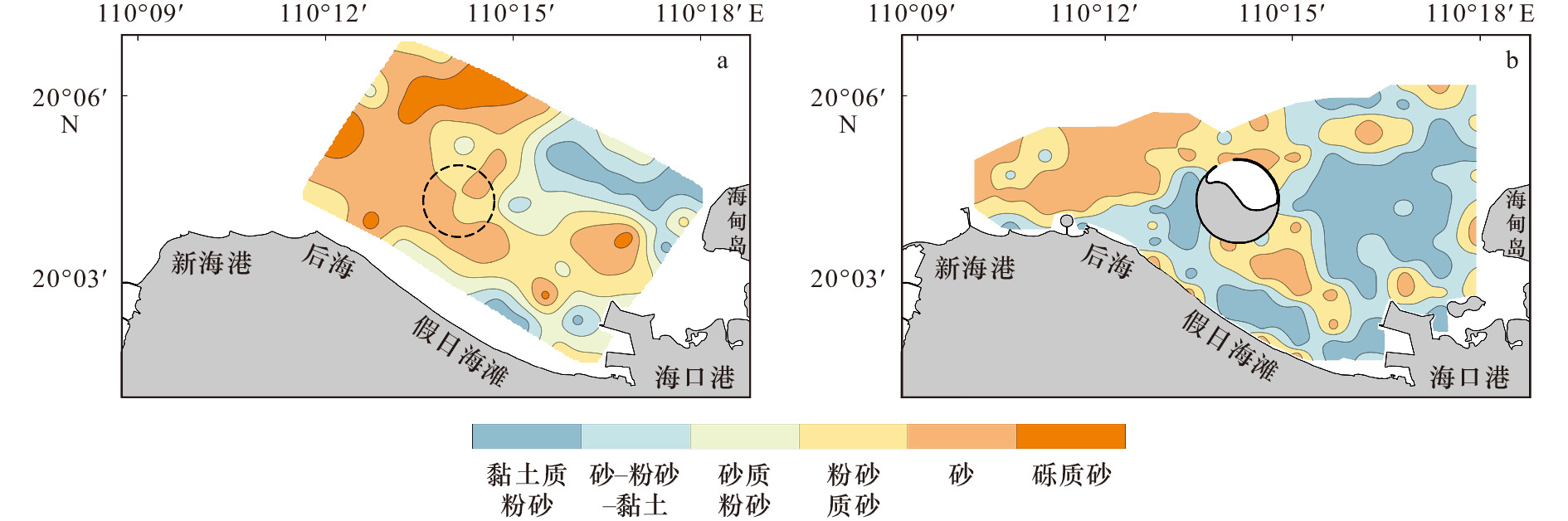
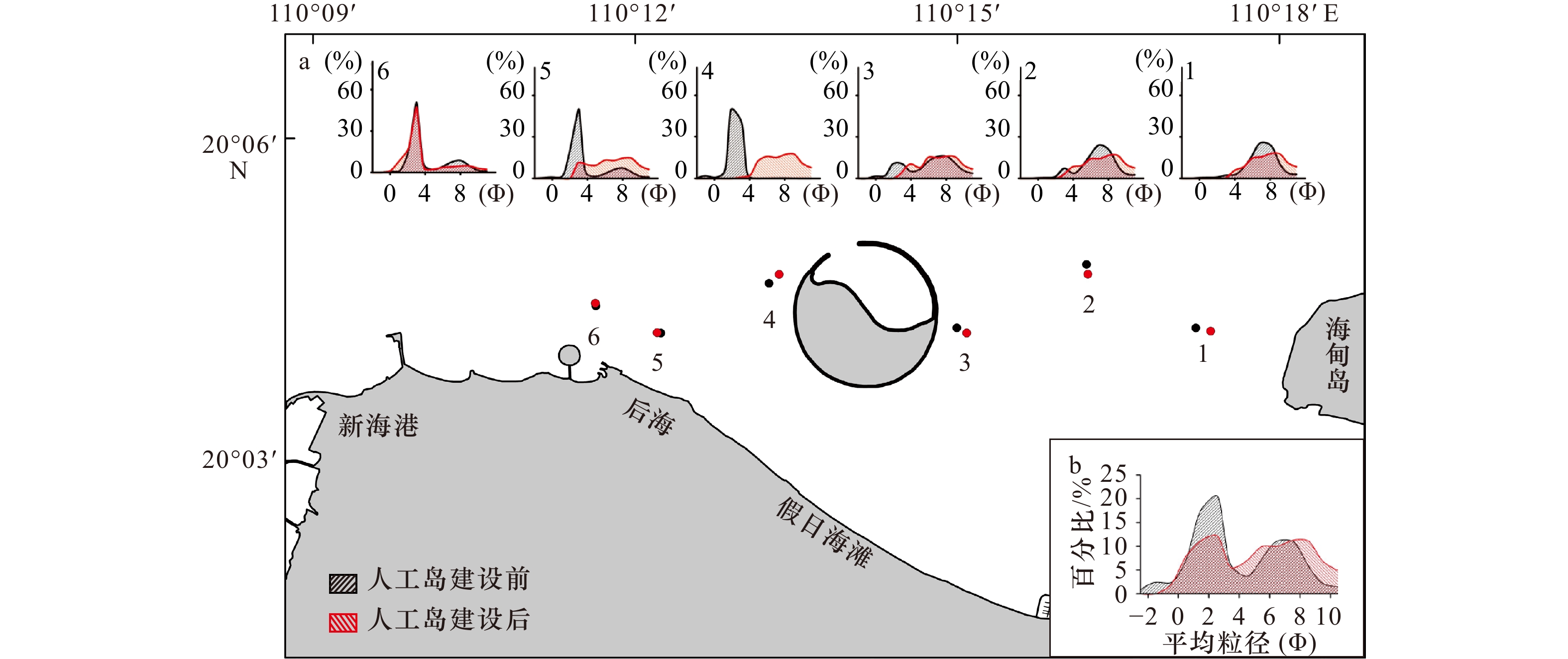
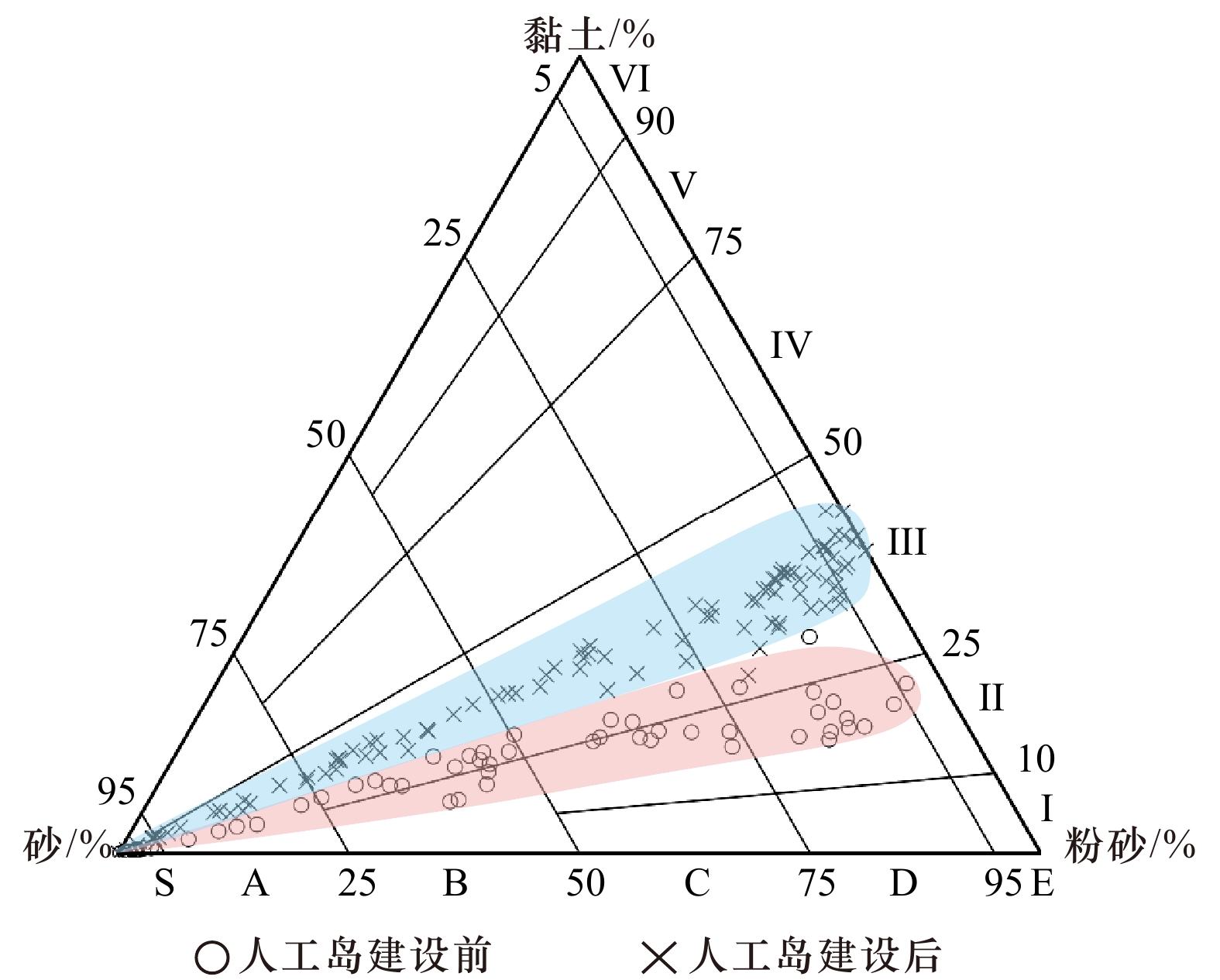
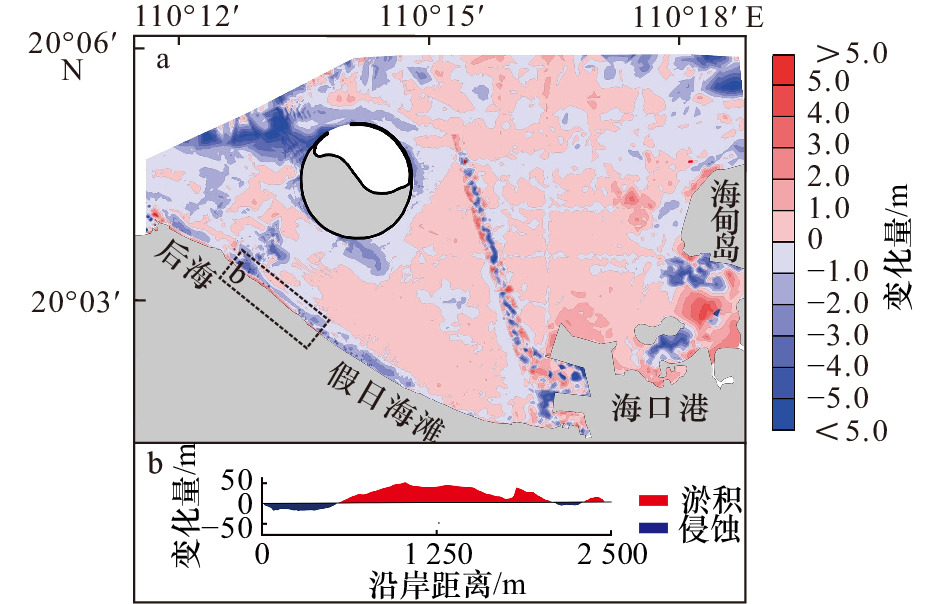
| [1] |
许世远, 王军, 石纯, 等. 沿海城市自然灾害风险研究[J]. 地理学报, 2006, 61(2): 127−138. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.02.002Xu Shiyuan, Wang Jun, Shi Chun, et al. Research of the natural disaster risk on coastal cities[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2006, 61(2): 127−138. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.02.002
|
| [2] |
陈程浩, 吕意华, 李伟巍, 等. 三亚红塘湾珊瑚礁生态状况研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(4): 138−146.Chen Chenghao, Lü Yihua, Li Weiwei, et al. A study on the ecological status of coral reef in Hongtang Bay, Sanya[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(4): 138−146.
|
| [3] |
宋南奇, 黄杰, 李滨勇, 等. 人工岛机场填海工程对生态环境影响的综合评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(8): 3703−3712. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.052Song Nanqi, Huang Jie, Li Binyong, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the impact of artificial island airport reclamation construction on marine eco-environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(8): 3703−3712. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.052
|
| [4] |
张晗. 人工岛建设对海洋生态环境的影响分析——以白沙湾为例[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2015.Zhang Han. Artificial islands impacts on the marine ecological environment analysis—in Baishawan as an example[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2015.
|
| [5] |
赵桂侠, 张晨, 张赫, 等. 人工岛布置方式对周围海域水动力及水交换影响研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2017, 36(2): 18−28. doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20170203Zhao Guixia, Zhang Chen, Zhang He, et al. Effect of artificial island layout on hydrodynamics and water exchange in the coastal waters[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2017, 36(2): 18−28. doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20170203
|
| [6] |
赵永印, 康苏海, 李旺生. 南海明珠二期建设对海口港3万吨级航道影响研究[J]. 水道港口, 2013, 34(4): 311−316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2013.04.006Zhao Yongyin, Kang Suhai, Li Wangsheng. Research on effect of Nanhaimingzhu artificial island on channel of Haikou Harbor[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2013, 34(4): 311−316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2013.04.006
|
| [7] |
张云飞. 海南人工岛对近岸环境影响遥感监测分析[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2019.Zhang Yunfei. Remote sensing monitoring and analysis of the impact of Hainan artificial island on nearshore environment[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2019.
|
| [8] |
陈可锋, 陆培东, 王艳红, 等. 江苏如东人工岛建设对周边水动力及泥沙冲淤的影响[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2008(1): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2008.01.003Chen Kefeng, Lu Peidong, Wang Yanhong, et al. Influence of construction of artificial island in Rudong, Jiangsu, upon hydrodynamics, erosion and siltation in surrounding water areas[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2008(1): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2008.01.003
|
| [9] |
许婷, 刘国亭, 温春鹏. 波流共同作用下大型离岸人工岛群工程海床冲淤预测[J]. 海岸工程, 2015, 34(4): 11−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2015.04.002Xu Ting, Liu Guoting, Wen Chunpeng. Prediction of seabed scouring and silting around large offshore artificial islands under wave-tide co-action[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2015, 34(4): 11−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2015.04.002
|
| [10] |
季荣耀, 徐群, 莫思平, 等. 港珠澳大桥人工岛对水沙动力环境的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(6): 829−836.Ji Rongyao, Xu Qun, Mo Siping, et al. Effects on the hydrodynamics and sediment environment by artificial islands of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(6): 829−836.
|
| [11] |
李汉英, 张红玉, 王霞, 等. 海洋工程对砂质海岸演变的影响——以海南万宁日月湾人工岛为例[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(4): 575−581. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190414Li Hanying, Zhang Hongyu, Wang Xia, et al. Influence on the sandy coast evolution of the ocean engineering—A case study of artificial Riyue island, Wanning city, Hainan Island[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(4): 575−581. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190414
|
| [12] |
石萍, 曹玲珑, 莫文渊, 等. 人工岛建设对海口湾西海岸岸滩稳定性影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(5): 57−63. doi: 10.11978/2014124Shi Ping, Cao Linglong, Mo Wenyuan, et al. Influence of man-made island construction on the stability of the beach in the west coast of Haikou Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(5): 57−63. doi: 10.11978/2014124
|
| [13] |
张丽, 乾东岳. 人工岛建设对铺前湾岸线的影响研究[J]. 中国水运, 2017, 17(1): 234−237.Zhang Li, Qian Dongyue. Influence of construction of artificial island on the shoreline of Puqian Bay[J]. China Water Transport, 2017, 17(1): 234−237.
|
| [14] |
任鹏, 孙志高, 王传远, 等. 人工岛建设对龙口湾表层沉积物粒度及黏土矿物组成特征的影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(4): 578−587. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014Ren Peng, Sun Zhigao, Wang Chuanyuan, et al. Impacts of construction of artificial islands on the flow-sediment regulation scheme on grain and clay compositions in the Longkou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2016, 34(4): 578−587. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014
|
| [15] |
王文介, 欧兴进. 南渡江河口的动力特征与地形发育[J]. 热带海洋, 1986, 5(4): 80−88.Wang Wenjie, Ou Xingjin. The dynamics and topographic development of the Nandujiang Estuary[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1986, 5(4): 80−88.
|
| [16] |
吴创收, 杨世伦, 罗向欣, 等. 近四十年南渡江水下三角洲的冲淤变化及其主控原因[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2011, 29(3): 339−345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.03.010Wu Chuangshou, Yang Shilun, Luo Xiangxin, et al. Erosion and accretion of the Nandu River underwater delta during 1963−2003[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2011, 29(3): 339−345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.03.010
|
| [17] |
Poppe L J, Eliason A H, Hastings M E. A Visual Basic program to classify sediments based on gravel-sand-silt-clay ratios[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2003, 29(6): 805−809.
|
| [18] |
Udden J A. Mechanical composition of clastic sediments[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1914, 25(1): 655−744. doi: 10.1130/GSAB-25-655
|
| [19] |
Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River Bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1957, 27: 3−26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
|
| [20] |
Flemming B W. A revised textural classification of gravel-free muddy sediments on the basis of ternary diagrams[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(10/11): 1125−1137.
|
| [21] |
Saccà C, Saccà D, Nucera P, et al. Composition and geochemistry of clay sediments offshore the northeastern Sicilian Coast (Southeastern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 92(4): 564−572. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.02.012
|
| [22] |
任韧希子, 陈沈良. 黄河三角洲的沉积动力分区[J]. 上海国土资源, 2012, 33(2): 62−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.02.016Ren Renxizi, Chen Shenliang. Sediment dynamics in the littoral zone of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Shanghai Land & Resource, 2012, 33(2): 62−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.02.016
|
| [23] |
唐诚, 赵艳, 张华, 等. 珠江口近30年海底表层沉积物粒度分布及其环境变化[J]. 海洋科学, 2013, 37(5): 61−70.Tang Cheng, Zhao Yan, Zhang Hua, et al. The changes of sea surface grain size distribution and its sedimentary environment during the last 30 years in the Zhujiang River Estuary[J]. Marine Sciences, 2013, 37(5): 61−70.
|
| [24] |
Gao Shu. A fortran program for grain-size trend analysis to define net sediment transport pathways[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 1996, 22(4): 449−452.
|
| [25] |
Gao Shu, Collins M. A critique of the ‘‘McLaren method’’ for defining sediment transport paths: Discussion[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1991, 61(1): 143−146. doi: 10.1306/D42676A9-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
|
| [26] |
Gao Shu, Collins M. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends, based upon definition of ‘‘transport vectors’’[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1992, 81(1/2): 47−60.
|
| [27] |
Pedreros R, Howa H L, Michel D. Application of grain size trend analysis for the determination of sediment transport pathways in intertidal areas[J]. Marine Geology, 1996, 135(1/4): 35−49.
|
| [28] |
陈斌, 印萍, 徐刚, 等. 浙江内陆架表层沉积物粒度分布特征及运移趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(6): 95−100.Chen Bin, Yin Ping, Xu Gang, et al. Suspended sediment transport patterns in the Zhejiang inner continental shelf in summer[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(6): 95−100.
|
| [29] |
陈宜展, 曹永港, 肖志建, 等. 海口湾海域潮流季节性特征分析[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 58(5): 73−79.Chen Yizhan, Cao Yonggang, Xiao Zhijian, et al. The seasonal variation of tidal currents in the Haikou Bay[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2019, 58(5): 73−79.
|
| [30] |
龚文平, 王宝灿. 海口湾港口建设的泥沙洄淤初步研究[J]. 海洋通报, 1996, 15(5): 61−67.Gong Wenping, Wang Baocan. Preliminary study of the siltation of harbors in Haikou Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1996, 15(5): 61−67.
|
| [31] |
陈沈良, 龚文平, 王宝灿. 南渡江三角洲海岸泥沙纵向运移与岸滩演变的响应[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1998(1): 23−32.Chen Shenliang, Gong Wenping, Wang Baocan. Longshore sediment transport and nearshore evolution response for the Nandujiang Delta, Hainan lsland[J]. Transaction of Oceanology and Limnology, 1998(1): 23−32.
|
| [32] |
阿卜杜合力力·海比尔. 基于河流生态健康的南渡江下游采砂研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2012.Abuduhelili·Haibier. Sand mining research of the Nandu River downstream based on the ecological health of the basin[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2012.
|
| [33] |
高抒. 沉积物粒径趋势分析: 原理与应用条件[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 826−836.Gao Shu. Grain size trend analysis: Principle and applicability[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 826−836.
|
| [34] |
贾建军, 程鹏, 高抒. 利用插值试验分析采样网格对粒度趋势分析的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(3): 135−141.Jia Jianjun, Cheng Peng, Gao Shu. Comparison between grain size trends derived from irregular and regular sampling grids with the help of gis interpolation tools[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(3): 135−141.
|
| [35] |
李占海, 柯贤坤, 王倩, 等. 琼州海峡水沙输运特征研究[J]. 地理研究, 2003, 22(2): 151−159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.02.003Li Zhanhai, Ke Xiankun, Wang Qian, et al. Characteristics of water and sediment transport in the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Geographical Research, 2003, 22(2): 151−159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.02.003
|
| [36] |
李占海, 柯贤坤. 琼州海峡潮流沉积物通量初步研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2000, 19(6): 42−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2000.06.007Li Zhanhai, Ke Xiankun. Prelimary study on tidally-induced sediment fluxes of the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2000, 19(6): 42−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2000.06.007
|
| [37] |
自然资源部第三海洋研究所. 海口市沙滩补砂可行性技术论证——西海岸水动力数学模型专题研究报告[R]. 厦门: 自然资源部第三海洋研究所, 2019.Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resource. Feasibility study on Beach sand replenishment technology of Haikou city—research report on hydrodynamic numerical model of western coast in Haikou City[R]. Xiamen: Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resource, 2019.
|
| [38] |
海南省海洋开发规划设计研究院. 海口湾南海明珠人工岛用海风险专题研究[R]. 海口: 海南省海洋开发规划设计研究院, 2012.Hainan Institute of Marine Development Planning and Design. A special study on the risk of sea using on Nanhaimingzhu artificial island, Haikou Bay[R]. Haikou: Hainan Institute of Marine Development Planning and Design, 2012.
|
| [39] |
自然资源部第三海洋研究所. 海口市沙滩补砂可行性技术论证——西海岸波浪数学模型专题研究报告[R]. 厦门: 自然资源部第三海洋研究所, 2019.Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resource. Feasibility study on beach sand replenishment technology of Haikou City—research report on numerical wave model of western coast in Haikou City[R]. Xiamen: Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resource, 2019.
|
| [40] |
刘晓强, 杨燕华. 海口港秀英港区航道泥沙淤积特征研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2018, 37(8): 64−74. doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20180807Liu Xiaoqiang, Yang Yanhua. Characteristics of sediment accumulation in the waterway of Xiuying Harbor District, Haikou Port[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2018, 37(8): 64−74. doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20180807
|




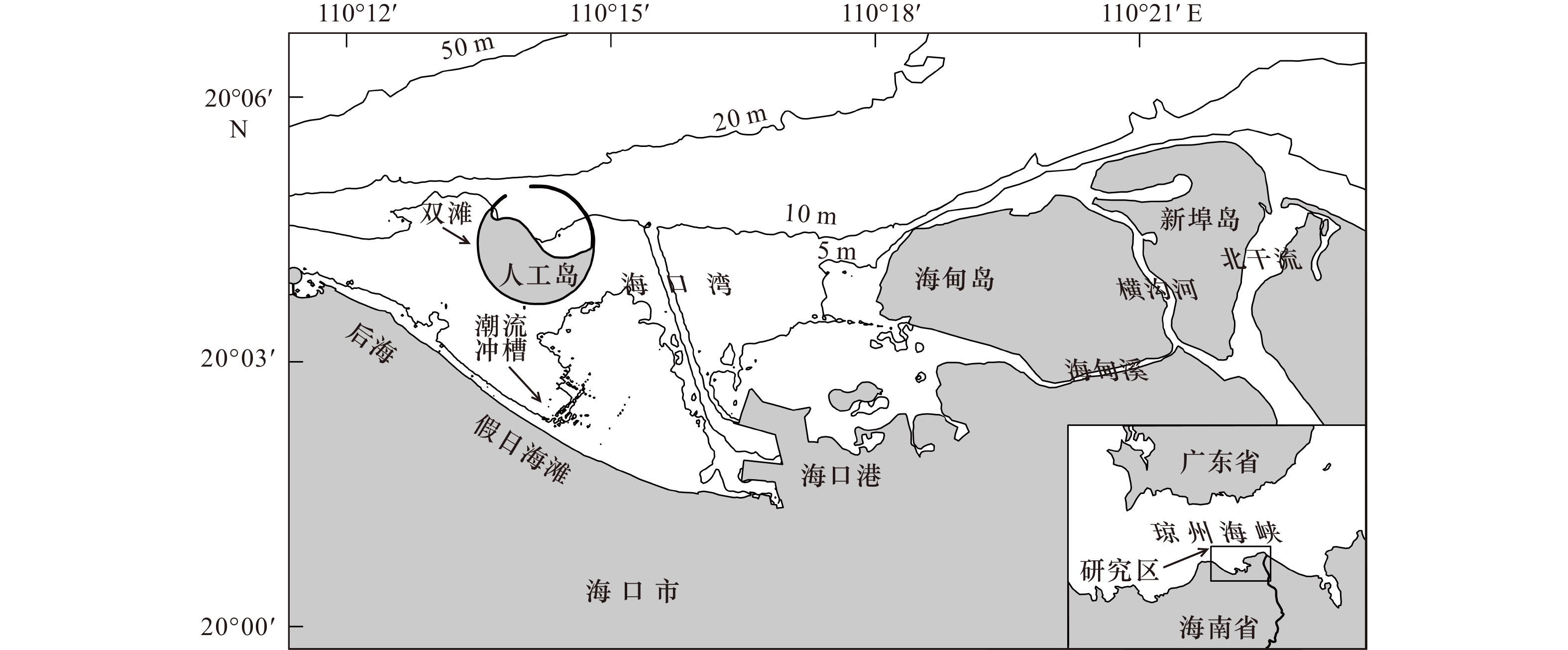
 下载:
下载: