Observational analysis on 3D distribution and seasonal variation of thermohaline characteristics in the Zhanjiang Bay
-
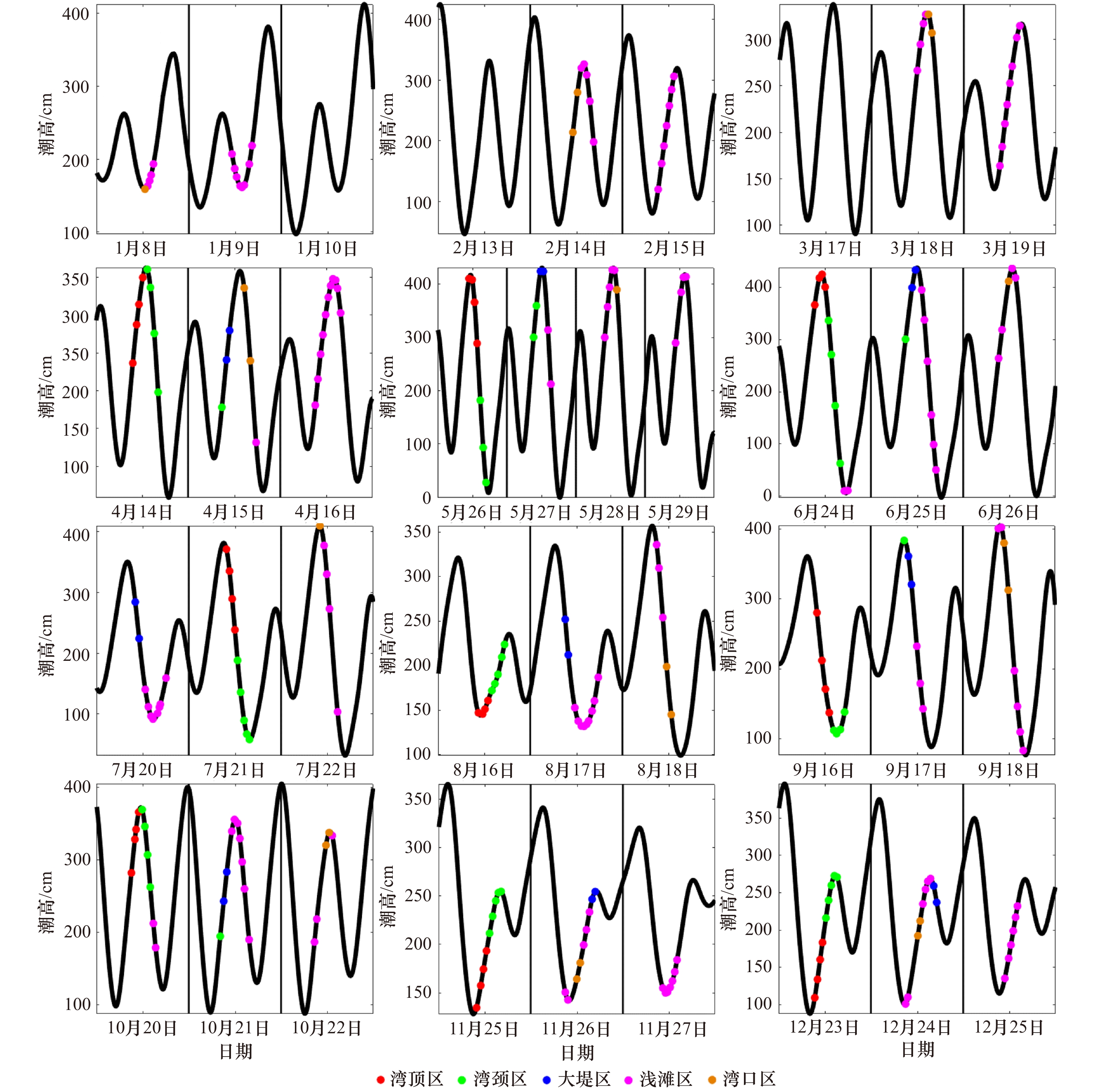
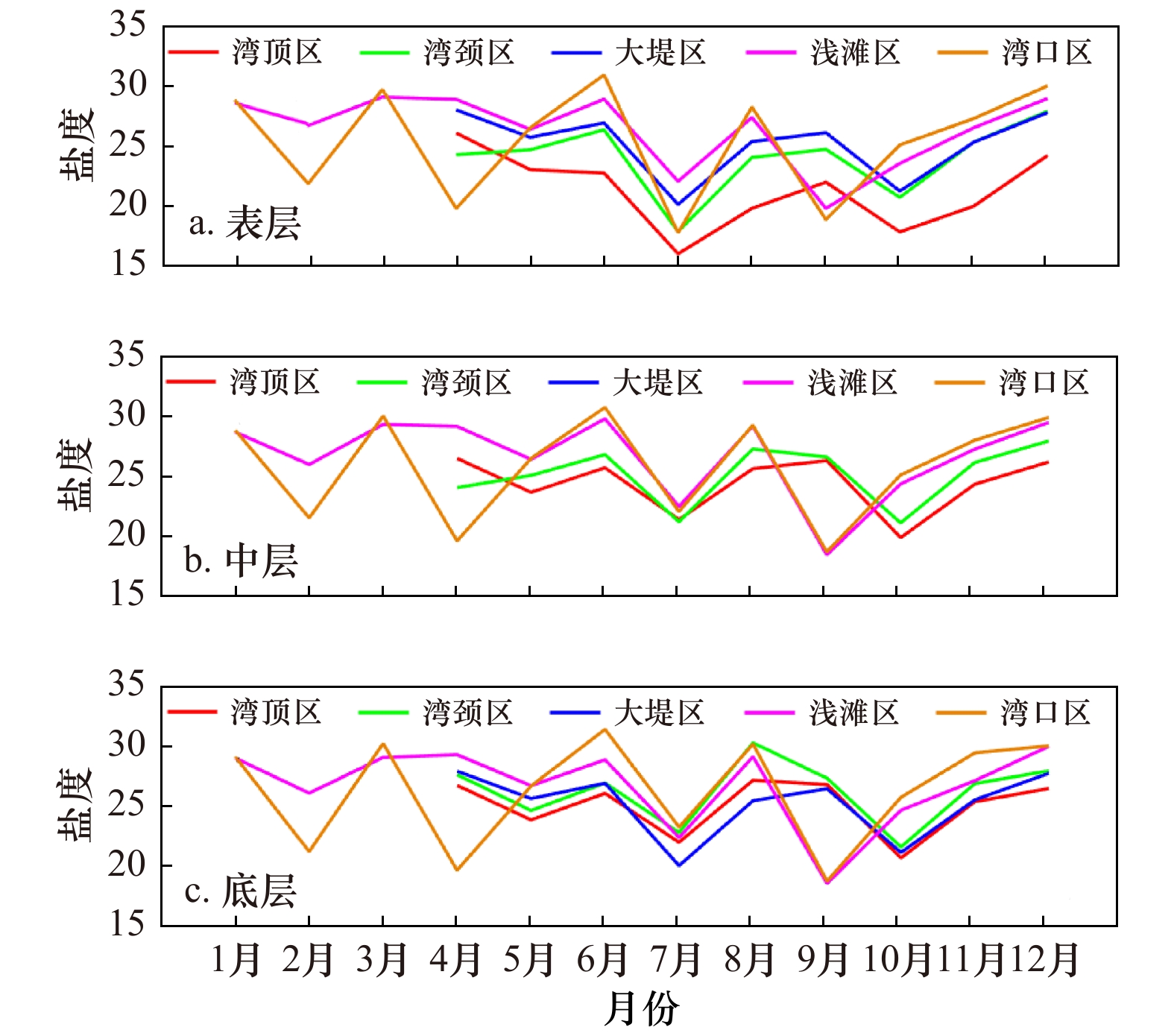
摘要: 利用2017年1−12月的现场观测数据,分析了湛江湾温盐的三维空间结构及季节变化特征。结果表明:(1) 2017年湛江湾各站位年平均温度为23~27℃、盐度为19~27、位势密度为11~17 kg/m3、浮性频率(N2)为7×10−5~5×10−3 s−2。浮性频率的垂向结构及水平分布与温度分布类似,而位势密度则与盐度的变化趋势几乎一致;(2)温度季节变化明显,夏季最高,秋季次之,冬季最低,冬夏温差最大达15℃,而盐度季节变化则不大。相较于季节引起的变化,涨落潮对温度以及盐度影响较小。温度跃层夏季最强,10 m处温度最大梯度可达到0.7℃/m,春秋季温跃层抬升至5 m附近,冬季水体上下混合均匀。夏季和秋季存在明显的盐跃层,盐度梯度最大可达到1.1 m−1。跃层上下温盐的季节变化规律一致;(3)水平分布上,从湾顶区、湾颈区、大堤区、浅滩区到湾口区,温度递减,盐度递增,湾顶区和湾口区平均温度差为2.3℃,盐度差为2.7。温盐图分析显示,不同季节水体呈现为不同的温盐条带,湾口区基本为低温、高盐水体,而湾顶区基本为高温、低盐水体,其他区域水体介于上述两者之间。Abstract: Using in-situ hydrographic observations from January to December 2017, 3D thermohaline structure and seasonal variation in the Zhanjiang Bay is investigated in this study. The results show that: (1) In 2017, the annual mean temperature is 23−27℃, the mean salinity is 19−27, the mean potential density is between 11−17 kg/m3, and the mean buoyancy frequency (N2) is about 7×10−5−5×10−3 s−2 in the Zhanjiang Bay. The vertical structure and horizontal distribution of N2 are similar to that of the temperature, while the distributions of potential density and salinity are similar. (2) The temperature has significant seasonality with the highest value in summer, followed by autumn, and the lowest in winter. The maximum temperature difference between winter and summer reaches 15℃, while the seasonal mean of the salinity varies slightly. The ebb and flood have less influence on temperature and salinity, comparing with their seasonal variations. The thermocline is the strongest in summer with the maximum gradient reaches 0.7℃/m at 10 m, whereas it shallows to 5 m in spring and fall, and the water well mixed in winter. The halocline is prominent in summer and fall, with the maximum gradient 1.1 m−1. The seasonal variation of the thermohaline in the upper layer and lower layer are consistent. (3) For the horizontal distribution, the temperature decreases and the salinity increases from the bay head, the mid bay, the bank region, the shoal region to the bay mouth. The average temperature difference between the bay head and the bay mouth is 2.3℃, and the salinity difference is 2.7. The temperature-salinity (θ-S) diagram shows banding distributions with one end as the low-temperature and high-salinity water in the bay mouth, one end as the high-temperature and low-salinity water in the bay head, and the other water masses are between them. Different bands are shown in different seasons.
-
Key words:
- Zhanjiang Bay /
- thermohaline characteristics /
- 3D structure /
- seasonal variation
-
图 10 各区域四季温盐图
灰色实线为等位势密度线;不同颜色的点分别代表各区域的站位;灰点为4个季节所有的观测值
Fig. 10 Seasonal temperature-salinity diagram in each region
The gray lines denote the potential density contours; the dots with different colors denote the observations in different regions; the gray dots denote all the observations in four seasons
-
[1] 冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999.Feng Shizuo, Li Fengqi, Li Shaojing. An Introduction to Marine Science[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1999. [2] 杨杰青, 史赟荣, 全为民, 等. 基于RDA与GAMs模型的东海近岸海域浮游动物与温盐关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8): 72−84.Yang Jieqing, Shi Yunrong, Quan Weimin, et al. Analysis of the relationships between zooplankton and temperature-salinity based on RDA and GAMs model in coastal East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(8): 72−84. [3] 李树华. 钦州湾的流况及其水文特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1988, 1988(3): 15−20.Li Shuhua. Flow condition and hydrologic character in the Qinzhou Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1988, 1988(3): 15−20. [4] 林宏阳, 安佰超, 陈照章, 等. 三沙湾夏、冬季节温、盐分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 厦门大学学报 (自然科学版), 2016, 55(3): 349−356.Lin Hongyang, An Baichao, Chen Zhaozhang, et al. Distribution of summertime and wintertime temperature and salinity in Sansha Bay[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2016, 55(3): 349−356. [5] 傅子琅, 胡建宇. 罗源湾的潮流和余流及水温的分布特征[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 1989, 28(1): 28−33.Fu Zilang, Hu Jianyu. Distribution features of tidal current residual current and temperature in Luoyuan Bay[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 1989, 28(1): 28−33. [6] 张远辉, 王伟强, 黄自强. 九龙江口盐度锋面及其营养盐的化学行为[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1999, 18(4): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.1999.04.001Zhang Yuanhui, Wang Weiqiang, Huang Ziqiang. Salinity fronts and chemical behaviour of nutrient in Jiulongjiang Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1999, 18(4): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.1999.04.001 [7] 刘广平, 胡建宇, 陈照章, 等. 九龙江口−厦门湾表层盐度分布特征及其与潮汐的关系[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 47(5): 710−713.Liu Guangping, Hu Jianyu, Chen Zhaozhang, et al. Distribution characteristics of sea surface salinity and its relations to tide in Jiulongjiang Estuary-Xiamen Bay[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2008, 47(5): 710−713. [8] 王晋沅, 江毓武. 九龙江河口盐度分布及其通量的动力过程分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 52(6): 835−841.Wang Jinyuan, Jiang Yuwu. The distribution of salinity and the dynamic process of salt flux in Jiulong River Estuary[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2013, 52(6): 835−841. [9] Pritchard D W. Salinity distribution and circulation in the Chesapeake Bay estuarine system[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1952, 11: 106−123. [10] Najarian T O, Harleman D R F, Thatcher M L. C & D Canal effect on salinity of Delaware estuary[J]. Journal of the Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Division, 1980, 106(1): 1−17. doi: 10.1061/JWPCDX.0000179 [11] Cohen B, McCarthy L T. Salinity of the Delaware Estuary[R]. Newark DE Delaware Geological Survey University of Delaware, 1962. [12] Posmentier E S, Racklin J W. Distribution of salinity and temperature in the Hudson Estuary[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1976, 6(5): 775−777. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1976)006<0775:DOSATI>2.0.CO;2 [13] Uncles R J, Bloomer N J, Frickers P E, et al. Seasonal variability of salinity, temperature, turbidity and suspended chlorophyll in the Tweed Estuary[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2000, 251−252: 115−124. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00405-8 [14] 应秩甫, 王鸿寿. 湛江湾的围海造地与潮汐通道系统[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1996, 35(6): 101−105.Ying Zhifu, Wang Hongshou. The relationship between fill-block engineering and tidal inlet system response in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1996, 35(6): 101−105. [15] 陈则实. 中国海湾志(第十分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1999.Chen Zeshi. Ocean bays of China (Volume Ten)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1999. [16] 张乔民, 宋朝景, 赵焕庭. 湛江湾溺谷型潮汐水道的发育[J]. 热带海洋, 1985, 4(1): 48−57.Zhang Qiaomin, Song Chaojing, Zhao Huanting. Development of the tidal channel of drowned valley type in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1985, 4(1): 48−57. [17] 林微, 张乔民, 赵焕庭. 湛江港潮汐汊道落潮三角洲动力场模拟和沉积动态分析[J]. 热带海洋, 1995, 14(1): 54−61.Lin Wei, Zhang Qiaomin, Zhao Huanting. A simulation of the hydrodynamic fields and analysis of sediment dynamics in Zhanjiang Ebb-Tidal delta[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1995, 14(1): 54−61. [18] 贺松林, 丁平兴, 孔亚珍, 等. 湛江湾沿岸工程冲淤影响的预测分析Ⅰ.动力地貌分析[J]. 海洋学报, 1997, 19(1): 55−63.He Songlin, Ding Pingxing, Kong Yazhen, et al. Predictive analysis of the impact of erosion and deposition of Zhanjiang Bay coastal engineering Ⅰ. dynamic geomorphological analysis[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1997, 19(1): 55−63. [19] 夏华永, 林迪洋, 钮智旺. 湛江湾填海工程对水动力条件的影响预测[J]. 海洋通报, 2006, 25(6): 47−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2006.06.007Xia Huayong, Lin Diyang, Niu Zhiwang. Prediction of effects of reclamation engineering on hydrodynamic conditions in the Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2006, 25(6): 47−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2006.06.007 [20] 张志飞, 诸裕良, 何杰. 多年围填海工程对湛江湾水动力环境的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2016(3): 96−104.Zhang Zhifei, Zhu Yuliang, He Jie. Influences of long term reclamation works on hydrodynamic environment in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2016(3): 96−104. [21] 陈达森, 严金辉. 湛江湾海区流场特征及其对水环境的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2006, 6(14): 2100−2103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2006.14.027Chen Dasen, Yan Jinhui. A characteristic and impact on water environment current in the gulf sea area of Zhanjiang[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2006, 6(14): 2100−2103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2006.14.027 [22] 李希彬, 孙晓燕, 宋军, 等. 湛江湾三维潮汐潮流数值模拟[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(5): 509−517. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.05.006Li Xibin, Sun Xiaoyan, Song Jun, et al. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of tidal current in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(5): 509−517. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.05.006 [23] 赵冲久. 湛江湾水文泥沙特性分析[J]. 水道港口, 1999(4): 16−21.Zhao Chongjiu. Hydrographic and sediment analysis of Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 1999(4): 16−21. [24] 赵婉璐, 郝瑞霞. 基于ECOMSED模型的湛江湾水道三维潮流数值模拟[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(4): 83−86.Zhao Wanlu, Hao Ruixia. Three dimensional numerical imitation of tidal current in the Zhanjiang Bay channel based on ECOMSED model[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(4): 83−86. [25] Lu Xuan, Zhou Fengxia, Chen Fajin, et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of sedimentary organic matter in a subtropical bay: implication for human interventions[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(4): 1362. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17041362 [26] 蒋城飞, 付东洋, 李强, 等. 秋季湛江港和入海口温盐结构及生态特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(11): 20−31.Jiang Chengfei, Fu Dongyang, Li Qiang, et al. Thermohaline structure and ecological characteristics of the Zhanjiang Bay and its estuary in autumn[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(11): 20−31. [27] 陈春亮, 梁春林, 卢仕严, 等. 电厂温排水对湛江湾海水温升的数值模拟及生态影响评价[J]. 台湾海峡, 2012, 31(4): 530−539.Chen Chunliang, Liang Chunlin, Lu Shiyan, et al. Numerical simulation of seawater temperature rising and the ecological evaluation of the effect of thermal discharged from a power plant in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2012, 31(4): 530−539. [28] 汤德福, 吴群河, 刘广立, 等. 近岸海域水温垂向分层及同步监测浮标研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(2): 238−242.Tang Defu, Wu Qunhe, Liu Guangli, et al. Research of vertical stratification and synchronous monitoring buoy of nearshore water temperature[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(2): 238−242. [29] 刘泉兵. 湛江湾海洋腐蚀环境及其对管线钢腐蚀行为的影响[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2018.Liu Quanbing. The marine corrosive environment in Zhanjiang Bay and its influence on corrosion behavior of the pipeline steel[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2018. [30] Zhou Fengxia, Lu Xuan, Chen Fajin, et al. Spatial-monthly variations and influencing factors of dissolved oxygen in surface water of Zhanjiang Bay, China[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(6): 403. doi: 10.3390/jmse8060403 [31] 林建国, 周雅静, 陈军. SBE19 CTD资料处理技术[J]. 海洋技术, 2000, 19(3): 60−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2000.03.012Lin Jianguo, Zhou Yajing, Chen Jun. SBE19 CTD data processing technology[J]. Ocean Technology, 2000, 19(3): 60−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2000.03.012 [32] Van Haren H, Laan M. An in-situ experiment identifying flow effects on temperature measurements using a pumped CTD in weakly stratified waters[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 111: 11−15. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2016.02.006 [33] 吴巍, 方欣华, 吴德星. 关于跃层深度确定方法的探讨[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2001(2): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2001.02.001Wu Wei, Fang Xinhua, Wu Dexing. On the methods of determining the depths of thermocline, halocline and pycnocline[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2001(2): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2001.02.001 [34] 国家海洋信息中心. 潮汐表(第3册台湾海峡至北部湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2017.National Marine Data and Information Service. Tide Tables (Vol. 3 from the Taiwan Straits to the Beibu Gulf)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2017. [35] 陈则实, 王文海, 吴桑云. 中国海湾引论[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2007.Chen Zeshi, Wang Wenhai, Wu Sangyun. Introduction to the Ocean Bays of China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2007. -





 下载:
下载: