Community composition and distribution characteristics of the benthic macroinvertebrates in the inland rivers of Chongming Island
-
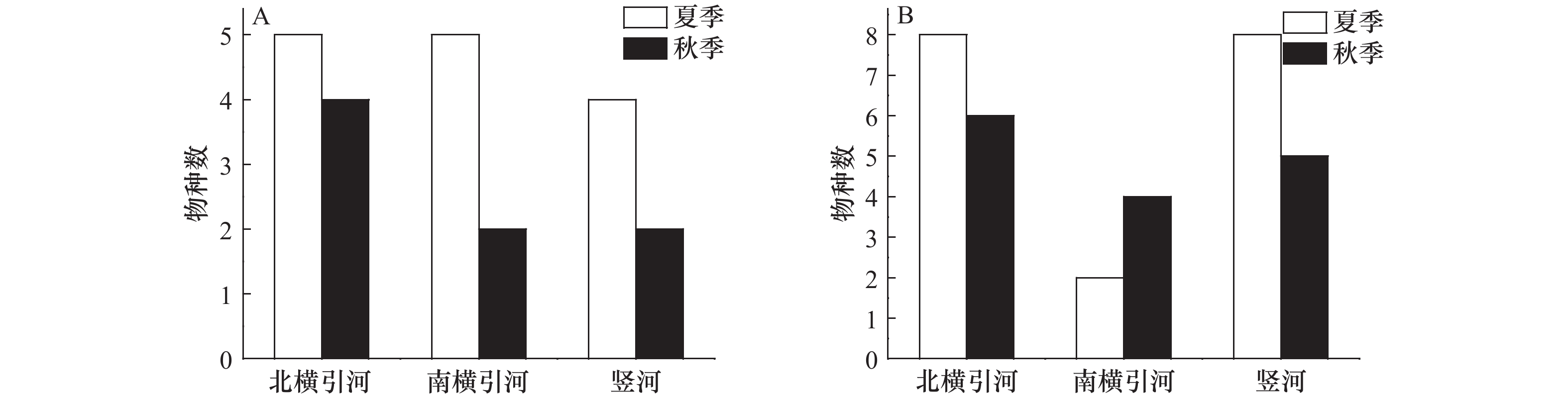
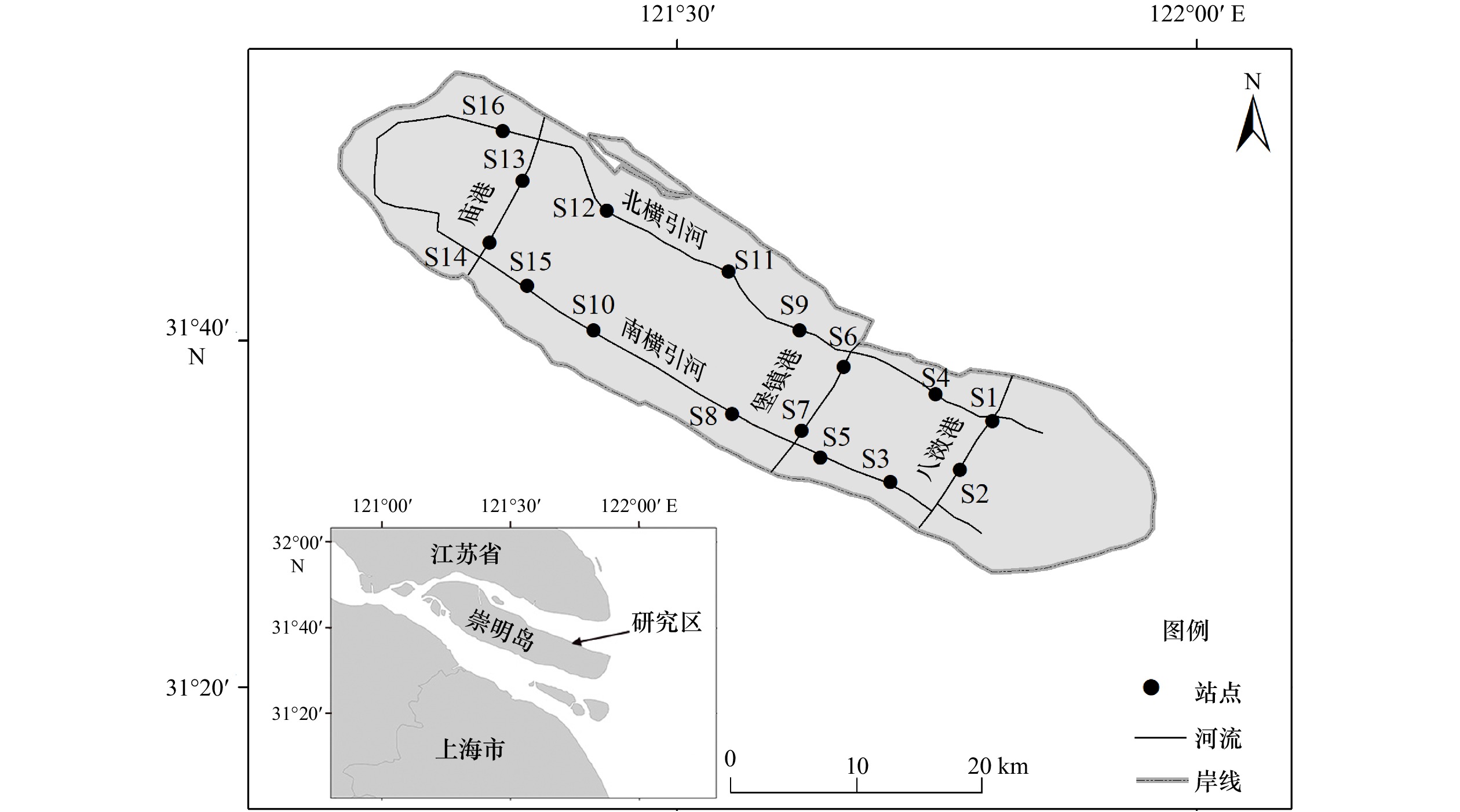
摘要: 大型底栖动物是河流生态系统中重要的生态类群,研究其群落组成及分布特征能为河流生态系统管理提供理论支撑。2018年6月(夏季)和11月(秋季),在崇明岛内河设置16个固定站点,开展了拖网和地笼相结合的大型底栖动物调查,分析研究了崇明岛内河大型底栖动物群落的组成与分布特征及影响因子。调查期间共采集到大型底栖动物14种,分属5目8科,主要为节肢动物。其中,淡水型10种,河口半咸水型3种,降海洄游型1种。从空间分布来看,北横引河记录12种,南横引河记录6种,竖河记录11种;不同河道大型底栖动物群落组成均以淡水型种类为主,主要优势物种为日本沼虾(Macrobrachium nipponense)和秀丽白虾(Exopalaemon modestus);北横引河大型底栖动物群落的物种数、多度及生物量均高于南横引河;而竖河介于两者之间。夏季大型底栖动物群落的物种数、多度和生物量均高于秋季,季节变化是崇明岛内河大型底栖动物群落组成变化的重要特征之一。综合来看,崇明岛内河大型底栖动物群落组成特征兼具内陆河流和河口区特点,它与崇明岛区位特征、河流水文及生境条件、水质特征及区域人类活动等多种因素有关。Abstract: The benthic macroinvertebrate is the important ecological group in river ecosystem. The study of the community composition and distribution characteristics on the benthic macroinvertebrate can provide theoretical support for river ecosystem management. In June (summer) and November (autumn) 2018, surveys on the benthic macroinvertebrate with trawl and ground cages were carried out in 16 fixed sampling sites in the inland rivers of Chongming Island. The community composition, distribution characteristics and corresponding influencing factors of the benthic macroinvertebrates were analyzed then. A total of 14 species belonging to 5 orders, 8 families of the benthic macroinvertebrates were collected in the surveys. Most of them were arthropods. Among them, 10 species were freshwater type, 3 species were estuarine brackish water type and 1 species was catadromous migration type. And 12, 6 and 11 benthic macroinvertebrate species were recorded in the Beiheng Canal, Nanheng Canal, and the vertical canals respectively. The dominants of the benthic macroinvertebrates were freshwater species, and the common species were Macrobrachium nipponense, and Exopalaemon modestus. The number of species, abundance and biomass of the benthic macroinvertebrates in the Beiheng Canal and the vertical canals were higher than those in the Nanheng Canal. The number of species, abundance and biomass of the benthic macroinvertebrates in the summer were higher than those in the autumn. Seasonal variations were one of the important features of the characteristics of the benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the inland rivers of Chongming Island. Add all these together, the inland rivers of Chongming Island had some characteristics of both estuaries and inland rivers, which were related to the geographical location, hydrological conditions, riverine habitats, water quality characteristics and regional human activities of the Chongming Island.
-
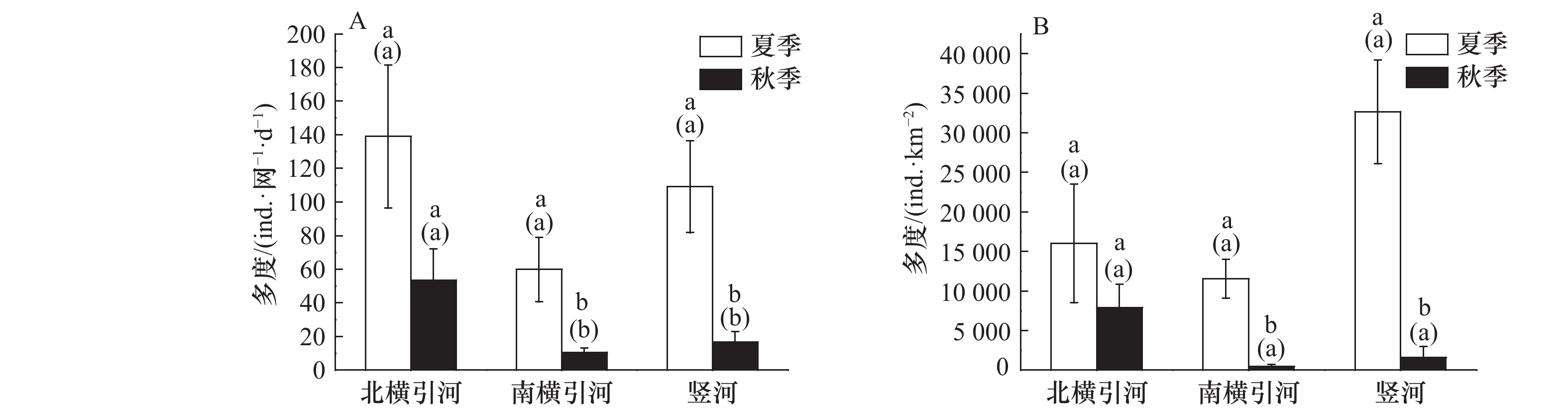
图 3 不同河段大型底栖动物多度
A. 地笼;B. 拖网;不同小写字母表示同一河段不同季节之间存在显著差异(p<0.05),括号中不同的小写字母表示同一季节不同河段之间存在显著差异(p<0.05)
Fig. 3 The abundance of the benthic macroinvertebrate in the different reaches
A. Ground cage; B. trawl; different lowercase letters indicate that there are significant differences between different seasons in the same river (p<0.05), and different lowercase letters in parentheses indicate that there are significant differences between different rivers in the same season (p<0.05)
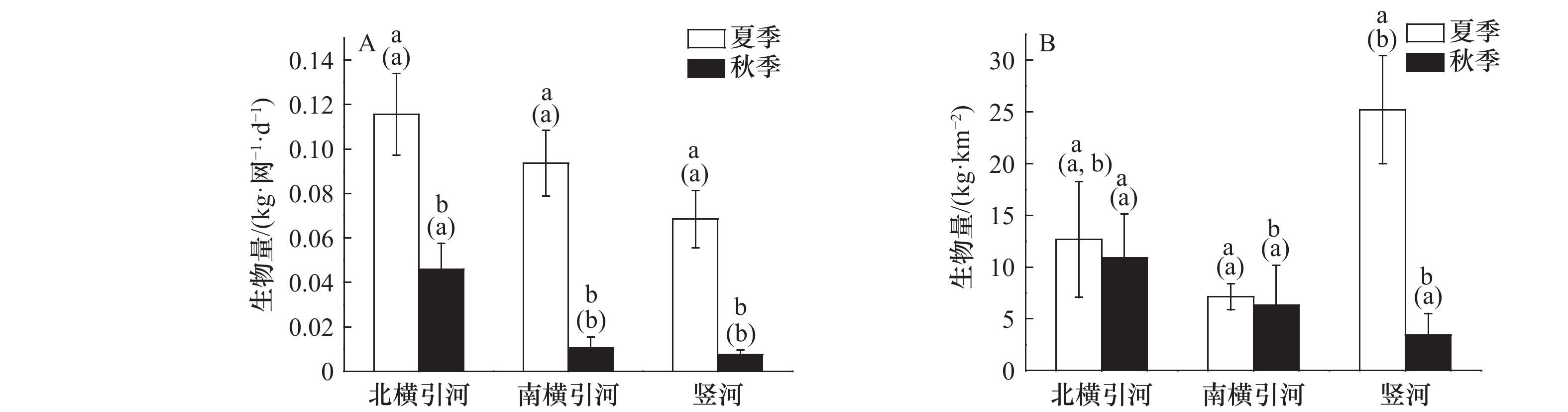
图 4 不同河段大型底栖动物生物量
A. 地笼;B. 拖网;不同小写字母表示同一河段不同季节之间存在显著差异(p<0.05),括号中不同的小写字母表示同一季节不同河段之间存在显著差异(p<0.05)
Fig. 4 The biomass of the benthic macroinvertebrate in the different reaches
A. Ground cage; B. trawl; different lowercase letters indicate that there are significant differences between different seasons in the same river section (p<0.05), and different lowercase letters in parentheses indicate that there are significant differences between different river sections in the same season (p<0.05)
表 1 崇明岛内河不同河段大型底栖动物群落组成特征
Tab. 1 Characteristics of the benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the different reaches of the inland rivers of Chongming Island
种类 北横引河 南横引河 竖河 %N %B IRI %N %B IRI %N %B IRI 十足目 Decapoda 日本沼虾Macrobrachium nipponense1, a, b 41.14 52.36 93.50 23.14 24.45 47.59 12.93 21.32 34.24 罗氏沼虾Macrobrachium rosenbergii1, b 0.12 0.55 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.63 0.11 秀丽白虾Exopalaemon modestus1, a, b 56.90 34.38 91.28 73.98 32.33 106.31 86.13 65.73 151.86 脊尾白虾Exopalaemon carinicauda2, b 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.25 0.05 安氏白虾Exopalaemon annandalei2, b 0.04 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 克氏原螯虾Procambarus clarkii1, a 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.19 1.36 0.31 0.00 0.00 0.00 中华绒螯蟹Eriocheir sinensis3, a, b 0.04 1.48 0.30 1.67 29.42 24.87 0.22 4.95 1.72 无齿螳臂相手蟹Chiromantes dehaani2, a 0.27 4.75 4.02 0.93 11.43 12.36 0.03 0.32 0.06 腹足目 Mesogastropoda 铜锈环棱螺Bellamya aeruginosa1, a, b 1.08 4.63 2.28 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.19 0.96 0.19 梨形环棱螺Bellamya purificata1, a, b 0.12 0.56 0.27 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.17 0.03 蚌目Unionoida 背角无齿蚌Anodonta woodiana1, b 0.12 0.33 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 1.23 0.22 三角帆蚌Hyriopsis cumingii1, b 0.04 0.13 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.32 0.06 帘蛤目Veneroida 河蚬Corbicula fluminea1, b 0.12 0.76 0.18 0.09 1.01 0.22 0.32 4.11 1.47 异柱目 Anisomyaria 湖沼股蛤 Limnoperna lacustris1, b 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 注:1. 淡水型;2. 河口半咸水型;3. 降海洄游型;a. 地笼;b. 拖网。 -
[1] Jiang Xiaoming, Xiong Jing, Xie Zhicai. Longitudinal and seasonal patterns of macroinvertebrate communities in a large undammed river system in Southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 440: 1−12. [2] 沈国英, 施并章. 海洋生态学[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.Shen Guoying, Shi Bingzhang. Marine Ecology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2002. [3] Chi Shiyun, Gong Yutian, Wang Hongjun, et al. A pilot macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index (MMI-CS) for assessing the ecological status of the Chishui River Basin, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 83: 84−95. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.07.045 [4] 邢圆, 吴小平, 欧阳珊, 等. 赣江水系大型底栖动物多样性与受胁因子初探[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 648−657. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018296Xing Yuan, Wu Xiaoping, Ouyang Shan, et al. Assessment of macrobenthos biodiversity and potential human-induced stressors in the Ganjiang River system[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2019, 27(6): 648−657. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018296 [5] 闫云君, 李晓宇. 汉江流域上游支流大型底栖动物群落结构特征与生物多样性[J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(5): 585−591. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.014Yan Yunjun, Li Xiaoyu. Community structure and biodiversity of macrozoobentos in a tributary of upper reaches of Hanjiang River[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2007, 19(5): 585−591. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.014 [6] 张宇航, 彭文启, 刘培斌, 等. 永定河流域春季大型底栖动物群落结构和空间格局[J]. 中国环境监测, 2019, 35(4): 31−39.Zhang Yuhang, Peng Wenqi, Liu Peibin, et al. Study on the community structure and spatial pattern of macroinvertebrate in the Yongding River Basin in spring[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2019, 35(4): 31−39. [7] 刘祥, 陈凯, 陈求稳, 等. 淮河流域典型河流夏秋季底栖动物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(6): 1928−1938.Liu Xiang, Chen Kai, Chen Qiuwen, et al. The community structure of macroinvertebrate and its relationship to the environmental factors in summer and autumn within typical reaches of Huai River Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(6): 1928−1938. [8] 江晶, 温芳妮, 顾鹏, 等. 湖北清江流域胡家溪大型底栖动物群落结构及水质评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(4): 547−555. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.04.014Jiang Jing, Wen Fangni, Gu Peng, et al. Community structure of macrozoobentos and bioassessment of water quality in Hujiaxi Stream of Qingjiang River Basin, Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2009, 21(4): 547−555. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.04.014 [9] 应荣弟, 徐华, 王振锋. 浅谈咸潮入侵对崇明水资源的影响及对策[J]. 上海水务, 2002(3): 37−41.Ying Rongdi, Xu Hua, Wang Zhenfeng. Talking on the influence of saltwater intrusion on water resources in Chongming and the corresponding countermeasures[J]. Shanghai Water, 2002(3): 37−41. [10] 张颖纯, 姜德刚, 李建华. 崇明岛“闸控型”河网水体富营养化特征及其影响因素[J]. 湖泊科学, 2013, 25(3): 366−372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2013.03.009Zhang Yingchun, Jiang Degang, Li Jianhua. Characteristics of eutrophication and its affecting factors in gate-controlled river network system of Chongming Island[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2013, 25(3): 366−372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2013.03.009 [11] 乐观. 崇明岛河道水质理化指标及其与三种主要浮游动物分布的相关性研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2008.Le Guan. Studies on physico-chemical parameter and its correlation with distribution of three main zooplanktons collected from rivers in Chongming Island[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2008. [12] 袁兴中, 陆健健, 刘红. 长江口新生沙洲底栖动物群落组成及多样性特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(2): 133−139.Yuan Xingzhong, Lu Jianjian, Liu Hong. Community structure and biodiversity characteristics of macrobenthos in the new shoal of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2002, 24(2): 133−139. [13] 张衡, 张瑛瑛, 刁山洲, 等. 长江口盐沼湿地不同亚生境的大型底栖动物群落组成和多样性差异[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(10): 3102−3109.Zhang Heng, Zhang Yingying, Diao Shanzhou, et al. Difference of macrobenthos community composition and diversity in different sub-habitats in salt marsh wetland of the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(10): 3102−3109. [14] 章飞军, 童春富, 谢志发, 等. 长江口潮间带大型底栖动物群落演替[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(12): 4944−4952. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.12.002Zhang Feijun, Tong Chunfu, Xie Zhifa, et al. The re-colonisation progress of intertidal benthic fauna community in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(12): 4944−4952. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.12.002 [15] 孙文. 崇明岛主要植物群落类型、分布及其生态景观协调性评价[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2013.Sun Wen. The main community types and distribution of Chongming Island and ecology and landscape coordination assessment of its plant communities[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2013. [16] 徐东. 浅谈崇明南横引河综合整治[J]. 吉林水利, 2005(2): 34−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2846.2005.02.015Xu Dong. Talking on the integrative regulation for diversion channel of Chongmingnanheng[J]. Jilin Water Resources, 2005(2): 34−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2846.2005.02.015 [17] 姜德刚, 李建华, 徐金燕, 等. 崇明岛富营养化河道溶解有机质的三维荧光光谱特征[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2019, 40(3): 33−40.Jiang Degang, Li Jianhua, Xu Jinyan, et al. Three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matter in a eutrophic river on Chongming Island[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2019, 40(3): 33−40. [18] 汪振华, 章守宇, 王凯. 三横山鱼礁生境鱼类和大型无脊椎动物群落特征[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(8): 2026−2035.Wang Zhenhua, Zhang Shouyu, Wang Kai. Fish and macroinvertebrates community structure in artificial habitat around Sanheng Isle, Shengsi, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(8): 2026−2035. [19] 童春富. 长江河口潮间带盐沼植被分布区及邻近光滩鱼类组成特征[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(20): 6501−6510. doi: 10.5846/stxb201203220391Tong Chunfu. Characteristics of the fish assemblages in the intertidal salt marsh zone and adjacent mudflat in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(20): 6501−6510. doi: 10.5846/stxb201203220391 [20] Wang Jinqing, Tang Long, Zhang Xiaodong, et al. Fine-scale environmental heterogeneities of tidal creeks affect distribution of crab burrows in a Chinese salt marsh[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2009, 35(12): 1685−1692. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.05.002 [21] 杨泽华, 童春富, 陆健健. 盐沼植物对大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(11): 4387−4393. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.11.002Yang Zehua, Tong Chunfu, Lu Jianjian. Effects of saltmarsh on the benthic macroinvertebrate community in Yangtze Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(11): 4387−4393. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.11.002 [22] 徐兆礼, 蒋玫, 白雪梅, 等. 长江口底栖动物生态研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 1999, 6(5): 59−62.Xu Zhaoli, Jiang Mei, Bai Xuemei, et al. An ecological study on benthos in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 1999, 6(5): 59−62. [23] 彭松耀, 赖子尼, 蒋万祥, 等. 珠江口大型底栖动物的群落结构及影响因子研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2010, 34(6): 1179−1189.Peng Songyao, Lai Zini, Jiang Wanxiang, et al. Study on community structure of macrozoobenthos and impact factors in pearl river estuary[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2010, 34(6): 1179−1189. [24] 许栋, 张博曦, 及春宁, 等. 梯级水库对南渡江干流底栖动物丰枯水期沿程变化的影响[J]. 水资源保护, 2019, 35(2): 60−66, 84. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2019.02.010Xu Dong, Zhang Boxi, Ji Chunning, et al. Streamwise variation of zoobenthos along main stream of Nandujiang River in wet and dry seasons under influence of cascade reservoirs[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2019, 35(2): 60−66, 84. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2019.02.010 [25] 堵南山. 中华绒螯蟹的洄游[J]. 水产科技情报, 2004, 31(2): 56−57, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1994.2004.02.001Du Nanshan. Migration of Chinese mitten-handed crab eriocheir sinensis[J]. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 2004, 31(2): 56−57, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1994.2004.02.001 [26] Jakobsson E. Seasonal community dynamics of macroinvertebrates in an Arctic stream[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2019, 35(5): 893−900. [27] Bass D, Gaskin B, Tedford K. Macroinvertebrate community structure and physicochemical conditions of a Northwestern Oklahoma Spring[C]//Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science. 2019, 98: 6−13. [28] Su Ping, Wang Xinxin, Lin Qidong, et al. Variability in macroinvertebrate community structure and its response to ecological factors of the Weihe River Basin, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2019, 140: 105595. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105595 [29] 王璐, 杨海军, 李昆, 等. 长白山源头溪流底栖动物群落结构季节动态[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4834−4842.Wang Lu, Yang Haijun, Li Kun, et al. Seasonal dynamics of macroinvertebrate community structure in a headwater stream in the Changbai Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4834−4842. [30] 郑子叶, 许亚红, 张郢, 等. 香溪河大型底栖无脊椎动物群落结构季节动态研究[J]. 生物资源, 2019, 41(6): 524−531.Zheng Ziye, Xu Yahong, Zhang Ying, et al. Seasonal dynamics of community structure of large benthic invertebrates in Xiangxi river[J]. Biotic Resources, 2019, 41(6): 524−531. [31] 蒋万祥, 贾兴焕, 周淑婵, 等. 香溪河大型底栖动物群落结构季节动态[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(4): 923−928.Jiang Wanxiang, Jia Xinghuan, Zhou Shuchan, et al. Seasonal dynamics of macrozoobenthos community structure in Xiangxi River[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(4): 923−928. [32] 苏华武, 江晶, 温芳妮, 等. 湖北清江流域叹气沟河底栖动物群落结构与水质生物学评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 2008, 20(4): 520−528. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.04.017Su Huawu, Jiang Jing, Wen Fangni, et al. Community structures of macrozoobenthos and bioassessment of water quality in Tanqigou Stream of Qingjiang River Basin, Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2008, 20(4): 520−528. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.04.017 [33] 庞翠超, 陶静, 吴小慧, 等. 强感潮河网生态治理工程综合评价[J]. 人民长江, 2016, 47(1): 15−22.Pang Cuichao, Tao Jing, Wu Xiaohui, et al. Comprehensive assessment of ecological harnessing project in strong tide river net[J]. Yangtze River, 2016, 47(1): 15−22. [34] 吴逢润, 童春富. 近30年长江口北支演变及其对物种多样性的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(2): 72−85.Wu Fengrun, Tong Chunfu. Evolution of the North Branch of Yangtze Estuary in last 30 years and corresponding effects on species diversity[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(2): 72−85. [35] 朱建荣, 吴辉, 顾玉亮. 长江河口北支倒灌盐通量数值分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2011, 29(3): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.03.002Zhu Jianrong, Wu Hui, Gu Yuliang. Numerical analysis of the inverted salt flux from the North Branch into the South Branch of Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2011, 29(3): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.03.002 [36] Li Lu, Zhu Jianrong, Wu Hui. Impacts of wind stress on saltwater intrusion in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(7): 1178−1192. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4311-1 [37] Zhang Erfeng, Savenije H H G, Wu Hui, et al. Analytical solution for salt intrusion in the Yangtze Estuary, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 91(4): 492−501. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.11.008 [38] Laprise R, Dodson J J. Nature of environmental variability experienced by benthic and pelagic animals in the St. Lawrence Estuary, Canada[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1993, 94: 129−139. doi: 10.3354/meps094129 [39] 张敬怀. 珠江口及邻近海域大型底栖动物多样性随盐度、水深的变化趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 302−310. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13141Zhang Jinghuai. The variation of biodiversity of macrobenthic fauna with salinity and water depth near the Pearl Estuary of the northern South China Sea[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2014, 22(3): 302−310. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13141 [40] 虞左明, 李瑾, 蔡飞. 西湖引水治理前后底栖动物群落的比较研究[J]. 杭州大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 24(1): 93−94.Yu Zuoming, Li Jin, Cai Fei. The comparative study on the changes of zoobenthic communities of the West Lake after drawing water from Qiantang River[J]. Journal of Hangzhou University (Natural Science), 1997, 24(1): 93−94. [41] Beisel J N, Usseglio-Polatera P, Thomas S, et al. Stream community structure in relation to spatial variation: the influence of mesohabitat characteristics[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1998, 389(1/3): 73−88. doi: 10.1023/A:1003519429979 [42] 张超文, 张堂林, 朱挺兵, 等. 洪泽湖大型底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2012, 33(3): 27−33.Zhang Chaowen, Zhang Tanglin, Zhu Tingbing, et al. Community structure of macrozoobenthos and its relationship with environmental factors in Lake Hongze[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2012, 33(3): 27−33. [43] Chen Liping, Zhang Ying, Liu Qigen, et al. Spatial variations of macrozoobenthos and sediment nutrients in Lake Yangcheng: Emphasis on effect of pen culture of Chinese mitten crab[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 37: 118−129. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.06.008 [44] Merz J E, Chan L K O. Effects of gravel augmentation on macroinvertebrate assemblages in a regulated California River[J]. River Research and Applications, 2005, 21(1): 61−74. doi: 10.1002/rra.819 [45] Downes B J, Lake P S, Schreiber E S G, et al. Habitat structure and regulation of local species diversity in a stony, upland stream[J]. Ecological Monographs, 1998, 68(2): 237−257. doi: 10.1890/0012-9615(1998)068[0237:HSAROL]2.0.CO;2 [46] 任海庆, 袁兴中, 刘红, 等. 环境因子对河流底栖无脊椎动物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(10): 3148−3156.Ren Haiqing, Yuan Xingzhong, Liu Hong, et al. The effects of environment factors on community structure of benthic invertebrate in rivers[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 3148−3156. [47] Thomsen A G, Friberg N. Growth and emergence of the stonefly Leuctra nigra in coniferous forest streams with contrasting pH[J]. Freshwater Biology, 2002, 47(6): 1159−1172. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00827.x [48] Duran M. Monitoring water quality using benthic macroinvertebrates and physicochemical parameters of Behzat stream in Turkey[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2006, 15(5): 709−717. [49] 任淑智. 北京地区河流中大型底栖无脊椎动物与水质关系的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 1991, 11(1): 31−46.Ren Shuzhi. Investigation on macroinvertebrate community and water quality in streams in beijing area[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1991, 11(1): 31−46. [50] 陈松, 姜德刚. 崇明岛河网水系营养状态分析与富营养化评价[J]. 中国水利, 2010(13): 35−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2010.13.019Chen Song, Jiang Degang. Nutrition condition analysis and eutrophication assessment of river network in Chongming island[J]. China Water Resources, 2010(13): 35−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2010.13.019 [51] 方光杰, 孙利元, 唐衍力, 等. 基于刺网和地笼渔获物的人工鱼礁区资源丰度比较研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(S1): 23−33.Fang Guangjie, Sun Liyuan, Tang Yanli, et al. A comparative study on fishery resource of artificial reefs based on gillnet and cage catches[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(S1): 23−33. [52] Harms J H, Wallace J R, Stewart I J. Analysis of fishery-independent hook and line-based data for use in the stock assessment of bocaccio rockfish (Sebastes paucispinis)[J]. Fisheries Research, 2010, 106(3): 298−309. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2010.08.010 [53] 陈勇, 郑小贤, 朱敬博, 等. 人工鱼礁区鱼类和大型无脊椎动物的调查方法[J]. 水产科学, 2008, 27(6): 316−319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2008.06.013Chen Yong, Zheng Xiaoxian, Zhu Jingbo, et al. Assessing methods of fish and macroinvertebrate in artificial reef areas[J]. Fisheries Science, 2008, 27(6): 316−319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2008.06.013 -




 下载:
下载: