The effects of spring-neap tide on sediment bedding on tidal flats: A numerical study
-
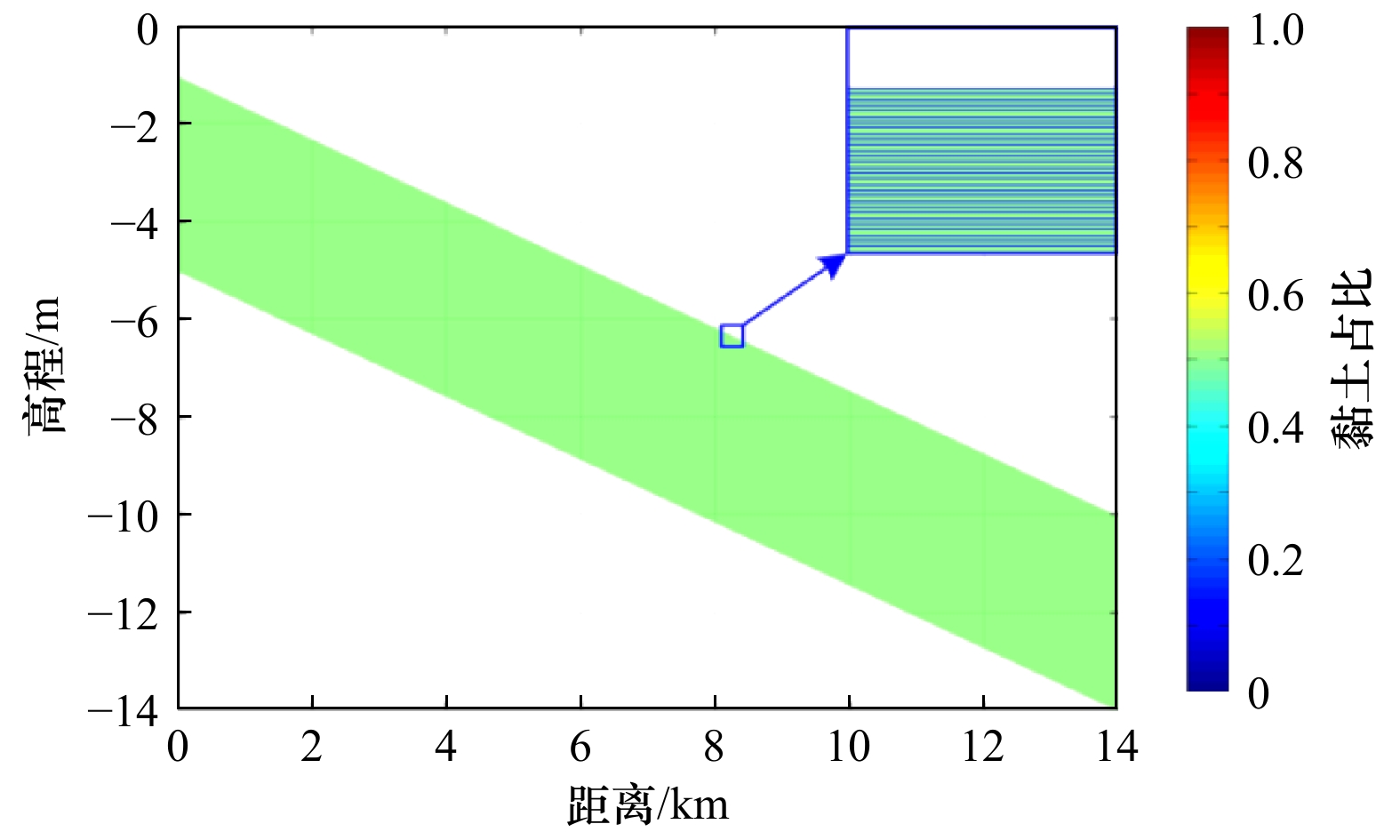
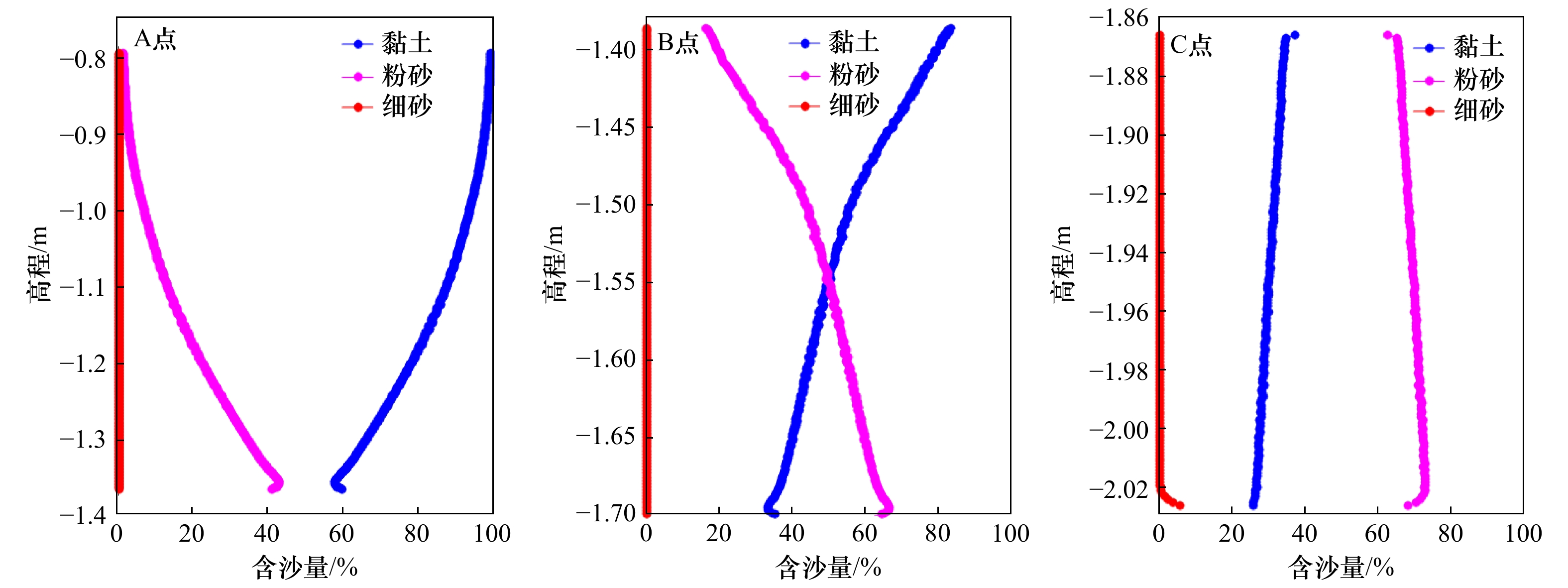
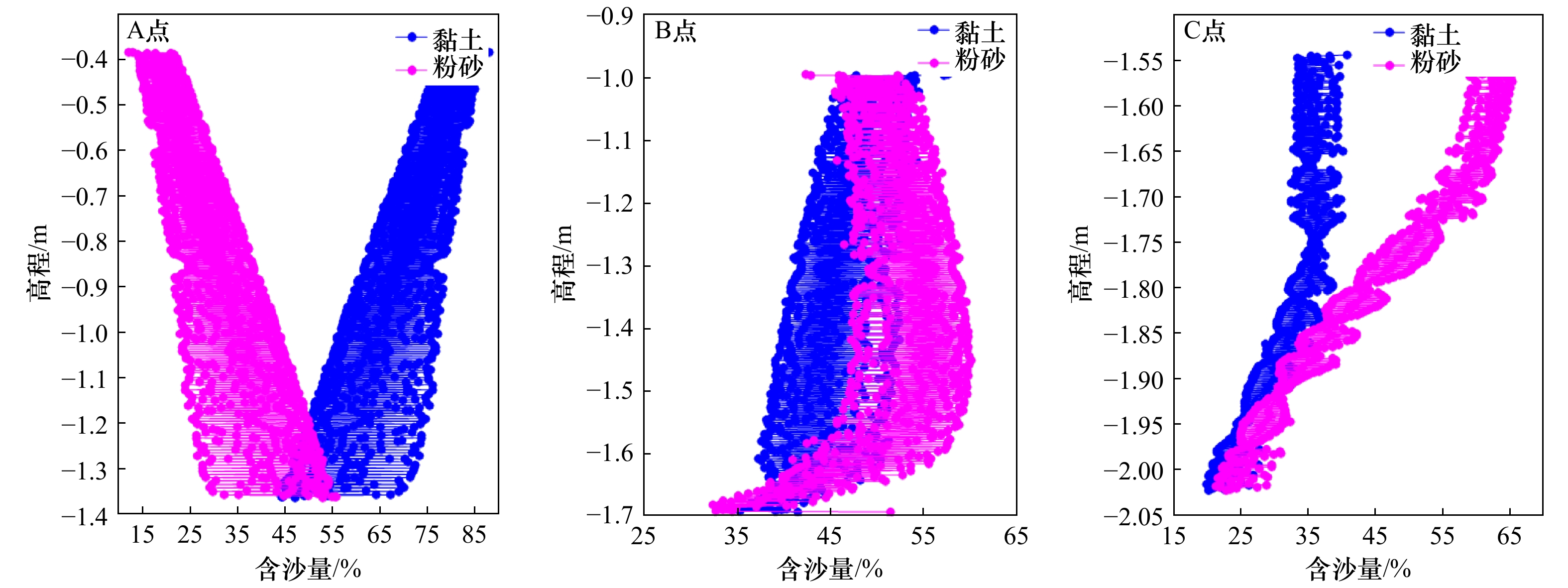
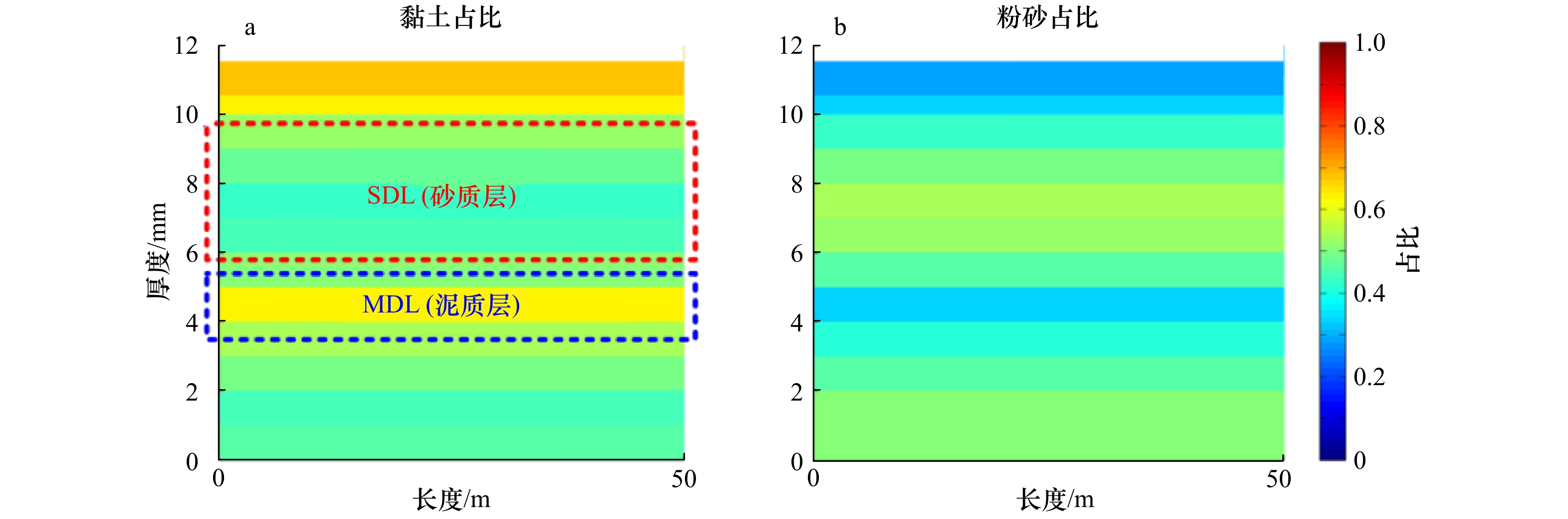
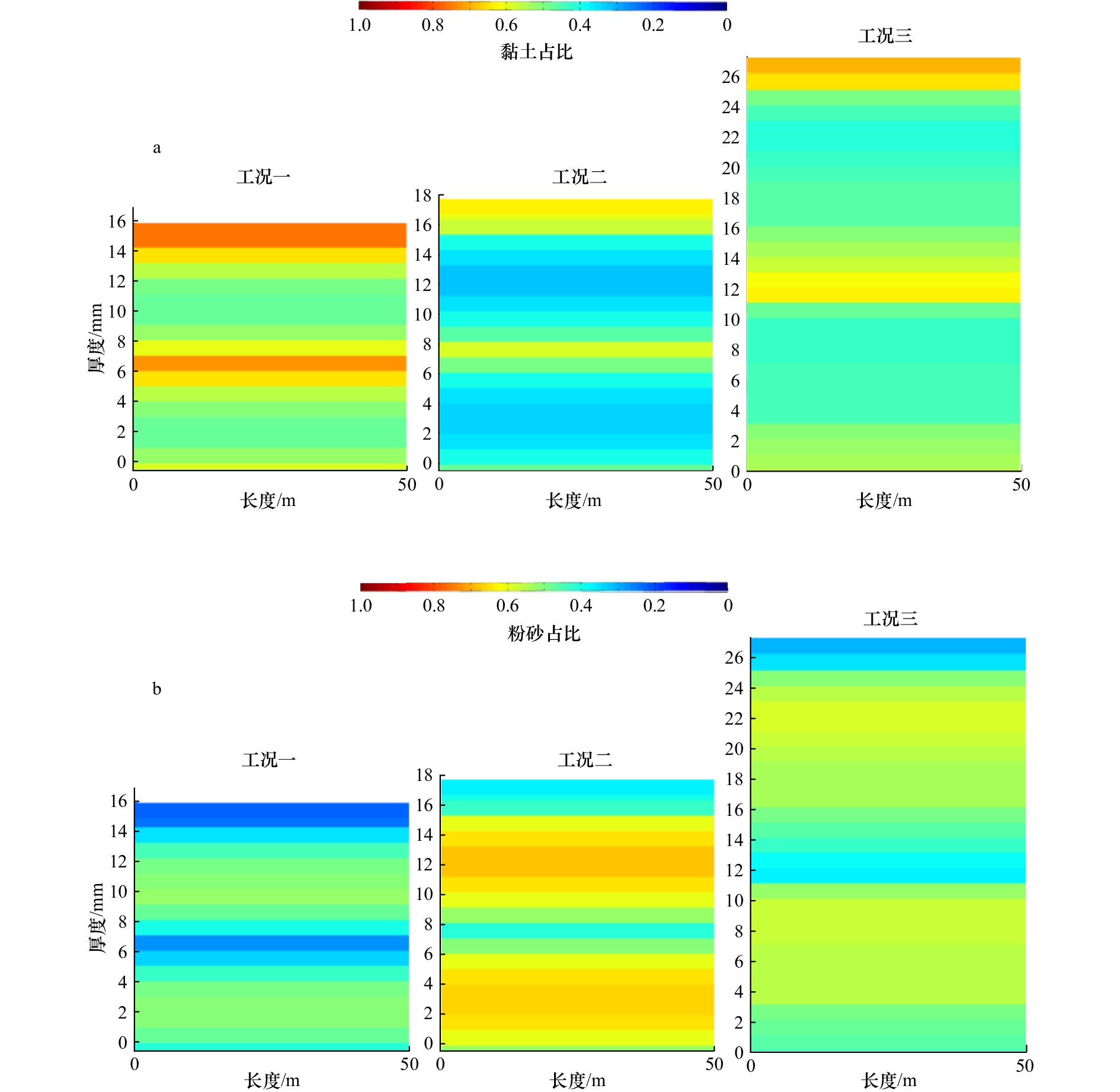
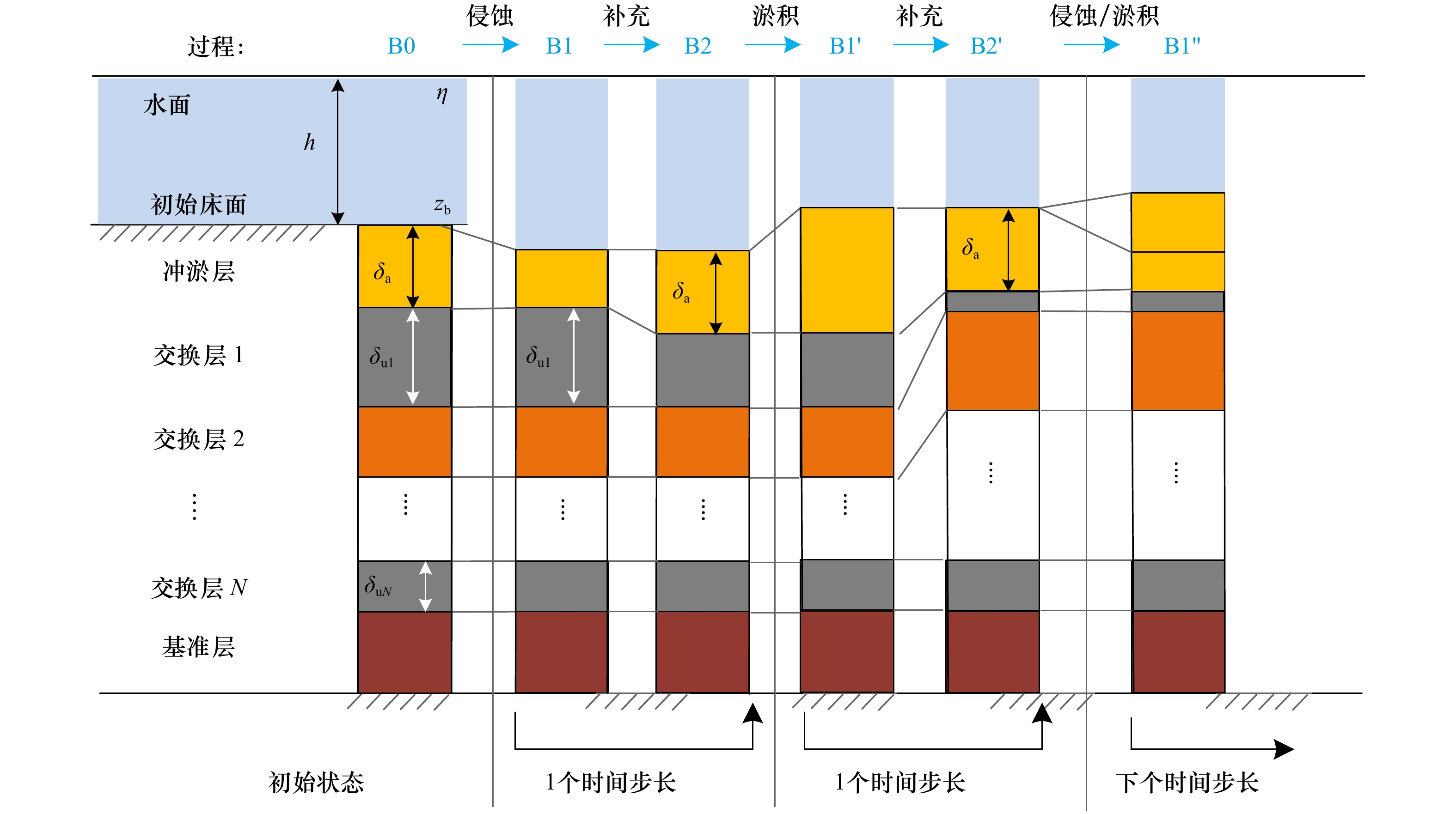
摘要: 潮滩垂向沉积韵律层的形成主要取决于周期性的潮汐条件,包括涨落潮、大小潮、季节性及更长时间尺度的潮汐特征,为探究大小潮周期对潮滩沉积物垂向层理形成机制的影响,应用一维潮流泥沙与底床分层数学模型,对周期性潮汐条件作用下潮滩垂向沉积韵律层形成机制进行了数值模拟研究。结果表明,大小潮的周期性是模型中沉积层理表现韵律性的主要原因之一,韵律层中单个层理结构对应于1个大小潮周期过程,层理结构由形成于小潮期间的泥质层及形成于大潮期间的砂质层组成,层理的厚度也呈旋回性变化,大潮时层理较厚而小潮时层理较薄。水体边界含沙量是影响潮汐层理结构的重要因子,边界含沙量中粉砂占比增大会使潮汐韵律层整体粗化且砂质层厚度增大,当边界含沙量整体显著增大时,潮滩上的垂向潮汐韵律层会更加完整且厚度明显增大。潮汐层理的形成与特征是多种因子共同作用的结果,后续需进一步探究包括波浪、风暴潮、潮滩生物等其他因子的作用。Abstract: The formation of vertical sedimentary rhythmic layers of tidal flat mainly depends on periodic tidal conditions, including flood and ebb tide, spring and neap tide, seasonal and longer term scale tidal characteristics. In order to investigate the distribution and mechanism of sediment bedding on tidal flats, a one-dimensional numerical model was used to simulate the rhythmic layers of long-term tidal flat bedding layers under spring and neap tidal cycles. Results indicate that the periodicity of spring-neap tide is the main reason for the rhythmicity of sedimentary bedding. One couplet in the rhythm layer corresponds to the spring-neap tidal period, which is formed by the mud-dominated layer during the neap tide and the sand-dominated layer during the spring tide. The thicknesses of layers also show a cyclical change: bedding layers are thicker during the spring tide and thinner during the neap tide. The boundary sediment concentration is also an important factor affecting the structure of tidal couplets. An increasing boundary concentration of silt makes the tidal rhythm layer coarser and increases the overall thickness of the sand-dominated layer. When the boundary sediment concentration significantly increases, the vertical tidal rhythm layers on the tidal flat are more intact with an evident increase in layer thickness. The formation and characteristics of tidal bedding layers are the result of the joint action of many factors (e.g., waves, storms, biological factors and etc.), which await further research effort in the future.
-
Key words:
- tidal flat /
- sediment sorting /
- tidal rhythm layers /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 水动力条件工况设置
Tab. 1 Hydrodynamic condition setting
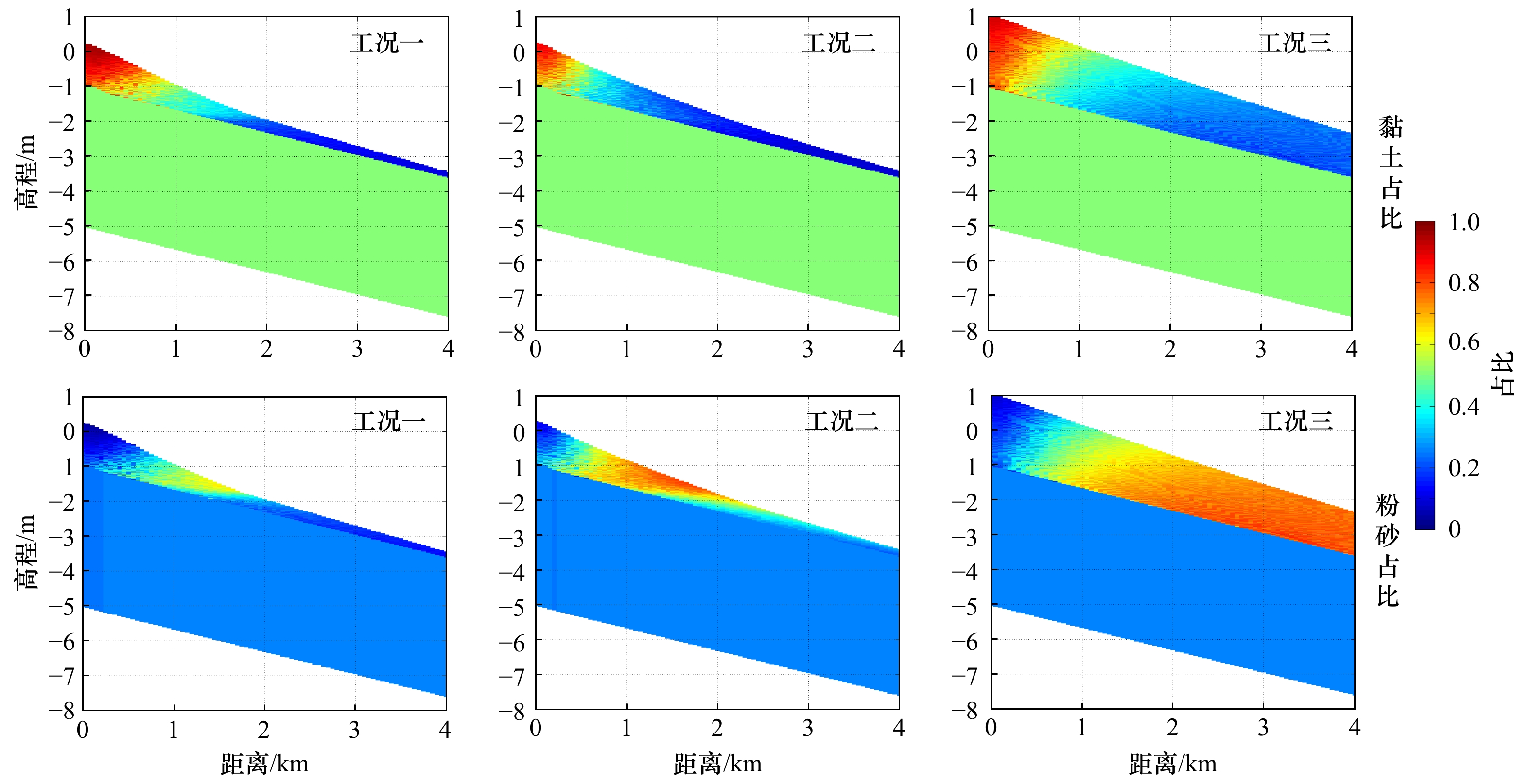
振幅/m 频率/((°)·h−1) 相位差/(°) 仅M2作用 工况1 M2 2.0 28.985 5 0 工况2 M2 2.5 28.985 5 0 工况3 M2 3.0 28.985 5 0 M2与S2叠加作用 工况4 M2 2 28.985 5 0 S2 0.4 30 0 工况5 M2 2 28.985 5 0 S2 0.8 30 0 工况6 M2 2 28.985 5 0 S2 1 30 0 表 2 3种工况的边界含沙量设置
Tab. 2 Three settings of sediment concentration
黏土含沙量/
(kg·m−3)粉砂含沙量/
(kg·m−3)细砂含沙量/
(kg·m−3)工况一 0.006 0.004 0.001 工况二 0.004 0.016 0.001 工况三 0.040 0.160 0.001 -
[1] Friedrichs C T. Tidal flat morphodynamics: A synthesis[M]//Wolanski E, McLusky D. Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science. Waltham: Academic Press, 2011: 137−170. [2] Choi K S, Park Y A. Late pleistocene silty tidal rhythmites in the macrotidal flat between Youngjong and Yongyou islands, west coast of Korea[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 167(3/4): 231−241. [3] Fan Daidu, Li Congxian, Archer A W, et al. Temporal distribution of diastems in deposits of an open-coast tidal flat with high suspended sediment concentrations[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(3/4): 173−181. [4] 龚小辉, 柏春广, 王建. 淤泥质潮滩沉积周期性研究综述[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2012, 35(1): 117−121.Gong Xiaohui, Bai Chunguang, Wang Jian. Review of research on sedimentary periodicity of tidal mud flat[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 35(1): 117−121. [5] Deloffre J, Verney R, Lafite R, et al. Sedimentation on intertidal mudflats in the lower part of macrotidal estuaries: Sedimentation rhythms and their preservation[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 241(1/4): 19−32. [6] 王建, 柏春广, 徐永辉. 江苏中部淤泥质潮滩潮汐层理成因机理和风暴沉积判别标志[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(4): 562−569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.04.014Wang Jian, Bai Chunguang, Xu Yonghui. Mechanism of silt-mud couplet of mud tidal flat and discrimination criteria of storm surge sedimentation in the middle Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(4): 562−569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.04.014 [7] 范代读, 李从先, 邓兵, 等. 潮汐周期在潮坪沉积中的记录[J]. 同济大学学报, 2002, 30(3): 281−285.Fan Daidu, Li Congxian, Deng Bing, et al. Tidal cycles recorded in tidal-flat deposits[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2002, 30(3): 281−285. [8] Fan Daidu, Guo Yanxia, Wang Ping, et al. Cross-shore variations in morphodynamic processes of an open-coast mudflat in the Changjiang Delta, China: With an emphasis on storm impacts[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2006, 26(4): 517−538. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.12.011 [9] Young I R, Verhagen L A. The growth of fetch limited waves in water of finite depth. Part 1. Total energy and peak frequency[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1996, 29(1/2): 47−78. [10] Van Rijn L C. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves. I: Initiation of motion, bed roughness, and bed-load transport[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 133(6): 649−667. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2007)133:6(649) [11] Fagherazzi S, Wiberg P L. Importance of wind conditions, fetch, and water levels on wave-generated shear stresses in shallow intertidal basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Earth Surface, 2009, 114(F3): F03022. [12] Roberts W, Le Hir P, Whitehouse R J S. Investigation using simple mathematical models of the effect of tidal currents and waves on the profile shape of intertidal mudflats[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(10/11): 1079−1097. [13] Green M O, Coco G. Review of wave-driven sediment resuspension and transport in estuaries[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2014, 52(1): 77−117. doi: 10.1002/2013RG000437 [14] Soulsby R. Dynamics of Marine Sands: A Manual for Practical Applications[M]. Thomas: Telford, 1997. [15] Winterwerp J C. On the sedimentation rate of cohesive sediment[J]. Proceedings in Marine Science, 2007, 8: 209−226. [16] 龚政, 靳闯, 张长宽, 等. 江苏淤泥质潮滩剖面演变现场观测[J]. 水科学进展, 2014, 25(6): 880−887.Gong Zheng, Jin Chuang, Zhang Changkuan, et al. Surface elevation variation of the Jiangsu mudflats: Field observation[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2014, 25(6): 880−887. [17] Zhou Zeng, Coco G, van der Wegen M, et al. Modeling sorting dynamics of cohesive and non-cohesive sediments on intertidal flats under the effect of tides and wind waves[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 104: 76−91. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.05.010 -




 下载:
下载: