Ultra-fast energy transfer process of recombinant allophycocyanin
-
摘要: 藻胆体是红、蓝藻特有的光合作用捕光天线复合物。别藻蓝蛋白(APC)是组成藻胆体高效能量传递的核心结构的主要成分。本文以基因重组的别藻蓝蛋白(rAPC)的单体和三聚体为材料,通过稳态光谱、圆二色光谱以及超快时间分辨光谱研究了rAPC的结构构象和能量传递过程。结果表明,rAPC在测试条件下能保持和天然APC一致的光谱特性和活性构象;rAPC单体组装成三聚体后,其α84PCB和β84PCB可以组成激子色素对,通过激子分裂提高三聚体的能量传递效率;超快时间分辨光谱结果显示,在rAPC三聚体中,能量从620 nm传至650 nm的时间为300~600 fs,同时存在着19 fs的激子态的电子退相干过程。这些结果为揭示藻胆体的高效能量传递机制提供了数据基础。Abstract: Phycobilisomes are photosynthetic light-harvesting antenna complexes unique to red algae and cyanobacteria. Allophycocyanin (APC) is the main component of the core structure of phycobilisomes. In this experiment, recombinant allophycocyanin (rAPC) was used as the material, and the structure conformation and energy transfer process of rAPC were studied through steady-state spectroscopy, circular dichroic spectroscopy, and ultrafast time-resolved spectroscopy. The results show that rAPC can maintain the same spectral characteristics and active conformation as natural APC under the test conditions; after rAPC monomers are assembled into trimer, the results confirmed that α84PCB and β84PCB can form an exciton pigment pair which can improve the energy transfer efficiency of the rAPC trimer through exciton splitting; ultrafast time-resolved spectroscopy results show that the energy transfer time from 620 nm to 650 nm is 300−600 fs, and there is also a 19 fs exciton state electronic decoherence process. These results provide a data basis for revealing the efficient energy transfer mechanism of phycobilisomes.
-
图 1 别藻蓝蛋白三聚体晶体结构图
结构信息下载于PDB数据库(http://www1.rcsb.org/),PDB码为4F0U;灰色螺旋为别藻蓝蛋白的螺旋结构,灰色杆代表色素分子;粉色螺旋和黄色螺旋组成了别藻蓝蛋白的单体,其中黄色螺旋为别藻蓝蛋白α亚基,粉色螺旋为别藻蓝蛋白β亚基;绿色杆代表α84PCB;粉色杆代表β84PCB
Fig. 1 Allophycocyanin trimer crystal structure
The structure data is downloaded from the PDB database (http://www1.rcsb.org/), PDB code is 4F0U; the gray spiral represents spiral structure of allophycocyani; the gray sticks represent pigment molecules; the pink spiral (β subunit) and the yellow spiral (α subunit) constitute the allophycocyanin monomer; green sticks represent α84PCB; pink sticks represent β84PCB
图 2 诱导后菌体的稳态光谱及荧光性质变化
a. 诱导前和诱导后的菌体在蓝光和绿光激发下的荧光发射图片;b. 诱导后绿色菌体的稳态吸收光谱和荧光发射光谱(Ex615 nm)
Fig. 2 Steady-state spectra and fluorescence properties of induced bacteria
a. Fluorescence emission pictures of the bacteria before and after induction (green light excitation); b. steady-state absorption and fluorescence emission spectra (Ex615 nm) of the blue-green bacteria after induction
图 3 rAPC三聚体纯化及亚基鉴定
a. rAPC蔗糖密度分离结果,上层rAPC单体,下层rAPC三聚体;b. rAPC三聚体;c. rAPC三聚体SDS-PAGE蛋白电泳图
Fig. 3 Purification and composition identification of rAPC trimer
a. rAPC sucrose density separation result, upper rAPC monomer, lower rAPC trimer; b. rAPC trimer; c. SDS-PAGE protein electrophoresis of rAPC trimer
图 4 rAPC单体和三聚体的稳态吸收光谱及荧光发射光谱
a. rAPC单体和三聚体的稳态吸收光谱,为了方便对比,进行了0~1区间的归一化处理,粉色虚线为单体吸收光谱的二阶导数图,灰色虚线为三聚体吸收光谱的二阶导数图;b. rAPC单体和三聚体的稳态荧光发射光谱,为了方便对比进行了0~100区间的归一化处理
Fig. 4 Steady-state absorption spectra and fluorescence spectra of rAPC trimer
a. The steady-state absorption spectra of rAPC monomer and trimer are normalized in the range of 0‒1 for the convenience of comparison, the pink dotted line is the second derivative diagram of the monomer absorption spectrum, and the gray dotted line is the second derivative diagram of the trimer absorption spectrum; b. the steady-state fluorescence emission spectra of rAPC monomer and trimer are normalized in the interval of 0‒100 for the convenience of comparison
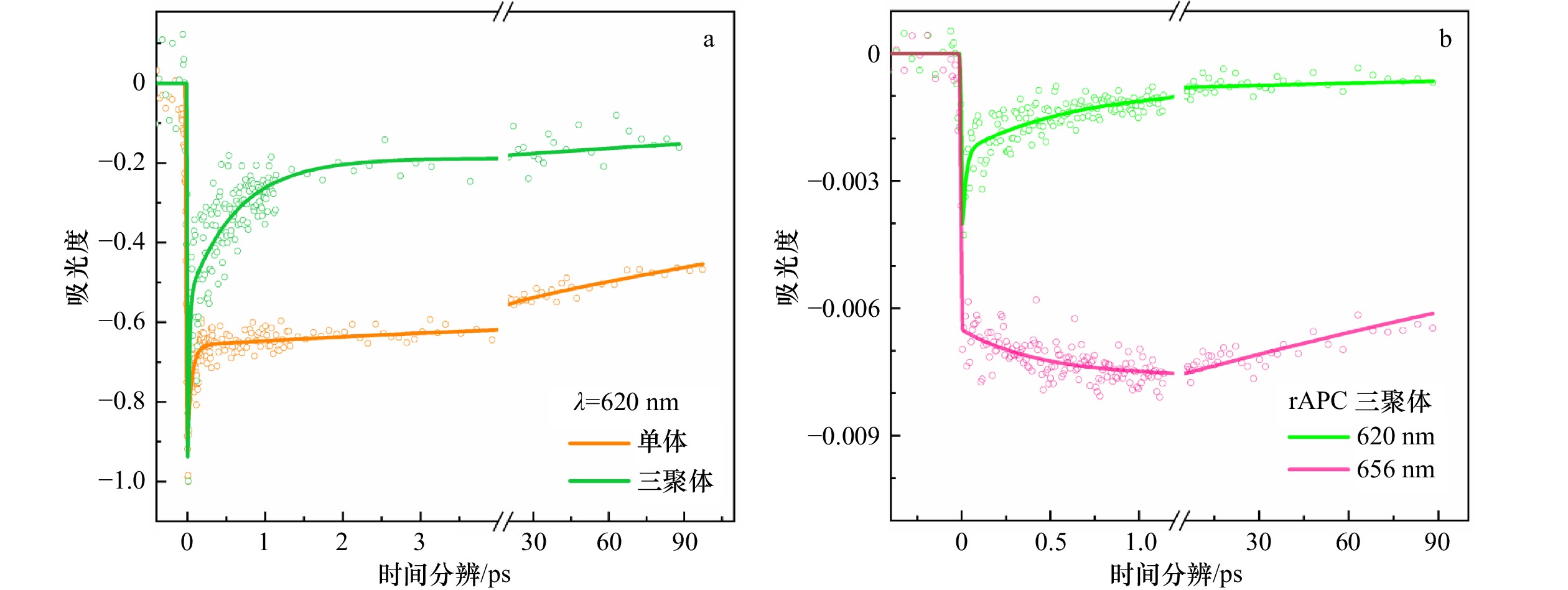
图 8 rAPC三聚体及单体的瞬态探测
a. rAPC单体和三聚体在620 nm处的能量传递动力学拟合曲线;b. rAPC三聚体在620 nm及656 nm处的能量传递动力学拟合曲线
Fig. 8 Transients detected of rAPC trimer and monomer
a. Fitting curve of energy transfer kinetics of rAPC monomer and trimer at 620 nm; b. fitting curve of energy transfer kinetics of rAPC trimer at 620 nm and 656 nm
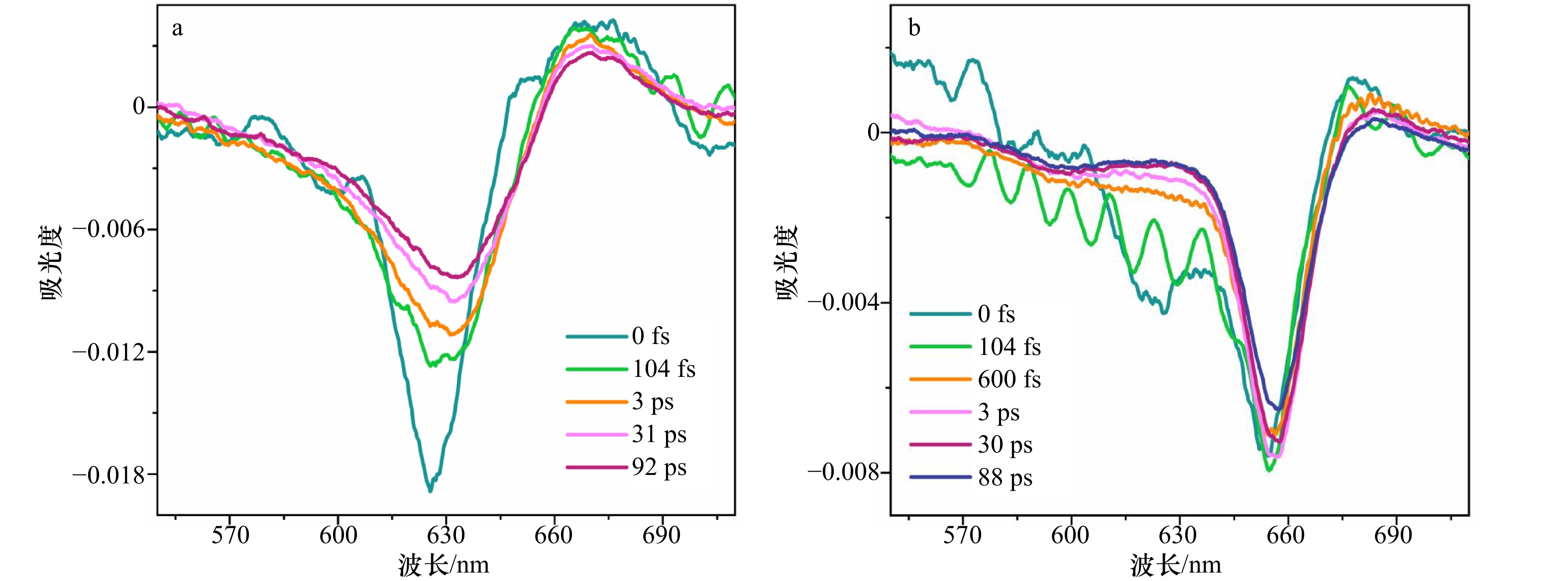
图 9 rAPC单体及三聚体不同时间下的瞬态光谱变化
a. rAPC单体在不同时间分辨率下的瞬态光谱变化;b. rAPC三聚体在不同时间分辨率下的瞬态光谱变化
Fig. 9 Energy transfer dynamics of rAPC monomer and trimer at several delay times
a. Transient spectral change of rAPC monomers at different time resolutions; b. transient spectral change of rAPC trimers at different time resolutions
表 1 rAPC单体和三聚体瞬态吸收动力学拟合常数
Tab. 1 The fitting constants of rAPC trimer transient absorption dynamics
样品 波长 时间寿命常数1 时间寿命常数2 时间寿命常数3 rAPC单体 620 nm (57±10)fs (7.4±4.8)ps 400 ps rAPC三聚体 620 nm (19±7)fs (630 ±100)fs 400 ps rAPC三聚体 656 nm − (470 ±100)fs 400 ps 注:−代表未拟合到时间寿命常数。 -
[1] Büchel C. Evolution and function of light harvesting proteins[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 172: 62−75. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.04.018 [2] Guglielmi G, Cohen-Bazire G, Bryant D A. The structure of Gloeobacter violaceus and its phycobilisomes[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 1981, 129(3): 181−189. doi: 10.1007/BF00425248 [3] Green B R. What happened to the phycobilisome?[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(11): 748. doi: 10.3390/biom9110748 [4] 王肖肖, 秦松, 杨革, 等. 藻胆体的结构与能量传递功能[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(12): 139−145. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170627002Wang Xiaoxiao, Qin Song, Yang Ge, et al. Structure and energy transfer of phycobilisome[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(12): 139−145. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170627002 [5] 赵福利, 张景民, 郑锡光, 等. 红藻藻胆体内部蛋白间的能量传递研究人工合成复合物R-PE/R-PC以及R-PE/APC内的能量传递[C]//第九届全国凝聚态光学性质学术会议论文集. 珠海: 中国物理学会, 1999.Zhao Fuli, Zhang Jingmin, Zheng Xiguang, et al. Energy transfer among proteins in the phycobilisome of red algae: Energy transfer in synthesized complex of R-PE/R-PC and R-PE/APC[C]//National Conference on Optical Properties of Condensed Matter. Zhuhai: Chinese Physical Society, 1999. [6] Kirilovsky D, Büchel C. Chapter Nine—Evolution and function of light-harvesting antenna in oxygenic photosynthesis[J]. Advances in Botanical Research, 2019, 91: 247−293. [7] Marx A, Adir N. Allophycocyanin and phycocyanin crystal structures reveal facets of phycobilisome assembly[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2013, 1827(3): 311−318. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.11.006 [8] Liu Jinyu, Jiang Tao, Zhang Jiping, et al. Crystal structure of allophycocyanin from red algae Porphyra yezoensis at 2.2-Å resolution[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1999, 274(24): 16945−16952. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.16945 [9] MacColl R. Allophycocyanin and energy transfer[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2004, 1657(2/3): 73−81. [10] Karpulevich A A, Maksimov E G, Sluchanko N N, et al. Highly efficient energy transfer from quantum dot to allophycocyanin in hybrid structures[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 2016, 160: 96−101. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.03.048 [11] Womick J M, Moran A M. Vibronic enhancement of exciton sizes and energy transport in photosynthetic complexes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(6): 1347−1356. doi: 10.1021/jp106713q [12] Zhang J M, Shiu Y J, Hayashi M, et al. Investigations of ultrafast exciton dynamics in allophycocyanin trimer[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2001, 105(39): 8878−8891. doi: 10.1021/jp011266a [13] Womick J M, Moran A M. Exciton coherence and energy transport in the light-harvesting dimers of allophycocyanin[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2009, 113(48): 15747−15759. doi: 10.1021/jp907644h [14] Edington M D, Riter R E, Beck W F. Evidence for coherent energy transfer in allophycocyanin trimers[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1995, 99(43): 15699−15704. doi: 10.1021/j100043a001 [15] Collini E, Wong C Y, Wilk K E, et al. Coherently wired light-harvesting in photosynthetic marine algae at ambient temperature[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7281): 644−647. doi: 10.1038/nature08811 [16] Dean J C, Mirkovic T, Toa Z S D, et al. Vibronic enhancement of algae light harvesting[J]. Chem, 2016, 1(6): 858−872. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2016.11.002 [17] Liu Shaofeng, Chen Yingjie, Lu Yandu, et al. Biosynthesis of fluorescent cyanobacterial allophycocyanin trimer in Escherichia coli[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2010, 105(2): 135−142. doi: 10.1007/s11120-010-9574-4 [18] Su Hainan, Xie Binbin, Chen Xiulan, et al. Efficient separation and purification of allophycocyanin from Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2010, 22(1): 65−70. doi: 10.1007/s10811-009-9427-8 [19] Dagnino-Leone J, Figueroa M, Uribe E, et al. Biosynthesis and characterization of a recombinant eukaryotic allophycocyanin using prokaryotic accessory enzymes[J]. Microbiology Open, 2020, 9(3): e989. [20] 李文军, 蒲洋, 牛壮, 等. 重组别藻蓝蛋白三聚体结构与功能[J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(16): 1699−1713. doi: 10.1360/N972016-01416Li Wenjun, Pu Yang, Niu Zhuang, et al. Structural and functional investigation of allophycocyanin trimer[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(16): 1699−1713. doi: 10.1360/N972016-01416 [21] Zhu Ruidan, Zou Jiading, Wang Zhuan, et al. Electronic state-resolved multimode-coupled vibrational wavepackets in oxazine 720 by two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2020, 124(45): 9333−9342. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.0c06559 [22] 王云鹏, 王专, 翁羽翔. 凝聚相分子振动量子拍的20 fs时间分辨光谱实时观测[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(31): 2895−2898. doi: 10.1360/972012-587Wang Yunpeng, Wang Zhuan, Weng Yuxiang. Real-time observation of vibrational quantum beat in condensed phase by 20 fs time-resolved spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(31): 2895−2898. doi: 10.1360/972012-587 [23] Roychoudhuri C. Causal Physics: Photons by Non-Interactions of Waves[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014. [24] Homoelle B J, Edington M D, Diffey W M, et al. Stimulated photon-echo and transient-grating studies of protein-matrix solvation dynamics and interexciton-state radiationless decay in α phycocyanin and allophycocyanin[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1998, 102(16): 3044−3052. doi: 10.1021/jp972782x [25] McGregor A, Klartag M, David L, et al. Allophycocyanin trimer stability and functionality are primarily due to polar enhanced hydrophobicity of the phycocyanobilin binding pocket[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2008, 384(2): 406−421. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.018 [26] Sonani R R, Gupta G D, Madamwar D, et al. Crystal structure of allophycocyanin from marine cyanobacterium Phormidium sp. A09DM[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0124580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124580 [27] Edington M D, Riter R E, Beck W F. Interexciton-state relaxation and exciton localization in allophycocyanin trimers[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(33): 14206−14217. doi: 10.1021/jp960454b [28] MacColl R. Cyanobacterial phycobilisomes[J]. Journal of Structural Biology, 1998, 124(2/3): 311−334. [29] Brejc K, Ficner R, Huber R, et al. Isolation, crystallization, crystal structure analysis and refinement of allophycocyanin from the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis at 2.3 Å resolution[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1995, 249(2): 424−440. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0307 [30] 苏海楠. 蓝藻与红藻中藻胆蛋白的活性构象研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2010.Su Hainan. Study on the active conformations of phycobiliproteins from cyanobacteria and red algae[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2010. [31] 蒲洋. 重组别藻蓝蛋白三聚体结构鉴定及敏化特性的研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013.Pu Yang. Structure determination and sensitization property study of recombinant allophycocyanin trimer[D]. Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013. [32] Van Grondelle R, Novoderezhkin V I. Energy transfer in photosynthesis: experimental insights and quantitative models[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2006, 8(7): 793−807. doi: 10.1039/B514032C [33] Beljonne D, Curutchet C, Scholes G D, et al. Beyond förster resonance energy transfer in biological and nanoscale systems[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2009, 113(19): 6583−6599. doi: 10.1021/jp900708f [34] Holzwarth A R, Bittersmann E, Reuter W, et al. Studies on chromophore coupling in isolated phycobiliproteins: III. Picosecond excited state kinetics and time-resolved fluorescence spectra of different allophycocyanins from Mastigocladus laminosus[J]. Biophysical Journal, 1990, 57: 133−145. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82514-5 [35] O’carra P, Murphy R F, Killilea S D. The native forms of the phycobilin chromophores of algal biliproteins. A clarification[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 1980, 187(2): 303−309. doi: 10.1042/bj1870303 [36] Croce R, Van Amerongen H. Natural strategies for photosynthetic light harvesting[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(7): 492−501. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1555 [37] Rodger A, Nordén B. Circular Dichroism and Linear Dichroism[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996. [38] Sreerama N, Woody R W. Computation and analysis of protein circular dichroism spectra[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2004, 383: 318−351. [39] Woody R W, Tinoco Jr I. Optical rotation of oriented helices. III. calculation of the rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism of the alpha- and 310-helix[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1967, 46(12): 4927−4945. doi: 10.1063/1.1840658 [40] Bhalerao R P, Gillbro T, Gustafsson P. Functional phycobilisome core structures in a phycocyanin-less mutant of cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1995, 45(1): 61−70. doi: 10.1007/BF00032236 [41] Csatorday K, MacColl R, Csizmadia V, et al. Exciton interaction in allophycocyanin[J]. Biochemistry, 1984, 23(26): 6466−6470. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a029 [42] Shiu Y J, Zhang J M, Hayashi M, et al. A transient absorption study of allophycocyanin[J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2002, 114(6): 611−621. doi: 10.1007/BF02708855 [43] Zhao Fuli, Zheng Xiguang, Zhang Jingmin, et al. Model of chromophore coupling in allophycocyanin aggregation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(14): 1224−1229. doi: 10.1007/BF02883230 [44] Donovan B, Walker L A, Yocum C F, et al. Transient absorption studies of the primary charge separation in photosystem II[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(5): 1945−1949. doi: 10.1021/jp951984v [45] Fleming G R, Cho M. Chromophore-solvent dynamics[J]. Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 47(1): 109−134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.47.1.109 [46] Bagchi B, Jana B. Solvation dynamics in dipolar liquids[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(6): 1936−1954. doi: 10.1039/b902048a [47] Cong Peijun, Deuel H P, Simon J D. Using optical coherence to measure the ultrafast electronic dephasing of large molecules in room-temperature liquids[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1993, 212(3/4): 367−373. [48] Wong C Y, Alvey R M, Turner D B, et al. Electronic coherence lineshapes reveal hidden excitonic correlations in photosynthetic light harvesting[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2012, 4(5): 396−404. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1302 [49] Riter R R, Edington M D, Beck W F. Protein-matrix solvation dynamics in the α subunit of C-phycocyanin[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(33): 14198−14205. doi: 10.1021/jp960453j -





 下载:
下载: