Effects of intestinal bacterial biofilms on settlement process of larvae and plantigrades in Mytilus coruscus
-
摘要: 为研究肠道细菌在厚壳贻贝(Mytilus coruscus)幼虫和稚贝生长发育过程中的作用,本研究从成体厚壳贻贝肠道中分离出了10株细菌,通过分别形成单一细菌生物被膜,检验其对厚壳贻贝幼虫和稚贝附着的影响和生物被膜特性。实验结果发现,10株肠道细菌所形成的生物被膜均能诱导厚壳贻贝幼虫和稚贝的附着,但不同种类肠道细菌的诱导能力不同,其中Bacillus sp.4对厚壳贻贝幼虫具有高诱导活性,Phaeobacter sp.1具有低诱导活性;Phaeobacter sp.1对厚壳贻贝稚贝具有高诱导活性,Bacillus sp.4具有低诱导活性。通过比较分析 Bacillus sp.4和Phaeobacter sp.1生物被膜的生物量及胞外产物发现,肠道细菌被膜细菌密度、膜厚和胞外脂类对厚壳贻贝幼虫的附着变态无影响,而胞外蛋白和胞外多糖可以影响幼虫的附着变态;对于厚壳贻贝稚贝的附着,肠道细菌被膜细菌密度、膜厚和胞外α-多糖均能影响其诱导活性,而胞外脂类和胞外蛋白无影响。本研究成果可为提高厚壳贻贝的健康生态养殖相关技术提供相关的指导,为解析生物被膜调控厚壳贻贝附着机制和该物种生态健康养殖提供理论依据。Abstract: Ten strains of bacteria were isolated from the gut of Mytilus coruscus to study its role in the settlement of larvae and plantigrade by forming biofilms. Results showed that the inducing ability of the biofilms formed by ten bacteria were different, although all of them could induce the settlement of larvae and plantigrade. In larvae, Bacillus sp.4 showed high inducing activity, while Phaeobacter sp.1 had low inducing activity. In plantigrades, Phaeobacter sp.1 showed high inducing activity, while Bacillus sp.4 showed low inducing activity. The polysaccharides and proteins from biofilms formed by Bacillus sp.4 and Phaeobacter sp.1 impacted larval settlement and metamorphosis, and the cell density, thickness and extracellular lipids of biofilm showed no effect on inducing activity of larval settlement and metamorphosis. For plantigrades, biofilm’s bacterial density, thickness and extracellular α-polysaccharide could induce plantigrades to the settlement, and the extracellular lipids and proteins of biofilms did not affect the settlement. This study is helpful for improving the healthy ecological culture of M. coruscus and to understand the settlement mechanism of M. coruscus.
-
Key words:
- intestinal bacteria /
- Mytilus coruscus /
- biofilm /
- inducing activity; settlement
-
图 2 不同肠道细菌对厚壳贻贝的诱导作用
A. 对幼虫变态附着的诱导活性;B. 对稚贝附着的诱导活性;不同字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)
Fig. 2 Induction of settlement of Mytilus coruscus on the different intestinal bacterial biofilms
A. Inducing activity of larval settlement and metamorphosis; B. inducing activity of plantigrade settlement; values that are significantly different between each other at p<0.05 are indicated by different letters
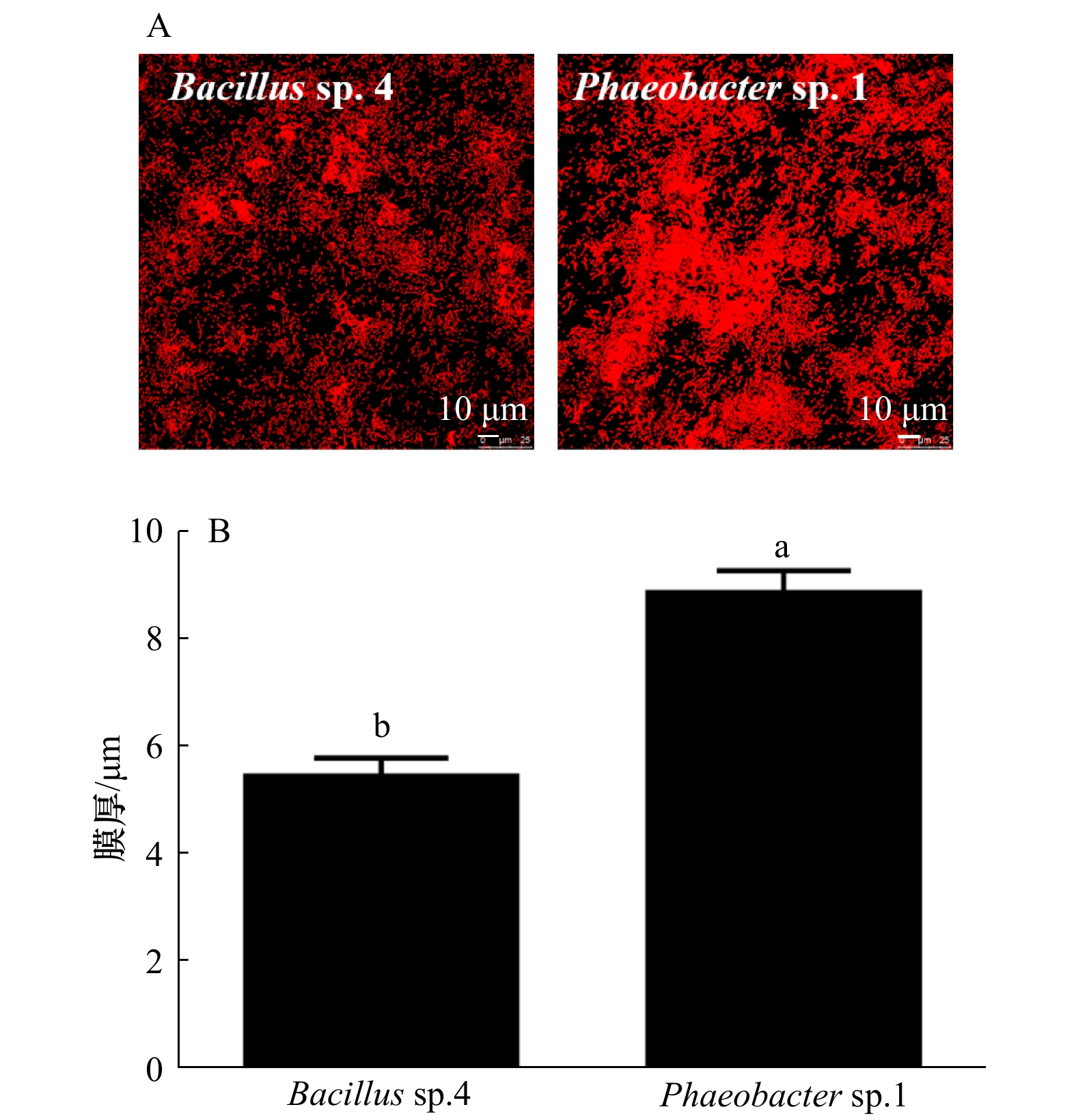
图 6 生物被膜的CLSM图像分析
脂类、蛋白质、α-多糖和β-多糖在生物被膜上的分布(A)和生物量(B);不同字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)
Fig. 6 The analysis of CLSM images of biofilms
The distribution (A) and biovolume (B) of lipids, proteins, α-polysaccharide and β-polysaccharide on BFs; values that are significantly different between each other at p < 0.05 are indicated by different letters
表 1 肠道细菌16S rRNA基因序列分析
Tab. 1 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis of the intestinal bacterial strains
菌株来源 比对菌株 比对序列号 测试菌株 上传序列号 相似度/% 厚壳贻贝肠道 Bacillus sp.4 KF933662 ECSMC2 KU845379 98 厚壳贻贝肠道 Paracoccus sp.2 KJ648494 ECSMC12 KU845388 97 厚壳贻贝肠道 Flavobacterium sp.1 KF933689 ECSMC8 KU845384 99 厚壳贻贝肠道 Arenibacter sp.1 JQ898120 ECSMC15 KU845393 99 厚壳贻贝肠道 Mesoflavibacter sp.1 NR134082 ECSMC14 KU845390 99 厚壳贻贝肠道 Pseudoalteromonas sp.30 NR114190 ECSMB30 KX099925 100 厚壳贻贝肠道 Tenacibaculum sp.3 JN128275 ECSMC3 KU845380 99 厚壳贻贝肠道 Ruegeria sp.2 MF359423 ECSMC5 KU845381 99 厚壳贻贝肠道 Ahrensia sp.1 KJ700633 ECSMC1 KU845378 99 厚壳贻贝肠道 Phaeobacter sp.1 HE584770 ECSMC6 KU845382 100 表 2 细菌密度与诱导活性的相关性分析
Tab. 2 Correlation analyses between the bacterial density and inducing activity
测试菌株 细菌密度 幼虫诱导活性 稚贝诱导活性 r p r p Bacillus sp.4 0.912 9 0.000 1* −0.642 0 0.118 7 Paracoccus sp.2 0.804 1 0.000 1* 0.835 2 0.000 1* Flavobacterium sp.1 0.227 2 0.182 7 0.874 2 0.000 1* Arenibacter sp.1 −0.010 8 0.950 0 0.747 4 0.002 7* Mesoflavibacter sp.1 0.247 0 0.146 5 0.426 1 0.196 3 Pseudoalteromonas sp.30 −0.672 7 0.000 1* 0.638 7 0.002 2* Tenacibaculum sp.3 0.260 4 0.125 0 0.174 7 0.237 4 Ruegeria sp.2 −0.461 9 0.004 6* 0.791 6 0.000 1* Ahrensia sp.1 0.344 1 0.039 9* 0.277 4 0.208 5 Phaeobacter sp.1 0.630 7 0.172 5 0.965 4 0.000 1* 注: *表示差异显著(p<0.05)。 表 3 本实验中肠道细菌的遗传距离
Tab. 3 Genetic distances of intestinal bacterial in tested
测试菌株 2 12 8 15 14 30 3 5 1 6 2 12 0.267 8 0.254 0.011 15 0.319 0.286 0.308 14 0.317 0.307 0.294 0.097 30 0.265 0.194 0.221 0.303 0.290 3 0.336 0.285 0.305 0.118 0.099 0.274 5 0.253 0.063 0.076 0.118 0.314 0.230 0.311 1 0.255 0.144 0.117 0.303 0.295 0.217 0.292 0.139 6 0.303 0.102 0.084 0.310 0.315 0.237 0.317 0.039 0.138 注: 1, 2, ···, 30 分别表示菌株ECSMC1, ECSMC2, ···, ECSMC30。 表 4 膜厚与诱导活性的相关性分析
Tab. 4 Correlation analyses between the biofilm thickness and inducing activity
测试菌株 生物被膜膜厚 幼虫诱导活性 稚贝诱导活性 r p r p Bacillus sp.4 0.376 4 0.108 7 0.264 2 0.075 6 Phaeobacter sp.1 0.375 3 0.115 4 0.886 4 0.000 1* 注: *表示差异显著(p<0.05)。 表 5 胞外产物与幼虫诱导活性的相关性分析
Tab. 5 Correlation analyses between extracellular product and inducing activity of larvae
测试菌株 生物被膜胞外产物生物量 脂类 蛋白质 α-多糖 β-多糖 r p r p r p r p Bacillus sp.4 0.363 4 0.094 2 0.486 5 0.000 1* 0.886 5 0.000 1* 0.753 2 0.000 1* Phaeobacter sp.1 0.484 5 0.265 8 −0.864 3 0.028 7* −0.642 4 0.147 5 −0.448 6 0.084 5 注: *表示差异显著(p < 0.05)。 表 6 胞外产物与稚贝诱导活性的相关性分析
Tab. 6 Correlation analyses between the extracellular product and inducing activity of plantigrade
测试菌株 生物被膜胞外产物生物量 脂类 蛋白质 α-多糖 β-多糖 r p r p r p r p Bacillus sp.4 0.765 3 0.219 5 0.592 5 0.1209 −0.764 3 0.037 1* −0.343 6 0.129 1 Phaeobacter sp.1 0.464 2 0.107 5 0.556 3 0.0753 0.669 8 0.044 3* 0.562 1 0.085 9 注: *表示差异显著(p < 0.05)。 -
[1] 常亚青. 贝类增养殖学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007.Chang Yaqing. Stock Enhancement and Culture in Mollusks[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2007. [2] 杨金龙, 郭行磐, 陈芋如, 等. 中湿度表面的海洋细菌对厚壳贻贝稚贝附着的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2015, 39(3): 421−428.Yang Jinlong, Guo Xingpan, Chen Yuru, et al. Effects of bacterial biofilms formed on middle wettability surfaces on settlement of plantigrades of the mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(3): 421−428. [3] 李太武. 海洋生物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2013.Li Taiwu. Marine Biology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2013. [4] 孙俊杰, 张显, 郭行磐, 等. 硅烷化表面海洋细菌对厚壳贻贝稚贝附着的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2015, 39(10): 1530−1538.Sun Junjie, Zhang Xian, Guo Xingpan, et al. Effects of marinebacteria from silanizing surfaces on plantigrade settlement of the mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(10): 1530−1538. [5] 张义浩, 赵盛龙. 嵊山列岛贻贝养殖种类生长发育调查[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2003, 22(1): 67−73.Zhang Yihao, Zhao Shenglong. Mussel species and growth developing investigation around Shengshan archipelago[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2003, 22(1): 67−73. [6] Dobretsov S, Qian Peiyuan. Facilitation and inhibition of larval attachment of the bryozoan Bugula neritina in association with mono-species and multi-species biofilms[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2006, 333(2): 263−274. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2006.01.019 [7] 柯才焕, 周时强, 田越, 等. 盘鲍幼体附着诱导的研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 2001, 20(1): 9−14.Ke Caihuan, Zhou Shiqiang, Tian Yue, et al. Induction of settlement in Japanese abalone, Haliotis discus discus[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2001, 20(1): 9−14. [8] Jouuchi T, Satuito C G, Kitamura H. Sugar compound products of the periphytic diatom Navicula ramosissima induce larval settlement in the barnacle, Amphibalanus amphitrite[J]. Marine Biology, 2007, 152(5): 1065−1076. doi: 10.1007/s00227-007-0753-6 [9] 梁箫, 童欢, 彭莉华, 等. 纤维素对海洋细菌生物被膜形成及厚壳贻贝幼虫附着变态的调控[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2020, 35(1): 75−82.Liang Xiao, Tong Huan, Peng Lihua, et al. Regulation of formation of biofilms and larval settlement and metamorphosis of mussel Mytilus coruscus by cellulose[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2020, 35(1): 75−82. [10] 梁箫, 刘红雨, 杨丽婷, 等. 弧菌生物被膜的动态演替对厚壳贻贝附着的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2020, 44(1): 118−129.Liang Xiao, Liu Hongyu, Yang Liting, et al. Effects of dynamic succession of Vibrio biofilms on settlement of the musselMytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2020, 44(1): 118−129. [11] 黄道芬, 梁箫, 彭莉华, 等. 不同来源海洋弧菌微生物被膜对厚壳贻贝稚贝附着的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2017, 41(7): 1140−1147.Huang Daofen, Liang Xiao, Peng Lihua, et al. Effects of Vibrio biofilms of different sources on settlement of plantigrades of the mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2017, 41(7): 1140−1147. [12] Peng Lihua, Liang Xiao, Xu Jiakang, et al. Monospecific biofilms of Pseudoalteromonas promote larval settlement and metamorphosis of Mytilus coruscus[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 2577. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59506-1 [13] 杨娜, 梁箫, 彭莉华, 等. 肠道细菌对厚壳贻贝稚贝附着的作用研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(11): 45−54. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170626001Yang Na, Liang Xiao, Peng Lihua, et al. Effects of gut bacteria on the settlement of spats of Mytilus coruscus[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(11): 45−54. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170626001 [14] 张偲, 张长生, 田新朋, 等. 中国海洋微生物多样性研究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2010, 25(6): 651−658.Zhang Si, Zhang Changsheng, Tian Xinpeng, et al. The study of diversities of marine microbes in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010, 25(6): 651−658. [15] 张庆芳, 杨超, 于爽, 等. 黄海海域海洋沉积物细菌多样性分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(2): 370−378.Zhang Qingfang, Yang Chao, Yu Shuang, et al. Bacterial diversity of marine sediments in the Yellow Sea[J]. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(2): 370−378. [16] Li Yifeng, Chen Yanwen, Xu Jiakang, et al. Temperature elevation and Vibrio cyclitrophicus infection reduce the diversity of haemolymph microbiome of the mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 16391. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52752-y [17] Dong Pengsheng, Guo Haipeng, Wang Yanting, et al. Gastrointestinal microbiota imbalance is triggered by the enrichment of Vibrio in subadult Litopenaeus vannamei with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease[J]. Aquaculture, 2021, 533: 736199. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736199 [18] Riquelme C, Toranzo A E, Barja J L, et al. Association of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio alginolyticus with larval mortalities of scallop (Argopecten purpuratus)[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 1996, 67(3): 213−218. doi: 10.1006/jipa.1996.0035 [19] Ardiç N, Ozyurt M. Case report: otitis due to Vibrio alginolyticus[J]. Mikrobiyoloji Bülteni, 2004, 38(1/2): 145−148. [20] 封会茹, 游京蓉, 刘玉堂, 等. 溶藻弧菌引起暴发型食物中毒的病原学研究[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2003, 15(4): 331−334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8456.2003.04.016Feng Huiru, You Jingrong, Liu Yutang, et al. Research of one abrupt food poisoning caused byVibrio alginolyticus[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2003, 15(4): 331−334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8456.2003.04.016 [21] 白瑶, 叶淑瑶, 江涛, 等. 水产品中创伤弧菌检测方法建立与应用[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2018, 30(6): 592−597.Bai Yao, Ye Shuyao, Jiang Tao, et al. Development and application of detection method for Vibrio vulnificus in aquatic products[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2018, 30(6): 592−597. [22] 杨春晓, 方艳梅, 魏泉德, 等. 珠海市海产品中2种致病性弧菌污染状况[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2018, 28(14): 1784−1785, 1792.Yang Chunxiao, Fang Yanmei, Wei Quande, et al. Contamination of two kinds of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood in Zhuhai[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2018, 28(14): 1784−1785, 1792. [23] Eckburg P B, Bik E M, Bernstein C N, et al. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5728): 1635−1638. doi: 10.1126/science.1110591 [24] He Qi, Wang Lin, Wang Fan, et al. Microbial fingerprinting detects intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in zebrafish models with chemically-induced enterocolitis[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2013, 13(1): 289. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-289 [25] Bates J M, Mittge E, Kuhlman J, et al. Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation[J]. Developmental Biology, 2006, 297(2): 374−386. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.05.006 [26] Li Yifeng, Guo Xingpan, Yang Jinlong, et al. Effects of bacterial biofilms on settlement of plantigrades of the mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Aquaculture, 2014, 433(6): 434−441. [27] Yang Jinlong, Shen Peijing, Liang Xiao, et al. Larval settlement and metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus coruscus in response to monospecific bacterial biofilms[J]. Biofouling, 2013, 29(3): 247−259. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2013.764412 [28] 周轩, 郭行磐, 陈芋如, 等. 低湿度表面的海洋附着细菌对厚壳贻贝附着的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2015, 30(1): 30−35. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-1388.2015.01.006Zhou Xuan, Guo Xingpan, Chen Yuru, et al. Effects of bacterial biofilms formed on low surface wettability on settlement of plantigrades of the mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2015, 30(1): 30−35. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-1388.2015.01.006 [29] Han Shaofeng, Liu Yuchun, Zhou Zhigang, et al. Analysis of bacterial diversity in the intestine of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) based on 16S rDNA gene sequences[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2010, 42(1): 47−56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02543.x [30] Cahill M M. Bacterial flora of fishes: a review[J]. Microbial Ecology, 1990, 19(1): 21−41. doi: 10.1007/BF02015051 [31] Bao Weiyang, Yang Jinlong, Satuito C G, et al. Larval metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in response toAlteromonas sp.1: evidence for two chemical cues?[J]. Marine Biology, 2007, 152(3): 657−666. doi: 10.1007/s00227-007-0720-2 [32] Tran C, Hadfield M G. Larvae of Pocillopora damicornis (Anthozoa) settle and metamorphose in response to surface-biofilm bacteria[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2011, 433: 85−96. doi: 10.3354/meps09192 [33] Liang Xiao, Zhang Xiukun, Peng Lihua, et al. The flagellar gene regulates biofilm formation and mussel larval settlement and metamorphosis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 710. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030710 [34] Peng Lihua, Liang Xiao, Chang Ruiheng, et al. A bacterial polysaccharide biosynthesis-related gene inversely regulates larval settlement and metamorphosis of Mytilus coruscus[J]. Biofouling, 2020, 36(7): 753−765. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2020.1807520 [35] 高伟, 郭行磐, 徐嘉康, 等. 微生物被膜形成因子及其对厚壳贻贝附着的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2017, 32(4): 405−409.Gao Wei, Guo Xingpan, Xu Jiakang, et al. Effects of environmental factors on formation of bacterial biofilms and settlement of plantigrades of mussel Mytilus coruscus[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2017, 32(4): 405−409. -




 下载:
下载: