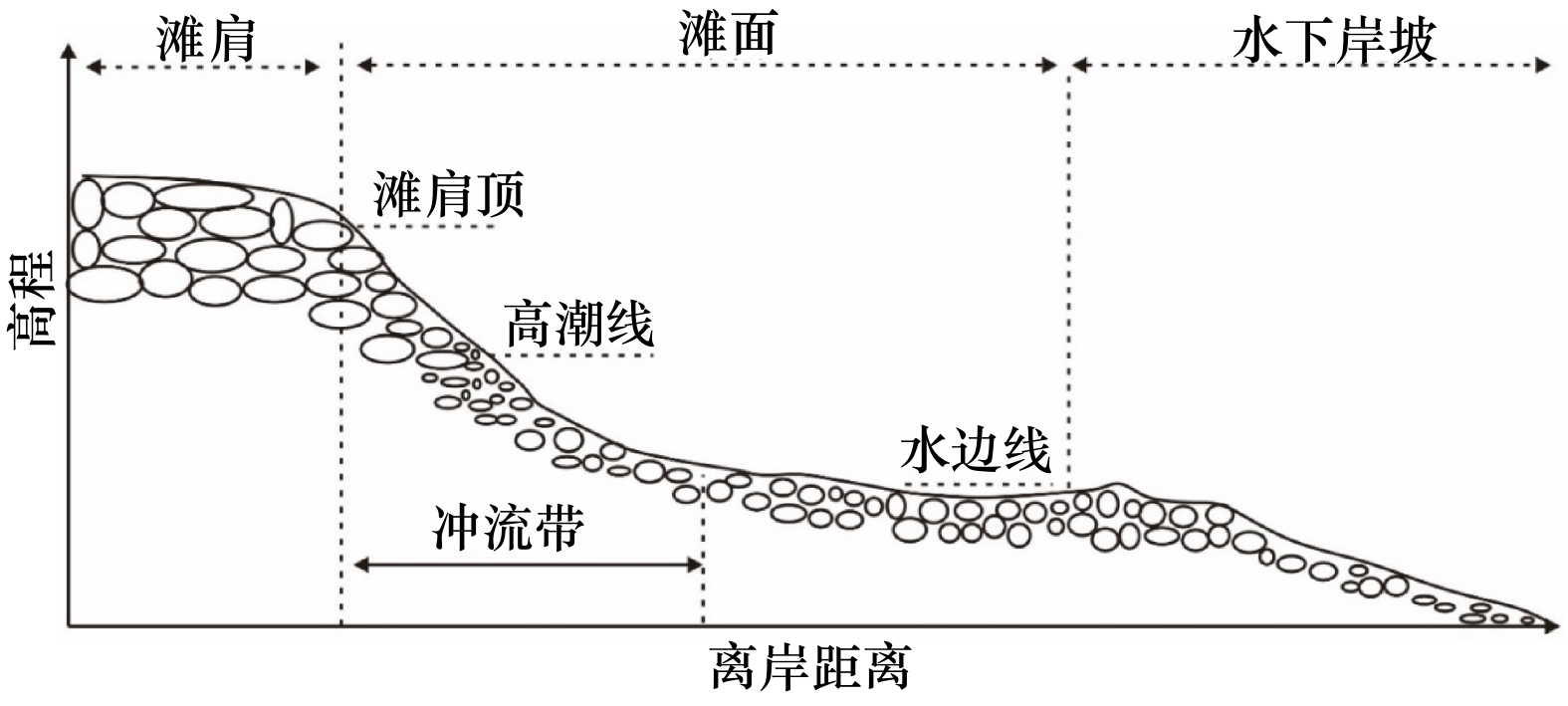
Morphological characteristics based on digital images of gravels from gravels beaches in the Changshan Island, Shandong Province
-
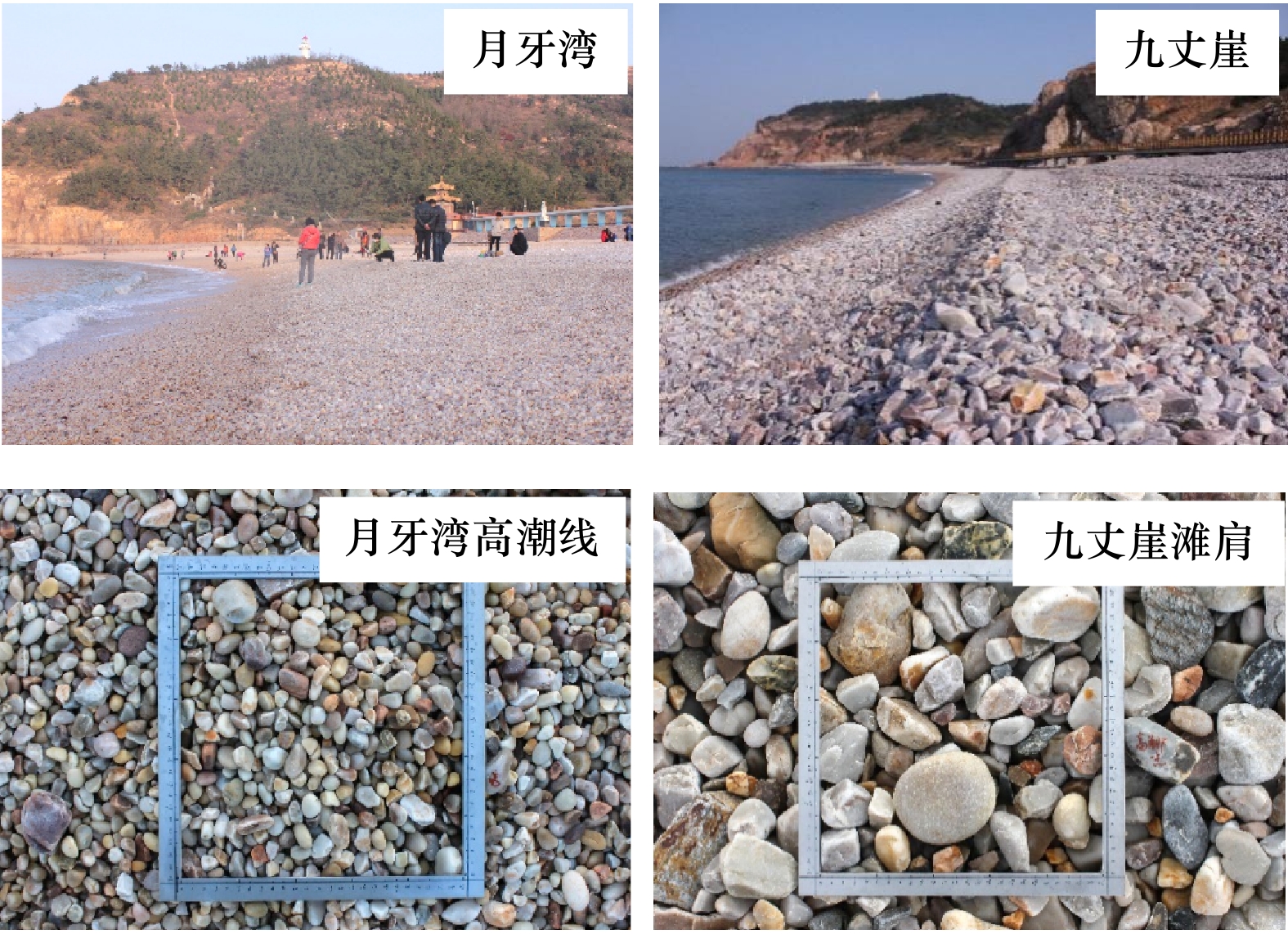
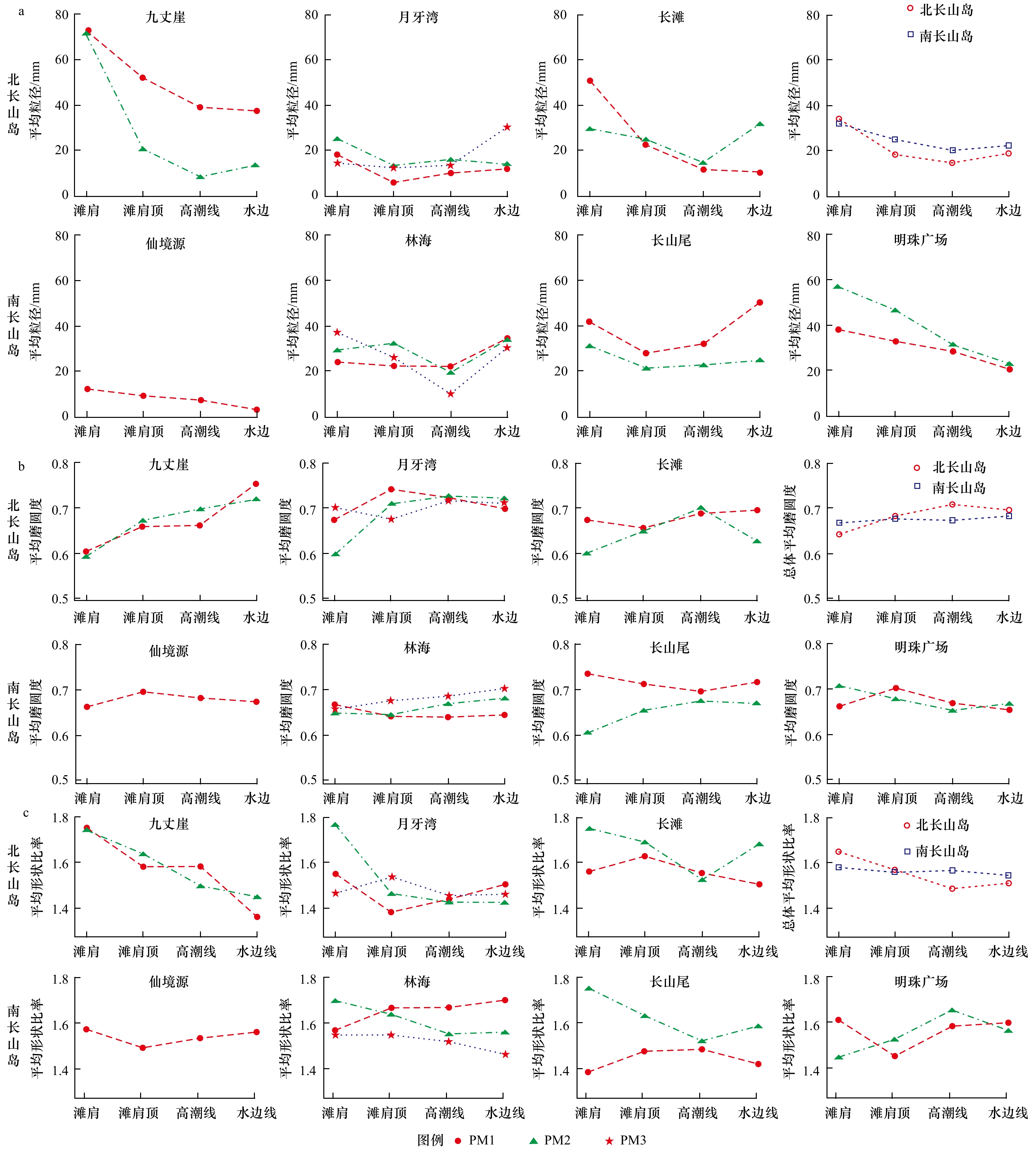
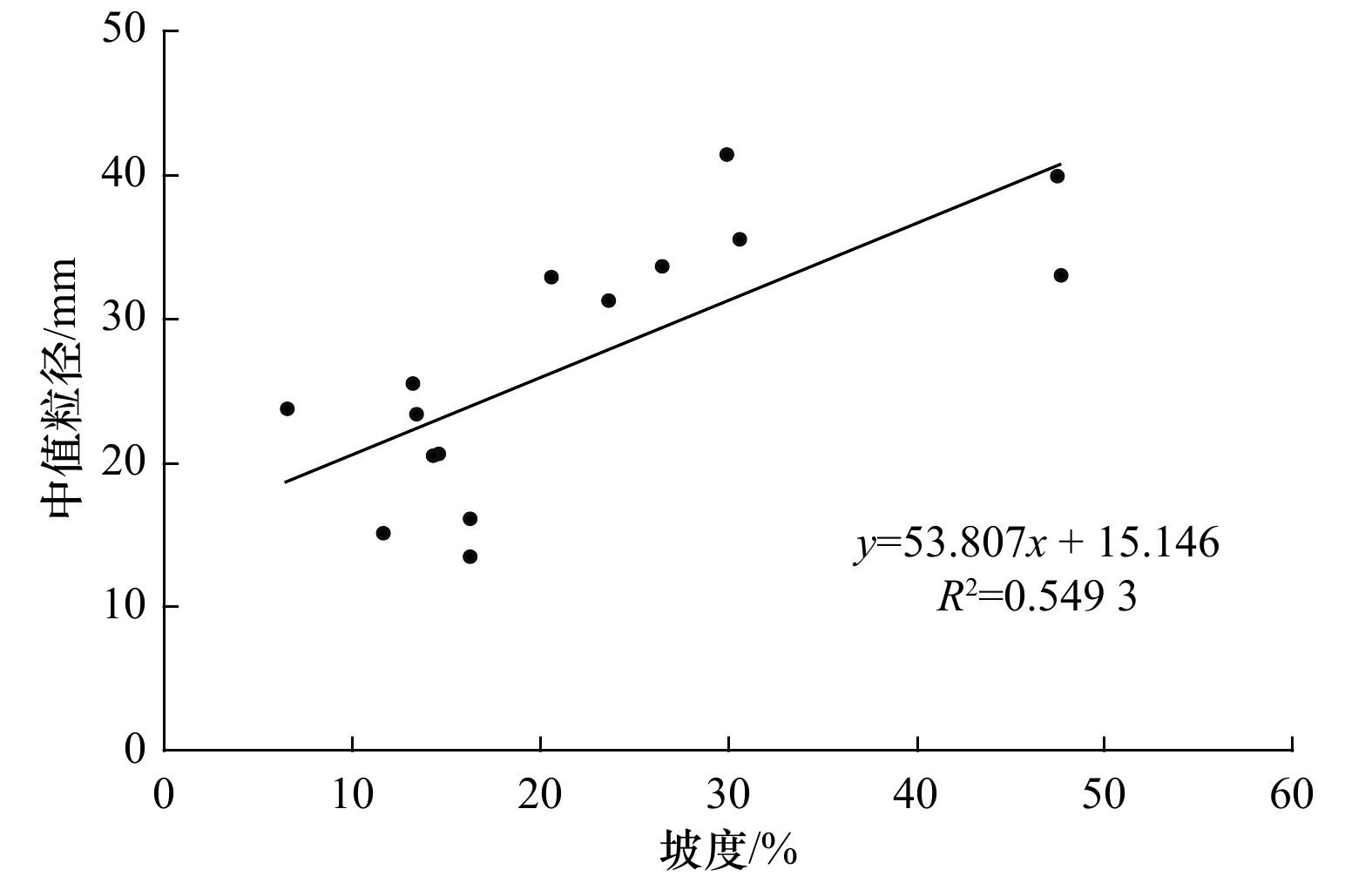
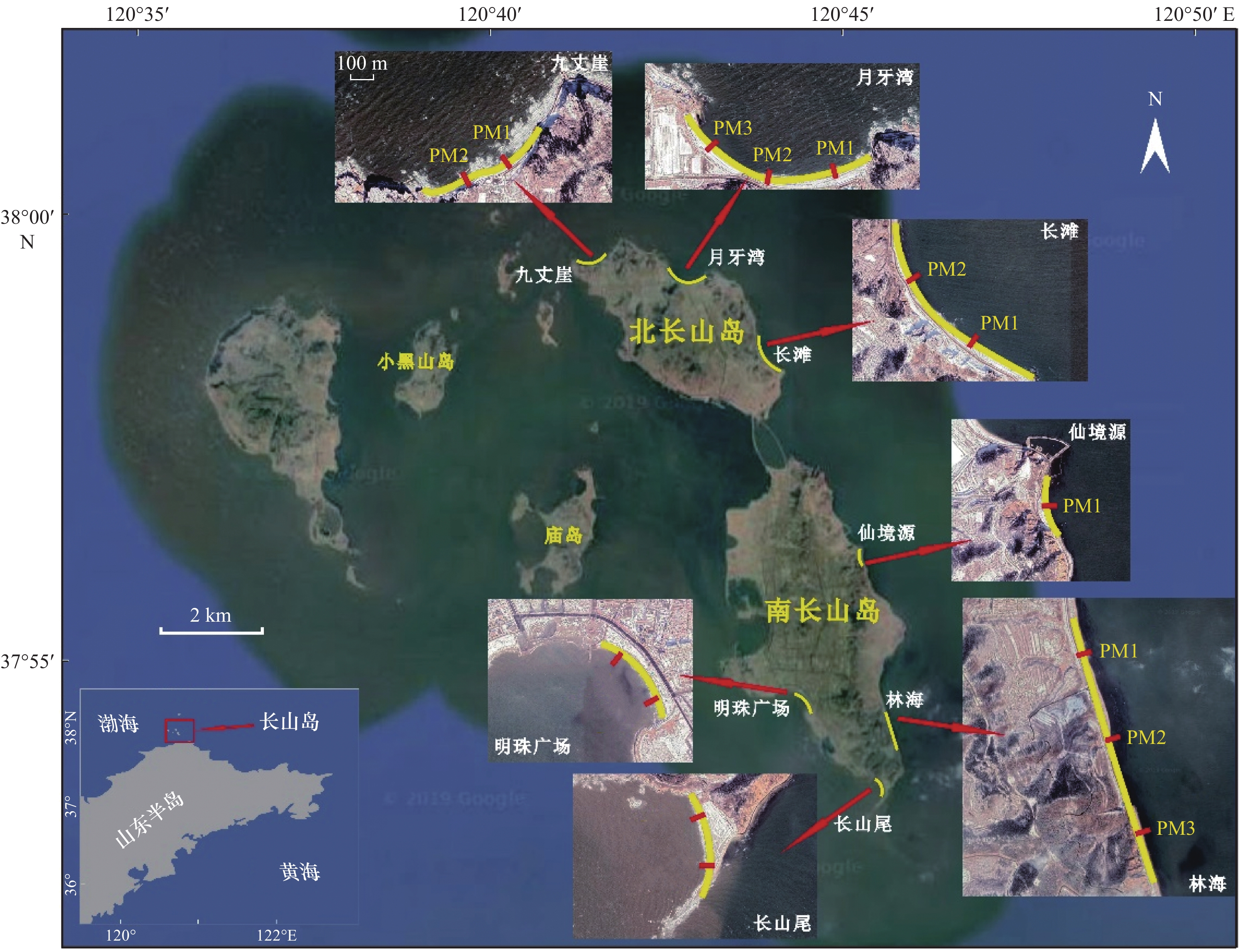
摘要: 天然砾石海滩作为一种高能环境下的海岸堆积体,因其粒径粗、孔隙度大等特征,是良好的海岸防护屏障。了解砾石海滩形成过程离不开砾石形貌这一重要参数,但要快速、准确获得大量砾石的定量参数比较困难。本文对山东北长山岛3个砾石海滩(九丈崖、月牙湾、长滩)、南长山岛的4个砾石海滩(仙境源、林海、长山尾和明珠广场)进行现场剖面测量并采集砾石样品及砾石图像,应用ImageJ软件对砾石进行原位无干扰数字图像测算,可以快速大量分析砾石粒径、磨圆度等形貌参数。结果显示:砾石的粒径范围为4~79 mm,主要集中在中砾,各海滩分选较好;其中,北长山岛海滩的砾石平均粒径略小于南长山岛,北长山岛九丈崖海滩的砾石平均粒径最大,南长山岛的仙境源海滩砾石平均粒径最小。向海方向从滩肩到高潮线平均粒径逐渐减小,但在水边线处增大。砾石磨圆度介于0.59~0.75之间,等级均为圆状,砾石海滩均已达到较成熟阶段;其中北长山岛的月牙湾海滩砾石磨圆最好,长滩海滩砾石的磨圆最差,由陆向海磨圆度值呈增大的趋势。形状比率范围介于1.36~1.77之间,与磨圆度呈明显负相关(R2=0.98),砾石由陆向海从长条状渐变为椭圆状。南、北长山岛的砾石海滩的砾石形貌受到物源、动力条件和人为活动的影响。研究区砾石海滩坡度范围为16%~35%,海滩坡度与沉积物粒径呈正相关。Abstract: As a kind of coastal accumulation body in high-energy environment, natural gravel beach is a good coastal protection barrier due to its coarse particle size and large porosity. The gravel morphology is an important parameter to understand the gravel formation process, but it is difficult to obtain the quantitative parameters of a large number of gravels quickly and accurately. In this study, we surveyed three gravel beaches (Jiuzhangya, Yueyawan, Changtan) in the Beichangshan Island, four gravel beaches (Xianjingyuan, Linhai, Changshanwei and Mingzhuguangchang) in the Nanchangshan Island in the Shandong Province. We measured beach profile, collected gravel samples and took gravel images. Using the software ImageJ for digital image measurement in situ without interference, we can quickly obtain a large number of gravel morphologic parameters, including particle size, grinding roundness and shape ratio. The results show that the range of the particle size is 4−79 mm, which was mainly pebbles. The average particle size of the beach in the Beichangshan Island is slightly smaller than that in the Nanchangshan Island, with the largest average particle size of gravels in the Jiuzhangya Beach of the Beichangshan Island and the smallest one in the Xianjingyuan Beach of the Nanchangshan Island. From beach berm to the high tidal line, the average particle size decreases gradually, but increases at waterline. The range of roundness of gravel is 0.59–0.75, and the grade is round. The gravel beaches have reached a relatively mature stage based on roundness, with the best roundness in the Yueyawan Beach and the worst roundness in the Changtan Beach of the Beichangshan Island. The gravel roundness increases from land to sea. The shape ratio ranges from 1.36 to 1.77, which is negatively correlated with the gravel roundness (R2=0.98). The gravel gradually changed from long strip to elliptic shape from land to sea. The gravel beaches morphology of the Changshan Island is affected by the provenances, dynamic conditions and human activities. The slope range of the gravel beach in the study area is 16%−35%, and they are positively correlated with the gravel particle size.
-
Key words:
- gravel beach /
- digital image /
- morphologic characteristics /
- control factors
-
表 1 软件统计得出的砾石颗粒形状参数(据文献[17])
Tab. 1 Gravel particle shape parameters obtained from software statistics (from reference [17])
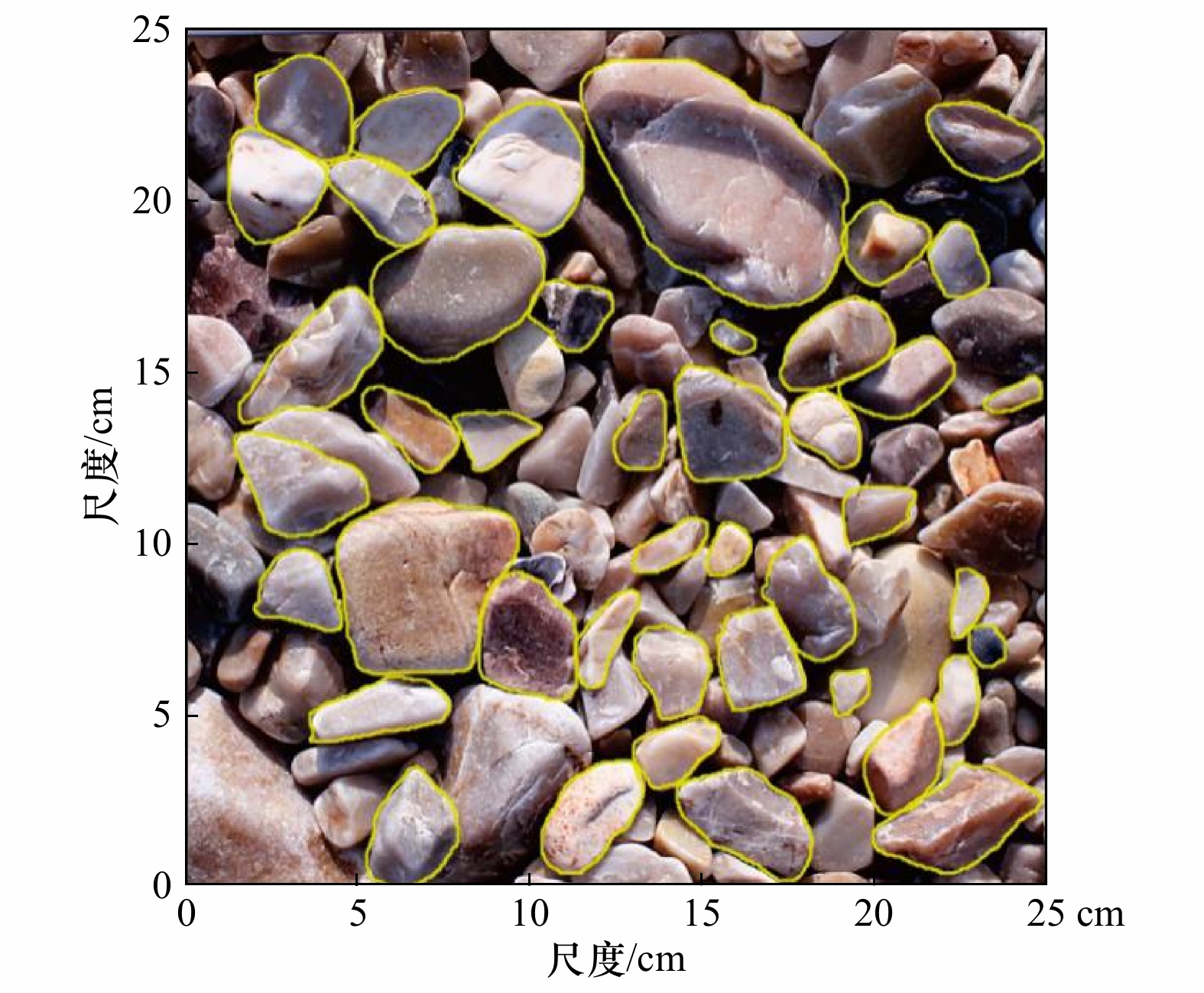
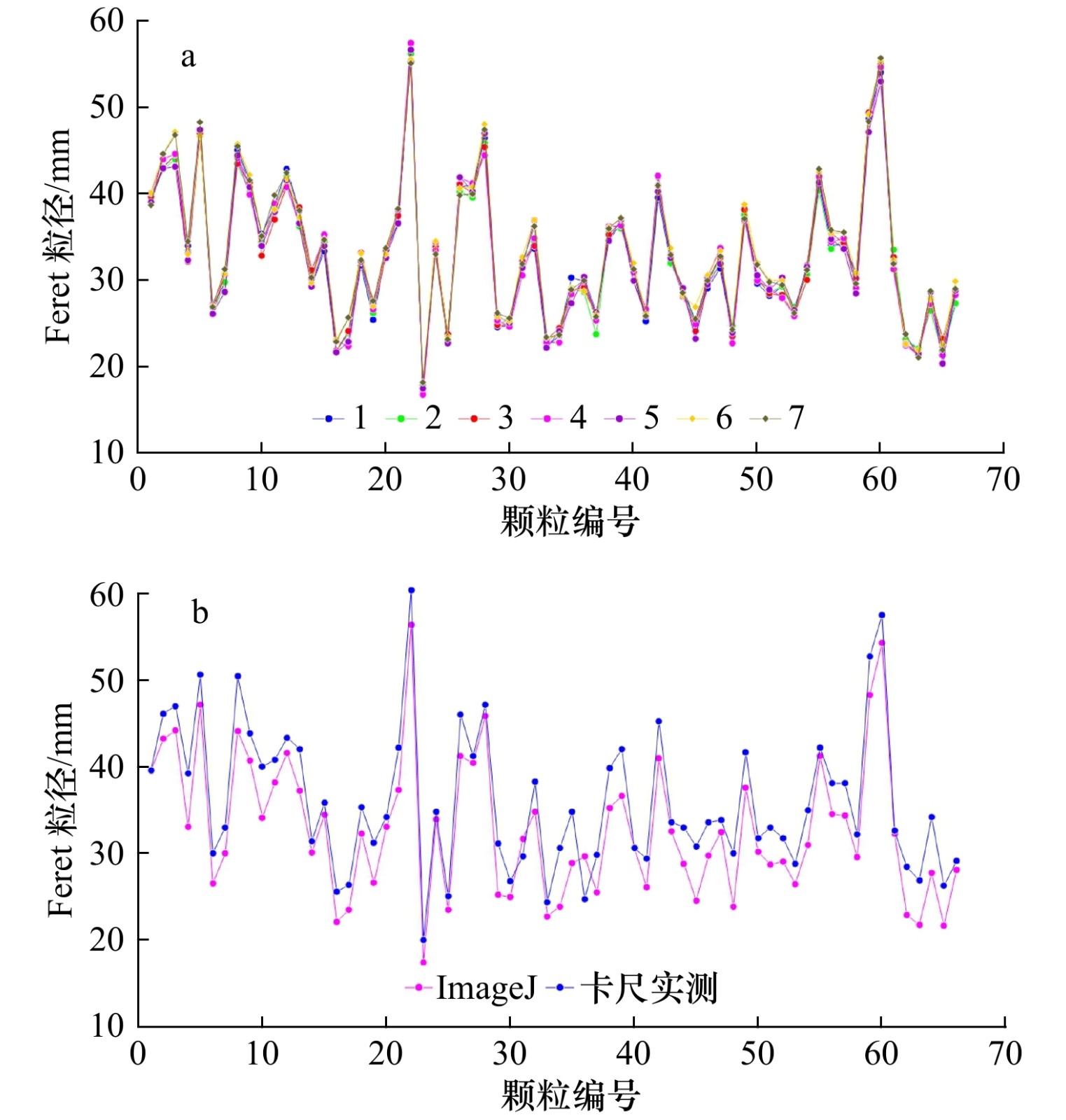
参数 计算方法 说明 颗粒面积(A) 软件自动统计所选颗粒包含的像素面积并转换为实际面积 以mm2表示 颗粒周长(P) 软件自动统计所选颗粒边缘像素长度并转换为实际长度 以mm表示 颗粒粒径(DF) ${D}_{{\rm{F}}}=\sqrt{{M}_{\min}^{2}+{M}_{\max}^{2}}$ 以Feret粒径(DF)表示,$ {M}_{\min} $和$ {M}_{\max} $分别为最小和最大Feret直径* 形状比率(AR) $ AR=\dfrac{{l}_{\max}}{{l}_{\min}} $ 颗粒长轴($ {l}_{\max} $)与短轴($ {l}_{\min} $)之比 磨圆度(RD) $ RD=\dfrac{4{\text π}\times A}{{P}^{2}} $ 颗粒的磨圆程度,圆形颗粒为1.0 注:*表示计算Feret直径时首先确定颗粒投影面的重心位置,然后计算通过重心位置的各个方向的直径大小,从而确定最大Feret直径($ {M}_{\max} $)与最小Feret直径($ {M}_{\min} $),这两个值表明了颗粒的形状特征和最小过筛粒径[26]。 表 2 砾石滩基本信息
Tab. 2 Basic information of different gravel beaches
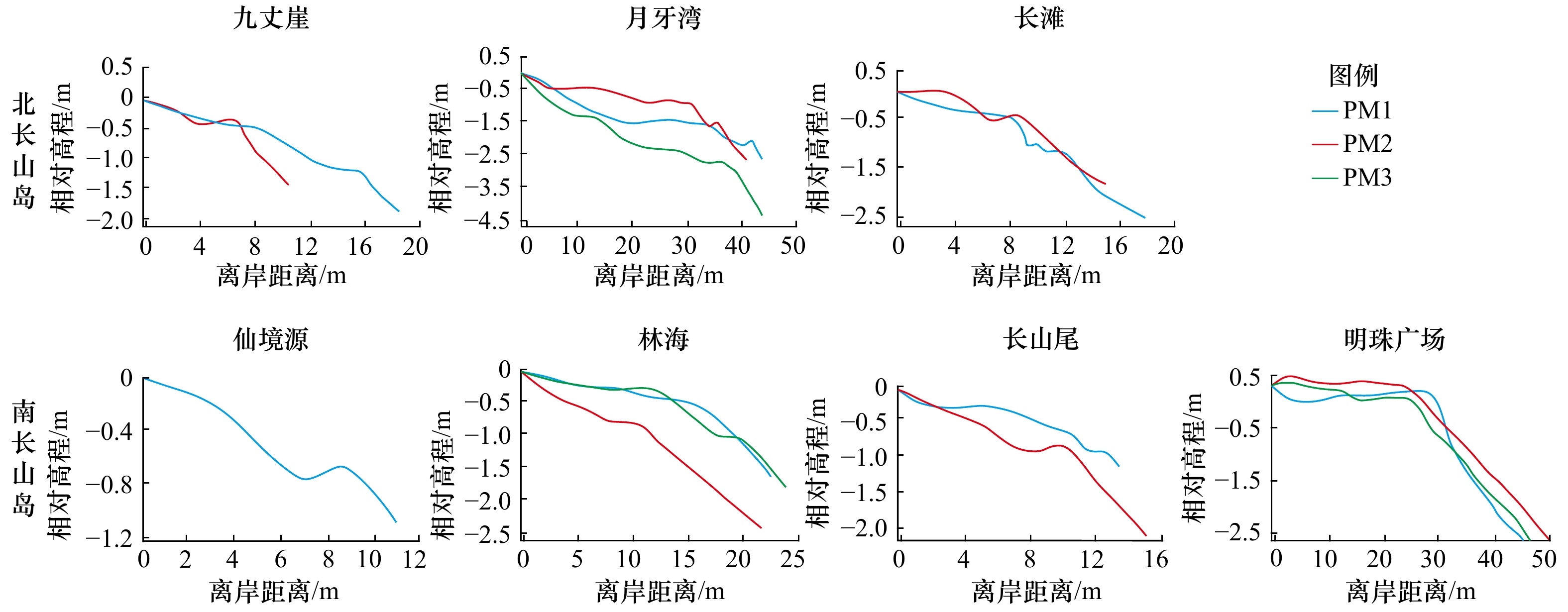
海岛 海滩 海滩长度/m 海滩宽度/m 朝向 平均坡度 北长山岛 九丈崖 620 50 NW 35% 月牙湾 954 50 N 21% 长滩 978 30 NE 25% 平均值 851 43 27% 南长山岛 仙境源 240 20 NE 16% 林海 480 30 E 28% 明珠广场 450 60 S 33% 长山尾 400 28 E 33% 平均值 523 46 28% 表 3 各海滩沉积物粒度参数及分布
Tab. 3 Grain size parameters and distribution of gravels at different beaches
海岛 海滩名称 平均粒径/mm 中值粒径/mm 分选系数 偏态 峰态 平均值 粒级* 平均值 等级 平均值 等级 平均值 等级 北长山岛 九丈崖 32.49 中砾 32.49 0.63 较好 0.05 近对称 1.01 中等 月牙湾 14.47 中砾 13.79 0.53 较好 −0.01 近对称 0.96 中等 长滩 22.96 中砾 22.40 0.59 较好 0.05 近对称 0.85 宽 平均 23.31 中砾 22.89 0.58 较好 0.03 近对称 0.94 中等 南长山岛 林海 25.32 中砾 25.66 0.50 较好 −0.06 近对称 0.97 中等 明珠广场 31.58 中砾 32.69 0.69 较好 −0.09 近对称 1.00 中等 长山尾 31.09 中砾 32.06 0.55 较好 0.10 近对称 1.04 中等 仙境源 7.72 细砾 7.69 0.51 较好 −0.02 近对称 0.88 宽 平均 24.23 中砾 24.52 0.56 较好 −0.02 近对称 0.97 中等 注:*粒级划分及命名参考GB/T 12763.8–2007 《海洋调查规范第8部分海洋地质地球物理调查》。 -
[1] Haslett S K. Coastal Systems[M]. London and New York: Routledge, 2000: 218. [2] 王爱军, 高抒, 杨旸. 浙江朱家尖岛砾石海滩沉积物分布及形态特征[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 40(6): 747−759.Wang Aijun, Gao Shu, Yang Yang. Sediment distribution and shape characteristics of gravel beaches, Zhujiajian Island, Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2004, 40(6): 747−759. [3] Johnson D W. Shore Processes and Shoreline Development[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1919: 39−40. [4] Ciavola P, Castiglione E. Sediment dynamics of mixed sand and gravel beaches at short time-scales[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2009, 56(1): 1751−1755. [5] Masselink G, Russell P, Blenkinsopp C, et al. Swash zone sediment transport, step dynamics and morphological response on a gravel beach[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 274(1/4): 50−68. [6] Harley M D, Andriolo U, Armaroli C, et al. Shoreline rotation and response to nourishment of a gravel embayed beach using a low-cost video monitoring technique: San Michele-Sassi Neri, Central Italy[J]. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 2014, 18(5): 551−565. [7] Stark N, Hay A E. Pebble and cobble transport on a steep, mega-tidal, mixed sand and gravel beach[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 382: 210−223. [8] 于跃, 蔡锋, 张挺, 等. 人工砾石海滩变化及输移率研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2017, 35(5): 79−87.Yu Yue, Cai Feng, Zhang Ting, et al. Study on evolution and transport rate of artificial gravel beach[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2017, 35(5): 79−87. [9] 徐杨杨, 庄振业, 赵东波, 等. 山东长岛砾石海滩侵蚀及修复[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(5): 22−28.Xu Yangyang, Zhuang Zhenye, Zhao Dongbo, et al. Erosion and restoration of the gravel beach around Long Island, Shandong[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(5): 22−28. [10] 束芳芳, 蔡锋, 戚洪帅, 等. 不同沉积物养护海滩对台风响应的差异性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(7): 103−115.Shu Fangfang, Cai Feng, Qi Hongshuai, et al. Study on various response to typhoon of nourished beaches with different sediments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(7): 103−115. [11] Shu Fangfang, Cai Feng, Qi Hongshuai, et al. Morphodynamics of an artificial cobble beach in Tianquan Bay, Xiamen, China[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2019, 18(4): 868−882. [12] Han Min, Yang D Y, Yu J, et al. Typhoon impact on a pure gravel beach as assessed through gravel movement and topographic change at Yeocha Beach, south coast of Korea[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2017, 33(4): 889−906. [13] 陶金雨, 张昌民, 郭旭光, 等.磨圆度定量表征在扇三角洲沉积微相判别中的应用——以玛湖凹陷百口泉组砾岩为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(05): 956-965.Tao Jinyu, Zhang Changmin, Guo Xuguang, et al. Application of quantitative roundness characterization to identify sedimentary microfacies in fan delta deposits: A case study of conglomerates in the Baikouquan Formation, Mahu Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(05): 956-965. [14] Powers M C. A new roundness scale for sedimentary particles[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1953, 23(2): 117−119. [15] Powers M C. Comparison chart for estimating roundness and sphericity[J]. AGI Data Sedimentary Petrology, 1982, 23(2): 117−119. [16] 王献礼, 张永双, 曲永新, 等. 基于数字图像处理技术的冰川堆积物粒度分析——以川西贡嘎山冰川堆积物为例[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(2/3): 469−475.Wang Xianli, Zhang Yongshuang, Qu Yongxin, et al. Grain size analysis of glacial deposits based on digital image processing technology[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(2/3): 469−475. [17] 钱广强, 董治宝, 罗万银, 等. 基于数字图像的中国西北地区戈壁表面砾石形貌特征研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(3): 625−633. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2013.00365Qian Guangqiang, Dong Zhibao, Luo Wanyin, et al. Gravel morphometric analysis based on digital images of different Gobi surfaces in Northwestern China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2014, 34(3): 625−633. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2013.00365 [18] 赵岩, 郑娇玉, 郭鹏, 等. ImageJ软件在泥石流固体颗粒分析中的应用[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(6): 877−881.Zhao Yan, Zheng Jiaoyu, Guo Peng, et al. Applications of the ImageJ software in analysis of solid grains in a debris flow gully[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2015, 51(6): 877−881. [19] 曹家欣. 山东庙岛列岛与蓬莱沿岸地貌[J]. 海洋学报, 1989, 11(5): 603−610.Cao Jiaxin. Miaodao Islands and Penglai Coast landforms in Shandong Province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1989, 11(5): 603−610. [20] 葛孚刚, 王志才, 王纪强, 等. 山东省长岛第四纪断裂活动初步研究[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 2010, 26(4): 13−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2010.04.003Ge Fugang, Wang Zhicai, Wang Jiqiang, et al. Preliminary study of quaternary faults on Changdao Island of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, 2010, 26(4): 13−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2010.04.003 [21] 高瑞华. 渤海海峡大风气候特征的初步分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2007: 25-27.Gao Ruihua. A preliminary analysis of the climatic characteristics on the gale over Bohai Straits[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2007: 25–27. [22] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 23.The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Bohai Geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985: 23. [23] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志(第三分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991: 186−189.Compilation Committee of China Bay. Journal of China Bay (Volume 3)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1991: 186−189. [24] 姜胜辉. 南、北长山岛海域沉积动力特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009: 12-16.Jiang Shenghui. Study of sedimentary dynamic character at the South and the North Changshan Islands Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009: 12−16. [25] 李福林, 夏东兴, 王文海, 等. 登州浅滩的形成、动态演化及其可恢复性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(6): 65−73.Li Fulin, Xia Dongxing, Wang Wenhai, et al. Discussion on the evolution cause and its recovery for the Dengzhou Shoal, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(6): 65−73. [26] Merkus H G, Bellantone M. Particle Size Measurements: Fundamentals, Practice, Quality[M]. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer, 2009: 533. [27] 蔡锋, 苏贤泽, 曹惠美, 等. 华南砂质海滩的动力地貌分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2005, 27(2): 106−114.Cai Feng, Su Xianze, Cao Huimei, et al. Analysis on morphodynamics of sandy beaches in South China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2005, 27(2): 106−114. [28] Kuenen P H. Experimental abrasion of pebbles: 2. rolling by current[J]. Journal of Geology, 1956, 64(4): 336-368. [29] 谢宗荣. 庙岛群岛地质的新认识[J]. 地质论评, 1959, 19(5): 226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1959.05.017Xie Zongrong. A new geological understanding for Miaodao Islands[J]. Geological Review, 1959, 19(5): 226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1959.05.017 [30] 金翔龙, 郑开云. 庙岛群岛地质的初步观察[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1964, 6(4): 364−370.Jin Xianglong, Zheng Kaiyun. A preliminary study on the geology of Miaodao Islands[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1964, 6(4): 364−370. [31] 崔金瑞, 夏东兴. 山东半岛海岸地貌与波浪、潮汐特征的关系[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1992, 10(3): 20−25.Cui Jinrui, Xia Dongxing. The relationship between coastal morphology and the characteristics of waves and tides of Shandong Peninsula[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 1992, 10(3): 20−25. [32] Komar P D. Beach Processes and Sedimentation[M]. 2nd ed. Englewood-Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1998. [33] Neate D J M. Underwater pebble grading of Chesil Bank[J]. Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association, 1967, 78(3): 419−426. [34] Driscoll E G. Experimental field study of shell abrasion[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1967, 37(4): 1117−1123. [35] 张伟. 渤海海峡南部海域地貌特征及控制因素研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014: 29.Zhang Wei. Study on the geomorphological characteristic and controlling factors in the southern Bohai Strait[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014: 29. [36] 王建华, 卜清军, 许长义. 渤海风暴潮研究进展简介[J]. 天津科技, 2014, 41(6): 71−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8945.2014.06.023Wang Jianhua, Bu Qingjun, Xu Changyi. Research progress of Bohai Sea storm surge[J]. Tianjin Science & Technology, 2014, 41(6): 71−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8945.2014.06.023 [37] 张国栋, 王益友, 朱静昌, 等. 现代滨岸风暴沉积——以舟山普陀岛、朱家尖岛为例[J]. 沉积学报, 1987, 5(2): 16−28.Zhang Guodong, Wang Yiyou, Zhu Jingchang, et al. Modern coastal storm deposits of Putuo Island and Zhujiajian Island, Zhoushan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1987, 5(2): 16−28. [38] 万兵力. 长山列岛国家地质公园主要地质遗迹特征与开发保护措施[J].山东国土资源, 2009, 25(4): 53-55.Wan Bingli. Main characteristics and the development protection measures of Changshan Islands National Geopark[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2009, 25(4): 53–55. [39] 刘乐军, 李培英, 王东亮, 等. 海岛环境下采石边坡的监测系统构建研究——以山东北长山岛山后村为例[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(1): 140−149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.01.014Liu Lejun, Li Peiying, Wang Dongliang, et al. Monitorting system designing and practicing for the qurry slope on rock island: a case study of Beichangshan Island, Shandong Province[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(1): 140−149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.01.014 [40] Kirk R M. Aspects of surf and runup processes on mixed sand and gravel beaches[J]. Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography, 1975, 57(1/2): 117−133. [41] Harrison W. Empirical equations for foreshore changes over a tidal cycle[J]. Marine Geology, 1969, 7(6): 529−551. [42] 王庆, 仲少云, 刘建华, 等. 山东庙岛海峡的峡道动力地貌[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2): 17−24.Wang Qing, Zhong Shaoyun, Liu Jianhua, et al. The channel dynamic geomorphology of Miaodao Strait, Shandong, China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(2): 17−24. -




 下载:
下载: