Extraction method for diffuse attenuation coefficient based on airborne LiDAR bathymetric water column waveform
-
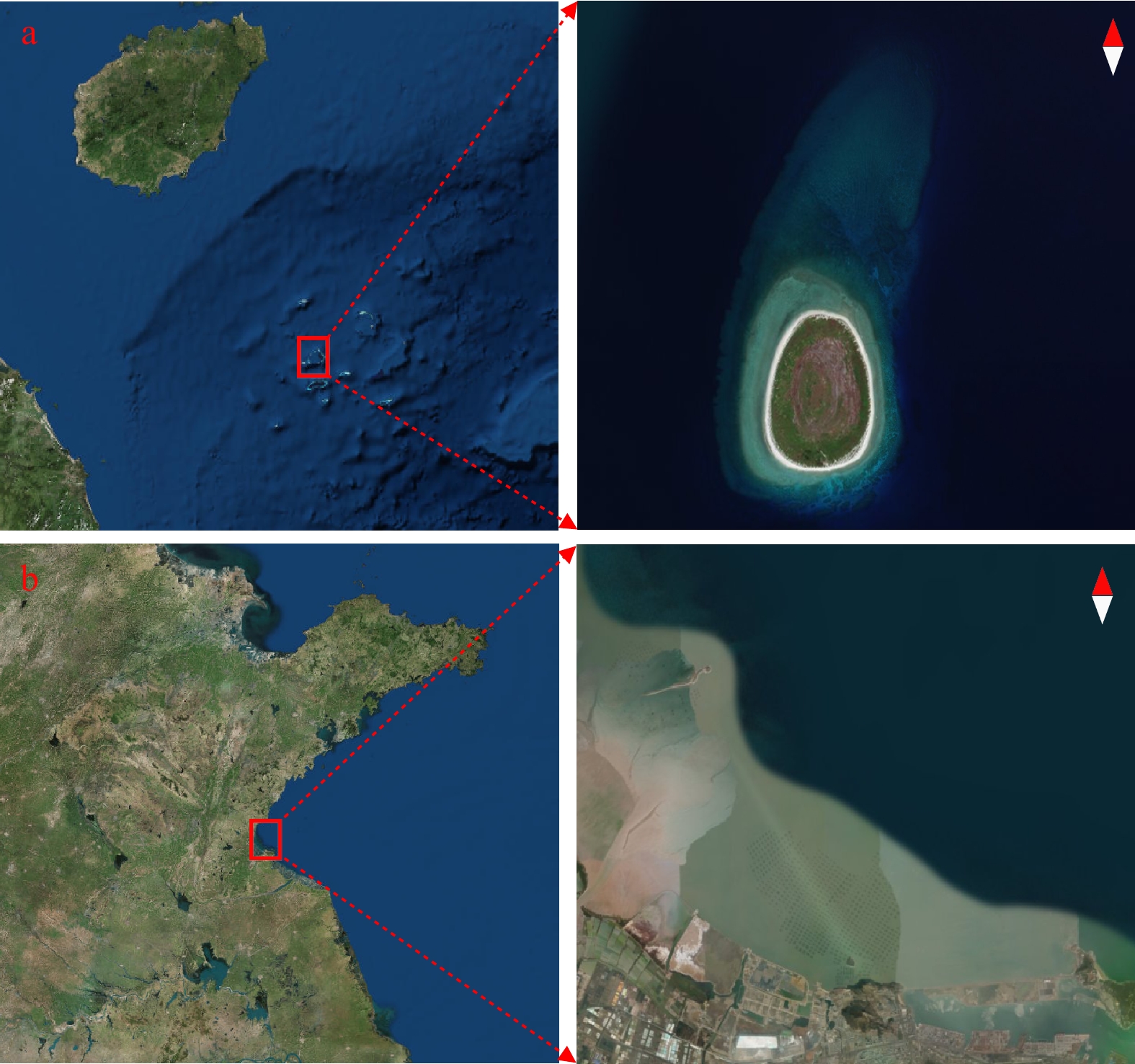
摘要: 漫衰减系数是一个重要的海洋光学参数,能够为水体环境变化、水质分析以及水产养殖等方面提供基础性数据。针对目前船载实地测量效率与分辨率低、卫星遥感反演精度与分辨率较低的局限性,本文提出一种基于机载LiDAR测深水体波形的漫衰减系数提取方法。该方法首先通过分层异构模型的机载LiDAR波形分解算法得到水体散射回波,利用激光在水体中的衰减特性,构建漫衰减系数提取模型,最终获取大面积水域漫衰减系数的空间分布。采用西沙甘泉岛与江苏连云港两个航次的实测数据对所提算法进行了验证,本算法无需每个测深点的水底底部回波强度和深度即可反演得到漫衰减系数,并且在浑浊水域也可取得较好的效果,表明在中国近海利用机载LiDAR测深系统能够有效获取高精度的漫衰减系数。Abstract: The diffuse attenuation coefficient (Kd) is an important marine optical parameter, which can provide the basic data for the water environment change, the water quality analysis and the aquaculture. There are some limitations of the traditional methods, such as the low efficiency and resolution of the traditional shipborne field measurement and the rough inversion accuracy and spatial resolution of the satellite remote sensing. Therefore, an extraction method for diffuse attenuation coefficient based on airborne LiDAR bathymetric water column waveform is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the water column contribution is decomposed by the waveform decomposition algorithm for airborne LiDAR bathymetry based on the layered heterogeneous model. Then, according to the attenuation characteristics of laser in water, the diffuse attenuation coefficient extraction model is constructed. Finally, the diffuse attenuation coefficient spatial distribution in a large area of water is obtained. The performance of the proposed method was verified by the measured data from the Ganquan Island in the Xisha Archipelago and the Lianyungang’s seacoast. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method could obtain the diffuse attenuation coefficient without the water bottom contribution intensity and depth information for each bathymetric point. And the good results were also achieved in turbid waters. Meanwhile, the proposed method showed the feasibility of employing the ALB system to obtain the high-precision diffuse attenuation coefficient in China coastal waters.
-
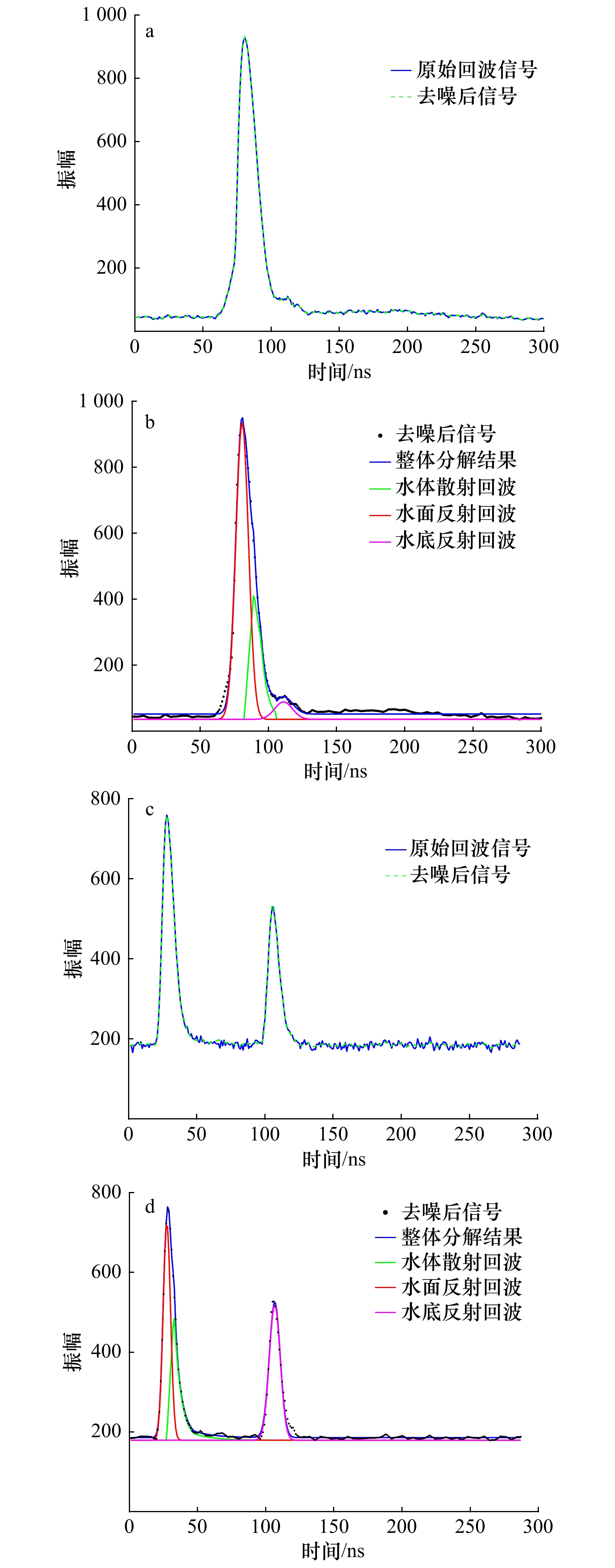
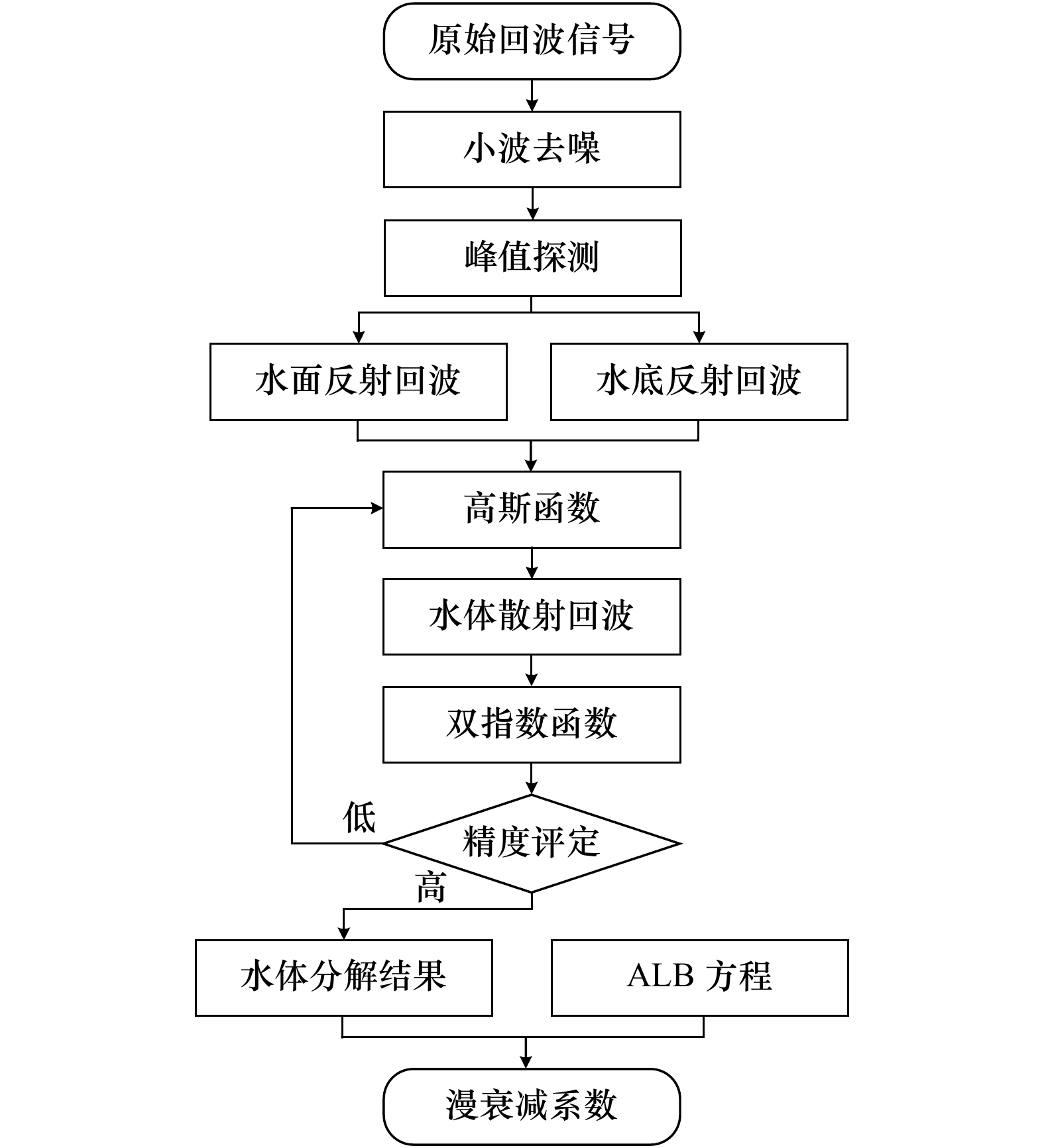
图 5 波形处理结果
a. 连云港波形去噪结果;b. 连云港波形分解结果;c. 甘泉岛波形去噪结果;d. 甘泉岛波形分解结果
Fig. 5 Waveform processing results
a. Waveform denoising results of the Lianyungang’s seacoast;b. waveform decomposition results of the Lianyungang’s seacoast;c. waveform denoising results of the Ganquan Island;d. waveform decomposition results of the Ganquan Island
表 1 Aquarius与CZMIL的技术参数
Tab. 1 Technical parameters of Aquarius and CZMIL
航次 甘泉岛 连云港 ALB名称 Aquarius CZMIL 波段 Green: 532 nm IR:1064 nm Green: 532 nm 脉冲频率 70 kHz 70 kHz (浅水),10 kHz (深水) 作业航高 300~500 m 400 m 最大探测深度 20 m Kd·DMAX = 3.75~4.0
(白天,海底反射率>15%)最小探测深度 − <0.15 m 扫描天底角 15° 20° 注:“−”表示“无数据”。 表 2 分解算法性能指标
Tab. 2 Performance indexes of waveform fitting algorithm
航次 指标 最小值 最大值 平均值 连云港 RMSE 7.4223 15.5780 10.0197 R2 0.8657 0.9975 0.9945 甘泉岛 RMSE 1.8440 13.1071 7.4710 R2 0.9799 0.9997 0.9947 表 3 漫衰减系数提取结果
Tab. 3 Extraction results of diffuse attenuation coefficient
航次 区块 传统方法漫衰减系数/m−1 文中算法漫衰减系数/m−1 甘泉岛 A 0.206 5 0.215 6 B 0.205 2 0.245 3 连云港 A 0.365 1 0.378 8 B 0.362 6 0.381 1 -
[1] Mobley C D. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters[M]. San Diego, CA, USA: Academic Press, 1994. [2] Philips D M, Abbot R H, Penny M F. Remote sensing of sea water turbidity with an airborne laser system[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1984, 17(8): 1749−1758. [3] Gomes A C C, Bernardo N, Do Carmo A C, et al. Diffuse attenuation coefficient retrieval in CDOM dominated inland water with high chlorophyll-a concentrations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1063. [4] Guenther G C. Airborne laser hydrography: system design and performance factors, NOAA Professional Paper Series National Ocean Service 1[R]. Rockville, MD: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 1985. [5] Smart J H, Kwon K H. Comparisons between in situ and remote sensing estimates of diffuse attenuation profiles[C]//CIS Selected Papers: Laser Remote Sensing of Natural Waters: From Theory to Practice. Washington, DC, USA: International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1996, 2964: 100-109. [6] Gordon H R, Smith R C, Ronald J, et al. Introduction to ocean optics[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 0489, Ocean Optics VI. Monterey, CA: SPIE, 1980: 14−55. [7] 李凯, 童晓冲, 张永生, 等. 黄海、东海区域漫衰减系数光谱遥感反演及激光测深性能评估[J]. 遥感学报, 2015, 19(5): 761−769.Li Kai, Tong Xiaochong, Zhang Yongsheng, et al. Inversion of diffuse attenuation coefficient spectral in the Yellow Sea/East China Sea and evaluation of laser bathymetric performance[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 19(5): 761−769. [8] 蒋兴伟, 何贤强, 林明森, 等. 中国海洋卫星遥感应用进展[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10): 113−124.Jiang Xingwei, He Xianqiang, Lin Mingsen, et al. Progresses on ocean satellite remote sensing application in China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(10): 113−124. [9] Billard B, Abbot R H, Penny M F. Airborne estimation of sea turbidity parameters from the WRELADS laser airborne depth sounder[J]. Applied Optics, 1986, 25(13): 2080−2088. [10] Ding Kai, Wang Chisheng, Tao Ming, et al. A new algorithm for retrieving diffuse attenuation coefficient based on big LiDAR bathymetry data[C]//International Symposium on Cyberspace Safety and Security. Cham: Springer, 2019: 133−142. [11] Yang Anxiu, Wu Ziyin, Yang Fanlin, et al. Filtering of airborne LiDAR bathymetry based on bidirectional cloth simulation[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 163: 49−61. [12] 吴自银, 阳凡林, 罗孝文, 等. 高分辨率海底地形地貌−探测处理理论与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.Wu Ziyin, Yang Fanlin, Luo Xiaowen, et al. High-Resolution Submarine Topography: Theory and Technology for Surveying and Post-Processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017. [13] 吴自银, 阳凡林, 李守军, 等. 高分辨率海底地形地貌−可视计算与科学应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.Wu Ziyin, Yang Fanlin, Li Shoujun, et al. High-Resolution Submarine Topography: Visual Computation and Scientific Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017. [14] Su Dianpeng, Yang Fanlin, Ma Yue, et al. Classification of coral reefs in the South China Sea by combining airborne LiDAR bathymetry bottom waveforms and bathymetric features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 815−828. [15] 亓超, 宿殿鹏, 王贤昆, 等. 基于分层异构模型的机载激光测深波形拟合算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(2): 206004.Qi Chao, Su Dianpeng, Wang Xiankun, et al. Fitting algorithm for airborne laser bathymetric waveforms based on layered heterogeneous model[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(2): 206004. [16] Rees W G. Physical Principles of Remote Sensing[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012. [17] Abdallah H, Baghdadi N, Bailly J S, et al. Wa-LiD: a new LiDAR simulator for waters[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 744−748. [18] 孙磊, 张志利, 谭立龙, 等. 采用小波阈值的时变光栅莫尔信号去噪方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2010, 39(3): 576−580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2010.03.040Sun Lei, Zhang Zhili, Tan Lilong, et al. Denoising method of dynamic grating Moiré signal based on wavelet threshold[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2010, 39(3): 576−580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2010.03.040 [19] 刘永明, 邓孺孺, 秦雁, 等. 机载激光雷达测深数据处理与应用[J]. 遥感学报, 2017, 21(6): 982−995.Liu Yongming, Deng Ruru, Qin Yan, et al. Data processing methods and applications of airborne LiDAR bathymetry[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(6): 982−995. [20] Hofton M A, Minster J B, Blair J B. Decomposition of laser altimeter waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(4): 1989−1996. [21] Ding Kai, Li Qingquan, Zhu Jiasong, et al. An improved quadrilateral fitting algorithm for the water column contribution in airborne bathymetric lidar waveforms[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 552. [22] Abdallah H, Bailly J S, Baghdadi N N, et al. Potential of space-borne LiDAR sensors for global bathymetry in coastal and inland waters[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(1): 202−216. [23] Abady L, Bailly J S, Baghdadi N, et al. Assessment of quadrilateral fitting of the water column contribution in lidar waveforms on bathymetry estimates[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(4): 813−817. [24] Klett J D. Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns[J]. Applied Optics, 1981, 20(2): 211−220. [25] Ramnath V, Feygels V, Kalluri H, et al. CZMIL (Coastal Zone Mapping and Imaging Lidar) bathymetric performance in diverse littoral zones[C]//OCEANS 2015-MTS/IEEE Washington. Washington, DC, USA: IEEE, 2015: 1−10. -




 下载:
下载: