Spatiotemporal variations of partial pressure of carbon dioxide in surface sea water in the Qiongzhou Strait in summer
-
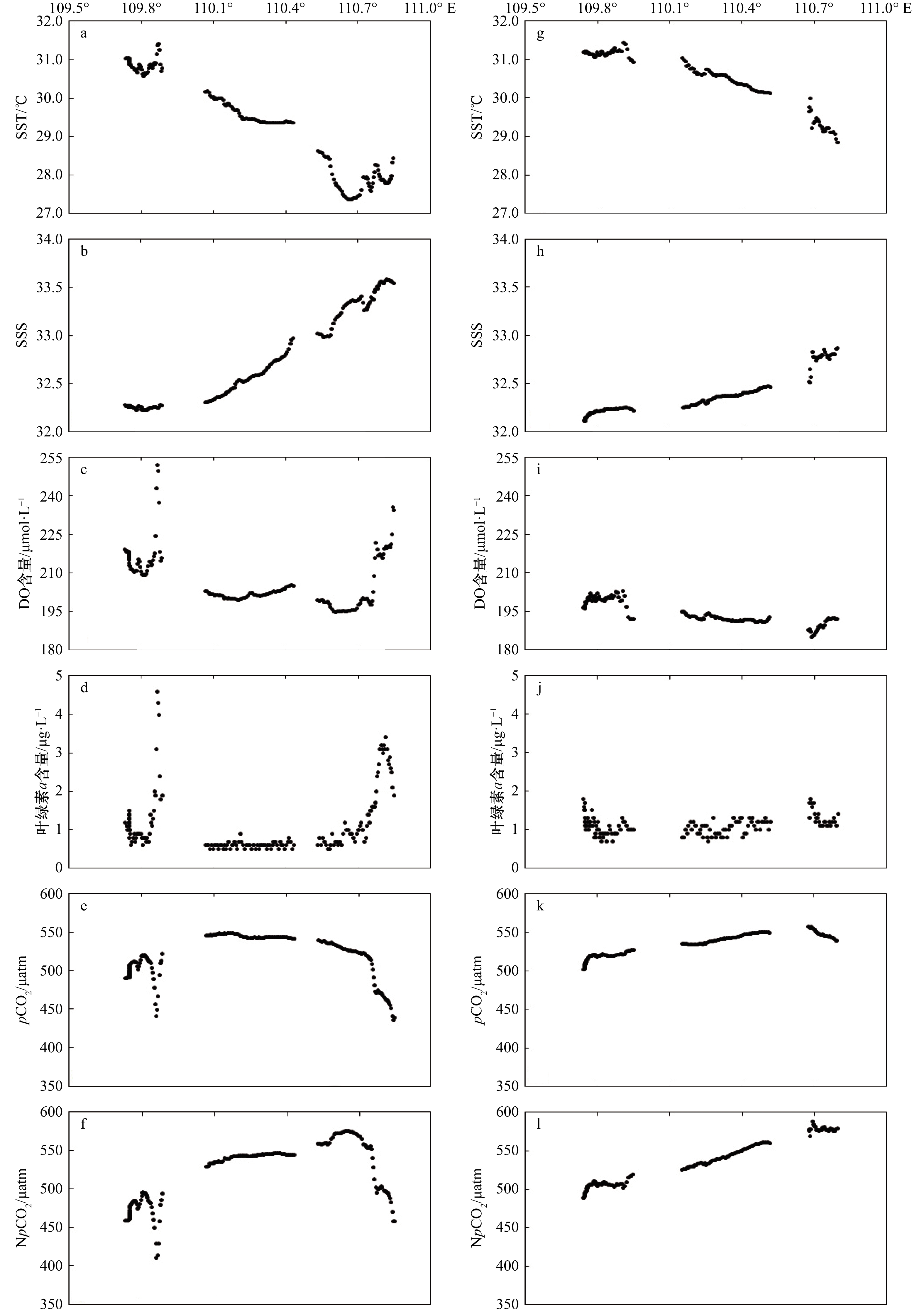
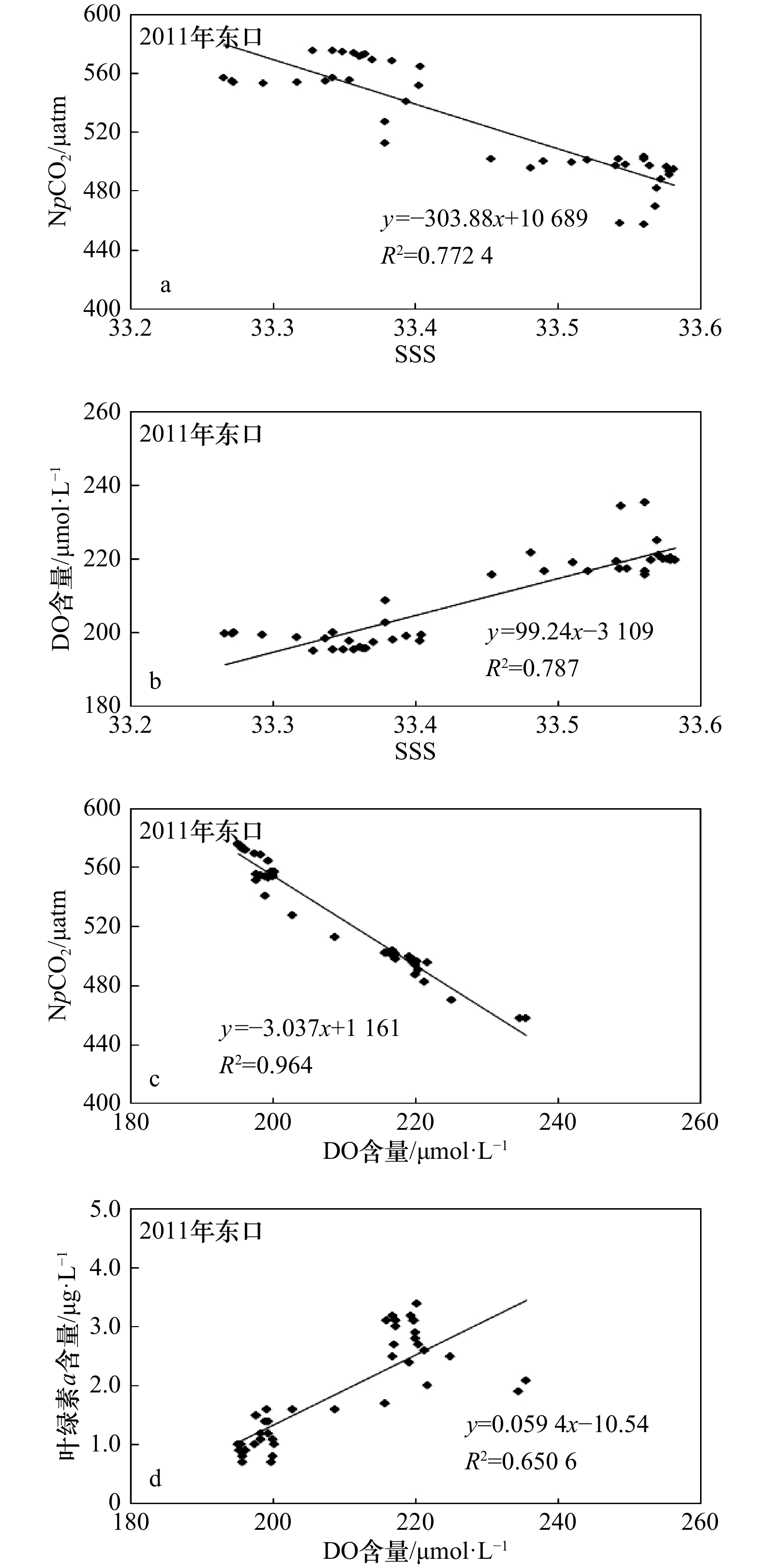
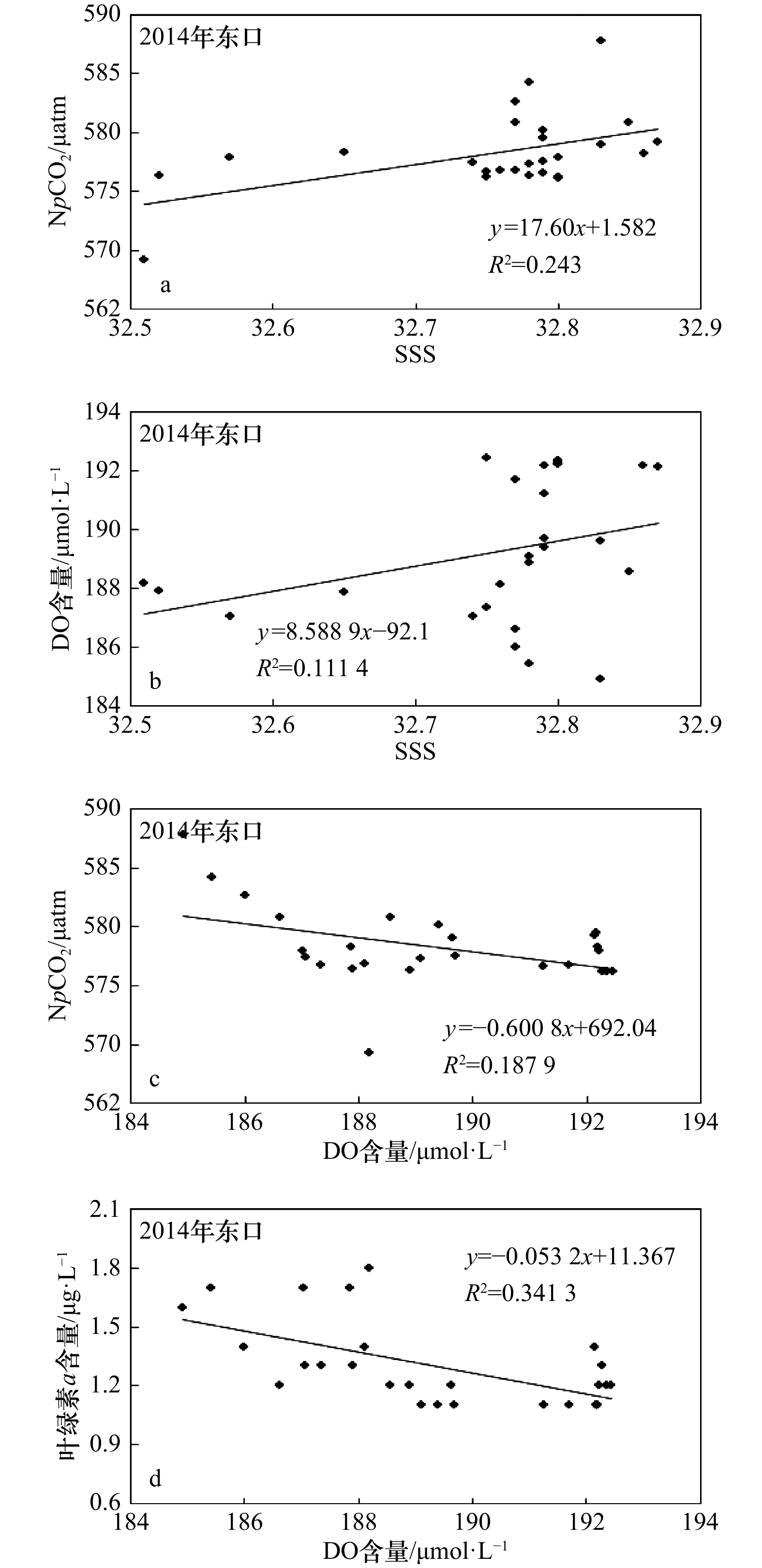
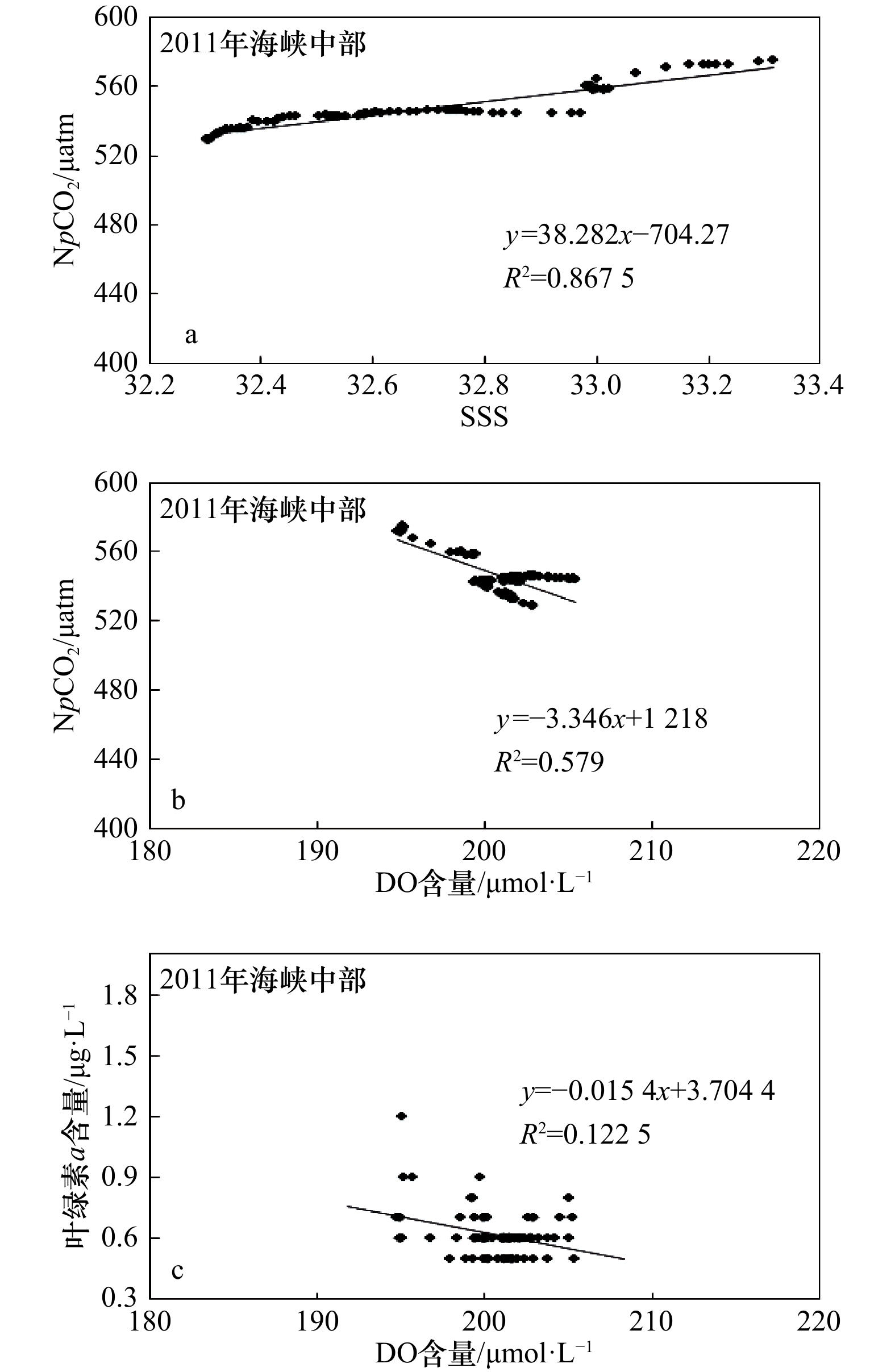
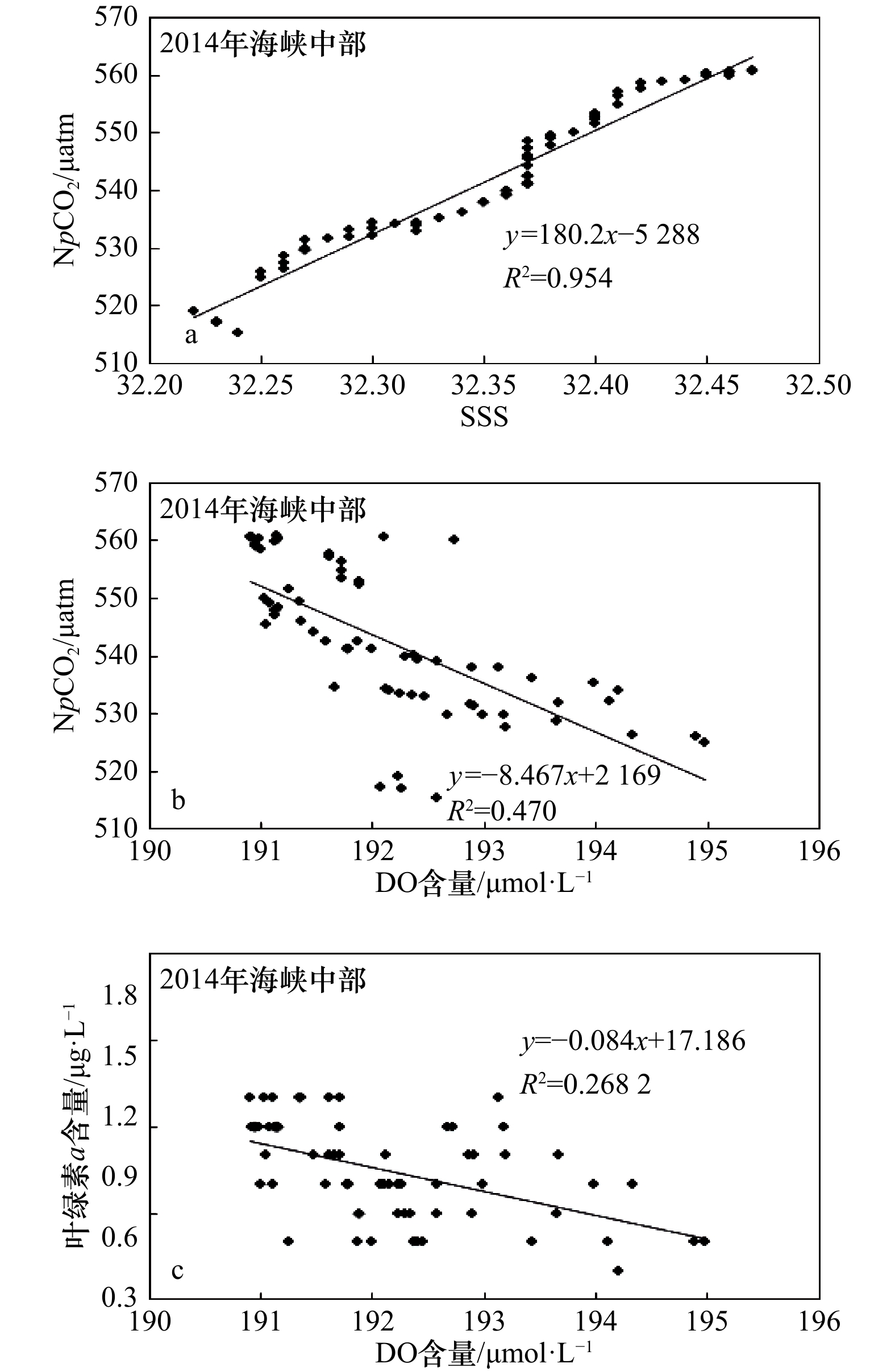
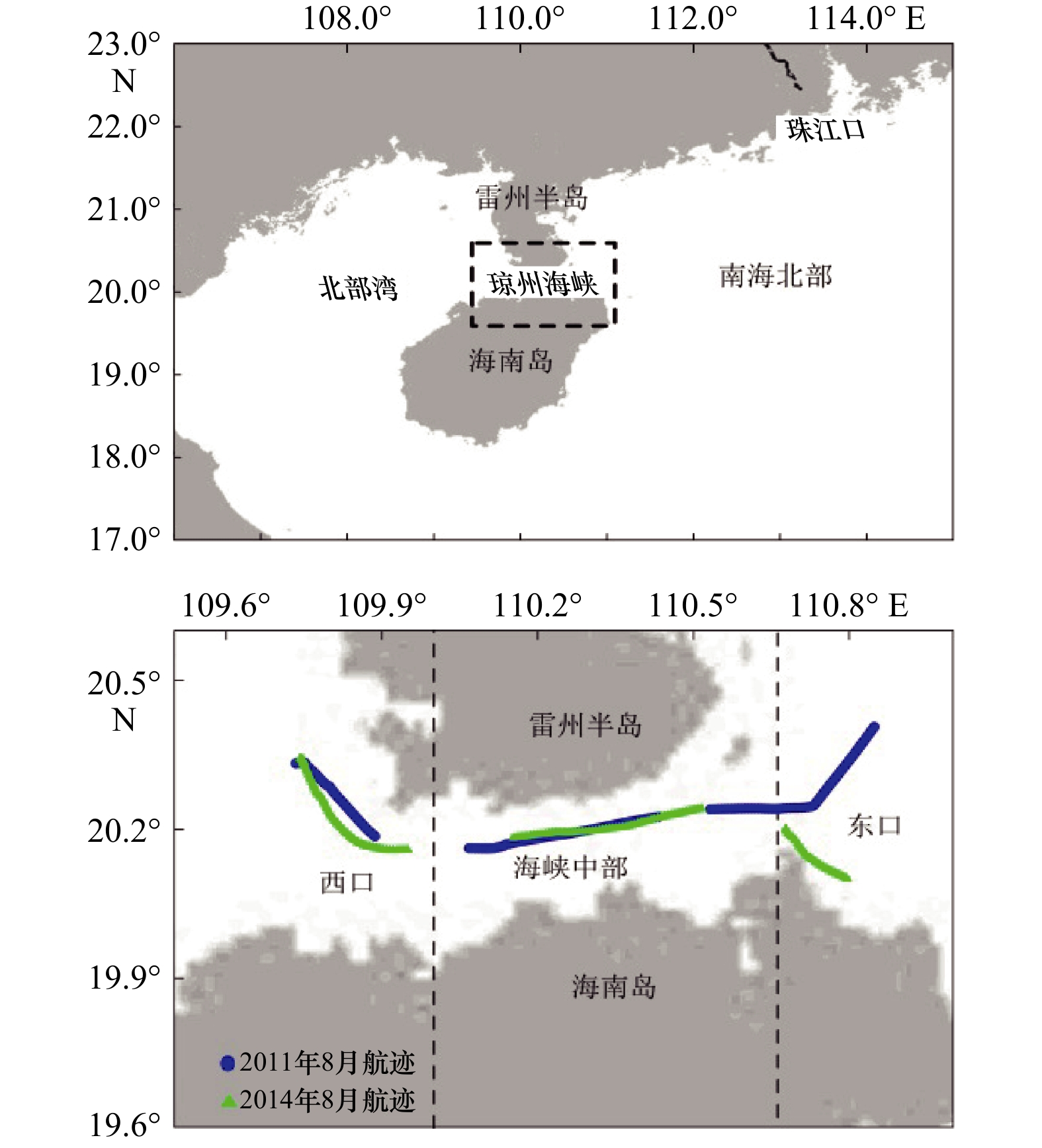
摘要: 采用船载海−气CO2连续观测系统于2011年和2014年夏季在琼州海峡开展了现场观测,分析研究了表层海水二氧化碳分压(pCO2)时空变化及其影响因子。2011年和2014年夏季pCO2分别为(516±29) μatm和(533±15) μatm,海−气CO2交换通量分别为(8.4±1.7) mmol/(m2·d)和(4.5±0.4) mmol/(m2·d),均是大气CO2的强源,高于相邻及相似海域,主要受控于东口海域上升流和海峡中部狭管效应。2011年夏季东口上升流增大pCO2的同时也促进了浮游植物繁殖,光合作用吸收水体CO2,降低了pCO2,而且受其影响,西口口门附近叶绿素a和溶解氧含量陡增,pCO2突降。2014年夏季东口海域上升流较弱,且观测海域垂直混合作用显著,pCO2和溶解氧分布特征与2001年夏季明显不同。海峡中部狭管效应造成水体输运速率大、混合作用强,浮游植物“来不及”生长,pCO2较高。Abstract: The sea surface temperature(SST), salinity(SSS), dissolved oxygen (DO), chlorophyll a(Chl a) and surface partial pressure of carbon dioxide(pCO2) was determined by underway measurement system in the Qiongzhou Strait in summer 2011 and 2014, and the spatiotemporal variations of pCO2 were analyzed and its control factors were explained. The averages of pCO2 in surface sea water were (516±29) μatm and (533±15) μatm, sea-air CO2 fluxes were (8.4±1.7) mmol/(m2·d) and (4.5±0.4) mmol/(m2·d) in summer 2011 and 2014, the Qiongzhou Strait acted as strong atmospheric CO2 source and was more higher than the adjacent and similar sea areas. The upwelling forced the CO2-enriched subsurface water to intrude the surface water and elevated pCO2 in the east mouth, also promoted biological productivity and absorbed CO2 from sea water, and also made the pCO2 drop and DO rise sharply in the vicinity of west mouth in summer 2011. The upwelling was weak in east mouth and vertical mixing was strong along ship-track in summer 2014, the distributions of pCO2 and DO were obviously different from that in summer 2011. Narrow channel effect was significant in the middle of Qiongzhou Strait, high water transportation speed with strong mixing resulted in weak photosynthetic activity, they altogether maintained high pCO2 in summer 2011 and 2014.
-
表 1 2011年和2014年夏季pCO2、NpCO2、pCO2a、ΔpCO2、SST、SSS、DO含量、叶绿素a含量、平均风速和海−气CO2交换通量的统计结果
Tab. 1 Summary of pCO2, NpCO2, pCO2a, SST, SSS, DO content, chlorophyll a content, average wind speed and sea-air CO2 flux estimation in summer 2011 and 2014
观测时间 观测海域 pCO2
/μatmNpCO2
/μatmpCO2a
/μatmΔpCO2
/μatmSST/℃ SSS DO含量
/μmol·L−1叶绿素a
含量/μg·L−1平均风速
/m·s−1海−气CO2交换通量
/mmol·(m2·d)-12011年夏季 琼州海峡 436~549 411~575 378±4 138 27.36~31.42 32.22~33.58 194.8~252.0 0.5~4.6 5.3±1.9 8.4±1.7 516±29 517±40 29.46±1.26 32.72±0.48 207.8±10.4 1.1±0.8 东口 436~527 458~575 113 27.36~28.43 33.27~33.58 195.0~235.6 0.7~3.4 6.7±1.8 491±30 527±37 27.80±0.27 33.44±0.11 209.0±12.0 1.9±0.9 海峡中部 528~549 529~575 164 27.44~30.19 32.30~33.32 194.8~205.4 0.5~1.2 9.9±0.4 542±5 547±12 29.26±0.71 32.69±0.28 200.6±2.6 0.6±0.1 西口 441~522 411~496 123 30.57~31.42 32.22~33.29 209.0~252.0 0.6~4.6 7.5±1.0 501±16 472±18 30.89±0.17 32.26±0.02 216.4±8.6 1.3±0.8 2014年夏季 琼州海峡 502~557 489~589 380±6 153 28.85~31.44 32.11~32.87 184.9~202.9 0.6~1.7 3.7±1.6 4.5±0.4 533±15 534±29 30.56±0.69 32.36±0.21 194.4±4.4 1.0±0.2 东口 539~557 569~589 169 28.85~29.98 32.51~32.87 184.9~192.4 1.0~1.7 5.0±0.2 549±6 578±6 29.31±0.26 32.76±0.09 198.3±2.4 1.2±0.2 海峡中部 526~551 515~561 161 30.12~31.04 32.22~32.47 190.9~195.0 0.6~1.2 4.8±0.2 541±7 542±13 30.52±0.26 32.35±0.07 192.2±1.0 0.9±0.2 西口 502~525 489~510 137 30.05~31.44 32.11~32.25 196.2~202.9 0.6~1.7 4.1±0.2 517±6 503±6 31.17±0.07 32.19±0.04 199.4±1.8 1.0±0.3 -
[1] Jiao Nianzhi, Liang Yantao, Zhang Yongyu, et al. Carbon pools and fluxes in the China Seas and adjacent oceans[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(11): 1535−1563. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9190-x [2] Sun Heng, Gao Zhongyong, Qi Di, et al. Surface seawater partial pressure of CO2 variability and air-sea CO2 fluxes in the Bering Sea in July 2010[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2020, 193: 104031. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2019.104031 [3] Longhurst A, Sathyendranath S, Platt T, et al. An estimate of global primary production in the ocean from satellite radiometer data[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1995, 17(6): 1245−1271. doi: 10.1093/plankt/17.6.1245 [4] Gattuso J P, Frankignoulle M, Wollast R. Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1998, 29: 405−434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.405 [5] Chen Jiyu, Chen Shenliang. Estuarine and coastal challenges in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2002, 20(2): 174−181. doi: 10.1007/BF02849656 [6] Vitousek P M, Mooney H A, Lubchenco J, et al. Human domination of earth's ecosystems[J]. Science, 1997, 277(5325): 494−499. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5325.494 [7] Dai Minhan, Cao Zhimian, Guo Xianghui, et al. Why are some marginal seas sources of atmospheric CO2?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(10): 2154−2158. doi: 10.1002/grl.50390 [8] Lohrenz S E, Cai Weijun, Chakraborty S, et al. Satellite estimation of coastal pCO2 and air-sea flux of carbon dioxide in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 207: 71−83. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.12.039 [9] Wanninkhof R, Triñanes J, Park G H, et al. Large decadal changes in air-sea CO2 fluxes in the Caribbean Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124(10): 6960−6982. doi: 10.1029/2019JC015366 [10] Zhai Weidong, Dai Minhan, Cai Weijun. Coupling of surface pCO2 and dissolved oxygen in the northern South China Sea: impacts of contrasting coastal processes[J]. Biogeosciences, 2009, 6(11): 2589−2598. doi: 10.5194/bg-6-2589-2009 [11] 翟惟东. 南海北部春季非水华期的CO2分压及其调控[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(6): 31−40.Zhai Weidong. Sea surface partial pressure of CO2 and its controls in the northern South China Sea in the non-bloom period in spring[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(6): 31−40. [12] 马玉, 高全洲, 李团结, 等. El Niño影响下春季南海北部表层水体CO2分压变化[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(10): 3581−3588.Ma Yu, Gao Quanzhou, Li Tuanjie, et al. The changes of partial pressure of carbon dioxide in surface water in the northern South China Sea under the influence of El Niño in spring[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(10): 3581−3588. [13] Li Qian, Guo Xianghui, Zhai Weidong, et al. Partial pressure of CO2 and air-sea CO2 fluxes in the South China Sea: synthesis of an 18-year dataset[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2020, 182: 102272. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102272 [14] 陈波, 严金辉, 王道儒, 等. 琼州海峡冬季水量输运计算[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2007, 37(3): 357−364.Chen Bo, Yan Jinhui, Wang Daoru, et al. The transport volume of water through the Qiongzhou Strait in the winter season[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2007, 37(3): 357−364. [15] Shi Maochong, Chen Changsheng, Xu Qichun, et al. The role of Qiongzhou Strait in the seasonal variation of the South China Sea circulation[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2002, 32(I): 103−121. [16] 杨士瑛, 鲍献文, 陈长胜, 等. 夏季粤西沿岸流特征及其产生机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(6): 1−8.Yang Shiying, Bao Xianwen, Chen Changsheng, et al. Analysis on characteristics and mechanism of current system in west coast of Guangdong Province in the summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2003, 25(6): 1−8. [17] 陈达森, 陈波, 严金辉, 等. 琼州海峡余流场季节性变化特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2006(2): 12−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.02.003Chen Dasen, Chen Bo, Yan Jinhui, et al. The seasonal variation characteristics of residual currents in the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2006(2): 12−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.02.003 [18] 侍茂崇, 陈春华, 黄方, 等. 琼州海峡冬末春初潮余流场特征[J]. 海洋学报, 1998, 20(1): 1−10.Shi Maochong, Chen Chunhua, Huang Fang, et al. Characteristics of tidal current and residual current in the Qiongzhou Straits in period between end of winter and beginning of spring[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1998, 20(1): 1−10. [19] 严昌天, 陈波, 杨仕英, 等. 琼州海峡中间断面冬季水量输运计算[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2008(1): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2008.01.001Yan Changtian, Chen Bo, Yang Shiying, et al. The transportation volume of water through the Qiongzhou Strait in winter season[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008(1): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2008.01.001 [20] Weiss R F, Price R A. Nitrous oxide solubility in water and seawater[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1980, 8(4): 347−359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(80)90024-9 [21] Sweeney C, Gloor E, Jacobson A R, et al. Constraining global air-sea gas exchange for CO2 with recent bomb 14C measurements[J]. Global Biogeochemistry Cycle, 2007, 21(2): GB2015. [22] Weiss R F. Carbon dioxide in water and seawater: the solubility of a non-ideal gas[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1974, 2(3): 203−215. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(74)90015-2 [23] Zhai Weidong, Dai Minhan, Chen Baoshan, et al. Seasonal variations of sea-air CO2 fluxes in the largest tropical marginal sea (South China Sea) based on multiple-year underway measurements[J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(4): 7775−7791. [24] Zhai Weidong, Dai Minhan. On the seasonal variation of air-sea CO2 fluxes in the outer Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary, East China Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2009, 117(1/4): 2−10. [25] Xue Liang, Zhang Longjun, Cai Weijun, et al. Air-sea CO2 fluxes in the southern Yellow Sea: an examination of the continental shelf pump hypothesis[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2011, 31(18): 1904−1914. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.09.002 [26] Rehder G, Suess E. Methane and pCO2 in the Kuroshio and the South China Sea during maximum summer surface temperatures[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2001, 75(1/2): 89−108. [27] 张远辉, 黄自强, 王伟强, 等. 台湾海峡二氧化碳研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 2000, 19(2): 163−169.Zhang Yuanhui, Huang Ziqiang, Wang Weiqiang, et al. A study of carbon dioxide in Taiwan Strait[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2000, 19(2): 163−169. [28] 王继纲, 蒋荣根, 陈文锋, 等. 春、秋季台湾海峡海−气CO2通量及其影响因素[J]. 应用海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 313−320.Wang Jigang, Jiang Ronggen, Chen Wenfeng, et al. Sea-air CO2 flux and its environmental factors in the Taiwan Strait in spring and autumn[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 313−320. [29] Padin X A, Vázquez-Rodríquez M, Ríos A F, et al. Surface CO2 measurements in the English Channel and Southern Bight of North Sea using voluntary observing ships[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2007, 66(1/4): 297−308. [30] De la Paz M, Gómez-Parra A, Forja J. Seasonal variability of surface fCO2 in the Strait of Gibraltar[J]. Aquatic Sciences, 2009, 71(1): 55−64. doi: 10.1007/s00027-008-8060-y [31] 杨士瑛, 陈波, 李培良. 用温盐资料研究夏季南海水通过琼州海峡进入北部湾的特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2006(1): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.01.001Yang Shiying, Chen Bo, Li Peiliang. A study of the characteristics of water transport from the South China Sea into Beibu Bay via the Qiongzhou Strait in summer in terms of temperature and salinity data[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2006(1): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.01.001 [32] 谢玲玲, 张书文, 赵辉. 琼东上升流研究概述[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(4): 35−41.Xie Lingling, Zhang Shuwen, Zhao Hui. Overview of studies on Qiongdong upwelling[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(4): 35−41. [33] Ianson D, Feely R A, Sabine C L, et al. Features of coastal upwelling regions that determine net air-sea CO2 flux[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2009, 65(5): 677−687. doi: 10.1007/s10872-009-0059-z [34] Yin Kedong. Monsoonal influence on seasonal variations in nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in coastal waters of Hong Kong in the vicinity of the Pearl River estuary[J]. Marine Ecology—Progress Series, 2002, 245: 111−122. doi: 10.3354/meps245111 [35] 仝长亮, 黎刚, 陈飞, 等. 海南岛东北部海域海砂资源特征及成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(1): 12−19.Tong Changliang, Li Gang, Chen Fei, et al. Geological characteristics and origin of marine sands in the northeast sea off Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(1): 12−19. [36] 汪彧, 经志友, 齐义泉. 2013年夏季琼东海域上升流观测研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(2): 40−49. doi: 10.11978/2015062Wang Yu, Jing Zhiyou, Qi Yiquan. Coastal upwelling off eastern Hainan Island observed in the summer of 2013[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(2): 40−49. doi: 10.11978/2015062 [37] 侍茂崇, 严金辉, 陈波, 等. 琼州海峡夏季三塘潮流谱分析和余流特征研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2011, 41(11): 1−4.Shi Maochong, Yan Jinhui, Chen Bo, et al. The spectrum analysis of tidal current and the study on residual current in summer near Santan in Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2011, 41(11): 1−4. [38] 李占海, 柯贤坤, 王倩, 等. 琼州海峡水沙输运特征研究[J]. 地理研究, 2003, 22(2): 151−159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.02.003Li Zhanhai, Ke Xiankun, Wang Qian, et al. Characteristics of water and sediment transport in the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Geographical Research, 2003, 22(2): 151−159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.02.003 [39] Yin Kedong, Harrison P J. Nitrogen over enrichment in subtropical Pearl River estuarine coastal waters: possible causes and consequences[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2008, 28(12): 1435−1442. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.07.010 [40] Zhou Weihua, Yin Kedong, Harrison P J, et al. The influence of late summer typhoons and high river discharge on water quality in Hong Kong waters[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2012, 111: 35−47. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.06.004 -




 下载:
下载: