Statistical characteristics of seabed sound velocity in the Jinzhou Bay based on high resolution sub-bottom profile data
-
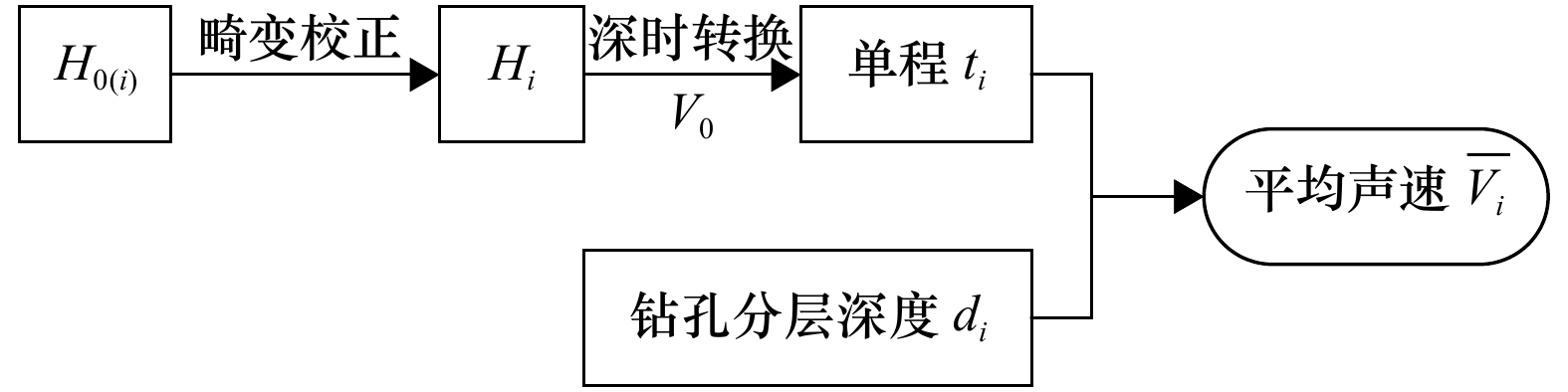
摘要: 声波在海底沉积物中的传播速度是一个重要参数,弄清海底沉积物中声速的变化规律具有极其重要的意义。以渤海金州湾海域为例,在进行畸变校正的基础上,基于高分辨率浅地层剖面与钻孔数据的对比分析,实现了全新世沉积层和基岩界面以上沉积层声速的准确反演,并采用统计学方法分析讨论了研究区内的声速特征和变化规律,结果表明,全新世沉积层平均声速的95%置信区间为1 449.60~1 655.72 m/s,平均值为1 560.34 m/s;基岩界面以上沉积层平均声速的95%置信区间为1 657.96~1 970.80 m/s,平均值为1 765.63 m/s;研究区内海底地层的声速与埋藏深度之间呈现明显的正线性相关关系,声速梯度为4.18 s−1。Abstract: The sound velocity of marine sedimentary sequence is an important parameter. Finding out the changing rule of the seabed sound velocity is of extremely important significance. On the basis of distortion correction, by comparatively analyzing of high resolution sub-bottom profile data and borehole data, the accurate inversions of sound velocity in Holocene and above-bedrock sedimentary sequence are achieved in the Jinzhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China. Then, the characteristics and changing rules of seabed sound velocity in the study area are analyzed and discussed by statistical method. The 95% confidence interval of sound velocity of Holocene sequence is 1 449.60 m/s to 1 655.72 m/s, and the average is 1 560.34 m/s. The 95% confidence interval of sound velocity of above-bedrock sequence is 1 657.96 m/s to 1 970.80 m/s, and the average is 1 765.63 m/s. There is a significant positive linear correlation between the sound velocity of the sedimentary sequence and the burial depth in the study area, and the gradient of sound velocity is 4.18 s−1.
-
表 1 全新世沉积层声速反演示例
Tab. 1 Sound velocity inversion for Holocene sequence
浅地层剖面数据信息 钻孔数据信息 反演声速/m·s−1 测线编号 水深/m 层底埋深/m 单程走时/ms 校正后走时/ms 过孔编号 层底埋深/m A2 6.76 11.77 7.36 7.83 B23 12.40 1 583.65 A5 6.10 13.89 8.68 9.25 H43 14.00 1 513.51 A5 6.10 11.96 7.48 8.02 H27 11.80 1 471.32 A5 6.00 10.70 6.69 7.21 H15 11.50 1 595.01 表 2 基岩面以上沉积层声速反演示例
Tab. 2 Sound velocity inversion for above-bedrock sequence
浅地层剖面数据信息 钻孔数据信息 反演声速/m·s−1 测线编号 水深/m 层底埋深/m 单程走时/ms 校正后走时/ms 过孔编号 层底埋深/m A5 6.10 59.67 37.29 38.13 H43 63.50 1 665.36 A5 6.10 66.03 41.27 42.12 H27 75.80 1 799.62 A5 6.00 49.14 30.71 31.54 H15 52.80 1 674.06 表 3 声速反演的误差分析
Tab. 3 Error analysis of sound velocity inversion
误差来源 误差大小 分层界面最浅时反演误差 分层界面最深时反演误差 浅剖界面划分 ±0.1 ms ±14.02 m/s ±1.10 m/s 钻孔分层深度 ±1 m/±1.5 m ±92.59 m/s ±10.98 m/s -
[1] Hamilton E L. Geoacoustic models of the sea floor[M]//Hampton L. Physics of Sound in Marine Sediments. Boston, MA: Springer, 1974: 181−221. [2] Hamilton E L. Geoacoustic modeling of the sea floor[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1980, 68(5): 1313−1340. doi: 10.1121/1.385100 [3] 王方旗. 海底沉积物声速研究的意义、方法及展望[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2016, 35(6): 96−104.Wang Fangqi. Significance, methods and prospect of the research on sound velocity in seabed sediments[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2016, 35(6): 96−104. [4] Biot M A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low frequency range[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1956, 28(2): 168−178. doi: 10.1121/1.1908239 [5] Biot M A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. II. Higher frequency range[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1956, 28(2): 179−191. doi: 10.1121/1.1908241 [6] Biot M A. Generalized theory of acoustic propagation in porous dissipative media[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1962, 34(9A): 1254−1264. doi: 10.1121/1.1918315 [7] 邹大鹏, 吴百海, 卢博. 海底沉积物声速经验方程的分析和研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2007, 29(4): 43−50.Zou Dapeng, Wu Baihai, Lu Bo. Analysis and study on the sound velocity empirical equations of seafloor sediments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2007, 29(4): 43−50. [8] 邹大鹏. 海底沉积物压缩波声速比与物理特性的关系[J]. 声学学报, 2018, 43(1): 41−51.Zou Dapeng. Relationship between the sound speed ratio of the compressional wave and the physical characteristics of seafloor sediments[J]. Acta Acustica, 2018, 43(1): 41−51. [9] 龙建军, 李赶先. 海底沉积物声速与物理性质的理论关系[J]. 声学学报, 2015, 40(3): 462−468.Long Jianjun, Li Ganxian. Theoretical relations between sound velocity and physical-mechanical properties for seafloor sediments[J]. Acta Acustica, 2015, 40(3): 462−468. [10] Hamilton E L, Shumway G, Menard H W, et al. Acoustic and other physical properties of shallow-water sediments off San Diego[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1955, 28(1): 1007. [11] Hamilton E L. Low sound velocities in high-porosity sediments[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1956, 28(1): 16−19. doi: 10.1121/1.1908208 [12] Stokes T L, Dunn D A. Acoustic and physical property correlation of marine sediments from the texas-louisiana continental shelf[C]//Oceans 2001. MTS/IEEE Conference and Exhibition, 2001: 2624−2633. [13] 梁元博, 卢博. 海底沉积物力学性质影响声速的物理机制[J]. 海洋学报, 1985, 7(1): 111−119.Liang Yuanbo, Lu Bo. The physical mechanism of the influence of the mechanical properties of seabed sediments on the sound velocity[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1985, 7(1): 111−119. [14] 卢博, 梁元博. 海洋沉积物声速与其物理−力学参数的相关性[J]. 热带海洋, 1991, 10(3): 96−100.Lu Bo, Liang Yuanbo. Correlation of sound velocities and physico-mechanical parameters of marine sediments[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1991, 10(3): 96−100. [15] 卢博, 梁元博. 中国东南沿海海洋沉积物物理参数与声速的统计相关[J]. 中国科学: B辑, 1994, 24(5): 556−560.Lu Bo, Liang Yuanbo. Statistical correlation between sound velocity and physical parameters of marine sediments in southeast china coast[J]. Science in China: Series B, 1994, 24(5): 556−560. [16] 卢博, 李传荣, 黄韶健, 等. 海底沉积物在应力-应变过程前后的微区变化特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2000, 22(4): 130−136.Lu Bo, Li Chuanrong, Huang Shaojian, et al. The Micro-area variance features of the seafloor sediment in stress-strain course back and forth[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2000, 22(4): 130−136. [17] 王方旗, 亓发庆, 姚菁, 等. 基于时间平均的海底沉积物声速预测[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(4): 84−90.Wang Fangqi, Qi Faqing, Yao Jing, et al. A study on forecasting sound velocity of sea-floor sediments based on the time-average method[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(4): 84−90. [18] 侯正瑜, 郭常升, 王景强. 南沙海域深水区表层沉积物声速与孔隙度相关关系[J]. 海洋科学, 2013, 37(7): 77−82.Hou Zhengyu, Guo Changsheng, Wang Jingqiang. Surface sediments acoustic velocity and porosity correlation in Nansha sea area abyssal region[J]. Marine Sciences, 2013, 37(7): 77−82. [19] 李赶先, 龙建军. 南海南部海域岛礁区海底珊瑚砂声速影响因素的初步研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(5): 152−160.Li Ganxian, Long Jianjun. A preliminary study of the sound velocity influence factors of submarine coral sand of islands sea area in southern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(5): 152−160. [20] Gorgas T J, Wilkens R H, Fu S S, et al. In situ acoustic and laboratory ultrasonic sound speed and attenuation measured in heterogeneous soft seabed sediments: Eel River shelf, California[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 182(1/2): 103−119. [21] Kim H S, Cho G C, Kwon T H. Effect of CO2 hydrate formation on seismic wave velocities of fine-grained sediments[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(6): 1787−1799. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20102 [22] Fu S S, Wilkens R H, Frazer L N. Acoustic lance: New in situ seafloor velocity profiles[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1996, 99(1): 234−242. doi: 10.1121/1.414506 [23] Best A I, Roberts J A, Somers M L. A new instrument for making in-situ acoustic and geotechnical measurements in seafloor sediments[J]. Underwater Technology, 1998, 23(3): 123−131. doi: 10.3723/175605498783259182 [24] Richardson M D, Briggs K B, Bibee L D, et al. Overview of SAX99: Environmental considerations[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2001, 26(1): 26−53. doi: 10.1109/48.917921 [25] Buckingham M J, Richardson M D. On tone-burst measurements of sound speed and attenuation in sandy marine sediments[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2002, 27(3): 429−453. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2002.1040929 [26] Richardson M, Briggs K, Reed A, et al. Characterization of the environment during SAX04: Preliminary results[C]. Proceedings of the International Conference "Underwater Acoustic Measurements: Technologies and Results", 2005: 285−292. [27] Robb G B N, Best A I, Dix J K, et al. Measurement of the in situ compressional wave properties of marine sediments[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2007, 32(2): 484−496. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2006.880430 [28] Ojha M, Sain K. Velocity-porosity and velocity-density relationship for shallow sediments in the kerala-konkan basin of western indian margin[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2014, 84(2): 187−191. doi: 10.1007/s12594-014-0122-2 [29] 陶春辉, 金肖兵, 金翔龙, 等. 多频海底声学原位测试系统研制和试用[J]. 海洋学报, 2006, 28(2): 46−50.Tao Chunhui, Jin Xiaobing, Jin Xianglong, et al. Development of multi-frequency in-situ marine sediment geoacoustic measuring system[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2006, 28(2): 46−50. [30] 郭常升, 窦玉坛, 谷明峰. 海底底质声学性质原位测量技术研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(8): 6−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.08.002Guo Changsheng, Dou Yutan, Gu Mingfeng. Development of in situ marine sediment acoustic measurement technique[J]. Marine Sciences, 2007, 31(8): 6−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.08.002 [31] 阚光明, 刘保华, 韩国忠, 等. 原位测量技术在黄海沉积声学调查中的应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(3): 88−94.Kan Guangming, Liu Baohua, Han Guozhong, et al. Application of in-situ measurement technology to the survey of seafloor sediment acoustic properties in the Huanghai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2010, 32(3): 88−94. [32] 侯正瑜, 郭常升, 王景强, 等. 一种新型海底沉积物声学原位测量系统的研制及应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(6): 1976−1984. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150613Hou Zhengyu, Guo Changsheng, Wang Jingqiang, et al. Development and application of a new type in-situ acoustic measurement system of seafloor sediment[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(6): 1976−1984. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150613 [33] Bryan G M. Sonobuoy Measurements in Thin Layers, Physics of Sound in Marine Sediments[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1974: 119−130. [34] 张叔英. 海底任意倾斜层的声速测量 (T2−X2法的分析)[J]. 声学学报, 1989, 14(3): 178−189.Zhang Shuying. Acoustic velocity measurements of arbitrarily dipped sediment layers (the T2−X2 approach) [J]. Acta Acustica, 1989, 14(3): 178−189. [35] 张叔英. 海底薄地层和硬地层声速测量方法的研究 (射线参数法和折射法分析)[J]. 声学学报, 1991, 16(3): 187−198.Zhang Shuying. A study of measuring acoustic velocities of thin and hard sea-bed layers[J]. Acta Acustica, 1991, 16(3): 187−198. [36] 段永侯. 渤海海岸带变迁及其环境地质效应[J]. 水文地质与工程地质, 2000, 27(3): 1−5.Duan Yonghou. Coastline changes of Bohai Sea and their environmental-geological effect[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2000, 27(3): 1−5. [37] 宋召军, 张志珣, 黄海军. 南黄海西部海域高分辨率声学地层及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(1): 33−40.Song Zhaojun, Zhang Zhixun, Huang Haijun. Characteristics and depositional setting of the high resolution shallow seismic profile in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(1): 33−40. [38] 王方旗, 胡光海, 吴永亭, 等. 渤海金州湾海域声学浅地层剖面及其解释[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2013, 31(1): 128−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2013.01.014Wang Fangqi, Hu Guanghai, Wu Yongting, et al. Acoustic subbottom profile and their interpretations in the Jinzhou Bay of the Bohai Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2013, 31(1): 128−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2013.01.014 [39] Hamilton E L. Sound velocity gradients in marine sediments[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1979, 65(4): 909−922. doi: 10.1121/1.382594 [40] 卢博. 海水—沉积物声速结构模式[J]. 海洋通报, 1995, 14(2): 42−47.Lu Bo. Model of sound velocity structure in seawater-sediments[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1995, 14(2): 42−47. [41] Brandes H G, Silva A J, Walter D J. Geo-acoustic characterization of calcareous seabed in the Florida Keys[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 182(1/2): 77−102. -





 下载:
下载: