Research on characteristic parameter distribution and generation period of internal waves in the Andaman Sea with MODIS
-
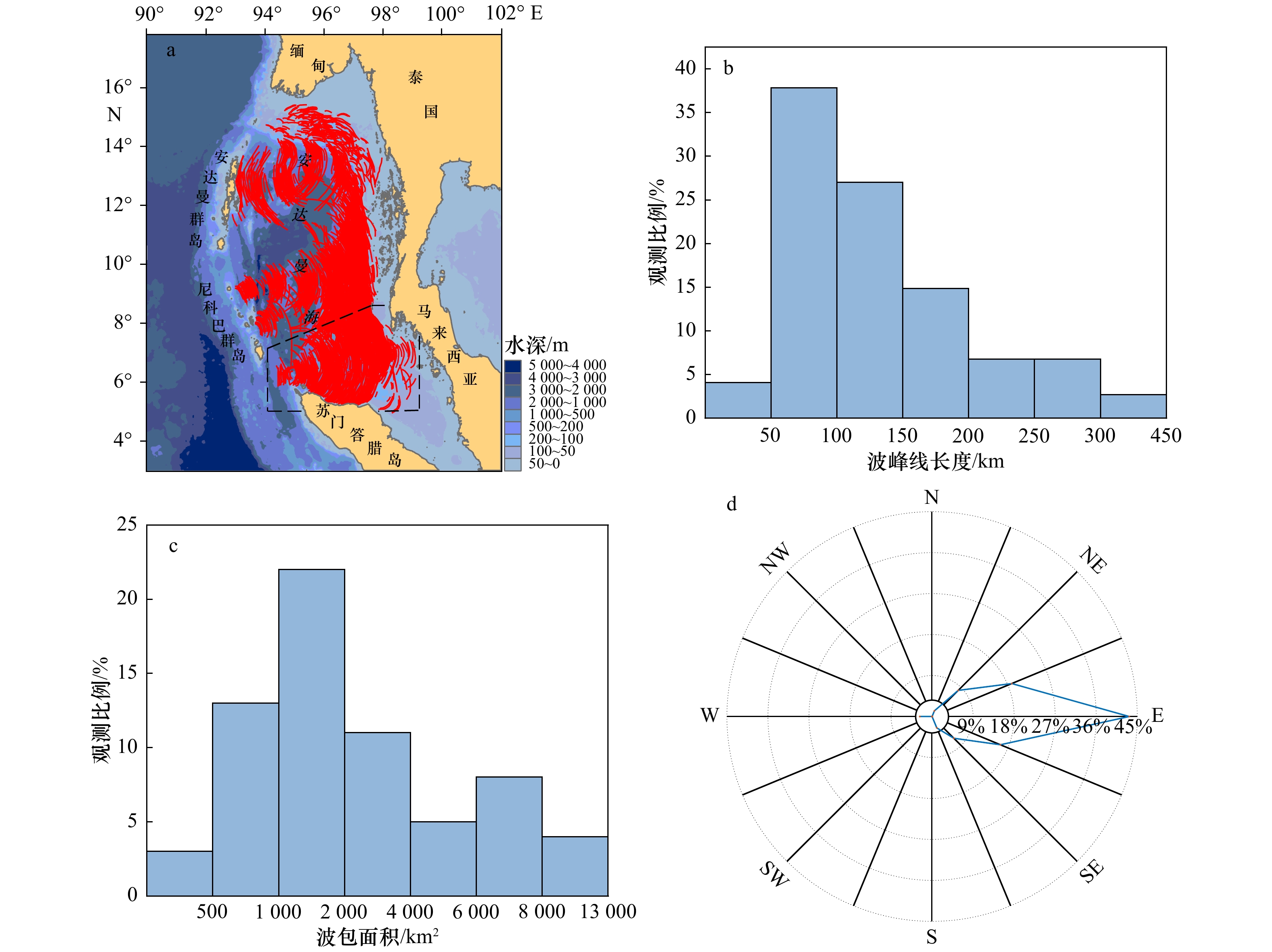
摘要: 本文基于2017年634幅MODIS影像分析了安达曼海3个典型区域的内波空间分布特征,定量统计了波峰线长度、波包面积等特征参数,利用射线追踪法探讨了内波的潜在激发源并推算了内波的生成周期。研究表明,安达曼海北部海域的内波空间尺度较小,前导波波峰线的平均长度约为107 km,平均波包面积约为1 860 km2,内波的传播方向主要为东向以及西南向。安达曼海中部海域内波前导波波峰线的平均长度约为133 km,平均波包面积约为3 503 km2,超过70%的内波沿东偏北方向传播。苏门答腊岛北部海域内波前导波波峰线的平均长度约为131 km,平均波包面积约为2 997 km2,内波的传播方向主要为东向、东北向及东南向。安达曼海共有7个潜在内波激发源,内波的生成时间间隔介于11.5~13 h,具有明显的半日周期特征。Abstract: Based on the 634 MODIS images acquired in 2017, a total of 1 793 internal waves information are extracted. The paper analyzes the spatial distribution of internal waves in three typical regions of the Andaman Sea, quantitatively counts the characteristic parameters such as the length of the leading waves and the area of the wave packets. The potential sources of internal waves are discussed by ray tracing method and estimates the generation period of internal waves. The results show that the internal waves in the northern Andaman Sea have a small spatial scale. The average length of the leading waves is about 107 km, the average wave packet area is about 1 860 km2, and the propagation direction is mainly eastward and southwestward. The average length of the leading waves in the central Andaman Sea is about 133 km, and the average wave packet area is about 3503 km2. More than 70% of the internal waves propagate in the northeast direction. The average length of the leading waves in the northern part of the Sumatra Island is about 131 km, the average wave packet area is about 2 997 km2, and the propagation direction of internal waves is mainly eastward, northeastward and southeastward. There are 7 potential internal wave sources in the Andaman Sea. The internal waves generation period is between 11.5 hours and 13 hours, which has obvious characteristics of half-day period.
-
Key words:
- MODIS /
- Andaman Sea /
- internal waves /
- characteristic parameter /
- generation period
-
表 1 2017年安达曼海内波MODIS影像获取数量
Tab. 1 The number of valid MODIS images of internal waves in the Andaman Sea in 2017
月份 MODIS影像数量/幅 月份 MODIS影像数量/幅 TERRA卫星 AQUA卫星 TERRA卫星 AQUA卫星 1 30 21 7 24 23 2 27 23 8 28 31 3 30 35 9 32 37 4 28 31 10 42 33 5 25 20 11 21 20 6 16 18 12 21 18 表 2 安达曼海内波特征参数
Tab. 2 Internal waves characteristic parameters in the Andaman Sea
特征参数 海域 最大值 最小值 平均值 中间值 前导波波峰线长度/km 北部 263 28 107 100.5 中部 350 29 133 118 南部 413 36 131 106 波包面积/km2 北部 5 882 119 1 860 1 607 中部 12 503 89 3 503 2 256 南部 12 740 353 2 997 1 686 表 3 安达曼海内波发生源位置
Tab. 3 Locations of sources of internal waves in the Andaman Sea
内波源 地理位置 S1 安达曼海北部大陆架 S2 科科海峡 S3 十度海峡 S4 卡尔尼科巴岛与特蕾莎岛之间 S5 特蕾莎岛与卡彻尔岛之间 S6 卡彻尔岛与小尼科巴岛之间 S7 苏门答腊岛西北部浅滩 表 4 安达曼海中部海域内波生成时间
Tab. 4 Internal waves generation time around the central Andaman Sea
波包 传播距离/km 传播时间/h 生成时间(UTC) 1 88.86 10.45 2017年3月12日20:32 2 201.54 23.71 2017年3月12日07:17 3 323.43 39.08 2017年3月11日17:00 4 423.87 49.86 2017年3月11日05:07 表 5 苏门答腊岛北部海域内波生成时间
Tab. 5 Internal waves generation time around the northern Sumatra Island
波包 传播距离/km 传播时间/h 生成时间(UTC) 1 124.18 14.78 2017年3月10日13:27 2 228.84 27.25 2017年3月10日00:59 3 327.52 39.00 2017年3月9日13:14 -
[1] 冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999: 90−195.Feng Shizuo, Li Fengqi, Li Shaojing. An Introduction to Marine Science[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1999: 90−195. [2] Rutenko A N. The effect of internal waves on the sound propagation in the shelf zone of the sea of Japan in different seasons[J]. Acoustical Physics, 2005, 51(4): 449−456. doi: 10.1134/1.1983608 [3] Jackson C. Internal wave detection using the moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2007, 112(C11): C11012. doi: 10.1029/2007JC004220 [4] Alpers W, Heng Wangchen, Hock L. Observation of internal waves in the Andaman Sea by ERS SAR[C]//IGARSS'97.1997 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings. Remote Sensing—A Scientific Vision for Sustainable Development. Singapore: IEEE, 1997, 4: 1518−1520. [5] Perry R B, Schimke G R. Large-amplitude internal waves observed off the northwest coast of Sumatra[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1965, 70(10): 2319−2324. doi: 10.1029/JZ070i010p02319 [6] Osborne A R, Provenzale A, Bergamasco L. The nonlinear Fourier analysis of internal solitons in the Andaman Sea[J]. Lettere Al Nuovo Cimento, 1983, 36(18): 593−599. doi: 10.1007/BF02754731 [7] Magalhaes J M, Da Silva J C B. Internal solitary waves in the Andaman Sea: New insights from SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 861. doi: 10.3390/rs10060861 [8] Zhou Liying, Yang Jingsong, Wang Juan, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of internal waves in the Andaman Sea based on satellite remote sensing[C]//2016 9th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI). Datong, China: IEEE, 2016: 624−628. [9] 周礼英. 基于遥感影像的安达曼海及其邻近海域内波分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.Zhou Liying. Analysis of internal waves in the Andaman Sea and its adjecent waters based on remote sensing images[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. [10] Bai Xiaolin, Liu Zhiyu, Li Xiaofeng, et al. Generation sites of internal solitary waves in the southern Taiwan Strait revealed by MODIS true-colour image observations[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2014, 35(11/12): 4086−4098. [11] Liu Binqing, Yang Hong, Ding Xianwen, et al. Fusion of SAR and MODIS images for oceanic internal waves tracking in the South China Sea[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8921, MIPPR 2013: Remote Sensing Image Processing, Geographic Information Systems, and Other Applications. Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2013: 89210L. [12] 孙丽娜, 张杰, 孟俊敏, 等. 基于多源遥感数据的日本海内波特征研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(3): 102−111.Sun Li’na, Zhang Jie, Meng Junmin, et al. Analysis of internal waves in the Japan Sea with multi-sensors remote sensing data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(3): 102−111. [13] 梅源, 张旭东, 孙丽娜, 等. 利用GF-1和MODIS准同步光学遥感图像反演内波参数的研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(2): 113−119.Mei Yuan, Zhang Xudong, Sun Li’na, et al. Study on inversion of internal wave parameter using GF-1 and MODIS quasi-synchronous optical remote sensing images[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(2): 113−119. [14] 史璐, 王晶, 梅源. 基于MODIS遥感影像的直布罗陀海峡内波传播特性研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(1): 394−390.Shi Lu, Wang Jing, Mei Yuan. Propagation characteristics of internal waves in the Strait of Gibraltar based on MODIS remote sensing images[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(1): 394−390. [15] 康健. 光学遥感影像中耀斑区内孤立波信息提取模型[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009.Kang Jian. Internal solitary wave retrieval model from sun glint of optical remote sensing images[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. [16] Amante C, Eakins B W. ETOPO1 1 arc-minute global relief model: procedures, data sources and analysis. NOAA technical memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24[R]. National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA, 2009. [17] Hong D B, Yang Chansu, Ouchi K. Estimation of internal wave velocity in the shallow South China Sea using single and multiple satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 6(6): 448−457. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2015.1034884 [18] 孙丽娜, 张杰, 孟俊敏. 基于遥感与现场观测数据的南海北部内波传播速度[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(3): 471−480.Sun Li’na, Zhang Jie, Meng Junmin. On propagation velocity of internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea with remote sensing and in-situ observations data[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(3): 471−480. [19] 黄松松, 王晶, 梅源, 等. 基于光学遥感的安达曼海内孤立波传播速度特性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(7): 15−21.Huang Songsong, Wang Jing, Mei Yuan, et al. The velocity characteristics of internal solitary waves in the Andaman Sea by optical remote sensing[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(7): 15−21. [20] Zhang Xudong, Wang Jing, Sun Li’na, et al. Study on the amplitude inversion of internal waves at Wenchang area of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(7): 14−19. doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0902-1 [21] Osborne A R, Burch T L. Internal solitons in the Andaman Sea[J]. Science, 1980, 208(4443): 451−460. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4443.451 -





 下载:
下载: