Provenance studies on sandy sediments on the northeastern shelf of the South China Sea based on heavy mineral geochemistry
-
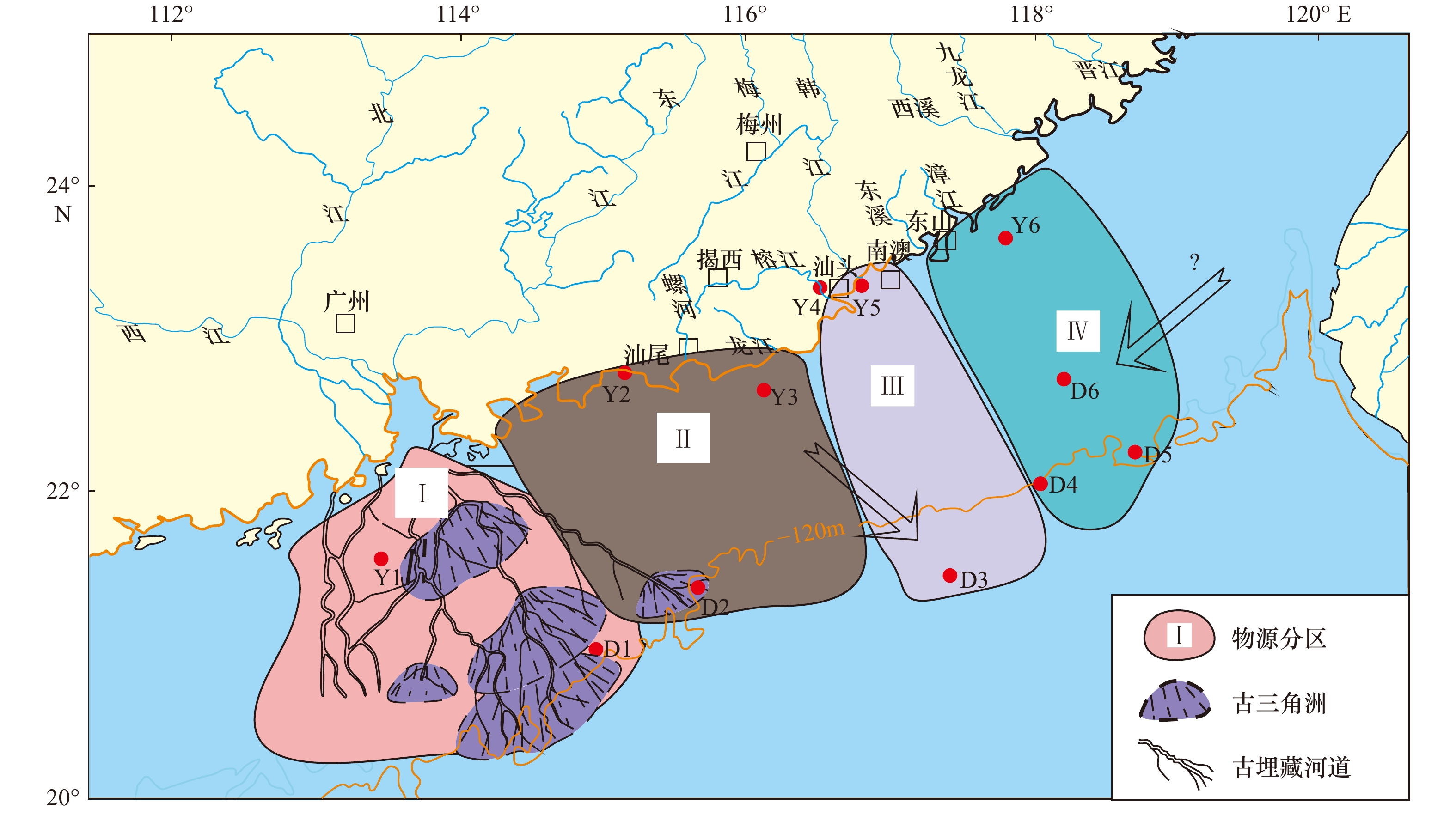
摘要: 物源是研究大陆架沉积物搬运过程、重建陆架古环境以及海洋砂矿资源勘查的重要信息。然而,陆架砂质沉积物普遍经历过多次搬运、分选和混合,这给物源识别带来极大的困难。南海东北部陆架砂质沉积物分布广泛,本文首次采用单矿物化学方法对其物源进行了新的解析。研究区表层砂质沉积物中电气石与角闪石为优势重矿物,两者含量呈现此消彼长的关系。电气石和石榴子石的电子探针数据显示:珠江、韩江沉积物影响海域,火成岩成因的电气石占60%左右,其主要来源为区内广泛发育的燕山期花岗岩的风化产物;莲花山断裂带和长乐−南澳断裂带附近的南海东北部沿岸小河沉积物中变质岩成因的电气石含量显著增高,最高可达70%,其来源为区内与断裂带伴生的变质岩风化物;矽卡岩成因的钙铝榴石在南澳岛以东的陆架沉积物中发现最多,这与华南陆域矽卡岩的分布区吻合。综合分析认为,重矿物的矿物化学方法可以减少分选效应的影响,利用多种矿物的矿物化学分异可以获得多维的信息,为陆架沉积物的物源判定提供便利。Abstract: The sediment provenance is important information to study on the transport process of shelf sediments, paleo-environmental changes and the formation of heavy mineral placers on the shelf. However, most shelf sediments are heavily reworked and repeatedly sorted, which cause the difficulty in indentifying their sources. This study firstly reported the work on heavy mineral provenance on the northeastern shelf of the South China Sea by using mineral chemistry, which has been proved to be a useful method to decrease the effect of hydrodynamic sorting. The provenance of shelf sediments was inferred by comparing the mineral assemblage and mineral chemical compositions of tourmaline and garnet between six marine sediment samples on the outer shelf and six offshore and coastal samples. In the study area, tourmaline and amphibole are dominant and monazite is present in some samples. Mineral chemical composition of tourmaline suggested the Zhujiang River and Hanjiang River are two dominant sediment suppliers. Sediments from the two big rivers contain abundant tourmaline from igneous rocks with the content of about 60% which are associated with widely-spreaded granitic rocks in the South China. Some small rivers distribute within the Lianhuashan and Changle-Nanao fracture zones are characterized by the high content of metamorphic tourmaline. These sediments can be traced on the northeastern shelf of the South China Sea by using chemical composition of tourmaline, suggesting small rivers are also important sediment suppliers on this studied shelf. Garnet sourced from sharn rocks is found on the eastern most shelf. The study highlights the importance of single-mineral chemistry in judging the provenance of shelf sediments which suffer from multiple sorting and have complex sources.
-
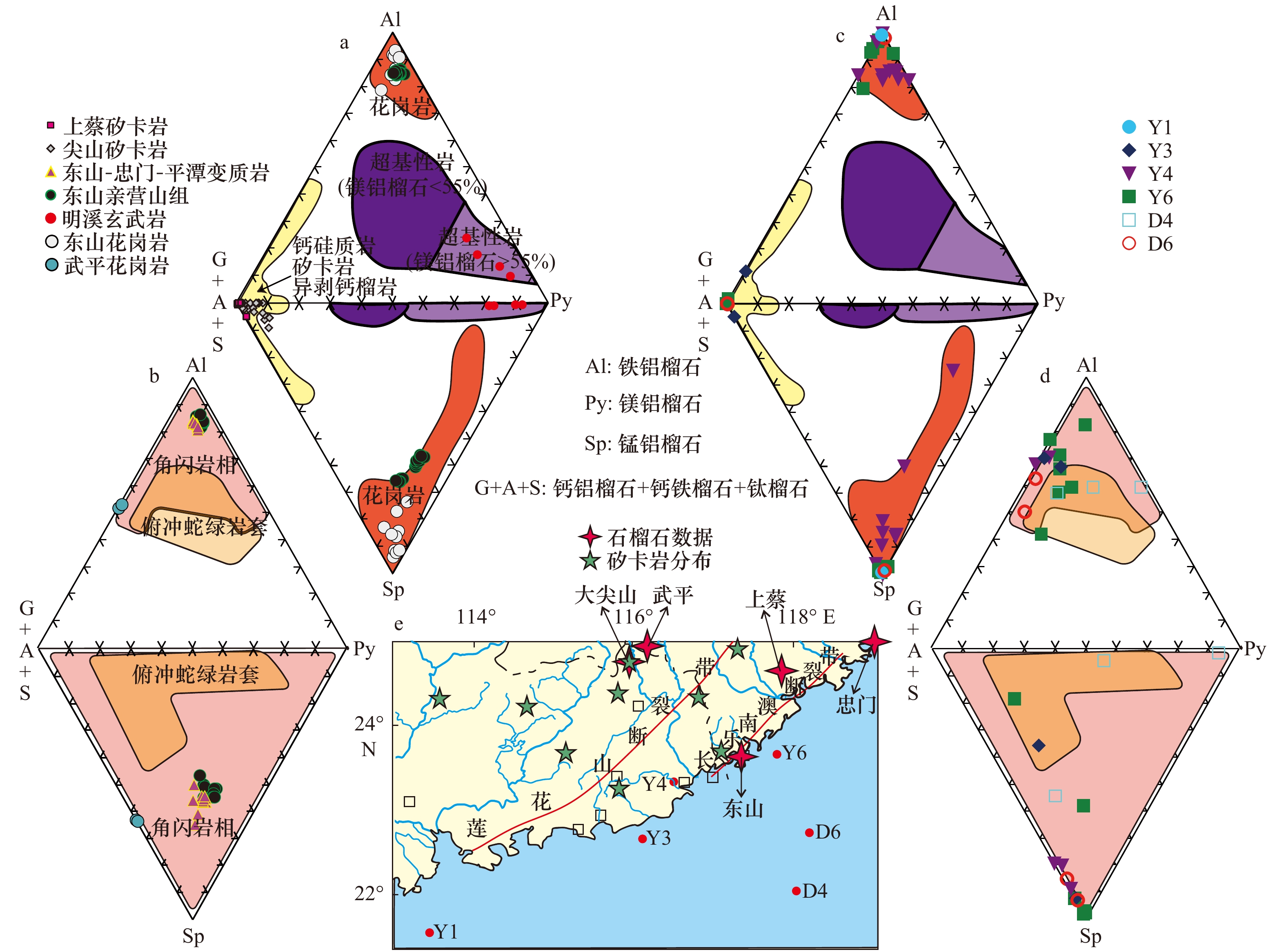
图 4 华南不同类型基岩及陆架沉积物中石榴子石成分投影图(石榴子石成分图解引自文献[26])
a和b为粤西典型基岩中石榴子石的化学组成;c和d为沉积物样品中石榴子石的化学组成
Fig. 4 Detrital garnet compositions from potential source rocks and studied samples on the shelf of eastern South China Sea (triangular plots using “end-member” garnets arecited from reference [26])
a and b are detrital garnet compositions from different bedrocks in eastern Guangdong and western Fujian; c and d are detrital garnet compositions from studied samples on the eastern shelf of South China Sea
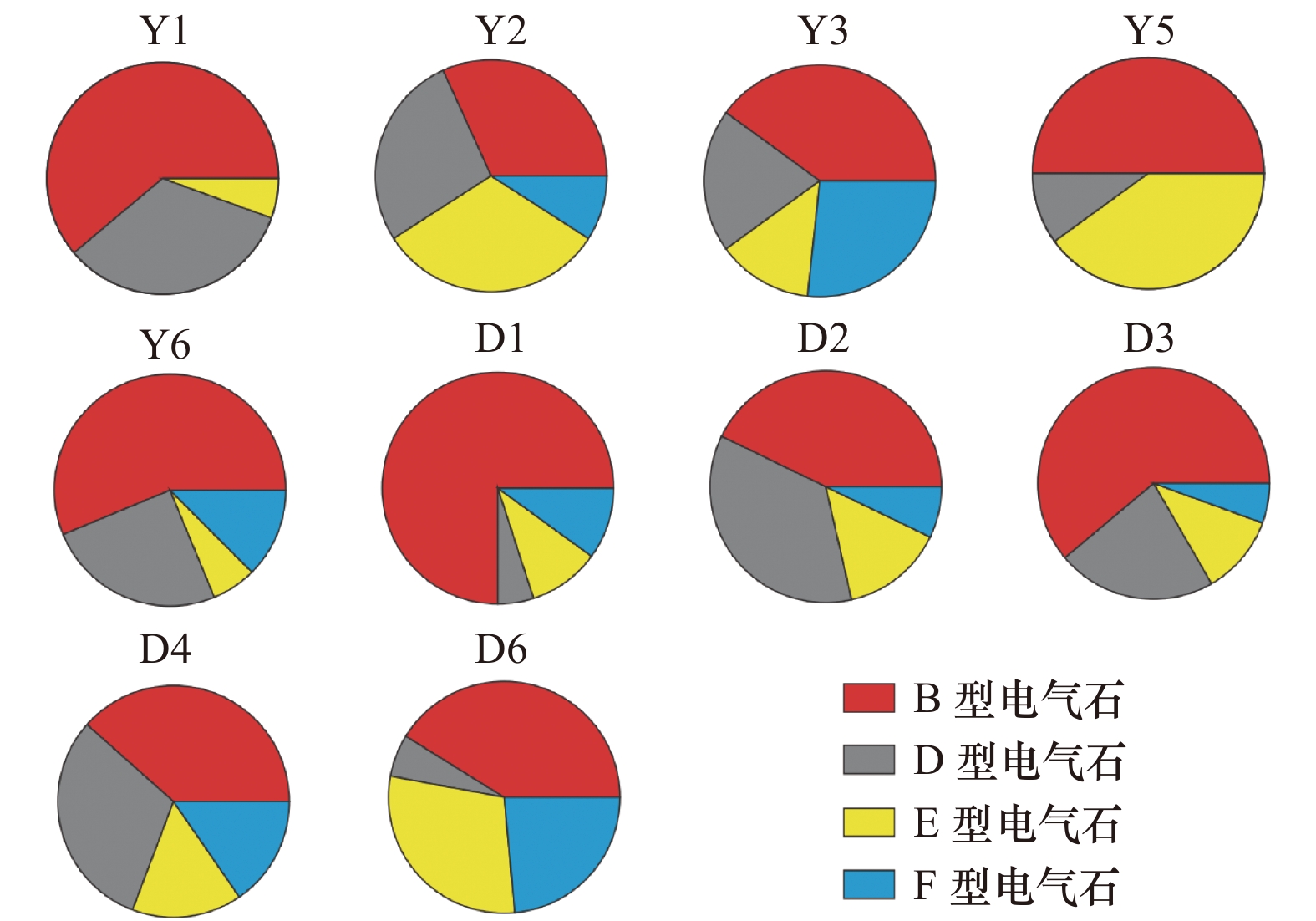
表 1 南海东北部陆架样品主要重矿物组成及重矿物指数
Tab. 1 Heavy mineral assemblage and indices of samples on the northeastern shelf of the South China Sea
Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 角闪石 3.6 37.7 51.3 30.1 19.5 16.7 5.8 57.6 23.9 57.5 17.3 3.4 电气石 40.2 42.1 21.2 17.3 2.4 23.2 61.9 27.4 43.1 15.9 2.0 4.3 绿帘石 1.8 0.4 8.1 5.1 3.2 0.7 0.4 0.9 0.5 4.6 − 3.0 石榴子石 0.3 0.2 1.3 2.4 − 4.2 0.6 0.7 2.7 1.0 1.0 1.0 磁铁矿 11.7 1.1 0.8 9.8 63.9 0.5 6.2 0.6 5.3 2.0 45.4 3.9 独居石 1.3 − − − − 0.2 0.6 − − 0.2 − 1.0 金红石 9.1 1.4 − 0.3 1.1 0.2 2.3 1.2 2.1 3.0 1.5 8.5 尖晶石 − 0.2 − − − − − − 2.1 − 0.5 4.1 锆石 0.3 0.9 5.6 6.9 0.6 3.0 0.8 0.4 − 2.4 0.5 0.8 含钛矿物 26.4 15.7 8.6 24.7 3.6 50.1 9.1 5.5 10.6 9.1 27.6 65.0 鉴定颗粒个数 386 568 396 594 532 431 514 675 188 503 196 609 GZi 50.0 16.7 18.5 25.5 − 58.1 42.9 62.5 100.0 29.4 66.7 54.5 Rzi 99.0 94.7 60.7 78.2 86.4 94.3 92.2 92.5 100.0 79.3 98.2 98.8 ZTR 49.5 44.4 26.8 24.6 4.1 26.5 65.0 29.0 45.2 21.3 4.1 13.6 注:−表示样品中没有此种矿物。 -
[1] Liu Zhifei, Trentesaux A, Clemens S C, et al. Clay mineral assemblages in the northern South China Sea: implications for East Asian monsoon evolution over the past 2 million years[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 201(1/3): 133−146. [2] Liu Jianguo, Steinke S, Vogt C, et al. Temporal and spatial patterns of sediment deposition in the northern South China Sea over the last 50, 000 years[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 465: 212−224. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.10.033 [3] 方建勇, 陈坚, 李云海, 等. 南海北部陆架表层沉积物重矿物分布特征及物源意义[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2014, 33(1): 11−20. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2014.01.002Fang Jianyong, Chen Jian, Li Yunhai, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy minerals on the surface sediments in continental shelf of northern South China Sea and its provenance significance[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 11−20. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2014.01.002 [4] 陈丽蓉. 中国海沉积矿物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 257−297.Chen Lirong. Sedimentary Mineralogy of the China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 257−297. [5] 邵磊, 乔培军, 庞雄, 等. 南海北部近代沉积物钕同位素分布及意义[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(1): 98−103. doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-1-98Shao Lei, Qiao Peijun, Pang Xiong, et al. Nd isotopic variations and its implications in the recent sediments from the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(1): 98−103. doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-1-98 [6] 赵利, 蔡观强, 钟和贤, 等. 南海北部陆架海域表层沉积物地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质学刊, 2017, 41(1): 103−111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2017.01.103Zhao Li, Cai Guanqiang, Zhong Hexian, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of the surface sediments from the continental shelf waters of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geology, 2017, 41(1): 103−111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2017.01.103 [7] 张楠, 王淑红, 陈翰, 等. 南海北部近海陆架表层沉积物类型及其稀土元素特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2014, 34(4): 503−511.Zhang Nan, Wang Shuhong, Chen Han, et al. Sediment types and their characteristics of rare-earth elements in surface sediments from shelf of northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2014, 34(4): 503−511. [8] Pe-Piper G, Piper D J W, Wang Ying, et al. Quaternary evolution of the rivers of northeast Hainan Island, China: tracking the history of avulsion from mineralogy and geochemistry of river and delta sands[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 333: 84−99. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.12.008 [9] Mange M A, Maurer H F W. Heavy Minerals in Colour[M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1991: 1−34. [10] Komar P D. The entrainment, transport and sorting of heavy minerals by waves and currents[M]//Mange M A, Wright D T. Heavy Minerals in Use. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007: 3−48. [11] Mange M A, Morton A C. Geochemistry of heavy minerals[M]//Mange M A, Wright D T. Heavy Minerals in Use. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007: 345−391. [12] Li Gang, Yan Wen, Zhong Lifeng, et al. Provenance of heavy mineral deposits on the northwestern shelf of the South China Sea, evidence from single-mineral chemistry[J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 363: 112−124. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.015 [13] 张仲英, 陈华堂, 刘瑞华, 等. 华南第四纪滨海砂矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 98−111.Zhang Zhongying, Chen Huatang, Liu Ruihua, et al. Quaternary Littoral Placer in South China[M]. Beijing: Geologic Press, 1992: 98−111. [14] 曹立, 刘建国, 何伟, 等. 华南沿岸大型河流粘土矿物组合特征及对南海北部沉积物的贡献[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(S2): 192−202.Cao Li, Liu Jianguo, He Wei, et al. Clay mineral assemblage features of major rivers along the South China coast and their contributions to the northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(S2): 192−202. [15] 徐晓春, 岳书仓. 粤东地区中生代火成岩的时空分布, 岩石特征及成岩物化条件[J]. 河北工业大学学报:自然科学版, 1993, 16(1): 1−12.Xu Xiaochun, Yue Shucang. The time-space relation and characteristics and forming physicochemical conditions of Mesozoic igneous rocks in eastern Guangdong area[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology: Natural Science, 1993, 16(1): 1−12. [16] 广东省地质矿产局. 广东省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988.Guangdong Geological Bureau. Regional Geology of Guangdong Province[M]. Beijing: Geologic Press, 1988. [17] 舒良树, 于津海, 王德滋. 长乐−南澳断裂带晚中生代岩浆活动与变质−变形关系[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000, 6(3): 368−378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2000.03.001Shu Liangshu, Yu Jinhai, Wang Dezi. Late Mesozoic granitic magmatism and its relation to metamorphism-ductile deformation in the Changle-Nan'ao Fault Zone, Fujian Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2000, 6(3): 368−378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2000.03.001 [18] 刘金芳, 刘忠, 顾翼炎, 等. 台湾海峡水文要素特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2002, 19(3): 22−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2002.03.003Liu Jinfang, Liu Zhong, Gu Yiyan, et al. Analysis of the hydrographic elements features in Taiwan Strait[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2002, 19(3): 22−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2002.03.003 [19] 杨士瑛, 鲍献文, 陈长胜, 等. 夏季粤西沿岸流特征及其产生机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(6): 1−8.Yang Shiying, Bao Xianwen, Chen Changsheng, et al. Analysis on characteristics and mechanism of current system in west coast of Guangdong Province in the summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2003, 25(6): 1−8. [20] 管秉贤. 南海暖流——广东外海一支冬季逆风流动的海流[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1978, 9(2): 117−127.Kwan P H. The warm current in the South China Sea: A current flowing against the wind in winter in the open sea off Guangdong Province[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1978, 9(2): 117−127. [21] 伍伯瑜. 台湾海峡及其邻近水域的流型和水文特征[J]. 海洋通报, 1983, 2(4): 1−8.Wu Boyu. The current pattern and hydrologic character in the Taiwan Strait and its adjacent waters[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1983, 2(4): 1−8. [22] 罗又郎, 冯伟文, 林怀兆. 南海表层沉积类型与沉积作用若干特征[J]. 热带海洋, 1994, 13(1): 47−54.Luo Youlang, Feng Weiwen, Lin Huaizhao. Bottom sediment types and depositional characteristics of sediments of the South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1994, 13(1): 47−54. [23] 李亮, 陈忠, 刘建国, 等. 南海北部表层沉积物类型及沉积环境区划[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(1): 54−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.01.007Li Liang, Chen Zhong, Liu Jianguo, et al. Distribution of surface sediment types and sedimentary environment divisions in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 54−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.01.007 [24] 肖尚斌, 陈木宏, 陆钧, 等. 南海北部陆架柱状沉积物记录的残留沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3): 1−5.Xiao Shangbin, Chen Muhong, Lu Jun, et al. New evidence for remnant deposits recorded by columnar sediments in the shelf of the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3): 1−5. [25] Richard L R. MinPet: mineralogical and petrological data processing system, version 2.02[S]. Gatineau: MinPet Geological Software, 1997. [26] Suggate S M, Hall R. Using detrital garnet compositions to determine provenance: a new compositional database and procedure[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2014, 386(1): 373−393. doi: 10.1144/SP386.8 [27] Wang Rucheng, Hu Huan, Zhang Aicheng, et al. Yttrium zoning in garnet from the Xihuashan granitic complex and its petrological implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(15): 1611−1615. doi: 10.1007/BF03183970 [28] 林嵘. 矽卡岩中石榴石特征与成矿关系的探讨──以上蔡硫−多金属矿区前峰西矿段为例[J]. 化工矿产地质, 1995, 17(2): 118−122.Lin Rong. Relanon of characteristic carnet to mineralization with an example from Qianfeng ore block of Shangcai polywetallic field[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 1995, 17(2): 118−122. [29] 叶庆同, 吴学汉, 李慕洁, 等. 广东尖山铁矿床中石榴石的标型特征和找矿意义[J]. 岩石矿物及测试, 1983, 2(3): 190−196.Ye Qingtong, Wu Xuehan, Li Mujie, et al. Typomorphic characteristic of garnet from Jianshan iron deposit in Guangdong and thier significance in exploration of deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Mineralogica et Analytica, 1983, 2(3): 190−196. [30] 陈斌. 福建平潭−东山变质带夕线石榴云母片岩中两期变质作用的岩相学证据及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1997, 13(3): 380−394. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1997.03.010Chen Bin. Petrographic evidences and tectonic significance for two phases of metamorphism in sillimanite- and garnet-bearing mica schists of Pintan-Dongshan metamorphic zone of eastern Fujian, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1997, 13(3): 380−394. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1997.03.010 [31] 黄长煌. 福建东山亲营山岩组变质岩石榴石−黑云母地质温度计的应用[J]. 华东地质, 2019, 40(1): 1−10.Huang Changhuang. Application of garnet-biotite geothermometer from the Qinyingshan Formation in Dongshan, Fujian Province[J]. East China Geology, 2019, 40(1): 1−10. [32] 汤德平, 罗维英. 福建明溪石榴石的宝石学研究[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志, 2000, 2(4): 7−11.Tang Deping, Luo Weiying. Gemmology of mingxi garnets, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2000, 2(4): 7−11. [33] 于津海, 赵蕾, 周旋. 闽东南含石榴子石I型花岗岩的矿物学特征及成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2004, 10(3): 364−377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2004.03.007Yu Jinhai, Zhao Lei, Zhou Xuan. Mineralogical characteristics and origin of garnet-bearing i-type Granitoids in southeastern Fujian Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2004, 10(3): 364−377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2004.03.007 [34] 于津海, 周新民, 赵蕾, 等. 壳幔作用导致武平花岗岩形成——Sr-Nd-Hf-U-Pb同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3): 651−664. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.03.007Yu Jinhai, Zhou Xinmin, Zhao Lei, et al. Mantle-crust interaction generating the Wuping granites: evidenced from Sr-Nd-Hf-U-Pb isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(3): 651−664. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.03.007 [35] Mücke A, Bhadra Chaudhuri J N. The continuous alteration of ilmenite through pseudorutile to leucoxene[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1991, 6(1): 25−44. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(91)90030-B [36] Henry D J, Guidotti C V. Tourmaline as a petrogenetic indicator mineral: an example from the staurolite-grade metapelites of NW Maine[J]. American Mineralogist, 1985, 70(1/2): 1−15. [37] 鲍才旺. 珠江口陆架区埋藏古河道与古三角洲[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(2): 25−34.Bao Caiwang. Buried ancient channels and deltas in the Zhujiang River Mouth shelf area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(2): 25−34. [38] 刘昭蜀, 赵焕庭, 范时清, 等. 南海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 109-115.Liu Zhaoshu, Zhao Huanting, Fan Shiqing, et al. Geology of the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 109−115. [39] Chen J, Halls C, Stanley C J. Tin-bearing skarns of South China: geological setting and mineralogy[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1992, 7(3): 225−248. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(92)90006-7 [40] Hanebuth T, Stattegger K, Grootes P M. Rapid flooding of the Sunda Shelf: a late-glacial sea-level record[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5468): 1033−1035. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5468.1033 [41] 陈欣树, 包砺彦, 陈俊仁, 等. 珠江口外陆架晚第四纪最低海面的发现[J]. 热带海洋, 1990, 9(4): 73−77.Chen Xinshu, Bao Liyan, Chen Junren, et al. Discovery of lowest sea level in late quaternary at the continental shelf off Pearl River Mouth[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1990, 9(4): 73−77. [42] Yim W W S, Huang G, Fontugne M R, et al. Postglacial sea-level changes in the northern South China Sea continental shelf: evidence for a post-8200 calendar yr BP meltwater pulse[J]. Quaternary International, 2006, 145−146: 55−67. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.07.005 -





 下载:
下载: